All Exams >
NEET >
Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Reproduction in Organisms for NEET Exam
Eye lens is formed from[1992]- a)ectoderm
- b)mesoderm
- c)endoderm
- d)ectoderm and mesoderm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Eye lens is formed from
[1992]
a)
ectoderm
b)
mesoderm
c)
endoderm
d)
ectoderm and mesoderm
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
The eye is derived from the neuroepithelium, surface ectoderm, and the extracellular mesenchyme which consists of both the neural crest and mesoderm. Neuroepithelium forms the retina, ciliary body, iris, and optic nerves. Surface ectoderm forms the lens, corneal epithelium and eyelid.
Syngamy can occur outside the body of the organism in[NEET Kar. 2013]- a)Fungi
- b)Mosses
- c)Algae
- d)Ferns
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Syngamy can occur outside the body of the organism in
[NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
Fungi
b)
Mosses
c)
Algae
d)
Ferns
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
In most aquatic organisms, such as a majority of algae and fishes as well as amphibians, syngamy occurs in the external medium (water) i.e., outside the body of the organism. This type of gametic fusion is called external fertilisation.
Which of the following animals are not viviparous?- a)Flying fox (bat)
- b)Elephant
- c)Platypus
- d)Whale
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following animals are not viviparous?
a)
Flying fox (bat)
b)
Elephant
c)
Platypus
d)
Whale
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
Platypus is not viviparous animal ....it is oviparous. option C
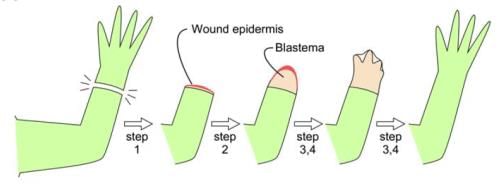
During regeneration, modification of an organ to other organ is known as[2001]- a)Morphogenesis
- b)Epimorphosis
- c)Morphallaxis
- d)Accretionary growth
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During regeneration, modification of an organ to other organ is known as
[2001]
a)
Morphogenesis
b)
Epimorphosis
c)
Morphallaxis
d)
Accretionary growth
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Epimorphosis is the replacement of a lost organ of the body by proliferating new cells from the surface of the wound or injured part.
Vegetative propagation in mint occurs by:[2009]- a)offset
- b)rhizome
- c)sucker
- d)runner
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Vegetative propagation in mint occurs by:
[2009]
a)
offset
b)
rhizome
c)
sucker
d)
runner

|
Naveen Menon answered |
Vegetative propagation in mint occurs through sucker. Vegetative reproduction is a type of asexual reproduction for plants, and is also called vegetative propagation, vegetative multiplication, or vegetative cloning. It is a process by which new plant “individuals” arise or are obtained without production of seeds or spores. It is both natural process in many plant species (as well as non-plant organisms such as bacteria and fungi) and one used or encouraged by horticulturists to obtain quantities of economically valuable plants. A related technique used in cultivation is tissue culture, which involves vegetative reproduction under sterile conditions.
In telolecithal egg the yolk is found[1993]- a)all over the egg
- b)on one side
- c)both the sides
- d)centre
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In telolecithal egg the yolk is found
[1993]
a)
all over the egg
b)
on one side
c)
both the sides
d)
centre

|
Diya Datta answered |
On the basis of distribution of yolk the eggs are of following types :
(i) Homolecithal : Evenly distributed yolk.
(ii) Telolecithal : hMost of the yolk near the vegetal pole, cytoplasm and nucleus lie near animal pole.
(iii) Centrolecithal : Centrally placed yolk surrounded by cytoplasm.
(i) Homolecithal : Evenly distributed yolk.
(ii) Telolecithal : hMost of the yolk near the vegetal pole, cytoplasm and nucleus lie near animal pole.
(iii) Centrolecithal : Centrally placed yolk surrounded by cytoplasm.
Select the wrong statement :[NEET 2013]- a)Anisogametes differ either in structure, function or behaviour.
- b)In Oomycetes female gamete is smaller and motile, while male gamete is larger and non-motile.
- c)Chalmydomonas exhibits both isogamy and anisogamy and Fucus shows oogamy.
- d)Isogametes are similar in structure, function and behaviour.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the wrong statement :
[NEET 2013]
a)
Anisogametes differ either in structure, function or behaviour.
b)
In Oomycetes female gamete is smaller and motile, while male gamete is larger and non-motile.
c)
Chalmydomonas exhibits both isogamy and anisogamy and Fucus shows oogamy.
d)
Isogametes are similar in structure, function and behaviour.

|
Palak Khanna answered |
In oomycetes female gamete is large and non motile while male gamete is small & motile.
The correct sequence in the process ofdevelopment of human embryo is [1998]- a)fertilization—zygote—cleavage— morula—blastula—gastrula
- b)fertilization—cleavage—morula— zygote—blastula—gastrula
- c)fertilization—zygote—blastula— morula—cleavage—gastrula
- d)cleavage—zygote—fertilization— morula—blastula—gastrula
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct sequence in the process ofdevelopment of human embryo is [1998]
a)
fertilization—zygote—cleavage— morula—blastula—gastrula
b)
fertilization—cleavage—morula— zygote—blastula—gastrula
c)
fertilization—zygote—blastula— morula—cleavage—gastrula
d)
cleavage—zygote—fertilization— morula—blastula—gastrula
|
|
Bhavana Desai answered |
→ cleavage → morula → blastula → gastrula → neurula → fetal development.
Blastopore is the opening of[2000]- a)coelenteron
- b)coelom
- c)blastocoel
- d)archenteron
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Blastopore is the opening of
[2000]
a)
coelenteron
b)
coelom
c)
blastocoel
d)
archenteron

|
Ayush Sengupta answered |
Blastopore is the transitory opening on the surface of gastrula through which the internal cavity archenteron) communicates with the exterior. It is formed by invagination of superficial cells during gastrulation.
Meroblastic cleavage refers to which type of division of egg?[1992]a)complete... moreb)incompletec)horizontald)spiralCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Pooja Saha answered |
Different types of segmentation or cleavages are found in animals depending upon the amount of yolk & its distribution: Holoblastic : Complete division.
Meroblastic : Division occurs only in cytoplasm but not in yolk. eg. fishes.
Meroblastic : Division occurs only in cytoplasm but not in yolk. eg. fishes.
Meiosis takes place in :[NEET 2013]- a)Conidia
- b)Gemmule
- c)Megaspore
- d)Meiocyte
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Meiosis takes place in :
[NEET 2013]
a)
Conidia
b)
Gemmule
c)
Megaspore
d)
Meiocyte

|
Shanaya Rane answered |
Meiosis takes place in meiocyte while Conidia and Gemmule are asexual structures and megaspore is haploid.
Which of the following processes is associated with a change in the cellular DNA amount?[1999]- a)Spore germination
- b)Cytokinesis
- c)Fertilization
- d)Blastulation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following processes is associated with a change in the cellular DNA amount?
[1999]
a)
Spore germination
b)
Cytokinesis
c)
Fertilization
d)
Blastulation

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
Cytokinesis involves division of the cytoplasm of the parent cell into its daughter cells. Fertilization involves the fusion of two haploid gametes. Blastulation refers to the process of cleavage in the zygote to form a blastula.
Monoecious plant of Chara shows occurrence of :[NEET 2013]- a)stamen and carpel of the same plant
- b)upper antheridium and lower oogonium on the same plant
- c)upper oogonium and lower antheridium on the same plant
- d)antheridiophore and archegoniophore on the same plant
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Monoecious plant of Chara shows occurrence of :
[NEET 2013]
a)
stamen and carpel of the same plant
b)
upper antheridium and lower oogonium on the same plant
c)
upper oogonium and lower antheridium on the same plant
d)
antheridiophore and archegoniophore on the same plant

|
Charvi Shah answered |
Male sex organ is called antheridium or globule while female sex organ is called oogonium. They develop on the same branchlet in the same plant in chara.
Which of the following flowers only once in its lifetime? [ NEET 2018]- a)Bamboo Species
- b)Jackfruit
- c)Mango
- d)Papaya
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following flowers only once in its lifetime? [ NEET 2018]
a)
Bamboo Species
b)
Jackfruit
c)
Mango
d)
Papaya
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Certain bamboo species are monocarpic, i.e., flower generally only once in their lifetime (after 50-100 years). Other plants (jackfruit, mango and papaya) are polycarpic, i.e., produce flowers and its many times during their lifetime.
Which one of the following is correctly matched[2012]- a)Onion - Bulb
- b)Ginger - Sucker
- c)Chlamydomonas - Conidia
- d)Yeast - Zoospores
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is correctly matched
[2012]
a)
Onion - Bulb
b)
Ginger - Sucker
c)
Chlamydomonas - Conidia
d)
Yeast - Zoospores

|
Shivani Tiwari answered |
Onion - Bulb - Undeground stem, Ginger - Rhizome, Chlamydomonas - Zoospore Yeast - ascospores
In an egg, the type of cleavage is determined by[1995]- a)shape and size of the sperm
- b)size and location of the nucleus
- c)amount and distribution of yolk
- d)number of egg membranes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an egg, the type of cleavage is determined by
[1995]
a)
shape and size of the sperm
b)
size and location of the nucleus
c)
amount and distribution of yolk
d)
number of egg membranes
|
|
Devika Chavan answered |
Explanation:
Cleavage is the process of cell division that occurs after fertilization of an egg cell by a sperm cell. The type of cleavage that occurs in an egg is determined by the amount and distribution of yolk present in the egg.
Yolk is a nutrient-rich substance that is stored in the egg to support the development of the embryo. The amount of yolk present in an egg varies among different species, and the type of cleavage that occurs in the egg is adapted to the amount and distribution of yolk.
Types of cleavage based on yolk distribution:
1. Isolecithal cleavage: In eggs that have a small amount of yolk that is uniformly distributed throughout the egg, cleavage occurs evenly and produces blastomeres of equal size. This type of cleavage is found in organisms such as sea urchins and frogs.
2. Mesolecithal cleavage: In eggs that have a moderate amount of yolk that is concentrated at one end of the egg, cleavage occurs only in the yolk-free cytoplasm at the animal pole, producing a small blastula on top of a large yolk mass. This type of cleavage is found in organisms such as fish and reptiles.
3. Telolecithal cleavage: In eggs that have a large amount of yolk that is concentrated at one end of the egg, cleavage occurs only in the small amount of cytoplasm at the animal pole, producing a disc-shaped blastula on top of a large yolk mass. This type of cleavage is found in organisms such as birds and mammals.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C, which states that the type of cleavage in an egg is determined by the amount and distribution of yolk.
Cleavage is the process of cell division that occurs after fertilization of an egg cell by a sperm cell. The type of cleavage that occurs in an egg is determined by the amount and distribution of yolk present in the egg.
Yolk is a nutrient-rich substance that is stored in the egg to support the development of the embryo. The amount of yolk present in an egg varies among different species, and the type of cleavage that occurs in the egg is adapted to the amount and distribution of yolk.
Types of cleavage based on yolk distribution:
1. Isolecithal cleavage: In eggs that have a small amount of yolk that is uniformly distributed throughout the egg, cleavage occurs evenly and produces blastomeres of equal size. This type of cleavage is found in organisms such as sea urchins and frogs.
2. Mesolecithal cleavage: In eggs that have a moderate amount of yolk that is concentrated at one end of the egg, cleavage occurs only in the yolk-free cytoplasm at the animal pole, producing a small blastula on top of a large yolk mass. This type of cleavage is found in organisms such as fish and reptiles.
3. Telolecithal cleavage: In eggs that have a large amount of yolk that is concentrated at one end of the egg, cleavage occurs only in the small amount of cytoplasm at the animal pole, producing a disc-shaped blastula on top of a large yolk mass. This type of cleavage is found in organisms such as birds and mammals.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C, which states that the type of cleavage in an egg is determined by the amount and distribution of yolk.
What is true about cleavage in fertilized egg of humans?[1994]- a)Meroblastic
- b)Starts when egg reaches uterus
- c)Starts in fallopian tube
- d)It is identical to normal mitosis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is true about cleavage in fertilized egg of humans?
[1994]
a)
Meroblastic
b)
Starts when egg reaches uterus
c)
Starts in fallopian tube
d)
It is identical to normal mitosis

|
Mahesh Saini answered |
After ovulation egg comes in fallopian tube where it is fertilized by the sperm & cleavage starts here only.
Termination of gastrulation is indicated by[1993]- a)obliteration of blastocoel
- b)obliteration of archenteron
- c)closure of blastopore
- d)closure of neural tube
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Termination of gastrulation is indicated by
[1993]
a)
obliteration of blastocoel
b)
obliteration of archenteron
c)
closure of blastopore
d)
closure of neural tube

|
Charvi Shah answered |
Gastrulation ends with the complete obliteration of blastocoel. The stage of three primary germ layers starts.
What is common between vegetative reproduction and apomixis?[2011M]- a)Both are applicable to only dicot plants
- b)Both bypass the flowering phase
- c)Both occur round the year
- d)Both produces progeny identical to the parent
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is common between vegetative reproduction and apomixis?
[2011M]
a)
Both are applicable to only dicot plants
b)
Both bypass the flowering phase
c)
Both occur round the year
d)
Both produces progeny identical to the parent

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
Vegetative reproduction and apomixis both are asexual methods of reproduction, which gives the progeny genetically similar to parent.
Which one of the following statements is not correct? [NEET 2016]- a)Offspring produced by the asexual reproduction are called clone.
- b)Microscopic, motile, asexual reproductive structures are called zoospores.
- c)In potato, banana and ginger, the plantlets arise from the internodes present in the modified stem.
- d)Water hyacinth, growing in the standing water, drains oxygen from water that leads to the death of fishes.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is not correct? [NEET 2016]
a)
Offspring produced by the asexual reproduction are called clone.
b)
Microscopic, motile, asexual reproductive structures are called zoospores.
c)
In potato, banana and ginger, the plantlets arise from the internodes present in the modified stem.
d)
Water hyacinth, growing in the standing water, drains oxygen from water that leads to the death of fishes.
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Potato, banana and ginger Propagate Vegetatively by their modified stems. Potato propagates by tuber which has buds over its eyes or nodes. These buds produce new plantlets. Banana and ginger propagate with the help of rhizomes which also have buds on nodes for the formation of new plantlets.
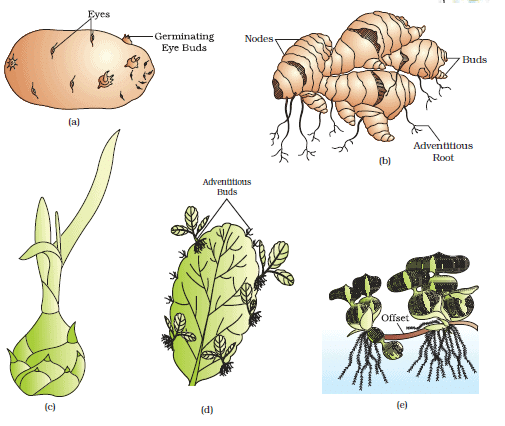
The “Eyes” of the potato tuber are[2011]- a)root buds
- b)flower buds
- c)shoot buds
- d)axillary buds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The “Eyes” of the potato tuber are
[2011]
a)
root buds
b)
flower buds
c)
shoot buds
d)
axillary buds

|
Kajal Bose answered |
The axillary buds of the potato tuber are called “eyes” in common language. They are found at the nodes of the stem tuber.
What is true for cleavage?[2002]- a)Size of embryo increases
- b)Size of cells decrease
- c)Size of cells increase
- d)Size of embryo decreases
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is true for cleavage?
[2002]
a)
Size of embryo increases
b)
Size of cells decrease
c)
Size of cells increase
d)
Size of embryo decreases

|
Sarthak Saini answered |
Cleavage involves repeated cell division without increase in size. But cell size decrease.
Vegetative propagule in Agave is as: [ NEET 2020]- a)Rhizome
- b)Bulbil
- c)Offset
- d)Eye
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Vegetative propagule in Agave is as: [ NEET 2020]
a)
Rhizome
b)
Bulbil
c)
Offset
d)
Eye
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Vegetative propagules in angiosperms: (a) Eyes of potato; (b) Rhizome of ginger; (c) Bulbil of Agave; (d) Leaf buds of Bryophyllum; (e) Offset of water hyacinth

Blastopore is[1992]- a)opening of neural tube
- b)opening of gastrocoel
- c)future anterior end of embryo
- d)found in blastula
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Blastopore is
[1992]
a)
opening of neural tube
b)
opening of gastrocoel
c)
future anterior end of embryo
d)
found in blastula

|
Swara Desai answered |
It is the small slit like opening on the dorsal side of gastrocoel also known as dorsal lip.
What is true about cells during cleavage?- a)They move from animal pole to vegetal pole
- b)They do not grow in size
- c)They consume little O2
- d)Their divisions resemble ordinary mitosis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is true about cells during cleavage?
a)
They move from animal pole to vegetal pole
b)
They do not grow in size
c)
They consume little O2
d)
Their divisions resemble ordinary mitosis
|
|
Nilanjan Kapoor answered |
Cells during Cleavage do not grow in size
Cleavage is a process of cell division that occurs immediately after fertilization. During cleavage, the zygote undergoes a series of rapid cell divisions to form a multicellular embryo. Here are some important facts about cells during cleavage:
- Cells divide rapidly: During cleavage, cells divide rapidly without any growth in size. As a result, the daughter cells become smaller and smaller with each division.
- Cells move: As the cells divide, they move from the site of fertilization (animal pole) towards the opposite pole (vegetal pole). This movement is facilitated by changes in the cytoskeleton and the presence of actin filaments.
- Mitosis: The cell divisions during cleavage are similar to ordinary mitosis, but they occur much faster and without any growth in size.
- Oxygen consumption: The cells during cleavage consume very little oxygen as they only need to produce enough energy to divide and move.
- Formation of blastula: After several rounds of cell division, the zygote forms a hollow ball of cells called a blastula. The blastula is the first stage of embryonic development and is characterized by a fluid-filled cavity called the blastocoel.
In summary, cells during cleavage divide rapidly without any growth in size, move from animal pole to vegetal pole, and consume very little oxygen. The end result is the formation of a blastula, which is the first stage of embryonic development.
Cleavage is a process of cell division that occurs immediately after fertilization. During cleavage, the zygote undergoes a series of rapid cell divisions to form a multicellular embryo. Here are some important facts about cells during cleavage:
- Cells divide rapidly: During cleavage, cells divide rapidly without any growth in size. As a result, the daughter cells become smaller and smaller with each division.
- Cells move: As the cells divide, they move from the site of fertilization (animal pole) towards the opposite pole (vegetal pole). This movement is facilitated by changes in the cytoskeleton and the presence of actin filaments.
- Mitosis: The cell divisions during cleavage are similar to ordinary mitosis, but they occur much faster and without any growth in size.
- Oxygen consumption: The cells during cleavage consume very little oxygen as they only need to produce enough energy to divide and move.
- Formation of blastula: After several rounds of cell division, the zygote forms a hollow ball of cells called a blastula. The blastula is the first stage of embryonic development and is characterized by a fluid-filled cavity called the blastocoel.
In summary, cells during cleavage divide rapidly without any growth in size, move from animal pole to vegetal pole, and consume very little oxygen. The end result is the formation of a blastula, which is the first stage of embryonic development.
In sonic plants, the female gamete develops into embryo without fertilisation. This phenomenon known as [ NEET 2019]- a)Parthenogenesis
- b)Autogamy
- c)Parthenocarpy
- d)Syngamy
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In sonic plants, the female gamete develops into embryo without fertilisation. This phenomenon known as [ NEET 2019]
a)
Parthenogenesis
b)
Autogamy
c)
Parthenocarpy
d)
Syngamy
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
- Parthenogenesis is the spontaneous development of an embryo from an unfertilised egg cell, It naturally occurs in variety of plants, where parthenogenesis usually is found in combination with apomeiosis (the omission of meiosis) and pseudogamous (with or without central cell fertilisation) endosperm formation, together known as apomixis (clonal seed production).
- Parthenocarpy is development of fruit without fertilisation.
The two nuclei at the end of the pollen tube are called- a)Tube nucleus and a generative nucleus
- b)Sperm and ovum
- c)Generative nucleus and stigma
- d)Tube nucleus and sperm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The two nuclei at the end of the pollen tube are called
a)
Tube nucleus and a generative nucleus
b)
Sperm and ovum
c)
Generative nucleus and stigma
d)
Tube nucleus and sperm
|
|
Ashwin Majumdar answered |
Tube nucleus and a generative nucleus
The two nuclei at the end of the pollen tube are referred to as the tube nucleus and the generative nucleus. This is a crucial stage in the process of fertilization in plants.
Tube nucleus:
- The tube nucleus is responsible for guiding the pollen tube through the style towards the ovule.
- It plays a role in the growth and elongation of the pollen tube, ensuring it reaches the ovule for fertilization.
Generative nucleus:
- The generative nucleus is involved in the formation of two sperm cells through mitosis.
- These sperm cells are essential for double fertilization in plants, where one sperm cell fuses with the egg cell to form the zygote, while the other sperm cell fuses with the central cell to form the endosperm.
In conclusion, the tube nucleus and the generative nucleus work together to ensure successful fertilization in plants by guiding the pollen tube and producing the necessary sperm cells for double fertilization.
Chapter doubts & questions for Reproduction in Organisms - Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Reproduction in Organisms - Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily