All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of February Week 1 for NEET Exam
What determines the natural frequency of a body?- a)Position of the body with respect to force applied
- b)Mass and speed of the body
- c)Oscillations in the body
- d)Elastic properties and dimensions of the body
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What determines the natural frequency of a body?
a)
Position of the body with respect to force applied
b)
Mass and speed of the body
c)
Oscillations in the body
d)
Elastic properties and dimensions of the body
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Natural frequency is the frequency at which a body tends to oscillate in the absence of any driving or damping force.
Free vibrations of any elastic body are called natural vibration and happen at a frequency called natural frequency. Natural vibrations are different from forced vibration which happen at frequency of applied force .
Free vibrations of any elastic body are called natural vibration and happen at a frequency called natural frequency. Natural vibrations are different from forced vibration which happen at frequency of applied force .
If  is the natural frequency of the system and
is the natural frequency of the system and  is the frequency of the external force that acts on an oscillating system then at resonance
is the frequency of the external force that acts on an oscillating system then at resonance- a)ωd ≥ ω
- b)ωd = ω
- c)ωd ≤ ω
- d)ωd ≠ ω
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If  is the natural frequency of the system and
is the natural frequency of the system and  is the frequency of the external force that acts on an oscillating system then at resonance
is the frequency of the external force that acts on an oscillating system then at resonance
 is the natural frequency of the system and
is the natural frequency of the system and  is the frequency of the external force that acts on an oscillating system then at resonance
is the frequency of the external force that acts on an oscillating system then at resonancea)
ωd ≥ ω
b)
ωd = ω
c)
ωd ≤ ω
d)
ωd ≠ ω
|
|
Om Desai answered |
When the natural frequency and external frequency of an object are equal the phenomenon is called resonance.
The restoring force in a simple harmonic motion is _________ in magnitude when the particle is instantaneously at rest.- a)zero
- b)maximum
- c)minimum
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The restoring force in a simple harmonic motion is _________ in magnitude when the particle is instantaneously at rest.
a)
zero
b)
maximum
c)
minimum
d)
none of these

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
The restoring force in a simple harmonic motion is maximum in magnitude when the particle is instantaneously at rest because in SHM object’s tendency is to return to mean position and here particle is instantaneously at rest after that instant restoring force will be max to bring particle to mean position.
If an external force with angular frequency ωd acts on an oscillating system with natural angular frequency ω, the system oscillates with angular frequency ωd. The amplitude of oscillations is the greatest when:- a)ωd > ω
- b)ωd < ω
- c)ωd ≥ ω
- d)ωd = ω
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If an external force with angular frequency ωd acts on an oscillating system with natural angular frequency ω, the system oscillates with angular frequency ωd. The amplitude of oscillations is the greatest when:
a)
ωd > ω
b)
ωd < ω
c)
ωd ≥ ω
d)
ωd = ω
|
|
Jyoti Aiims Aspirant answered |
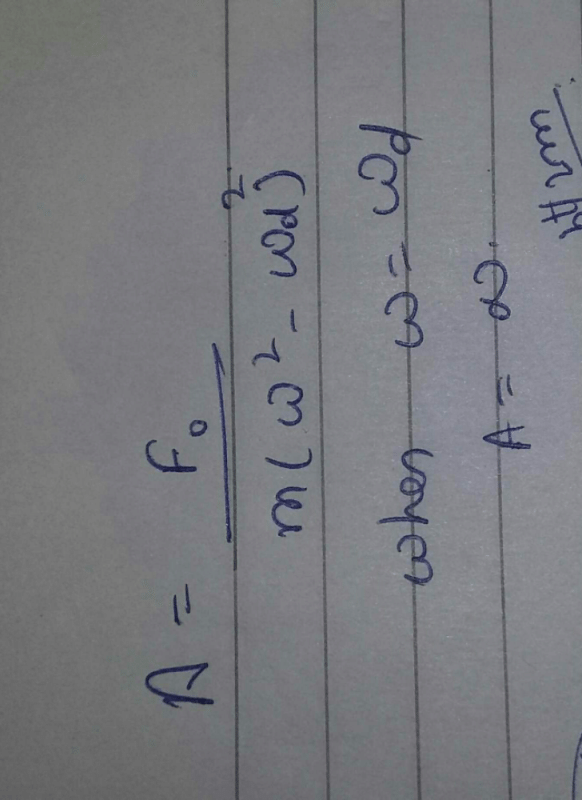
Under what condition angular frequency ω of the damped oscillator would be equivalent to angular velocity Ω of the undamped oscillator.- a)Velocity of oscillator is small
- b)Damping constant, b is small
- c)Damping constant ,b is large
- d)Force applied is small
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Under what condition angular frequency ω of the damped oscillator would be equivalent to angular velocity Ω of the undamped oscillator.
a)
Velocity of oscillator is small
b)
Damping constant, b is small
c)
Damping constant ,b is large
d)
Force applied is small
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
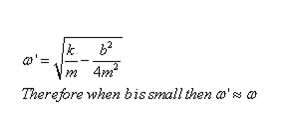
The amplitude of S.H.M at resonance is _______ in the ideal case of zero damping.- a)Maximum
- b)Minimum
- c)Zero
- d)Infinite
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The amplitude of S.H.M at resonance is _______ in the ideal case of zero damping.
a)
Maximum
b)
Minimum
c)
Zero
d)
Infinite
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
In an ideal environment where there is no resistance to oscillation motion i.e. damping is zero, when we oscillate a system at its resonant frequency since there is no opposition to oscillation, the amplitude will go on increasing and reach infinity.
During the propagation of a nerve impulse, the action potential results from the movement of- a)K+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
- b)Na+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
- c)K+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
- d)Na+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During the propagation of a nerve impulse, the action potential results from the movement of
a)
K+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
b)
Na+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
c)
K+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
d)
Na+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Action potential is a change in electrical potential that occurs across a plasma membrane during the passage of a nerve impulse. During this period, there is a localized and translent switch in electric potential across the membrane from -70 mV to +45 mV. It is due to the fact that the sodium channels open and the potassium channels remain closed. As a result, sodium channels permit the influx of Na+ by diffusion from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid.
In the ideal case of zero damping, the amplitude of simple harmonic motion at resonance is:- a)zero
- b)infinite
- c)cannot be said
- d)varies from zero to infinite
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the ideal case of zero damping, the amplitude of simple harmonic motion at resonance is:
a)
zero
b)
infinite
c)
cannot be said
d)
varies from zero to infinite
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
In an ideal environment where there is no resistance to oscillatory motion, that is, damping is zero, when we oscillate a system at its resonant frequency, since there is no opposition to oscillation, a very large value of amplitude will be recorded. Forced oscillation is when you apply an external oscillating force.
Read the given statements and select the correct ones.
(i) Autonomic neural system transmits impulses from the CNS to the voluntary organs and striated muscles of the body.
(ii) Unmyelinated nerve fibres do not have Schwann cells which form the myelin sheath.
(iii) Axonal membrane of a neuron while not conducting any impulse is comparatively more permeable to potassium ions (K+) than to sodium ions (Na+).
(iv) A synapse is formed by the membranes of a presynaptic neuron and a post synaptic neuron.- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(iii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct ones.
(i) Autonomic neural system transmits impulses from the CNS to the voluntary organs and striated muscles of the body.
(ii) Unmyelinated nerve fibres do not have Schwann cells which form the myelin sheath.
(iii) Axonal membrane of a neuron while not conducting any impulse is comparatively more permeable to potassium ions (K+) than to sodium ions (Na+).
(iv) A synapse is formed by the membranes of a presynaptic neuron and a post synaptic neuron.
(i) Autonomic neural system transmits impulses from the CNS to the voluntary organs and striated muscles of the body.
(ii) Unmyelinated nerve fibres do not have Schwann cells which form the myelin sheath.
(iii) Axonal membrane of a neuron while not conducting any impulse is comparatively more permeable to potassium ions (K+) than to sodium ions (Na+).
(iv) A synapse is formed by the membranes of a presynaptic neuron and a post synaptic neuron.
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(iii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iv)
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Autonomic neural system controls and coordinates such organs which are under involuntary control and unstriated muscles of the body. Unmyelinated nerve fibres have Schwann cells which do not form myelin sheath.
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect about the electrical synapse?
