All Exams >
MCAT >
MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations >
All Questions
All questions of Work and Energy of Point Object Systems (PHY) for MCAT Exam
Which of the following best characterizes the work–energy theorem?- a)The work done by any force is proportional only to the magnitude of that force.
- b)The total work done on any object is equal to the change in kinetic energy for that object.
- c)The work done on an object by any force is proportional to the change in kinetic energy for that object.
- d)The work done by an applied force on an object is equal to the change in kinetic energy of that object.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following best characterizes the work–energy theorem?
a)
The work done by any force is proportional only to the magnitude of that force.
b)
The total work done on any object is equal to the change in kinetic energy for that object.
c)
The work done on an object by any force is proportional to the change in kinetic energy for that object.
d)
The work done by an applied force on an object is equal to the change in kinetic energy of that object.

|
Orion Classes answered |
The work–energy theorem relates the total work done on an object by all forces to the change in kinetic energy experienced by the same object. While the work done by a force is indeed proportional to the magnitude of the force, it is also proportional to the displacement of the object, eliminating choice (A). The change in kinetic energy is equal—not proportional—to the total work done on the object; further, it is the net force, not any force, that relates to the work done on an object, eliminating choice (C). Finally, the change in kinetic energy of the object is equal to the work done by all of the forces acting on the object combined, not just the applied force, which eliminates choice (D).
Josh, who has a mass of 80 kg, and Sarah, who has a mass of 50 kg, jump off a 20 m tall building and land on a fire net. The net compresses, and they bounce back up at the same time. Which of the following statements is NOT true?- a)Sarah will bounce higher than Josh.
- b)For Josh, the change in speed from the start of the jump to contacting the net is
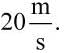
- c)Josh will experience a greater force upon impact than Sarah.
- d)The energy in this event is converted from potential to kinetic to elastic to kinetic.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Josh, who has a mass of 80 kg, and Sarah, who has a mass of 50 kg, jump off a 20 m tall building and land on a fire net. The net compresses, and they bounce back up at the same time. Which of the following statements is NOT true?
a)
Sarah will bounce higher than Josh.
b)
For Josh, the change in speed from the start of the jump to contacting the net is 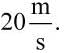
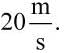
c)
Josh will experience a greater force upon impact than Sarah.
d)
The energy in this event is converted from potential to kinetic to elastic to kinetic.

|
Orion Classes answered |
Sarah will not bounce higher than Josh. Assuming that mechanical energy is conserved, Sarah and Josh will start with a given amount of potential energy, which is converted into kinetic energy, then elastic potential energy, then kinetic energy again with no loss of energy from the system, eliminating choice (D). By this logic, both individuals should return to the same starting height. Josh starts with
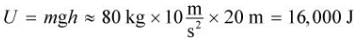
of potential energy. At the moment he hits the net, all of this potential energy has been converted into kinetic energy. Therefore,
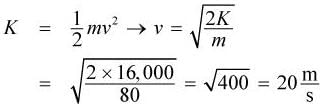
eliminating choice (B). Josh will experience a greater force upon impact because the net exerts a force proportional to weight; the higher the weight, the larger the force exerted by the net, eliminating choice (C).
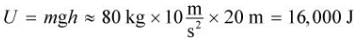
of potential energy. At the moment he hits the net, all of this potential energy has been converted into kinetic energy. Therefore,
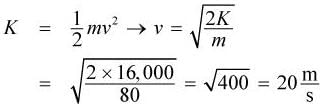
eliminating choice (B). Josh will experience a greater force upon impact because the net exerts a force proportional to weight; the higher the weight, the larger the force exerted by the net, eliminating choice (C).
Mechanical advantage and efficiency are both ratios. Which of the following is true regarding the quantities used in these ratios?- a)Mechanical advantage compares values of work; efficiency compares values of power.
- b)Mechanical advantage compares values of forces; efficiency compares values of work.
- c)Mechanical advantage compares values of power; efficiency compares values of energy.
- d)Mechanical advantage compares values of work; efficiency compares values of forces.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mechanical advantage and efficiency are both ratios. Which of the following is true regarding the quantities used in these ratios?
a)
Mechanical advantage compares values of work; efficiency compares values of power.
b)
Mechanical advantage compares values of forces; efficiency compares values of work.
c)
Mechanical advantage compares values of power; efficiency compares values of energy.
d)
Mechanical advantage compares values of work; efficiency compares values of forces.

|
Orion Classes answered |
Mechanical advantage is a ratio of the output force generated given a particular input force. Efficiency is a ratio of the useful work performed by a system compared to the work performed on the system.
A weight lifter lifts a 275 kg barbell from the ground to a height of 2.4 m. How much work has he done in lifting the barbell, and how much work is required to hold the weight at that height?- a)3234 J and 0 J, respectively
- b)3234 J and 3234 J, respectively
- c)6468 J and 0 J, respectively
- d)6468 J and 6468 J, respectively
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A weight lifter lifts a 275 kg barbell from the ground to a height of 2.4 m. How much work has he done in lifting the barbell, and how much work is required to hold the weight at that height?
a)
3234 J and 0 J, respectively
b)
3234 J and 3234 J, respectively
c)
6468 J and 0 J, respectively
d)
6468 J and 6468 J, respectively

|
Orion Classes answered |
Because the weight of the barbell (force acting downward) is 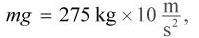 or about 2750 N, it follows that the weightlifter must exert an equal and opposite force of 2750 N on the barbell. The work done in lifting the barbell is therefore W = Fd cos θ = (2750 N)(2.4 m)(cos 0) ≈ 7000 J. Using the same equation, it follows that the work done to hold the barbell in place is W = Fd cos θ = (2750 N)(0 m)(cos θ) = 0 J. Because the barbell is held in place and there is no displacement, the work done is zero.
or about 2750 N, it follows that the weightlifter must exert an equal and opposite force of 2750 N on the barbell. The work done in lifting the barbell is therefore W = Fd cos θ = (2750 N)(2.4 m)(cos 0) ≈ 7000 J. Using the same equation, it follows that the work done to hold the barbell in place is W = Fd cos θ = (2750 N)(0 m)(cos θ) = 0 J. Because the barbell is held in place and there is no displacement, the work done is zero.
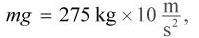 or about 2750 N, it follows that the weightlifter must exert an equal and opposite force of 2750 N on the barbell. The work done in lifting the barbell is therefore W = Fd cos θ = (2750 N)(2.4 m)(cos 0) ≈ 7000 J. Using the same equation, it follows that the work done to hold the barbell in place is W = Fd cos θ = (2750 N)(0 m)(cos θ) = 0 J. Because the barbell is held in place and there is no displacement, the work done is zero.
or about 2750 N, it follows that the weightlifter must exert an equal and opposite force of 2750 N on the barbell. The work done in lifting the barbell is therefore W = Fd cos θ = (2750 N)(2.4 m)(cos 0) ≈ 7000 J. Using the same equation, it follows that the work done to hold the barbell in place is W = Fd cos θ = (2750 N)(0 m)(cos θ) = 0 J. Because the barbell is held in place and there is no displacement, the work done is zero.Which of the following is a conservative force?- a)Air resistance
- b)Friction
- c)Gravity
- d)Convection
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a conservative force?
a)
Air resistance
b)
Friction
c)
Gravity
d)
Convection

|
Orion Classes answered |
Gravity is a conservative force because it is pathway independent and it does not dissipate mechanical energy. Air resistance and friction—choices (A) and (B)—are nonconservative forces that dissipate energy thermally. Convection is not a force, but a method of heat transfer, eliminating choice (D).
5 m3 of a gas are brought from an initial pressure of 1 kPa to a pressure of 3 kPa through an isochoric process. During this process, the work performed by the gas is:- a)–10 kJ
- b)–10 J
- c)0 J
- d)+10 kJ
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
5 m3 of a gas are brought from an initial pressure of 1 kPa to a pressure of 3 kPa through an isochoric process. During this process, the work performed by the gas is:
a)
–10 kJ
b)
–10 J
c)
0 J
d)
+10 kJ

|
Orion Classes answered |
An isochoric process, by definition, is one in which the gas system undergoes no change in volume. If the gas neither expands nor is compressed, then no work is performed. Remember that work in a thermodynamic system is the area under a P–V curve; if the change in volume is 0, then the area under the curve is also 0.
A tractor pulls a log with a mass of 500 kg along the ground for 100 m. The rope (between the tractor and the log) makes an angle of 30° with the ground and is acted on by a tensile force of 5000 N. How much work does the tractor perform in this scenario? (Note: sin 30° = 0.5, cos 30° = 0.866, tan 30° = 0.577)- a)250 kJ
- b)289 kJ
- c)433 kJ
- d)500 kJ
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A tractor pulls a log with a mass of 500 kg along the ground for 100 m. The rope (between the tractor and the log) makes an angle of 30° with the ground and is acted on by a tensile force of 5000 N. How much work does the tractor perform in this scenario? (Note: sin 30° = 0.5, cos 30° = 0.866, tan 30° = 0.577)
a)
250 kJ
b)
289 kJ
c)
433 kJ
d)
500 kJ

|
Orion Classes answered |
The work done by the tractor can be calculated from the equation
W = Fd cos θ = (5000 N)(100 m)(cos 30°) = (5000)(100)(0.866) ≈ 5000 × 80 = 400,000 J = 400 kJ.
W = Fd cos θ = (5000 N)(100 m)(cos 30°) = (5000)(100)(0.866) ≈ 5000 × 80 = 400,000 J = 400 kJ.
A 2000 kg experimental car can accelerate from 0 to 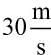 in 6 s. What is the average power of the engine needed to achieve this acceleration?
in 6 s. What is the average power of the engine needed to achieve this acceleration?- a)150 W
- b)150 kW
- c)900 W
- d)900 kW
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A 2000 kg experimental car can accelerate from 0 to 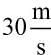 in 6 s. What is the average power of the engine needed to achieve this acceleration?
in 6 s. What is the average power of the engine needed to achieve this acceleration?
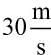 in 6 s. What is the average power of the engine needed to achieve this acceleration?
in 6 s. What is the average power of the engine needed to achieve this acceleration?a)
150 W
b)
150 kW
c)
900 W
d)
900 kW

|
Orion Classes answered |
The work done by the engine is equal to the change in kinetic energy of the car:
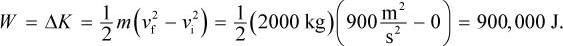
The average power therefore is
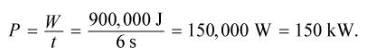
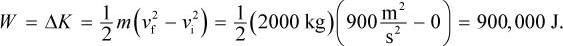
The average power therefore is
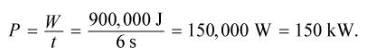
A consumer is comparing two new cars. Car A exerts 250 horsepower, while Car B exerts 300 horsepower. The consumer is most concerned about the peak velocity that the car can reach. Which of the following statements would best inform the consumer's decision? (Note: 1 horsepower = 745.7 W)- a)Car A and Car B both have unlimited velocities, ignoring nonconservative forces.
- b)Car A will reach its peak velocity more quickly than Car B.
- c)Car A will dissipate less energy to the surroundings than Car B.
- d)Car A will have a lower peak velocity than Car B.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A consumer is comparing two new cars. Car A exerts 250 horsepower, while Car B exerts 300 horsepower. The consumer is most concerned about the peak velocity that the car can reach. Which of the following statements would best inform the consumer's decision? (Note: 1 horsepower = 745.7 W)
a)
Car A and Car B both have unlimited velocities, ignoring nonconservative forces.
b)
Car A will reach its peak velocity more quickly than Car B.
c)
Car A will dissipate less energy to the surroundings than Car B.
d)
Car A will have a lower peak velocity than Car B.

|
Orion Classes answered |
Horsepower is a unit of power, as evidenced by the name and the conversion factor given in the question stem. Power is a rate of energy expenditure over time. Given unlimited time, both cars are capable of unlimited increases in (kinetic) energy, meaning that they have unlimited maximum velocities. The fact that Car B has a higher power rating means that it will reach any given velocity faster than Car A, eliminating choice (B). There is not enough information to make any judgments on the efficiency of the cars, eliminating choice (C). While it may take longer for Car A to reach a given velocity, both cars have unlimited maximum velocities according to the information given in the stem, eliminating choice (D).
A 40 kg block is resting at a height of 5 m off the ground. If the block is released and falls to the ground, which of the following is closest to its total mechanical energy at a height of 2 m, assuming negligible air resistance?- a)0 J
- b)400 J
- c)800 J
- d)2000 J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A 40 kg block is resting at a height of 5 m off the ground. If the block is released and falls to the ground, which of the following is closest to its total mechanical energy at a height of 2 m, assuming negligible air resistance?
a)
0 J
b)
400 J
c)
800 J
d)
2000 J

|
Orion Classes answered |
Assuming negligible air resistance, conservation of energy states that the total mechanical energy of the block is constant as it falls. At the starting height of 5 m, the block only has potential energy equal to
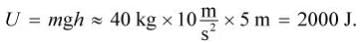
Because the kinetic energy at this point is 0 J, the total mechanical energy is 2000 J at any point during the block's descent.
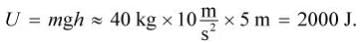
Because the kinetic energy at this point is 0 J, the total mechanical energy is 2000 J at any point during the block's descent.
Chapter doubts & questions for Work and Energy of Point Object Systems (PHY) - MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Work and Energy of Point Object Systems (PHY) - MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations
336 videos|223 docs|109 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









