All Exams >
MCAT >
MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations >
All Questions
All questions of Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins (OC, BC) for MCAT Exam
Electrophoretic separation at pH 6 of a sample of polypeptide 1 (mw 100) polypeptide 2 (mw 200) and polypeptide 3 (mw 400) would result in which of the following?
(Note: the isoelectric point of each polypeptide occurs at pH 6)- a)Polypeptide 1 would move the farthest
- b)Polypeptide 2 would move the farthest
- c)Polypeptide 3 would move the farthest
- d)None of the polypeptides would move
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Electrophoretic separation at pH 6 of a sample of polypeptide 1 (mw 100) polypeptide 2 (mw 200) and polypeptide 3 (mw 400) would result in which of the following?
(Note: the isoelectric point of each polypeptide occurs at pH 6)
(Note: the isoelectric point of each polypeptide occurs at pH 6)
a)
Polypeptide 1 would move the farthest
b)
Polypeptide 2 would move the farthest
c)
Polypeptide 3 would move the farthest
d)
None of the polypeptides would move
|
|
Natalie Mitchell answered |
- **Explanation:**
- **Isoelectric Point (pI):** The isoelectric point (pI) is the pH at which a molecule carries no net electrical charge. At this pH, the molecule will not migrate in an electric field during electrophoresis. For polypeptides, the pI is typically around the average of the pKa values of its constituent amino acids.
- **Electrophoretic Separation:** In electrophoretic separation, molecules migrate towards the electrode of opposite charge based on their net charge. At a pH above the pI of a molecule, it will carry a net negative charge and migrate towards the positive electrode. At a pH below the pI, it will carry a net positive charge and migrate towards the negative electrode.
- **Given Scenario:** In this scenario, the electrophoretic separation is carried out at pH 6, which is the isoelectric point for all three polypeptides (pI = 6). At pH 6, all three polypeptides will have no net charge and will not migrate in the electric field.
- **Conclusion:** Therefore, none of the polypeptides (Polypeptide 1, Polypeptide 2, and Polypeptide 3) would move during electrophoretic separation at pH 6. This is because their charges are balanced at pH 6, resulting in no net migration in the electric field.
- **Answer:** Option D - None of the polypeptides would move
- **Isoelectric Point (pI):** The isoelectric point (pI) is the pH at which a molecule carries no net electrical charge. At this pH, the molecule will not migrate in an electric field during electrophoresis. For polypeptides, the pI is typically around the average of the pKa values of its constituent amino acids.
- **Electrophoretic Separation:** In electrophoretic separation, molecules migrate towards the electrode of opposite charge based on their net charge. At a pH above the pI of a molecule, it will carry a net negative charge and migrate towards the positive electrode. At a pH below the pI, it will carry a net positive charge and migrate towards the negative electrode.
- **Given Scenario:** In this scenario, the electrophoretic separation is carried out at pH 6, which is the isoelectric point for all three polypeptides (pI = 6). At pH 6, all three polypeptides will have no net charge and will not migrate in the electric field.
- **Conclusion:** Therefore, none of the polypeptides (Polypeptide 1, Polypeptide 2, and Polypeptide 3) would move during electrophoretic separation at pH 6. This is because their charges are balanced at pH 6, resulting in no net migration in the electric field.
- **Answer:** Option D - None of the polypeptides would move
The amino acids in hemoglobin (or any protein) uniformly have which of the following configurations?- a)L
- b)R
- c)S
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The amino acids in hemoglobin (or any protein) uniformly have which of the following configurations?
a)
L
b)
R
c)
S
d)
D
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Configurations (either relative or absolute) in amino acids refers to the stereochemical configuration around the chiral carbon.
- Due to differences in the priority of different amino acid side chains, not all amino acids have the same "Absolute Configuration", which refers the R/S naming convention. Some amino acids are R, and some are S.
- However, all amino acids have the same "Relative Configuration", which refers to the D/L naming convention. All biologically produced amino acids are in the L configuration.
Electrophoretic separation of leucine from a protein sample would be least effective at which of the following pH values?- a)7.4
- b)2.4
- c)1.4
- d)0.4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Electrophoretic separation of leucine from a protein sample would be least effective at which of the following pH values?
a)
7.4
b)
2.4
c)
1.4
d)
0.4

|
Orion Classes answered |
- Leucine has an aliphatic side chain.
- At physiological pH, leucine exists as a zwitterion.
- Electrophoretic separation of leucine from a protein sample would be least effective at pH 7.4.
An amino acid that yields acetoacetyl CoA during the catabolism of its carbon skeleton will be considered as ________.- a)Glycogenic
- b)Ketogenic
- c)Both glycogenic and ketogenic
- d)Essential
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An amino acid that yields acetoacetyl CoA during the catabolism of its carbon skeleton will be considered as ________.
a)
Glycogenic
b)
Ketogenic
c)
Both glycogenic and ketogenic
d)
Essential

|
Orion Classes answered |
In case of Glycogenic amino acids pyruvate metabolites are formed and in case of ketogenic amino acids acetoacyl CoA is formed during the catabolism.
If pK1 = 2.34 and pK2 = 9.60, then the isoelectric point pI is?- a)5.87
- b)5.97
- c)3.67
- d)11.94
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If pK1 = 2.34 and pK2 = 9.60, then the isoelectric point pI is?
a)
5.87
b)
5.97
c)
3.67
d)
11.94

|
Orion Classes answered |
pI = 1⁄2 (pK1 + pK2) = 1⁄2 (2.34 + 9.60) = 5.97.
All hydrophobic amino acids (valine, leucine, isoleucine, etc.) share which of the following properties?- a)Nonpolar uncharged R groups
- b)Polar uncharged R groups
- c)Basic R groups
- d)Acidic R groups
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
All hydrophobic amino acids (valine, leucine, isoleucine, etc.) share which of the following properties?
a)
Nonpolar uncharged R groups
b)
Polar uncharged R groups
c)
Basic R groups
d)
Acidic R groups
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Hydrophobic amino acids prefer to minimize their interactions with water molecules.
- Polar, acidic, and basic R groups all share partial or full charges, which interact favorably with polar water molecules.
- All hydrophobic amino acids share nonpolar uncharged R groups.
Which of the following amino acids has a net negative charge at physiologic pH (~7.4)?- a)Glutamic Acid
- b)Histidine
- c)Lysine
- d)Asparagine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following amino acids has a net negative charge at physiologic pH (~7.4)?
a)
Glutamic Acid
b)
Histidine
c)
Lysine
d)
Asparagine
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Amino acids with acidic side groups carry a net negative charge at physiologic pH.
- Glutamate (glutamic acid) has a side group containing a carboxylic acid.
- Glutamate has a net negative charge at physiologic pH.
Identify the amino acids containing nonpolar, aliphatic R groups.- a)Phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan
- b)Glycine, alanine, leucine
- c)Lysine, arginine, histidine
- d)Serine, threonine, cysteine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the amino acids containing nonpolar, aliphatic R groups.
a)
Phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan
b)
Glycine, alanine, leucine
c)
Lysine, arginine, histidine
d)
Serine, threonine, cysteine
|
|
Ava Brown answered |
Understanding Nonpolar, Aliphatic Amino Acids
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, and their properties are determined by their R groups (side chains). Nonpolar, aliphatic amino acids have hydrophobic side chains that do not interact favorably with water.
Identifying Nonpolar, Aliphatic Amino Acids
The correct answer to the question is option 'B', which includes the following amino acids:
Why Options A, C, and D Are Incorrect
Conclusion
In summary, the amino acids listed in option 'B' are characterized by their nonpolar, aliphatic side chains, distinguishing them from the other options that include polar or aromatic amino acids. Understanding these classifications is essential for grasping protein structure and function in biochemistry.
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, and their properties are determined by their R groups (side chains). Nonpolar, aliphatic amino acids have hydrophobic side chains that do not interact favorably with water.
Identifying Nonpolar, Aliphatic Amino Acids
The correct answer to the question is option 'B', which includes the following amino acids:
- Glycine - The simplest amino acid with a hydrogen as its side chain, making it nonpolar.
- Alanine - Contains a methyl group as its R group, also classified as nonpolar.
- Leucine - Has a branched-chain structure, contributing to its nonpolar nature.
Why Options A, C, and D Are Incorrect
- Option A (Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan) - Contains aromatic rings, making them more polar than purely aliphatic amino acids.
- Option C (Lysine, Arginine, Histidine) - These are polar and positively charged amino acids due to their side chains containing nitrogen.
- Option D (Serine, Threonine, Cysteine) - These amino acids contain hydroxyl or thiol groups, which are polar and can form hydrogen bonds.
Conclusion
In summary, the amino acids listed in option 'B' are characterized by their nonpolar, aliphatic side chains, distinguishing them from the other options that include polar or aromatic amino acids. Understanding these classifications is essential for grasping protein structure and function in biochemistry.
Which among the following is both glucogenic and ketogenic?- a)Isoleucine
- b)Leucine
- c)Lysine
- d)Histidine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is both glucogenic and ketogenic?
a)
Isoleucine
b)
Leucine
c)
Lysine
d)
Histidine

|
Orion Classes answered |
Isoleucine produces both glucose and ketone bodies as an energy source.
The unique cyclic structure of which of the following amino acids plays a central role in the formation of alpha helices and beta sheets?- a)Proline
- b)Arginine
- c)Valine
- d)Lysine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The unique cyclic structure of which of the following amino acids plays a central role in the formation of alpha helices and beta sheets?
a)
Proline
b)
Arginine
c)
Valine
d)
Lysine
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Alpha helices and beta sheets are two three dimensional motifs that regularly appear in local segments of amino acids.
- Proline has a unique cyclic structure which differentiates it from the other common amino acids.
- Proline plays a central role in the FORMATION of alpha helices and beta sheets. While proline's unique structure may also disrupt both alpha helixes and beta sheets, it's ability to make sharp turns facilitates the FORMATION of both structures, with proline commonly being found at the beginning of alpha helices or at the turns in beta sheets.
The two amino acids having R groups with a negative net charge at pH 7.0 are __________.- a)Aspartate and glutamate
- b)Arginine and histidine
- c)Cysteine and methionine
- d)Proline and valine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The two amino acids having R groups with a negative net charge at pH 7.0 are __________.
a)
Aspartate and glutamate
b)
Arginine and histidine
c)
Cysteine and methionine
d)
Proline and valine
|
|
Benjamin White answered |
Aspartate and Glutamate
Aspartate and glutamate are the two amino acids with R groups that have a negative net charge at pH 7.0. This charge is due to the presence of carboxyl groups in their side chains that can ionize and become negatively charged at neutral pH.
Aspartate
- Aspartate, also known as aspartic acid, has a side chain with a carboxyl group that can ionize to form a negatively charged carboxylate ion at pH 7.0. This gives aspartate a net negative charge at neutral pH.
Glutamate
- Glutamate, also known as glutamic acid, has a side chain that contains a carboxyl group similar to aspartate. This carboxyl group can also ionize to form a negatively charged carboxylate ion at pH 7.0, resulting in a negative net charge for glutamate at neutral pH.
Therefore, at pH 7.0, both aspartate and glutamate have R groups with a negative net charge, making them the two amino acids with this characteristic.
Aspartate and glutamate are the two amino acids with R groups that have a negative net charge at pH 7.0. This charge is due to the presence of carboxyl groups in their side chains that can ionize and become negatively charged at neutral pH.
Aspartate
- Aspartate, also known as aspartic acid, has a side chain with a carboxyl group that can ionize to form a negatively charged carboxylate ion at pH 7.0. This gives aspartate a net negative charge at neutral pH.
Glutamate
- Glutamate, also known as glutamic acid, has a side chain that contains a carboxyl group similar to aspartate. This carboxyl group can also ionize to form a negatively charged carboxylate ion at pH 7.0, resulting in a negative net charge for glutamate at neutral pH.
Therefore, at pH 7.0, both aspartate and glutamate have R groups with a negative net charge, making them the two amino acids with this characteristic.
Which of the following is a true statement?- a)Tryptophan and tyrosine are significantly more polar than phenylalanine
- b)Leucine is commonly used as an ingredient in the buffers of SDS page
- c)Aspartate is an essential amino acid
- d)Lysine is a non-essential amino acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a true statement?
a)
Tryptophan and tyrosine are significantly more polar than phenylalanine
b)
Leucine is commonly used as an ingredient in the buffers of SDS page
c)
Aspartate is an essential amino acid
d)
Lysine is a non-essential amino acid
|
|
Elizabeth Lee answered |
Explanation:
Tryptophan and tyrosine are significantly more polar than phenylalanine:
- Tryptophan and tyrosine contain polar functional groups such as hydroxyl and amino groups, making them more polar compared to phenylalanine which lacks such groups.
- The presence of polar groups in tryptophan and tyrosine allows for interactions with water molecules, leading to their higher polarity.
This statement is true because tryptophan and tyrosine have more polar side chains compared to phenylalanine, which is a nonpolar amino acid. The polarity of an amino acid side chain is determined by the presence of polar functional groups such as hydroxyl (-OH) and amino (-NH2) groups. Tryptophan and tyrosine both contain these polar functional groups in their side chains, making them significantly more polar than phenylalanine, which lacks such groups. This increased polarity allows tryptophan and tyrosine to interact more readily with water molecules and other polar substances, influencing their behavior in biological systems.
Tryptophan and tyrosine are significantly more polar than phenylalanine:
- Tryptophan and tyrosine contain polar functional groups such as hydroxyl and amino groups, making them more polar compared to phenylalanine which lacks such groups.
- The presence of polar groups in tryptophan and tyrosine allows for interactions with water molecules, leading to their higher polarity.
This statement is true because tryptophan and tyrosine have more polar side chains compared to phenylalanine, which is a nonpolar amino acid. The polarity of an amino acid side chain is determined by the presence of polar functional groups such as hydroxyl (-OH) and amino (-NH2) groups. Tryptophan and tyrosine both contain these polar functional groups in their side chains, making them significantly more polar than phenylalanine, which lacks such groups. This increased polarity allows tryptophan and tyrosine to interact more readily with water molecules and other polar substances, influencing their behavior in biological systems.
Hydrogen bonding between separate subunits of DNA polymerase is an example of which of the following?- a)1 degree structure
- b)2 degree structure
- c)3 degree structure
- d)4 degree structure
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen bonding between separate subunits of DNA polymerase is an example of which of the following?
a)
1 degree structure
b)
2 degree structure
c)
3 degree structure
d)
4 degree structure
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- 1 degree structure through 3 degree structure have to do with individual polypeptides.
- 4 degree structure refers to the global three dimensional arrangements found in multi-subunit proteins.
- Hydrogen bonding between separate subunits of DNA polymerase is an example of 4 degree structure.
A polypeptide with a net positive charge at physiologic pH (~7.4) most likely contains amino acids with R groups of what type?- a)Acidic R groups
- b)Aromatic R groups
- c)Aliphatic R groups
- d)Basic R groups
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A polypeptide with a net positive charge at physiologic pH (~7.4) most likely contains amino acids with R groups of what type?
a)
Acidic R groups
b)
Aromatic R groups
c)
Aliphatic R groups
d)
Basic R groups
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- At physiologic pH, basic functional groups will be protonated, attaining a positive charge.
- Aliphatic R groups are saturated hydrocarbons.
- A polypeptide with a net positive charge at physiologic pH most likely has a basic R group.
Which of the following properties of a protein is least likely to be affected by changes in pH?- a)Tertiary structure
- b)Primary structure
- c)Secondary structure
- d)Net charge
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following properties of a protein is least likely to be affected by changes in pH?
a)
Tertiary structure
b)
Primary structure
c)
Secondary structure
d)
Net charge
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Primary structure is the amino acid sequence of a protein plus the peptide bonds joining them together.
- Change in pH are unlikely to alter amino acid sequence or break peptide bonds.
- The primary structure of a protein is least likely to be affected by changes in pH.
Which of the following is an essential amino acid?- a)Cysteine
- b)Asparagine
- c)Glutamine
- d)Phenylalanine
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an essential amino acid?
a)
Cysteine
b)
Asparagine
c)
Glutamine
d)
Phenylalanine

|
Orion Classes answered |
Phenylalanine is one of the 9 essential amino acids.
Which is not a true statement?- a)
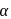 -carbon of
-carbon of 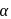 -amino acid is asymmetric
-amino acid is asymmetric - b)All proteins are found in
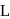 -form
-form - c)Human body can synthesize all proteins they need
- d)At pH
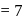 both amino acids and carboxylic groups exist in the ionised form
both amino acids and carboxylic groups exist in the ionised form
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is not a true statement?
a)
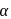 -carbon of
-carbon of 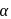 -amino acid is asymmetric
-amino acid is asymmetricb)
All proteins are found in 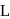 -form
-form
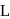 -form
-formc)
Human body can synthesize all proteins they need
d)
At pH 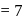 both amino acids and carboxylic groups exist in the ionised form
both amino acids and carboxylic groups exist in the ionised form
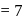 both amino acids and carboxylic groups exist in the ionised form
both amino acids and carboxylic groups exist in the ionised form

|
Tarun Kaushik answered |
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amine  and carboxyl (-COOH) functional groups, along with a side chain (R group) specific to each amino acid. a -carbon of cc-amino acid is asymmetric. Hence this statement is true. Proteins exist in both D and L-form. So, option (2) is an incorrect statement. The body synthesizes all of its own proteins. The proteins that you obtain through your food are broken down in the digestive system into individual amino acids, which enter the blood stream in the small intestine. From there, they are transported by the blood stream into cells, where they are reassembled into new proteins with the help of ribosomes. This is necessary because proteins are specialized molecules that have to be built in a precise manner in order to perform their function. At
and carboxyl (-COOH) functional groups, along with a side chain (R group) specific to each amino acid. a -carbon of cc-amino acid is asymmetric. Hence this statement is true. Proteins exist in both D and L-form. So, option (2) is an incorrect statement. The body synthesizes all of its own proteins. The proteins that you obtain through your food are broken down in the digestive system into individual amino acids, which enter the blood stream in the small intestine. From there, they are transported by the blood stream into cells, where they are reassembled into new proteins with the help of ribosomes. This is necessary because proteins are specialized molecules that have to be built in a precise manner in order to perform their function. At 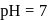 , both amino and carboxylic groups exist in ionised form i.e. zwitter ion.
, both amino and carboxylic groups exist in ionised form i.e. zwitter ion.
 and carboxyl (-COOH) functional groups, along with a side chain (R group) specific to each amino acid. a -carbon of cc-amino acid is asymmetric. Hence this statement is true. Proteins exist in both D and L-form. So, option (2) is an incorrect statement. The body synthesizes all of its own proteins. The proteins that you obtain through your food are broken down in the digestive system into individual amino acids, which enter the blood stream in the small intestine. From there, they are transported by the blood stream into cells, where they are reassembled into new proteins with the help of ribosomes. This is necessary because proteins are specialized molecules that have to be built in a precise manner in order to perform their function. At
and carboxyl (-COOH) functional groups, along with a side chain (R group) specific to each amino acid. a -carbon of cc-amino acid is asymmetric. Hence this statement is true. Proteins exist in both D and L-form. So, option (2) is an incorrect statement. The body synthesizes all of its own proteins. The proteins that you obtain through your food are broken down in the digestive system into individual amino acids, which enter the blood stream in the small intestine. From there, they are transported by the blood stream into cells, where they are reassembled into new proteins with the help of ribosomes. This is necessary because proteins are specialized molecules that have to be built in a precise manner in order to perform their function. At 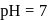 , both amino and carboxylic groups exist in ionised form i.e. zwitter ion.
, both amino and carboxylic groups exist in ionised form i.e. zwitter ion.Which among the following is a non-essential amino acid?- a)Serine
- b)Threonine
- c)Lysine
- d)Histidine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is a non-essential amino acid?
a)
Serine
b)
Threonine
c)
Lysine
d)
Histidine

|
Orion Classes answered |
Serine is one of the 11 non-essential amino acids.
Which of the following is an imino acid?- a)Alanine
- b)Glycine
- c)Proline
- d)Serine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an imino acid?
a)
Alanine
b)
Glycine
c)
Proline
d)
Serine

|
Orion Classes answered |
Proline is secondary amino acid also called as an imino acid as it contains –C = NH – OH group.
The alpha helix is an example of which of the following structural properties of proteins?- a)secondary structure
- b)quaternary structure
- c)primary structure
- d)tertiary structure
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The alpha helix is an example of which of the following structural properties of proteins?
a)
secondary structure
b)
quaternary structure
c)
primary structure
d)
tertiary structure

|
Orion Classes answered |
- Secondary structure refers to the three dimensional arrangement of small segments of amino acids in a polypeptide.
- The alpha helix is three dimensional arrangement of amino acids in a polypeptide, where the chain takes on a telephone-cord-like shape.
- The alpha helix is an example of secondary structure.
N-acetyl-cysteine replenishes: (JIPMER 2012)- a)Glutathione
- b)Glycine
- c)Glutamate
- d)GABA
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Glutathione
b)
Glycine
c)
Glutamate
d)
GABA

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The functional component of both Glutathione and N-Acetyl Cysteine is the sulfhydryl group found in Cysteine. Therefore, N-Acetyl Cysteine serves to replenish Glutathione.
Number of chiral centers in isoleucine is?- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of chiral centers in isoleucine is?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4

|
Orion Classes answered |
H5 C2 – C ̇H(CH3)- C ̇H(NH2) – COOH
The structure clearly shows two chiral centers of isoleucine.
The structure clearly shows two chiral centers of isoleucine.
Chapter doubts & questions for Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins (OC, BC) - MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins (OC, BC) - MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations
336 videos|223 docs|109 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









