All Exams >
Mechanical Engineering >
SSC JE Mechanical Mock Test Series 2026 >
All Questions
All questions of Refrigeration & Air conditioning for Mechanical Engineering Exam
Cryogenics refers to- a)refrigeration at low temperate
- b)thermodynamic analysis at low temperature
- c)engineering field concerned with equipment in the range of – 150°C to absolute zero
- d)Refrigeration under vaccum conditions
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cryogenics refers to
a)
refrigeration at low temperate
b)
thermodynamic analysis at low temperature
c)
engineering field concerned with equipment in the range of – 150°C to absolute zero
d)
Refrigeration under vaccum conditions
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Cryogenics is the branches of engineering that involve the study of very low temperatures, how to produce them, and how materials behave at those temperatures.
The cryogenic temperature range has been defined as from −150 °C (123 K) to absolute zero (−273 °C), the temperature at which molecular motion comes as close as theoretically possible to ceasing completely.
Absorption system normally uses the following refrigerant:- a)Freon - 11
- b)Freon - 22
- c)CO2
- d)Ammonia
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Absorption system normally uses the following refrigerant:
a)
Freon - 11
b)
Freon - 22
c)
CO2
d)
Ammonia
|
|
Yash Patel answered |
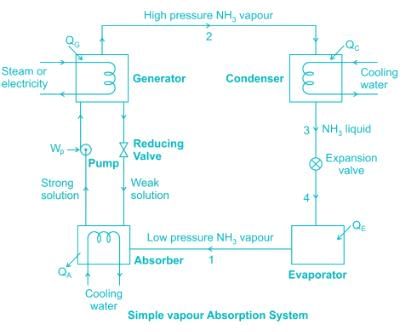
The absorption refrigeration system differs fundamentally from vapor compression system only in the method of compressing the refrigerant. An absorber, generator and pump in the absorption refrigerating system replace the compressor of a vapor compression system.
The two commonly used refrigerant pairs are ammonia – water and lithium bromide – water.
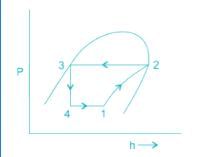
A simple saturated refrigeration cycle has the following state points. Enthalpy after compression = 425 kJ/kg; enthaly after throttling = 125 kJ/kg; enthalpy before compression = 375 kJ/kg. The COP of refrigeration is: - a)5
- b)3.5
- c)6
- d)Not possible to find with this data
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A simple saturated refrigeration cycle has the following state points. Enthalpy after compression = 425 kJ/kg; enthaly after throttling = 125 kJ/kg; enthalpy before compression = 375 kJ/kg. The COP of refrigeration is:
a)
5
b)
3.5
c)
6
d)
Not possible to find with this data

|
Hiral Sharma answered |
Pick up the correct statement - - a)The refrigerant should have high thermal conductivity and low freezing temperature
- b)The refrigerator should have low heat transfer coefficient and high latent heat.
- c)The refrigerant should have high specific volume and high latent heat.
- d)The refrigerator should have high specific volume and low latent heat
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Pick up the correct statement -
a)
The refrigerant should have high thermal conductivity and low freezing temperature
b)
The refrigerator should have low heat transfer coefficient and high latent heat.
c)
The refrigerant should have high specific volume and high latent heat.
d)
The refrigerator should have high specific volume and low latent heat
|
|
Akshara Rane answered |
Required Properties of Ideal Refrigerant:
1) The refrigerant should have low boiling point and low freezing point.
2) It must have low specific heat and high latent heat. Because high specific heat decreases the refrigerating effect per kg of refrigerant and high latent heat at low temperature increases the refrigerating effect per kg of refrigerant.
3) It must have high critical pressure and temperature to avoid large power requirements.
4) The pressures required to be maintained in the evaporator and condenser should be low enough to reduce the material cost and must be positive to avoid leakage of air into the system.
5) It should have low specific volume to reduce the size of the compressor.
6) It must have high thermal conductivity and high heat transfer coefficient to reduce the area of heat transfer in evaporator and condenser.
7) It should be non-flammable, non-explosive, non-toxic and non-corrosive.
8) It should not have any bad effects on the stored material or food, when any leak develops in the system.
9) It must have high miscibility with lubricating oil and it should not have reacting properly with lubricating oil in the temperature range of the system.
10) It should give high COP in the working temperature range. This is necessary to reduce the running cost of the system.
If ha is enthalpy of dry air, hy is enthalpy of water vapour and w is specific humidity, the enthalpy of moist air will be- a)ha + hv
- b)ha + whv
- c)hv + wha
- d)hv + ha/w
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If ha is enthalpy of dry air, hy is enthalpy of water vapour and w is specific humidity, the enthalpy of moist air will be
a)
ha + hv
b)
ha + whv
c)
hv + wha
d)
hv + ha/w
|
|
Nandini Basak answered |
The correct answer is option 'B': ha whv. Let's understand why this is the right answer.
Enthalpy of Dry Air (ha):
Enthalpy is the total energy content of a substance and is given by the sum of its internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. In the case of dry air, the enthalpy is solely dependent on its temperature. Therefore, the enthalpy of dry air can be represented as ha.
Enthalpy of Water Vapor (hv):
Similar to dry air, the enthalpy of water vapor is also dependent on its temperature. However, water vapor has an additional enthalpy due to its phase change. This enthalpy is known as the latent heat of vaporization. Therefore, the enthalpy of water vapor can be represented as hv.
Specific Humidity (w):
Specific humidity is the mass of water vapor present in a unit mass of moist air. It is a measure of the moisture content in the air. Specific humidity is given by the ratio of the mass of water vapor to the sum of the mass of dry air and the mass of water vapor. It can be represented as w.
Enthalpy of Moist Air:
When dry air and water vapor are combined, they form moist air. The enthalpy of moist air is the sum of the enthalpy of dry air and the enthalpy of water vapor. Since the enthalpy of dry air is ha and the enthalpy of water vapor is hv, the enthalpy of moist air can be represented as ha + hv.
However, we need to consider the specific humidity (w) as well. The specific humidity represents the ratio of the mass of water vapor to the sum of the mass of dry air and the mass of water vapor. Therefore, we need to multiply the enthalpy of water vapor (hv) by the specific humidity (w) to account for the mass of water vapor present in the moist air. Hence, the final expression for the enthalpy of moist air is ha + whv.
Therefore, option 'B' (ha whv) is the correct answer.
Enthalpy of Dry Air (ha):
Enthalpy is the total energy content of a substance and is given by the sum of its internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. In the case of dry air, the enthalpy is solely dependent on its temperature. Therefore, the enthalpy of dry air can be represented as ha.
Enthalpy of Water Vapor (hv):
Similar to dry air, the enthalpy of water vapor is also dependent on its temperature. However, water vapor has an additional enthalpy due to its phase change. This enthalpy is known as the latent heat of vaporization. Therefore, the enthalpy of water vapor can be represented as hv.
Specific Humidity (w):
Specific humidity is the mass of water vapor present in a unit mass of moist air. It is a measure of the moisture content in the air. Specific humidity is given by the ratio of the mass of water vapor to the sum of the mass of dry air and the mass of water vapor. It can be represented as w.
Enthalpy of Moist Air:
When dry air and water vapor are combined, they form moist air. The enthalpy of moist air is the sum of the enthalpy of dry air and the enthalpy of water vapor. Since the enthalpy of dry air is ha and the enthalpy of water vapor is hv, the enthalpy of moist air can be represented as ha + hv.
However, we need to consider the specific humidity (w) as well. The specific humidity represents the ratio of the mass of water vapor to the sum of the mass of dry air and the mass of water vapor. Therefore, we need to multiply the enthalpy of water vapor (hv) by the specific humidity (w) to account for the mass of water vapor present in the moist air. Hence, the final expression for the enthalpy of moist air is ha + whv.
Therefore, option 'B' (ha whv) is the correct answer.
A Carnot cycle refrigerator operates between 250 K and 300 K. Its coefficient of performance is- a)6
- b)5
- c)1.2
- d)0.8
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A Carnot cycle refrigerator operates between 250 K and 300 K. Its coefficient of performance is
a)
6
b)
5
c)
1.2
d)
0.8
|
|
Mrinalini Sharma answered |
Introduction:
The Carnot cycle is a theoretical thermodynamic cycle that consists of four processes: isothermal expansion, adiabatic expansion, isothermal compression, and adiabatic compression. It is an idealized cycle that represents the maximum possible efficiency for a heat engine or the maximum possible coefficient of performance for a refrigerator.
Given:
- Temperature of the low-temperature reservoir (T1) = 250 K
- Temperature of the high-temperature reservoir (T2) = 300 K
Coefficient of Performance:
The coefficient of performance (COP) is a measure of the efficiency of a refrigerator or a heat pump. For a refrigerator, the COP is defined as the ratio of the desired cooling effect (Q2) to the work input (W). Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
COP = Q2 / W
Calculating the COP:
In a Carnot cycle refrigerator, the work input (W) is given by:
W = Q2 - Q1
where Q1 is the heat rejected to the low-temperature reservoir.
The Carnot efficiency (η) is given by:
η = 1 - (T1 / T2)
For a Carnot cycle refrigerator, the COP can be expressed as:
COP = Q2 / (Q2 - Q1)
Since Q1 is equal to T1 multiplied by the heat absorbed from the low-temperature reservoir, and Q2 is equal to T2 multiplied by the heat rejected to the high-temperature reservoir, we can rewrite the COP equation as:
COP = T2 / (T2 - T1)
Substituting the given values, we have:
COP = 300 K / (300 K - 250 K)
= 300 K / 50 K
= 6
Conclusion:
Therefore, the coefficient of performance (COP) of the Carnot cycle refrigerator operating between 250 K and 300 K is 6, which corresponds to option B.
The Carnot cycle is a theoretical thermodynamic cycle that consists of four processes: isothermal expansion, adiabatic expansion, isothermal compression, and adiabatic compression. It is an idealized cycle that represents the maximum possible efficiency for a heat engine or the maximum possible coefficient of performance for a refrigerator.
Given:
- Temperature of the low-temperature reservoir (T1) = 250 K
- Temperature of the high-temperature reservoir (T2) = 300 K
Coefficient of Performance:
The coefficient of performance (COP) is a measure of the efficiency of a refrigerator or a heat pump. For a refrigerator, the COP is defined as the ratio of the desired cooling effect (Q2) to the work input (W). Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
COP = Q2 / W
Calculating the COP:
In a Carnot cycle refrigerator, the work input (W) is given by:
W = Q2 - Q1
where Q1 is the heat rejected to the low-temperature reservoir.
The Carnot efficiency (η) is given by:
η = 1 - (T1 / T2)
For a Carnot cycle refrigerator, the COP can be expressed as:
COP = Q2 / (Q2 - Q1)
Since Q1 is equal to T1 multiplied by the heat absorbed from the low-temperature reservoir, and Q2 is equal to T2 multiplied by the heat rejected to the high-temperature reservoir, we can rewrite the COP equation as:
COP = T2 / (T2 - T1)
Substituting the given values, we have:
COP = 300 K / (300 K - 250 K)
= 300 K / 50 K
= 6
Conclusion:
Therefore, the coefficient of performance (COP) of the Carnot cycle refrigerator operating between 250 K and 300 K is 6, which corresponds to option B.
COP of air refrigerator is related with COP of vapour compression refrigerator as- a)(COP)air > (COP)vap.c.
- b)(COP)air < (COP)vap.c.
- c)(COP)air = (COP)vap.c.
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
COP of air refrigerator is related with COP of vapour compression refrigerator as
a)
(COP)air > (COP)vap.c.
b)
(COP)air < (COP)vap.c.
c)
(COP)air = (COP)vap.c.
d)
None of these

|
Nilesh Verma answered |
Is always greater than (COP)vapour compression refrigerator.
b) (COP)air is always equal to (COP)vapour compression refrigerator.
c) (COP)air is always less than (COP)vapour compression refrigerator.
d) (COP)air can be greater or less than (COP)vapour compression refrigerator depending on the operating conditions.
b) (COP)air is always equal to (COP)vapour compression refrigerator.
c) (COP)air is always less than (COP)vapour compression refrigerator.
d) (COP)air can be greater or less than (COP)vapour compression refrigerator depending on the operating conditions.
In a mechanical refrigeration system, the refrigerant has the maximum temperature:- a)before expansion valve
- b)between compressor and condenser
- c)between condenser and evaporator
- d)between compressor and evaporator
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a mechanical refrigeration system, the refrigerant has the maximum temperature:
a)
before expansion valve
b)
between compressor and condenser
c)
between condenser and evaporator
d)
between compressor and evaporator

|
Divya Kulkarni answered |
The exit condition after evaporation is saturated vapour which is compressed in the compressor and become superheated (having the maximum temperature) and then passed to the condenser.
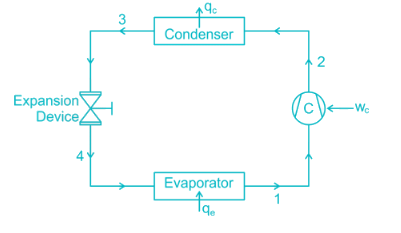
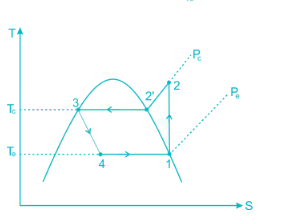
Condition of refrigerator after leaving the compressor and before entering condenser is- a)Super-heated vapor
- b)Saturated liquid
- c)Saturated mixture
- d)Saturated Vapor
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Condition of refrigerator after leaving the compressor and before entering condenser is
a)
Super-heated vapor
b)
Saturated liquid
c)
Saturated mixture
d)
Saturated Vapor

|
Anagha Mehta answered |
In Evaporator: As the liquid refrigerant flows through the evaporator, it absorbs heat and changes from the liquid state to a saturated vapour.
In Compressor: Due to the work done on it during compression, the gas further superheated. Therefore the temperature of the discharge gas will be much higher than the saturation temperature of vapour corresponding to discharge pressure.
In Condenser: In the condenser, the temperature of the superheated vapour has to be brought down to its saturation temperature before it can be condensed into a liquid.
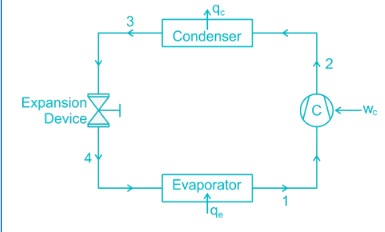
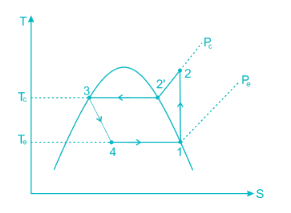
The exit condition after evaporation is saturated vapour which is compressed in the compressor and become super-heated and then passed to the condenser.
1 ton of refrigeration implies heat transfer at the rate of- a)210 kJ/min
- b)210 kJ/sec
- c)1000 kJ/hr
- d)2 kJ/hr
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
1 ton of refrigeration implies heat transfer at the rate of
a)
210 kJ/min
b)
210 kJ/sec
c)
1000 kJ/hr
d)
2 kJ/hr
|
|
Aditya Chavan answered |
1 ton of refrigeration refers to the amount of heat transfer required to freeze one ton (2,000 pounds) of water into ice at 32°F in 24 hours. It is a unit used to measure the cooling capacity of refrigeration systems.
The correct answer is option 'A' - 210 kJ/min.
Let's break down the explanation:
1. Understanding the Concept:
Refrigeration is the process of removing heat from a space or substance to lower its temperature. The cooling capacity of a refrigeration system is measured in tons of refrigeration. One ton of refrigeration is equal to the amount of heat transfer required to freeze one ton of water in 24 hours.
2. Conversion Factors:
To determine the heat transfer rate in different units, we need to use appropriate conversion factors. Here are the conversion factors involved in this question:
- 1 ton of refrigeration = 12,000 British Thermal Units per hour (BTU/hr)
- 1 BTU/hr = 0.29307107 watts (W)
- 1 watt (W) = 1 joule per second (J/s)
- 1 joule (J) = 0.001 kilojoules (kJ)
3. Calculating the Heat Transfer Rate:
To convert the cooling capacity from tons of refrigeration to kilojoules per minute, we can use the following steps:
- Convert 1 ton of refrigeration to BTU/hr:
1 ton of refrigeration = 12,000 BTU/hr
- Convert BTU/hr to watts:
12,000 BTU/hr * 0.29307107 W/BTU = 3,517.65 W
- Convert watts to kilojoules per second (kJ/s):
3,517.65 W * 1 J/s / 1 W * 0.001 kJ/J = 3.51765 kJ/s
- Convert kilojoules per second to kilojoules per minute:
3.51765 kJ/s * 60 s/min = 210.96 kJ/min
Rounding off the answer to the nearest whole number, we get 210 kJ/min, which is the correct answer (option 'A').
To summarize, 1 ton of refrigeration implies a heat transfer rate of 210 kJ/min. This means that a refrigeration system with a cooling capacity of 1 ton can remove 210 kilojoules of heat from a space or substance every minute.
The correct answer is option 'A' - 210 kJ/min.
Let's break down the explanation:
1. Understanding the Concept:
Refrigeration is the process of removing heat from a space or substance to lower its temperature. The cooling capacity of a refrigeration system is measured in tons of refrigeration. One ton of refrigeration is equal to the amount of heat transfer required to freeze one ton of water in 24 hours.
2. Conversion Factors:
To determine the heat transfer rate in different units, we need to use appropriate conversion factors. Here are the conversion factors involved in this question:
- 1 ton of refrigeration = 12,000 British Thermal Units per hour (BTU/hr)
- 1 BTU/hr = 0.29307107 watts (W)
- 1 watt (W) = 1 joule per second (J/s)
- 1 joule (J) = 0.001 kilojoules (kJ)
3. Calculating the Heat Transfer Rate:
To convert the cooling capacity from tons of refrigeration to kilojoules per minute, we can use the following steps:
- Convert 1 ton of refrigeration to BTU/hr:
1 ton of refrigeration = 12,000 BTU/hr
- Convert BTU/hr to watts:
12,000 BTU/hr * 0.29307107 W/BTU = 3,517.65 W
- Convert watts to kilojoules per second (kJ/s):
3,517.65 W * 1 J/s / 1 W * 0.001 kJ/J = 3.51765 kJ/s
- Convert kilojoules per second to kilojoules per minute:
3.51765 kJ/s * 60 s/min = 210.96 kJ/min
Rounding off the answer to the nearest whole number, we get 210 kJ/min, which is the correct answer (option 'A').
To summarize, 1 ton of refrigeration implies a heat transfer rate of 210 kJ/min. This means that a refrigeration system with a cooling capacity of 1 ton can remove 210 kilojoules of heat from a space or substance every minute.
R-12 is preferred over R-22 in deep freezer because- a)It has lower operating pressure
- b)It gives higher COP
- c)It is miscible with oil over a large range of
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
R-12 is preferred over R-22 in deep freezer because
a)
It has lower operating pressure
b)
It gives higher COP
c)
It is miscible with oil over a large range of
d)
All of the above
|
|
Sagnik Choudhary answered |
R-12 or Freon 12 is used in domestic refrigerators and freezers, liquid chillers, dehumidifiers, ice makers, water coolers, water fountains and transport refrigeration. The wide range of applications of the refrigerant are due to its safe properties.
Properties of R12 and its Advantages
1) Safe properties: Refrigerant R12 is nontoxic, nonflammable, and non-explosive.
2) Suitable for wide range of operating conditions: R12 has the boiling point of -29.8°C due to which it condenses at the moderate pressures at the atmospheric temperature. This means the discharge pressure of the compressor should be only moderate. This helps in using the compressor of low compression ratio that has higher efficiency.
3) Miscibility with oil: Refrigerant R12 is miscible with the compressor oil under all the operating conditions. So, there is no problem of the oil return back to compressor.
R12 has low refrigerating effect.
The purpose of installing a flash chamber in the refrigeration circuit is to:- a)improve overall heat transfer co-efficient
- b)reduce pressure losses through the evaporator
- c)reduce the size of the evaporator by avoiding vapours going to the evaporator
- d)all of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The purpose of installing a flash chamber in the refrigeration circuit is to:
a)
improve overall heat transfer co-efficient
b)
reduce pressure losses through the evaporator
c)
reduce the size of the evaporator by avoiding vapours going to the evaporator
d)
all of the above
|
|
Anu Deshpande answered |
After Condenser condenses the refrigerant, it is passed through an expansion valve to reduce its pressure to evaporator pressure. But while doing so, some of the liquid converts to vapor again. So, to avoid vapor to enter evaporator, a flash chamber is used.
A flash chamber is a device which separates liquid from vapors. Only liquid is then passed to evaporator and the vapors will be passed to the compressor directly.
To ensure perfect pressure reduction and maximum liquid to be passed through evaporator, multiple no of flash chamber can be used in refrigeration cycle.
Flash chamber reduces the size of evaporator and it does not have any effect over COP and the system.
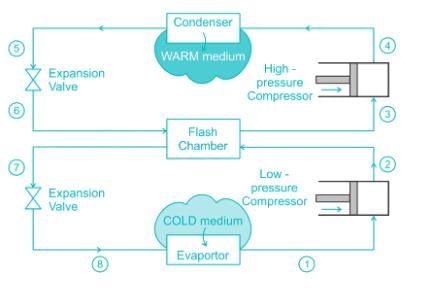
In Electrolux refrigerator ________- a)Ammonia is absorted in hydrogen
- b)Ammonia is absorbed in water
- c)Ammonia evaporates in hydrogen
- d)Hydrogen evaporates in ammonia
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In Electrolux refrigerator ________
a)
Ammonia is absorted in hydrogen
b)
Ammonia is absorbed in water
c)
Ammonia evaporates in hydrogen
d)
Hydrogen evaporates in ammonia

|
Niharika Yadav answered |
Electrolux refrigerator is a domestic refrigerator and is the best known absorption type of refrigerator.
- The ammonia liquid leaving the condenser enters the evaporator and evaporates into the hydrogen at the low temperature corresponding to its low partial pressure.
- The mixture of ammonia and hydrogen passes to the absorber into which is also admitted water from the separator.
- The water absorbs the ammonia and the hydrogen returns to the evaporator. In the absorber the ammonia therefore passes from the ammonia circuit into water circuit as ammonia in water solution.
- This strong solution passes to the generator where it is heated, and the vapor given off rises to the separator.
- The water with the vapor is separated out and a weak solution of ammonia is passed back to the absorber, thus completing the water circuit.
- The ammonia vapor rises from the separator to the condenser where it is condensed and then returned to the evaporator.
The throttling operation in a refrigeration cycle is carries out in:- a)Evaporator
- b)Discharge valve
- c)Capillary tube
- d)Expansion valve
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The throttling operation in a refrigeration cycle is carries out in:
a)
Evaporator
b)
Discharge valve
c)
Capillary tube
d)
Expansion valve
|
|
Nayanika Yadav answered |
Throttling operation in a refrigeration cycle is carried out in the Expansion Valve.
Explanation:
The expansion valve is a key component in a refrigeration cycle that controls the flow of refrigerant from the high-pressure side to the low-pressure side of the system. It is responsible for creating a pressure drop in the refrigerant, which allows it to expand and cool down.
The throttling operation in the expansion valve can be explained in the following steps:
1. Pressure reduction: The high-pressure refrigerant from the condenser enters the expansion valve. The valve restricts the flow of refrigerant, causing a significant pressure drop. This pressure reduction is necessary for the refrigerant to change from a high-pressure liquid to a low-pressure mixture of liquid and vapor.
2. Temperature drop: As the refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, it undergoes a rapid expansion due to the pressure drop. This expansion results in a decrease in the refrigerant's temperature. The refrigerant absorbs heat from its surroundings, which leads to a cooling effect.
3. Phase change: The refrigerant undergoes a phase change from a saturated liquid to a saturated vapor during the throttling process. This phase change occurs as a result of the reduced pressure and temperature drop in the expansion valve.
4. Quality control: The expansion valve also helps to regulate the quality of the refrigerant leaving the valve. It ensures that the refrigerant leaving the expansion valve is in the desired state, with the correct ratio of liquid to vapor. This is important for the proper functioning of the evaporator and the overall refrigeration cycle.
The expansion valve plays a crucial role in the refrigeration cycle by controlling the flow and pressure of the refrigerant. It allows for the efficient transfer of heat from the conditioned space to the evaporator, where the refrigerant absorbs heat and cools down the space. Without the expansion valve, the refrigeration cycle would not be able to operate effectively, and the desired cooling effect would not be achieved.
Explanation:
The expansion valve is a key component in a refrigeration cycle that controls the flow of refrigerant from the high-pressure side to the low-pressure side of the system. It is responsible for creating a pressure drop in the refrigerant, which allows it to expand and cool down.
The throttling operation in the expansion valve can be explained in the following steps:
1. Pressure reduction: The high-pressure refrigerant from the condenser enters the expansion valve. The valve restricts the flow of refrigerant, causing a significant pressure drop. This pressure reduction is necessary for the refrigerant to change from a high-pressure liquid to a low-pressure mixture of liquid and vapor.
2. Temperature drop: As the refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, it undergoes a rapid expansion due to the pressure drop. This expansion results in a decrease in the refrigerant's temperature. The refrigerant absorbs heat from its surroundings, which leads to a cooling effect.
3. Phase change: The refrigerant undergoes a phase change from a saturated liquid to a saturated vapor during the throttling process. This phase change occurs as a result of the reduced pressure and temperature drop in the expansion valve.
4. Quality control: The expansion valve also helps to regulate the quality of the refrigerant leaving the valve. It ensures that the refrigerant leaving the expansion valve is in the desired state, with the correct ratio of liquid to vapor. This is important for the proper functioning of the evaporator and the overall refrigeration cycle.
The expansion valve plays a crucial role in the refrigeration cycle by controlling the flow and pressure of the refrigerant. It allows for the efficient transfer of heat from the conditioned space to the evaporator, where the refrigerant absorbs heat and cools down the space. Without the expansion valve, the refrigeration cycle would not be able to operate effectively, and the desired cooling effect would not be achieved.
Bell – Coleman cycle is applicable to:- a)Vapour compressor refrigeration
- b)Vapor absorption refrigeration
- c)Air refrigeration
- d)All of them
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Bell – Coleman cycle is applicable to:
a)
Vapour compressor refrigeration
b)
Vapor absorption refrigeration
c)
Air refrigeration
d)
All of them
|
|
Sagarika Mukherjee answered |
Air Refrigeration System and Bell-Coleman Cycle or Reversed Brayton Cycle:
- In air refrigeration system, air is taken into the compressor from atmosphere and compressed.
- The hot compressed air is cooled in heat exchanger upto the atmospheric temperature (in ideal conditions).
- The cooled air is then expanded in an expander. The temperature of the air coming out from the expander is below the atmospheric temperature due to isentropic expansion.
- The low temperature air coming out from the expander enters into the evaporator and absorbs the heat. The cycle is repeated.
At 100% Rh, the three characteristics DBT (Dry Bulb Temperature), WBT (Wet Bulb Temperature) & DPT (Dew Point Temperature) are- a)Different
- b)Equal
- c)Any two are equal
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
At 100% Rh, the three characteristics DBT (Dry Bulb Temperature), WBT (Wet Bulb Temperature) & DPT (Dew Point Temperature) are
a)
Different
b)
Equal
c)
Any two are equal
d)
None of the above

|
Rahul Chauhan answered |
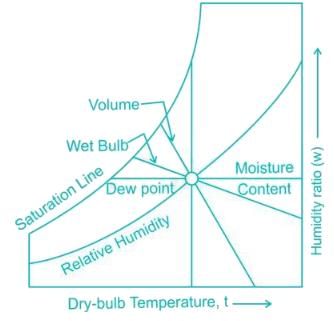
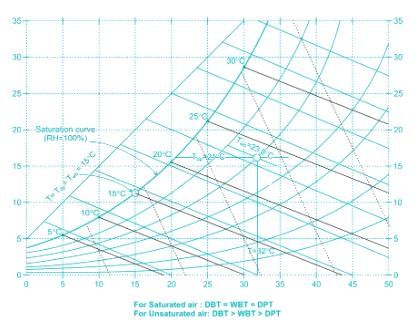
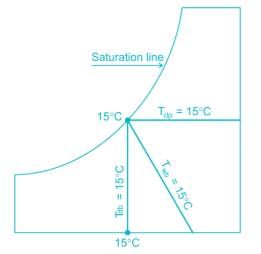
When relative humidity of the air is 100%, i.e the air is saturated, the dew point temperature (DPT) equals the wet bulb temperature (WBT), which is also equal to the dry bulb temperature.
So DBT = WBT = DPT
For unsaturated air:
DBT > WBT > DPT
Formation of frost on evaporator in refrigerator- a)Is essential for energy conservation
- b)Can be avoided by proper design
- c)Increase heat transfer rate
- d)results in loss of heat due to poor heat transfer
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Formation of frost on evaporator in refrigerator
a)
Is essential for energy conservation
b)
Can be avoided by proper design
c)
Increase heat transfer rate
d)
results in loss of heat due to poor heat transfer
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
In the evaporator working below freezing point temperature of water, frosting is a very common phenomenon. Due to frosting the ice is formed on the evaporator tubes. As ice is a bad conductor of heat this will decrease the heat transfer.
The expression 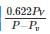 0.622PVP−Pv is used to determine
0.622PVP−Pv is used to determine- a)Relative humidity
- b)Specific humidity
- c)Degree of saturation
- d)Partial pressure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The expression 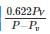 0.622PVP−Pv is used to determine
0.622PVP−Pv is used to determine
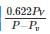 0.622PVP−Pv is used to determine
0.622PVP−Pv is used to determinea)
Relative humidity
b)
Specific humidity
c)
Degree of saturation
d)
Partial pressure
|
|
Akshat Mehta answered |
Humidity ratio/Specific humidity, w (kg/kg) of a given moist air sample is defined as the ratio of the mass of water vapour (mw) to the mass of dry air (ma) contained in the sample.
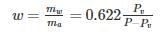
Relative humidity (ϕ):
It is defined as the ratio of partial pressure of water vapour (pv)in a mixture to the saturation pressure (ps) of pure water at the same temperature of the mixture.
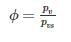
A house requires 2 × 105 kJ/h of heat for heating during winter the work done to operate heat pump is 3 × 104 kJ/h then COP will be ________- a)6.66
- b)6
- c)66.66
- d)0.66
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A house requires 2 × 105 kJ/h of heat for heating during winter the work done to operate heat pump is 3 × 104 kJ/h then COP will be ________
a)
6.66
b)
6
c)
66.66
d)
0.66
|
|
Yash Das answered |
COP of Heat Pump is defined as the ratio of heat transfer to hot reservoir to net work transfer to the heat pump.
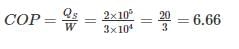
The coefficient of performance is the ratio of the refrigerant effect to the _____.A. Heat of compressionB. Work done by the compressorC. Enthalpy increase in compressor- a)Only A
- b)Only B
- c)Only C
- d)A, B and C
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The coefficient of performance is the ratio of the refrigerant effect to the _____.
A. Heat of compression
B. Work done by the compressor
C. Enthalpy increase in compressor
a)
Only A
b)
Only B
c)
Only C
d)
A, B and C
|
|
Devansh Nambiar answered |
The coefficient of performance is the ratio of heat extracted in the refrigerator to the work done on the refrigerant.
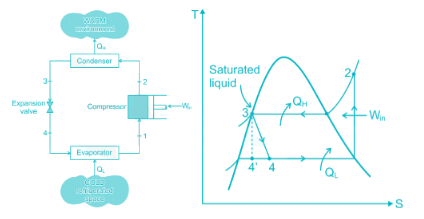
Work done by compressor, Win = QH - QL (Heat of compression) = h2 - h1 (Enthalpy increase in compressor)
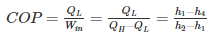
Chapter doubts & questions for Refrigeration & Air conditioning - SSC JE Mechanical Mock Test Series 2026 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Refrigeration & Air conditioning - SSC JE Mechanical Mock Test Series 2026 in English & Hindi are available as part of Mechanical Engineering exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
SSC JE Mechanical Mock Test Series 2026
3 videos|1 docs|55 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









