All Exams >
Civil Engineering (CE) >
6 Months Preparation for GATE Civil Engg >
All Questions
All questions of Shallow Foundation and Bearing Capacity for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam
As per IS 2131 - 1981, the drive weight used in standard penetration test (SPT) is ______ KG- a)50
- b)63.5
- c)42.5
- d)75
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
As per IS 2131 - 1981, the drive weight used in standard penetration test (SPT) is ______ KG
a)
50
b)
63.5
c)
42.5
d)
75
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
SPT test can be conducted to determine:
a) Relative Density of sands
b) Angle of internal friction
c) Unconfined compressive strength of clays
d) Ultimate bearing capacity on the basis of shear criteria
e) Allowable bearing pressure on the basis of settlement criteria
In this test, the split spoon sampler is driven by dynamic mechanism of hammer. This test is conducted either at every 2 to 5 meter interval or at the change of stratum.
Note:
The weight of the hammer is 63.5 kg.
The height of free fall is 750 mm or 75 cm.
The inner and outer diameter of the sampler is 35 mm and 50.5 mm respectively.
Which of the following pose a limitation to plate load test?- a)Effect of size of foundation and Test on cohesive soil
- b)Load increment
- c)None of the mentioned
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pose a limitation to plate load test?
a)
Effect of size of foundation and Test on cohesive soil
b)
Load increment
c)
None of the mentioned
d)
All of the mentioned

|
Crack Gate answered |
A limitation of plate load test is
i) Effect of the size of foundation. For clayey soils the ultimate pressure for a large foundation is the same as that of the test plate. But in dense sandy soils, the bearing capacity increases, with the size of the foundation
ii) Plate load test is essentially a short duration test, and hence the test does not give the ultimate settlement, particularly in the case of cohesive soil.
i) Effect of the size of foundation. For clayey soils the ultimate pressure for a large foundation is the same as that of the test plate. But in dense sandy soils, the bearing capacity increases, with the size of the foundation
ii) Plate load test is essentially a short duration test, and hence the test does not give the ultimate settlement, particularly in the case of cohesive soil.
Which of the following N factors has the widest range of values?- a)Nc
- b)Nq
- c)Nγ
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following N factors has the widest range of values?
a)
Nc
b)
Nq
c)
Nγ
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
The Nγ factor has the widest suggested range of any value of N factors. A literature value reveals that for φ = 40°, 38≤ Nγ≤192.
Rankine considered the first soil element (element 1) at ___________- a)Base of the structure
- b)Below the foundation
- c)Edge of the footing
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rankine considered the first soil element (element 1) at ___________
a)
Base of the structure
b)
Below the foundation
c)
Edge of the footing
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Rankine considered the equilibrium of two soil elements, The first one immediately below the foundation (element 1).
State of equilibrium is fully developed in which of the following bearing capacity failures?- a)Local shear failure
- b)General shear failure
- c)Punching shear failure
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
State of equilibrium is fully developed in which of the following bearing capacity failures?
a)
Local shear failure
b)
General shear failure
c)
Punching shear failure
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
In general shear failure, when the pressure approaches the value of qf, the state of equilibrium is reached initially in the soil around the soil and gradually spreads, ultimately the state of plastic equilibrium is fully developed throughout the soil above the failure surfaces.
An embankment is to be constructed with granular soil (bulk unit weight = 20 kN/m3) on a saturated clayey silt deposit (undrained shear strength = 25 kPa). Assuming undrained general shear failure and bearing capacity factor of 5.7, the maximum height (in m) of the embankment at the point of failure is- a)7.1
- b)5.0
- c)4.5
- d)2.5
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An embankment is to be constructed with granular soil (bulk unit weight = 20 kN/m3) on a saturated clayey silt deposit (undrained shear strength = 25 kPa). Assuming undrained general shear failure and bearing capacity factor of 5.7, the maximum height (in m) of the embankment at the point of failure is
a)
7.1
b)
5.0
c)
4.5
d)
2.5
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Given,
bulk unit weight (γb) = 20 kN/m3
Undrained shear strength (S = C) = 25 kPa
Bearing Capacity Nc = 5.7, General Shear Failure
We know qu = CNc
qu = γ Df = 25 × (5.7)
20 × Df = 142.5
Df = 7.124 m
In a standard penetration test, what is the weight of the hammer and the dropping height used as per IS 2131-1981?- a)63.5 kg, 450 mm
- b)4.89 kg, 450 mm
- c)2.6 kg, 310 mm
- d)63.5 kg, 750mm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a standard penetration test, what is the weight of the hammer and the dropping height used as per IS 2131-1981?
a)
63.5 kg, 450 mm
b)
4.89 kg, 450 mm
c)
2.6 kg, 310 mm
d)
63.5 kg, 750mm
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
SPT test can be conducted to determine:
(a) Relative Density of sands
(b) Angle of internal friction
(c) Unconfined compressive strength of clays
(d) Ultimate bearing capacity on the basis of shear criteria
(e) Allowable bearing pressure on the basis of settlement criteria
In this test, the split spoon sampler is driven by dynamic mechanism of hammer. This test is conducted either at every 2 to 5 meter interval or at the change of stratum.
Note:
The weight of the hammer is 63.5 kg.
The height of free fall is 750 mm or 75 cm.
The inner and outer diameter of the sampler is 35 mm and 50.5 mm respectively.
Which of the following is an essential difference between Vesic’s and Hansen’s procedure?- a)Different values of Nγ and Variation on some of Hansen inclination
- b)Different value of Nq and Nc
- c)None of the mentioned
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an essential difference between Vesic’s and Hansen’s procedure?
a)
Different values of Nγ and Variation on some of Hansen inclination
b)
Different value of Nq and Nc
c)
None of the mentioned
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
The essential difference in Vesic’s and Hansen’s procedure are i) use of slightly different values of Ny and ii) a variation on some of Hansen’s inclination, base and ground factors.
In the Bowl’s method for finding the effect of water table, which of the following factor is used for soil in the wedge zone?- a)Water reduction factor
- b)Effective unit weight
- c)Overburden pressure
- d)Average unit weight
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the Bowl’s method for finding the effect of water table, which of the following factor is used for soil in the wedge zone?
a)
Water reduction factor
b)
Effective unit weight
c)
Overburden pressure
d)
Average unit weight
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
In the third method (Bowles, 1988), no water reduction factor is used, but effective unit weight (γe) is used for the soil in the wedge zone.
In general shear failure, continuous failure is developed between ______________- a)Ground surface and footing
- b)Edge of the footing and ground surface
- c)Foundation and the ground surface
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In general shear failure, continuous failure is developed between ______________
a)
Ground surface and footing
b)
Edge of the footing and ground surface
c)
Foundation and the ground surface
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
In the case of general shear failure, continuous failure surface develops between the edges of the footing and the ground surface.
The value of Nc and Nq are same for, which of the following methods?- a)Meyerhof
- b)Hansen
- c)Vesic
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of Nc and Nq are same for, which of the following methods?
a)
Meyerhof
b)
Hansen
c)
Vesic
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
The value of Nc and Nq are same for Meyerhof, Hansen and Vesic method, while subscripts for Nγ identify the author, i.e. N γ(H) = valued by Hansen etc.
What is the maximum permissible differential settlement for isolated foundation on clay as per I.S. code?- a)25 mm
- b)40 mm
- c)25 mm to 40 mm
- d)65 mm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the maximum permissible differential settlement for isolated foundation on clay as per I.S. code?
a)
25 mm
b)
40 mm
c)
25 mm to 40 mm
d)
65 mm
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
IS code specification for permissible settlement:
(i) Total Permissible settlement:
- For isolated footing on clay = 65 mm
- For isolated footing on sand = 40 mm
- For raft footing on clay = 65-100 mm
- For raft footing on sand = 40-65 mm
(ii) Permissible Differential settlement:
- For isolated footing on clay = 40 mm
- For isolated footing on sand = 25 mm
(iii) Permissible angular settlement:
- For high framed structure < 1/500
- To prevent all type of minor damage < 1/1000
Note: For multi-storeyed buildings having isolated foundations on sand, the maximum permissible settlement is 60 mm [ For multistorey buildings having isolated foundations take the higher load as compare to single storey buildings having isolated foundations. So that deflection caused by multistorey building having isolated foundation higher than 40 mm (from the safer side)]
The equation Nc = (Nq – 1) cot φ, have been adopted by ___________- a)Terzaghi and Peck
- b)Hansen
- c)Vesic
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The equation Nc = (Nq – 1) cot φ, have been adopted by ___________
a)
Terzaghi and Peck
b)
Hansen
c)
Vesic
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
The two equations Nc = (Nq – 1) cot φ and Nq = tan2 (45 + φ/2) ex tan φ have been adopted by i) Terzaghi and Peck ii) Hansen iii) Vesic iv) Meyerhof and Bureau of Indian standards.
Local shear failure is associated with soils having _________- a)High compressibility
- b)High pore pressure
- c)Low porosity
- d)Low compressibility
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Local shear failure is associated with soils having _________
a)
High compressibility
b)
High pore pressure
c)
Low porosity
d)
Low compressibility
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Local shear failure occurs in soil having high compressibility and in sands having relative density lying between 35 and 70 percent.
The net safe bearing capacity is defined by which of the following equation?- a)qns=qnf / F
- b)qns = qnf + σ̅
- c)qns = qf – σ̅
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The net safe bearing capacity is defined by which of the following equation?
a)
qns=qnf / F
b)
qns = qnf + σ̅
c)
qns = qf – σ̅
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
The net safe bearing capacity is the net ultimate bearing capacity divided by a factor of safety F i.e., qns = qnf/F.
Which of the following equation has been recommended by Indian standard for finding reduction factor in water table?- a)R w = 0.5 (1 + z w2/B)
- b)R w = (1 + z w2/B)
- c)R w = c Nc + σ̅. Nq + 0.5γBNγ
- d)R w = z w2 / B
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following equation has been recommended by Indian standard for finding reduction factor in water table?
a)
R w = 0.5 (1 + z w2/B)
b)
R w = (1 + z w2/B)
c)
R w = c Nc + σ̅. Nq + 0.5γBNγ
d)
R w = z w2 / B
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Rw =Rw2 = 5 (1 + z w2 / B) has been recommended by Indian standard at a depth D1 below the ground level.
According to the assumptions in Terzaghi’s analysis, the soil is _______________- a)Homogeneous and Isotropic
- b)Non Homogeneous
- c)None of the mentioned
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
According to the assumptions in Terzaghi’s analysis, the soil is _______________
a)
Homogeneous and Isotropic
b)
Non Homogeneous
c)
None of the mentioned
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
In Terzaghi’s analysis the soil is homogeneous and isotropic and its shear strength is represented by Coulomb’s equation.
Rankine considered the equilibrium of second soil element at __________- a)Base of the structure
- b)Below the foundation
- c)Edge of the footing
- d)Top of the foundation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Rankine considered the equilibrium of second soil element at __________
a)
Base of the structure
b)
Below the foundation
c)
Edge of the footing
d)
Top of the foundation
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Rankine considered the equilibrium of the other soil element (element 2) beyond the edge of the footing, but adjacent to element 1.
For analysis of pavements and determination of modulus of sub-grade reaction by plate load test, the most representative value of modulus reaction can be obtained at a pressure of______g/cm2- a)1.70
- b)0.20
- c)2.50
- d)0.70
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For analysis of pavements and determination of modulus of sub-grade reaction by plate load test, the most representative value of modulus reaction can be obtained at a pressure of______g/cm2
a)
1.70
b)
0.20
c)
2.50
d)
0.70
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Concept:
Plate load test:
- The plate load test is a field test, which is performed to determine the ultimate bearing capacity of the soil and the probable settlement under a given load.
- This test is very popular for the selection and design of shallow foundation.
Procedure:
- Excavate test pit up to the desired depth. The pit size should be at least 5 times the size of the test plate (Bp).
- At the center of the pit, a small hole or depression is created. The size of the hole is the same as the size of the steel plate.
- A mild steel plate is used as a load-bearing plate whose thickness should be at least 25 mm thickness and size may vary from 300 mm to 750 mm. The plate can be square or circular. Generally, a square plate is used for square footing and a circular plate is used for circular footing.
- A column is placed at the center of the plate. The load is transferred to the plate through the centrally placed column.
- The load can be transferred to the column either by the gravity loading method or by the truss method.
- At least two dial gauges should be placed at diagonal corners of the plate to record the settlement. The gauges are placed on a platform so that it does not settle with the plate.
- Apply a seating load of 0.7 g/cm2 or T/m2 and release before the actual loading starts.
- The initial readings are noted.
- The load is then applied through the hydraulic jack and increased gradually. The increment is generally one-fifth of the expected safe bearing capacity or one-tenth of the ultimate bearing capacity or any other smaller value. The applied load is noted from the pressure gauge.
- The settlement is observed for each increment and from the dial gauge. After increasing the load-settlement should be observed after 1, 4, 10, 20, 40, and 60 minutes and then at hourly intervals until the rate of settlement is less than .02 mm per hour. The readings are noted in tabular form.
- After completing the collection of data for a particular loading, the next load increment is applied and readings are noted under new load. This increment and data collection is repeated until the maximum load is applied. The maximum load is generally 1.5 times the expected ultimate load or 3 times of the expected allowable bearing pressure.
When the water table is above the base of the footing, the submerged weight ‘γ’ can be used to compute __________- a)Effective pressure and Surcharge
- b)Pore pressure
- c)None of the mentioned
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When the water table is above the base of the footing, the submerged weight ‘γ’ can be used to compute __________
a)
Effective pressure and Surcharge
b)
Pore pressure
c)
None of the mentioned
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
When the water table is above the base of the footing, the submerged weight ‘γ’ should be used for the soil below the water table for computing the effective pressure or the surcharge.
The bearing capacity of cohesion-less soil at the ground surface is __________- a)Unity
- b)Less than one
- c)Zero
- d)Greater than one
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The bearing capacity of cohesion-less soil at the ground surface is __________
a)
Unity
b)
Less than one
c)
Zero
d)
Greater than one
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
According to Rankine’s equation bearing capacity of cohesion less soil is zero at the ground surface.
A strip footing is resting on the ground surface of a pure clay bed having an undrained cohesion cu. The ultimate bearing capacity of the footing is equal to- a)2πcu
- b)πcu
- c)(π + 1)cu
- d)(π + 2)cu
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A strip footing is resting on the ground surface of a pure clay bed having an undrained cohesion cu. The ultimate bearing capacity of the footing is equal to
a)
2πcu
b)
πcu
c)
(π + 1)cu
d)
(π + 2)cu
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Ultimate bearing capacity for a strip footing is
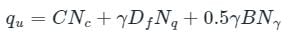
For pure clay, Nc = 5.14, Nq = 1 and Nγ = 0 (∵ assuming smooth footing)
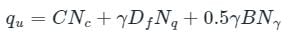
For pure clay, Nc = 5.14, Nq = 1 and Nγ = 0 (∵ assuming smooth footing)
Footing is on the ground surface i.e. D = 0
qu = cuNc
qu = 5.14 cu
qu = (π + 2)cu
The concept of analysis of bearing capacity failure was first developed by ___________- a)Terzaghi
- b)Meyerhof
- c)Prandtl
- d)Darcy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The concept of analysis of bearing capacity failure was first developed by ___________
a)
Terzaghi
b)
Meyerhof
c)
Prandtl
d)
Darcy
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
The concept of failure analysis was first developed by Prandtl, and later extended by Terzaghi, Meyerhof and others.
For purely cohesive soil, the bearing capacity is given by which of the following equation?- a)qf = 5.7 c + σ̅
- b)qf = c + σ̅
- c)qf = 5.7 c
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For purely cohesive soil, the bearing capacity is given by which of the following equation?
a)
qf = 5.7 c + σ̅
b)
qf = c + σ̅
c)
qf = 5.7 c
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
For purely cohesive soil the bearing capacity is
qf = c Nc + σ̅ Nq = 5.7 c + σ̅
Where σ̅ = γ D if the water table is below the base of the footing.
qf = c Nc + σ̅ Nq = 5.7 c + σ̅
Where σ̅ = γ D if the water table is below the base of the footing.
In local shear failure, the development of plastic equilibrium is ______________- a)Full
- b)Partial
- c)Zero
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In local shear failure, the development of plastic equilibrium is ______________
a)
Full
b)
Partial
c)
Zero
d)
None of the mentioned

|
Bhaskar Rane answered |
In local shear failure, the development of plastic equilibrium is Full.
Explanation:
Local shear failure occurs when a section of a structural member, such as a beam or column, fails due to excessive shear forces. It is characterized by the formation of a plastic hinge, which is a localized region of the member that undergoes plastic deformation.
When a plastic hinge forms, the material in that region of the member starts to yield and undergoes permanent deformation. This plastic deformation allows the member to redistribute the excessive shear forces and achieve a state of plastic equilibrium.
In local shear failure, the development of plastic equilibrium is full, which means that the plastic hinge forms and the member is able to redistribute the shear forces throughout the plastic region. This plastic redistribution of forces helps to prevent further failure and collapse of the member.
The formation of a plastic hinge is an important mechanism in structural engineering because it allows the member to absorb and dissipate energy during extreme loading conditions, such as earthquakes or high wind events. The plastic deformation in the hinge region absorbs energy and helps to prevent sudden and catastrophic failure of the member.
It is worth noting that the development of plastic equilibrium in local shear failure is different from global shear failure. In global shear failure, the entire member fails in shear, without the formation of a plastic hinge. In this case, the development of plastic equilibrium is zero, as there is no redistribution of forces and the member collapses.
Overall, in local shear failure, the development of plastic equilibrium is full, allowing the member to redistribute shear forces and prevent further failure.
Explanation:
Local shear failure occurs when a section of a structural member, such as a beam or column, fails due to excessive shear forces. It is characterized by the formation of a plastic hinge, which is a localized region of the member that undergoes plastic deformation.
When a plastic hinge forms, the material in that region of the member starts to yield and undergoes permanent deformation. This plastic deformation allows the member to redistribute the excessive shear forces and achieve a state of plastic equilibrium.
In local shear failure, the development of plastic equilibrium is full, which means that the plastic hinge forms and the member is able to redistribute the shear forces throughout the plastic region. This plastic redistribution of forces helps to prevent further failure and collapse of the member.
The formation of a plastic hinge is an important mechanism in structural engineering because it allows the member to absorb and dissipate energy during extreme loading conditions, such as earthquakes or high wind events. The plastic deformation in the hinge region absorbs energy and helps to prevent sudden and catastrophic failure of the member.
It is worth noting that the development of plastic equilibrium in local shear failure is different from global shear failure. In global shear failure, the entire member fails in shear, without the formation of a plastic hinge. In this case, the development of plastic equilibrium is zero, as there is no redistribution of forces and the member collapses.
Overall, in local shear failure, the development of plastic equilibrium is full, allowing the member to redistribute shear forces and prevent further failure.
Which of the following is a limitation, of assumption in Terzaghi’s analysis?- a)φ changes when the soil is compressed and strip footing has a rough base
- b)Soil is homogeneous
- c)None of the mentioned
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a limitation, of assumption in Terzaghi’s analysis?
a)
φ changes when the soil is compressed and strip footing has a rough base
b)
Soil is homogeneous
c)
None of the mentioned
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
As the soil compress, φ changes; slight downward movement of footing may not develop fully the plastic planes.
Punching shear may occur in loose sand with density less than ___________- a)45 %
- b)50 %
- c)35 %
- d)20 %
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Punching shear may occur in loose sand with density less than ___________
a)
45 %
b)
50 %
c)
35 %
d)
20 %
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Punching shear may occur in relatively loose sand with relative density less than 35 %.
When a state of equilibrium is reached under the footing?- a)Load on footing increase
- b)Load on footing decreases
- c)Safe bearing capacity of the soil is reached
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When a state of equilibrium is reached under the footing?
a)
Load on footing increase
b)
Load on footing decreases
c)
Safe bearing capacity of the soil is reached
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
When the load on footing increases, and approaches a value qf, a state of plastic equilibrium is reached under the footing.
In local shear failure, the failure surface do not reach the ground surface because ____________- a)Compression of soil under the footing
- b)Ultimate bearing capacity is not well defined
- c)Failure is defined by large settlements
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In local shear failure, the failure surface do not reach the ground surface because ____________
a)
Compression of soil under the footing
b)
Ultimate bearing capacity is not well defined
c)
Failure is defined by large settlements
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
In local shear failure there is a significant compression of the soil under the footing and only partial development of state of plastic equilibrium. Due to this reason, the failure surface does not reach the ground.
According to Terzaghi theory, what is the value of coefficient (Nc) for an angle of shear resistance (ϕ) = 0?- a)9.14
- b)5.70
- c)5.14
- d)5.50
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Terzaghi theory, what is the value of coefficient (Nc) for an angle of shear resistance (ϕ) = 0?
a)
9.14
b)
5.70
c)
5.14
d)
5.50
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
As per Terzaghi's method, ultimate bearing capacity of strip footing is given by the equation
qu = CNc + γDf.Nq + 0.5.B.γNγ
Where, B = Width of footing (Least lateral dimension)
Df = Depth of footing below G.L.
γDf = Surcharge at foundation level.
Nc, Nq, Nγ are bearing capacity factors which depend upon frictional angle of soil.
For purely cohesive soils, ϕ = 0°
Nc = 5.7, Nq = 1 and Nγ = 0
Which of the following are original Terzaghi values for Nγ?- a)34° and 48°
- b)60°
- c)None of the mentioned
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are original Terzaghi values for Nγ?
a)
34° and 48°
b)
60°
c)
None of the mentioned
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
The values of Nγ for φ of 34° and 48° are the original Terzaghi values which were used by Bowles to back compute Kpγ.
During the state of shear failure, which of the following principal stress relationship exist?- a)σ1 = σ tan α + 2c tan α
- b)σ1 = σ3 tan2 α + 2c tan α
- c)σ1 = 2c tan α
- d)σ1 = σ3 tan α
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During the state of shear failure, which of the following principal stress relationship exist?
a)
σ1 = σ tan α + 2c tan α
b)
σ1 = σ3 tan2 α + 2c tan α
c)
σ1 = 2c tan α
d)
σ1 = σ3 tan α
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
During the state of shear failure (plastic equilibrium), the following principal stress relationship exists σ1 = σ3 tan2 α + 2c tan α
for cohesion-less soil,σ1 = σ3 tan2 α.
for cohesion-less soil,σ1 = σ3 tan2 α.
The unit soil pressure or safe bearing pressure is also known as:- a)Net Allowable Bearing Pressure
- b)Net Safe Settlement Pressure
- c)Net Ultimate Bearing Pressure
- d)Gross Safe Bearing Pressure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The unit soil pressure or safe bearing pressure is also known as:
a)
Net Allowable Bearing Pressure
b)
Net Safe Settlement Pressure
c)
Net Ultimate Bearing Pressure
d)
Gross Safe Bearing Pressure
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Concepts:
The maximum pressure a soil can withstand without undergoing settlement in excess of the permissible value for the structure is called allowable bearing capacity or net safe bearing pressure or safe bearing pressure.
The maximum pressure a soil can withstand without the occurrence of shear failure is called ultimate bearing capacity of soil (qu).
The net pressure at the base of foundation in excess of initial overburden pressure which a soil can withstand without shear failure called net ultimate bearing capacity.
Or
Qnu = qu - Overburden pressure(q)
When factor of safety is applied on the net ultimate bearing capacity, then it is called net safe bearing capacity (qns).
Safe bearing capacity: qs = qns + Effective overburden pressure
Observed N-value of an SPT test is 21. The N-value after correcting for dilatancy is- a)18
- b)21
- c)19
- d)15
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Observed N-value of an SPT test is 21. The N-value after correcting for dilatancy is
a)
18
b)
21
c)
19
d)
15
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Concept;
Dilatancy correction:
It is to be applied when No obtained after overburden correction, exceeds 15 in saturated fine sands and silts. IS: 2131-1981 incorporates the Terzaghi and Peck recommended dilatancy correction (when No > 15) using the equation
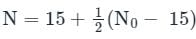
N0 - SPT value after overburden correction
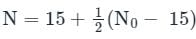
N0 - SPT value after overburden correction
Calculation:
Given: N0 = 21
N = 15 + 1/2(21−15)
⇒ N = 18
Which of the following is a characteristic of general shear failure?
- a)A well – defined failure pattern
- b)Sudden, catastrophic failure accompanied by tilting of foundation
- c)All of the mentioned
- d)Bulging of the ground surface adjacent to the foundation.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a characteristic of general shear failure?
a)
A well – defined failure pattern
b)
Sudden, catastrophic failure accompanied by tilting of foundation
c)
All of the mentioned
d)
Bulging of the ground surface adjacent to the foundation.

|
Neha Mukherjee answered |
General shear failure in soil occurs when the shearing force applied to the soil exceeds its shear strength, leading to a sudden and catastrophic failure. This type of failure is characterized by several distinct features, one of which is the bulging of the shearing mass of soil.
Here is a detailed explanation of each characteristic of general shear failure:
1. Bulging of shearing mass of soil:
During general shear failure, the soil mass undergoes significant deformation in the form of bulging. This bulging occurs along the failure plane and is caused by the lateral displacement of soil particles. As the shearing force increases, the soil particles are pushed aside, resulting in the expansion and bulging of the soil mass. This bulging is a visible indication of the failure and can be observed on the surface of the soil.
2. Failure is sudden:
General shear failure is an abrupt and rapid process. The failure occurs when the applied shear stress exceeds the shear strength of the soil, leading to a sudden collapse or rupture. This failure is characterized by a rapid loss of strength and stability, often resulting in significant damage or collapse of structures built on or within the soil.
3. Failure is not accompanied by compressibility of soil:
Unlike other modes of failure, such as compressive failure or bearing failure, general shear failure is not accompanied by significant compressibility of the soil. The failure occurs primarily due to the shearing forces acting on the soil mass, rather than compressive forces. As a result, the failure is characterized by lateral movement and deformation, rather than vertical compression.
In conclusion, the characteristic of general shear failure that is mentioned in the given options is the bulging of the shearing mass of soil. This bulging is a visible indication of the failure and occurs due to the lateral displacement of soil particles along the failure plane. The other options, such as compressibility of soil and sudden failure, are not exclusive to general shear failure but may be observed in other types of soil failure as well.
Here is a detailed explanation of each characteristic of general shear failure:
1. Bulging of shearing mass of soil:
During general shear failure, the soil mass undergoes significant deformation in the form of bulging. This bulging occurs along the failure plane and is caused by the lateral displacement of soil particles. As the shearing force increases, the soil particles are pushed aside, resulting in the expansion and bulging of the soil mass. This bulging is a visible indication of the failure and can be observed on the surface of the soil.
2. Failure is sudden:
General shear failure is an abrupt and rapid process. The failure occurs when the applied shear stress exceeds the shear strength of the soil, leading to a sudden collapse or rupture. This failure is characterized by a rapid loss of strength and stability, often resulting in significant damage or collapse of structures built on or within the soil.
3. Failure is not accompanied by compressibility of soil:
Unlike other modes of failure, such as compressive failure or bearing failure, general shear failure is not accompanied by significant compressibility of the soil. The failure occurs primarily due to the shearing forces acting on the soil mass, rather than compressive forces. As a result, the failure is characterized by lateral movement and deformation, rather than vertical compression.
In conclusion, the characteristic of general shear failure that is mentioned in the given options is the bulging of the shearing mass of soil. This bulging is a visible indication of the failure and occurs due to the lateral displacement of soil particles along the failure plane. The other options, such as compressibility of soil and sudden failure, are not exclusive to general shear failure but may be observed in other types of soil failure as well.
Which of the following is not one of the characteristics of a local shear failure?- a)Failure is defined by large settlements
- b)Failure surface do not reach the ground surface
- c)Failure is sudden
- d)Ultimate bearing capacity is not well defined
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not one of the characteristics of a local shear failure?
a)
Failure is defined by large settlements
b)
Failure surface do not reach the ground surface
c)
Failure is sudden
d)
Ultimate bearing capacity is not well defined
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
In local shear stress there is no tilting of footing and therefore the failure is not sudden.
Vesic observed _____________ types of bearing capacity failures.- a)2
- b)4
- c)3
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Vesic observed _____________ types of bearing capacity failures.
a)
2
b)
4
c)
3
d)
5
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
In 1963, Vesic observed three types of bearing capacity failures:
i) General shear failure
ii) Local shear failure
iii) Punching shear failure.
i) General shear failure
ii) Local shear failure
iii) Punching shear failure.
The gross pressure intensity (q) of a structure is ___________- a)Total pressure at base of the footing
- b)Excess pressure after the construction of the structure
- c)Minimum pressure intensity at the base
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The gross pressure intensity (q) of a structure is ___________
a)
Total pressure at base of the footing
b)
Excess pressure after the construction of the structure
c)
Minimum pressure intensity at the base
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
The gross pressure intensity q is the total pressure at the base of the footing due to the weight of the superstructure.
Terzaghi’s bearing capacity equation is not applicable for ____________- a)Depth effect and Inclination factor
- b)Narrow slope
- c)None of the mentioned
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Terzaghi’s bearing capacity equation is not applicable for ____________
a)
Depth effect and Inclination factor
b)
Narrow slope
c)
None of the mentioned
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Terzaghi assumed the value of angle ψ = φ, which is not true. Since footings are normally rough, ψ has been found close to 45° + φ/2 than to φ, thus Terzaghi’s bearing capacity equations do not have provision for including depth effects, inclination factors, etc.
The safe bearing capacity can also be referred as _________- a)Net safe bearing capacity
- b)Ultimate bearing capacity
- c)Safe bearing pressure
- d)Net soil pressure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The safe bearing capacity can also be referred as _________
a)
Net safe bearing capacity
b)
Ultimate bearing capacity
c)
Safe bearing pressure
d)
Net soil pressure
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Sometimes, the safe bearing capacity is also referred to as the ultimate bearing capacity qf divided by a factor of safety F.
For purely cohesive soil, local shear failure may be assumed to occur when the soil is ___________- a)Medium to soft
- b)Soft to medium
- c)Hard
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For purely cohesive soil, local shear failure may be assumed to occur when the soil is ___________
a)
Medium to soft
b)
Soft to medium
c)
Hard
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
For purely cohesive soil, local shear failure may be assumed to occur when the soil is soft to medium, with an unconfined compressive strength qu ≤ 100 kN/m2.
When a footing fails due to insufficient bearing capacity, distinct failure patterns are developed depending upon _________- a)Failure mechanism
- b)Plastic equilibrium
- c)Shear strength
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When a footing fails due to insufficient bearing capacity, distinct failure patterns are developed depending upon _________
a)
Failure mechanism
b)
Plastic equilibrium
c)
Shear strength
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Experimental investigations have indicated that when a footing fails due to insufficient bearing capacity, distinct failure patterns are developed, depending upon the type of failure mechanism.
The symbol σ̅, represent which of the following term?- a)Ultimate bearing capacity
- b)Effective surcharge
- c)Gross pressure intensity
- d)Bearing capacity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The symbol σ̅, represent which of the following term?
a)
Ultimate bearing capacity
b)
Effective surcharge
c)
Gross pressure intensity
d)
Bearing capacity
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
σ̅ represents the effective surcharge at the base level of the foundation, assuming total unit weight for the portion of the soil above the water table and submerged unit weight for the portion below the water table.
For clay soil the value of n can be taken as _____________ in the absence of test data.- a)0. 4 to 0.5
- b)0.20 to 0.25
- c)0.003 to 0.05
- d)0.08 to 0.10
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For clay soil the value of n can be taken as _____________ in the absence of test data.
a)
0. 4 to 0.5
b)
0.20 to 0.25
c)
0.003 to 0.05
d)
0.08 to 0.10
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
The value of index n can be determined by carrying out two or more plate load tests on different size plate. In absence of test data, the following values of n can be adopted:
Dense sand : 0.4 to 0.5
Loose sand : 0.20 to 0.25
Clay : 0.003 to 0.05
Sand clay : 0.08 to 0.10.
Dense sand : 0.4 to 0.5
Loose sand : 0.20 to 0.25
Clay : 0.003 to 0.05
Sand clay : 0.08 to 0.10.
The ultimate bearing capacity and the net ultimate capacity are connected by the relation ____________- a)qf = qnf +/- σ̅ and qf = qf – σ̅
- b)qf = qnf – σ̅
- c)None of the mentioned
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The ultimate bearing capacity and the net ultimate capacity are connected by the relation ____________
a)
qf = qnf +/- σ̅ and qf = qf – σ̅
b)
qf = qnf – σ̅
c)
None of the mentioned
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
The ultimate bearing capacity qf and the net ultimate capacity are connected by the following relation:
qf = qnf + σ̅ (or) qf = qf – σ̅
where σ̅ is the effective surcharge at the base level of the foundation.
qf = qnf + σ̅ (or) qf = qf – σ̅
where σ̅ is the effective surcharge at the base level of the foundation.
Which of the following type of loading method is popular now-a-days?- a)Gravity loading platform
- b)Reaction truss
- c)Concrete blocks
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following type of loading method is popular now-a-days?
a)
Gravity loading platform
b)
Reaction truss
c)
Concrete blocks
d)
All of the mentioned

|
Crack Gate answered |
The use of reaction truss is more popular now-a-days since this is simple, quick and less clumsy.
The parameters Nc, Nq, Nγ in the equations of bearing capacity failure are known as _________- a)Constant head
- b)Bearing capacity factors
- c)Effective pressure
- d)Load intensity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The parameters Nc, Nq, Nγ in the equations of bearing capacity failure are known as _________
a)
Constant head
b)
Bearing capacity factors
c)
Effective pressure
d)
Load intensity
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
The parameters Nc, Nq, Nγ are the dimensionless numbers, known as bearing capacity factors depending only on the angle of shearing resistance of the soil.
Local shear failure generally occurs in ___________- a)Dense sand
- b)Non-cohesive soil
- c)Loose sand
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Local shear failure generally occurs in ___________
a)
Dense sand
b)
Non-cohesive soil
c)
Loose sand
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Local shear failure generally occurs in loose sand while general shear failure occurs in dense sand.
Meyerhof’s extended the analysis of plastic equilibrium of a surface footing to __________- a)Shallow foundation and Deep foundation
- b)Inclined foundation
- c)None of the mentioned
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Meyerhof’s extended the analysis of plastic equilibrium of a surface footing to __________
a)
Shallow foundation and Deep foundation
b)
Inclined foundation
c)
None of the mentioned
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
M Meyerhof’s extended the analysis of plastic equilibrium of a surface footing to Shallow and Deep foundation according to both Terzaghi and Meyerhof analysis.
Which of the following term does not contribute to q f?- a)Nc
- b)Nγ
- c)Nq
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following term does not contribute to q f?
a)
Nc
b)
Nγ
c)
Nq
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
The Nγ term does not contribute significantly to qf so that almost any reasonable value can be used. Bureau of Indian standards (BIS) recommends using the value of Nγ, given by Vesic.
Chapter doubts & questions for Shallow Foundation and Bearing Capacity - 6 Months Preparation for GATE Civil Engg 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Shallow Foundation and Bearing Capacity - 6 Months Preparation for GATE Civil Engg in English & Hindi are available as part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
6 Months Preparation for GATE Civil Engg
488 videos|1261 docs|878 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









