All questions of Computer Organisation & Architecture for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam
The difference in the address and data connection between DRAM’s and SDRAM’s is _______- a)The requirement of more address lines in SDRAM’s
- b)The usage of a buffer in SDRAM’s
- c)The usage of more number of pins in SDRAM’s
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The difference in the address and data connection between DRAM’s and SDRAM’s is _______
a)
The requirement of more address lines in SDRAM’s
b)
The usage of a buffer in SDRAM’s
c)
The usage of more number of pins in SDRAM’s
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Maitri Dey answered |
The key difference between the address and data connection in DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory) lies in their respective functionalities.
1. Address Connection:
The address connection in DRAM is responsible for specifying the location of the memory cell that needs to be accessed. It is used to select a specific row and column within the memory array. The address connection receives the address signals from the memory controller or the CPU, which are used to activate the appropriate row and column lines in the memory array.
The address connection is typically a multi-bit bus since it needs to accommodate a large number of memory cells in the DRAM array. The number of address lines determines the maximum amount of memory that can be accessed by the DRAM.
2. Data Connection:
The data connection in DRAM is used for transferring the actual data to be stored or retrieved from the memory cells. It is responsible for carrying the bits of information between the memory cells and the memory controller or the CPU.
The data connection is typically a wider bus compared to the address connection since it needs to transfer a larger amount of data. The width of the data bus determines the number of bits that can be transferred simultaneously, which affects the overall data transfer rate of the DRAM.
In summary, the address connection in DRAM is used to specify the location of the memory cell to be accessed, while the data connection is responsible for transferring the actual data between the memory cells and the memory controller/CPU. The address connection selects the row and column lines, whereas the data connection transfers the bits of information.
1. Address Connection:
The address connection in DRAM is responsible for specifying the location of the memory cell that needs to be accessed. It is used to select a specific row and column within the memory array. The address connection receives the address signals from the memory controller or the CPU, which are used to activate the appropriate row and column lines in the memory array.
The address connection is typically a multi-bit bus since it needs to accommodate a large number of memory cells in the DRAM array. The number of address lines determines the maximum amount of memory that can be accessed by the DRAM.
2. Data Connection:
The data connection in DRAM is used for transferring the actual data to be stored or retrieved from the memory cells. It is responsible for carrying the bits of information between the memory cells and the memory controller or the CPU.
The data connection is typically a wider bus compared to the address connection since it needs to transfer a larger amount of data. The width of the data bus determines the number of bits that can be transferred simultaneously, which affects the overall data transfer rate of the DRAM.
In summary, the address connection in DRAM is used to specify the location of the memory cell to be accessed, while the data connection is responsible for transferring the actual data between the memory cells and the memory controller/CPU. The address connection selects the row and column lines, whereas the data connection transfers the bits of information.
Which of the following statements is/are true?- a)Parallelism is high in horizontal microprogrammed control unit as compared to vertical microprogrammed control unit.
- b)Hardwired control unit is slower compared to microprogrammed control unit.
- c)In 2’s complement sum carry flag and overflow are the same.
- d)In 2’s complement sum if the sum of two negative numbers yields a positive result, the sum has overflowed.
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is/are true?
a)
Parallelism is high in horizontal microprogrammed control unit as compared to vertical microprogrammed control unit.
b)
Hardwired control unit is slower compared to microprogrammed control unit.
c)
In 2’s complement sum carry flag and overflow are the same.
d)
In 2’s complement sum if the sum of two negative numbers yields a positive result, the sum has overflowed.
|
|
Samridhi Ahuja answered |
Explanation of the Statements
The statements provided pertain to computer architecture and binary arithmetic. Let's analyze each statement to understand their validity.
Statement A: Parallelism in Control Units
- True:
- In a horizontal microprogrammed control unit, multiple control signals can be generated simultaneously, allowing for higher parallelism.
- Conversely, vertical microprogrammed control units use fewer bits to represent control signals, leading to more sequential operations and less parallelism.
Statement B: Speed of Control Units
- False:
- Hardwired control units are generally faster than microprogrammed control units.
- This is because hardwired control units use fixed logic circuits, resulting in quicker response times compared to the more flexible but slower microprogrammed approach.
Statement C: Carry Flag and Overflow in 2's Complement
- False:
- In 2's complement arithmetic, the carry flag and overflow flag are not the same.
- The carry flag indicates a carry out of the most significant bit, while the overflow flag indicates that the result of an operation has exceeded the representational capacity of the number format.
Statement D: Overflow in 2's Complement Arithmetic
- True:
- In 2's complement notation, if the sum of two negative numbers results in a positive number, it indicates an overflow.
- This occurs because the representation cannot accommodate the resulting value, leading to an incorrect sign.
Conclusion
The correct answers are indeed options A and D, as they accurately describe the characteristics of parallelism in control units and the behavior of overflow in 2's complement arithmetic.
The statements provided pertain to computer architecture and binary arithmetic. Let's analyze each statement to understand their validity.
Statement A: Parallelism in Control Units
- True:
- In a horizontal microprogrammed control unit, multiple control signals can be generated simultaneously, allowing for higher parallelism.
- Conversely, vertical microprogrammed control units use fewer bits to represent control signals, leading to more sequential operations and less parallelism.
Statement B: Speed of Control Units
- False:
- Hardwired control units are generally faster than microprogrammed control units.
- This is because hardwired control units use fixed logic circuits, resulting in quicker response times compared to the more flexible but slower microprogrammed approach.
Statement C: Carry Flag and Overflow in 2's Complement
- False:
- In 2's complement arithmetic, the carry flag and overflow flag are not the same.
- The carry flag indicates a carry out of the most significant bit, while the overflow flag indicates that the result of an operation has exceeded the representational capacity of the number format.
Statement D: Overflow in 2's Complement Arithmetic
- True:
- In 2's complement notation, if the sum of two negative numbers results in a positive number, it indicates an overflow.
- This occurs because the representation cannot accommodate the resulting value, leading to an incorrect sign.
Conclusion
The correct answers are indeed options A and D, as they accurately describe the characteristics of parallelism in control units and the behavior of overflow in 2's complement arithmetic.
To reduce the memory access time we generally make use of ______- a)SDRAM’s
- b)Heaps
- c)Cache’s
- d)Higher capacity RAM’s
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
To reduce the memory access time we generally make use of ______
a)
SDRAM’s
b)
Heaps
c)
Cache’s
d)
Higher capacity RAM’s
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
The time required to access a part of the memory for data retrieval.
The VLIW architecture follows _____ approach to achieve parallelism.- a)SISD
- b)MIMD
- c)MISD
- d)SIMD
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The VLIW architecture follows _____ approach to achieve parallelism.
a)
SISD
b)
MIMD
c)
MISD
d)
SIMD
|
|
Puja Bajaj answered |
Understanding VLIW Architecture
VLIW, or Very Long Instruction Word, architecture is designed to exploit instruction-level parallelism (ILP) by executing multiple operations simultaneously. This is primarily achieved through a MIMD (Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data) approach.
Key Features of VLIW Architecture
- Instruction Bundling: VLIW compiles multiple independent instructions into a single long instruction word, which the processor can execute in parallel. Each instruction in the bundle can operate on different data streams.
- Static Scheduling: The compiler is responsible for scheduling instructions at compile time, allowing for better optimization of resources. This eliminates the need for complex hardware control logic that dynamically schedules instructions at runtime.
- Parallel Execution: By using MIMD, VLIW can execute different instructions on different data simultaneously, maximizing throughput and efficiency.
Comparison with Other Architectures
- SISD (Single Instruction, Single Data): Processes one instruction at a time, leading to limited parallelism.
- SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data): Executes the same instruction across multiple data points but does not support different instructions executing simultaneously.
- MISD (Multiple Instruction, Single Data): Rarely used in practice, as it involves multiple instructions acting on a single data stream, which is not ideal for most applications.
Conclusion
The VLIW architecture's reliance on MIMD allows it to effectively use parallelism by enabling the simultaneous execution of diverse instructions. This design choice makes VLIW particularly powerful for applications requiring high-performance computing capabilities.
VLIW, or Very Long Instruction Word, architecture is designed to exploit instruction-level parallelism (ILP) by executing multiple operations simultaneously. This is primarily achieved through a MIMD (Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data) approach.
Key Features of VLIW Architecture
- Instruction Bundling: VLIW compiles multiple independent instructions into a single long instruction word, which the processor can execute in parallel. Each instruction in the bundle can operate on different data streams.
- Static Scheduling: The compiler is responsible for scheduling instructions at compile time, allowing for better optimization of resources. This eliminates the need for complex hardware control logic that dynamically schedules instructions at runtime.
- Parallel Execution: By using MIMD, VLIW can execute different instructions on different data simultaneously, maximizing throughput and efficiency.
Comparison with Other Architectures
- SISD (Single Instruction, Single Data): Processes one instruction at a time, leading to limited parallelism.
- SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data): Executes the same instruction across multiple data points but does not support different instructions executing simultaneously.
- MISD (Multiple Instruction, Single Data): Rarely used in practice, as it involves multiple instructions acting on a single data stream, which is not ideal for most applications.
Conclusion
The VLIW architecture's reliance on MIMD allows it to effectively use parallelism by enabling the simultaneous execution of diverse instructions. This design choice makes VLIW particularly powerful for applications requiring high-performance computing capabilities.
The small extremely fast, RAM’s all called as ________
- a)Cache
- b)Accumulators
- c)Stacks
- d)Heaps
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The small extremely fast, RAM’s all called as ________
a)
Cache
b)
Accumulators
c)
Stacks
d)
Heaps
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
Cache’s are extremely essential in single BUS organisation to achieve fast operation.
________ are the different type/s of generating control signals.- a)Hardwired
- b)Micro-instruction
- c)Micro-programmed
- d)Both Micro-programmed and Hardwired
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
________ are the different type/s of generating control signals.
a)
Hardwired
b)
Micro-instruction
c)
Micro-programmed
d)
Both Micro-programmed and Hardwired
|
|
Eesha Bhat answered |
The above is used to generate control signals in different types of system architectures.
The first instructor of bootstrap loader program of an operating system is stored in ____________.- a)RAM
- b)Hard Disk
- c)BIOS
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The first instructor of bootstrap loader program of an operating system is stored in ____________.
a)
RAM
b)
Hard Disk
c)
BIOS
d)
None
|
|
Dipika Chavan answered |
The first instructor of bootstrap loader program of an operating system is stored in BIOS.
The bootstrap loader program, also known as the bootstrap code or boot code, is a small program that is responsible for loading the operating system into the computer's memory and initializing the system. It is the first code that is executed when the computer is powered on or restarted.
Explanation:
The bootstrap loader program is stored in the Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) of the computer. BIOS is a firmware that is embedded on a motherboard and contains the basic instructions and settings required for the computer to start up. It is responsible for the initial hardware initialization and provides low-level functions for the operating system.
When the computer is powered on, the BIOS is the first component that is executed. It performs a power-on self-test (POST) to check the hardware components and then searches for the bootstrap loader program. The BIOS locates the bootstrap loader program in a specific location, typically in a reserved area of the ROM or EEPROM chip on the motherboard.
Once the bootstrap loader program is located, the BIOS transfers control to it. The bootstrap loader program then takes over and loads the operating system into the computer's memory from a storage device, such as a hard disk or a USB drive. It performs various initialization tasks, sets up the system environment, and prepares the computer for the execution of the operating system.
Since the bootstrap loader program is stored in the BIOS, it is not affected by changes or modifications in the storage devices or operating systems. This allows the computer to start up and load the operating system even if the storage devices are replaced or upgraded.
In conclusion, the first instructor of the bootstrap loader program of an operating system is stored in the BIOS. The BIOS plays a crucial role in the boot process by locating and executing the bootstrap loader program, which then loads the operating system into the computer's memory.
The bootstrap loader program, also known as the bootstrap code or boot code, is a small program that is responsible for loading the operating system into the computer's memory and initializing the system. It is the first code that is executed when the computer is powered on or restarted.
Explanation:
The bootstrap loader program is stored in the Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) of the computer. BIOS is a firmware that is embedded on a motherboard and contains the basic instructions and settings required for the computer to start up. It is responsible for the initial hardware initialization and provides low-level functions for the operating system.
When the computer is powered on, the BIOS is the first component that is executed. It performs a power-on self-test (POST) to check the hardware components and then searches for the bootstrap loader program. The BIOS locates the bootstrap loader program in a specific location, typically in a reserved area of the ROM or EEPROM chip on the motherboard.
Once the bootstrap loader program is located, the BIOS transfers control to it. The bootstrap loader program then takes over and loads the operating system into the computer's memory from a storage device, such as a hard disk or a USB drive. It performs various initialization tasks, sets up the system environment, and prepares the computer for the execution of the operating system.
Since the bootstrap loader program is stored in the BIOS, it is not affected by changes or modifications in the storage devices or operating systems. This allows the computer to start up and load the operating system even if the storage devices are replaced or upgraded.
In conclusion, the first instructor of the bootstrap loader program of an operating system is stored in the BIOS. The BIOS plays a crucial role in the boot process by locating and executing the bootstrap loader program, which then loads the operating system into the computer's memory.
Which of the following architecture is suitable for a wide range of data types?- a)IA-32
- b)ARM
- c)ASUS firebird
- d)68000
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following architecture is suitable for a wide range of data types?
a)
IA-32
b)
ARM
c)
ASUS firebird
d)
68000
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
IA-32 architecture is suitable for a wide range of data types.
A processor has 300 distinct instructions and 70 general-purpose registers. A 32-bit instruction word has an opcode, two register operands, and an immediate operand. The number of bits available for the immediate operand field is_____
Correct answer is '9'. Can you explain this answer?
A processor has 300 distinct instructions and 70 general-purpose registers. A 32-bit instruction word has an opcode, two register operands, and an immediate operand. The number of bits available for the immediate operand field is_____
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
Concept:
The given data,
Distinct instructions= 300
General-purpose registers = 70
opcode instruction word = 32-bit
Two register operands and an immediate operand.
Each instruction has 32 bits. To support 300 instructions, the opcode must contain 9-bits.
Register operand1 requires 7 bits, since the total registers are 70, Register operand 2 also requires 7 bits.
So, 32 - (9+7+7) = 9 bits are left over for immediate operand.
Hence the correct answer is 9.
Consider the following table:
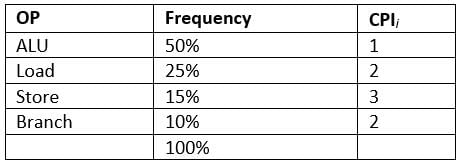
Which of the following is true about the average CPI of the above given table?- a)ALU takes ~27.27% of the total cycles.
- b)Load takes ~27.27% of the total cycles.
- c)Store takes ~27.27% of the total cycles.
- d)Branch takes ~10.10% of the total cycles.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following table:

Which of the following is true about the average CPI of the above given table?

Which of the following is true about the average CPI of the above given table?
a)
ALU takes ~27.27% of the total cycles.
b)
Load takes ~27.27% of the total cycles.
c)
Store takes ~27.27% of the total cycles.
d)
Branch takes ~10.10% of the total cycles.

|
Riverdale Learning Institute answered |
CPI: Cycles per instruction or clock per instruction is used as a measure of processors' performance, that is, number of CPU cycles required to execute and instruction at low level. One instruction consists of ALU, Load, Store and Branch.
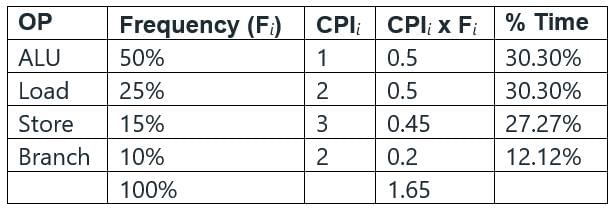

- ALU takes ~30.30% of the total cycles.
- Load takes ~30.30% of the total cycles.
- Store takes ~27.27% of total cycles.
- Branch takes ~12.12% of total cycles.
Which of the following is NOT one of the types of buses?- a)Control bus
- b)Data bus
- c)Address bus
- d)Utility bus
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT one of the types of buses?
a)
Control bus
b)
Data bus
c)
Address bus
d)
Utility bus
|
|
Niti Basu answered |
Types of Buses in a Computer System
The buses in a computer system facilitate the communication between different components such as the CPU, memory, and peripherals. They are essential for the transfer of data, addresses, and control signals within the system.
Control Bus
- The control bus is responsible for transmitting control signals between the CPU and other components.
- These signals include commands to read from or write to memory, signals to initiate input/output operations, and interrupt signals.
Data Bus
- The data bus is used for transferring data between the CPU, memory, and I/O devices.
- It carries the actual data being processed by the system.
Address Bus
- The address bus is used to specify a physical address in memory or an I/O device.
- It allows the CPU to communicate with specific locations in memory or peripherals.
Utility Bus
- The term "utility bus" is not commonly used in the context of computer architecture or buses.
- There is no standard definition or functionality associated with a utility bus in computer systems.
In conclusion, the control bus, data bus, and address bus are fundamental types of buses in a computer system, whereas the utility bus is not a recognized type of bus in the typical architecture of computers.
The controller multiplexes the addresses after getting the _____ signal.- a)INTR
- b)ACK
- c)RESET
- d)Request
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The controller multiplexes the addresses after getting the _____ signal.
a)
INTR
b)
ACK
c)
RESET
d)
Request
|
|
Eesha Bhat answered |
The controller gets the request from the device needing the memory read or write operation and then it multiplexes the address.
The small extremely fast, RAM’s all called as ________- a)Heaps
- b)Accumulators
- c)Stacks
- d)Cache
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The small extremely fast, RAM’s all called as ________
a)
Heaps
b)
Accumulators
c)
Stacks
d)
Cache
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
Cache’s are extremely essential in single BUS organisation to achieve fast operation.
A stack-based CPU organization uses_______ address instructions- a)2
- b)0
- c)1
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A stack-based CPU organization uses_______ address instructions
a)
2
b)
0
c)
1
d)
3
|
|
Shilpa Joshi answered |
In a stack-based CPU organization, the CPU primarily relies on a stack for storing and accessing data. In this type of organization, the stack is used as the primary data structure for storing and retrieving operands and results during the execution of instructions.
Addressing Modes in CPU Organization:
When it comes to addressing modes, there are different ways in which instructions can specify the location of data operands. Some common addressing modes include immediate addressing, direct addressing, indirect addressing, and register addressing.
Immediate addressing mode is used when the operand value is directly specified in the instruction itself. Direct addressing mode is used when the operand value is stored at a specific memory location. Indirect addressing mode is used when the instruction specifies a memory address where the actual operand value is stored. Register addressing mode is used when the operand value is stored in a specific register.
Address Instructions in Stack-Based CPU Organization:
In a stack-based CPU organization, the stack is used as the primary data structure for storing and accessing operands. This means that the instructions in a stack-based CPU organization do not explicitly specify memory addresses or registers for operand retrieval. Instead, the operands are implicitly accessed from the top of the stack.
Since the stack is used for operand storage, the instructions in a stack-based CPU organization typically do not contain address fields. Therefore, the answer to the given question is option 'B' (0 address instructions).
Explanation:
0 address instructions mean that the instructions do not contain any address fields. Instead, the operands are implicitly accessed from the top of the stack. This is because the stack is the primary data structure in a stack-based CPU organization, and the operands are pushed onto the stack before an operation and popped from the stack after the operation.
In a stack-based CPU organization, the instructions only need to specify the operation to be performed (such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.), and the CPU automatically accesses the operands from the top of the stack.
This type of organization simplifies the instruction format and eliminates the need for explicit address fields in the instructions. It also allows for a more compact instruction set and reduces the complexity of the CPU architecture.
Overall, in a stack-based CPU organization, 0 address instructions are used because the operands are implicitly accessed from the top of the stack, eliminating the need for explicit address fields in the instructions.
Addressing Modes in CPU Organization:
When it comes to addressing modes, there are different ways in which instructions can specify the location of data operands. Some common addressing modes include immediate addressing, direct addressing, indirect addressing, and register addressing.
Immediate addressing mode is used when the operand value is directly specified in the instruction itself. Direct addressing mode is used when the operand value is stored at a specific memory location. Indirect addressing mode is used when the instruction specifies a memory address where the actual operand value is stored. Register addressing mode is used when the operand value is stored in a specific register.
Address Instructions in Stack-Based CPU Organization:
In a stack-based CPU organization, the stack is used as the primary data structure for storing and accessing operands. This means that the instructions in a stack-based CPU organization do not explicitly specify memory addresses or registers for operand retrieval. Instead, the operands are implicitly accessed from the top of the stack.
Since the stack is used for operand storage, the instructions in a stack-based CPU organization typically do not contain address fields. Therefore, the answer to the given question is option 'B' (0 address instructions).
Explanation:
0 address instructions mean that the instructions do not contain any address fields. Instead, the operands are implicitly accessed from the top of the stack. This is because the stack is the primary data structure in a stack-based CPU organization, and the operands are pushed onto the stack before an operation and popped from the stack after the operation.
In a stack-based CPU organization, the instructions only need to specify the operation to be performed (such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.), and the CPU automatically accesses the operands from the top of the stack.
This type of organization simplifies the instruction format and eliminates the need for explicit address fields in the instructions. It also allows for a more compact instruction set and reduces the complexity of the CPU architecture.
Overall, in a stack-based CPU organization, 0 address instructions are used because the operands are implicitly accessed from the top of the stack, eliminating the need for explicit address fields in the instructions.
The reason for the cells to lose their state over time is ________- a)Use of Shift registers
- b)The lower voltage levels
- c)Usage of capacitors to store the charge
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The reason for the cells to lose their state over time is ________
a)
Use of Shift registers
b)
The lower voltage levels
c)
Usage of capacitors to store the charge
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
Since capacitors are used the charge dissipates over time.
What is the full form of ISA?- a)Industry Standard Architecture
- b)International Standard Architecture
- c)International American Standard
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the full form of ISA?
a)
Industry Standard Architecture
b)
International Standard Architecture
c)
International American Standard
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
The ISA is an architectural standard developed by IBM for its PC’s.
In CISC architecture most of the complex instructions are stored in _____- a)CMOS
- b)Register
- c)Transistors
- d)Diodes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In CISC architecture most of the complex instructions are stored in _____
a)
CMOS
b)
Register
c)
Transistors
d)
Diodes
|
|
Anoushka Dey answered |
Introduction:
In CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer) architecture, the processor is designed to execute a wide range of complex instructions. These instructions are stored in various components of the system. Among these components, the complex instructions are primarily stored in transistors.
Explanation:
In CISC architecture, the focus is on providing a rich set of instructions that can perform complex operations. These instructions are designed to be executed directly by the processor. To store these complex instructions, transistors are used.
Transistors:
Transistors are semiconductor devices that can amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. They are the fundamental building blocks of modern electronic devices and integrated circuits (ICs). In CISC architecture, transistors are used to store complex instructions in the form of logic gates. These logic gates are combined to form the desired instruction set.
CMOS:
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) is a technology used to implement transistors. It is a type of semiconductor technology that uses both p-type and n-type MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) to create logic gates and memory cells. While CMOS technology is used in the implementation of transistors, it is not directly responsible for storing complex instructions in CISC architecture.
Register:
Registers are high-speed storage locations within the processor that are used to hold data and instructions temporarily. They are used to store intermediate results during the execution of instructions. While registers play a crucial role in the execution of complex instructions, they are not the primary storage location for these instructions in CISC architecture.
Diodes:
Diodes are electronic components that allow current to flow in only one direction. They are used in various applications such as rectification, signal modulation, and switching. However, in CISC architecture, diodes are not primarily used to store complex instructions.
Conclusion:
In CISC architecture, the complex instructions are primarily stored in transistors. Transistors, implemented using CMOS technology, form the logic gates that store and execute these instructions. While registers play a crucial role in the execution of these instructions, they are not the primary storage location. Diodes, on the other hand, are not directly involved in the storage of complex instructions in CISC architecture.
In CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer) architecture, the processor is designed to execute a wide range of complex instructions. These instructions are stored in various components of the system. Among these components, the complex instructions are primarily stored in transistors.
Explanation:
In CISC architecture, the focus is on providing a rich set of instructions that can perform complex operations. These instructions are designed to be executed directly by the processor. To store these complex instructions, transistors are used.
Transistors:
Transistors are semiconductor devices that can amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. They are the fundamental building blocks of modern electronic devices and integrated circuits (ICs). In CISC architecture, transistors are used to store complex instructions in the form of logic gates. These logic gates are combined to form the desired instruction set.
CMOS:
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) is a technology used to implement transistors. It is a type of semiconductor technology that uses both p-type and n-type MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) to create logic gates and memory cells. While CMOS technology is used in the implementation of transistors, it is not directly responsible for storing complex instructions in CISC architecture.
Register:
Registers are high-speed storage locations within the processor that are used to hold data and instructions temporarily. They are used to store intermediate results during the execution of instructions. While registers play a crucial role in the execution of complex instructions, they are not the primary storage location for these instructions in CISC architecture.
Diodes:
Diodes are electronic components that allow current to flow in only one direction. They are used in various applications such as rectification, signal modulation, and switching. However, in CISC architecture, diodes are not primarily used to store complex instructions.
Conclusion:
In CISC architecture, the complex instructions are primarily stored in transistors. Transistors, implemented using CMOS technology, form the logic gates that store and execute these instructions. While registers play a crucial role in the execution of these instructions, they are not the primary storage location. Diodes, on the other hand, are not directly involved in the storage of complex instructions in CISC architecture.
Network of Communication protocol is formed by one master and ___ slaves with a unique address.- a)230
- b)237
- c)247
- d)245
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Network of Communication protocol is formed by one master and ___ slaves with a unique address.
a)
230
b)
237
c)
247
d)
245
|
|
Yash Verma answered |
Network of Communication Protocol
A network of communication protocol is a set of rules that govern communication between electronic devices. It is used to ensure that the devices can communicate with each other effectively. In this network, there is one master and multiple slaves.
Number of Slaves in the Network
The question asks how many slaves are in the network of communication protocol. The answer is:
c)247
Explanation
In a network of communication protocol, there is one master and multiple slaves. The slaves are electronic devices that communicate with the master. Each slave has a unique address that is used to identify it on the network. The address is usually an 8-bit number, which means that there can be up to 256 slaves on the network.
However, not all 8-bit numbers can be used as addresses. Some of them are reserved for special purposes, such as broadcast messages or identifying the master. Therefore, the maximum number of slaves that can be used in a network of communication protocol is 247.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a network of communication protocol is a set of rules that govern communication between electronic devices. There is one master and multiple slaves in this network. Each slave has a unique address that is used to identify it on the network. The maximum number of slaves that can be used in a network of communication protocol is 247.
A network of communication protocol is a set of rules that govern communication between electronic devices. It is used to ensure that the devices can communicate with each other effectively. In this network, there is one master and multiple slaves.
Number of Slaves in the Network
The question asks how many slaves are in the network of communication protocol. The answer is:
c)247
Explanation
In a network of communication protocol, there is one master and multiple slaves. The slaves are electronic devices that communicate with the master. Each slave has a unique address that is used to identify it on the network. The address is usually an 8-bit number, which means that there can be up to 256 slaves on the network.
However, not all 8-bit numbers can be used as addresses. Some of them are reserved for special purposes, such as broadcast messages or identifying the master. Therefore, the maximum number of slaves that can be used in a network of communication protocol is 247.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a network of communication protocol is a set of rules that govern communication between electronic devices. There is one master and multiple slaves in this network. Each slave has a unique address that is used to identify it on the network. The maximum number of slaves that can be used in a network of communication protocol is 247.
Which of the following is the subcategories of computer architecture?- a)Microarchitecture
- b)Instruction set architecture
- c)Systems design
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the subcategories of computer architecture?
a)
Microarchitecture
b)
Instruction set architecture
c)
Systems design
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Raj Datta answered |
Subcategories of Computer Architecture
Computer architecture is the design of computer systems including hardware components and software systems. It can be divided into several subcategories, including:
1. Microarchitecture
Microarchitecture refers to the design of a single processor or a single computational element. It involves the implementation of the instruction set architecture (ISA) and the organization of functional units such as the arithmetic logic unit (ALU), control unit, and memory hierarchy.
2. Instruction Set Architecture
Instruction set architecture (ISA) is the set of instructions that a processor can execute. It defines the interface between software and hardware and provides the programmer with a set of instructions to perform operations.
3. Systems Design
Systems design refers to the design of computer systems that include multiple processors, communication networks, and input/output devices. It involves the design of the interconnects, memory hierarchy, and input/output subsystems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, computer architecture can be divided into several subcategories, including microarchitecture, instruction set architecture, and systems design. Microarchitecture involves the design of a single processor, instruction set architecture defines the set of instructions a processor can execute, and systems design involves the design of computer systems that include multiple processors and input/output devices.
Computer architecture is the design of computer systems including hardware components and software systems. It can be divided into several subcategories, including:
1. Microarchitecture
Microarchitecture refers to the design of a single processor or a single computational element. It involves the implementation of the instruction set architecture (ISA) and the organization of functional units such as the arithmetic logic unit (ALU), control unit, and memory hierarchy.
2. Instruction Set Architecture
Instruction set architecture (ISA) is the set of instructions that a processor can execute. It defines the interface between software and hardware and provides the programmer with a set of instructions to perform operations.
3. Systems Design
Systems design refers to the design of computer systems that include multiple processors, communication networks, and input/output devices. It involves the design of the interconnects, memory hierarchy, and input/output subsystems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, computer architecture can be divided into several subcategories, including microarchitecture, instruction set architecture, and systems design. Microarchitecture involves the design of a single processor, instruction set architecture defines the set of instructions a processor can execute, and systems design involves the design of computer systems that include multiple processors and input/output devices.
What does CSA stands for?- a)Computer Service Architecture
- b)Computer Speed Addition
- c)Carry Save Addition
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What does CSA stands for?
a)
Computer Service Architecture
b)
Computer Speed Addition
c)
Carry Save Addition
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Rohan Patel answered |
CSA stands for Carry Save Addition.
Explanation:
Carry Save Addition (CSA) is a digital arithmetic operation that is used to add multiple binary numbers together. It is commonly used in high-speed arithmetic circuits, such as adders and multipliers.
Here is a detailed explanation of what Carry Save Addition entails:
1. Binary Addition:
In binary addition, two binary numbers are added together bit by bit, starting from the rightmost bit. The sum of each bit is computed along with a carry bit, which is propagated to the next bit.
For example, consider adding two binary numbers: 1011 and 1101.
```
1 0 1 1
+ 1 1 0 1
__________
1 0 0 0
```
2. Carry Save Addition:
Carry Save Addition takes a different approach to binary addition. Instead of computing the sum and carry for each bit, it focuses on saving the carry bits for later addition.
In Carry Save Addition, the sum of each bit is computed independently, and the carry bits are stored separately. The carry bits are then added together separately.
For example, consider adding the same two binary numbers (1011 and 1101) using Carry Save Addition:
```
1 0 1 1
+ 1 1 0 1
__________
0 0 1 0 (Sum)
```
The carry bits are stored as follows:
```
1 0 1 1
+ 1 1 0 1
__________
1 0 0 0 (C0)
1 0 0 (C1)
0 0 (C2)
0 (C3)
```
3. Advantages of Carry Save Addition:
Carry Save Addition has several advantages in certain arithmetic circuits:
- It enables parallel addition, as each bit can be added independently.
- It reduces the number of carry propagations and critical paths, leading to improved speed in high-speed arithmetic circuits.
- It allows for efficient implementation of multioperand addition and multiplication.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, CSA stands for Carry Save Addition, which is a digital arithmetic operation used in high-speed arithmetic circuits. It focuses on saving the carry bits for later addition, resulting in improved speed and efficiency.
Explanation:
Carry Save Addition (CSA) is a digital arithmetic operation that is used to add multiple binary numbers together. It is commonly used in high-speed arithmetic circuits, such as adders and multipliers.
Here is a detailed explanation of what Carry Save Addition entails:
1. Binary Addition:
In binary addition, two binary numbers are added together bit by bit, starting from the rightmost bit. The sum of each bit is computed along with a carry bit, which is propagated to the next bit.
For example, consider adding two binary numbers: 1011 and 1101.
```
1 0 1 1
+ 1 1 0 1
__________
1 0 0 0
```
2. Carry Save Addition:
Carry Save Addition takes a different approach to binary addition. Instead of computing the sum and carry for each bit, it focuses on saving the carry bits for later addition.
In Carry Save Addition, the sum of each bit is computed independently, and the carry bits are stored separately. The carry bits are then added together separately.
For example, consider adding the same two binary numbers (1011 and 1101) using Carry Save Addition:
```
1 0 1 1
+ 1 1 0 1
__________
0 0 1 0 (Sum)
```
The carry bits are stored as follows:
```
1 0 1 1
+ 1 1 0 1
__________
1 0 0 0 (C0)
1 0 0 (C1)
0 0 (C2)
0 (C3)
```
3. Advantages of Carry Save Addition:
Carry Save Addition has several advantages in certain arithmetic circuits:
- It enables parallel addition, as each bit can be added independently.
- It reduces the number of carry propagations and critical paths, leading to improved speed in high-speed arithmetic circuits.
- It allows for efficient implementation of multioperand addition and multiplication.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, CSA stands for Carry Save Addition, which is a digital arithmetic operation used in high-speed arithmetic circuits. It focuses on saving the carry bits for later addition, resulting in improved speed and efficiency.
Which of the following is a type of computer architecture?- a)Microarchitecture
- b)Harvard Architecture
- c)Von-Neumann Architecture
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a type of computer architecture?
a)
Microarchitecture
b)
Harvard Architecture
c)
Von-Neumann Architecture
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Eesha Bhat answered |
Below are the types of Computer Architecture:
i) Von-Neumann Architecture
ii) Harvard Architecture
iii) Instruction Set Architecture
iv) Microarchitecture
v) System Design
i) Von-Neumann Architecture
ii) Harvard Architecture
iii) Instruction Set Architecture
iv) Microarchitecture
v) System Design
What is computer architecture?- a)set of categories and methods that specify the functioning, organisation, and implementation of computer systems
- b)set of principles and methods that specify the functioning, organisation, and implementation of computer systems
- c)set of functions and methods that specify the functioning, organisation, and implementation of computer systems
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is computer architecture?
a)
set of categories and methods that specify the functioning, organisation, and implementation of computer systems
b)
set of principles and methods that specify the functioning, organisation, and implementation of computer systems
c)
set of functions and methods that specify the functioning, organisation, and implementation of computer systems
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Eesha Bhat answered |
A set of principles and methods that specify the functioning, organisation, and implementation of computer systems is known as computer architecture. A system’s architecture refers to its structure in terms of the system’s individually specified components and their interrelationships.
1 gigabyte is equal to-- a)1391 megabytes
- b)1024 kilobytes
- c)1024 megabytes
- d)1150 megabytes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
1 gigabyte is equal to-
a)
1391 megabytes
b)
1024 kilobytes
c)
1024 megabytes
d)
1150 megabytes
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
Key Points
- 1 gigabyte = 230 bytes = 210 × 220 bytes
- Since 1 megabyte = 220 bytes
- 1 gigabyte = 210 × megabytes
- 1 gigabyte = 1024 megabytes
Therefore option 3 is correct.
Permanent Memory of a computer is known as-- a)RAM
- b)CD-ROM
- c)ROM
- d)CPU
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Permanent Memory of a computer is known as-
a)
RAM
b)
CD-ROM
c)
ROM
d)
CPU
|
|
Eesha Bhat answered |
Key Points
- The permanent memory of a computer is known as ROM(Read-only memory).
- In computers and other electronic devices, read-only memory (ROM) is a form of non-volatile memory.
- After the memory unit is manufactured, data contained in ROM cannot be electronically changed. Read-only memory, also known as firmware, is useful for storing software that is rarely updated during the life of the device.
- Plug-in cartridges containing ROM can be used to distribute software applications (such as video games) for programmable computers.
- Read-only memory refers to memory that is hard-wired and cannot be modified electronically after manufactures, such as a diode matrix or a mask ROM integrated circuit (IC).
______ is the fastest to read from and write to than the other kinds of storage in a computer.- a)Floppy disk
- b)Hard disk
- c)CD-ROM
- d)RAM
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
______ is the fastest to read from and write to than the other kinds of storage in a computer.
a)
Floppy disk
b)
Hard disk
c)
CD-ROM
d)
RAM
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
- RAM is the fastest to read from and write to than the other kinds of storage in a computer.
- It is Volatile or temporary memory.
- Data gets erased when the power supply is off.
- Faster memory than ROM.
- It is used in the normal operations of a computer after starting up and loading the operating system.
- CD-ROM for "Compact Disc Read-Only Memory".
- CD-ROM is a CD that can be read by a computer with an optical drive.
- Floppy Disk is a type of disk storage composed of a disk of the thin and flexible magnetic storage medium.
- It is used for backup purpose.
- It is a type of secondary storage.
- The storage capacity of a common floppy disk is 1.44 MB.
- The hard disk is the main device for storing data in the computer.
- It uses magnetic technology (nowadays optical technology for storing data).
- It has a strong coating above the magnetic metallic oxide in order to protect the major components.
The memory devices which are similar to EEPROM but differ in the cost effectiveness is ______- a)CMOS
- b)Memory sticks
- c)Blue-ray devices
- d)Flash memory
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The memory devices which are similar to EEPROM but differ in the cost effectiveness is ______
a)
CMOS
b)
Memory sticks
c)
Blue-ray devices
d)
Flash memory
|
|
Eesha Bhat answered |
The flash memory functions similar to the EEPROM but is much cheaper.
Chapter doubts & questions for Computer Organisation & Architecture - GATE Computer Science Engineering(CSE) 2026 Mock Test Series 2025 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Computer Organisation & Architecture - GATE Computer Science Engineering(CSE) 2026 Mock Test Series in English & Hindi are available as part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