(i) At electrical synapses, the membranes of pre and post synaptic neurons are in very close proximity.
(ii) Electrical current can flow directly from one neuron into the other across the synapses
(iii) Transmission of an impulse across electrical synapses is very similar to impulse conduction along single axon
(iv) Electrica synapses pass electrical signal between cells with the use of Ach.
(v) Electrical synapses are fast.
(vi) Electrical synapses are rare in our system.- a)(ii), (iv) and (v)
- b)(i) and (iii)
- c)(iv) only
- d)(i), (v) and (vi)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect about the electrical synapse?
(i) At electrical synapses, the membranes of pre and post synaptic neurons are in very close proximity.
(ii) Electrical current can flow directly from one neuron into the other across the synapses
(iii) Transmission of an impulse across electrical synapses is very similar to impulse conduction along single axon
(iv) Electrica synapses pass electrical signal between cells with the use of Ach.
(v) Electrical synapses are fast.
(vi) Electrical synapses are rare in our system.
(i) At electrical synapses, the membranes of pre and post synaptic neurons are in very close proximity.
(ii) Electrical current can flow directly from one neuron into the other across the synapses
(iii) Transmission of an impulse across electrical synapses is very similar to impulse conduction along single axon
(iv) Electrica synapses pass electrical signal between cells with the use of Ach.
(v) Electrical synapses are fast.
(vi) Electrical synapses are rare in our system.
a)
(ii), (iv) and (v)
b)
(i) and (iii)
c)
(iv) only
d)
(i), (v) and (vi)
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
At electrical synapse, the transfer of impulse occurs by purely electrical means without involving any neurotransmitter.
The phenomenon of increase in amplitude when the driving force is close to the natural frequency of the oscillator is known as- a)Accelerated Amplitude
- b)Epoch
- c)Resonance
- d)Dampening
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The phenomenon of increase in amplitude when the driving force is close to the natural frequency of the oscillator is known as
a)
Accelerated Amplitude
b)
Epoch
c)
Resonance
d)
Dampening
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
The phenomenon of increase in amplitude when the driving force is close to the natural frequency of the oscillator is known as. The phenomenon of increase in amplitude when the driving force is close to the natural frequency of the oscillator is known as resonance.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
(i) Synaptic cleft of neurons secrete adrenaline.
(ii) Myelinated nerve fibres are enveloped with Schwann cells, which from a myelin sheath around the axon.
(iii) Non-myelinated nerve fibre is enclosed by a Schwann cell that does not form a myelin sheath.
(iv) Spinal and cranial nerves are made of non-melinated nerve fibres.- a)Statements (i) and (ii) are correct but statements (iii) and (iv) are incorrect
- b)Statements (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct but statement (iv) is incorrect
- c)Statement (iii) and (iv) are correct but statement (i) and (ii) are incorrect
- d)Statement (ii) and (iii) are correct but statements (i) and (iv) are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
(i) Synaptic cleft of neurons secrete adrenaline.
(ii) Myelinated nerve fibres are enveloped with Schwann cells, which from a myelin sheath around the axon.
(iii) Non-myelinated nerve fibre is enclosed by a Schwann cell that does not form a myelin sheath.
(iv) Spinal and cranial nerves are made of non-melinated nerve fibres.
(i) Synaptic cleft of neurons secrete adrenaline.
(ii) Myelinated nerve fibres are enveloped with Schwann cells, which from a myelin sheath around the axon.
(iii) Non-myelinated nerve fibre is enclosed by a Schwann cell that does not form a myelin sheath.
(iv) Spinal and cranial nerves are made of non-melinated nerve fibres.
a)
Statements (i) and (ii) are correct but statements (iii) and (iv) are incorrect
b)
Statements (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct but statement (iv) is incorrect
c)
Statement (iii) and (iv) are correct but statement (i) and (ii) are incorrect
d)
Statement (ii) and (iii) are correct but statements (i) and (iv) are incorrect
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Synaptic vesicles of the synaptic knob secrete neurotransmitter (e.g., adrenaline). Spinal nerves and cranial nerves are myelinated nerves.
Under forced oscillation, the phase of the harmonic motion of the particle and phase of driving force- a)Are same
- b)Are different
- c)Both are zero
- d)Not present
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Under forced oscillation, the phase of the harmonic motion of the particle and phase of driving force
a)
Are same
b)
Are different
c)
Both are zero
d)
Not present
|
|
Pratibha Sharma answered |
Harmonic motion is the natural motion of a body(we consider no air friction) under no force where as damped oscillation are under force hence the iscilation are different
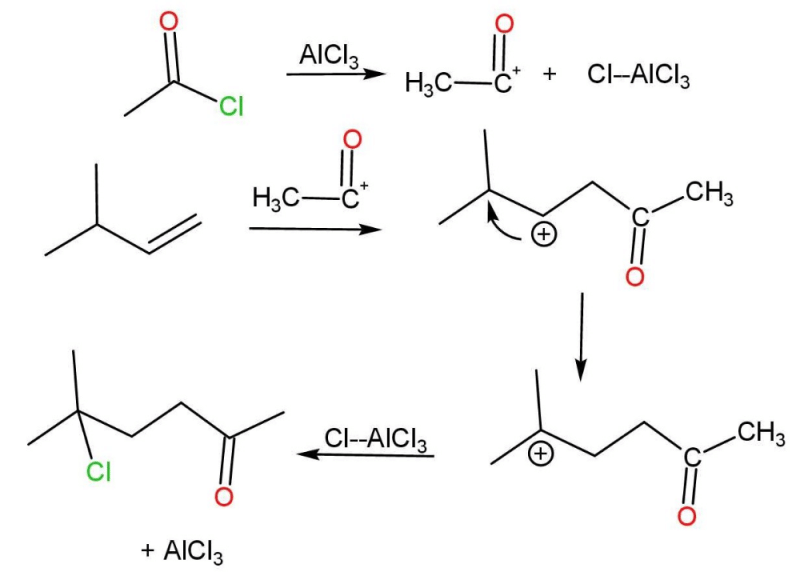
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 7) This section contains 7 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. What is true about the reaction given below?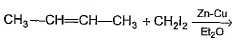
- a)Reaction involves a carbocation intermediate
- b)Reaction involves a carbanion intermediate
- c)Meso or racemic products are formed depending on configuration at double bond
- d)Product is an acyclic alkane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 7) This section contains 7 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. What is true about the reaction given below?
a)
Reaction involves a carbocation intermediate
b)
Reaction involves a carbanion intermediate
c)
Meso or racemic products are formed depending on configuration at double bond
d)
Product is an acyclic alkane

|
Karan Kumar answered |
Correct answer is option 'C'
Sodium-potassium pump transports- a)Na+ and K+ out of the neuron
- b)Na+ and K+ into the neuron
- c)Na+ into the neuron and K+ out of the neuron
- d)K+ into the neuron and Na+ out of the neuron
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Sodium-potassium pump transports
a)
Na+ and K+ out of the neuron
b)
Na+ and K+ into the neuron
c)
Na+ into the neuron and K+ out of the neuron
d)
K+ into the neuron and Na+ out of the neuron
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Each Na+ -K+ pump expels three Na+ ions for every two K+ ions imported.
Energy is supplied to the damped oscillatory system at the same rate at which it is dissipating energy, then the amplitude of such oscillations would become constant. Such oscillations are called- a)Damped oscillations
- b)Undamped oscillations
- c)Coupled oscillations
- d)Maintained oscillations
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Energy is supplied to the damped oscillatory system at the same rate at which it is dissipating energy, then the amplitude of such oscillations would become constant. Such oscillations are called
a)
Damped oscillations
b)
Undamped oscillations
c)
Coupled oscillations
d)
Maintained oscillations
|
|
Anoushka Basu answered |
Energy is supplied to the damped oscillatory system at the same rate at which it is dissipating energy, and then the amplitude of such oscillations would become constant. Such oscillations are called maintained oscillations. By the definition of maintained oscillations.
How does the pre-synaptic neuron transmit an impulse across the synaptic cleft to the post-synaptic neuron?- a)By electrical current flowing directly between the neurons across the synaptic cleft.
- b)By the release of neurotransmitters from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft.
- c)By ion flow through the synaptic cleft without the need for neurotransmitters.
- d)By a direct connection between the axon terminal and the post-synaptic membrane.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
By electrical current flowing directly between the neurons across the synaptic cleft.
b)
By the release of neurotransmitters from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft.
c)
By ion flow through the synaptic cleft without the need for neurotransmitters.
d)
By a direct connection between the axon terminal and the post-synaptic membrane.

|
Ambition Institute answered |
The pre-synaptic neuron transmits an impulse to the post-synaptic neuron by releasing neurotransmitters from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to specific receptors on the post-synaptic membrane.
Hydrogenation of alkenes can be carried out in the presence of- a)copper
- b)zinc
- c)aluminium
- d)nickel
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogenation of alkenes can be carried out in the presence of
a)
copper
b)
zinc
c)
aluminium
d)
nickel

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons such as alkenes add Hydrogen in the presence of catalysts such as Ni to form saturated hydrocarbons. This is called an addition reaction.
- The reaction is commonly used in the hydrogenation of vegetable oils using a Nickel catalyst.
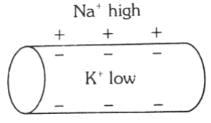
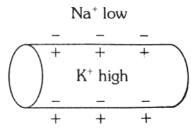
Which of the following options illustrates the distribution of Na+ and K+ ions in a section of non-myelinated axon which is at resting potential?- a)
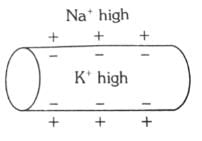
- b)
- c)
- d)
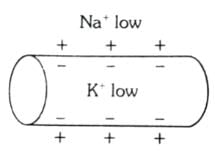
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following options illustrates the distribution of Na+ and K+ ions in a section of non-myelinated axon which is at resting potential?
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
When a neuron is at resting potential i.e., not conducting any impulse; the axonal membrane is comparatively more permeable to K+ ions and nearly impermeable to Na+ ions. Consequently, the axoplasm inside the axon contains high concentration of K+ ions. In contrast, the fluid outside the axon has a high concentration of Na+ ions and thus forms a concentration gradient.
Direction (Q . No. 14) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.Q. Match the alkenes from Column I with the stereochemistry of addition product(s) obtained with Br2/CCI4 in presence of FeBr3.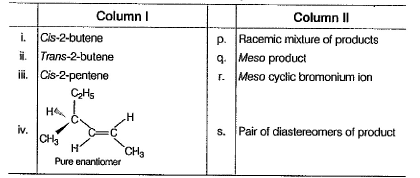

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q . No. 14) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.
Q. Match the alkenes from Column I with the stereochemistry of addition product(s) obtained with Br2/CCI4 in presence of FeBr3.
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Inayat Khan answered |
Option b is correct
Read the given paragraph.
In the resting state, the axonal membrane is (i) with more (ii) charged ions outside than inside. This unequal distribution of ions os due to (1) the selective permeability of the membrane, which forms an almost impenetrable barrier to (iii) and (2) the action of the (iv) which pumps (v) Na+ out of the neuron for every (vi) K+ brought in.
Select the option that correctly fills the blanks in the paragraph.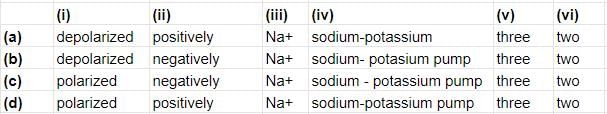
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given paragraph.
In the resting state, the axonal membrane is (i) with more (ii) charged ions outside than inside. This unequal distribution of ions os due to (1) the selective permeability of the membrane, which forms an almost impenetrable barrier to (iii) and (2) the action of the (iv) which pumps (v) Na+ out of the neuron for every (vi) K+ brought in.
Select the option that correctly fills the blanks in the paragraph.
In the resting state, the axonal membrane is (i) with more (ii) charged ions outside than inside. This unequal distribution of ions os due to (1) the selective permeability of the membrane, which forms an almost impenetrable barrier to (iii) and (2) the action of the (iv) which pumps (v) Na+ out of the neuron for every (vi) K+ brought in.
Select the option that correctly fills the blanks in the paragraph.

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
In the resting state, the axonal membrane is polarised with more positively charged ions outside than inside, unequal distribution of ions is due to the selective permeability of the membrane, which forms impermeable barrier to sodium ion and the action of the sodium which pumps three sodium ions out of the neuron for every two potassium ions brought in.
Thus, the correct option is '(i) - polarised, (ii) - positively, (iii) - Na + , (iv) - sodium - potassium pump, (v) - three, (vi) - two.'
Thus, the correct option is '(i) - polarised, (ii) - positively, (iii) - Na + , (iv) - sodium - potassium pump, (v) - three, (vi) - two.'
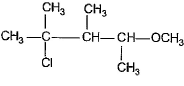
What is the major addition product in the reaction given below?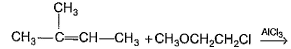
- a)
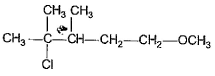
- b)
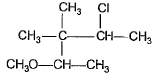
- c)
- d)
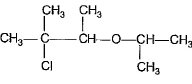
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the major addition product in the reaction given below?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Rutuja Pawar answered |
This is according to markownicoffs rule
Which of the following is true about electrical synapses?- a)Electrical synapses involve the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft.
- b)Electrical synapses have a gap called the synaptic cleft that separates the neurons.
- c)Electrical synapses allow direct electrical current flow between the pre- and post-synaptic neurons.
- d)Electrical synapses are more common in the human nervous system than chemical synapses.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Electrical synapses involve the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft.
b)
Electrical synapses have a gap called the synaptic cleft that separates the neurons.
c)
Electrical synapses allow direct electrical current flow between the pre- and post-synaptic neurons.
d)
Electrical synapses are more common in the human nervous system than chemical synapses.

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Electrical synapses allow direct electrical current flow between the pre- and post-synaptic neurons without the need for neurotransmitters or synaptic clefts. These synapses are rare in the human nervous system.
What is major product in the following reaction?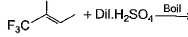
- a)
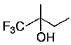
- b)
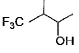
- c)

- d)
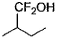
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is major product in the following reaction?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Nimish Somani answered |
According to anti- markonikoffs rule OH will be attached to that carbon which is having more no. of hydrogens.
What are the expected product(s) in the following reaction?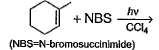
- a)
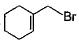
- b)
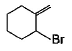
- c)
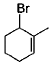
- d)

Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the expected product(s) in the following reaction?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Ameya Choudhury answered |
The correct answer is Option A,B,C,D.
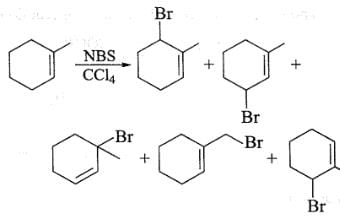

Unidirectional transmission of a nerve impulse through nerve fibre is due to the fact that- a)nerve fibre is insulated by a medullary sheath
- b)sodium pump starts operating only at the cyton and then continues into the nerve fibre
- c)neurotransmitters are released by dendrites and not by axon endings
- d)neurotransmitters are released by the axon endings and not by dendrites
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Unidirectional transmission of a nerve impulse through nerve fibre is due to the fact that
a)
nerve fibre is insulated by a medullary sheath
b)
sodium pump starts operating only at the cyton and then continues into the nerve fibre
c)
neurotransmitters are released by dendrites and not by axon endings
d)
neurotransmitters are released by the axon endings and not by dendrites
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
A nerve impulse is transmitted from one neuron to another with the help of chemicals called neurotransmitters that are released by the axon endings formed by the membrane of a pre-synaptic neuron which may or may not be separated by synaptic cleft.
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 and13) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageCaryophyllene (C15H24) contain a six membered ring and on ozonolysis gives following product.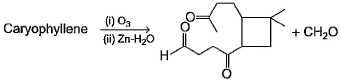 Q. The structure of caryophyllene is
Q. The structure of caryophyllene is- a)
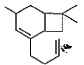
- b)
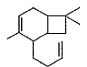
- c)
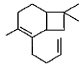
- d)
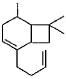
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 and13) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
Caryophyllene (C15H24) contain a six membered ring and on ozonolysis gives following product.
Q. The structure of caryophyllene is
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Ashish Mishra answered |
C is correct.
Chapter doubts & questions for February Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of February Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup