All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of May Week 2 for NEET Exam
The amount of work done in moving a charge from one point to another along an equipotential line or surface charge is- a)Zero
- b)Infinity
- c)One
- d)Two
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The amount of work done in moving a charge from one point to another along an equipotential line or surface charge is
a)
Zero
b)
Infinity
c)
One
d)
Two
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Since Potential difference between two points in equipotential surfaces is zero, the work done between two points in equipotential surface is also zero.
The electrostatic potential energy between two charges q1 and q2 separated by a distance by r is given by- a)
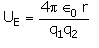
- b)
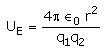
- c)
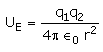
- d)
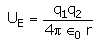
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The electrostatic potential energy between two charges q1 and q2 separated by a distance by r is given by
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Khushi Mittal answered |
Energy = force × distance U=Kq1q2/r^2 × r U=Kq1q2/r
Salt bridge is indicated in the cell representation by :- a)I
- b)!!
- c)((
- d)II
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Salt bridge is indicated in the cell representation by :
a)
I
b)
!!
c)
((
d)
II
|
|
Khushi Pandey answered |
Indicàted by Twø parallel linés (||)
. In the construction of a salt bridge, saturated solution of KNO3 is used because:- a)Velocity of K+ and NO3– are same
- b)Velocity of NO3– is greater than that of K+
- c)Velocity of K+ is greater than that of NO3–
- d)KNO3 is highly soluble in water
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
. In the construction of a salt bridge, saturated solution of KNO3 is used because:
a)
Velocity of K+ and NO3– are same
b)
Velocity of NO3– is greater than that of K+
c)
Velocity of K+ is greater than that of NO3–
d)
KNO3 is highly soluble in water
|
|
Riya Agarwal answered |
Velocities of both should be same to balance the amount of both ions in the soln. if the vel of any of them is more...then its ions will release more
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is
- A:
Zero
- B:
Infinity
- C:
Nonzero finite
- D:
None of the above
The answer is a.
The potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is
Zero
Infinity
Nonzero finite
None of the above

|
.mie. answered |
Answer is 0 as there are no other sources of electrostatic potential .... against which an external agent must do work.... in moving the point charge.... from infinity to its final location.... therefore correct opt is A
In bringing an electron towards another electron, the electrostatic potential energy of the system- a)becomes zero
- b)decreases
- c)remains same
- d)increases
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In bringing an electron towards another electron, the electrostatic potential energy of the system
a)
becomes zero
b)
decreases
c)
remains same
d)
increases
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The electron has negative charge. When an electron is bringing towards another electron, then due to same negative charge repulsive force is produced between them. So, to bring them closer a work is done against this repulsive force. This work is stored in the form of electrostatic potential energy. Thus, electrostatic potential energy of system increases.
Alternative: Electrostatic potential energy of system of two electrons
U=[1/4πε0][(−e)(−e)/r] = [1/4πε0](e^2/r)
Thus, as r decreases, potential energy U increases.
If a unit charge is taken from one part to another part over an equipotential surface, then what is the change in electrostatic potential energy of the charge?- a)10 J
- b)100 J
- c)1 J
- d)0 J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If a unit charge is taken from one part to another part over an equipotential surface, then what is the change in electrostatic potential energy of the charge?
a)
10 J
b)
100 J
c)
1 J
d)
0 J

|
Utsav Srivastava answered |
Equipotential surface means the potential on every. point on that surface is constant. it means the change in potential on equipotential surface is zero we know that... ( electrostatic potential energy = change in potential × charge.)... ... according to this electrostatic potential energy is zero
In an electrochemical cell, the electrode having a lower reduction potential will act as:- a)Salt bridge
- b)Electrolyte
- c)Anode
- d)Cathode
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an electrochemical cell, the electrode having a lower reduction potential will act as:
a)
Salt bridge
b)
Electrolyte
c)
Anode
d)
Cathode
|
|
Sargam Singh answered |
A substance with lower reduction potential has more tendency to oxidize .in a electrochemical cell anode performs oxidation reaction hence the electrode will function as a anode
The potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is
- a)Zero
- b)Infinity
- c)Non zero finite
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is
a)
Zero
b)
Infinity
c)
Non zero finite
d)
None of the above
|
|
Manoj Chauhan answered |
Explanation:
Potential energy is defined as the work done by an external force in bringing a system from infinity to its position. Hence, the potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is given by -
U = qV
where, q is the charge of the point charge and V is the potential at its position.
Now, let's consider the two cases -
Case 1: When the point charge is at infinity
At infinity, the potential is zero as the electric field due to a point charge decreases as we move away from it. Hence, the potential energy of the system containing only one point charge at infinity is zero.
U = qV = q x 0 = 0
Case 2: When the point charge is at a finite distance from infinity
In this case, the potential energy of the system will be non-zero finite as the potential at the position of the point charge will be non-zero.
U = qV ≠ 0
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option 'A' i.e. zero as the potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is zero when the point charge is at infinity.
Potential energy is defined as the work done by an external force in bringing a system from infinity to its position. Hence, the potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is given by -
U = qV
where, q is the charge of the point charge and V is the potential at its position.
Now, let's consider the two cases -
Case 1: When the point charge is at infinity
At infinity, the potential is zero as the electric field due to a point charge decreases as we move away from it. Hence, the potential energy of the system containing only one point charge at infinity is zero.
U = qV = q x 0 = 0
Case 2: When the point charge is at a finite distance from infinity
In this case, the potential energy of the system will be non-zero finite as the potential at the position of the point charge will be non-zero.
U = qV ≠ 0
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option 'A' i.e. zero as the potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is zero when the point charge is at infinity.
During electrolysis, the reaction that takes place at cathode is:- a)Hydrolysis
- b)Reduction
- c)Oxidation
- d)Neutralization
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During electrolysis, the reaction that takes place at cathode is:
a)
Hydrolysis
b)
Reduction
c)
Oxidation
d)
Neutralization
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
The electrode at which oxidation takes place is known as the anode, while the electrode at which reduction take place is called the cathode. If you see galvanic cell reduction take place at the left electrode, so the left one is the cathode. Oxidation takes place at the right electrode, so the right one is the anode.
During electrolysis, the reaction that takes place at anode is:- a)Reduction
- b)Neutralization
- c)Hydrolysis
- d)Oxidation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
During electrolysis, the reaction that takes place at anode is:
a)
Reduction
b)
Neutralization
c)
Hydrolysis
d)
Oxidation
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
Oxidation takes place at the right electrode, so the right one is the anode. While in electrolytic cell reduction takes place at the right electrode, so right one is the cathode. Oxidation takes place at the left electrode, so the left one is the anode.
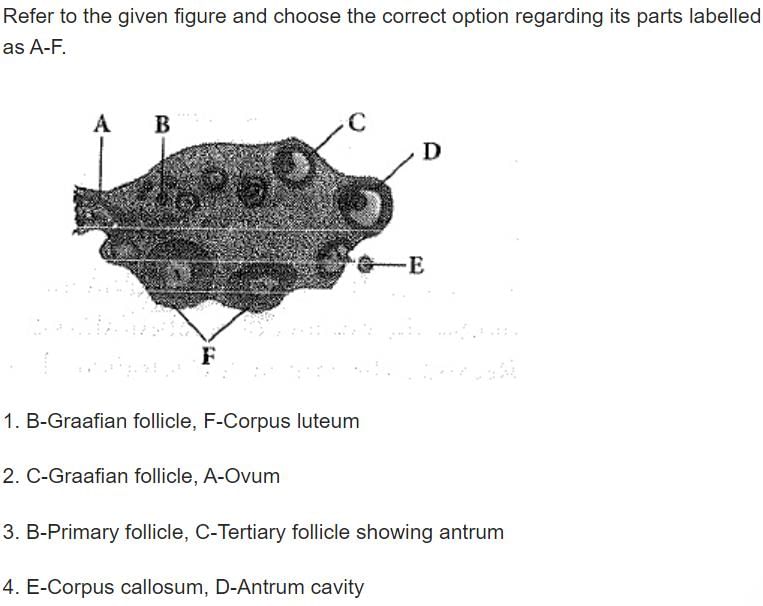
Select the correct option of haploid cells from the following groups:- a)Primary oocyte, Secondary oocyte, Spermatid
- b)Secondary spermatocyte, First polar body, Ovum
- c)Spermatogonia, Primary spermatocyte, Spermatid
- d)Primary spermatocyte, Secondary spermatocyte, Second polar body
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct option of haploid cells from the following groups:
a)
Primary oocyte, Secondary oocyte, Spermatid
b)
Secondary spermatocyte, First polar body, Ovum
c)
Spermatogonia, Primary spermatocyte, Spermatid
d)
Primary spermatocyte, Secondary spermatocyte, Second polar body
|
|
Sakshi Yadav answered |
Haploid Cells in Meiosis
In meiosis, the process of cell division that produces gametes, haploid cells are formed through two rounds of division. Each round of division involves a reduction in the number of chromosomes from diploid (2n) to haploid (n).
Option B is the correct answer because all three cells listed are haploid:
- Secondary spermatocyte: This cell is formed during meiosis I in the male reproductive system. It is the result of the division of a primary spermatocyte and contains 23 chromosomes (n) instead of 46 (2n).
- First polar body: This cell is formed during meiosis I in the female reproductive system. It is the result of the division of a primary oocyte and contains 23 chromosomes (n).
- Ovum: This cell is formed during meiosis II in the female reproductive system. It is the result of the division of a secondary oocyte and contains 23 chromosomes (n).
Options A, C, and D are incorrect because they include cells that are not haploid:
- Primary oocyte and secondary oocyte: These cells are both diploid (2n) because they have not yet undergone meiosis I.
- Spermatogonia and primary spermatocyte: These cells are both diploid (2n) because they are in the early stages of meiosis in the male reproductive system.
- Spermatid, secondary spermatocyte, and second polar body: These cells are haploid, but they are not all present in the same stage of meiosis. Spermatids are formed during meiosis II in the male reproductive system, while secondary spermatocytes and second polar bodies are formed during meiosis I in the male and female reproductive systems, respectively.
In meiosis, the process of cell division that produces gametes, haploid cells are formed through two rounds of division. Each round of division involves a reduction in the number of chromosomes from diploid (2n) to haploid (n).
Option B is the correct answer because all three cells listed are haploid:
- Secondary spermatocyte: This cell is formed during meiosis I in the male reproductive system. It is the result of the division of a primary spermatocyte and contains 23 chromosomes (n) instead of 46 (2n).
- First polar body: This cell is formed during meiosis I in the female reproductive system. It is the result of the division of a primary oocyte and contains 23 chromosomes (n).
- Ovum: This cell is formed during meiosis II in the female reproductive system. It is the result of the division of a secondary oocyte and contains 23 chromosomes (n).
Options A, C, and D are incorrect because they include cells that are not haploid:
- Primary oocyte and secondary oocyte: These cells are both diploid (2n) because they have not yet undergone meiosis I.
- Spermatogonia and primary spermatocyte: These cells are both diploid (2n) because they are in the early stages of meiosis in the male reproductive system.
- Spermatid, secondary spermatocyte, and second polar body: These cells are haploid, but they are not all present in the same stage of meiosis. Spermatids are formed during meiosis II in the male reproductive system, while secondary spermatocytes and second polar bodies are formed during meiosis I in the male and female reproductive systems, respectively.
A charge q = 1.0 C moves distance of 1.5 m in the direction of a uniform electric field E of magnitude 2.0 N/C. Find its change in electrostatic potential energy.- a)2 J
- b)3 J
- c)4 J
- d)1 J
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A charge q = 1.0 C moves distance of 1.5 m in the direction of a uniform electric field E of magnitude 2.0 N/C. Find its change in electrostatic potential energy.
a)
2 J
b)
3 J
c)
4 J
d)
1 J

|
Anchal Maurya answered |
Force (F)=E•q=2×1=2,. Energy (E)=F•d=2×1.5=3 joule
Negative mutual potential energy corresponds to attraction between two charges- a)False
- b)True
- c)Can’t predict
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Negative mutual potential energy corresponds to attraction between two charges
a)
False
b)
True
c)
Can’t predict
d)
None of the above

|
Soham Rastogi answered |
The formula for electric potential energy of system of 2 charges is (kq1q2)/r, if the result comes out to be negative,one of the charges has to be negative and one has to be positive, because there can be no other case in which it comes out to be negative. Since opposite charges attract each other,hence the answer is True.
The cell representation of the given reaction is:
Zn(s) + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu(s)- a)Zn|zn2+||Cu2+|Cu
- b)Cu2+|Cu||Zn|zn2+
- c)Zn|zn2+||Cu|Cu2+
- d)Cu|Cu2+||zn2+|Zn
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The cell representation of the given reaction is:
Zn(s) + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu(s)
Zn(s) + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu(s)
a)
Zn|zn2+||Cu2+|Cu
b)
Cu2+|Cu||Zn|zn2+
c)
Zn|zn2+||Cu|Cu2+
d)
Cu|Cu2+||zn2+|Zn
|
|
Atishay Jain answered |
Answer is A because Zn oxidized in Zn+2 and Cu+2 reduced in Cu.So Zn is anode and Cu is cathode.
If a salt bridge is removed between the half cells, the voltage- a)Decreases to zero
- b)Increases
- c)Increases rapidly
- d)Do not change
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a salt bridge is removed between the half cells, the voltage
a)
Decreases to zero
b)
Increases
c)
Increases rapidly
d)
Do not change
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
The purpose of a salt bridge is not to move electrons from the electrolyte, rather maintain charge balance because the electrons are moving from one-half cell to the other. The electrons flow from the anode to the cathode thus if a salt bridge is removed between the half cells, the voltage becomes zero.
In a Daniel cell, the oxidation and reduction halves occur at:- a)copper and zinc electrodes respectively
- b)zinc and copper electrodes respectively
- c)both occur at copper electrode respectively
- d)both occur at zinc electrode respectively
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a Daniel cell, the oxidation and reduction halves occur at:
a)
copper and zinc electrodes respectively
b)
zinc and copper electrodes respectively
c)
both occur at copper electrode respectively
d)
both occur at zinc electrode respectively
|
|
Ameya Pillai answered |
The correct answer is option 'B': zinc and copper electrodes respectively.
Explanation:
A Daniel cell is an electrochemical cell that consists of two half-cells connected by a salt bridge. The two half-cells are the oxidation half-cell and the reduction half-cell.
1. Oxidation Half-Cell:
In the oxidation half-cell, oxidation occurs. This means that electrons are lost by the electrode material and transferred to the external circuit. In the Daniel cell, the zinc electrode is the site of oxidation. Zinc atoms lose two electrons to form Zn2+ ions:
Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e-
2. Reduction Half-Cell:
In the reduction half-cell, reduction occurs. This means that electrons are gained by the electrode material from the external circuit. In the Daniel cell, the copper electrode is the site of reduction. Copper(II) ions from the copper sulfate solution in the reduction half-cell gain two electrons to form copper atoms:
Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s)
3. Overall Cell Reaction:
The overall cell reaction can be obtained by combining the oxidation and reduction half-reactions. Since the number of electrons lost in the oxidation half-reaction is equal to the number of electrons gained in the reduction half-reaction, the two half-reactions can be added together to obtain the overall cell reaction:
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
4. Cell Diagram:
The cell diagram for a Daniel cell is represented as:
Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || Cu2+(aq) | Cu(s)
In conclusion, in a Daniel cell, the oxidation half occurs at the zinc electrode and the reduction half occurs at the copper electrode. This allows for the flow of electrons from the zinc electrode to the copper electrode through the external circuit, generating an electric current.
Explanation:
A Daniel cell is an electrochemical cell that consists of two half-cells connected by a salt bridge. The two half-cells are the oxidation half-cell and the reduction half-cell.
1. Oxidation Half-Cell:
In the oxidation half-cell, oxidation occurs. This means that electrons are lost by the electrode material and transferred to the external circuit. In the Daniel cell, the zinc electrode is the site of oxidation. Zinc atoms lose two electrons to form Zn2+ ions:
Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e-
2. Reduction Half-Cell:
In the reduction half-cell, reduction occurs. This means that electrons are gained by the electrode material from the external circuit. In the Daniel cell, the copper electrode is the site of reduction. Copper(II) ions from the copper sulfate solution in the reduction half-cell gain two electrons to form copper atoms:
Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s)
3. Overall Cell Reaction:
The overall cell reaction can be obtained by combining the oxidation and reduction half-reactions. Since the number of electrons lost in the oxidation half-reaction is equal to the number of electrons gained in the reduction half-reaction, the two half-reactions can be added together to obtain the overall cell reaction:
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
4. Cell Diagram:
The cell diagram for a Daniel cell is represented as:
Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || Cu2+(aq) | Cu(s)
In conclusion, in a Daniel cell, the oxidation half occurs at the zinc electrode and the reduction half occurs at the copper electrode. This allows for the flow of electrons from the zinc electrode to the copper electrode through the external circuit, generating an electric current.
What is released at ovulation?- a)Primary oocyte arrested at meiosis I
- b)Primary oocyte arrested at meiosis II
- c)Secondary oocyte arrested at meiosis I
- d)Secondary oocyte arrested at meiosis II
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Primary oocyte arrested at meiosis I
b)
Primary oocyte arrested at meiosis II
c)
Secondary oocyte arrested at meiosis I
d)
Secondary oocyte arrested at meiosis II

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
At ovulation, a secondary oocyte arrested at meiosis II is released from the ovary. This secondary oocyte will only complete meiosis II if it is fertilized by a sperm.
In an electrochemical cell, the electrode having a higher reduction potential will act as:- a)salt bridge
- b)Electrolyte
- c)Anode
- d)Cathode
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In an electrochemical cell, the electrode having a higher reduction potential will act as:
a)
salt bridge
b)
Electrolyte
c)
Anode
d)
Cathode
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The correct answer is option D.
Reduction potential refers to the voltage required to reduce a material under standard conditions. If a material has a higher reduction potential it takes more energy to reduce it than a lower reduction potential material. Therefore the higher reduction potential material is actually oxidized to reduce the lower reduction potential material.
Cathode- The electrode where reduction occurs and
The one with the highest reduction potential selected as the reduction half-reaction and therefore is cathode.
Cathode- The electrode where reduction occurs and
The one with the highest reduction potential selected as the reduction half-reaction and therefore is cathode.
During spermatogenesis, what is the number of chromosomes in each secondary spermatocyte?- a) 23 chromosomes
- b) 46 chromosomes
- c) 92 chromosomes
- d) 69 chromosomes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During spermatogenesis, what is the number of chromosomes in each secondary spermatocyte?
a)
23 chromosomes
b)
46 chromosomes
c)
92 chromosomes
d)
69 chromosomes

|
Eveleen Kaur answered |
As in spermatogenesis or in any gametogenesis we undergo meiosis , and during meiosis the cells received at end have half the no. of cell which was divided
MEIOSIS FOR SPERMATOGENESIS BY CELL HAVING 46 CHROMOSOMES > CHROMOSOMES , DNA AND CELLULAR APPARATUS DOUBLED { 92 CHROMOSOMES }> 2 CELLS FORMED WITH 46 CHROMOSOMES > THESE CELLS FURTHER DIVIDE TO GAMETE CELLS HAVING HALF THE NO. OF CHROMOSOMES THAT IS 23 AND GIVE TOTAL OF 4 GAMETE CELLS HAVING 23 CHROMOSOMES
HOPE IT WAS HELPFUL
The cell representation of the given reactions is:
Zn(s) + 2Ag+ → Zn2+ + 2Ag(s)- a)Ag | Ag+||Zn2+|Zn
- b)Zn2+|Zn||Ag | Ag+
- c)Ag+| Ag||Zn|Zn2+
- d)Zn|Zn2+||Ag+|Ag
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The cell representation of the given reactions is:
Zn(s) + 2Ag+ → Zn2+ + 2Ag(s)
Zn(s) + 2Ag+ → Zn2+ + 2Ag(s)
a)
Ag | Ag+||Zn2+|Zn
b)
Zn2+|Zn||Ag | Ag+
c)
Ag+| Ag||Zn|Zn2+
d)
Zn|Zn2+||Ag+|Ag
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The galvanic cell in which the given reaction takes place is depicted as:
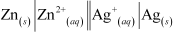
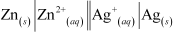
The correct sequence of spermatogenetic stages leading to the formation of sperms in athe mature human testis is - a)spermatocyte - spermatogonia - spermatid - sperms
- b)spermatogonia - spermatocyte - spermatid -sperms
- c)spermatid-spermatocyte-spermatogonia -sperms
- d)spermatogonia-spermatid-spermatocyte -sperms
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct sequence of spermatogenetic stages leading to the formation of sperms in a
the mature human testis is
a)
spermatocyte - spermatogonia - spermatid - sperms
b)
spermatogonia - spermatocyte - spermatid -sperms
c)
spermatid-spermatocyte-spermatogonia -sperms
d)
spermatogonia-spermatid-spermatocyte -sperms

|
Bs Academy answered |
The correct sequence of spermatogenetic stages leading to the formation of sperms in a mature human testis is:
- Spermatogonia
- Spermatocyte
- Spermatid
- Sperms
Explanation:
- Spermatogonia are the undifferentiated cells in the testes.
- Spermatogonia undergo mitosis to form primary spermatocytes.
- Primary spermatocytes undergo meiosis to form secondary spermatocytes which further differentiate into spermatids.
- Spermatids mature into sperm cells through the process of spermiogenesis.
- Spermatogonia
- Spermatocyte
- Spermatid
- Sperms
Explanation:
- Spermatogonia are the undifferentiated cells in the testes.
- Spermatogonia undergo mitosis to form primary spermatocytes.
- Primary spermatocytes undergo meiosis to form secondary spermatocytes which further differentiate into spermatids.
- Spermatids mature into sperm cells through the process of spermiogenesis.
Oogenesis differs from spermatogenesis in a number of aspects. One of the following is, however, a similarity between the two:- a)Growth phase is prolonged in both of them and starts before birth
- b)Both give rise to non-motile gametes
- c)Both produce an equal number of gametes
- d)Both occur inside the primary sex organ
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Oogenesis differs from spermatogenesis in a number of aspects. One of the following is, however, a similarity between the two:
a)
Growth phase is prolonged in both of them and starts before birth
b)
Both give rise to non-motile gametes
c)
Both produce an equal number of gametes
d)
Both occur inside the primary sex organ

|
Stepway Academy answered |
The correct similarity between oogenesis and spermatogenesis is that both occur inside the primary sex organs:
Oogenesis occurs in the ovaries (female primary sex organ).
Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes (male primary sex organ).
Other options are incorrect:
The growth phase in oogenesis is prolonged and starts before birth, but in spermatogenesis, it starts at puberty.
Oogenesis produces non-motile ova, while spermatogenesis produces motile sperm.
Oogenesis typically produces one viable gamete per cycle, while spermatogenesis produces millions of sperm continuously.
Thus, the correct answer is Option D.
Oogenesis occurs in the ovaries (female primary sex organ).
Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes (male primary sex organ).
Other options are incorrect:
The growth phase in oogenesis is prolonged and starts before birth, but in spermatogenesis, it starts at puberty.
Oogenesis produces non-motile ova, while spermatogenesis produces motile sperm.
Oogenesis typically produces one viable gamete per cycle, while spermatogenesis produces millions of sperm continuously.
Thus, the correct answer is Option D.
The division of a primary oocyte results in:- a)Unequal cells: a smaller haploid secondary oocyte and a larger diploid polar body
- b)Unequal cells: a larger haploid secondary oocyte and a smaller haploid polar body
- c)Unequal cells: a smaller diploid secondary oocyte and a larger haploid polar body
- d)Equal cells: a haploid secondary oocyte and a haploid polar body
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The division of a primary oocyte results in:
a)
Unequal cells: a smaller haploid secondary oocyte and a larger diploid polar body
b)
Unequal cells: a larger haploid secondary oocyte and a smaller haploid polar body
c)
Unequal cells: a smaller diploid secondary oocyte and a larger haploid polar body
d)
Equal cells: a haploid secondary oocyte and a haploid polar body

|
Stepway Academy answered |
The process you're asking about occurs during oogenesis, which is the formation of egg cells (ova) in females. Here's how it works:
- Primary Oocyte: The primary oocyte is a diploid cell, meaning it has two sets of chromosomes (2n). This cell begins the first meiotic division.
- First Meiotic Division: During the first meiotic division, the primary oocyte divides unevenly. This asymmetrical division results in two cells:
- Secondary Oocyte: This is the larger cell, and it contains most of the cytoplasm from the original primary oocyte. It is haploid, meaning it has only one set of chromosomes (n).
- First Polar Body: This is the smaller cell, which also has a haploid set of chromosomes (n) but very little cytoplasm. The polar body is generally considered non-functional and may eventually degenerate.
- Reason for Unequal Division: The unequal division ensures that the secondary oocyte retains enough cytoplasm and organelles to support early development if fertilization occurs. The polar body, being smaller and less resourced, is a byproduct of this process.
If fertilization occurs, the secondary oocyte will undergo a second meiotic division to form the mature ovum and another polar body. However, only one functional egg cell is produced from the original primary oocyte.
This process ensures that the resulting egg has enough nutrients and cellular machinery to support the early stages of embryonic development.
Positive mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges corresponds to- a)Repulsion
- b)Attraction
- c)Can’t predict
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Positive mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges corresponds to
a)
Repulsion
b)
Attraction
c)
Can’t predict
d)
None of the above
|
|
Kiran Khanna answered |
Explanation:
The mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges is given by,
U = (1/4πε0) * (q1q2/r)
where q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the charges, r is the distance between them, and ε0 is the permittivity of free space.
If the charges are of the same sign, i.e., both positive or both negative, then the product q1q2 is positive. As a result, the mutual potential energy U will also be positive. This means that the charges will experience a repulsive force, and will tend to move away from each other.
On the other hand, if the charges are of opposite sign, i.e., one positive and the other negative, then the product q1q2 will be negative. As a result, the mutual potential energy U will also be negative. This means that the charges will experience an attractive force, and will tend to move towards each other.
Therefore, we can conclude that a positive mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges corresponds to repulsion between the charges.
The mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges is given by,
U = (1/4πε0) * (q1q2/r)
where q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the charges, r is the distance between them, and ε0 is the permittivity of free space.
If the charges are of the same sign, i.e., both positive or both negative, then the product q1q2 is positive. As a result, the mutual potential energy U will also be positive. This means that the charges will experience a repulsive force, and will tend to move away from each other.
On the other hand, if the charges are of opposite sign, i.e., one positive and the other negative, then the product q1q2 will be negative. As a result, the mutual potential energy U will also be negative. This means that the charges will experience an attractive force, and will tend to move towards each other.
Therefore, we can conclude that a positive mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges corresponds to repulsion between the charges.
Which of the following cells during gametogenesis is normally diploid?- a)Primary polar body
- b)Spermatid
- c)Spermatogonia
- d)Secondary polar body
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following cells during gametogenesis is normally diploid?
a)
Primary polar body
b)
Spermatid
c)
Spermatogonia
d)
Secondary polar body

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
During gametogenesis, the cell that is normally diploid is:
- Spermatogonia
- Spermatogonia are the diploid cells in the testes that undergo mitosis to produce more spermatogonia or differentiate into primary spermatocytes.
- They are the germ cells that give rise to sperm cells through the process of spermatogenesis.
Therefore, the correct answer is C: Spermatogonia.
- Spermatogonia
- Spermatogonia are the diploid cells in the testes that undergo mitosis to produce more spermatogonia or differentiate into primary spermatocytes.
- They are the germ cells that give rise to sperm cells through the process of spermatogenesis.
Therefore, the correct answer is C: Spermatogonia.
Q. Which of the following cells provide nutrition to the male germ cells in the seminiferous tubules?- a)Leydig cells
- b)Sertoli cells
- c)Spermatogonia
- d)Interstitial cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Q. Which of the following cells provide nutrition to the male germ cells in the seminiferous tubules?
a)
Leydig cells
b)
Sertoli cells
c)
Spermatogonia
d)
Interstitial cells

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The correct answer is B: Sertoli cells.
- Sertoli cells:
- Located in the seminiferous tubules of the testes.
- Provide support and nutrition to developing male germ cells (spermatogonia) through various stages of spermatogenesis.
- Create a blood-testis barrier, protecting germ cells from harmful substances.
- Secrete growth factors and hormones essential for germ cell development and maturation.
- Sertoli cells:
- Located in the seminiferous tubules of the testes.
- Provide support and nutrition to developing male germ cells (spermatogonia) through various stages of spermatogenesis.
- Create a blood-testis barrier, protecting germ cells from harmful substances.
- Secrete growth factors and hormones essential for germ cell development and maturation.
These functions make Sertoli cells crucial for the proper development and nourishment of male germ cells.
What initiates the process of spermatogenesis in males at puberty?- a) Increase in testosterone levels
- b) Secretion of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
- c) Secretion of luteinising hormone (LH)
- d) Secretion of gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What initiates the process of spermatogenesis in males at puberty?
a)
Increase in testosterone levels
b)
Secretion of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
c)
Secretion of luteinising hormone (LH)
d)
Secretion of gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)
|
|
Abhijeet Iyer answered |
Initiation of Spermatogenesis at Puberty
Spermatogenesis is the process of sperm cell development, and its initiation during puberty is a crucial aspect of male reproductive health. The triggering mechanism involves several hormones, but the primary initiator is the secretion of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH).
Role of GnRH
- Location of Secretion: GnRH is produced in the hypothalamus.
- Function: It stimulates the anterior pituitary gland to release two key hormones: Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH).
Subsequent Hormonal Cascade
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH):
- Stimulates Sertoli cells in the testes.
- Promotes the maturation of sperm cells and supports spermatogenesis.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH):
- Stimulates Leydig cells in the testes to produce testosterone.
- Testosterone plays a vital role in the development of male secondary sexual characteristics and further supports spermatogenesis.
Significance of Increased Testosterone Levels
- While testosterone is crucial for the process, it is the increase in GnRH that sets off the hormonal cascade.
- Testosterone’s effects are felt after the initial stimulation by GnRH, making it a secondary player in the initiation.
Conclusion
In summary, the initiation of spermatogenesis at puberty is primarily driven by the secretion of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH), which subsequently leads to increased levels of FSH and LH, and eventually testosterone. This interplay of hormones is essential for the development of male fertility.
Spermatogenesis is the process of sperm cell development, and its initiation during puberty is a crucial aspect of male reproductive health. The triggering mechanism involves several hormones, but the primary initiator is the secretion of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH).
Role of GnRH
- Location of Secretion: GnRH is produced in the hypothalamus.
- Function: It stimulates the anterior pituitary gland to release two key hormones: Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH).
Subsequent Hormonal Cascade
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH):
- Stimulates Sertoli cells in the testes.
- Promotes the maturation of sperm cells and supports spermatogenesis.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH):
- Stimulates Leydig cells in the testes to produce testosterone.
- Testosterone plays a vital role in the development of male secondary sexual characteristics and further supports spermatogenesis.
Significance of Increased Testosterone Levels
- While testosterone is crucial for the process, it is the increase in GnRH that sets off the hormonal cascade.
- Testosterone’s effects are felt after the initial stimulation by GnRH, making it a secondary player in the initiation.
Conclusion
In summary, the initiation of spermatogenesis at puberty is primarily driven by the secretion of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH), which subsequently leads to increased levels of FSH and LH, and eventually testosterone. This interplay of hormones is essential for the development of male fertility.
A particle of mass 1 kg and charge 1/3μC is projected towards a non conducting fixed spherical shell having the same charge uniformly distributed on its surface. The minimum initial velocity V0 of projection of particle required if the particle just grazes the shell is
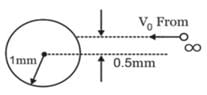
- a)
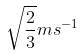
- b)
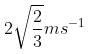
- c)2/3 ms-1
- d)1 ms-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle of mass 1 kg and charge 1/3μC is projected towards a non conducting fixed spherical shell having the same charge uniformly distributed on its surface. The minimum initial velocity V0 of projection of particle required if the particle just grazes the shell is


a)
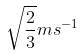
b)
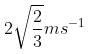
c)
2/3 ms-1
d)
1 ms-1
|
|
Amar Shah answered |
From conservation of angular momentum,

from conservation of energy,
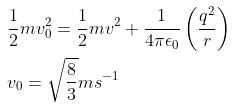

from conservation of energy,
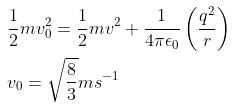
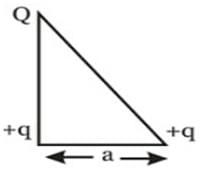
Three point charges Q, +q and +q are placed at the vertices of a right-angled isosceles triangle as shown in the figure. If the net electrostaic energy of the configuration is zero, find the value Q\q is [Take √2 = 1.4]
- a)-2q
- b)+q
- c)
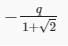
- d)
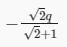
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Three point charges Q, +q and +q are placed at the vertices of a right-angled isosceles triangle as shown in the figure. If the net electrostaic energy of the configuration is zero, find the value Q\q is [Take √2 = 1.4]

a)
-2q
b)
+q
c)
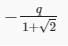
d)
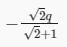
|
|
Raghavendra Rane answered |
Given,
The distance between them when the electrostatic energy between two charges q1 and q2 is given as 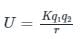
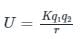
According to the principle of superposition, total energy of the charge system as shown in the figure below is
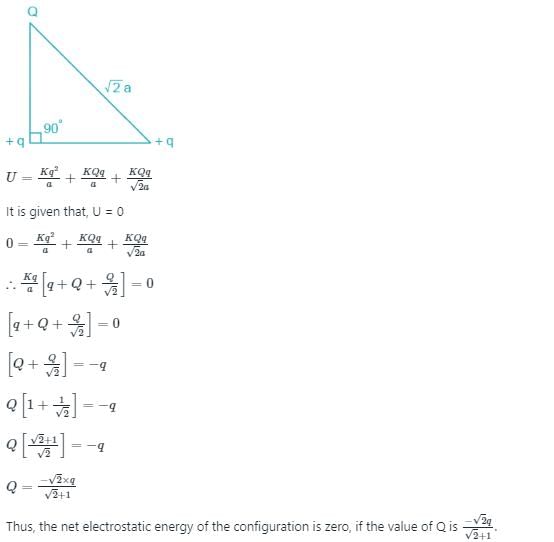
Chapter doubts & questions for May Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of May Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup