All Exams >
CA Foundation >
Business Economics for CA Foundation >
All Questions
All questions of Determination of National Income for CA Foundation Exam
An example of capital goods is- a)Microwave
- b)Plant
- c)Fan
- d)TV
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of capital goods is
a)
Microwave
b)
Plant
c)
Fan
d)
TV
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
Capital goods are man-made, durable items businesses use to produce goods and services. They include tools, buildings, vehicles, machinery and equipment.
Capital goods are also called durable goods, real capital, and economic capital. Some experts just refer to them as "capital." This last term is confusing because it can also mean financial capital. In accounting, capital goods are treated as fixed assets. They’re also known as “plant, property, and equipment.”
Capital goods are also called durable goods, real capital, and economic capital. Some experts just refer to them as "capital." This last term is confusing because it can also mean financial capital. In accounting, capital goods are treated as fixed assets. They’re also known as “plant, property, and equipment.”
An example of durable goods is- a)Coal
- b)Fan
- c)Milk
- d)Pepsi
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of durable goods is
a)
Coal
b)
Fan
c)
Milk
d)
Pepsi
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
Durable goods are a category of consumer products ... morethat do not need to be purchased frequently because they are made to last for a long time (usually
When will the domestic income be greater than the national income?- a)IF Net factor income earned from abroad is zero
- b)IF Net factor income earned from abroad is 1
- c)IF is negative
- d)IF Net factor income earned from abroad is positive
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When will the domestic income be greater than the national income?
a)
IF Net factor income earned from abroad is zero
b)
IF Net factor income earned from abroad is 1
c)
IF is negative
d)
IF Net factor income earned from abroad is positive
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
Gross National Income = Gross Domestic Income + Net Factor Income from Abroad
where,
Net Factor Income from Abroad = Factor Income earned from Abroad- Factor Income Paid Abroad
Thus, from here we can derive that Domestic Factor Income will be greater than the National Income when Factor income paid Abroad is more than Factor income earned from Abroad.
Net Factor Income from Abroad = Factor Income earned from Abroad- Factor Income Paid Abroad
Thus, from here we can derive that Domestic Factor Income will be greater than the National Income when Factor income paid Abroad is more than Factor income earned from Abroad.
An example of consumption goods is- a)plant
- b)Coal
- c)machine
- d)Fruits
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of consumption goods is
a)
plant
b)
Coal
c)
machine
d)
Fruits

|
Sai Mishra answered |
Goods which are consumed for their own sake to satisfy current wants of consumers directly are called consumption (or consumer) goods.
Capital goods are fixed assets of producers which are repeatedly used in production of other goods and services. Alternatively durable goods which are bought for producing other goods but not for meeting immediate needs of the consumer are called capital goods.
In final goods- a)Value is added
- b)Values is not added
- c)Value cannot be added anymore
- d)Value should not be added
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In final goods
a)
Value is added
b)
Values is not added
c)
Value cannot be added anymore
d)
Value should not be added

|
Sakshi Agrawal answered |
Because it is used for immediate consumption .
it does not required any further processing
it does not required any further processing
State which one of the following is true.- a)Gross domestic capital formation is always greater than gross fixed capital formation.
- b)Nominal GDP can never be less that real GDP
- c)Capital formation is a flow
- d)Bread is always a consumer good.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
State which one of the following is true.
a)
Gross domestic capital formation is always greater than gross fixed capital formation.
b)
Nominal GDP can never be less that real GDP
c)
Capital formation is a flow
d)
Bread is always a consumer good.
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
True, because it is measured over a period of time.
Which of the following in an example of macro economics- a)Inflation
- b)Consumer’s equilibrium
- c)Price determination
- d)Producer’s equilibrium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following in an example of macro economics
a)
Inflation
b)
Consumer’s equilibrium
c)
Price determination
d)
Producer’s equilibrium
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
Inflation means roaming of money that goes from one hand to other as macro economics deals with whole economy the money in this form passes from one hand to another.
An example of transfer payments is- a)Old age pension
- b)Retirement pension
- c)Free meals in the company canteen
- d)Employers’ contribution for social security
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of transfer payments is
a)
Old age pension
b)
Retirement pension
c)
Free meals in the company canteen
d)
Employers’ contribution for social security
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
Transfer payments are unilateral ( one sided payments ) no corresponding flow of goods and services for example: donation, old age pension, unemployment allowance etc
Can the net factor income earned from abroad be negative?- a)Never
- b)No
- c)Can’t say
- d)Yes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Can the net factor income earned from abroad be negative?
a)
Never
b)
No
c)
Can’t say
d)
Yes
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
Net factor income earned from abroad which is used... more to differentiate between national income and domestic income.Alternatively NFIA is the difference between factor incomes
Can the net indirect taxes be negative?- a)Yes
- b)Never
- c)Can’t say
- d)No
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Can the net indirect taxes be negative?
a)
Yes
b)
Never
c)
Can’t say
d)
No
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
True: It can happen when NFIA is negative i.e., factor income paid to abroad is more than factor income received from abroad.
Final goods are those- a)Which are for resale
- b)Which are for long term use
- c)Which capital can buy
- d)Which are for final consumption
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Final goods are those
a)
Which are for resale
b)
Which are for long term use
c)
Which capital can buy
d)
Which are for final consumption

|
Abhishek Choudhary answered |
Question hi answer hai iska.....'Final goods' -Means No Further production is required....it is ready for Consumption like-,Milk is a final good if it is purchased to drink,Bicycle that is sold to consumer is a final good or consumer goods.
This a MCQ (Multiple Choice Question) based practice test of Chapter 2 - National Income Accounting of Economics of Class XII (12) for the quick revision/preparation of School Board examinationsQ Explain the meaning of non-market activities- a)Involuntary
- b)Non marketable
- c)Economic
- d)Production
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
This a MCQ (Multiple Choice Question) based practice test of Chapter 2 - National Income Accounting of Economics of Class XII (12) for the quick revision/preparation of School Board examinations
Q Explain the meaning of non-market activities
a)
Involuntary
b)
Non marketable
c)
Economic
d)
Production
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Non market Activities -
1) Non market activities are those activities primarily undertaken for the purpose of self-consumption. These activities don't give profit as they are for self consumption.
2) The output of the non market activities is neither for sale in the market nor for earning profit. These activities can be for consumption and processing of primary products for one's own use.
3) Example : A farmer cultivates primarily for himself and his family and not for earning profit.
Can the change in inventories be in negative?- a)No
- b)Yes
- c)Can’t say
- d)Never
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Can the change in inventories be in negative?
a)
No
b)
Yes
c)
Can’t say
d)
Never
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
An increase in inventory indicates that a company ... morehas purchased more goods than it has sold. ... In other words, you
Real GNP is same as- a)Nominal GNP
- b)GNP at current prices
- c)GNP at constant prices
- d)GNP less Net factor income from abroad
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Real GNP is same as
a)
Nominal GNP
b)
GNP at current prices
c)
GNP at constant prices
d)
GNP less Net factor income from abroad

|
Meera Rane answered |
Explanation:
- GNP stands for Gross National Product which is the total value of goods and services produced by a country in a given period of time.
- Real GNP refers to the GNP that has been adjusted for inflation, and it is measured in constant prices.
- Nominal GNP refers to the GNP that has not been adjusted for inflation, and it is measured in current prices.
- Net factor income from abroad refers to the income received by a country from abroad minus the income paid by the country to foreign entities.
- Therefore, Real GNP is the GNP that has been adjusted for inflation and is measured in constant prices.
- Real GNP is a more accurate measure of a country's economic performance than Nominal GNP because it takes into account the effects of inflation.
- Real GNP can be calculated by using a price index such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI) or the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) deflator to adjust Nominal GNP for inflation.
Can the gross domestic product be greater than the gross national product?- a)No
- b)Never
- c)Yes
- d)Can’t say
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Can the gross domestic product be greater than the gross national product?
a)
No
b)
Never
c)
Yes
d)
Can’t say
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
Yes, it is possible for GDP to be higher than GNP and it is also possible for GNP to be higher than GDP. GNP greater than GDP is best for a country because it means that the population of that country will have a greater total income (i.e. total output) than if GDP was greater than GNP.
An example of semi durable goods is- a)TV
- b)Fan
- c)Crockery
- d)Milk
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of semi durable goods is
a)
TV
b)
Fan
c)
Crockery
d)
Milk

|
Samiksha Nair answered |
Well to understand this question at frst we hve to... more understand what is meant by
In a two sector circular flow model the two sectors are- a)Firm and household
- b)Government and household
- c)Government and financial system
- d)Firm and government
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a two sector circular flow model the two sectors are
a)
Firm and household
b)
Government and household
c)
Government and financial system
d)
Firm and government

|
Cooking With Keerat answered |
As households are the provider of Fops(factors of production) and firms i.e producers in return provide services and final products..They both are complimentary to each others...Households spend their money on goods and services rendered by producers/firms and producers spend on FOPs like land,labour,capital,entrepreneurship skills in change of wages,rent,interest and profit
This is two sector economy..where as three and four sector economy has govt.(G) and foreign exhange(X-M)
hope this will help you
This is two sector economy..where as three and four sector economy has govt.(G) and foreign exhange(X-M)
hope this will help you
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:The Centre on Saturday increased the budgetary allocation for the environment ministry from last fiscal by nearly five percent for 2020-21 with no change in the amount allotted to pollution abatement and climate change action plan.Union Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, allocated ₹ 3,100 crore for the ministry out of which ₹ 460 crore were allotted to control pollution, which is the same as the money it received in the last budget.Control of pollution has been conceptualized to provide financial assistance to Pollution Control Boards/Committees and funding to National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).Similarly, budget for pollution abatement, which was cut by 50 percent last year from 2018-19, remained unchanged at ₹ 10 crore.The minister also announced that states, which are formulating and implementing plans for ensuring cleaner air in cities above one million population should be encouraged.Real GDP and Welfare are ___________ related with each other.- a)Directly
- b)Indirectly
- c)Inversely
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
The Centre on Saturday increased the budgetary allocation for the environment ministry from last fiscal by nearly five percent for 2020-21 with no change in the amount allotted to pollution abatement and climate change action plan.
Union Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, allocated ₹ 3,100 crore for the ministry out of which ₹ 460 crore were allotted to control pollution, which is the same as the money it received in the last budget.
Control of pollution has been conceptualized to provide financial assistance to Pollution Control Boards/Committees and funding to National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).
Similarly, budget for pollution abatement, which was cut by 50 percent last year from 2018-19, remained unchanged at ₹ 10 crore.
The minister also announced that states, which are formulating and implementing plans for ensuring cleaner air in cities above one million population should be encouraged.
Real GDP and Welfare are ___________ related with each other.
a)
Directly
b)
Indirectly
c)
Inversely
d)
None of the above
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Real GDP and Welfare are related with each other as rise in the real GDP leads to rise in the welfare.
Nominal GNP is same as- a)Real GNP
- b)GNP less Net factor income from abroad
- c)GNP at constant prices
- d)GNP at current prices
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Nominal GNP is same as
a)
Real GNP
b)
GNP less Net factor income from abroad
c)
GNP at constant prices
d)
GNP at current prices
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
The answer is a.
GNP Deflator: It is clear that nominal GNP usually exceeds real GNP because of inflation. Greater the difference between nominal and real GNP, greater is the inflation. It may happen that GNP data at constant prices may not be available in the economy.
Real flow is the flow of- a)Money
- b)Goods and services
- c)Services only
- d)Goods only
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Real flow is the flow of
a)
Money
b)
Goods and services
c)
Services only
d)
Goods only

|
Shagan Chahal answered |
Real flows refer to the flow of the actual goods or services, while money flows refer to the payments for the services (wages, for example) or consumption payments.
State which one of the following is true .- a)Royalty is not a factor income
- b)Rent is a factor income
- c)Subsidies is a factor payment
- d)Tax is a factor income
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
State which one of the following is true .
a)
Royalty is not a factor income
b)
Rent is a factor income
c)
Subsidies is a factor payment
d)
Tax is a factor income

|
Gopal Sengupta answered |
Explanation:
Factor income is the income that is earned through factors of production such as land, labor, capital, and enterprise. Here, we need to identify the factor income among the given options.
a) Royalty: Royalty is the amount paid to the owner of an asset for its use. It is not a factor income as it is not earned through any factor of production.
b) Rent: Rent is the payment made to the owner of land or any other asset for its use. It is a factor income as it is earned through land, which is a factor of production.
c) Subsidies: Subsidies are the financial assistance provided by the government to promote an industry or a product. It is not a factor payment as it is not earned through any factor of production.
d) Tax: Tax is a financial charge imposed by the government on individuals or businesses for the income earned or goods and services consumed. It is not a factor income as it is not earned through any factor of production.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B, Rent is a factor income.
Factor income is the income that is earned through factors of production such as land, labor, capital, and enterprise. Here, we need to identify the factor income among the given options.
a) Royalty: Royalty is the amount paid to the owner of an asset for its use. It is not a factor income as it is not earned through any factor of production.
b) Rent: Rent is the payment made to the owner of land or any other asset for its use. It is a factor income as it is earned through land, which is a factor of production.
c) Subsidies: Subsidies are the financial assistance provided by the government to promote an industry or a product. It is not a factor payment as it is not earned through any factor of production.
d) Tax: Tax is a financial charge imposed by the government on individuals or businesses for the income earned or goods and services consumed. It is not a factor income as it is not earned through any factor of production.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B, Rent is a factor income.
Money flow is the flow of- a)Factor payments
- b)Services only
- c)Goods only
- d)Goods and services only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Money flow is the flow of
a)
Factor payments
b)
Services only
c)
Goods only
d)
Goods and services only
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
Former flow happens in factor market while latter flow happens in goods market. Money flow refers to the flow of factor payments from firms to households and payment for goods and services by households to firms.
In intermediate goods- a)Values are already added
- b)Value is yet to be added
- c)Value should not be added
- d)Value cannot be added anymore
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In intermediate goods
a)
Values are already added
b)
Value is yet to be added
c)
Value should not be added
d)
Value cannot be added anymore
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
Intermediate goods or producer goods or semi-finished products are goods , such as partly finished goods, used as inputs in the production of other goods including final goods. A firm may make and then use intermediate goods, or make and then sell, or buy then use them.
Microeconomics is different from macroeconomic s as- a)Microeconomics deals with prices only
- b)Microeconomics deals with government’s decisions
- c)Microeconomics deals with economic behaviour
- d)Microeconomics deals with individual behaviour
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Microeconomics is different from macroeconomic s as
a)
Microeconomics deals with prices only
b)
Microeconomics deals with government’s decisions
c)
Microeconomics deals with economic behaviour
d)
Microeconomics deals with individual behaviour

|
Swara Saha answered |
Policies and their impact on the economyc)Microeconomics focuses on individual and small group behavior and decision-making related to the allocation of resourcesd)Microeconomics focuses on overall economic indicators such as GDP and inflation rates.
Answer: c) Microeconomics focuses on individual and small group behavior and decision-making related to the allocation of resources.
Explanation: Microeconomics is a branch of economics that examines the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources. It focuses on the study of small economic units such as individuals, households, and firms. In contrast, macroeconomics deals with the overall performance of the economy and its key indicators such as GDP, inflation, and unemployment.
Answer: c) Microeconomics focuses on individual and small group behavior and decision-making related to the allocation of resources.
Explanation: Microeconomics is a branch of economics that examines the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources. It focuses on the study of small economic units such as individuals, households, and firms. In contrast, macroeconomics deals with the overall performance of the economy and its key indicators such as GDP, inflation, and unemployment.
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:The country’s real gross domestic product (GDP) is likely to expand by 11 percent in the next financial year due to a faster economic recovery and on a low base, says a report. The report by domestic rating agency Brickwork Ratings said economic activities are slowly reaching Pre-COVID levels following the relaxation of the lockdown, except in sectors that remain affected by social distancing norms.“With progress in developing an effective vaccine for COVID-19 and signals of faster-than-expected recovery in the domestic economy, and also supported by a low base, we expect the real GDP to grow at 11 percent in F/Y 22, from the estimated contraction of 7 percent to 7.5 percent in F/Y 21,” the agency said.According to the first advance estimates of national income released by the National Statistical Office (NSO), the country’s GDP is estimated to contract by a record 7.7 percent during the current financial year.What will be the growth rate of GDP according to the NSO? - a)– 7.7%
- b)+7.7%
- c)+11%
- d)– 7.5%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
The country’s real gross domestic product (GDP) is likely to expand by 11 percent in the next financial year due to a faster economic recovery and on a low base, says a report. The report by domestic rating agency Brickwork Ratings said economic activities are slowly reaching Pre-COVID levels following the relaxation of the lockdown, except in sectors that remain affected by social distancing norms.
“With progress in developing an effective vaccine for COVID-19 and signals of faster-than-expected recovery in the domestic economy, and also supported by a low base, we expect the real GDP to grow at 11 percent in F/Y 22, from the estimated contraction of 7 percent to 7.5 percent in F/Y 21,” the agency said.
According to the first advance estimates of national income released by the National Statistical Office (NSO), the country’s GDP is estimated to contract by a record 7.7 percent during the current financial year.
What will be the growth rate of GDP according to the NSO?
a)
– 7.7%
b)
+7.7%
c)
+11%
d)
– 7.5%

|
Navya Sengupta answered |
Explanation:
Growth Rate of GDP According to NSO:
- The National Statistical Office (NSO) has estimated that the country's GDP will contract by a record 7.7% during the current financial year.
This indicates that the GDP is expected to shrink by 7.7% as per the first advance estimates released by the NSO. The negative growth rate suggests a contraction in the economy's overall output and performance during the specified period.
Growth Rate of GDP According to NSO:
- The National Statistical Office (NSO) has estimated that the country's GDP will contract by a record 7.7% during the current financial year.
This indicates that the GDP is expected to shrink by 7.7% as per the first advance estimates released by the NSO. The negative growth rate suggests a contraction in the economy's overall output and performance during the specified period.
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:The Centre on Saturday increased the budgetary allocation for the environment ministry from last fiscal by nearly five percent for 2020-21 with no change in the amount allotted to pollution abatement and climate change action plan.Union Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, allocated ₹ 3,100 crore for the ministry out of which ₹ 460 crore were allotted to control pollution, which is the same as the money it received in the last budget.Control of pollution has been conceptualized to provide financial assistance to Pollution Control Boards/Committees and funding to National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).Similarly, budget for pollution abatement, which was cut by 50 percent last year from 2018-19, remained unchanged at ₹ 10 crore.The minister also announced that states, which are formulating and implementing plans for ensuring cleaner air in cities above one million population should be encouraged.Why is the policy implemented?- a)To ensure clear air
- b)To ensure clear water
- c)To ensure clean roads
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
The Centre on Saturday increased the budgetary allocation for the environment ministry from last fiscal by nearly five percent for 2020-21 with no change in the amount allotted to pollution abatement and climate change action plan.
Union Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, allocated ₹ 3,100 crore for the ministry out of which ₹ 460 crore were allotted to control pollution, which is the same as the money it received in the last budget.
Control of pollution has been conceptualized to provide financial assistance to Pollution Control Boards/Committees and funding to National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).
Similarly, budget for pollution abatement, which was cut by 50 percent last year from 2018-19, remained unchanged at ₹ 10 crore.
The minister also announced that states, which are formulating and implementing plans for ensuring cleaner air in cities above one million population should be encouraged.
Why is the policy implemented?
a)
To ensure clear air
b)
To ensure clear water
c)
To ensure clean roads
d)
All of the above
|
|
Priyanka Khatri answered |
It helps to identify how, when, and by whom implementation will be assessed. Monitoring of implementation keeps everyone involved aware of any possible barriers as well as any intended and unintended impacts of the work. After implementation, resources and other supports from stakeholders may decrease.
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:Circular Income Flow in a Two Sector Economy: In the figure given we can see that upper loop shows the resources such as land, capital and entrepreneurial ability flow from households to firms in the direction shown by the arrow direction.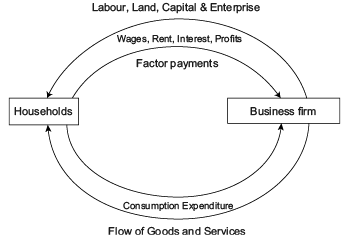 The money flows from firms to the households as factor payments in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits, shown by the arrow direction.The lower part of the figure shows the flow of money from households to firms in the form of consumption expenditure done by the households to purchase the goods and services produced by the firms, making the flow of goods and services from firms to households.Thus, we see that money flows from business firms to households as factor payments and then it flows from households to firms. Thus, there is, in fact, a circular flow of money or income. This is how the economy functions.Which of the following is not an assumption of a two sector model of Circular Flow of Income?
The money flows from firms to the households as factor payments in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits, shown by the arrow direction.The lower part of the figure shows the flow of money from households to firms in the form of consumption expenditure done by the households to purchase the goods and services produced by the firms, making the flow of goods and services from firms to households.Thus, we see that money flows from business firms to households as factor payments and then it flows from households to firms. Thus, there is, in fact, a circular flow of money or income. This is how the economy functions.Which of the following is not an assumption of a two sector model of Circular Flow of Income?- a)Domestic economy comprises only 2 sectors, the producers and the households.
- b)The households spend their entire income, so that there is no saving.
- c)Domestic economy is an open economy (no exports and imports).
- d)There is no government in the economy.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
Circular Income Flow in a Two Sector Economy: In the figure given we can see that upper loop shows the resources such as land, capital and entrepreneurial ability flow from households to firms in the direction shown by the arrow direction.

The money flows from firms to the households as factor payments in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits, shown by the arrow direction.
The lower part of the figure shows the flow of money from households to firms in the form of consumption expenditure done by the households to purchase the goods and services produced by the firms, making the flow of goods and services from firms to households.
Thus, we see that money flows from business firms to households as factor payments and then it flows from households to firms. Thus, there is, in fact, a circular flow of money or income. This is how the economy functions.
Which of the following is not an assumption of a two sector model of Circular Flow of Income?
a)
Domestic economy comprises only 2 sectors, the producers and the households.
b)
The households spend their entire income, so that there is no saving.
c)
Domestic economy is an open economy (no exports and imports).
d)
There is no government in the economy.
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
The two sector economy has the following assumptions:
- There are only two sectors in the economy; household sector and business sector.
- No government interventions over the economic activities.
- Business sectors do not carry out any import or export activities, creating a closed economy.
Final goods are those goods- a)Which are used either for final consumption or for investment
- b)Which are used for final consumption
- c)which are used for final production
- d)Which are used for investment
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Final goods are those goods
a)
Which are used either for final consumption or for investment
b)
Which are used for final consumption
c)
which are used for final production
d)
Which are used for investment
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Consumer goods are ultimately consumed, rather than used in the production of another good. For example, a microwave oven or a bicycle that is sold to a consumer is a final good or consumer good, but the components that are sold to be used in those goods are intermediate goods.
An example of non durable goods is- a)TV
- b)Milk
- c)Microwave
- d)None of These
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of non durable goods is
a)
TV
b)
Milk
c)
Microwave
d)
None of These
|
|
Amrutha Roy answered |
Milk and Bread are examples of Non-durable good. Non-durable gods are those goods which are used-up in a single act of consumption. Bread and milk are used-up in a single act of consumption. The same milk or bread cannot be used again.
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:The country’s real gross domestic product (GDP) is likely to expand by 11 percent in the next financial year due to a faster economic recovery and on a low base, says a report. The report by domestic rating agency Brickwork Ratings said economic activities are slowly reaching Pre-COVID levels following the relaxation of the lockdown, except in sectors that remain affected by social distancing norms.“With progress in developing an effective vaccine for COVID-19 and signals of faster-than-expected recovery in the domestic economy, and also supported by a low base, we expect the real GDP to grow at 11 percent in F/Y 22, from the estimated contraction of 7 percent to 7.5 percent in F/Y 21,” the agency said.According to the first advance estimates of national income released by the National Statistical Office (NSO), the country’s GDP is estimated to contract by a record 7.7 percent during the current financial year.Real GDP is when the goods and services are produced by all producing units in the domestic territory of a country during an accounting year and valued at ___________ prices or constant price.- a)base year's
- b)current year's
- c)both (A) and (B)
- d)neither (A) nor (B)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
The country’s real gross domestic product (GDP) is likely to expand by 11 percent in the next financial year due to a faster economic recovery and on a low base, says a report. The report by domestic rating agency Brickwork Ratings said economic activities are slowly reaching Pre-COVID levels following the relaxation of the lockdown, except in sectors that remain affected by social distancing norms.
“With progress in developing an effective vaccine for COVID-19 and signals of faster-than-expected recovery in the domestic economy, and also supported by a low base, we expect the real GDP to grow at 11 percent in F/Y 22, from the estimated contraction of 7 percent to 7.5 percent in F/Y 21,” the agency said.
According to the first advance estimates of national income released by the National Statistical Office (NSO), the country’s GDP is estimated to contract by a record 7.7 percent during the current financial year.
Real GDP is when the goods and services are produced by all producing units in the domestic territory of a country during an accounting year and valued at ___________ prices or constant price.
a)
base year's
b)
current year's
c)
both (A) and (B)
d)
neither (A) nor (B)
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Real GDP is the value of final goods and services produced in a given year expressed in terms of the prices in a base year. To calculate Real GDP, we use base year prices and multiply them by current year quantities for all the goods and services produced in an economy.
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:The Centre on Saturday increased the budgetary allocation for the environment ministry from last fiscal by nearly five percent for 2020-21 with no change in the amount allotted to pollution abatement and climate change action plan.Union Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, allocated ₹ 3,100 crore for the ministry out of which ₹ 460 crore were allotted to control pollution, which is the same as the money it received in the last budget.Control of pollution has been conceptualized to provide financial assistance to Pollution Control Boards/Committees and funding to National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).Similarly, budget for pollution abatement, which was cut by 50 percent last year from 2018-19, remained unchanged at ₹ 10 crore.The minister also announced that states, which are formulating and implementing plans for ensuring cleaner air in cities above one million population should be encouraged.What type of externality will the increase in budget allocation create?- a)Negative
- b)Positive
- c)Neutral
- d)Can’t be said
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
The Centre on Saturday increased the budgetary allocation for the environment ministry from last fiscal by nearly five percent for 2020-21 with no change in the amount allotted to pollution abatement and climate change action plan.
Union Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, allocated ₹ 3,100 crore for the ministry out of which ₹ 460 crore were allotted to control pollution, which is the same as the money it received in the last budget.
Control of pollution has been conceptualized to provide financial assistance to Pollution Control Boards/Committees and funding to National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).
Similarly, budget for pollution abatement, which was cut by 50 percent last year from 2018-19, remained unchanged at ₹ 10 crore.
The minister also announced that states, which are formulating and implementing plans for ensuring cleaner air in cities above one million population should be encouraged.
What type of externality will the increase in budget allocation create?
a)
Negative
b)
Positive
c)
Neutral
d)
Can’t be said
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
Positive externalities refer to positive impact of an economic activity on the others without involving any price.
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:The country’s real gross domestic product (GDP) is likely to expand by 11 percent in the next financial year due to a faster economic recovery and on a low base, says a report. The report by domestic rating agency Brickwork Ratings said economic activities are slowly reaching Pre-COVID levels following the relaxation of the lockdown, except in sectors that remain affected by social distancing norms.“With progress in developing an effective vaccine for COVID-19 and signals of faster-than-expected recovery in the domestic economy, and also supported by a low base, we expect the real GDP to grow at 11 percent in F/Y 22, from the estimated contraction of 7 percent to 7.5 percent in F/Y 21,” the agency said.According to the first advance estimates of national income released by the National Statistical Office (NSO), the country’s GDP is estimated to contract by a record 7.7 percent during the current financial year.Assertion (A): Real GDP is the true indicator of the growth of the economy.Reason (R): Real GDP is nominal GDP adjusted for inflation used to measure the actual growth of production.Select the correct alternative from the following: - a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
The country’s real gross domestic product (GDP) is likely to expand by 11 percent in the next financial year due to a faster economic recovery and on a low base, says a report. The report by domestic rating agency Brickwork Ratings said economic activities are slowly reaching Pre-COVID levels following the relaxation of the lockdown, except in sectors that remain affected by social distancing norms.
“With progress in developing an effective vaccine for COVID-19 and signals of faster-than-expected recovery in the domestic economy, and also supported by a low base, we expect the real GDP to grow at 11 percent in F/Y 22, from the estimated contraction of 7 percent to 7.5 percent in F/Y 21,” the agency said.
According to the first advance estimates of national income released by the National Statistical Office (NSO), the country’s GDP is estimated to contract by a record 7.7 percent during the current financial year.
Assertion (A): Real GDP is the true indicator of the growth of the economy.
Reason (R): Real GDP is nominal GDP adjusted for inflation used to measure the actual growth of production.
Select the correct alternative from the following:
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Nominal GDP is the total value of all goods and services produced in a given time period, usually quarterly or annually. Real GDP is nominal GDP adjusted for inflation. Real GDP is used to measure the actual growth of production without any distorting effects from inflation.
An example of factor payments is- a)Retirement pension
- b)Employers’ contribution for social security
- c)Old age pension
- d)Unemployees’ contribution for social security
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of factor payments is
a)
Retirement pension
b)
Employers’ contribution for social security
c)
Old age pension
d)
Unemployees’ contribution for social security
|
|
Saranya Dasgupta answered |
' wages
c)Corporate profits
d)Interest on loans
b)Employers' wages are an example of factor payments. Factor payments refer to payments made to the factors of production, which include labor, capital, land, and entrepreneurship. Employers' wages are payments made to the factor of production, labor, for their contribution to the production process.
c)Corporate profits
d)Interest on loans
b)Employers' wages are an example of factor payments. Factor payments refer to payments made to the factors of production, which include labor, capital, land, and entrepreneurship. Employers' wages are payments made to the factor of production, labor, for their contribution to the production process.
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:The Centre on Saturday increased the budgetary allocation for the environment ministry from last fiscal by nearly five percent for 2020-21 with no change in the amount allotted to pollution abatement and climate change action plan.Union Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, allocated ₹ 3,100 crore for the ministry out of which ₹ 460 crore were allotted to control pollution, which is the same as the money it received in the last budget.Control of pollution has been conceptualized to provide financial assistance to Pollution Control Boards/Committees and funding to National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).Similarly, budget for pollution abatement, which was cut by 50 percent last year from 2018-19, remained unchanged at ₹ 10 crore.The minister also announced that states, which are formulating and implementing plans for ensuring cleaner air in cities above one million population should be encouraged.___________ means material well-being of the people. - a)Externality
- b)Welfare
- c)Economy
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
The Centre on Saturday increased the budgetary allocation for the environment ministry from last fiscal by nearly five percent for 2020-21 with no change in the amount allotted to pollution abatement and climate change action plan.
Union Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, allocated ₹ 3,100 crore for the ministry out of which ₹ 460 crore were allotted to control pollution, which is the same as the money it received in the last budget.
Control of pollution has been conceptualized to provide financial assistance to Pollution Control Boards/Committees and funding to National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).
Similarly, budget for pollution abatement, which was cut by 50 percent last year from 2018-19, remained unchanged at ₹ 10 crore.
The minister also announced that states, which are formulating and implementing plans for ensuring cleaner air in cities above one million population should be encouraged.
___________ means material well-being of the people.
a)
Externality
b)
Welfare
c)
Economy
d)
None of the above

|
Anushka Desai answered |
Understanding Material Well-Being
Material well-being refers to the economic condition and overall quality of life of individuals within a society. It encompasses the availability of resources, access to basic needs, and the general prosperity of the population.
Why Option 'B' (Welfare) is Correct
- Definition of Welfare: Welfare specifically pertains to the well-being and prosperity of individuals and communities. It includes factors such as income, health, education, and access to resources that enhance the quality of life.
- Context of the Case: In the context of the budgetary allocation for the environment ministry, the emphasis on controlling pollution and promoting cleaner air directly impacts the welfare of citizens. Cleaner environments lead to better health outcomes, improved living conditions, and overall enhanced quality of life.
- Contrast with Other Options:
- Externality: This term refers to the unintended side effects of economic activities on third parties. While related to welfare, it does not directly define material well-being.
- Economy: This term describes the system of production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services but does not specifically denote the well-being of individuals.
- None of the Above: This option is incorrect because welfare accurately captures the essence of material well-being.
Conclusion
In summary, welfare is the most appropriate term that encapsulates the concept of material well-being, especially in the context of governmental policies aimed at improving the living conditions of the populace.
Material well-being refers to the economic condition and overall quality of life of individuals within a society. It encompasses the availability of resources, access to basic needs, and the general prosperity of the population.
Why Option 'B' (Welfare) is Correct
- Definition of Welfare: Welfare specifically pertains to the well-being and prosperity of individuals and communities. It includes factors such as income, health, education, and access to resources that enhance the quality of life.
- Context of the Case: In the context of the budgetary allocation for the environment ministry, the emphasis on controlling pollution and promoting cleaner air directly impacts the welfare of citizens. Cleaner environments lead to better health outcomes, improved living conditions, and overall enhanced quality of life.
- Contrast with Other Options:
- Externality: This term refers to the unintended side effects of economic activities on third parties. While related to welfare, it does not directly define material well-being.
- Economy: This term describes the system of production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services but does not specifically denote the well-being of individuals.
- None of the Above: This option is incorrect because welfare accurately captures the essence of material well-being.
Conclusion
In summary, welfare is the most appropriate term that encapsulates the concept of material well-being, especially in the context of governmental policies aimed at improving the living conditions of the populace.
In a three sector circular flow model the three sectors are- a)Government and financial system & firm
- b)Firm and government & abroad
- c)Firm and household & government
- d)Government and household & financial system
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a three sector circular flow model the three sectors are
a)
Government and financial system & firm
b)
Firm and government & abroad
c)
Firm and household & government
d)
Government and household & financial system
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
B)Households and firms
c)International sector or rest of the world
c)International sector or rest of the world
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:The country’s real gross domestic product (GDP) is likely to expand by 11 percent in the next financial year due to a faster economic recovery and on a low base, says a report. The report by domestic rating agency Brickwork Ratings said economic activities are slowly reaching Pre-COVID levels following the relaxation of the lockdown, except in sectors that remain affected by social distancing norms.“With progress in developing an effective vaccine for COVID-19 and signals of faster-than-expected recovery in the domestic economy, and also supported by a low base, we expect the real GDP to grow at 11 percent in F/Y 22, from the estimated contraction of 7 percent to 7.5 percent in F/Y 21,” the agency said.According to the first advance estimates of national income released by the National Statistical Office (NSO), the country’s GDP is estimated to contract by a record 7.7 percent during the current financial year.Choose one of the correct alternatives given below:Assertion (A): The country's real gross domestic product is likely to expand.Reason (R): Some sectors remain affected by social distancing norms.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
The country’s real gross domestic product (GDP) is likely to expand by 11 percent in the next financial year due to a faster economic recovery and on a low base, says a report. The report by domestic rating agency Brickwork Ratings said economic activities are slowly reaching Pre-COVID levels following the relaxation of the lockdown, except in sectors that remain affected by social distancing norms.
“With progress in developing an effective vaccine for COVID-19 and signals of faster-than-expected recovery in the domestic economy, and also supported by a low base, we expect the real GDP to grow at 11 percent in F/Y 22, from the estimated contraction of 7 percent to 7.5 percent in F/Y 21,” the agency said.
According to the first advance estimates of national income released by the National Statistical Office (NSO), the country’s GDP is estimated to contract by a record 7.7 percent during the current financial year.
Choose one of the correct alternatives given below:
Assertion (A): The country's real gross domestic product is likely to expand.
Reason (R): Some sectors remain affected by social distancing norms.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
The country's real gross domestic product is likely to expand due to a faster economic recovery following the relaxation of the lockdown.
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:Circular Income Flow in a Two Sector Economy: In the figure given we can see that upper loop shows the resources such as land, capital and entrepreneurial ability flow from households to firms in the direction shown by the arrow direction.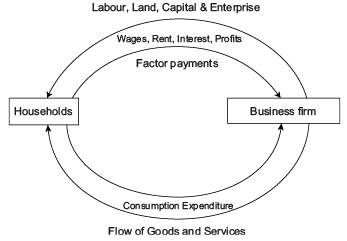 The money flows from firms to the households as factor payments in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits, shown by the arrow direction.The lower part of the figure shows the flow of money from households to firms in the form of consumption expenditure done by the households to purchase the goods and services produced by the firms, making the flow of goods and services from firms to households.Thus, we see that money flows from business firms to households as factor payments and then it flows from households to firms. Thus, there is, in fact, a circular flow of money or income. This is how the economy functions.Money Flows from __________ to ____________ as factor payments.
The money flows from firms to the households as factor payments in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits, shown by the arrow direction.The lower part of the figure shows the flow of money from households to firms in the form of consumption expenditure done by the households to purchase the goods and services produced by the firms, making the flow of goods and services from firms to households.Thus, we see that money flows from business firms to households as factor payments and then it flows from households to firms. Thus, there is, in fact, a circular flow of money or income. This is how the economy functions.Money Flows from __________ to ____________ as factor payments.- a)Firms, households
- b)Households, firms
- c)Government, firms
- d)Households, government
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
Circular Income Flow in a Two Sector Economy: In the figure given we can see that upper loop shows the resources such as land, capital and entrepreneurial ability flow from households to firms in the direction shown by the arrow direction.

The money flows from firms to the households as factor payments in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits, shown by the arrow direction.
The lower part of the figure shows the flow of money from households to firms in the form of consumption expenditure done by the households to purchase the goods and services produced by the firms, making the flow of goods and services from firms to households.
Thus, we see that money flows from business firms to households as factor payments and then it flows from households to firms. Thus, there is, in fact, a circular flow of money or income. This is how the economy functions.
Money Flows from __________ to ____________ as factor payments.
a)
Firms, households
b)
Households, firms
c)
Government, firms
d)
Households, government
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Firms: Households own all the factors of production: land, labor, capital. These factors of production are sold to the firms to produce goods and services through factor markets.
Household: Households own all the factors of production: land, labor, capital. These factors of production are sold to the firms to produce goods and services through factor markets.
What must be added to domestic factor income to obtain national income?- a)Net factor income earned from abroad
- b)Net taxes earned from abroad
- c)Net factor interest earned from abroad
- d)Net factor retained earnings from abroad
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What must be added to domestic factor income to obtain national income?
a)
Net factor income earned from abroad
b)
Net taxes earned from abroad
c)
Net factor interest earned from abroad
d)
Net factor retained earnings from abroad
|
|
Naveen Kulkarni answered |
The Relationship Between Domestic Factor Income and National Income
To understand the relationship between domestic factor income and national income, we need to first define these terms.
Domestic Factor Income: Domestic factor income refers to the income earned by domestic factors of production, such as labor and capital, within a country's borders. It includes wages, salaries, rent, and profits earned by individuals and businesses within the domestic economy.
National Income: National income, on the other hand, is the total income earned by all factors of production, both domestic and foreign, within a country's borders. It includes domestic factor income as well as net factor income from abroad.
Net Factor Income from Abroad: Net factor income from abroad is the difference between the income earned by domestic factors of production in foreign countries and the income earned by foreign factors of production within the domestic economy. It includes wages, salaries, rent, and profits earned by domestic factors abroad, minus the income earned by foreign factors in the domestic economy.
The Role of Net Factor Income from Abroad in Calculating National Income:
Now, let's consider the question at hand - what must be added to domestic factor income to obtain national income? The correct answer is option 'A', which is net factor income earned from abroad.
Net factor income from abroad is an important component of national income as it represents the income earned by domestic factors of production in foreign countries. By including this income in the calculation of national income, we get a more comprehensive measure of the total income generated within a country's borders.
Including net factor income from abroad is necessary because factors of production, such as labor and capital, can also earn income outside of the domestic economy. For example, a domestic company may have subsidiaries or branches in foreign countries where it earns profits. Similarly, domestic workers may find employment opportunities abroad and earn wages there.
By adding net factor income from abroad to domestic factor income, we capture the income earned by domestic factors both within the domestic economy and abroad. This provides a more accurate measure of the total income generated by a country's factors of production.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, when calculating national income, we need to add net factor income from abroad to domestic factor income. This is because net factor income from abroad represents the income earned by domestic factors of production in foreign countries, which is an important component of a country's total income. Including this income provides a more comprehensive measure of national income and helps capture the income generated by a country's factors of production both domestically and abroad.
To understand the relationship between domestic factor income and national income, we need to first define these terms.
Domestic Factor Income: Domestic factor income refers to the income earned by domestic factors of production, such as labor and capital, within a country's borders. It includes wages, salaries, rent, and profits earned by individuals and businesses within the domestic economy.
National Income: National income, on the other hand, is the total income earned by all factors of production, both domestic and foreign, within a country's borders. It includes domestic factor income as well as net factor income from abroad.
Net Factor Income from Abroad: Net factor income from abroad is the difference between the income earned by domestic factors of production in foreign countries and the income earned by foreign factors of production within the domestic economy. It includes wages, salaries, rent, and profits earned by domestic factors abroad, minus the income earned by foreign factors in the domestic economy.
The Role of Net Factor Income from Abroad in Calculating National Income:
Now, let's consider the question at hand - what must be added to domestic factor income to obtain national income? The correct answer is option 'A', which is net factor income earned from abroad.
Net factor income from abroad is an important component of national income as it represents the income earned by domestic factors of production in foreign countries. By including this income in the calculation of national income, we get a more comprehensive measure of the total income generated within a country's borders.
Including net factor income from abroad is necessary because factors of production, such as labor and capital, can also earn income outside of the domestic economy. For example, a domestic company may have subsidiaries or branches in foreign countries where it earns profits. Similarly, domestic workers may find employment opportunities abroad and earn wages there.
By adding net factor income from abroad to domestic factor income, we capture the income earned by domestic factors both within the domestic economy and abroad. This provides a more accurate measure of the total income generated by a country's factors of production.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, when calculating national income, we need to add net factor income from abroad to domestic factor income. This is because net factor income from abroad represents the income earned by domestic factors of production in foreign countries, which is an important component of a country's total income. Including this income provides a more comprehensive measure of national income and helps capture the income generated by a country's factors of production both domestically and abroad.
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:Circular Income Flow in a Two Sector Economy: In the figure given we can see that upper loop shows the resources such as land, capital and entrepreneurial ability flow from households to firms in the direction shown by the arrow direction.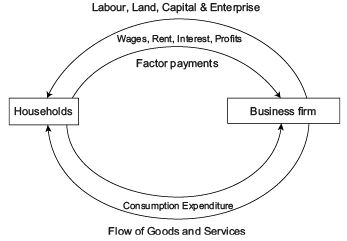 The money flows from firms to the households as factor payments in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits, shown by the arrow direction.The lower part of the figure shows the flow of money from households to firms in the form of consumption expenditure done by the households to purchase the goods and services produced by the firms, making the flow of goods and services from firms to households.Thus, we see that money flows from business firms to households as factor payments and then it flows from households to firms. Thus, there is, in fact, a circular flow of money or income. This is how the economy functions.Circular flow of income refers to the flow of activities of production, income generation and expenditure involving different ___________ of the economy.
The money flows from firms to the households as factor payments in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits, shown by the arrow direction.The lower part of the figure shows the flow of money from households to firms in the form of consumption expenditure done by the households to purchase the goods and services produced by the firms, making the flow of goods and services from firms to households.Thus, we see that money flows from business firms to households as factor payments and then it flows from households to firms. Thus, there is, in fact, a circular flow of money or income. This is how the economy functions.Circular flow of income refers to the flow of activities of production, income generation and expenditure involving different ___________ of the economy.- a)Sector
- b)Aspect
- c)Type
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
Circular Income Flow in a Two Sector Economy: In the figure given we can see that upper loop shows the resources such as land, capital and entrepreneurial ability flow from households to firms in the direction shown by the arrow direction.

The money flows from firms to the households as factor payments in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits, shown by the arrow direction.
The lower part of the figure shows the flow of money from households to firms in the form of consumption expenditure done by the households to purchase the goods and services produced by the firms, making the flow of goods and services from firms to households.
Thus, we see that money flows from business firms to households as factor payments and then it flows from households to firms. Thus, there is, in fact, a circular flow of money or income. This is how the economy functions.
Circular flow of income refers to the flow of activities of production, income generation and expenditure involving different ___________ of the economy.
a)
Sector
b)
Aspect
c)
Type
d)
None of the above
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Two sectors of the economy
(a) Households
(b) Firms
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:Circular Income Flow in a Two Sector Economy: In the figure given we can see that upper loop shows the resources such as land, capital and entrepreneurial ability flow from households to firms in the direction shown by the arrow direction.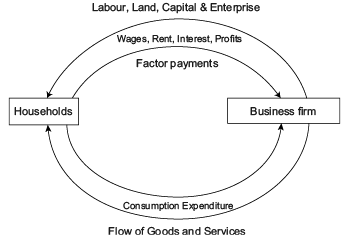 The money flows from firms to the households as factor payments in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits, shown by the arrow direction.The lower part of the figure shows the flow of money from households to firms in the form of consumption expenditure done by the households to purchase the goods and services produced by the firms, making the flow of goods and services from firms to households.Thus, we see that money flows from business firms to households as factor payments and then it flows from households to firms. Thus, there is, in fact, a circular flow of money or income. This is how the economy functions.Which of the following is not the significance of Circular Flow of Income?
The money flows from firms to the households as factor payments in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits, shown by the arrow direction.The lower part of the figure shows the flow of money from households to firms in the form of consumption expenditure done by the households to purchase the goods and services produced by the firms, making the flow of goods and services from firms to households.Thus, we see that money flows from business firms to households as factor payments and then it flows from households to firms. Thus, there is, in fact, a circular flow of money or income. This is how the economy functions.Which of the following is not the significance of Circular Flow of Income?- a)It reflects structure of an economy.
- b)It shows interdependence among different sectors.
- c)It shows injections and leakages from flow of money.
- d)It does not help in estimation of national income and related aggregates.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
Circular Income Flow in a Two Sector Economy: In the figure given we can see that upper loop shows the resources such as land, capital and entrepreneurial ability flow from households to firms in the direction shown by the arrow direction.

The money flows from firms to the households as factor payments in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits, shown by the arrow direction.
The lower part of the figure shows the flow of money from households to firms in the form of consumption expenditure done by the households to purchase the goods and services produced by the firms, making the flow of goods and services from firms to households.
Thus, we see that money flows from business firms to households as factor payments and then it flows from households to firms. Thus, there is, in fact, a circular flow of money or income. This is how the economy functions.
Which of the following is not the significance of Circular Flow of Income?
a)
It reflects structure of an economy.
b)
It shows interdependence among different sectors.
c)
It shows injections and leakages from flow of money.
d)
It does not help in estimation of national income and related aggregates.
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
- The basic purpose of the circular flow model is to understand how money moves within an economy.
- It breaks the economy down into two primary players: households and corporations.
- It separates the markets that these participants operate in as markets for goods and services and the markets for the factors of production.
Chapter doubts & questions for Determination of National Income - Business Economics for CA Foundation 2025 is part of CA Foundation exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the CA Foundation exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for CA Foundation 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Determination of National Income - Business Economics for CA Foundation in English & Hindi are available as part of CA Foundation exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CA Foundation Exam by signing up for free.
Business Economics for CA Foundation
86 videos|200 docs|58 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup











