All Exams >
MCAT >
MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations >
All Questions
All questions of Fluids (PHY) for MCAT Exam
The angle of contact for the liquid which wets the walls of the vessel is- a)acute
- b)zero
- c)obtuse
- d)900
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle of contact for the liquid which wets the walls of the vessel is
a)
acute
b)
zero
c)
obtuse
d)
900
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
When liquid molecules are attracted strongly to themselves and weakly to those of solids, it costs lots of energy to create liquid-solid surface and liquid then does not wet the solid.
For Example:
Mercury molecules (which make an obtuse angle with glass) have a strong force of attraction between themselves and a weak force of attraction toward solids. Hence, they tend to form drops.
On the other hand, water molecules make acute angles with glass. They have a weak force of attraction between themselves and a strong force of attraction toward solids. Hence, they tend to spread out.
The surface tension of a soap solution is 0.05 Nm-1. How much work is done to produce a soap bubble of radius 0.03 m?- a)1.8 x 10-2 J
- b)2.1 x 10-3J
- c)1.5 x 10-2 J
- d)1.1 x 10-3 J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The surface tension of a soap solution is 0.05 Nm-1. How much work is done to produce a soap bubble of radius 0.03 m?
a)
1.8 x 10-2 J
b)
2.1 x 10-3J
c)
1.5 x 10-2 J
d)
1.1 x 10-3 J
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Work done=total surface x Surface tension
=2x4πr2xσ
=2x4x3.14(0.03)2x 0.05
=1.1x10-3J
=2x4πr2xσ
=2x4x3.14(0.03)2x 0.05
=1.1x10-3J
A non-viscous liquid flows through a hose. Liquid enters with velocity 6.4 m/s and leaves with velocity 2.5 m/s. What is the ratio of radii of the hose where the liquid enters and where it leaves?
- a)5:1
- b)5:8
- c)8:5
- d)8:1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A non-viscous liquid flows through a hose. Liquid enters with velocity 6.4 m/s and leaves with velocity 2.5 m/s. What is the ratio of radii of the hose where the liquid enters and where it leaves?
a)
5:1
b)
5:8
c)
8:5
d)
8:1
|
|
Pavyasree D answered |
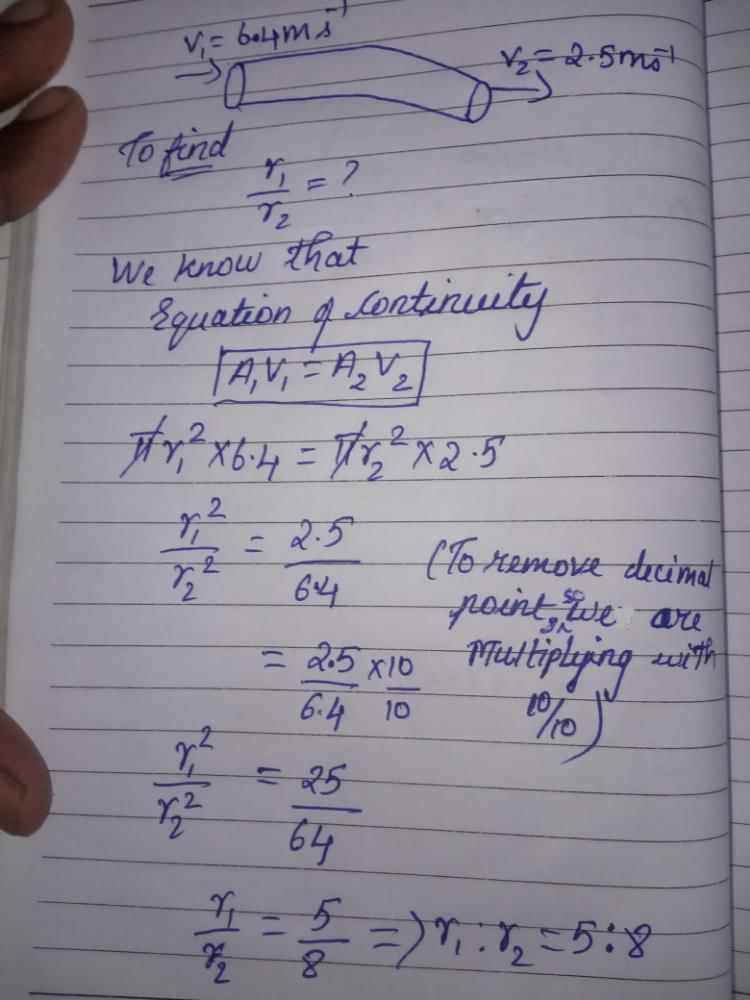
Which of the following expression is true for surface tension?- a)σ = -F/1
- b)σ = F/1
- c)σ = F.1
- d)σ = F.1.A
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following expression is true for surface tension?
a)
σ = -F/1
b)
σ = F/1
c)
σ = F.1
d)
σ = F.1.A
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
The force acting on this line is proportional to the length of this line. If l is the length of imaginary line and F the total force on either side of the line then,
F∝l
⇒ F=Sl
Or, surface tension, S=force/length
From this expression, Surface tension can be defined as the force acting per unit length of an imaginary line drawn on the liquid surface, the direction of force being perpendicular to this line and tangential to the liquid surface.it is denoted by S and it is a scalar quantity.
F∝l
⇒ F=Sl
Or, surface tension, S=force/length
From this expression, Surface tension can be defined as the force acting per unit length of an imaginary line drawn on the liquid surface, the direction of force being perpendicular to this line and tangential to the liquid surface.it is denoted by S and it is a scalar quantity.
In case of streamlined flow of liquid, the loss of energy is- a)infinite
- b)maximum
- c)minimum
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In case of streamlined flow of liquid, the loss of energy is
a)
infinite
b)
maximum
c)
minimum
d)
zero
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
In case of streamlined flow of liquid, the loss of energy is minimum because different layers glide over one another without intermixing. Therefore, there is no collision between the molecules of different layers, and hence minimum energy loss.
Fire fighters have a jet attached to the head of their water pipes. This is done to- a)increase the mass of water flowing out in one second
- b)increase the volume of water flowing out in one second
- c)increase the velocity of water flowing out in one second
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Fire fighters have a jet attached to the head of their water pipes. This is done to
a)
increase the mass of water flowing out in one second
b)
increase the volume of water flowing out in one second
c)
increase the velocity of water flowing out in one second
d)
none of these
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
In case of flowing fluids: product of pressure at any cross-section of pipe (in which fluid is flowing) and area of cross-section is constant. So, (PA) at source = (PA) at exit point and as we know that the cross section of the jet is less than the source (fire hydrant) => pressure at exit point (just outside jet) will be greater resulting more velocity of water at exit point. This way water can cover large distance so fire fighters can maintain a safe distance with fire.
Option B seems correct at first but in a closed pipe amount of water in will always be equal to amount of water out for any interval (considering a solid pipe) as option B is incorrect. Now option A should also be incorrect
As Mass = density × volume.
Option B seems correct at first but in a closed pipe amount of water in will always be equal to amount of water out for any interval (considering a solid pipe) as option B is incorrect. Now option A should also be incorrect
As Mass = density × volume.
When the salt is added to water, the surface tension of liquid mixture will- a)Increase
- b)Depends on the quantity of water
- c)Decrease
- d)Remain unaltered
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When the salt is added to water, the surface tension of liquid mixture will
a)
Increase
b)
Depends on the quantity of water
c)
Decrease
d)
Remain unaltered
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
NaCl salts cause an increase of the surface tension and the residence time of interfacial water molecules.
A garden sprinkler has 150 small holes, each of 2 mm2 area. If water is supplied at the rate of 0.3 litres/s, then find the average velocity of the spray.- a)300 cm/s
- b)22.5 cm/s
- c)0.1 cm/s
- d)100 cm/s
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A garden sprinkler has 150 small holes, each of 2 mm2 area. If water is supplied at the rate of 0.3 litres/s, then find the average velocity of the spray.
a)
300 cm/s
b)
22.5 cm/s
c)
0.1 cm/s
d)
100 cm/s
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
We know by the conservation of volume we get that
0.3 L/sec = 150 x 0.02 cm2 x v
Where v is the speed of the spray,
And we know 1L = 1 cm3
Hence we get v = 150 x 0.02 cm2 / .3 cm3/s
= 100 cm2/s
0.3 L/sec = 150 x 0.02 cm2 x v
Where v is the speed of the spray,
And we know 1L = 1 cm3
Hence we get v = 150 x 0.02 cm2 / .3 cm3/s
= 100 cm2/s
When wetting agents like soap or dyes are added to water, the angle of contact becomes- a)900
- b)600
- c)Large
- d)Small
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When wetting agents like soap or dyes are added to water, the angle of contact becomes
a)
900
b)
600
c)
Large
d)
Small
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
When wetting agents like soap or dyes are added to water, the angle of contact becomes small. This happens so that the particles penetrate well and become effective.
Angle of contact of water proofing agent are generally- a)large
- b)small
- c)less then 200
- d)Can be either large or small
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Angle of contact of water proofing agent are generally
a)
large
b)
small
c)
less then 200
d)
Can be either large or small
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Generally, if the water contact angle is smaller than 90DEG, the solid surface is considered hydrophilic and if the water contact angle is larger than 90DEG, the solid surface is considered hydrophobic.
The liquid that does not wet the solid surface has an ______ angle of contact.- a)900
- b)acute
- c)obtuse
- d)600
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The liquid that does not wet the solid surface has an ______ angle of contact.
a)
900
b)
acute
c)
obtuse
d)
600

|
Aashika Packiaselvam answered |
The angle should be obtuse.... cuz at this angle, the liquid surface moves away from the solid surface and hence cannot wet the solid.
The flow of liquid in which its layer slides over another without mixing, is called- a)Laminar flow
- b)Turbulent flow
- c)non-viscous flow
- d)Ideal Flow
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The flow of liquid in which its layer slides over another without mixing, is called
a)
Laminar flow
b)
Turbulent flow
c)
non-viscous flow
d)
Ideal Flow
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The word lamellar literally means line the fluid flows in lines when we see an ideal fluid, each particle follows a fixed line and there are numerous of this type in each layer so they don't lag each other.
The property by virtue of which the free surface of a liquid at rest behaves like an elastic stretched membrane tending to contract so as to occupy minimum surface area is known as- a)Bernoulli’s principle
- b)Surface tension
- c)Surface energy
- d)Viscosity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The property by virtue of which the free surface of a liquid at rest behaves like an elastic stretched membrane tending to contract so as to occupy minimum surface area is known as
a)
Bernoulli’s principle
b)
Surface tension
c)
Surface energy
d)
Viscosity
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
The property by virtue of which the free surface of a liquid at rest behaves like an elastic stretched membrane tending to contract so as to occupy minimum surface area is known as surface tension. By the definition of surface tension.
The equation of continuity is a special case of the law of conservation of- a)Energy
- b)Angular momentum
- c)Mass
- d)Momentum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The equation of continuity is a special case of the law of conservation of
a)
Energy
b)
Angular momentum
c)
Mass
d)
Momentum
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Because equation of continuity depends on mass and equation of continuity play a major role in mass.
When the gauge pressure is doubled, what happens to the absolute pressure?- a)It increases by a factor less than 2.
- b)It stays the same.
- c)It is halved.
- d)It doubles.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When the gauge pressure is doubled, what happens to the absolute pressure?
a)
It increases by a factor less than 2.
b)
It stays the same.
c)
It is halved.
d)
It doubles.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Absolute pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure plus gauge pressure.
- Atmospheric pressure is 101,300 Pa, while a typical gauge pressure for a tire is 30 psi or 207 Pa.
- Since atmospheric pressure is relatively large compared to most gauge pressures, doubling the gauge pressure would not end up doubling the absolute pressure.
- To use the tire example, if the gauge is 414 Pa, then absolute pressure would be 101,314 Pa. Absolute pressure increase by a factor less than 2.
Deep water runs almost still. What does it explain.- a)Surface energy
- b)Equation of continuity
- c)Magnus effect
- d)Bernoulli’s Theorem
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Deep water runs almost still. What does it explain.
a)
Surface energy
b)
Equation of continuity
c)
Magnus effect
d)
Bernoulli’s Theorem

|
Akshay Shah answered |
The equation of continuity for incompressible fluids states that the product of speed and cross-sectional area is always a constant.If a river becomes much deeper, the cross-sectional area becomes large and so the speed of flow is reduced. This is the origin of the expression “still waters run deep”
Pascal's law states that pressure at a point is equal in all directions, in a- a)static solid
- b)static fluid
- c)static gas
- d)moving fluid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Pascal's law states that pressure at a point is equal in all directions, in a
a)
static solid
b)
static fluid
c)
static gas
d)
moving fluid
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Concept:
According to Blaise Pascal, a French scientist observed that the pressure in a fluid at rest is the same at all points if they are at the same height and it is termed Pascal’s Law.
According to Blaise Pascal, a French scientist observed that the pressure in a fluid at rest is the same at all points if they are at the same height and it is termed Pascal’s Law.
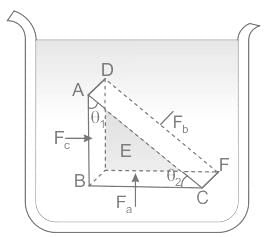
Proof of Pascal's law. ABC-DEF is an element of the interior of a fluid at rest. This element is in the form of a right-angled prism. The element is small so that the effect of gravity can be ignored, but it has been enlarged for the sake of clarity
i.e., the pressure exerted by the fluid on an object at a certain height will be the same in all direction and hence it can be expressed as
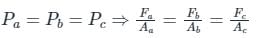
From the above fig. we can see that the force against area within a fluid at rest will always experience pressure perpendicular to their surface area, and the object will experience equal pressure throughout the surface.
And there are a number of devices, such as hydraulic lift and hydraulic brakes, are based on Pascal’s law, these devices used fluids for transmitting pressure.
Flow of water in hilly area is an example of streamline flow.- a)False, if the slope is not smooth
- b)always false
- c)True, only if the slope is smooth
- d)always true
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Flow of water in hilly area is an example of streamline flow.
a)
False, if the slope is not smooth
b)
always false
c)
True, only if the slope is smooth
d)
always true
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Streamline and turbulent flow. When the flow of liquid is such that the velocity, v of every particle at any point of the fluid is constant then the flow is said to be steady or streamline flow. The path followed by a particle of the fluid in stream-line flow is called steady or streamline flow.
Find the force required at the plunger which has 3 cm diameter, and the diameter of the hydraulic press is 30 cm. It is used for lifting a weight of 30 kN.- a)200 N
- b)150 N
- c)100 N
- d)300 N
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the force required at the plunger which has 3 cm diameter, and the diameter of the hydraulic press is 30 cm. It is used for lifting a weight of 30 kN.
a)
200 N
b)
150 N
c)
100 N
d)
300 N

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Concept:
Pascal’s Law:
- It was given by Blaise pascal
- It is also known as the principle of transmission of fluid pressure
- It states that the pressure change at any point in a confined incompressible fluid is transmitted throughout the fluid such that the same change occurs everywhere.
- Alternate definition:- The pressure applied to any part of the enclosed liquid will be transmitted equally in all directions through the liquid.
Applications:
- The underlying principle of hydraulic jack and hydraulic press.
- Force amplification in the braking system of most motor vehicles.
- Used in artesian wells, water towers, and dams.
Calculation:
Given:
Diameter of plunger, d = 3 cm, Diameter of ram, D = 30 cm, Force required at the plunger = ?, Weight = 30 kN
According to pascals law,
Pressure applied at ram = Pressure exerted on the plunger
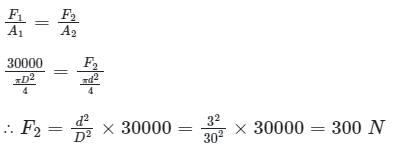
Here, F2 = force required on the plunger
Assertion (A): Pressure is equal in all directions at a point in an ideal fluid flow.
Reason (R): Pascal's law is valid for all fluids.- a)A is true, R is true, and it explains A
- b)A is true, R is true, but it does not explain A
- c)A is true, R is false
- d)A is false, R is true
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Pressure is equal in all directions at a point in an ideal fluid flow.
Reason (R): Pascal's law is valid for all fluids.
Reason (R): Pascal's law is valid for all fluids.
a)
A is true, R is true, and it explains A
b)
A is true, R is true, but it does not explain A
c)
A is true, R is false
d)
A is false, R is true

|
Pallabi Bajaj answered |
• Assertion (A): Pressure is equal in all directions at a point in an ideal fluid flow.
• Reason (R): Pascal's law is valid for all fluids.
Explanation:
• Pascal’s law states that the pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted equally in all directions without any loss. This law is applicable to both liquids and gases.
• In an ideal fluid flow, the fluid is assumed to be incompressible and have no viscosity. Due to this, the fluid particles can move freely without any resistance.
• At a point in an ideal fluid flow, the pressure is exerted equally in all directions. This is because the pressure at a point in a fluid is dependent only on the depth of the fluid column above that point.
• The pressure at a point in a fluid is given by the formula P = ρgh, where P is pressure, ρ is density, g is acceleration due to gravity, and h is depth.
• As the depth of the fluid column above a point is the same in all directions, the pressure at that point is also the same in all directions.
• Therefore, the assertion is true.
• Pascal’s law is applicable to all fluids, whether ideal or real. It states that the pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted equally in all directions without any loss.
• Therefore, the reason is also true.
• The reason explains the assertion.
• Hence, option A is the correct answer.
• Reason (R): Pascal's law is valid for all fluids.
Explanation:
• Pascal’s law states that the pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted equally in all directions without any loss. This law is applicable to both liquids and gases.
• In an ideal fluid flow, the fluid is assumed to be incompressible and have no viscosity. Due to this, the fluid particles can move freely without any resistance.
• At a point in an ideal fluid flow, the pressure is exerted equally in all directions. This is because the pressure at a point in a fluid is dependent only on the depth of the fluid column above that point.
• The pressure at a point in a fluid is given by the formula P = ρgh, where P is pressure, ρ is density, g is acceleration due to gravity, and h is depth.
• As the depth of the fluid column above a point is the same in all directions, the pressure at that point is also the same in all directions.
• Therefore, the assertion is true.
• Pascal’s law is applicable to all fluids, whether ideal or real. It states that the pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted equally in all directions without any loss.
• Therefore, the reason is also true.
• The reason explains the assertion.
• Hence, option A is the correct answer.
A patient is scheduled to receive an intravenous injection of medication that must be at least 109.3 kilopascals at the injection point before going into surgery. If the patient is lying on a bed 0.9 meters high, what is the minimum height above the ground that the nurse must suspend the bag to achieve that pressure at the injection point?
(ρfluid = 1020 kg/m3)- a)2.0 m
- b)0.80 m
- c)1.7 m
- d)2.3 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A patient is scheduled to receive an intravenous injection of medication that must be at least 109.3 kilopascals at the injection point before going into surgery. If the patient is lying on a bed 0.9 meters high, what is the minimum height above the ground that the nurse must suspend the bag to achieve that pressure at the injection point?
(ρfluid = 1020 kg/m3)
(ρfluid = 1020 kg/m3)
a)
2.0 m
b)
0.80 m
c)
1.7 m
d)
2.3 m
|
|
Ava Brown answered |
Given Data:
- Pressure required at the injection point = 109.3 kPa
- Height of the bed = 0.9 meters
- Density of the fluid (ρ) = 1020 kg/m³
Formula:
Pressure at a certain height in a fluid is given by the formula:
P = ρgh
Where:
P = Pressure
ρ = Density of the fluid
g = Acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s²)
h = Height
Calculation:
Given P = 109.3 kPa = 109300 Pa
ρ = 1020 kg/m³
g = 9.81 m/s²
h = ?
Convert kPa to Pa:
109.3 kPa = 109.3 * 1000 = 109300 Pa
Using the formula P = ρgh, we can solve for h:
h = P / (ρg)
h = 109300 / (1020 * 9.81)
h ≈ 11.18 meters
Since the bed is 0.9 meters high, the bag must be suspended at a height above the ground that is the difference between the total height required and the height of the bed:
Height above the ground = 11.18 - 0.9 ≈ 10.28 meters
Therefore, the minimum height above the ground that the nurse must suspend the bag to achieve the required pressure at the injection point is approximately 10.28 meters, which is closest to option C (1.7 m).
A 30 kilogram object is dropped into acetic acid, which has a specific gravity of 1.06. Once it is immersed in acetic acid, the object has an apparent weight of 240 N. What is the object’s specific gravity?- a)8.5
- b)5.3
- c)0.17
- d)1.3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A 30 kilogram object is dropped into acetic acid, which has a specific gravity of 1.06. Once it is immersed in acetic acid, the object has an apparent weight of 240 N. What is the object’s specific gravity?
a)
8.5
b)
5.3
c)
0.17
d)
1.3
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Convert 30 kg to Newtons, which would be 300 N. With an apparent weight of 240 N, the buoyant force gives it an upward push of 60 N.
- The buoyant force of 60 N accounts for the displaced volume of acetic acid, and we know the object weighs 300 N.
- Setup a ratio of FB(aceticacid)/Wobject = paceticacid/pobject
- 60/300 = 1.06/x, so 60·5 = 300 and 1.06·5 must equal x, which is 5.3.
A straight or curved path, such that tangent to it at any point gives the direction of flow of liquid at that point is known as- a)Turbulent flow
- b)Terminal flow
- c)Random flow
- d)Streamline flow
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A straight or curved path, such that tangent to it at any point gives the direction of flow of liquid at that point is known as
a)
Turbulent flow
b)
Terminal flow
c)
Random flow
d)
Streamline flow

|
Madhavan Patel answered |
Streamflow is the characteristics that determine how the water of the stream will move in a stream channel. Streamflow can either be streamline/ laminar flow or turbulent flow. In this topic, we will study the concept of streamline flow.
As per Pascal’s law:- a)intensity of pressure at a point in a moving fluid is equal in the direction of applied force.
- b)intensity of pressure at a point in a static fluid is equal in all directions.
- c)intensity of pressure at a point in a moving fluid is equal in all directions
- d)intensity of pressure at a point in a static fluid is equal in the direction of applied force.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
As per Pascal’s law:
a)
intensity of pressure at a point in a moving fluid is equal in the direction of applied force.
b)
intensity of pressure at a point in a static fluid is equal in all directions.
c)
intensity of pressure at a point in a moving fluid is equal in all directions
d)
intensity of pressure at a point in a static fluid is equal in the direction of applied force.

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Concept:
- Pascal’s principle: Pascal’s Law is the principle of transmission of fluid-pressure.
- It says that "a pressure exerted anywhere in a point of the confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions throughout the fluid”.
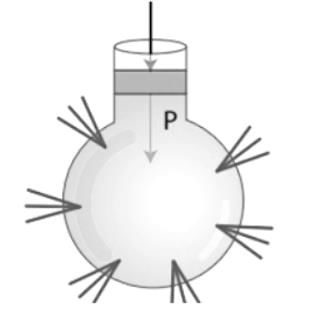
EXPLANATION:
- Centrifuge: Centrifugation is used to separate the contents of mixtures according to their size and density. The centrifuge works on the principle of sedimentation.
- Hydraulic Lift: The lift that uses pascal's law and used to lift objects with the help of fluid is called hydraulic lift. It works on Pascal's law. So option 2 is correct.
- Motor: A motor is an electrical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It works on the principle that a current-carrying conductor experiences a mechanical force when it is placed in a magnetic field.
- Lever: A lever is a simple machine that is made up of two load arms and a fulcrum. The distance from the fulcrum can be used to determine how the input and output forces are related to each other.
A gold crown recently acquired is suspected to be brass covered in gold. The crown weighs 25.0 N in air and has an apparent weight of 22.5 N in fresh water. Based on these results, which of the following conclusions is correct?
(ρgold = 19,300 kg/m3, ρbrass = 8300-8700 kg/m3)- a)It is likely that the crown is made of gold only.
- b)It is likely that the crown is made of half brass and half gold.
- c)It is likely that the crown is made of brass covered in gold.
- d)It is likely that the crown is made of brass only.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A gold crown recently acquired is suspected to be brass covered in gold. The crown weighs 25.0 N in air and has an apparent weight of 22.5 N in fresh water. Based on these results, which of the following conclusions is correct?
(ρgold = 19,300 kg/m3, ρbrass = 8300-8700 kg/m3)
(ρgold = 19,300 kg/m3, ρbrass = 8300-8700 kg/m3)
a)
It is likely that the crown is made of gold only.
b)
It is likely that the crown is made of half brass and half gold.
c)
It is likely that the crown is made of brass covered in gold.
d)
It is likely that the crown is made of brass only.
|
|
Jack Reed answered |
The crown weighs less in water than in air, indicating that it experiences an upward buoyant force in water. This means that the crown displaces a volume of water equal to its own volume. Since the crown is suspected to be brass covered in gold, and brass is denser than gold, it is likely that the crown is not made entirely of gold.
Therefore, the correct conclusion is that the crown is not made entirely of gold.
Therefore, the correct conclusion is that the crown is not made entirely of gold.
The pressure intensity at a point in a fluid is the same in all directions, only when the fluid- a)is frictionless
- b)is frictionless and incompressible
- c)has no relative motion between adjacent fluid layers
- d)has zero viscosity and is at rest
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The pressure intensity at a point in a fluid is the same in all directions, only when the fluid
a)
is frictionless
b)
is frictionless and incompressible
c)
has no relative motion between adjacent fluid layers
d)
has zero viscosity and is at rest

|
Aashna Chakraborty answered |
The pressure intensity at a point in a fluid is the same in all directions only when the fluid has no relative motion between adjacent fluid layers. This is based on the principle of fluid statics, which states that a fluid at rest will exert equal pressure on all surfaces in contact with it. Let us understand this in detail:
Principle of Fluid Statics:
The principle of fluid statics states that a fluid at rest will exert equal pressure on all surfaces in contact with it. This is because the pressure at any point in a fluid is determined by the weight of the fluid above it, and this weight is transmitted equally in all directions. Therefore, the pressure at any point in a fluid is the same in all directions.
Explanation of the correct option:
Option (c) states that the pressure intensity at a point in a fluid is the same in all directions only when the fluid has no relative motion between adjacent fluid layers. This is because if there is relative motion between adjacent fluid layers, it will create shear stresses, which will result in a pressure gradient in the fluid. This pressure gradient will cause the pressure intensity to be different in different directions, violating the principle of fluid statics.
Importance of fluid statics in engineering:
Fluid statics is an important concept in engineering, especially in the design of hydraulic systems. Understanding the principle of fluid statics is essential in determining the pressure distribution in a fluid and designing systems that can withstand these pressures. This principle is also important in the design of dams, reservoirs, and other structures that interact with fluids.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the pressure intensity at a point in a fluid is the same in all directions only when the fluid has no relative motion between adjacent fluid layers. This principle is essential in understanding the behavior of fluids at rest and is important in the design of hydraulic systems and other structures that interact with fluids.
Principle of Fluid Statics:
The principle of fluid statics states that a fluid at rest will exert equal pressure on all surfaces in contact with it. This is because the pressure at any point in a fluid is determined by the weight of the fluid above it, and this weight is transmitted equally in all directions. Therefore, the pressure at any point in a fluid is the same in all directions.
Explanation of the correct option:
Option (c) states that the pressure intensity at a point in a fluid is the same in all directions only when the fluid has no relative motion between adjacent fluid layers. This is because if there is relative motion between adjacent fluid layers, it will create shear stresses, which will result in a pressure gradient in the fluid. This pressure gradient will cause the pressure intensity to be different in different directions, violating the principle of fluid statics.
Importance of fluid statics in engineering:
Fluid statics is an important concept in engineering, especially in the design of hydraulic systems. Understanding the principle of fluid statics is essential in determining the pressure distribution in a fluid and designing systems that can withstand these pressures. This principle is also important in the design of dams, reservoirs, and other structures that interact with fluids.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the pressure intensity at a point in a fluid is the same in all directions only when the fluid has no relative motion between adjacent fluid layers. This principle is essential in understanding the behavior of fluids at rest and is important in the design of hydraulic systems and other structures that interact with fluids.
The force required to take away a flat plate of radius 4 cm from the surface of water is (surface tension of water = 70 dyne/cm)- a)1589. 2 dyne/cm
- b)1645.3 dyne/cm
- c)1758.4 dyne/cm
- d)1221.2 dyne/cm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The force required to take away a flat plate of radius 4 cm from the surface of water is (surface tension of water = 70 dyne/cm)
a)
1589. 2 dyne/cm
b)
1645.3 dyne/cm
c)
1758.4 dyne/cm
d)
1221.2 dyne/cm
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
Force due to surface tension acts all along the circumference of the circular plate. Therefore, force required to take away of plate is,
F = T x 2πr = 70 x 2 x 3.14 x 4 = 1758.4 dyne/cm
There is a 1-liter container filled with 500 milliliters of water placed on top of a scale displaying 80 pounds. When a metal cube is submerged tied to a string end into the container, which of the following statements accurately describes the result?- a)The cube’s density must be provided to predict what will happen.
- b)The scale will remain at 80 pounds until the cube is floating on top of the water fully submerged.
- c)The scale will register a weight greater than 80 pounds due to Newton’s Third Law.
- d)The scale will remain at 80 pounds unless the cube touches the bottom of the bowl.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
There is a 1-liter container filled with 500 milliliters of water placed on top of a scale displaying 80 pounds. When a metal cube is submerged tied to a string end into the container, which of the following statements accurately describes the result?
a)
The cube’s density must be provided to predict what will happen.
b)
The scale will remain at 80 pounds until the cube is floating on top of the water fully submerged.
c)
The scale will register a weight greater than 80 pounds due to Newton’s Third Law.
d)
The scale will remain at 80 pounds unless the cube touches the bottom of the bowl.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- When the cube is submerged, the object floats in equilibrium.
- There must be a buoyant force keeping the object afloat pushing upward.
- According to Newton’s Third Law, there should be an equal and opposite force downwards.
- That additional force will cause the scale to register a weight greater than 80 pounds.
A hydraulic press has a ram of 15 cm diameter and plunger of 1.5 cm. It is required to lift a weight of 1000 kg. The force required on the plunger is equal to:- a)10 kg
- b)100 kg
- c)1000 kg
- d)10,000 kg
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A hydraulic press has a ram of 15 cm diameter and plunger of 1.5 cm. It is required to lift a weight of 1000 kg. The force required on the plunger is equal to:
a)
10 kg
b)
100 kg
c)
1000 kg
d)
10,000 kg
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Concept:
Pascal’s Law:
Pascal’s Law:
- It was given by Blaise pascal
- It is also known as principle of transmission of fluid pressure
- It states that the pressure change at any point in a confined incompressible fluid is transmitted throughout the fluid such that the same change occurs everywhere.
- Alternate definition:- The pressure applied to any part of the enclosed liquid will be transmitted equally in all directions through the liquid.
Applications:
- The underlying principle of hydraulic jack and hydraulic press.
- Force amplification in the braking system of most motor vehicles.
- Used in artesian wells, water towers and dams.
Calculation:
Given:
Diameter of plunger, d = 1.5 cm, Diameter of ram, D = 15 cm, weight exerted on the ram, F1 = 1000 kg
According to pascals law,
Pressure applied at plunger = Pressure exerted on the ram
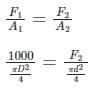
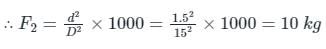
Here, F2 = force required on the plunger
Given:
Diameter of plunger, d = 1.5 cm, Diameter of ram, D = 15 cm, weight exerted on the ram, F1 = 1000 kg
According to pascals law,
Pressure applied at plunger = Pressure exerted on the ram
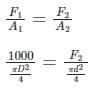
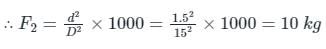
Here, F2 = force required on the plunger
A hydraulic press has a ram of 20 cm diameter and a plunger of 3 cm diameter. It is used for lifting a weight of 30 kN. Find the force required at the plunger.- a)975 N
- b)1075 N
- c)875 N
- d)675 N
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A hydraulic press has a ram of 20 cm diameter and a plunger of 3 cm diameter. It is used for lifting a weight of 30 kN. Find the force required at the plunger.
a)
975 N
b)
1075 N
c)
875 N
d)
675 N
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Concept:
Pascal’s Law:
Pascal’s Law:
- It was given by Blaise pascal
- It is also known as the principle of transmission of fluid pressure
- It states that the pressure change at any point in a confined incompressible fluid is transmitted throughout the fluid such that the same change occurs everywhere.
- Alternate definition:- The pressure applied to any part of the enclosed liquid will be transmitted equally in all directions through the liquid.
Applications:
- The underlying principle of hydraulic jack and hydraulic press.
- Force amplification in the braking system of most motor vehicles.
- Used in artesian wells, water towers, and dams.
Calculation:
Given:
Diameter of plunger, d = 3 cm, Diameter of ram, D = 20 cm, Force required at the plunger = ?, Weight = 30 kN
According to pascals law,
Pressure applied at ram = Pressure exerted on the plunger
Given:
Diameter of plunger, d = 3 cm, Diameter of ram, D = 20 cm, Force required at the plunger = ?, Weight = 30 kN
According to pascals law,
Pressure applied at ram = Pressure exerted on the plunger
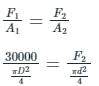
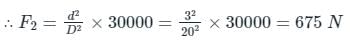
Here, F2 = force required on the plunger
A hydraulic lift has two pistons with area 1 m2 and 0.25 m2. What is the force exerted by the smaller piston when 40 N is placed on the larger piston?- a)160 N
- b)10 N
- c)40 N
- d)Cannot be determined
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A hydraulic lift has two pistons with area 1 m2 and 0.25 m2. What is the force exerted by the smaller piston when 40 N is placed on the larger piston?
a)
160 N
b)
10 N
c)
40 N
d)
Cannot be determined

|
Arien Instructors answered |
CONCEPT:
- Pascals Law: In a fluid at rest in a closed container, the external static pressure applied on a confined liquid is transmitted without loss to every portion of the fluid and to the walls of the container.
- In Pascal's law, the effect of gravity is neglected.
CALCULATION:
Given that A1 = 0.25 m2 and A2 = 1 m2; F2 = 40N F1 = ?
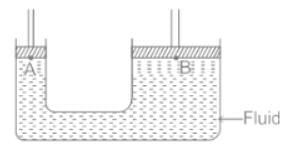
From Pascal's Law, the pressure inside the liquid will be equal at every place. So the pressure at A and B will be equal.
PA = PB

So the correct answer is option 2.
An air bubble of radius 'r' doubles its radius as it rises from a depth 'h' to the surface of the lake at a constant temperature. If the atmospheric pressure is equal to 10 m height of the water column, neglecting surface tension the value of 'h' is:- a)90 m
- b)70 m
- c)60 m
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An air bubble of radius 'r' doubles its radius as it rises from a depth 'h' to the surface of the lake at a constant temperature. If the atmospheric pressure is equal to 10 m height of the water column, neglecting surface tension the value of 'h' is:
a)
90 m
b)
70 m
c)
60 m
d)
None of these

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Concept:
Find the expression for both volume and pressure at the bottom and at the surface of the lake. Then at constant temperature try to find the solution with the help of P-V relation.
Hydrostatic Pressure:
Hydrostatic pressure can be defined as the pressure that is exerted by a fluid at equilibrium to an object at a depth due to the gravitational force. It can be given as,
p = ρgh
Calculation:
Given:
Patm = 10 m (height of water column)
At the bottom of the lake, the radius of the air bubble is r.
At the surface of the lake, the radius of the bubble will be 2r.
Volume of the bubble at the bottom of the lake 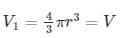
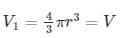
Volume of the bubble at the surface of the lake 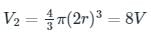
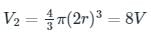
Now the atmospheric pressure at the surface is = 2 m.
Atmospheric pressure at the bottom will be
P1 = Patm + Pressure at the bottom of the water at height h
P1 = (10 + h) m
The temperature has been given constant, therefore
P1V1 = P2V2
(10 + h)V = 10 × 8V
10 + h = 80
h = 70 m
Balls A and B of equal mass are floating in a swimming pool, as shown below. Which will produce a greater buoyant force?
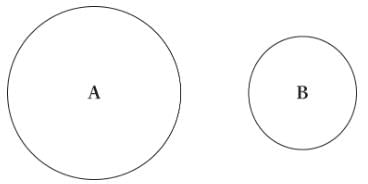
- a)Ball A
- b)Ball B
- c)The forces will be equal.
- d)It is impossible to know without knowing the volume of each ball.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Balls A and B of equal mass are floating in a swimming pool, as shown below. Which will produce a greater buoyant force?


a)
Ball A
b)
Ball B
c)
The forces will be equal.
d)
It is impossible to know without knowing the volume of each ball.

|
Orion Classes answered |
The buoyant force (Fbuoy) is equal to the weight of water displaced, which is quantitatively expressed as
Fbuoy = mfluid displacedg = ρfluidVfluid displacedg
The volume of displaced fluid is equal to the volume of the ball. The density of the fluid remains constant. Therefore, because ball A has a larger volume, it will displace more water and experience a larger buoyant force.
The volume of displaced fluid is equal to the volume of the ball. The density of the fluid remains constant. Therefore, because ball A has a larger volume, it will displace more water and experience a larger buoyant force.
The figure shown represents a section through a horizontal pipe of varying diameters into which four open vertical pipes connect. If water is allowed to flow through the pipe in the direction indicated, in which of the vertical pipes will the water level be lowest?
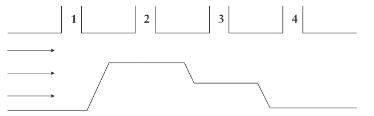
- a)Pipe 1
- b)Pipe 2
- c)Pipe 3
- d)Pipe 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The figure shown represents a section through a horizontal pipe of varying diameters into which four open vertical pipes connect. If water is allowed to flow through the pipe in the direction indicated, in which of the vertical pipes will the water level be lowest?


a)
Pipe 1
b)
Pipe 2
c)
Pipe 3
d)
Pipe 4

|
Orion Classes answered |
It is not necessary to do any calculations to answer this question. The open vertical pipes are exposed to the same atmospheric pressure; therefore, differences in the heights of the columns of water in the vertical pipes is dependent only on the differences in hydrostatic pressures in the horizontal pipe. Because the horizontal pipe has variable cross-sectional area, water will flow the fastest and the hydrostatic pressure will have its lowest value where the horizontal pipe is narrowest; this is called the Venturi effect. As a result, pipe 2 will have the lowest water level.
What property of a fluid allows it to exert pressure equally in all directions?- a)Viscosity
- b)Surface tension
- c)Compressibility
- d)Incompressibility
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What property of a fluid allows it to exert pressure equally in all directions?
a)
Viscosity
b)
Surface tension
c)
Compressibility
d)
Incompressibility

|
Orion Classes answered |
Incompressibility is the property of a fluid that allows it to exert pressure equally in all directions. Since the fluid cannot be compressed, any force applied to it is transmitted equally in all directions, resulting in equal pressure distribution.
According to _______, the intensity of pressure in a liquid at rest is constant in all directions.- a)Newton's law
- b)Boyles law
- c)hydrostatic law
- d)Pascal's law
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
According to _______, the intensity of pressure in a liquid at rest is constant in all directions.
a)
Newton's law
b)
Boyles law
c)
hydrostatic law
d)
Pascal's law

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Pascal’s principle:
- Pascal’s Law is the principle of transmission of fluid pressure.
- It says that "a pressure exerted anywhere in a point of the confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions throughout the fluid”.
_____ gives an idea about the pressure in a static fluid.- a)Grashof’s law
- b)Weber’s law
- c)Pascal’s law
- d)Newton’s law
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
_____ gives an idea about the pressure in a static fluid.
a)
Grashof’s law
b)
Weber’s law
c)
Pascal’s law
d)
Newton’s law
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Pascal's law:
According to Pascal’s Law, the pressure or intensity of pressure at a point in a static fluid is equal in all directions.
This law is valid for the cases of fluid flow where shear stresses do not exist. The cases are
According to Pascal’s Law, the pressure or intensity of pressure at a point in a static fluid is equal in all directions.
This law is valid for the cases of fluid flow where shear stresses do not exist. The cases are
- Fluid at rest
- No relative motion exists between different fluid layers. For example, fluid at a constant linear acceleration in a container
- Ideal fluid flow where viscous force is negligible

As per Pascal’s law:- a)intensity of pressure at a point in a moving fluid is equal in the direction of applied force.
- b)intensity of pressure at a point in a static fluid is equal in all directions.
- c)intensity of pressure at a point in a moving fluid is equal in all directions
- d)intensity of pressure at a point in a static fluid is equal in the direction of applied force.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
As per Pascal’s law:
a)
intensity of pressure at a point in a moving fluid is equal in the direction of applied force.
b)
intensity of pressure at a point in a static fluid is equal in all directions.
c)
intensity of pressure at a point in a moving fluid is equal in all directions
d)
intensity of pressure at a point in a static fluid is equal in the direction of applied force.
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
- Centrifuge: Centrifugation is used to separate the contents of mixtures according to their size and density. The centrifuge works on the principle of sedimentation.
- Hydraulic Lift: The lift that uses pascal's law and used to lift objects with the help of fluid is called hydraulic lift. It works on Pascal's law. So option 2 is correct.
- Motor: A motor is an electrical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It works on the principle that a current-carrying conductor experiences a mechanical force when it is placed in a magnetic field.
- Lever: A lever is a simple machine that is made up of two load arms and a fulcrum. The distance from the fulcrum can be used to determine how the input and output forces are related to each other.
Objects A and B are submerged at a depth of 1 m in a liquid with a specific gravity of 0.877. Given that the density of object B is one-third that of object A and that the gauge pressure of object A is 3 atm, what is the gauge pressure of object B? (Note: Assume atmospheric pressure is 1 atm and g = 9.8 m/s2).- a)1 atm
- b)2 atm
- c)3 atm
- d)9 atm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Objects A and B are submerged at a depth of 1 m in a liquid with a specific gravity of 0.877. Given that the density of object B is one-third that of object A and that the gauge pressure of object A is 3 atm, what is the gauge pressure of object B? (Note: Assume atmospheric pressure is 1 atm and g = 9.8 m/s2).
a)
1 atm
b)
2 atm
c)
3 atm
d)
9 atm

|
Orion Classes answered |
The absolute and gauge pressures depend only on the density of the fluid, not that of the object. When the pressure at the surface is equal to atmospheric pressure, the gauge pressure is given by Pgauge = ρgz, where ρ represents the density of the fluid, not the object. These objects are also at the same depth, so they must have the same gauge pressure.
The pressure inside a soap bubble of radius R and surface tension S is
- a)2S/R
- b)4S/R
- c)4S.R
- d)2S/R
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The pressure inside a soap bubble of radius R and surface tension S is
a)
2S/R
b)
4S/R
c)
4S.R
d)
2S/R
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
If R is the radius of a soap bubble and S its surface tension, then the excess pressure inside is 4S/R.
A hydraulic press has a ram of 15 cm diameter and plunger of 1.5 cm. It is required to lift a weight of 1000 kg. The force required on the plunger is equal to:- a)10 kg
- b)100 kg
- c)1000 kg
- d)10,000 kg
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A hydraulic press has a ram of 15 cm diameter and plunger of 1.5 cm. It is required to lift a weight of 1000 kg. The force required on the plunger is equal to:
a)
10 kg
b)
100 kg
c)
1000 kg
d)
10,000 kg

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Concept:
Pascal’s Law:
- It was given by Blaise pascal
- It is also known as principle of transmission of fluid pressure
- It states that the pressure change at any point in a confined incompressible fluid is transmitted throughout the fluid such that the same change occurs everywhere.
- Alternate definition:- The pressure applied to any part of the enclosed liquid will be transmitted equally in all directions through the liquid.
Applications:
- The underlying principle of hydraulic jack and hydraulic press.
- Force amplification in the braking system of most motor vehicles.
- Used in artesian wells, water towers and dams.
Calculation:
Given:
Diameter of plunger, d = 1.5 cm, Diameter of ram, D = 15 cm, weight exerted on the ram, F1 = 1000 kg
According to pascals law,
Pressure applied at plunger = Pressure exerted on the ram
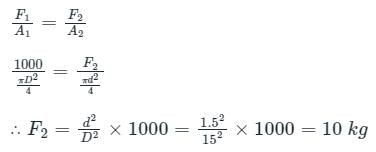
Here, F2 = force required on the plunger
At what depth from surface of water, the pressure will be equal to three times the atmosphere pressure? Given atmospheric pressure = 10 N/cm2 and g = 9.8 m/s2.- a)20.4 m
- b)5.6 m
- c)2.8 m
- d)10.2 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At what depth from surface of water, the pressure will be equal to three times the atmosphere pressure? Given atmospheric pressure = 10 N/cm2 and g = 9.8 m/s2.
a)
20.4 m
b)
5.6 m
c)
2.8 m
d)
10.2 m

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Concept:
- Gauge pressure inside the water at the depth of ℎ m will be:
Pgauge = ρgh N/m2
- Derived using Bernoulli's equation
Calculation:
Given: Patm = 10 N/cm2 = 10× 104 N/ m2 , ρ = 1000 kg/m3, g = 9.8m/s2
Patm= 105Pa
- Now Pgauge should be equal to three times Patm
Pabs = Patm + Pgauge
⇒ 3 × Patm = Patm + ρgh
⇒ ρgh = 2× Patm
⇒ 1000 × 9.8 × h = 2 × 105
⇒ h = 20.4m
- Hence at the depth of 20.4m the pressure inside the water will be three times the atmospheric pressure.
Additional Information
- Gauge pressure or relative pressure (Pg) is the difference between the measured pressure and the local atmospheric pressure.
- Absolute pressure is the actual pressure at a point measured with respect to vacuum pressure i.e. zero pressure.
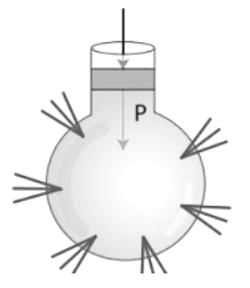
From the given image, which of the following statements are true according to Pascal's law?
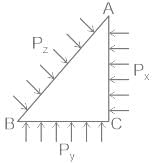
- a)Px = Py = Pz
- b)Px > Py > Pz
- c)Px < Py < Pz
- d)Px + Py + Pz = 0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
From the given image, which of the following statements are true according to Pascal's law?


a)
Px = Py = Pz
b)
Px > Py > Pz
c)
Px < Py < Pz
d)
Px + Py + Pz = 0
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Pascal's Law:
- "Any force applied to a confined fluid is transmitted uniformly in all directions throughout the fluid regardless of the shape of the container".

The main applications of the hydraulic system are as follows:
- Industrial: Automated production lines, machine tool industries, Paper industries.
- Mobile hydraulics: Material handling equipment, commercial vehicles, tunnel boring equipment.
- Automobiles: It is used in the systems like hydraulic brakes, shock absorbers, steering system.
- Marine applications: It mostly covers ocean-going vessels, fishing boats, and naval equipment.
Which of the following data sets is sufficient to determine the linear speed through an area of a rigid pipe?- a)The cross sectional area in another segment of pipe and the cross sectional area in the region of interest
- b)The Reynolds number, viscosity of the fluid, density, and diameter of the pipe
- c)The radius of the pipe, pressure gradient, viscosity, and length of the pipe
- d)The absolute pressure and density
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following data sets is sufficient to determine the linear speed through an area of a rigid pipe?
a)
The cross sectional area in another segment of pipe and the cross sectional area in the region of interest
b)
The Reynolds number, viscosity of the fluid, density, and diameter of the pipe
c)
The radius of the pipe, pressure gradient, viscosity, and length of the pipe
d)
The absolute pressure and density

|
Orion Classes answered |
The data given in choice (C) are sufficient to determine the flow rate through Poiseuille's law, which can then be used to determine the linear speed by dividing by the cross-sectional area (which could be determined from the radius, as well). Choice (A) would be sufficient if we also knew the flow rate in the other segment of pipe; one could use the continuity equation to determine the linear speed. The data in choice (B) could be used to determine the critical speed at which turbulent flow begins, but there is no indication that there is turbulent flow. The data in choice (D) could be used to determine the depth of an object in a fluid.
Two wooden balls of equal volume but different density are held beneath the surface of a container of water. Ball A has a density of 0.5 g/m3, and ball B has a density of 0.7 g/cm3. When the balls are released, they will accelerate upward to the surface. What is the relationship between the acceleration of ball A and that of ball B?- a)Ball A has the greater acceleration.
- b)Ball B has the greater acceleration.
- c)Balls A and B have the same acceleration.
- d)It cannot be determined from information given.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two wooden balls of equal volume but different density are held beneath the surface of a container of water. Ball A has a density of 0.5 g/m3, and ball B has a density of 0.7 g/cm3. When the balls are released, they will accelerate upward to the surface. What is the relationship between the acceleration of ball A and that of ball B?
a)
Ball A has the greater acceleration.
b)
Ball B has the greater acceleration.
c)
Balls A and B have the same acceleration.
d)
It cannot be determined from information given.

|
Orion Classes answered |
Using Newton's second law, Fnet = ma, we obtain the following equation:
Fbuoy ? mg = ma
Thus,

Both balls experience the same buoyant force because they are in the same liquid and have the same volume (Fbuoy = ρVg). Thus, the ball with the smaller mass experiences the greater acceleration. Because both balls have the same volume, the ball with the smaller density has the smaller mass (m = ρV), which is ball A.
Fbuoy ? mg = ma
Thus,

Both balls experience the same buoyant force because they are in the same liquid and have the same volume (Fbuoy = ρVg). Thus, the ball with the smaller mass experiences the greater acceleration. Because both balls have the same volume, the ball with the smaller density has the smaller mass (m = ρV), which is ball A.
A low-pressure weather system can decrease the atmospheric pressure from 1 atm to 0.99 atm. By what percent will this decrease the force on a rectangular window from the outside? (Note: Assume the window is 6 m by 3 m and the glass is 3 cm thick.)- a)1%
- b)10%
- c)1/3%
- d)30%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A low-pressure weather system can decrease the atmospheric pressure from 1 atm to 0.99 atm. By what percent will this decrease the force on a rectangular window from the outside? (Note: Assume the window is 6 m by 3 m and the glass is 3 cm thick.)
a)
1%
b)
10%
c)
1/3%
d)
30%

|
Orion Classes answered |
This question is a simple application of the definition of pressure, which is force per area. If pressure decreases 1 percent and area does not change, the force will be decreased by 1 percent. Note that the other measurements given do not play a role in our calculations.
A liquid is filled in a large cylindrical container. The pressure exerted by the liquid on the wall of the container depends on- a)Density of liquid
- b)Gravity
- c)Depth of liquid
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A liquid is filled in a large cylindrical container. The pressure exerted by the liquid on the wall of the container depends on
a)
Density of liquid
b)
Gravity
c)
Depth of liquid
d)
All of these

|
Arien Instructors answered |
CONCEPT:
- Pressure: Pressure is defined as the physical force exerted on an object. The unit of pressure is Pascal.
The basic formula for pressure is given by:
P = F/A, Where P is pressure, F = force, A = area.
The pressure exerted by a liquid on the wall of container can be given by
P = ρ h g, Where ρ = density of liquid, h = height of the liquid, g = gravity.
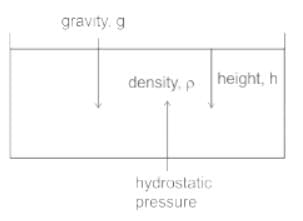
EXPLANATION:
- The pressure exerted by a liquid on the wall of container can be given by
P = ρ h g, Where ρ = density of liquid, h = height of the liquid, g = gravity.
- Thus it depends on the density of the liquid, height of the liquid in the container, and the acceleration due to gravity. So option 4 is correct.
Which of the following laws states that pressure or intensity of pressure at a point in static fluid is equal in all directions?- a)Darcy's law
- b)Newton's law
- c)Hydrostatic law
- d)Pascal's law
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following laws states that pressure or intensity of pressure at a point in static fluid is equal in all directions?
a)
Darcy's law
b)
Newton's law
c)
Hydrostatic law
d)
Pascal's law

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Pascal’s law: Pascal’s Law is the principle of transmission of fluid-pressure, It says that "a pressure exerted anywhere in a point of the confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions throughout the fluid”.
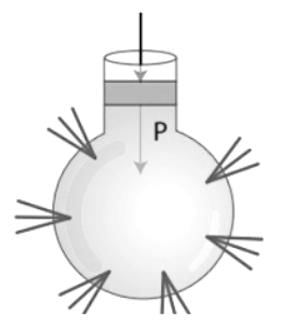

The resultant pressure on a body submerged in a fluid due to the fluid acts at which of the following points in the body?- a)Centre of pressure
- b)Centre of mass
- c)Centre of buoyancy
- d)Metacentre
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The resultant pressure on a body submerged in a fluid due to the fluid acts at which of the following points in the body?
a)
Centre of pressure
b)
Centre of mass
c)
Centre of buoyancy
d)
Metacentre

|
Arien Instructors answered |
CONCEPT:
- When a body is submerged in a fluid, it experiences pressure due to the surrounding fluid.
- The resultant of the pressure due to the fluid acts at a point in the body.
- Centre of pressure: The point where the total sum of (or resultant) pressure due to the fluid acts on a body submerged inside it.
EXPLANATION:
- The resultant pressure on a body submerged in a fluid acts on a point on a body called the centre of pressure.
Additional Information
- Centre of mass: The point where all the mass of a body is assumed to be concentrated.
- Centre of buoyancy: The centre of gravity of the volume of fluid displaced by the body submerged in the fluid is called the centre of buoyancy.
- Metacentre: The point at which an imaginary vertical line passing through the centre of buoyancy and centre of gravity intersects the imaginary vertical line through a new centre of buoyancy created when the body is displaced, or tipped, in the fluid.
Chapter doubts & questions for Fluids (PHY) - MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Fluids (PHY) - MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations
336 videos|223 docs|109 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










