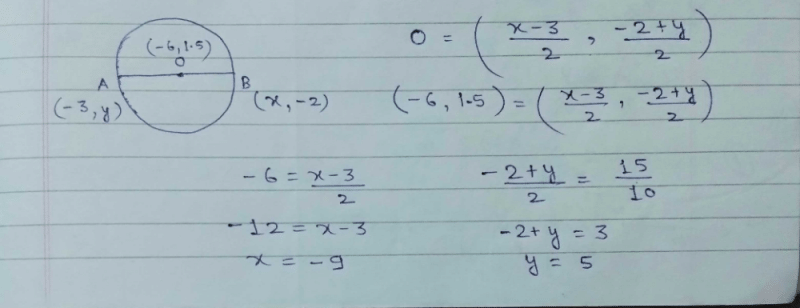All Exams >
Class 10 >
Weekly Tests for Class 10 Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of August Week 3 for Class 10 Exam
Which place in India is ideal for utilising tidal energy?
- a)Gulf of Kachchh
- b)Gulf of Khambhat
- c)Both A and B
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which place in India is ideal for utilising tidal energy?
a)
Gulf of Kachchh
b)
Gulf of Khambhat
c)
Both A and B
d)
None of these

|
Arshiya Mehta answered |
In India, the Gulf of Kachchh, provides ideal conditions for utilising tidal energy. A 900 mw tidal energy power plant is set up here by the National Hydropower Corporation.
The line segment joining (2, – 3) and (5, 6) is divided by x-axis in the ratio:- a)2 : 1
- b)3 : 1
- c)1 : 2
- d)1 : 3.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The line segment joining (2, – 3) and (5, 6) is divided by x-axis in the ratio:
a)
2 : 1
b)
3 : 1
c)
1 : 2
d)
1 : 3.
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
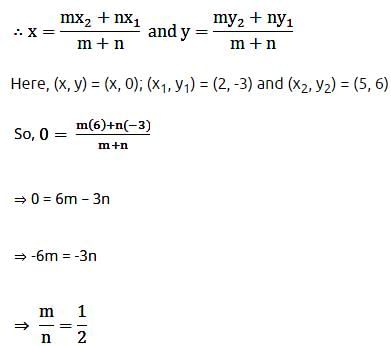
Hence, the ratio is 1:2 and the division is internal.
Which out of the following is a non-conventional source of energy? - a)Atomic energy
- b)Firewood
- c)Coal
- d)Natural gas
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which out of the following is a non-conventional source of energy?
a)
Atomic energy
b)
Firewood
c)
Coal
d)
Natural gas
|
|
Madhu Sulaniya answered |
The sources of energy which are exhaustible and being produced continuously in nature are called nonconventional energy or renewable sources of energy. atomic energy is the only option.
The Monazite sands of Kerala are rich in: - a)coal
- b)uranium
- c)thorium
- d)platinum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
coal
b)
uranium
c)
thorium
d)
platinum
|
|
Varun Kapoor answered |
Due to the alpha decay of thorium and uranium, monazite contains a significant amount of helium, which can be extracted by heating. Monazite is an important ore for thorium, lanthanum, and cerium. It is often found in placer deposits. India, Madagascar, and South Africa have large deposits of monazite sands.
What is low grade brown coal called?- a)Bituminous
- b)Anthracite
- c)Lignite
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is low grade brown coal called?
a)
Bituminous
b)
Anthracite
c)
Lignite
d)
None of these
|
|
Aditya Kumar answered |
Lignite, often referred to as brown coal, is a soft, brown, combustible, sedimentary rock formed from naturally compressed peat. It is considered the lowest rank of coal due to its relatively low heat content.
Which out of the following is derived from the ocean waters? - a)Limestone
- b)Sandstone
- c)Cobalt
- d)Bromine
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Limestone
b)
Sandstone
c)
Cobalt
d)
Bromine
|
|
Rahul Desai answered |
The most recoverable form of bromine is from soluble salts found in seawater, salt lakes, inland seas and brine wells. Sea water contains bromine in about 65 parts per million (ppm) but bromine is found in much higher concentrations (2,500 to 10,000 ppm) in inland seas and brine wells.
Which mineral is used for generating atomic or nuclear power? - a)Coal
- b)Bauxite
- c)Uranium
- d)Copper
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which mineral is used for generating atomic or nuclear power?
a)
Coal
b)
Bauxite
c)
Uranium
d)
Copper
|
|
Alok Verma answered |
C is the correct option.Uranium and Thorium, which are available in Jharkhand and the Aravalli ranges of Rajasthan are used for generating atomic or nuclear power. The Monazite sands of Kerala is also rich in Thorium.
What are the Khetri mines famous for?- a)Coal
- b)Copper
- c)Iron
- d)Gold
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the Khetri mines famous for?
a)
Coal
b)
Copper
c)
Iron
d)
Gold
|
|
Sneha Shah answered |
B is the correct option.Khetri is actually two towns, "Khetri Town" founded by Raja Khet Singhji Nirwan and "Khetri Nagar" which is about 10 km away from Khetri. Khetri Nagar, well known for its “Copper” Project, was built by and is under the control of Hindustan Copper Limited, a public sector undertaking under the Government of India.
What is 'Rat hole' mining? - a)Mining in places where there are lots of rats
- b)Mining done by family members in the form of a long narrow tunnel
- c)Mining that kills rats
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is 'Rat hole' mining?
a)
Mining in places where there are lots of rats
b)
Mining done by family members in the form of a long narrow tunnel
c)
Mining that kills rats
d)
None of these
|
|
Arun Kumar answered |
Rat-hole mining is a primitive and hazardous method of mining for coal, with tunnels that are only 3-4 feet in diameter (hence, rat-hole), leading to pits ranging from 5-100 sq. mt deep.
For the triangle whose sides are along the lines y = 15, 3x – 4y = 0, 5x + 12y = 0, the incentre is :- a)(1, 8)
- b)(8, 1)
- c)(-1, 8)
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For the triangle whose sides are along the lines y = 15, 3x – 4y = 0, 5x + 12y = 0, the incentre is :
a)
(1, 8)
b)
(8, 1)
c)
(-1, 8)
d)
None of these
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Given equations:
3x – 4y = 0 …(1)
5x+12y = 0 …(2)
Y-15 = 0 …(3)
From the given equations, (1), (2) and (3) represent the sides AB, BC and CA respectively.
Solving (1) and (2), we get
x= 0, and y= 0
Therefore, the side AB and BC intersect at the point B (0, 0)
Solving (1) and (3), we get
x= 20, y= 15
Hence, the side AB and CA intersect at the point A (20, 15)
Solving (2) and (3), we get
x= -36, y = 15
Thus, the side BC and CA intersect at the point C (-36, 15)
Now,
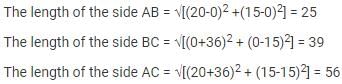
BC = a = 39
CA = b = 56
AB = c = 25
Similarly, (x1, y1) = A(20, 15)
CA = b = 56
AB = c = 25
Similarly, (x1, y1) = A(20, 15)
(x2, y2) = B(0, 0)
(x3, y3) = C(-36, 15)
(x3, y3) = C(-36, 15)
Therefore, incentre is
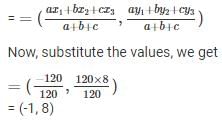
In which kind of rocks are the minerals deposited and accumulated in the strata's?- a)Igneous rocks
- b)Metamorphic rocks
- c)Sedimentary rocks
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which kind of rocks are the minerals deposited and accumulated in the strata's?
a)
Igneous rocks
b)
Metamorphic rocks
c)
Sedimentary rocks
d)
None of these
|
|
Arun Khatri answered |
C is the correct option.Minerals are found in layers or strata in sedimentary rocks. Minerals are accumulated in horizontal strata after being exposed to high heat and pressure for a long period of time. Coal, iron ore, gypsum, potash salt etc are formed in this way.
Practice Test/Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with Solutions of Chapter "Coordinate Geometry" are available for CBSE Class 10 Mathematics (Maths) and have been compiled as per the syllabus of CBSE Class 10 Mathematics (Maths) Q. The distance between the points (a, b) and (– a, – b) is :- a)a2+b2
- b)
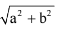
- c)0
- d)
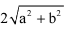
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Practice Test/Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with Solutions of Chapter "Coordinate Geometry" are available for CBSE Class 10 Mathematics (Maths) and have been compiled as per the syllabus of CBSE Class 10 Mathematics (Maths)
Q. The distance between the points (a, b) and (– a, – b) is :
a)
a2+b2
b)
c)
0
d)

|
Flembe Academy answered |
We have distance formula as d = 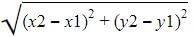
Where x1=a,y1=b,x2=-a,y2=-b
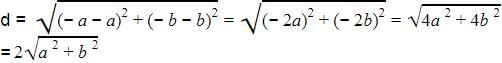
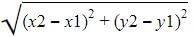
Where x1=a,y1=b,x2=-a,y2=-b
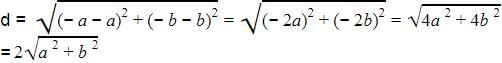
The Koderma-Gaya-Hazaribagh belt of Jharkhand is a leading producer of: - a)copper
- b)manganese
- c)iron ore
- d)mica
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Koderma-Gaya-Hazaribagh belt of Jharkhand is a leading producer of:
a)
copper
b)
manganese
c)
iron ore
d)
mica
|
|
Shounak Desai answered |
D is the correct option.Koderma district is rich in minerals. The Koderma district and the Lokai-Indarwa area covers the southern part of Great Mica-Belt of Jharkhand, Bihar, and India.
Which part of the nervous system serves as the main coordinating center for receiving information and controlling voluntary actions?- a)Peripheral nervous system
- b)Spinal cord only
- c)Central nervous system
- d)Cranial nerves
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Peripheral nervous system
b)
Spinal cord only
c)
Central nervous system
d)
Cranial nerves

|
Kds Coaching answered |
The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, is the main coordinating center of the body. It receives information from all parts of the body, integrates it, and sends messages to muscles to control voluntary actions such as writing, talking, and moving. The peripheral nervous system facilitates communication between the CNS and other body parts but does not serve as the main control center.
Nagarcoil and Jaisalmer are well-known for the effective use of ?- a)tidal energy
- b)geothermal energy
- c)wind energy
- d)biogas
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Nagarcoil and Jaisalmer are well-known for the effective use of ?
a)
tidal energy
b)
geothermal energy
c)
wind energy
d)
biogas
|
|
Raghavendra Iyer answered |
C is the correct option. Nagercoil and Jaisalmer are well known for effective use of wind energy in the country.
The distance between points (a + b, b + c) and (a – b, c – b) is :- a)
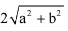
- b)
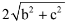
- c)
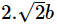
- d)
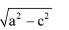
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The distance between points (a + b, b + c) and (a – b, c – b) is :
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Distance between two point is
root[{(a+b)-(a-b)}^2] + [{(b+c)-(c-b)}^2]
=root [{(a+b-a+b)^2}] + [((b+c-c+b)}^2]
=root[(2b)^2 + (2b)^2]
=root[4b^2 +4b^2]
=root[8b^2]
=2.root(2)b
The co-ordinates of the points which divides the join of (– 2, – 2) and (– 5, 7) in the ratio 2 : 1 is :- a)(4, – 4)
- b)(– 3, 1)
- c)(– 4, 4)
- d)(1, – 3).
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The co-ordinates of the points which divides the join of (– 2, – 2) and (– 5, 7) in the ratio 2 : 1 is :
a)
(4, – 4)
b)
(– 3, 1)
c)
(– 4, 4)
d)
(1, – 3).

|
Kamna Science Academy answered |
To find the co-ordinates that divide the line segment joining the points (–2, –2) and (–5, 7) in the ratio 2:1, use the section formula:
- Let the points be:
- x1 = –2, y1 = –2
- x2 = –5, y2 = 7
- Using the section formula, the co-ordinates are calculated as follows:
- x = (m2x1 + m1x2) / (m1 + m2)
- y = (m2y1 + m1y2) / (m1 + m2)
- Here, m1 = 2 and m2 = 1.
- Substituting the values:
- x = (1 × (–2) + 2 × (–5)) / (2 + 1) = (–2 – 10) / 3 = –4
- y = (1 × (–2) + 2 × 7) / (2 + 1) = (–2 + 14) / 3 = 4
- The result is the point (–4, 4).
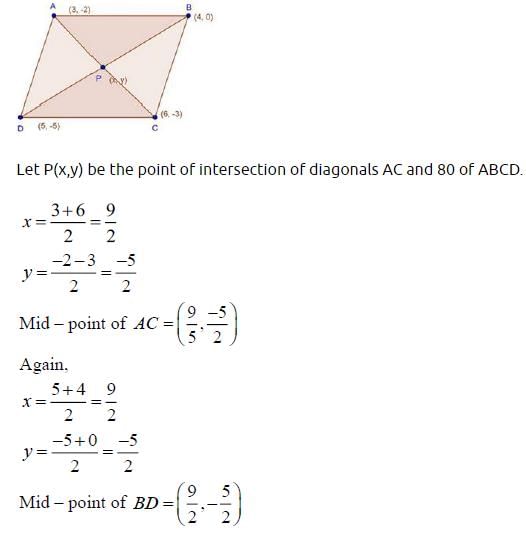
If two vertices of a parallelogram are (3, 2) and (–1, 0) and the diagonals intersect at (2, –5), then the other two vertices are :- a)(1, –10), (5, –12)
- b)(1, –12), (5, –10)
- c)(2, –10), (5, –12)
- d)(1, – 10), (2, – 12)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If two vertices of a parallelogram are (3, 2) and (–1, 0) and the diagonals intersect at (2, –5), then the other two vertices are :
a)
(1, –10), (5, –12)
b)
(1, –12), (5, –10)
c)
(2, –10), (5, –12)
d)
(1, – 10), (2, – 12)
|
|
Parth Chawla answered |
Let's call the two given vertices A and B, with coordinates (3, 2) and (x, y) respectively.
Since a parallelogram has opposite sides that are parallel, we can find the coordinates of the other two vertices by applying the same translation to points A and B.
To find the translation, we can subtract the x-coordinate of point A from the x-coordinate of point B, and subtract the y-coordinate of point A from the y-coordinate of point B:
x - 3 = 3 - 3 = 0
y - 2 = 2 - 2 = 0
So the translation is (0, 0).
To find the coordinates of the other two vertices, we can add the translation to points A and B:
Point A + translation = (3, 2) + (0, 0) = (3, 2)
Point B + translation = (x, y) + (0, 0) = (x, y)
Therefore, the other two vertices of the parallelogram are (3, 2) and (x, y).
Since a parallelogram has opposite sides that are parallel, we can find the coordinates of the other two vertices by applying the same translation to points A and B.
To find the translation, we can subtract the x-coordinate of point A from the x-coordinate of point B, and subtract the y-coordinate of point A from the y-coordinate of point B:
x - 3 = 3 - 3 = 0
y - 2 = 2 - 2 = 0
So the translation is (0, 0).
To find the coordinates of the other two vertices, we can add the translation to points A and B:
Point A + translation = (3, 2) + (0, 0) = (3, 2)
Point B + translation = (x, y) + (0, 0) = (x, y)
Therefore, the other two vertices of the parallelogram are (3, 2) and (x, y).
If (3, 2), (4, k) and (5, 3) are collinear then k is equal to :- a)3/2
- b)2/5
- c)5/2
- d)3/5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If (3, 2), (4, k) and (5, 3) are collinear then k is equal to :
a)
3/2
b)
2/5
c)
5/2
d)
3/5
|
|
Swara sharma answered |
To determine the value of k, we need to check if the three given points (3, 2), (4, k), and (5, 3) are collinear. Two points are collinear if the slope between them is the same as the slope between any other two points on the line.
Calculating the slope between (3, 2) and (4, k):
The slope formula is given by:
m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
Using the coordinates (3, 2) and (4, k), we have:
m = (k - 2) / (4 - 3)
m = (k - 2) / 1
m = k - 2
Calculating the slope between (4, k) and (5, 3):
Using the coordinates (4, k) and (5, 3), we have:
m = (3 - k) / (5 - 4)
m = (3 - k) / 1
m = 3 - k
Since the two slopes are equal, we can equate them:
k - 2 = 3 - k
Solving this equation for k:
2k = 5
k = 5/2
Therefore, the value of k is 5/2, which corresponds to option C.
Calculating the slope between (3, 2) and (4, k):
The slope formula is given by:
m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
Using the coordinates (3, 2) and (4, k), we have:
m = (k - 2) / (4 - 3)
m = (k - 2) / 1
m = k - 2
Calculating the slope between (4, k) and (5, 3):
Using the coordinates (4, k) and (5, 3), we have:
m = (3 - k) / (5 - 4)
m = (3 - k) / 1
m = 3 - k
Since the two slopes are equal, we can equate them:
k - 2 = 3 - k
Solving this equation for k:
2k = 5
k = 5/2
Therefore, the value of k is 5/2, which corresponds to option C.
The co-ordinates of the point on x-axis which is equidistant from the points (5, 4) and (– 2, 3) are :- a)(2, 0)
- b)(3, 0)
- c)(0, 2)
- d)(0, 3).
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The co-ordinates of the point on x-axis which is equidistant from the points (5, 4) and (– 2, 3) are :
a)
(2, 0)
b)
(3, 0)
c)
(0, 2)
d)
(0, 3).

|
Surbhi Gupta answered |
Let the point on x-axis be (a,0)
Since PA = PB PA2 = PB2
(a + 2)2 + (0 - 5)2 = (a - 2)2 + (0 + 3)2
(a + 2)2 - (a - 2)2 = 9 - 25 = -16
8a = -16 a = -2.
The required point is (-2,0).
Which state in India is the largest producer of bauxite? - a)Odisha
- b)Karnataka
- c)Maharashtra
- d)Kerala
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which state in India is the largest producer of bauxite?
a)
Odisha
b)
Karnataka
c)
Maharashtra
d)
Kerala
|
|
Harshita Jain answered |
Odisha is the largest bauxite producing state accounting for more than half of the total production of India.The main bauxite belt is in kalahandi and Koraput districts.
The points (1, 7), (4, 2), (– 1, 1) and (– 4, 4) are the vertices of a :- a)parallelogram
- b)rhombus
- c)rectangle
- d)square.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The points (1, 7), (4, 2), (– 1, 1) and (– 4, 4) are the vertices of a :
a)
parallelogram
b)
rhombus
c)
rectangle
d)
square.
|
|
Rahul Kapoor answered |
Given points are (1,7),(4,2),(-1,-1),(-4,4)
Let the points are A,B,C,D.
Distance formula = √(x₂-x₁)^2+(y₂-y₁)^2
AB = √(4-1)^2+(2-7)^2
= √9+25
= √34
BC = √(-1-4)^2+(-1-2)^2
= √25+9
= √34
CD = √(-4-(-1))^2+(4-(-1))^2
= √9+25
= √34
DA = √(1-(-4))^2+(7-4)^2
= √25+9
= √34
We know that the all sides of the square are equal.
Here by the distance formula, we got the for sides equal .
So,from this we can say that these points are the vertices of a square.
The points (– 2, 2), (8, – 2) and (– 4, – 3) are the vertices of a :- a)equilateral Δ
- b)isosceles Δ
- c)right Δ
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The points (– 2, 2), (8, – 2) and (– 4, – 3) are the vertices of a :
a)
equilateral Δ
b)
isosceles Δ
c)
right Δ
d)
None of these
|
|
Izumi answered |
Let A(-2, 2)
B(8, -2)
C(-4, -3)
distance
AB=√(x2-x1) ²+(y2-y1) ²
=√(8+2) ²+(-2-2) ²=√100+16=√116
BC=√(-4-8) ²+(-3+2) ²=√144+1=√145
AC=√(-4+2) ²+(-3-2) ²=√4+25=√29
from the above
AB²=(√116) ²=116
BC²=(√145) ²=145
AC²=(√29) ²=29
AB²+AC²=BC²=145units
hence, by Converse of Pythagoras theorem
ABC is a right triangle
and hence,
A, B, C are the vertices of a right ∆
hence, option (C) is correct
B(8, -2)
C(-4, -3)
distance
AB=√(x2-x1) ²+(y2-y1) ²
=√(8+2) ²+(-2-2) ²=√100+16=√116
BC=√(-4-8) ²+(-3+2) ²=√144+1=√145
AC=√(-4+2) ²+(-3-2) ²=√4+25=√29
from the above
AB²=(√116) ²=116
BC²=(√145) ²=145
AC²=(√29) ²=29
AB²+AC²=BC²=145units
hence, by Converse of Pythagoras theorem
ABC is a right triangle
and hence,
A, B, C are the vertices of a right ∆
hence, option (C) is correct
Which out of the following minerals is formed as a result of evaporation in the arid regions? - a)Gypsum
- b)Zinc
- c)Coal
- d)Copper
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which out of the following minerals is formed as a result of evaporation in the arid regions?
a)
Gypsum
b)
Zinc
c)
Coal
d)
Copper
|
|
Meha shukla answered |
- Gypsum is formed as a result of evaporation.
- Minerals are formed in various forms in the earth and they normally are formed in layers or beds through the sedimentary rocks.
- Minerals are formed in various forms in the earth and they normally are formed in layers or beds through the sedimentary rocks.
Which out of the following minerals is formed by the decomposition of surface rocks, and leaves a residual mass of weathered material? - a)Gold
- b)Bauxite
- c)Zinc
- d)Coal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which out of the following minerals is formed by the decomposition of surface rocks, and leaves a residual mass of weathered material?
a)
Gold
b)
Bauxite
c)
Zinc
d)
Coal
|
|
Dhruv Choudhury answered |
B is the correct option.Bauxite is a mineral which is formed by decomposition of rocks, leaving a residual mass of weathered material.
For the triangle whose sides are along the lines x = 0, y = 0 and x/6+y/8 = 1, the incentre is :- a)(3, 4)
- b)(2, 2)
- c)(2, 3)
- d)(3, 2)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For the triangle whose sides are along the lines x = 0, y = 0 and x/6+y/8 = 1, the incentre is :
a)
(3, 4)
b)
(2, 2)
c)
(2, 3)
d)
(3, 2)
|
|
Kalyan singh answered |
Finding the Incentre of a Triangle
To find the incentre of a triangle, we need to find the point where the angle bisectors of the triangle meet. The angle bisectors are the lines that divide the angles of the triangle into two equal parts. The incentre is the intersection of these angle bisectors and is equidistant from all three sides of the triangle.
Given Triangle
The triangle in the question has sides along the lines x = 0, y = 0 and x/6 y/8 = 1. Let's first plot these lines on a graph to get a visual representation of the triangle.
We can see that the triangle is a right-angled triangle with vertices at (0, 0), (6, 0) and (0, 8). Now, let's find the equation of the angle bisectors of this triangle.
Finding the Equation of Angle Bisectors
To find the equation of the angle bisectors, we need to first find the equations of the two lines that form each angle. We can then find the midpoint of these lines and the slope of the angle bisector. Finally, we can use the point-slope form of a line to find the equation of the angle bisector.
Let's start with the angle formed by sides (0, 0) to (6, 0) and (0, 8). The equation of the line joining these two points is y = -3/4x + 8. Now, let's find the equation of the line perpendicular to this line that passes through the midpoint of the line segment joining (0, 0) and (6, 0).
The midpoint of the line segment joining (0, 0) and (6, 0) is (3, 0). The slope of the line joining (0, 0) and (6, 0) is 0. Therefore, the slope of the line perpendicular to this line is undefined (since it is a vertical line). The equation of the line passing through (3, 0) with undefined slope is x = 3.
Using the same method, we can find the equation of the angle bisector of the angle formed by sides (0, 0) to (0, 8) and (6, 0). The equation of the line joining these two points is y = 8/6x = 4/3x. The midpoint of the line segment joining (0, 0) and (0, 8) is (0, 4). The slope of the line joining (0, 0) and (0, 8) is undefined. Therefore, the slope of the line perpendicular to this line is 0. The equation of the line passing through (0, 4) with slope 0 is y = 4.
Intersection of Angle Bisectors
Now that we have the equations of the two angle bisectors, we can find their intersection point, which is the incentre of the triangle. The intersection point is the solution to the system of equations:
x = 3
y = 4
y = 4
The solution to this system of equations is (3, 4), which is option (c). Therefore, the incentre of the triangle whose sides are along the lines x = 0, y = 0 and x/6 y/8 = 1 is
To find the incentre of a triangle, we need to find the point where the angle bisectors of the triangle meet. The angle bisectors are the lines that divide the angles of the triangle into two equal parts. The incentre is the intersection of these angle bisectors and is equidistant from all three sides of the triangle.
Given Triangle
The triangle in the question has sides along the lines x = 0, y = 0 and x/6 y/8 = 1. Let's first plot these lines on a graph to get a visual representation of the triangle.
We can see that the triangle is a right-angled triangle with vertices at (0, 0), (6, 0) and (0, 8). Now, let's find the equation of the angle bisectors of this triangle.
Finding the Equation of Angle Bisectors
To find the equation of the angle bisectors, we need to first find the equations of the two lines that form each angle. We can then find the midpoint of these lines and the slope of the angle bisector. Finally, we can use the point-slope form of a line to find the equation of the angle bisector.
Let's start with the angle formed by sides (0, 0) to (6, 0) and (0, 8). The equation of the line joining these two points is y = -3/4x + 8. Now, let's find the equation of the line perpendicular to this line that passes through the midpoint of the line segment joining (0, 0) and (6, 0).
The midpoint of the line segment joining (0, 0) and (6, 0) is (3, 0). The slope of the line joining (0, 0) and (6, 0) is 0. Therefore, the slope of the line perpendicular to this line is undefined (since it is a vertical line). The equation of the line passing through (3, 0) with undefined slope is x = 3.
Using the same method, we can find the equation of the angle bisector of the angle formed by sides (0, 0) to (0, 8) and (6, 0). The equation of the line joining these two points is y = 8/6x = 4/3x. The midpoint of the line segment joining (0, 0) and (0, 8) is (0, 4). The slope of the line joining (0, 0) and (0, 8) is undefined. Therefore, the slope of the line perpendicular to this line is 0. The equation of the line passing through (0, 4) with slope 0 is y = 4.
Intersection of Angle Bisectors
Now that we have the equations of the two angle bisectors, we can find their intersection point, which is the incentre of the triangle. The intersection point is the solution to the system of equations:
x = 3
y = 4
y = 4
The solution to this system of equations is (3, 4), which is option (c). Therefore, the incentre of the triangle whose sides are along the lines x = 0, y = 0 and x/6 y/8 = 1 is
The distance between A (1, 3) and B (x, 7) is 5. The value of x > 0 is :- a)4
- b)2
- c)1
- d)3.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The distance between A (1, 3) and B (x, 7) is 5. The value of x > 0 is :
a)
4
b)
2
c)
1
d)
3.

|
Kamna Science Academy answered |
The distance between points A(1, 3) and B(x, 7) is given by the distance formula:
sqrt((x - 1)² + (7 - 3)²) = 5
Simplify inside the square root:
sqrt((x - 1)² + 16) = 5
Square both sides to remove the square root:
(x - 1)² + 16 = 25
Subtract 16 from both sides:
(x - 1)² = 9
Take the square root of both sides:
x - 1 = ±3
So, x = 1 + 3 = 4 or x = 1 - 3 = -2
Since x > 0, the valid solution is x = 4.
The answer is A.
What involuntary actions are controlled by the Medulla in the hindbrain?- a)Regulation of respiration
- b)Control of posture and balance
- c)Precision of voluntary actions
- d)Reflex movements of head, neck, and trunk
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer??
a)
Regulation of respiration
b)
Control of posture and balance
c)
Precision of voluntary actions
d)
Reflex movements of head, neck, and trunk
|
|
Sanaya sharma answered |
Involuntary Actions Controlled by the Medulla
The medulla oblongata is a crucial part of the hindbrain, responsible for regulating several vital involuntary actions essential for survival.
Regulation of Respiration
- The medulla plays a key role in controlling the rhythm and rate of breathing.
- It contains respiratory centers that send signals to the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, facilitating inhalation and exhalation.
- It responds to changes in carbon dioxide and oxygen levels in the blood, ensuring the body's respiratory needs are met.
Other Functions of the Medulla
- While respiration is a primary function, the medulla also regulates:
- Heart rate: It influences cardiac function by controlling the autonomic nervous system.
- Blood pressure: It helps in maintaining blood pressure through vasomotor control.
- Reflex actions: The medulla is involved in reflexes such as coughing, sneezing, and swallowing.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
- Control of Posture and Balance: This function is primarily managed by the cerebellum, which coordinates muscle movements and maintains balance.
- Precision of Voluntary Actions: The motor cortex and basal ganglia are responsible for the precision and coordination of voluntary movements, not the medulla.
- Reflex Movements of Head, Neck, and Trunk: While the medulla does play a role in some reflex actions, it is not the primary center for all reflex movements of the head, neck, and trunk, which involve different neural pathways.
Conclusion
In summary, the medulla oblongata’s primary involuntary action is the regulation of respiration, making option 'A' the correct answer. Its role in maintaining vital functions is essential for life.
The medulla oblongata is a crucial part of the hindbrain, responsible for regulating several vital involuntary actions essential for survival.
Regulation of Respiration
- The medulla plays a key role in controlling the rhythm and rate of breathing.
- It contains respiratory centers that send signals to the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, facilitating inhalation and exhalation.
- It responds to changes in carbon dioxide and oxygen levels in the blood, ensuring the body's respiratory needs are met.
Other Functions of the Medulla
- While respiration is a primary function, the medulla also regulates:
- Heart rate: It influences cardiac function by controlling the autonomic nervous system.
- Blood pressure: It helps in maintaining blood pressure through vasomotor control.
- Reflex actions: The medulla is involved in reflexes such as coughing, sneezing, and swallowing.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
- Control of Posture and Balance: This function is primarily managed by the cerebellum, which coordinates muscle movements and maintains balance.
- Precision of Voluntary Actions: The motor cortex and basal ganglia are responsible for the precision and coordination of voluntary movements, not the medulla.
- Reflex Movements of Head, Neck, and Trunk: While the medulla does play a role in some reflex actions, it is not the primary center for all reflex movements of the head, neck, and trunk, which involve different neural pathways.
Conclusion
In summary, the medulla oblongata’s primary involuntary action is the regulation of respiration, making option 'A' the correct answer. Its role in maintaining vital functions is essential for life.
Chapter doubts & questions for August Week 3 - Weekly Tests for Class 10 Preparation 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of August Week 3 - Weekly Tests for Class 10 Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily