All Exams >
Computer Science Engineering (CSE) >
6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE >
All Questions
All questions of Network Layer for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam
Which one of the following is not a function of network layer?- a)routing
- b)inter-networking
- c)congestion control
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a function of network layer?
a)
routing
b)
inter-networking
c)
congestion control
d)
none of the mentioned
|
|
Avinash Mehta answered |
Network Layer :-
The network layer is responsible for the source-to-destination delivery of a packet, possibly across multiple networks (links).
Other functions of the network layer include the following :-
Logical addressing :- In order to identify each device on internetwork uniquely, network layer defines an addressing scheme.
Routing :- The network layer protocols determine which route is suitable from source to destination.
In OSPF, which protocol is used to discover neighbour routers automatically?- a)Link state protocol
- b)Error-correction protocol
- c)Routing information protocol
- d)Hello protocol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In OSPF, which protocol is used to discover neighbour routers automatically?
a)
Link state protocol
b)
Error-correction protocol
c)
Routing information protocol
d)
Hello protocol
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: Hello protocol is used to discover neighbour routers automatically.
Explanation: Hello protocol is used to discover neighbour routers automatically.
The network layer concerns with- a)bits
- b)frames
- c)packets
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The network layer concerns with
a)
bits
b)
frames
c)
packets
d)
none of the mentioned

|
Bijoy Kapoor answered |
The network layer is responsible for routing packets from the source to destination. The routing algorithm is the piece of software that decides where a packet goes next (e.g., which output line, or which node on a broadcast channel).
For connectionless networks, the routing decision is made for each datagram. For connection-oriented networks, the decision is made once, at circuit setup time.
RIP is- a)Protocol used for transmission of IP datagrams across a serial line
- b)Resource information protocol
- c)Protocol used to exchange information between the routers
- d)Protocol used to exchanger information between the layers
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
RIP is
a)
Protocol used for transmission of IP datagrams across a serial line
b)
Resource information protocol
c)
Protocol used to exchange information between the routers
d)
Protocol used to exchanger information between the layers
|
|
Prisha Sharma answered |
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a routing protocol based on the distance vector algorithm, In this each router periodically shares its knowledge about the entire network with its neighbours.
Which packet is NOT an OSPF packet type?- a)LSU
- b)LSR
- c)DBD
- d)Query
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which packet is NOT an OSPF packet type?
a)
LSU
b)
LSR
c)
DBD
d)
Query
|
|
Shubham Ghoshal answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: Query packet is NOT an OSPF packet type.
Explanation: Query packet is NOT an OSPF packet type.
Who can send ICMP error-reporting messages?
- a)Routers
- b)Destination hosts
- c)Source host
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Who can send ICMP error-reporting messages?
a)
Routers
b)
Destination hosts
c)
Source host
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Krithika Kaur answered |
Both router and destination host can send ICMP error-reporting message to inform the source host about any failure or error occurred in packet.
Distance vector protocols use the concept of split horizon, but link-state routing protocols, such as OSPF, do not. - a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Distance vector protocols use the concept of split horizon, but link-state routing protocols, such as OSPF, do not.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Shubham Ghoshal answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: Distance vector protocols use the concept of split horizon, but link-state routing protocols, such as OSPF, do not use this.
Explanation: Distance vector protocols use the concept of split horizon, but link-state routing protocols, such as OSPF, do not use this.
In virtual circuit network each packet contains- a)full source and destination address
- b)a short VC number
- c)both (a) and (b)
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In virtual circuit network each packet contains
a)
full source and destination address
b)
a short VC number
c)
both (a) and (b)
d)
none of the mentioned
|
|
Raghav Joshi answered |
Explanation:
Virtual Circuit Network is a type of network in which a dedicated path is established between the source and destination before transmitting the data. In this network, each packet contains a short VC (Virtual Circuit) number instead of a full source and destination address.
Advantages of using VC number:
- It reduces the overhead of routing and forwarding packets by eliminating the need for address lookup in each router along the path.
- It provides faster and more efficient packet switching as the network can quickly route the packets based on the VC number.
Disadvantages of using VC number:
- It requires a lot of resources to establish and maintain the virtual circuit path, which can result in higher latency and delay in transmission.
- It can also lead to network congestion as multiple virtual circuits may share the same physical link.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'B', which states that each packet in a virtual circuit network contains a short VC number instead of a full source and destination address.
Virtual Circuit Network is a type of network in which a dedicated path is established between the source and destination before transmitting the data. In this network, each packet contains a short VC (Virtual Circuit) number instead of a full source and destination address.
Advantages of using VC number:
- It reduces the overhead of routing and forwarding packets by eliminating the need for address lookup in each router along the path.
- It provides faster and more efficient packet switching as the network can quickly route the packets based on the VC number.
Disadvantages of using VC number:
- It requires a lot of resources to establish and maintain the virtual circuit path, which can result in higher latency and delay in transmission.
- It can also lead to network congestion as multiple virtual circuits may share the same physical link.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'B', which states that each packet in a virtual circuit network contains a short VC number instead of a full source and destination address.
Which protocol use distance vector routing?- a)OSPF
- b)BGP
- c)RIP
- d)PPP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which protocol use distance vector routing?
a)
OSPF
b)
BGP
c)
RIP
d)
PPP
|
|
Yash Patel answered |
Routing information protocol uses a distance vector protocol.
During normal IP packet forwarding by routers which of the following packet fields are updated?- a)IP header source address
- b)IP header destination address
- c)IP header TTL
- d)IP header check sum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During normal IP packet forwarding by routers which of the following packet fields are updated?
a)
IP header source address
b)
IP header destination address
c)
IP header TTL
d)
IP header check sum
|
|
Nilesh Mukherjee answered |
During forwarding of an IP packet by routers, the packet fields namely IP header source address and IP header destination address remains same whereas check own and TTL are updated.
How many bits internet address is assigned to each host on a TCP/IP internet which is used in all communication with the host?- a)16 bits
- b)32 bits
- c)48 bits
- d)64 bits
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many bits internet address is assigned to each host on a TCP/IP internet which is used in all communication with the host?
a)
16 bits
b)
32 bits
c)
48 bits
d)
64 bits
|
|
Krish Datta answered |
Internet address has 32 bits, which is assigned to each host for communication on network.
The frame relay committed information rate represents- a)Maximum data rate on the network
- b)Steady state data rate on the network
- c)Minimum data rate on the network
- d)Interface data rate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The frame relay committed information rate represents
a)
Maximum data rate on the network
b)
Steady state data rate on the network
c)
Minimum data rate on the network
d)
Interface data rate
|
|
Mainak Kulkarni answered |
Frame relay committed information rate represents minimum data rate on the network.
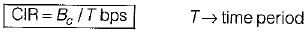
Here cumulative number of bits sent during the predefined period should not exceed Bc.
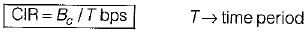
Here cumulative number of bits sent during the predefined period should not exceed Bc.
An example of a network layer is- a)Internet Protocol (IP)-ARPANET
- b)X.25 Packet Level Protocol (PLP)-ISO
- c)Source routing and domain naming-USENET
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of a network layer is
a)
Internet Protocol (IP)-ARPANET
b)
X.25 Packet Level Protocol (PLP)-ISO
c)
Source routing and domain naming-USENET
d)
All of these
|
|
Mira Rane answered |
Internet protocol (IP-ARPA NET, X.25 packet level protocoi-ISO and source routing and domain naming-USENET are example of network layer.
Multidestination routing- a)is same as broadcast routing
- b)contains the list of all destinations
- c)data is not sent by packets
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Multidestination routing
a)
is same as broadcast routing
b)
contains the list of all destinations
c)
data is not sent by packets
d)
none of the mentioned

|
Anirban Khanna answered |
Algorithms for effectively routing messages from a source to multiple destination nodes in a store-and-forward computer network are studied. The focus is on minimizing the network cost (NC), which is the sum of weights of the links in the routing path.
Which multicast address does the OSPF Hello protocol use?- a)224.0.0.5
- b)224.0.0.6
- c)224.0.0.7
- d)224.0.0.8
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which multicast address does the OSPF Hello protocol use?
a)
224.0.0.5
b)
224.0.0.6
c)
224.0.0.7
d)
224.0.0.8
|
|
Vaibhav Patel answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: 224.0.0.5 is the multicast address does the OSPF Hello protocol use.
Explanation: 224.0.0.5 is the multicast address does the OSPF Hello protocol use.
The computation of the shortest path in OSPF is usually done by- a)Bellman-ford algorithm
- b)Routing information protocol
- c)Dijkstra’s algorithm
- d)Distance vector routing
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The computation of the shortest path in OSPF is usually done by
a)
Bellman-ford algorithm
b)
Routing information protocol
c)
Dijkstra’s algorithm
d)
Distance vector routing
|
|
Jay Basu answered |
Explanation:
Dijkstra's Algorithm:
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) uses Dijkstra's algorithm to compute the shortest path.
- Dijkstra's algorithm is a graph search algorithm that solves the single-source shortest path problem for a graph with non-negative edge weights.
- It starts at the source node and explores the neighboring nodes to find the shortest path to all other nodes in the graph.
Bellman-Ford Algorithm:
- The Bellman-Ford algorithm is another algorithm used for finding the shortest path in a network.
- It can handle graphs with negative edge weights but is not typically used in OSPF.
Routing Information Protocol (RIP):
- RIP is another routing protocol that uses distance vector routing, which is different from OSPF.
- It does not use Dijkstra's algorithm for computing the shortest path.
Distance Vector Routing:
- Distance vector routing, used by protocols like RIP, determines the best path based on the number of hops to a destination.
- OSPF, on the other hand, uses Dijkstra's algorithm which considers the actual cost or weight of the paths.
In conclusion, OSPF uses Dijkstra's algorithm for computing the shortest path because it is efficient and suitable for networks with non-negative edge weights.
Dijkstra's Algorithm:
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) uses Dijkstra's algorithm to compute the shortest path.
- Dijkstra's algorithm is a graph search algorithm that solves the single-source shortest path problem for a graph with non-negative edge weights.
- It starts at the source node and explores the neighboring nodes to find the shortest path to all other nodes in the graph.
Bellman-Ford Algorithm:
- The Bellman-Ford algorithm is another algorithm used for finding the shortest path in a network.
- It can handle graphs with negative edge weights but is not typically used in OSPF.
Routing Information Protocol (RIP):
- RIP is another routing protocol that uses distance vector routing, which is different from OSPF.
- It does not use Dijkstra's algorithm for computing the shortest path.
Distance Vector Routing:
- Distance vector routing, used by protocols like RIP, determines the best path based on the number of hops to a destination.
- OSPF, on the other hand, uses Dijkstra's algorithm which considers the actual cost or weight of the paths.
In conclusion, OSPF uses Dijkstra's algorithm for computing the shortest path because it is efficient and suitable for networks with non-negative edge weights.
Which of the following is not a type of OSPF packet?- a)Hello
- b)Link-state request
- c)Link-state response
- d)Link-state ACK
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a type of OSPF packet?
a)
Hello
b)
Link-state request
c)
Link-state response
d)
Link-state ACK
|
|
Vaibhav Choudhary answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: Five types of OSPF packets are: Hello, Database description, Link-state request, Link-state update, Link-state ACK
Explanation: Five types of OSPF packets are: Hello, Database description, Link-state request, Link-state update, Link-state ACK
At which interval does OSPF refresh LSAs?- a)10 seconds
- b)30 seconds
- c)30 minutes
- d)1 hour
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
At which interval does OSPF refresh LSAs?
a)
10 seconds
b)
30 seconds
c)
30 minutes
d)
1 hour
|
|
Tanvi Datta answered |
Understanding OSPF LSA Refresh Interval
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a widely used routing protocol in large networks. One of the critical components of OSPF is the Link State Advertisement (LSA), which contains information about the network topology.
LSA Refresh Interval
- OSPF LSAs have a default refresh interval of 30 minutes.
- This means that an OSPF router will resend its LSAs to its neighbors every 30 minutes to ensure that all routers have the most current network information.
Why 30 Minutes?
- Stability: The 30-minute interval helps in maintaining stability in the network. Frequent updates may lead to unnecessary processing and bandwidth consumption.
- Network Changes: While LSAs are refreshed every 30 minutes, OSPF also has mechanisms to immediately propagate changes in the network topology through triggered updates. This ensures that routers can quickly adapt to changes without waiting for the next refresh.
- Age of LSAs: Each LSA has an age field that increments over time. If an LSA reaches an age of 60 minutes, it is considered stale and will be removed from the database, prompting a refresh.
Conclusion
- The correct answer to the interval at which OSPF refreshes LSAs is indeed 30 minutes (not 1 hour). It’s important to understand how this interval balances network efficiency with the need for up-to-date routing information.
By grasping the OSPF LSA refresh interval, network engineers can better manage and optimize their routing protocols for performance and reliability.
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a widely used routing protocol in large networks. One of the critical components of OSPF is the Link State Advertisement (LSA), which contains information about the network topology.
LSA Refresh Interval
- OSPF LSAs have a default refresh interval of 30 minutes.
- This means that an OSPF router will resend its LSAs to its neighbors every 30 minutes to ensure that all routers have the most current network information.
Why 30 Minutes?
- Stability: The 30-minute interval helps in maintaining stability in the network. Frequent updates may lead to unnecessary processing and bandwidth consumption.
- Network Changes: While LSAs are refreshed every 30 minutes, OSPF also has mechanisms to immediately propagate changes in the network topology through triggered updates. This ensures that routers can quickly adapt to changes without waiting for the next refresh.
- Age of LSAs: Each LSA has an age field that increments over time. If an LSA reaches an age of 60 minutes, it is considered stale and will be removed from the database, prompting a refresh.
Conclusion
- The correct answer to the interval at which OSPF refreshes LSAs is indeed 30 minutes (not 1 hour). It’s important to understand how this interval balances network efficiency with the need for up-to-date routing information.
By grasping the OSPF LSA refresh interval, network engineers can better manage and optimize their routing protocols for performance and reliability.
Which of the following is not a service primitive?- a)Connect
- b)Listen
- c)Send
- d)Sound
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a service primitive?
a)
Connect
b)
Listen
c)
Send
d)
Sound
|
|
Ujwal Nambiar answered |
Service Primitives
Service primitives are the basic building blocks of communication protocols. They define the operations that can be performed on a communication service. There are typically four types of service primitives: connect, listen, send, and receive.
Connect
The connect primitive is used to establish a connection between two entities in a communication network. It allows the initiating entity to request a connection to a specific destination entity.
Listen
The listen primitive is used to wait for incoming connection requests. It allows an entity to passively listen for connection requests and accept them when they arrive.
Send
The send primitive is used to send data from one entity to another. It allows the sending entity to transmit data to the destination entity over an established connection.
Sound
The option 'D' in this question, "Sound," is not a service primitive. Sound refers to auditory perception resulting from vibrations that can be detected by the human ear. It is not a communication operation or a service provided by a communication protocol.
Explanation
In the given options, connect, listen, and send are all service primitives commonly used in communication protocols. These primitives are essential for establishing connections, listening for incoming requests, and transmitting data. However, sound is not a service primitive as it does not relate to communication protocols or network operations.
Sound is a sensory perception and not a service or operation that can be performed on a communication network. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - Sound.
Service primitives are the basic building blocks of communication protocols. They define the operations that can be performed on a communication service. There are typically four types of service primitives: connect, listen, send, and receive.
Connect
The connect primitive is used to establish a connection between two entities in a communication network. It allows the initiating entity to request a connection to a specific destination entity.
Listen
The listen primitive is used to wait for incoming connection requests. It allows an entity to passively listen for connection requests and accept them when they arrive.
Send
The send primitive is used to send data from one entity to another. It allows the sending entity to transmit data to the destination entity over an established connection.
Sound
The option 'D' in this question, "Sound," is not a service primitive. Sound refers to auditory perception resulting from vibrations that can be detected by the human ear. It is not a communication operation or a service provided by a communication protocol.
Explanation
In the given options, connect, listen, and send are all service primitives commonly used in communication protocols. These primitives are essential for establishing connections, listening for incoming requests, and transmitting data. However, sound is not a service primitive as it does not relate to communication protocols or network operations.
Sound is a sensory perception and not a service or operation that can be performed on a communication network. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - Sound.
Which one of the following routing algorithm can be used for network layer design?- a)shortest path algorithm
- b)distance vector routing
- c)link state routing
- d)all of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following routing algorithm can be used for network layer design?
a)
shortest path algorithm
b)
distance vector routing
c)
link state routing
d)
all of the mentioned
|
|
Rajeev Menon answered |
The routing algorithm is what decides where a packet should go next. There are several routing techniques like shortest path algorithm, static and dynamic routing, decentralized routing, distance vector routing, link state routing, Hierarchical routing etc.
A Go-Back-N ARQ uses a window of size 15. How many bits are needed to define the sequence number?- a)15
- b)4
- c)16
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A Go-Back-N ARQ uses a window of size 15. How many bits are needed to define the sequence number?
a)
15
b)
4
c)
16
d)
5
|
|
Megha Yadav answered |
Formula:
Window size (Go Back N) = 2n-1
Where n is bits needed
So, 15 = 2n-1
16 = 2n
So, n = 4
Window size (Go Back N) = 2n-1
Where n is bits needed
So, 15 = 2n-1
16 = 2n
So, n = 4
To prevent silly window syndrome created by a sender that is sending data at a very slow rate _______ can be used.- a)Clark’s solution
- b)Nagle’s algorithm
- c)Both (a) and (b)
- d)Delayed acknowledgment
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
To prevent silly window syndrome created by a sender that is sending data at a very slow rate _______ can be used.
a)
Clark’s solution
b)
Nagle’s algorithm
c)
Both (a) and (b)
d)
Delayed acknowledgment
|
|
Rajveer Chatterjee answered |
Nagle's algo is used to prevent silly window syndrome created by a sender that send data at a very slow rate.
Which protocol use link state routing?- a)BGP
- b)OSPF
- c)RIP
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which protocol use link state routing?
a)
BGP
b)
OSPF
c)
RIP
d)
None of these
|
|
Nandini Joshi answered |
Link state routing is a type of routing protocol that is used to determine the best path for data packets to travel through a network. It is based on the concept of each router having a complete map of the network, including the status and cost of each link. This allows the routers to make informed decisions about the best path to forward packets.
The correct answer to the question is option 'B', which states that OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) uses link state routing. OSPF is a widely used routing protocol that is used in IP networks, particularly in large enterprise networks. It is designed to be scalable and efficient, and it uses link state routing to determine the shortest path between routers.
Here is a detailed explanation of why OSPF uses link state routing:
1. Link State Database:
- In OSPF, each router maintains a Link State Database (LSDB) that contains information about the network topology.
- The LSDB is built by exchanging Link State Advertisements (LSAs) between routers.
- LSAs contain information about the router's neighbors, the links it is connected to, and the cost of those links.
- By exchanging LSAs, routers can build a complete map of the network and have the same information about the network topology.
2. SPF Algorithm:
- OSPF uses a Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm to calculate the best path for packets to travel.
- The SPF algorithm takes into account the cost of each link, which is determined by the administrator.
- It calculates the shortest path by summing up the costs of the links along a path.
- The path with the lowest total cost is considered the best path, and packets are forwarded along that path.
3. Dynamic Updates:
- OSPF supports dynamic updates, which means that routers can exchange LSAs to keep the LSDB up to date.
- When a link goes down or a new link is added to the network, routers exchange LSAs to inform each other about the changes.
- This allows OSPF to adapt to changes in the network and recalculate the best path if necessary.
In conclusion, OSPF is an example of a routing protocol that uses link state routing. It maintains a Link State Database and uses the SPF algorithm to calculate the best path for packets to travel through the network. OSPF is widely used in large networks because of its scalability and efficiency.
The correct answer to the question is option 'B', which states that OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) uses link state routing. OSPF is a widely used routing protocol that is used in IP networks, particularly in large enterprise networks. It is designed to be scalable and efficient, and it uses link state routing to determine the shortest path between routers.
Here is a detailed explanation of why OSPF uses link state routing:
1. Link State Database:
- In OSPF, each router maintains a Link State Database (LSDB) that contains information about the network topology.
- The LSDB is built by exchanging Link State Advertisements (LSAs) between routers.
- LSAs contain information about the router's neighbors, the links it is connected to, and the cost of those links.
- By exchanging LSAs, routers can build a complete map of the network and have the same information about the network topology.
2. SPF Algorithm:
- OSPF uses a Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm to calculate the best path for packets to travel.
- The SPF algorithm takes into account the cost of each link, which is determined by the administrator.
- It calculates the shortest path by summing up the costs of the links along a path.
- The path with the lowest total cost is considered the best path, and packets are forwarded along that path.
3. Dynamic Updates:
- OSPF supports dynamic updates, which means that routers can exchange LSAs to keep the LSDB up to date.
- When a link goes down or a new link is added to the network, routers exchange LSAs to inform each other about the changes.
- This allows OSPF to adapt to changes in the network and recalculate the best path if necessary.
In conclusion, OSPF is an example of a routing protocol that uses link state routing. It maintains a Link State Database and uses the SPF algorithm to calculate the best path for packets to travel through the network. OSPF is widely used in large networks because of its scalability and efficiency.
Correct order of the operations of OSPF
1. Hello packets
2. Propagation of link-state information and building of routing tables
3. Establishing adjacencies and synchronisation database- a)1-2-3
- b)1-3-2
- c)3-2-1
- d)2-1-3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct order of the operations of OSPF
1. Hello packets
2. Propagation of link-state information and building of routing tables
3. Establishing adjacencies and synchronisation database
1. Hello packets
2. Propagation of link-state information and building of routing tables
3. Establishing adjacencies and synchronisation database
a)
1-2-3
b)
1-3-2
c)
3-2-1
d)
2-1-3
|
|
Shubham Ghoshal answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: None.
Explanation: None.
Which of the following is false with respect to the features of OSPF- a)Support for fixed-length sunbathing by including the subnet mask in the routing message
- b)More flexible link cost than can range from 1 to 65535
- c)Use of designated router
- d)Distribution of traffic over multiple paths that have equal cost to the destination
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is false with respect to the features of OSPF
a)
Support for fixed-length sunbathing by including the subnet mask in the routing message
b)
More flexible link cost than can range from 1 to 65535
c)
Use of designated router
d)
Distribution of traffic over multiple paths that have equal cost to the destination
|
|
Shubham Ghoshal answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: Support for variable-length sunbathing by including the subnet mask in the routing message.
Explanation: Support for variable-length sunbathing by including the subnet mask in the routing message.
What is the IP protocol number for OSPF packets?- a)89
- b)86
- c)20
- d)76
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the IP protocol number for OSPF packets?
a)
89
b)
86
c)
20
d)
76
|
|
Rashi Banerjee answered |
Explanation:
OSPF Protocol Number:
- The IP protocol number for OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) packets is 89.
- OSPF is a routing protocol that uses a link-state algorithm to determine the best path to a destination network.
Understanding Protocol Numbers:
- In networking, protocol numbers are used to identify different network protocols at the IP layer.
- These numbers are included in the IP header to indicate the specific protocol being used.
Significance of Protocol Number 89:
- OSPF uses protocol number 89 to differentiate its packets from other types of network traffic.
- This allows routers to identify OSPF packets and process them according to the OSPF protocol rules.
Conclusion:
- In summary, the protocol number for OSPF packets is 89, which is crucial for routers to correctly identify and handle OSPF traffic in a network environment.
OSPF Protocol Number:
- The IP protocol number for OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) packets is 89.
- OSPF is a routing protocol that uses a link-state algorithm to determine the best path to a destination network.
Understanding Protocol Numbers:
- In networking, protocol numbers are used to identify different network protocols at the IP layer.
- These numbers are included in the IP header to indicate the specific protocol being used.
Significance of Protocol Number 89:
- OSPF uses protocol number 89 to differentiate its packets from other types of network traffic.
- This allows routers to identify OSPF packets and process them according to the OSPF protocol rules.
Conclusion:
- In summary, the protocol number for OSPF packets is 89, which is crucial for routers to correctly identify and handle OSPF traffic in a network environment.
Which one of the following algorithm is not used for congestion control?- a)traffic aware routing
- b)admission control
- c)load shedding
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following algorithm is not used for congestion control?
a)
traffic aware routing
b)
admission control
c)
load shedding
d)
none of the mentioned

|
Shivam Sharma answered |
a) traffic aware routing
b) admission control
c) load shedding
Packets of the same session may be routed through different paths in- a)TCP, but not UDP
- b)TCP and UDP
- c)UDP, but not TCP
- d)Neither TCP nor UDP
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Packets of the same session may be routed through different paths in
a)
TCP, but not UDP
b)
TCP and UDP
c)
UDP, but not TCP
d)
Neither TCP nor UDP
|
|
Moumita Yadav answered |
Explanation:
In computer networking, packets are the basic units of data that are transmitted over a network. They contain the payload (data) as well as the necessary information for routing and delivering the data to the intended destination.
Routing in TCP:
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is a reliable and connection-oriented protocol. It establishes a connection between two endpoints before transmitting data. The packets in a TCP session are sent in a sequential order and they are received at the destination in the same order. TCP ensures that the packets are delivered reliably and in order by using mechanisms like acknowledgment, retransmission, and flow control.
When it comes to routing, TCP packets are routed based on the IP addresses and port numbers of the source and destination. Once the connection is established, the routing path remains fixed for the duration of the session. This means that all the packets of a TCP session will follow the same path from the source to the destination. Therefore, packets of the same TCP session will be routed through the same path.
Routing in UDP:
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a connectionless and unreliable protocol. It does not establish a connection before transmitting data and does not guarantee delivery or order of packets. Each UDP packet is independent and can take a different path to reach the destination. UDP does not have any built-in mechanisms for acknowledgment, retransmission, or flow control.
Since UDP does not maintain any connection state, the packets of a UDP session can be routed through different paths. The routing decisions are made by the routers based on factors like network congestion, availability of routes, and load balancing. Therefore, it is possible for packets of the same UDP session to take different paths.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, packets of the same session may be routed through different paths in both TCP and UDP. However, TCP ensures that the packets are delivered reliably and in order, while UDP does not provide such guarantees.
In computer networking, packets are the basic units of data that are transmitted over a network. They contain the payload (data) as well as the necessary information for routing and delivering the data to the intended destination.
Routing in TCP:
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is a reliable and connection-oriented protocol. It establishes a connection between two endpoints before transmitting data. The packets in a TCP session are sent in a sequential order and they are received at the destination in the same order. TCP ensures that the packets are delivered reliably and in order by using mechanisms like acknowledgment, retransmission, and flow control.
When it comes to routing, TCP packets are routed based on the IP addresses and port numbers of the source and destination. Once the connection is established, the routing path remains fixed for the duration of the session. This means that all the packets of a TCP session will follow the same path from the source to the destination. Therefore, packets of the same TCP session will be routed through the same path.
Routing in UDP:
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a connectionless and unreliable protocol. It does not establish a connection before transmitting data and does not guarantee delivery or order of packets. Each UDP packet is independent and can take a different path to reach the destination. UDP does not have any built-in mechanisms for acknowledgment, retransmission, or flow control.
Since UDP does not maintain any connection state, the packets of a UDP session can be routed through different paths. The routing decisions are made by the routers based on factors like network congestion, availability of routes, and load balancing. Therefore, it is possible for packets of the same UDP session to take different paths.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, packets of the same session may be routed through different paths in both TCP and UDP. However, TCP ensures that the packets are delivered reliably and in order, while UDP does not provide such guarantees.
Which of the following is incorrect regarding the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)?- a)When something unexpected occurs in routers those events are reported by the ICMP.
- b)ICMP is also used to test the connectivity.
- c)ICMP and BOOTP protocols are equivalent in their usage.
- d)Each ICMP message type is encapsulated in a IP packet.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is incorrect regarding the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)?
a)
When something unexpected occurs in routers those events are reported by the ICMP.
b)
ICMP is also used to test the connectivity.
c)
ICMP and BOOTP protocols are equivalent in their usage.
d)
Each ICMP message type is encapsulated in a IP packet.
|
|
Manasa Dey answered |
ICMP is error reporting protocol used when something unexpected occurs in routers, used to test connectivity while BOOTP is IP protocol network to automatically assigned an IP address to network devices from a configuration server.
In ______ , data are sent or processed at a very inefficient rate, such as 1 byte at a time.- a)Nagle’s syndrome
- b)Silly window syndrome
- c)Sliding window syndrome
- d)Delayed acknowledgment
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In ______ , data are sent or processed at a very inefficient rate, such as 1 byte at a time.
a)
Nagle’s syndrome
b)
Silly window syndrome
c)
Sliding window syndrome
d)
Delayed acknowledgment
|
|
Surbhi Kaur answered |
Silly window syndrome problem can degrade TCP performance. This problem occurs when data are passed to the sending TCP entity in large blocks, but interactive application on the receiving side reads data T byte at a time.
Brouter- a)Is a type of bridge
- b)Works at all the layers Of OS I model
- c)Is able to bridge those protocols that are not routable
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Brouter
a)
Is a type of bridge
b)
Works at all the layers Of OS I model
c)
Is able to bridge those protocols that are not routable
d)
None of these
|
|
Arka Shah answered |
Brouter is a device, which is combination of functionality of bridge and router. So, it works till network layer and is able to bridge those protocol that are not routable.
Which field is NOT a field within an OSPF packet header?- a)Packet length
- b)Router ID
- c)Authentication type
- d)Maxage time
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which field is NOT a field within an OSPF packet header?
a)
Packet length
b)
Router ID
c)
Authentication type
d)
Maxage time
|
|
Garima Dasgupta answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: Maxage timeis NOT a field within an OSPF packet header.
Explanation: Maxage timeis NOT a field within an OSPF packet header.
At which layer of the OSI model the router configuration problem reside- a)Transport
- b)Network
- c)Logical Link
- d)Physical
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
At which layer of the OSI model the router configuration problem reside
a)
Transport
b)
Network
c)
Logical Link
d)
Physical
|
|
Jatin Joshi answered |
Routers are the networking devices that operate on network layer. Hence at network layer, the router configuration problem reside.
The 4 byte IP address consists of- a)network address
- b)host address
- c)both (a) and (b)
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The 4 byte IP address consists of
a)
network address
b)
host address
c)
both (a) and (b)
d)
none of the mentioned
|
|
Preethi Basu answered |
Explanation:
- The 4 byte IP address consists of both network address and host address.
- The IP address is divided into two parts, the network address and the host address.
- The network address is used to identify the network, while the host address is used to identify the specific device on that network.
- The network address is determined by the class of IP address, which can be Class A, B, or C.
- The host address is determined by the subnet mask, which is used to divide the network into smaller subnetworks.
- Together, the network address and the host address make up the complete IP address, which is used to route data between devices on different networks.
An ACK number of 1000 in TCP always means that- a)999 bytes have been successfully received
- b)1000 bytes have been successfully received
- c)1001 bytes have been successfully received
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An ACK number of 1000 in TCP always means that
a)
999 bytes have been successfully received
b)
1000 bytes have been successfully received
c)
1001 bytes have been successfully received
d)
None of these
|
|
Vaibhav Choudhary answered |
Since sequence number of byte in any segment in TCP start from any number, so we cannot tell how many bytes successively received, on ACK number 1000.
A TCP message consisting of 2100 bytes is passed to IP for delivery across two networks. The first network can carry a maximum payload of 1200 bytes per frame and the second network can carry a maximum payload of 400 bytes per frame, excluding network overhead. Assume that IP overhead per packet is 20 bytes. What is the total IP overhead in the second network for this transmission?- a)40 bytes
- b)80 bytes
- c)120 bytes
- d)160 bytes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A TCP message consisting of 2100 bytes is passed to IP for delivery across two networks. The first network can carry a maximum payload of 1200 bytes per frame and the second network can carry a maximum payload of 400 bytes per frame, excluding network overhead. Assume that IP overhead per packet is 20 bytes. What is the total IP overhead in the second network for this transmission?
a)
40 bytes
b)
80 bytes
c)
120 bytes
d)
160 bytes
|
|
Shivam Dasgupta answered |
In the question they have directly given the payload so 2100 will be divided into 1200 and 904 (900 is not a multiple of 8 so we have to pad 4 bits in order to make it a multiple of 8).
Now in second network payload is 400 B.
So 1200 bytes packet will be divided in 400,400, 400 with each having 20 B header, and 900 will be divided into 400,400 and 104 (4 bits padded) each having 20 B header.
So total overhead is 20 x 6 = 120 B.
Now in second network payload is 400 B.
So 1200 bytes packet will be divided in 400,400, 400 with each having 20 B header, and 900 will be divided into 400,400 and 104 (4 bits padded) each having 20 B header.
So total overhead is 20 x 6 = 120 B.
Which of the following type of ICMP messages need to be encapsulated into an IP datagram?- a)Time exceeded
- b)Multicasting
- c)Echo reply
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following type of ICMP messages need to be encapsulated into an IP datagram?
a)
Time exceeded
b)
Multicasting
c)
Echo reply
d)
All of these
|
|
Ameya Basak answered |
Time exceeded; echo reply and multicasting ICMP messages needs to be encapsulated into if data gram to the sender side.
In OSPF header, which field is used to detect errors in the packet?
- a)Type
- b)Area ID
- c)Checksum field
- d)Authentication type
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In OSPF header, which field is used to detect errors in the packet?
a)
Type
b)
Area ID
c)
Checksum field
d)
Authentication type
|
|
Madhurima Chakraborty answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: Checksum field is used to detect errors.
Explanation: Checksum field is used to detect errors.
An OSPF router receives an LSA. The router checks its sequence number and finds thatthis number is higher than the sequence number it already has. Which two tasks doesthe router perform with the LSA?- a)Ignores the LSA
- b)Adds it to the database
- c)Sends newer LSU update to source router
- d)Floods the LSA to the other routers
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An OSPF router receives an LSA. The router checks its sequence number and finds thatthis number is higher than the sequence number it already has. Which two tasks doesthe router perform with the LSA?
a)
Ignores the LSA
b)
Adds it to the database
c)
Sends newer LSU update to source router
d)
Floods the LSA to the other routers
|
|
Maulik Iyer answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: An OSPF router receives an LSA. The router checks its sequence number and finds that this number is higher than the sequence number Adds it to the database, Floods the LSA to the other routers.
Explanation: An OSPF router receives an LSA. The router checks its sequence number and finds that this number is higher than the sequence number Adds it to the database, Floods the LSA to the other routers.
The parameter which gives the probability of the transport layer itself spontaneously terminating a connection due to internal problems is called- a)Protection
- b)Resilience
- c)Option negotiation
- d)Transfer failure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The parameter which gives the probability of the transport layer itself spontaneously terminating a connection due to internal problems is called
a)
Protection
b)
Resilience
c)
Option negotiation
d)
Transfer failure
|
|
Shraddha Iyer answered |
Resilence is a probability of transport layer to terminate a connection due to internal problems.
ICMP is primarily used for- a)error and diagnostic functions
- b)addressing
- c)forwarding
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
ICMP is primarily used for
a)
error and diagnostic functions
b)
addressing
c)
forwarding
d)
none of the mentioned

|
Bijoy Kapoor answered |
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is primarily used for error and diagnostic functions.
Here are the details of ICMP:
- ICMP is mainly used to determine whether or not data is reaching its intended destination in a timely manner.
- Commonly, the ICMP protocol is used on network devices, such as routers.
- ICMP is crucial for error reporting and testing, but it can also be used in distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
Hence Option (A) is correct
For short notes on the chapter Network Layer click on the link given below:
How many digits of the network user Address are known as the DNIC (Data Network Identification Code)?- a)First three
- b)First four
- c)First five
- d)First seven
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many digits of the network user Address are known as the DNIC (Data Network Identification Code)?
a)
First three
b)
First four
c)
First five
d)
First seven
|
|
Athul Pillai answered |
As per the format, the first 4 digits of the international data number, the three digits that may represent the counter code one 1-digit network code i.e. the network digit.
The division of a message into segments, is a function of the- a)Physical
- b)Data link
- c)Transport
- d)Network
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The division of a message into segments, is a function of the
a)
Physical
b)
Data link
c)
Transport
d)
Network
|
|
Anisha Ahuja answered |
Message comes from application layer divide into segments at transport layer
The main characteristic of routing algorithm is the following:- a)The algorithm should produce results in a stable manner in varying traffic conditions.
- b)The algorithm must be fair in selecting routes.
- c)The algorithm must be able to cope with changes in topology.
- d)Ail of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The main characteristic of routing algorithm is the following:
a)
The algorithm should produce results in a stable manner in varying traffic conditions.
b)
The algorithm must be fair in selecting routes.
c)
The algorithm must be able to cope with changes in topology.
d)
Ail of these
|
|
Megha Yadav answered |
Routing algorithm:
(i) Produce results in a stable manner in varying traffic conditions.
(ii) It is fair in selecting routes for communication.
(iii) The changes in the topology are well adjudged.
(i) Produce results in a stable manner in varying traffic conditions.
(ii) It is fair in selecting routes for communication.
(iii) The changes in the topology are well adjudged.
In OSPF database descriptor packet, which field is used to detect a missing packet- a)LSA header
- b)MS
- c)Database descriptor sequence number
- d)Options
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In OSPF database descriptor packet, which field is used to detect a missing packet
a)
LSA header
b)
MS
c)
Database descriptor sequence number
d)
Options
|
|
Rishabh Sharma answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: Sequence number field is used to detect a missing packet.
Explanation: Sequence number field is used to detect a missing packet.
An OSPF router receives an LSA, the router checks its sequence number, and thisnumber matches the sequence number of the LSA that the receiving router already has.What does the receiving router do with the LSA?- a)Ignores the LSA
- b)Adds it to the database
- c)Sends newer LSU update to source router
- d)Floods the LSA to the other routers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An OSPF router receives an LSA, the router checks its sequence number, and thisnumber matches the sequence number of the LSA that the receiving router already has.What does the receiving router do with the LSA?
a)
Ignores the LSA
b)
Adds it to the database
c)
Sends newer LSU update to source router
d)
Floods the LSA to the other routers
|
|
Shubham Ghoshal answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: An OSPF router receives an LSA, the router checks its sequence number, and this number matches the sequence number of the LSA that the receiving router already has Ignores the LSA.
Explanation: An OSPF router receives an LSA, the router checks its sequence number, and this number matches the sequence number of the LSA that the receiving router already has Ignores the LSA.
In OSPF database descriptor packet, if more database descriptor packet flows, ‘M’ field is set to- a)1
- b)0
- c)more
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In OSPF database descriptor packet, if more database descriptor packet flows, ‘M’ field is set to
a)
1
b)
0
c)
more
d)
none
|
|
Krish Datta answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: M bit is set to 1.
Explanation: M bit is set to 1.
Which of the following is false?- a) Bridges operate at the MAC layer
- b) Routers filter out unnecessary network traffic and remove it from network segments
- c) Routers cannot act as bridges
- d) Routers are often said to implement firewall
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is false?
a)
Bridges operate at the MAC layer
b)
Routers filter out unnecessary network traffic and remove it from network segments
c)
Routers cannot act as bridges
d)
Routers are often said to implement firewall
|
|
Sounak Joshi answered |
Routers can act as bridges we can use routers to bridge devices to our wireless network.
In OSPF database descriptor packet, which field is used to indicate that the router is master- a)M
- b)MS
- c)I
- d)Options
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In OSPF database descriptor packet, which field is used to indicate that the router is master
a)
M
b)
MS
c)
I
d)
Options
|
|
Rajesh Malik answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: MS bit is set if the router is master, otherwise slave.
Explanation: MS bit is set if the router is master, otherwise slave.
The outcome of Dijkstra’s calculation is used to populate the __________- a)Topology table
- b)Routing table
- c)Neighbor table
- d)Adjacency table
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The outcome of Dijkstra’s calculation is used to populate the __________
a)
Topology table
b)
Routing table
c)
Neighbor table
d)
Adjacency table
|
|
Shounak Sharma answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: The outcome of Dijkstra’s calculation is used to populate the Routing table
Explanation: The outcome of Dijkstra’s calculation is used to populate the Routing table
Chapter doubts & questions for Network Layer - 6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE 2025 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Network Layer - 6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE in English & Hindi are available as part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam by signing up for free.
6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE
453 videos|1305 docs|700 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily










