All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of October Week 4 for NEET Exam
A slender homogeneous rod of length 2L floats partly immersed in water, being supported by a string fastened to one of its ends, as shown. The specific gravity of the rod is 0.75. The length of rod that extends out of water is 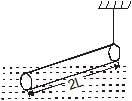
- a)L
- b)
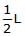
- c)
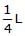
- d)3L
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A slender homogeneous rod of length 2L floats partly immersed in water, being supported by a string fastened to one of its ends, as shown. The specific gravity of the rod is 0.75. The length of rod that extends out of water is
a)
L
b)
c)
d)
3L
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
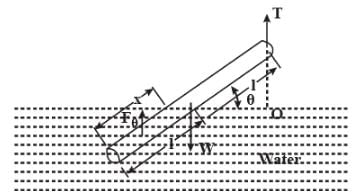
Let's say x length of the rod is dipped into the water.
Since the buoyant force acts through the centre of gravity the displaced water , the condition for rotational equilibrium is, taking moments about a point O along the line of action of T,
0=Στo
⇒0=wl cosθ−FB(2l−x/2)cosθ
⇒0=ρrodgA(2l)(lcosθ)−ρwatergAx(2l−x/2)cosθ
⇒0=(1/2ρwatergAcosθ) (x2−4lx+4 (ρrod/ρwater)l2) where A=cross section area
⇒x2−4lx+3l2=0
⇒x=l,3l.
x=3l is not a possible solution, hence 2l−x=2l−l=l length of the rod extends out of the water.
How many of the following are Lewis bases?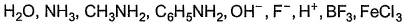
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
How many of the following are Lewis bases?
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Total number of compounds acting as Lewis base in the given example is 6. H+ and BF3 are electron deficient so they can't act as Lewis base while FeCl3 acts as Lewis acid so all the other compounds except these three are Lewis base.
End-products of aerobic respiration are- a)Carbon dioxide and energy
- b)Sugar and oxygen
- c)Carbon dioxide, water and energy
- d)Water and energy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
End-products of aerobic respiration are
a)
Carbon dioxide and energy
b)
Sugar and oxygen
c)
Carbon dioxide, water and energy
d)
Water and energy
|
|
Vartika Shukla answered |
Aerobic respiration is the complete oxidation of sugars in presence of oxygen.
The carbohydrates are broken down into CO₂ and H₂O and this releases energy. This energy is stored in the form of ATP and later used in the body.
So, the correct option is 'Carbon dioxide, water, and energy'
The carbohydrates are broken down into CO₂ and H₂O and this releases energy. This energy is stored in the form of ATP and later used in the body.
So, the correct option is 'Carbon dioxide, water, and energy'
In the following reaction,
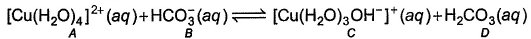
Species behaving as Bronsted-Lowry acids are- a)A,D
- b)B,C
- c)A,B
- d)B,D
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following reaction,
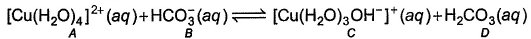
Species behaving as Bronsted-Lowry acids are
Species behaving as Bronsted-Lowry acids are
a)
A,D
b)
B,C
c)
A,B
d)
B,D
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Bronsted lowry acids are those acids which donate H+. In the reaction, A and D are giving H+. So, these both are bronsted lowry acid.
large tank is filled with water to a height H. A small hole is made at the base of the tank. It takes T1 time to decrease the height of water to H/h, (h > 1) and it takes T2 time to take out the rest of water. If T1 = T2, then the value of h is :- a)2
- b)3
- c)4
- d)
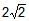
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
large tank is filled with water to a height H. A small hole is made at the base of the tank. It takes T1 time to decrease the height of water to H/h, (h > 1) and it takes T2 time to take out the rest of water. If T1 = T2, then the value of h is :
a)
2
b)
3
c)
4
d)
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
t=A/a √2/g[√H1−√H2]
T1= A/a√2/g[√H1√H/η]
T2=A/a√2/g[√H/η−0]
Given, T1=T2
√H−√H/η=√H/η−0
⇒√H=2√H/η
⇒η=4
T1= A/a√2/g[√H1√H/η]
T2=A/a√2/g[√H/η−0]
Given, T1=T2
√H−√H/η=√H/η−0
⇒√H=2√H/η
⇒η=4
Energy equivalent of NADH is how many number of ATP molecules?- a)2
- b)3
- c)38
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Energy equivalent of NADH is how many number of ATP molecules?
a)
2
b)
3
c)
38
d)
6

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Each NADH molecule theoretically yields 3 ATP molecules during chemiosmosis. However, in some tissues, NADH requires more energy to cross the mitochondrial membrane and some of its potential is lost.
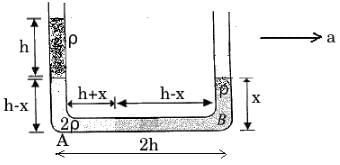
The vertical limbs of a U shaped tube are filled with a liquid of density r upto a height h on each side. The horizontal portion of the U tube having length 2h contains a liquid of density 2r. The U tube is moved horizontally with an accelerator g/2 parallel to the horizontal arm. The difference in heights in liquid levels in the two vertical limbs, at steady state will be- a)2h/7
- b)8h/7
- c)4h/7
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The vertical limbs of a U shaped tube are filled with a liquid of density r upto a height h on each side. The horizontal portion of the U tube having length 2h contains a liquid of density 2r. The U tube is moved horizontally with an accelerator g/2 parallel to the horizontal arm. The difference in heights in liquid levels in the two vertical limbs, at steady state will be
a)
2h/7
b)
8h/7
c)
4h/7
d)
None
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Given:
a=g/2
Pressure at A
PA=Po+ρgh+(2ρ)g(h−x)=Po+3ρgh−2ρgx
Pressure at B
PB=Po+ρgx
Using
PA−PB=[2ρ(h+x)+ρ(h−x)]a
∴ (Po+3ρgh−2ρgx)−(Po+ρgx)=[3ρh+ρx]×g/2
OR 3ρgh−3ρgx=3ρgh/2+1ρgx/2
OR 3ρgh/2=7ρgx/2 ⟹x=3h/7
∴ Difference in the heights between two columns ΔH=(2h−x)−x=2h−2x
⟹ ΔH=2h−6h/7=8h/7
a=g/2
Pressure at A
PA=Po+ρgh+(2ρ)g(h−x)=Po+3ρgh−2ρgx
Pressure at B
PB=Po+ρgx
Using
PA−PB=[2ρ(h+x)+ρ(h−x)]a
∴ (Po+3ρgh−2ρgx)−(Po+ρgx)=[3ρh+ρx]×g/2
OR 3ρgh−3ρgx=3ρgh/2+1ρgx/2
OR 3ρgh/2=7ρgx/2 ⟹x=3h/7
∴ Difference in the heights between two columns ΔH=(2h−x)−x=2h−2x
⟹ ΔH=2h−6h/7=8h/7

In the figure shown, the heavy cylinder (radius R) resting on a smooth surface separates two liquids of densities 2r and 3r. The height `h' for the equilibrium of cylinder must be 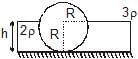
- a)3R/2
- b)
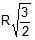
- c) R√2
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the figure shown, the heavy cylinder (radius R) resting on a smooth surface separates two liquids of densities 2r and 3r. The height `h' for the equilibrium of cylinder must be
a)
3R/2
b)
c)
R√2
d)
None
|
|
Om Desai answered |
First, let’s concentrate on the force exerted by the liquid of density 3ρ on the cylinder in the horizontal direction.
Let the length of the cylinder be L.
Consider a small segment of length rdθ at an angle θ from the horizontal line.
Height of this segment from the topmost point of fluid 3ρ is R sinθ
Hence, the pressure exerted by the fluid will be 3ρgRsinθ
The force exerted in the horizontal direction, dF=3ρgRsinθRLcosθdθ
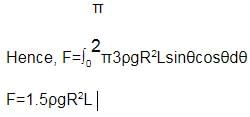
Similarly, proceeding for the fluid with density 2ρ
Height of any segment, above horizontal =h−R−Rsinθ
below horizontal, h−R+Rsinθ
Thus, horizontal force on the cylinder because of fluid,
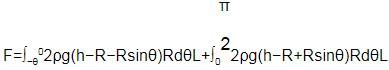
For equilibrium, both the forces should be equal, hence solving the above equation,
h = R √3/2
Let the length of the cylinder be L.
Consider a small segment of length rdθ at an angle θ from the horizontal line.
Height of this segment from the topmost point of fluid 3ρ is R sinθ
Hence, the pressure exerted by the fluid will be 3ρgRsinθ
The force exerted in the horizontal direction, dF=3ρgRsinθRLcosθdθ
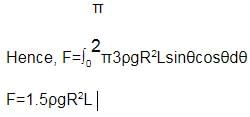
Similarly, proceeding for the fluid with density 2ρ
Height of any segment, above horizontal =h−R−Rsinθ
below horizontal, h−R+Rsinθ
Thus, horizontal force on the cylinder because of fluid,
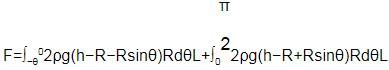
For equilibrium, both the forces should be equal, hence solving the above equation,
h = R √3/2
PH can be kept constant with help of- a)saturated solution
- b)unsaturated solution
- c)buffer solution
- d)super saturated solution
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
PH can be kept constant with help of
a)
saturated solution
b)
unsaturated solution
c)
buffer solution
d)
super saturated solution
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
A buffer is an aqueous solution containing a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. ... It is used to prevent any change in the pH of a solution, regardless of solute. Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-15) This section contains 15 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. Which of the following is least likely to behave as Lewis base?- a)OH-
- b)H2O
- c)NH3
- d)BF3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-15) This section contains 15 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Which of the following is least likely to behave as Lewis base?
a)
OH-
b)
H2O
c)
NH3
d)
BF3
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Electron rich species are called lewis base. Among the given, BF3 is an electron deficient species, so have a capacity of electrons accepting instead of donating that's why it is least likely to act as a lewis base. It is a lewis acid.
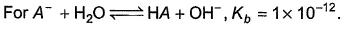
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
The correct answer is 2
Here
we know [OH-][H+]=10-14 at 25 degree Celsius
so pka+pkb=14
hence answer is 2
Here
we know [OH-][H+]=10-14 at 25 degree Celsius
so pka+pkb=14
hence answer is 2
Some liquid is filled in a cylindrical vessel of radius R. Let F1 be the force applied by the liquid on the bottom of the cylinder. Now the same liquid is poured into a vessel of uniform square cross-section of side R. Let F2 be the force applied by the liquid on the bottom of this new vessel. Then :- a) F1 = pF2
- b)F1 =
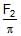
- c)F1 =
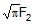
- d) F1 = F2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Some liquid is filled in a cylindrical vessel of radius R. Let F1 be the force applied by the liquid on the bottom of the cylinder. Now the same liquid is poured into a vessel of uniform square cross-section of side R. Let F2 be the force applied by the liquid on the bottom of this new vessel. Then :
a)
F1 = pF2
b)
F1 = 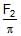
c)
F1 = 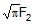
d)
F1 = F2

|
Lohit Matani answered |
Force applied on the base is equal to the weight of the liquid, since in both cases the same liquid has been poured in the container, it will exert the same force on the base of the container.
F1=F2
F1=F2
Which of the following will produce a buffer solution when mixed in equal volumes ?- a)0.1 mol dm–3 NH4OH and 0.1 mol dm–3 HCl
- b)0.05 mol dm–3 NH4OH and 0.1 mol dm–3 HCl
- c)0.1 mol dm–3 NH4OH and 0.05 mol dm–3 HCl
- d)0.1 mol dm–3 CH4COONa and 0.1 mol dm–3 NaOH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following will produce a buffer solution when mixed in equal volumes ?
a)
0.1 mol dm–3 NH4OH and 0.1 mol dm–3 HCl
b)
0.05 mol dm–3 NH4OH and 0.1 mol dm–3 HCl
c)
0.1 mol dm–3 NH4OH and 0.05 mol dm–3 HCl
d)
0.1 mol dm–3 CH4COONa and 0.1 mol dm–3 NaOH
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
In (c), all HCl will be neutralized and NH4Cl will be formed. Also some NH4OH will be left unneutralized. Thus, the final solution will contain NH4OH and NH4Cl and hence will form a buffer.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Acidic strength is in order
- A:
H2O < CH3COOH < HF < NH3
- B:
NH3 < H2O < CH3COOH < HF
- C:
HF < CH3COOH < H2O < NH3
- D:
H2O < NH3 < HF < CH3COOH
The answer is b.
Acidic strength is in order
H2O < CH3COOH < HF < NH3
NH3 < H2O < CH3COOH < HF
HF < CH3COOH < H2O < NH3
H2O < NH3 < HF < CH3COOH
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
When we move from left to right, electronegativity of central atom increases. Due to this nature, central atom has more tendency to break its bond with H and acquire negative charge. So, while moving from left to right, acidic strength increase.
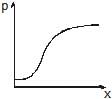
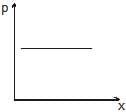
Water flows through a frictionless duct with a cross-section varying as shown in figure. Pressure p at points along the axis is represented by 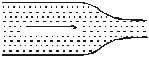
- a)
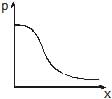
- b)
- c)
- d)
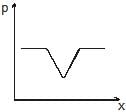
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Water flows through a frictionless duct with a cross-section varying as shown in figure. Pressure p at points along the axis is represented by
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
When the cross section of duct decreases the velocity of water increases and in accordance with Bernoulli's theorem the pressure decreases at that place.
Therefore, in this case, the pressure remains constant initially and then decreases as the area of cross section decreases along the neck of the tube and then remains constant along the mouth of the tube.
Hence, the graph in option A is correct.
Therefore, in this case, the pressure remains constant initially and then decreases as the area of cross section decreases along the neck of the tube and then remains constant along the mouth of the tube.
Hence, the graph in option A is correct.
A large tank is filled with water (density = 103 kg/m3). A small hole is made at a depth 10m below water surface. The range of water issuing out of the hole is Ron ground. What extra pressure must be applied on the water surface so that the range becomes 2R (take 1 atm = 105 Pa and g = 10 m/s2) : 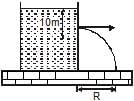
- a)9 Atm
- b)4 Atm
- c)5 Atm
- d)3 Atm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A large tank is filled with water (density = 103 kg/m3). A small hole is made at a depth 10m below water surface. The range of water issuing out of the hole is Ron ground. What extra pressure must be applied on the water surface so that the range becomes 2R (take 1 atm = 105 Pa and g = 10 m/s2) :
a)
9 Atm
b)
4 Atm
c)
5 Atm
d)
3 Atm
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Range will become twice, if the velocity of efflux becomes twice. Since velocity of efflux is √2gh, it will become twice, if h becomes 4 times, or 40m.
Thus, an extra pressure equivalent to 30m of water should be applied.
1atm=0.76×13.6 m of water =10.336m of water
30m of water ≈3atm
Thus, an extra pressure equivalent to 30m of water should be applied.
1atm=0.76×13.6 m of water =10.336m of water
30m of water ≈3atm
An open cubical tank was initially fully filled with water. When the tank was accelerated on a horizontal plane along one of its side it was found that one third of volume of water spilled out. The acceleration was- a) g/4
- b) g/3
- c)3g/2
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An open cubical tank was initially fully filled with water. When the tank was accelerated on a horizontal plane along one of its side it was found that one third of volume of water spilled out. The acceleration was
a)
g/4
b)
g/3
c)
3g/2
d)
None
|
|
Pooja Kulkarni answered |
Let say the tank is accelerating by some acceleration a, such that the rest water in the tanks forms shape like this -
Acceleration, a is right wards.
Where let say h is the height from top till which there is no water
Now if we say V is total volume and B is area of its base and S be its height
We have ½ h X B = V / 3
Thus we get h = S/3
Thus the angle in this cross section of vacant triangle is tan-1 ⅓
Also the same triangle relates a and g, which can be seen when we make the block a inertial frame by adding pseudo force of magnitude ma and directing leftwards, thus we get a/g = ⅓
Thus we get a = g/3

Acceleration, a is right wards.
Where let say h is the height from top till which there is no water
Now if we say V is total volume and B is area of its base and S be its height
We have ½ h X B = V / 3
Thus we get h = S/3
Thus the angle in this cross section of vacant triangle is tan-1 ⅓
Also the same triangle relates a and g, which can be seen when we make the block a inertial frame by adding pseudo force of magnitude ma and directing leftwards, thus we get a/g = ⅓
Thus we get a = g/3
There is a metal cube inside a block of ice which is floating on the surface of water. The ice melts completely and metal falls in the water. Water level in thecontainer- a) Rises
- b)Falls
- c)Remains same
- d)Nothing can be concluded
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
There is a metal cube inside a block of ice which is floating on the surface of water. The ice melts completely and metal falls in the water. Water level in the
container
a)
Rises
b)
Falls
c)
Remains same
d)
Nothing can be concluded
|
|
Sinjini Pillai answered |
Vt = total volume, Vi = volume of ice, Vm = volume of metal, Vw = volume of water
Vt = Vw + Vi + Vm
Since Mi = Mw and ρi x Vi = (ρw)i x (Vw)i and ρi < (ρw)i
So, Vi > (Vw)i
Finally, Vt = (Vw)i + Vi + Vm
Vt = Vw + Vi + Vm
Since Mi = Mw and ρi x Vi = (ρw)i x (Vw)i and ρi < (ρw)i
So, Vi > (Vw)i
Finally, Vt = (Vw)i + Vi + Vm
Which one of the following molecular hydrides acts as a Lewis acid?- a)CH4
- b)NH3
- c)H2O
- d)B2H6
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following molecular hydrides acts as a Lewis acid?
a)
CH4
b)
NH3
c)
H2O
d)
B2H6
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
B2H6 is an electron deficient species. Soit will act as Lewis acid.
A heavy hollow cone of radius R and height h is placed on a horizontal table surface, with its flat base on the table. The whole volume inside the cone is filled with water of density r. The circular rim of the cone's base has a watertight seal with the table's surface and the top apex of the cone has a small hole. Neglecting atmospheric pressure find the total upward force exerted by water on the cone is- a)(2/3)pR2hrg
- b)(1/3)pR2hrg
- c)pR2hrg
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A heavy hollow cone of radius R and height h is placed on a horizontal table surface, with its flat base on the table. The whole volume inside the cone is filled with water of density r. The circular rim of the cone's base has a watertight seal with the table's surface and the top apex of the cone has a small hole. Neglecting atmospheric pressure find the total upward force exerted by water on the cone is
a)
(2/3)pR2hrg
b)
(1/3)pR2hrg
c)
pR2hrg
d)
None
|
|
Sandeep Chawla answered |
Total force exerted on the base by water and cone’s slant surface = mg = 1/3 πR2 Hρg downwards
Force exerted by the water = (ρgH) (πR2) (downwards)
So force exerted by the slant surface = 2/3 ρgH πR2 (upwards)
So force exerted by water on slant surface = 2/3 ρgHπR2
Force exerted by the water = (ρgH) (πR2) (downwards)
So force exerted by the slant surface = 2/3 ρgH πR2 (upwards)
So force exerted by water on slant surface = 2/3 ρgHπR2
The end-product of oxidative phosphorylation is- a)ATP + H2O
- b)Oxygen
- c)ADP
- d)NADH
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The end-product of oxidative phosphorylation is
a)
ATP + H2O
b)
Oxygen
c)
ADP
d)
NADH
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The NADH carries electrons to the oxidative phosphorylation step of cellular respiration, which occurs inside of the mitochondrion Water (H2O) and ATP (energy carrier) At the end of electron transport, oxygen is the final electron acceptor, and it combines also with hydrogen ions to form H2O.
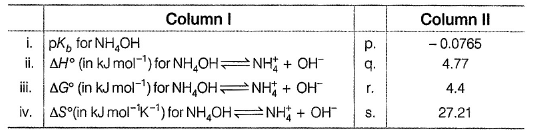
Direction Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.Q. The following thermodynamic quantities are given at 298 K.
Match the parameters given in Column I with their respective values given in Column II.

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.
Q. The following thermodynamic quantities are given at 298 K.
Match the parameters given in Column I with their respective values given in Column II.
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Vishal Kumar answered |
D
A hollow cone floats with its axis vertical upto one-third of its height in a liquid of relative density 0.8 and with its vertex submerged. When another liquid of relative density r is filled in it upto one-third of its height, the cone floats upto half its vertical height. The height of the cone is 0.10 m and radius of the circular base is 0.05 m. The specific gravity r is given by- a)1.0
- b)1.5
- c)2.1
- d)1.9
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A hollow cone floats with its axis vertical upto one-third of its height in a liquid of relative density 0.8 and with its vertex submerged. When another liquid of relative density r is filled in it upto one-third of its height, the cone floats upto half its vertical height. The height of the cone is 0.10 m and radius of the circular base is 0.05 m. The specific gravity r is given by
a)
1.0
b)
1.5
c)
2.1
d)
1.9
|
|
Sanchita Mukherjee answered |
Let the volume of cylinder be V and density to be ρ1
Vρ1g=V×800×g/27..(1) ,Volume of cone with height is h/3 is V/27
Vρ1g+Vρg/27=V×800g/8 ..(2) ,Volume of cone with height is h/2 is V/8
from above equation we ρ=800×19/8
Specific gravity =1900/1000=1.9
Vρ1g=V×800×g/27..(1) ,Volume of cone with height is h/3 is V/27
Vρ1g+Vρg/27=V×800g/8 ..(2) ,Volume of cone with height is h/2 is V/8
from above equation we ρ=800×19/8
Specific gravity =1900/1000=1.9
The species present in solution when CO2 dissolved in water, are[IIT JEE 2006]- a)
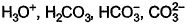
- b)
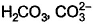
- c)
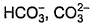
- d)
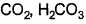
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The species present in solution when CO2 dissolved in water, are
[IIT JEE 2006]
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
H2CO3 is formed by dissolution of CO2 into water. This dissociates into H+ and HCO3-. This is the first dissociation of H2CO3. Since HCO3- has another H, it again dissociates to H+ and CO32-. H+ obtained attacks the lone pair of H2O to form H3O+. So H3O+, HCO3-, CO32-, H2CO3 are present in water when CO2 is dissolved in water.
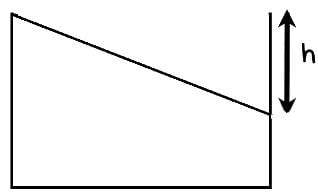
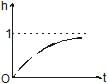
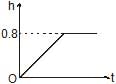
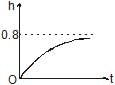
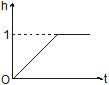
A cylindrical tank of height 1 m and cross section area A = 4000 cm2 is initially empty when it is kept under a tap of cross sectional area 1 cm2. Water starts flowing from the tap at t = 0, with a speed = 2 m/s. There is a small hole in the base of the tank of cross-sectional area 0.5 cm2. The variation of height of water in tank (in meters) with time t is best depicted by- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A cylindrical tank of height 1 m and cross section area A = 4000 cm2 is initially empty when it is kept under a tap of cross sectional area 1 cm2. Water starts flowing from the tap at t = 0, with a speed = 2 m/s. There is a small hole in the base of the tank of cross-sectional area 0.5 cm2. The variation of height of water in tank (in meters) with time t is best depicted by
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Poulomi Singh answered |
We know the velocity of the water from the tap and the cross-sectional area of the tank. There is a rise in water level and as the water level rises the velocity of efflux through the bottom hole also increases.
In ETS cytochromes (electron acceptors), ATP synthesis are arranged in series of- a)Cyt b - c - a - a3
- b)Cyt b - c1 - c - a - a3
- c)Cyt b - a3 - a - c
- d)Cyt b - c - c1 - a3 - a
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In ETS cytochromes (electron acceptors), ATP synthesis are arranged in series of
a)
Cyt b - c - a - a3
b)
Cyt b - c1 - c - a - a3
c)
Cyt b - a3 - a - c
d)
Cyt b - c - c1 - a3 - a

|
EduRev NEET answered |
- In ETS cytochromes (electron acceptors), ATP synthesis are arranged in series of Cyt b - c1 - c - a - a3.
- Cytochromes are the electron carriers in different electron transport complexes in the membrane of the mitochondria which help in the formation of ATP by the process of oxidative phosphorylation.
- The sequence of the movement of the electrons include cytochromes b, cytochrome c, cytochrome a, and cytochrome a3.
Two cyllinders of same cross-section and length L but made of two material of densities d1and d2 are cemented together to form a cylinder of length 2L. The combination floats in a liquid of density d with a length L/2 above the surface of the liquid. If d1> d2 then :- a)
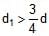
- b)
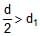
- c)
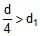
- d)d < d1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two cyllinders of same cross-section and length L but made of two material of densities d1and d2 are cemented together to form a cylinder of length 2L. The combination floats in a liquid of density d with a length L/2 above the surface of the liquid. If d1> d2 then :
a)
b)
c)
d)
d < d1
|
|
Yash Ghoshal answered |
If we make the fbd of the body we get,
(A x L x d2 + A x L x d2) g = (A x 3L/2 X d)g
Thus we get that
d1 + d2 = 3/2d
And as d2 < d1
We get d1 + d2 < d1 + d1
Thus we get 2 d1 > 3d/2
Thus we get d1 > 3d/4
(A x L x d2 + A x L x d2) g = (A x 3L/2 X d)g
Thus we get that
d1 + d2 = 3/2d
And as d2 < d1
We get d1 + d2 < d1 + d1
Thus we get 2 d1 > 3d/2
Thus we get d1 > 3d/4
A container of large surface area is filled with liquid of density r. A cubical block of side edge a and mass M is floating in it with four-fifth of its volume submerged. If a coin of mass m is placed gently on the top surface of the block is just submerged. M is- a) 4m/5
- b)m/5
- c)4m
- d)5m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A container of large surface area is filled with liquid of density r. A cubical block of side edge a and mass M is floating in it with four-fifth of its volume submerged. If a coin of mass m is placed gently on the top surface of the block is just submerged. M is
a)
4m/5
b)
m/5
c)
4m
d)
5m
|
|
Aaditya Pillai answered |
Understanding the Floating Block
When a block floats in a liquid, it displaces a volume of liquid equal to its weight. In this scenario, we have a cubical block of side edge "a" and mass "M," floating in a liquid of density "r." Since four-fifths of the block's volume is submerged, we can denote the submerged volume as:
- Volume of the block = a^3
- Submerged volume = (4/5) * a^3
The weight of the displaced liquid equals the weight of the block:
- Weight of displaced liquid = r * (4/5) * a^3 * g
- Weight of the block = M * g
Thus, we have:
- M * g = r * (4/5) * a^3 * g
From this, we can simplify to find M:
- M = r * (4/5) * a^3
Adding the Coin
When a coin of mass "m" is placed on top of the block, it causes the block to sink further. Since the coin just causes the block to be fully submerged, the total weight now includes both the block and the coin:
- Total weight = (M + m) * g
Now, the total displaced volume must equal the weight of the total system:
- Displaced volume = a^3 (since the block is fully submerged)
The weight of the displaced liquid is now:
- Weight of displaced liquid = r * a^3 * g
Equating the weights gives:
- (M + m) * g = r * a^3 * g
Cancelling "g" from both sides, we get:
- M + m = r * a^3
Finding "M"
From our earlier equation:
- M = r * (4/5) * a^3
Substituting this into the new equation:
- (r * (4/5) * a^3) + m = r * a^3
Rearranging yields:
- m = r * a^3 * (1 - 4/5) = r * a^3 / 5
Now substituting this back into our expression for M:
- M = 4m
Thus, the correct answer is:
The Correct Answer
- M = 4m (Option C)
When a block floats in a liquid, it displaces a volume of liquid equal to its weight. In this scenario, we have a cubical block of side edge "a" and mass "M," floating in a liquid of density "r." Since four-fifths of the block's volume is submerged, we can denote the submerged volume as:
- Volume of the block = a^3
- Submerged volume = (4/5) * a^3
The weight of the displaced liquid equals the weight of the block:
- Weight of displaced liquid = r * (4/5) * a^3 * g
- Weight of the block = M * g
Thus, we have:
- M * g = r * (4/5) * a^3 * g
From this, we can simplify to find M:
- M = r * (4/5) * a^3
Adding the Coin
When a coin of mass "m" is placed on top of the block, it causes the block to sink further. Since the coin just causes the block to be fully submerged, the total weight now includes both the block and the coin:
- Total weight = (M + m) * g
Now, the total displaced volume must equal the weight of the total system:
- Displaced volume = a^3 (since the block is fully submerged)
The weight of the displaced liquid is now:
- Weight of displaced liquid = r * a^3 * g
Equating the weights gives:
- (M + m) * g = r * a^3 * g
Cancelling "g" from both sides, we get:
- M + m = r * a^3
Finding "M"
From our earlier equation:
- M = r * (4/5) * a^3
Substituting this into the new equation:
- (r * (4/5) * a^3) + m = r * a^3
Rearranging yields:
- m = r * a^3 * (1 - 4/5) = r * a^3 / 5
Now substituting this back into our expression for M:
- M = 4m
Thus, the correct answer is:
The Correct Answer
- M = 4m (Option C)
A vertical cylindrical container of base area A and upper cross-section area A1 making an angle 30° with the horizontal is placed in an open rainy field as shown near another cylindrical container having same base area A. The ratio of rates of collection of water in the two containers will be. 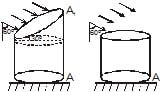
- a)
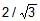
- b)
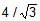
- c)2
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A vertical cylindrical container of base area A and upper cross-section area A1 making an angle 30° with the horizontal is placed in an open rainy field as shown near another cylindrical container having same base area A. The ratio of rates of collection of water in the two containers will be.
a)
b)
c)
2
d)
None
|
|
Anirban Shah answered |
In first container the Area vector is along the direction of rain. Rate of water collection in first container is A1×velocity of rain.
In second cylinder the component of Area vector along the direction of rain is A1cos60°=A1/2. So, rate of water collection in second container is 0.5A1×velocity of rain.
The ratio of water collection is 2.
In second cylinder the component of Area vector along the direction of rain is A1cos60°=A1/2. So, rate of water collection in second container is 0.5A1×velocity of rain.
The ratio of water collection is 2.
A cork of density 0.5 gcm-3 floats on a calm swimming pool. The fraction of the cork's volume which is under water is- a)0%
- b)25%
- c)10%
- d)50%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A cork of density 0.5 gcm-3 floats on a calm swimming pool. The fraction of the cork's volume which is under water is
a)
0%
b)
25%
c)
10%
d)
50%
|
|
Ananya Datta answered |
Question:
A cork of density 0.5 g/cm³ floats on a calm swimming pool. The fraction of the cork's volume which is underwater is:
a) 0%
b) 25%
c) 10%
d) 50%
Answer:
To determine the fraction of the cork's volume that is underwater, we need to analyze the buoyant force acting on the cork.
Buoyant Force:
The buoyant force is the upward force exerted on an object submerged in a fluid. It is given by the formula:
Buoyant force = weight of the fluid displaced
Archimedes' Principle:
According to Archimedes' principle, an object submerged in a fluid experiences an upward buoyant force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
Analysis:
In this case, the cork is floating on a calm swimming pool, which means the buoyant force acting on the cork is equal to its weight. We know that the density of the cork is 0.5 g/cm³.
To determine the fraction of the cork's volume underwater, we need to compare the densities of the cork and the fluid (water). If the density of the cork is less than the density of water, it will float.
Calculation:
The density of water is approximately 1 g/cm³. Since the density of the cork (0.5 g/cm³) is less than the density of water, it will float.
When an object floats, the buoyant force is equal to its weight. This means that the weight of the cork is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the cork.
Since the cork is floating, it displaces an amount of water equal to its own weight. Therefore, the fraction of the cork's volume underwater is equal to the ratio of the cork's weight to the weight of the fluid displaced.
The fraction of the cork's volume underwater can be calculated using the formula:
Fraction underwater = Weight of cork / Weight of fluid displaced
Since the weight of the cork is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced, the fraction underwater is equal to 1, or 100%.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer is option d) 50%.
A cork of density 0.5 g/cm³ floats on a calm swimming pool. The fraction of the cork's volume which is underwater is:
a) 0%
b) 25%
c) 10%
d) 50%
Answer:
To determine the fraction of the cork's volume that is underwater, we need to analyze the buoyant force acting on the cork.
Buoyant Force:
The buoyant force is the upward force exerted on an object submerged in a fluid. It is given by the formula:
Buoyant force = weight of the fluid displaced
Archimedes' Principle:
According to Archimedes' principle, an object submerged in a fluid experiences an upward buoyant force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
Analysis:
In this case, the cork is floating on a calm swimming pool, which means the buoyant force acting on the cork is equal to its weight. We know that the density of the cork is 0.5 g/cm³.
To determine the fraction of the cork's volume underwater, we need to compare the densities of the cork and the fluid (water). If the density of the cork is less than the density of water, it will float.
Calculation:
The density of water is approximately 1 g/cm³. Since the density of the cork (0.5 g/cm³) is less than the density of water, it will float.
When an object floats, the buoyant force is equal to its weight. This means that the weight of the cork is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the cork.
Since the cork is floating, it displaces an amount of water equal to its own weight. Therefore, the fraction of the cork's volume underwater is equal to the ratio of the cork's weight to the weight of the fluid displaced.
The fraction of the cork's volume underwater can be calculated using the formula:
Fraction underwater = Weight of cork / Weight of fluid displaced
Since the weight of the cork is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced, the fraction underwater is equal to 1, or 100%.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer is option d) 50%.
A tank is filled up to a height 2H with a liquid and is placedon a platform of height H from the ground. The distance x from the ground where a small hole is punched to get the maximum range R is :
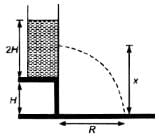
- a)H
- b)1.25 H
- c)1.5 H
- d)2 H
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A tank is filled up to a height 2H with a liquid and is placedon a platform of height H from the ground. The distance x from the ground where a small hole is punched to get the maximum range R is :


a)
H
b)
1.25 H
c)
1.5 H
d)
2 H
|
|
Anand Kapoor answered |
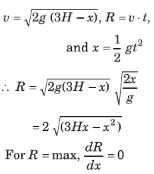
A cubical box of wine has a small spout located in one of the bottom corners. When the box is full and placed on a level surface, opening the spout results in a flow of wine with a initial speed of v0 (see figure). When the box is half empty, someone tilts it at 45º so that the spout is at the lowest point (see figure). When the spout is opened the wine will flow out with a speed of 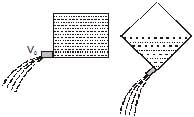
- a) v0
- b) v0/2
- c)
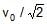
- d)
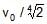
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A cubical box of wine has a small spout located in one of the bottom corners. When the box is full and placed on a level surface, opening the spout results in a flow of wine with a initial speed of v0 (see figure). When the box is half empty, someone tilts it at 45º so that the spout is at the lowest point (see figure). When the spout is opened the wine will flow out with a speed of
a)
v0
b)
v0/2
c)
d)
|
|
Malavika Roy answered |
According to Torricelli's Theorem velocity of efflux i.e. the velocity with which the liquid flows out of a hole is equal to √2gh where h is the depth of the hole below the liquid surface.
Let’s say side of the cube is a, so we have
vo=√2ga
When cubical box is half empty, height of wine surface above the spout is half of the diagonal of the cube's face, i.e. (√2a)/2=a/√2
Now the speed of the wine from the spout is v′=√2g(a/√2)=vo/(2)1/4
Let’s say side of the cube is a, so we have
vo=√2ga
When cubical box is half empty, height of wine surface above the spout is half of the diagonal of the cube's face, i.e. (√2a)/2=a/√2
Now the speed of the wine from the spout is v′=√2g(a/√2)=vo/(2)1/4
Oxidative phosphorylation involves simultaneous oxidation and phosphorylation to finally form- a)NADP
- b)Pyruvate
- c)DPN
- d)ATP
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxidative phosphorylation involves simultaneous oxidation and phosphorylation to finally form
a)
NADP
b)
Pyruvate
c)
DPN
d)
ATP

|
Madhurima Dasgupta answered |
Krebs cycle occurs inside the matrix of mitochondria. The cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle. It includes stepwise oxidative and cyclic degradation of activated acetate derived from pyruvic acid.
Chapter doubts & questions for October Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of October Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup