All Exams >
MCAT >
MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations >
All Questions
All questions of Separations & Purifications (OC, BC) for MCAT Exam
Which of the following additional set of conditions (listed first the adsorbent and second the solvent or eluent) would produce the following TLC plates?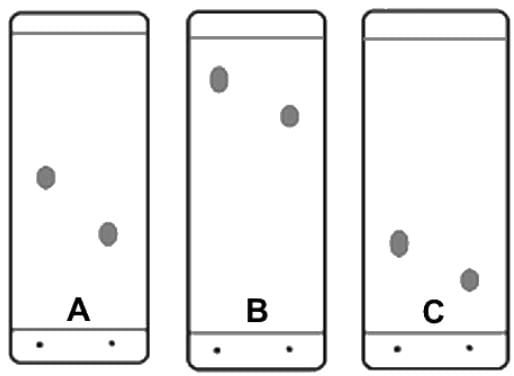
- a)Plate A: silica gel, benzene; Plate B: alumina gel, petroleum ether; Plate C: silica gel, carbon tetrachloride
- b)Plate A: silica gel, cyclohexane; Plate B: silica gel, acetone, Plate C: alumina gel, petroleum ether
- c)Plate A: cellulose, cyclohexane; Plate B: alumina gel, petroleum ether; Plate C: silica gel, methanol
- d)Plate A: alumina gel, ethanol; Plate B: alumina gel, petroleum ether; Plate C: silica gel, benzene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following additional set of conditions (listed first the adsorbent and second the solvent or eluent) would produce the following TLC plates?

a)
Plate A: silica gel, benzene; Plate B: alumina gel, petroleum ether; Plate C: silica gel, carbon tetrachloride
b)
Plate A: silica gel, cyclohexane; Plate B: silica gel, acetone, Plate C: alumina gel, petroleum ether
c)
Plate A: cellulose, cyclohexane; Plate B: alumina gel, petroleum ether; Plate C: silica gel, methanol
d)
Plate A: alumina gel, ethanol; Plate B: alumina gel, petroleum ether; Plate C: silica gel, benzene
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
In terms of solvents, cyclohexane, benzene, petroleum ether, and carbon tetrachloride have the least eluting power, while acetone, methanol, and ethanol have greater eluting power.
If plate A has alumina gel as adsorbent and ethanol as eluent, plate B could not have a greater Rf with the same adsorbent and petroleum ether as eluent. The Rf's would be switched.
Since cellulose is the least adsorptive, when plate A has cellulose as adsorbent and cyclohexane as eluent, the Rf values should be greater.
Two answer choices have that plate A using silica gel as the adsorbent and solvent with a low eluting power, i.e. cyclohexane and benzene. Let’s evaluate plate B. In order for the Rf to increase, the adsorbent must have less adsorptive power or the eluent must have greater eluting power.
Only when plate B has silica gel as adsorbent and acetone as eluent does the chromatograph match. Here, the eluent (acetone) has a greater eluting power.
As final confirmation, look at plate C. It has an adsorbent of alumina gel, which has a greater adsorptive power, so Rf values would decrease. The answer is that Plate A: silica gel, cyclohexane, Plate B: silica gel, acetone, and Plate C: alumina gel, petroleum ether.
In the chlorination of 2-methylbutane at 300°, all four possible monosubstitution products (compounds A-D) are created. On a purely statistical basis, the ratio of the products (50%:25%:17%:8%) should correlate with the number of available hydrogens at the various positions, 6:3:2:1 respectively. A gas chromatograph separation was performed after the reaction was complete to evaluate the experimental ratios of the 4 products. Which of the following statements most accurately describes the gas chromatogram?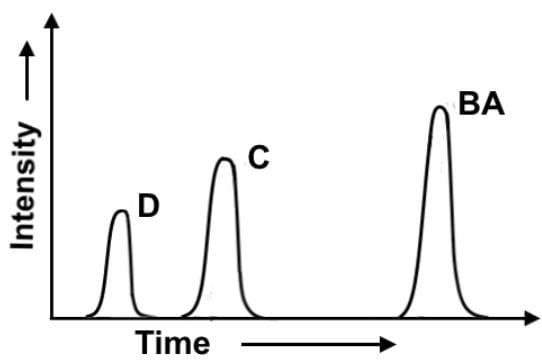
- a)The ratio of the areas under the peaks is 2:3:4, and product D has the lowest yield at about 22%.
- b)Products A and B form one peak together because of their nearly identical solubility in the adsorbent.
- c)The four products are separated due to their affinity for the adsorbent in the column, and product A elutes out of the column first.
- d)The smallest peak corresponds to 2-chloro-2-methylbutane, and it elutes the quickest because it has the lowest boiling point.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the chlorination of 2-methylbutane at 300°, all four possible monosubstitution products (compounds A-D) are created. On a purely statistical basis, the ratio of the products (50%:25%:17%:8%) should correlate with the number of available hydrogens at the various positions, 6:3:2:1 respectively. A gas chromatograph separation was performed after the reaction was complete to evaluate the experimental ratios of the 4 products. Which of the following statements most accurately describes the gas chromatogram?

a)
The ratio of the areas under the peaks is 2:3:4, and product D has the lowest yield at about 22%.
b)
Products A and B form one peak together because of their nearly identical solubility in the adsorbent.
c)
The four products are separated due to their affinity for the adsorbent in the column, and product A elutes out of the column first.
d)
The smallest peak corresponds to 2-chloro-2-methylbutane, and it elutes the quickest because it has the lowest boiling point.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The four products are separated by boiling point, and product D elutes out of the column first.
Products A and B form one peak together because of their nearly identical boiling points.
The ratio of the areas under the peaks is 22:33:45 or approximately 2:3:4. Here, it is ambiguous whether the lowest yield product is D since product A and B falls under the highest peak. In fact, product A is the lowest yield at 15%, and product B comes in at 30%.
The smallest peak or peak D does correspond to 2-chloro-2-methylbutane, meaning it has the lowest boiling point. It is the most compact and branched of all the chlorinated methylbutanes, so it has the least van der Waals force, hence lowest boiling point.
To address the last point, it elutes the quickest because it has the lowest boiling point. Since it is further to the right, it elutes first. It was also mentioned earlier that the products are separated by boiling point.
A distillation procedure is performed with a starting mixture of 25% X and 75% Y, and the distillation steps have been superimposed onto the liquid-vapor phase diagram. Which of the following statements best describes this distillation process in relation to the phase diagram?
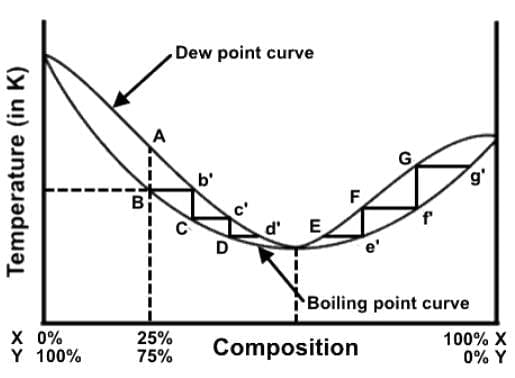
- a)Heating a 25% X : 75% Y mixture to temperature B will generate a vapor of a composition A over a liquid of a composition B.
- b)During a distillation of a 25% X : 75% Y mixture, the procedure will progress from point B to point G and beyond until the mixture is 100% X.
- c)At a composition D, the distillate will boil at a lower temperature because it has a lower percentage of X than the original mixture.
- d)Point B is the boiling point of the original mixture at a composition B, and the vapor that is collected at that temperature has composition b’.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A distillation procedure is performed with a starting mixture of 25% X and 75% Y, and the distillation steps have been superimposed onto the liquid-vapor phase diagram. Which of the following statements best describes this distillation process in relation to the phase diagram?


a)
Heating a 25% X : 75% Y mixture to temperature B will generate a vapor of a composition A over a liquid of a composition B.
b)
During a distillation of a 25% X : 75% Y mixture, the procedure will progress from point B to point G and beyond until the mixture is 100% X.
c)
At a composition D, the distillate will boil at a lower temperature because it has a lower percentage of X than the original mixture.
d)
Point B is the boiling point of the original mixture at a composition B, and the vapor that is collected at that temperature has composition b’.

|
Orion Classes answered |
Here we have a liquid-vapor phase diagram for an azeotrope. More specifically, this is a positive azeotrope, which is pressure-maximum and temperature-minimum, and will boil at a lower temperature than any other ratio of its constituents.
This is the distillation procedure. Heating a mixture with a composition B will boil at a temperature Bb’, and the vapor will have a composition b’ and will condense with a liquid composition C. By heating this condensed liquid it will boil at temperature Cc’.
The procedure progresses from point B to point d’ until reaching the azeotropic point. When starting right of the azeotrope point, the experiment progresses from points g’ to e’ closing in on the azeotrope point from the other direction. Remember that at the azeotrope point, the two compounds cannot be separated by simple distillation methods.
At a composition D, the distillate will boil at a lower temperature because it has a lower percentage of Y than the original mixture.
An azeotrope is a mixture of liquids whose proportions cannot be changed by simple distillation because, when it is boiled, the vapor has the same proportions of constituents as the unboiled mixture. From an azeotropic mixture of 95% ethanol and 5% water, which of the following methods would NOT allow for further purification of ethanol at the azeotropic point?- a)Dissolution of a salt like potassium acetate into mixture and then distillation
- b)Distillation conducted in an all-nitrogen gas (N2) environment
- c)Addition of an additional agent like cyclohexane to the mixture to form a ternary azeotrope and then distillation
- d)Addition of calcium oxide to the mixture and then filtration
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An azeotrope is a mixture of liquids whose proportions cannot be changed by simple distillation because, when it is boiled, the vapor has the same proportions of constituents as the unboiled mixture. From an azeotropic mixture of 95% ethanol and 5% water, which of the following methods would NOT allow for further purification of ethanol at the azeotropic point?
a)
Dissolution of a salt like potassium acetate into mixture and then distillation
b)
Distillation conducted in an all-nitrogen gas (N2) environment
c)
Addition of an additional agent like cyclohexane to the mixture to form a ternary azeotrope and then distillation
d)
Addition of calcium oxide to the mixture and then filtration
|
|
Bella Perry answered |
Understanding Azeotropes
Azeotropes are unique mixtures where the composition of vapor and liquid phases remains constant during distillation. This makes separating the components challenging.
Why Option B is Incorrect
In the context of separating ethanol from a 95% ethanol and 5% water azeotrope:
Distillation in an All-Nitrogen Environment
- Conducting distillation in an all-nitrogen environment does not alter the vapor-liquid equilibrium of the azeotropic mixture.
- Nitrogen does not interact or react with either ethanol or water, so it cannot change the boiling point or vapor composition.
- As a result, the same azeotropic composition will still be achieved, preventing further purification of ethanol.
Methods That Allow Purification
A) Dissolution of a Salt
- Adding potassium acetate can break the azeotropic behavior by changing the interactions in the solution.
- This affects the boiling points and allows for separation via distillation.
C) Addition of Cyclohexane
- Introducing cyclohexane can create a new ternary azeotrope, which can subsequently be distilled to separate ethanol from water.
D) Addition of Calcium Oxide
- Calcium oxide can absorb water from the mixture, effectively shifting the composition.
- This change allows distillation to yield a higher concentration of ethanol.
Conclusion
Thus, option B, distillation in an all-nitrogen environment, is the method that would NOT facilitate further purification of ethanol from the azeotropic mixture.
Azeotropes are unique mixtures where the composition of vapor and liquid phases remains constant during distillation. This makes separating the components challenging.
Why Option B is Incorrect
In the context of separating ethanol from a 95% ethanol and 5% water azeotrope:
Distillation in an All-Nitrogen Environment
- Conducting distillation in an all-nitrogen environment does not alter the vapor-liquid equilibrium of the azeotropic mixture.
- Nitrogen does not interact or react with either ethanol or water, so it cannot change the boiling point or vapor composition.
- As a result, the same azeotropic composition will still be achieved, preventing further purification of ethanol.
Methods That Allow Purification
A) Dissolution of a Salt
- Adding potassium acetate can break the azeotropic behavior by changing the interactions in the solution.
- This affects the boiling points and allows for separation via distillation.
C) Addition of Cyclohexane
- Introducing cyclohexane can create a new ternary azeotrope, which can subsequently be distilled to separate ethanol from water.
D) Addition of Calcium Oxide
- Calcium oxide can absorb water from the mixture, effectively shifting the composition.
- This change allows distillation to yield a higher concentration of ethanol.
Conclusion
Thus, option B, distillation in an all-nitrogen environment, is the method that would NOT facilitate further purification of ethanol from the azeotropic mixture.
A tetrapeptide Tuffsin has the following amino acid sequence: Thr-Lys-Pro-Arg. Tuftsin binds to specific receptors on the surface of macrophages stimulating their migration and phagocytic activity. Proteins can be separated electrophoretically on the basis of net charge by isoelectric focusing in a pH gradient. At pH = 6, what is the overall charge of the tetrapeptide and the direction of travel in the gel?- a)overall charge of -1 that travels to the anode
- b)overall charge of +2 that travels to the cathode
- c)overall charge of +1 that travels to the cathode
- d)overall charge of +3 that travels to the anode
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A tetrapeptide Tuffsin has the following amino acid sequence: Thr-Lys-Pro-Arg. Tuftsin binds to specific receptors on the surface of macrophages stimulating their migration and phagocytic activity. Proteins can be separated electrophoretically on the basis of net charge by isoelectric focusing in a pH gradient. At pH = 6, what is the overall charge of the tetrapeptide and the direction of travel in the gel?
a)
overall charge of -1 that travels to the anode
b)
overall charge of +2 that travels to the cathode
c)
overall charge of +1 that travels to the cathode
d)
overall charge of +3 that travels to the anode
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The tetrapeptide has two basic amino acids: lysine and arginine. The other two, proline and threonine, do not have R groups to consider.
Lysine and arginine have two amine groups with pKa’s around 10 and above. Arginine has an exceptionally high pKα of 12.48 due to the resonance of the guadinium.
Threonine starts the sequence, so there is a terminal amino group to consider. Generally, amino groups have pKa's from about below 9 to above 10, so basically 9-10.
Arginine ends the sequence, so we have to consider its terminal carboxy group. Generally, carboxy groups have pK
a
’s of under 2 to 3, so 2-3.At pH = 6, only the carboxy group has relinquished its proton to form the carboxylate ion and will bear a negative charge of -1. The 3 amino groups will all still be protonated and bear a positive charge of +1. The net total charge is +3 plus -1 for +2.
Now to consider how it travels on the gel electrophoresis. It is clearly positively charged, since pH < pI definitely, the tetrapeptide travels to the cathode.
What solvent would be most effective at purifying through recrystallization a quantity of sugar contaminated with some table salt?- a)Benzene
- b)Petroleum ether
- c)Water
- d)Ethanol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What solvent would be most effective at purifying through recrystallization a quantity of sugar contaminated with some table salt?
a)
Benzene
b)
Petroleum ether
c)
Water
d)
Ethanol
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Like dissolves like. Sugars are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, and salt is an ionic compound.
Water can dissolve both sugar through hydrogen bonding and salt through solvation. Water is not effective in recrystallization for either.
Benzene and petroleum ether are both very non-polar. It would not dissolve salt to any appreciable degree.
Petroleum ether is a mixture of alkanes (pentane, hexane, heptane, etc.) and should not be confused with the ether functional group.
Ethanol would dissolve sugar and allow for its separation from table salt through recrystallization.
500 mL of water and 500 mL of dichloromethane (d = 1.3 g/mL) are added to a mixture containing benzoic acid, cresol, methoxyethane, and N-methylethanamine. Four solutions are available for extraction of the mixture: HCN, HCl, NaOH, and LiHCO3. After the initial wash, the top layer from each extraction was retained and one of the preceding solutions was added. Which of the following statements most accurately describes this procedure?- a)After washing with LiHCO3 and then NaOH, only N-methylethanamine and methoxyethane remain in the separatory funnel.
- b)Methoxyethane will only be extracted upon protonation into a carbocation.
- c)Benzoic acid can be extracted and isolated with either LiHCO3 or NaOH.
- d)Cresol must be extracted first with a strong mineral acid such as HCl.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
500 mL of water and 500 mL of dichloromethane (d = 1.3 g/mL) are added to a mixture containing benzoic acid, cresol, methoxyethane, and N-methylethanamine. Four solutions are available for extraction of the mixture: HCN, HCl, NaOH, and LiHCO3. After the initial wash, the top layer from each extraction was retained and one of the preceding solutions was added. Which of the following statements most accurately describes this procedure?
a)
After washing with LiHCO3 and then NaOH, only N-methylethanamine and methoxyethane remain in the separatory funnel.
b)
Methoxyethane will only be extracted upon protonation into a carbocation.
c)
Benzoic acid can be extracted and isolated with either LiHCO3 or NaOH.
d)
Cresol must be extracted first with a strong mineral acid such as HCl.
|
|
Ella Baker answered |
Explanation:
Benzoic Acid Extraction:
- Benzoic acid can be extracted and isolated with either LiHCO3 or NaOH.
- Both LiHCO3 and NaOH solutions are basic and will ionize the benzoic acid into its conjugate base form, making it soluble in the aqueous layer and allowing for extraction.
Methoxyethane Extraction:
- Methoxyethane will not only be extracted upon protonation into a carbocation.
- Methoxyethane is a neutral compound and will partition between the aqueous and organic layers based on its solubility in each solvent.
Cresol Extraction:
- Cresol does not need to be extracted first with a strong mineral acid such as HCl.
- Cresol is typically more soluble in basic solutions, so it can be extracted using either LiHCO3 or NaOH.
Therefore, the most accurate statement is that benzoic acid can be extracted and isolated with either LiHCO3 or NaOH.
Benzoic Acid Extraction:
- Benzoic acid can be extracted and isolated with either LiHCO3 or NaOH.
- Both LiHCO3 and NaOH solutions are basic and will ionize the benzoic acid into its conjugate base form, making it soluble in the aqueous layer and allowing for extraction.
Methoxyethane Extraction:
- Methoxyethane will not only be extracted upon protonation into a carbocation.
- Methoxyethane is a neutral compound and will partition between the aqueous and organic layers based on its solubility in each solvent.
Cresol Extraction:
- Cresol does not need to be extracted first with a strong mineral acid such as HCl.
- Cresol is typically more soluble in basic solutions, so it can be extracted using either LiHCO3 or NaOH.
Therefore, the most accurate statement is that benzoic acid can be extracted and isolated with either LiHCO3 or NaOH.
On which of the following physical properties does the separation of the constituents of a mixture by column chromatography depend?- a)Boiling points
- b)Indices of refraction
- c)Differential adsorption
- d)Molecular weight
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
On which of the following physical properties does the separation of the constituents of a mixture by column chromatography depend?
a)
Boiling points
b)
Indices of refraction
c)
Differential adsorption
d)
Molecular weight
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Column chromatography is based around the choice of the adsorbent, whether it be polar or non-polar. Ion-exchange, affinity, and size-exclusion are some of the additional uses of column chromatography that takes advantage of a solute’s charge, ability to bind antibodies and to navigate through small porous beads.
Gas chromatography can be used to separate a mixture by boiling points.
Size-exclusion chromatography can be used to separate a mixture by molecular weight, but size, of course, foremost.
Column chromatography separates mostly by differential adsorption or how well a solute adheres to the adsorbent in the column.
Which of the following statements most accurately describes thin-layer chromatography?- a)The mobile phase is the solvent, also called the eluent, and moves by gravity through the column.
- b)The stationary phase consists of a solid non-polar adsorbent, usually silica or alumina gel.
- c)A solvent with a greater eluting power than petroleum ether is acetic acid.
- d)Rf start text, end text, start subscript, f, end subscript is constant only if the temperature and solvent system is also unchanged.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements most accurately describes thin-layer chromatography?
a)
The mobile phase is the solvent, also called the eluent, and moves by gravity through the column.
b)
The stationary phase consists of a solid non-polar adsorbent, usually silica or alumina gel.
c)
A solvent with a greater eluting power than petroleum ether is acetic acid.
d)
Rf start text, end text, start subscript, f, end subscript is constant only if the temperature and solvent system is also unchanged.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
In thin-layer chromatography, there is a mobile phase or solvent which can vary in its eluting power. The more polar a solvent, the greater the eluting power. This eluent usually moves by capillary action up the plate, not by gravity.
The stationary phase consists of a solid polar, not non-polar, adsorbent, usually silica or alumina gel.
Rf values are only constant from one experiment to another if all the following conditions are also constant: solvent system, adsorbent, thickness of the adsorbent, amount of material spotted, and temperature
The correct answer is that a solvent with a greater eluting power than petroleum ether is acetic acid. Here is the order of eluting power from least to greatest: petroleum ether (hexane; pentane), cyclohexane, carbon tetrachloride, benzene, dichloromethane, chloroform, ether (anhydrous), ethyl acetate (anhydrous), acetone (anhydrous), ethanol, methanol, water, pyridine, and finally organic acids.
Duloxetine or Cymbalta® (1) is a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) prescribed for major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain. A racemic mixture of Duloxetine (2) is dissolved in a mixture of toluene and methanol to which solution is also added optically active mandelic acid (3). Sodium hydroxide is added to obtain the final product (5). Which of the following statements most accurately describes the role of the various compounds?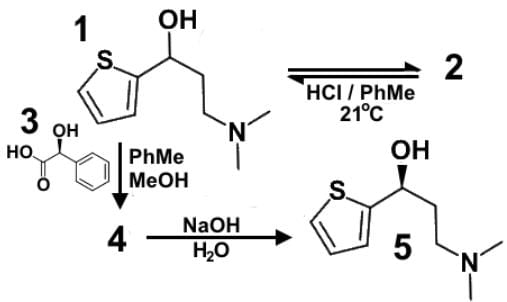
- a)Compound 4 is the (S,S) diastereomeric salt made from the ammonium and mandelate ion and separated by precipitation.
- b)Compound 4 is the protonated form of the alcohol group, protonated at the oxygen.
- c)Compound 5 is R-isomer of Duloxetine and precipitates upon deprotonation with sodium hydroxide.
- d)Compound 3 is (R)-mandelic acid and is considered a chiral resolving agent.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Duloxetine or Cymbalta® (1) is a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) prescribed for major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain. A racemic mixture of Duloxetine (2) is dissolved in a mixture of toluene and methanol to which solution is also added optically active mandelic acid (3). Sodium hydroxide is added to obtain the final product (5). Which of the following statements most accurately describes the role of the various compounds?

a)
Compound 4 is the (S,S) diastereomeric salt made from the ammonium and mandelate ion and separated by precipitation.
b)
Compound 4 is the protonated form of the alcohol group, protonated at the oxygen.
c)
Compound 5 is R-isomer of Duloxetine and precipitates upon deprotonation with sodium hydroxide.
d)
Compound 3 is (R)-mandelic acid and is considered a chiral resolving agent.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Here we have a mechanism for chiral resolution for the drug Duloxetine. Generally, a racemic mixture is resolved into its enantiomer through a chiral resolving agent.
The chiral resolving agent here is mandelic acid without having assigned stereochemistry. The molecule that is shown is (S)-mandelic acid. It will protonate the amine group in the Duloxetine.
Upon protonation, the ammonium ion is formed, and mandelic acid becomes the mandalate ion. There are two diastereomeric salts formed, (R)-Duloxetine-(S)-mandalate and (S)-Duloxetine-(S)-mandalate.
Compound 5 needs to have the stereochemistry assigned, which is (S)-mandelic acid.
Compound 4 is the (S,S) diastereometric salt and can be separated by precipitation, leaving (R)-Duloxetine behind.
Chapter doubts & questions for Separations & Purifications (OC, BC) - MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Separations & Purifications (OC, BC) - MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations
336 videos|223 docs|109 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









