All questions of Chapter 3: Bank Reconciliation Statement for CA Foundation Exam
The credit balance of Rs. 2,000 in the bank column of the cash book was carried forwarded as its debit balance. When overdraft as per pass book is starting point: - a)Rs. 2,000 will be deducted
- b)Rs. 2,000 will be added
- c)Rs. 4,000 will be deducted
- d)Rs. 4,000 will be added
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Sonal Patel answered |
When the credit balance of Rs. 2,000 in the bank column of the cash book was carried forward as its debit balance, it means that the cash book shows an overdraft balance of Rs. 2,000 instead of a credit balance.
Now, we need to compare this balance with the balance as per pass book. If the pass book shows an overdraft balance, then we need to deduct it from the cash book balance. If the pass book shows a credit balance, then we need to add it to the cash book balance.
In this question, the starting point is given as the pass book showing an overdraft balance. Therefore, we need to deduct this balance from the cash book balance.
So, the calculation would be:
Cash book balance (overdraft) = Rs. 2,000 (debit balance)
Pass book balance (overdraft) = Given
Overdraft as per pass book = Pass book balance - Cash book balance
Since the pass book balance is an overdraft balance, it would be higher than the cash book balance (overdraft). Therefore, we need to deduct the cash book balance from the pass book balance.
Overdraft as per pass book = Pass book balance - Cash book balance
Overdraft as per pass book = (Given) - Rs. 2,000
Overdraft as per pass book = Rs. (Given - 2,000)
Hence, option C. Rs. 4,000 will be deducted is the correct answer.
The Cash book showed an overdraft of Rs.1,500 but the pass book made up to same date should that cheques of Rs. 100, Rs. 50 and Rs. 125 had not been presented for payment and a cheque of Rs. 400 had not been cleared. The balance as per the Cash Book will be:
- a)Rs. 1,100
- b)Rs. 1,625
- c)Rs. 2,175
- d)Rs. 1,375
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Rithika Nair answered |
Overdraft in Cash Book = Rs. 1,500
Cheques not presented for payment = Rs. 100 + Rs. 50 + Rs. 125 = Rs. 275
Cheque not cleared = Rs. 400
To find: Balance as per Cash Book
Solution:
Step 1: Adjust the cheques not presented for payment
Cash Book balance = Overdraft - Cheques not presented for payment
Cash Book balance = Rs. 1,500 - Rs. 275 = Rs. 1,225
Step 2: Adjust the cheque not cleared
Cash Book balance = Cash Book balance - Cheque not cleared
Cash Book balance = Rs. 1,225 - Rs. 400 = Rs. 825
Step 3: Compare with Pass Book balance
As per the Pass Book, there are no transactions that have not been recorded in the Cash Book. Therefore, the balance as per Pass Book is the actual balance.
Pass Book balance = Cash Book balance + Overdraft
Pass Book balance = Rs. 825 + Rs. 1,500 = Rs. 2,325
Therefore, the balance as per Cash Book is Rs. 825 and the correct option is (b) Rs. 1,625.
Balance as per pass book Rs. 20,000 Rs. 4,000 were directly deposited by a customer into the bank. Then the balance as per cash book is:
- a)Rs. 24,000
- b)Rs. 18,000
- c)Rs. 16,000
- d)Rs. 22,000
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Charvi Roy answered |
Balance as per pass book = Rs. 20,000
Direct deposit by customer = Rs. 4,000
To find:
Balance as per cash book
Solution:
The cash book is a record of all transactions related to cash inflows and outflows. It includes all transactions related to cash, bank, and discount. The passbook is a copy of the customer's account in the bank's books, which shows all transactions done by the customer in the bank.
To find the balance as per cash book, we need to consider the following:
1. Direct deposit by customer:
When a customer directly deposits money into the bank account, it will not be recorded in the cash book until the bank receives the information. Therefore, the balance as per cash book will be less than the balance as per passbook until the bank updates the account.
In this case, the customer deposited Rs. 4,000 directly into the bank, which is not recorded in the cash book. Therefore, the balance as per cash book will be Rs. 20,000.
2. Bank charges and interest:
The bank may charge some fees or interest on the account, which will be recorded in the passbook. However, it may not be recorded in the cash book until the bank receives the information. Therefore, the balance as per cash book may differ from the balance as per passbook.
3. Cheques issued and deposited:
If a cheque is issued by the customer, it will be recorded in the cash book as an outflow. If a cheque is deposited, it will be recorded as an inflow. However, it may take some time for the cheque to clear, and the amount will be updated in the passbook only after clearance. Therefore, the balance as per cash book may differ from the balance as per passbook until the cheque is cleared.
In this case, we do not have any information about bank charges, interest or cheques issued/deposited. Therefore, we can assume that there are no such transactions.
Therefore, the balance as per cash book = balance as per passbook - direct deposit by customer
= Rs. 20,000 - Rs. 4,000
= Rs. 16,000
Hence, the correct answer is option C - Rs. 16,000.
Favourable balance as per Cash Book Rs. 5,000. Debit side of Cash Book under cast by Rs. 2.000. Cheque deposited into bank Rs. 3,000 dishonoured but no entry for dishonour is made in cash book. Balance as per Pass Book is :- a)Rs. 4,000
- b)Rs. 10,000
- c)Rs. 6,000
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Subhankar Sen answered |
Favourable balance as per Cash Book = Rs. 5,000
Debit side of Cash Book under cast by Rs. 2,000.
Therefore, the revised balance as per Cash Book = Rs. (5,000 - 2,000) = Rs. 3,000.
Cheque deposited into bank Rs. 3,000 dishonoured but no entry for dishonour is made in cash book.
Hence, the balance as per Cash Book should be further reduced by Rs. 3,000.
Therefore, the actual balance as per Cash Book = Rs. (3,000 - 3,000) = Rs. 0.
Now, we need to reconcile the Pass Book balance with the actual balance as per Cash Book.
The Pass Book balance will only reflect the amount of Rs. 3,000 that was deposited into the bank and not the dishonour.
Hence, the Pass Book balance will be Rs. (5,000 + 3,000) = Rs. 8,000.
However, since the actual balance as per Cash Book is Rs. 0, the correct balance as per Pass Book will be reduced by Rs. 8,000.
Therefore, the correct balance as per Pass Book = Rs. (8,000 - 8,000) = Rs. 4,000.
Hence, the correct answer is option 'A' - Rs. 4,000.
The credit balance as per pass book of Mr. X was Rs. 65,600. Cheques issued but not presented for payment Rs. 75,800. Cheques deposited by one of the customers of the bank but wrongly credited in Mr. X account Rs. 20,600. The balance as per cash book will be:-- a)Rs. 30,800 Debit
- b)Rs. 30,800 overdraft
- c)Rs. 1,20,800 Debit
- d)Rs. 10,400 overdraft.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Raghavendra Choudhury answered |
Credit balance as per pass book = Rs. 65,600
Cheques issued but not presented for payment = Rs. 75,800
Cheques deposited by a customer but wrongly credited in Mr. X account = Rs. 20,600
To calculate the balance as per cash book, we need to adjust the above items in the credit balance as per pass book.
Step 1: Adjust the cheques issued but not presented for payment
Credit balance as per pass book = Rs. 65,600
Less: Cheques issued but not presented for payment = Rs. 75,800
Adjusted balance = Rs. (10,200) (overdraft)
Step 2: Adjust the cheques deposited by a customer but wrongly credited in Mr. X account
Credit balance as per pass book = Rs. (10,200) (overdraft)
Add: Cheques deposited by a customer but wrongly credited in Mr. X account = Rs. 20,600
Adjusted balance = Rs. 10,400 (overdraft)
Therefore, the balance as per cash book will be Rs. 10,400 (overdraft).
Credit balance as per cash Book Rs. 10,000
Bank charged interest Rs. 150
Cheques issued but not presented for payment Rs. 2,500
Balance as per pass Book will be :
- a)Rs. 7,650
- b)Rs. 12,350
- c)Rs. 12,650
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bank charged interest Rs. 150
Cheques issued but not presented for payment Rs. 2,500
Balance as per pass Book will be :

|
Ruchi Mishra answered |
Credit balance as per Cash Book = Rs. 10,000
Bank charged interest = Rs. 150
Cheques issued but not presented for payment = Rs. 2,500
Step 1: Add Interest Charged by the Bank
Rs. 10,000 + Rs. 150 = Rs. 10,150
Step 2: Deduct Cheques Issued but not Presented for Payment
Rs. 10,150 - Rs. 2,500 = Rs. 7,650
Therefore, the balance as per Pass Book will be Rs. 7,650.
Explanation
When there is a difference between the balance as per Cash Book and Pass Book, it is necessary to reconcile the accounts. In this case, the credit balance as per Cash Book is Rs. 10,000. However, the Bank has charged interest of Rs. 150, which needs to be added to the Credit balance. After adding the interest, the balance becomes Rs. 10,150.
Further, there were cheques issued but not presented for payment, which reduces the balance. In this case, the amount of cheques issued but not presented for payment is Rs. 2,500. Therefore, this amount needs to be deducted from the balance. After deducting the amount of cheques issued but not presented for payment, the balance becomes Rs. 7,650.
Hence, the correct answer is option 'A'.
Debit balance as per Cash Book of ABC Enterprises as on 31.3.2006 is Rs. 1,500.Cheques deposited but not cleared amounts to Rs. 100 and Cheques issued but not presented of Rs. 150. The bank allowed interest amounting Rs. 50 and collected dividend Rs. 50 on behalf of ABC Enterprises. Balance as per pass book should be- a)1,600.
- b)1,450.
- c)1,850.
- d)1,650.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Freedom Institute answered |
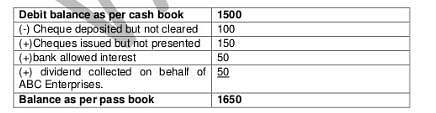
When drawing up a Bank Reconciliation Statement, if you start with a debit balance as per the Bank Statement, the unpresented cheques should be:- a)Added;
- b)Deducted;
- c)Not required to be adjusted.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Devanshi Rane answered |
Bank Reconciliation Statement is a statement that reconciles the bank balance as per the company's books with the bank balance as per the bank statement. The statement helps in identifying the discrepancies and errors between the two balances.
Debit Balance occurs when the bank balance as per the bank statement is more than the bank balance as per the company's books. In this case, the company owes money to the bank.
Unpresented Cheques
Unpresented Cheques are the cheques issued by the company but not yet presented to the bank for payment. These cheques are included in the company's books, but not in the bank statement, resulting in a difference between the two balances.
Adjustment of Unpresented Cheques
When drawing up a Bank Reconciliation Statement with a debit balance as per the Bank Statement, the unpresented cheques should be added to the bank balance as per the company's books. This adjustment will increase the bank balance, bringing it closer to the bank balance as per the bank statement.
Reason for Adding Unpresented Cheques
Unpresented Cheques represent the company's liabilities, and hence, should be added to the bank balance as per the company's books. The company owes money to the bank for these cheques, and hence, the bank balance should be increased accordingly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when drawing up a Bank Reconciliation Statement with a debit balance as per the Bank Statement, the unpresented cheques should be added to the bank balance as per the company's books. This adjustment will bring the bank balance closer to the bank balance as per the bank statement, helping the company identify any discrepancies and errors.
The payment side of Cash Book is under cast by Rs. 250. If the starting point of BRS is the Overdraft Balance as per Pass Book, then what would be the treatment to reach to Overdraft Balance of Cash Book ?
- a)Less 250
- b)Add 250
- c)Add 500
- d)Less 500
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
Debit balance as per cash book Rs.2000
Cheques deposited but not cleared Rs. 100
Cheques issued but not presented Rs. 150
Bank allowed interest Rs. 50
Bank collected dividend Rs. 50
Balance as per Pass Book will be:
- a)Rs. 2,100
- b)Rs. 1,950
- c)Rs. 2,350
- d)Rs. 2,150
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cheques deposited but not cleared Rs. 100
Cheques issued but not presented Rs. 150
Bank allowed interest Rs. 50
Bank collected dividend Rs. 50
Balance as per Pass Book will be:

|
Mihir Banerjee answered |
To find the balance as per Pass Book, we need to make adjustments for the following items:
1) Cheques deposited but not cleared: This means that the bank has not yet credited the account for the cheques deposited. So, we need to add this amount to the balance as per Cash Book.
Cheques deposited but not cleared = Rs. 100
Adjusted balance = Rs. 2,000 + Rs. 100 = Rs. 2,100
2) Cheques issued but not presented: This means that the cheques issued by the company have not yet been presented to the bank for payment. So, we need to deduct this amount from the balance as per Cash Book.
Cheques issued but not presented = Rs. 150
Adjusted balance = Rs. 2,100 - Rs. 150 = Rs. 1,950
3) Bank allowed interest: This means that the bank has credited the account with interest. So, we need to add this amount to the adjusted balance.
Bank allowed interest = Rs. 50
Adjusted balance = Rs. 1,950 + Rs. 50 = Rs. 2,000
4) Bank collected dividend: This means that the bank has debited the account for the dividend collected. So, we need to deduct this amount from the adjusted balance.
Bank collected dividend = Rs. 50
Adjusted balance = Rs. 2,000 - Rs. 50 = Rs. 1,950
Therefore, the balance as per Pass Book is Rs. 2,150.
Debit balance as per cash book Rs.2000
Cheques deposited but not cleared Rs. 100
Cheques issued but not presented Rs. 150
Bank allowed interest Rs. 50
Bank collected dividend Rs. 50
Balance as per Pass Book will be:
- a)Rs. 2,100
- b)Rs. 1,950
- c)Rs. 2,350
- d)Rs. 2,150
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cheques deposited but not cleared Rs. 100
Cheques issued but not presented Rs. 150
Bank allowed interest Rs. 50
Bank collected dividend Rs. 50
Balance as per Pass Book will be:

|
Niharika Chavan answered |
Debit balance as per cash book = Rs. 2000
Cheques deposited but not cleared = Rs. 100
Cheques issued but not presented = Rs. 150
Bank allowed interest = Rs. 50
Bank collected dividend = Rs. 50
Adding the above transactions:
2000 + 100 - 150 + 50 + 50 = Rs. 2,050
Adjustment for Cheques:
Cheques issued but not presented = Rs. 150
Cheques deposited but not cleared = Rs. 100
Net adjustment for cheques = Rs. 50 (150 - 100)
Adding net adjustment for cheques to the balance as per pass book:
Rs. 2,050 + Rs. 50 = Rs. 2,100
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - Rs. 2,150.
Bank Overdraft as per cash book is Rs. 10,500. Interest debited by bank Rs. 3,500 for which advice was not received by account holder. Cheques deposited but not credited by bank Rs. 7,500. Cheques issued but not yet presented Rs. 9,500. What is the Overdraft amount as per Pass Book?- a)Rs. 12,000
- b)Rs. 16,000
- c)Rs. 5,000
- d)Rs. 9,000
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Nipun Tuteja answered |
- Adjust for Bank Interest: The bank debited Rs. 3,500 for interest not known to the account holder. This increases the overdraft, so add Rs. 3,500.
- Adjust for Deposited but Uncredited Cheques: Cheques amounting to Rs. 7,500 are deposited but not yet credited by the bank. This also increases the overdraft, so add Rs. 7,500.
- Adjust for Issued but Unpresented Cheques: Cheques issued but not yet presented amount to Rs. 9,500. This reduces the overdraft, so subtract Rs. 9,500.
- Calculate Overdraft as per Pass Book:
\[
\text{Overdraft as per Pass Book} = 10,500 + 3,500 + 7,500 - 9,500 = 12,000
\]
- Correct Answer: A: Rs. 12,000
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A Bank Reconciliation Statement is a
- A:
part of Cash Book;
- B:
part of Bank Account;
- C:
part of financial statements,
- D:
none of the above.
The answer is c.
A Bank Reconciliation Statement is a
part of Cash Book;
part of Bank Account;
part of financial statements,
none of the above.

|
Lakshya Raj answered |
Which of these types of errors are not detected during Bank Reconciliation’:
- a)Cash embezzlement by cashier
- b)Cheques deposited but not credited by bank
- c)Casting mistakes in bank column of cash book
- d)Interest or commission charged by the bank not accounted in cash book
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Devanshi Rane answered |
1. Errors in recording transactions in the bank statement: Bank reconciliation only compares the bank statement with the company's records. If there are errors in recording transactions in the bank statement, such as duplicate entries or incorrect amounts, they will not be detected during bank reconciliation.
2. Errors in recording transactions in the company's books: Bank reconciliation compares the bank statement with the company's records to identify any discrepancies. However, if there are errors in recording transactions in the company's books, such as incorrect amounts or incorrect accounts, they may not be detected during bank reconciliation.
3. Errors in timing: Bank reconciliation compares the timing of transactions recorded in the bank statement with the company's records. However, if there are errors in timing, such as recording a transaction in the wrong period or recording a transaction on the wrong date, they may not be detected during bank reconciliation.
4. Errors in reconciliation process: Bank reconciliation is a process that involves comparing the bank statement with the company's records to identify any discrepancies. However, if there are errors in the reconciliation process itself, such as incorrect calculations or incorrect matching of transactions, they may not be detected during bank reconciliation.
When the balance as per Cash Book is the starting point, direct deposits by customers are.- a)Added
- b)Subtracted
- c)Not required to be adjusted
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Harjindra Singh answered |
When drawing up a Bank Reconciliation Statement, if you start with a debit balance as per the Bank Statement, the unpresented cheques should be:- a)Added
- b)Deducted
- c)Not required to be adjusted
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Aditi Joshi answered |
| Bank Reconciliation Statement |
Introduction to Bank Reconciliation Statement
A Bank Reconciliation Statement is a statement prepared by a business to reconcile the difference between the bank balance as per the company's records and the bank balance as per the bank statement. It ensures that both balances are in agreement by comparing the financial transactions recorded by the business with those recorded by the bank.
Debit Balance as per the Bank Statement
When starting with a debit balance as per the bank statement, it means that the bank statement shows a higher balance than the company's records. This can happen due to various reasons such as outstanding checks, deposits in transit, bank errors, or other reconciling items.
Unpresented Cheques
Unpresented cheques refer to checks issued by the company that have not yet been presented to the bank for payment. These checks are recorded in the company's books as payments but have not yet been deducted from the bank balance.
Addition of Unpresented Cheques
To reconcile the difference between the bank balance as per the company's records and the bank statement, the unpresented cheques need to be added to the bank balance as per the bank statement. This adjustment is made because the bank statement does not reflect the deduction of these checks, resulting in a higher balance.
Reasoning behind Adding Unpresented Cheques
The reason for adding the unpresented cheques is to align the bank balance as per the bank statement with the company's records. Since the company has already recorded these checks as payments, they need to be added to the bank balance to reflect the correct position.
Example
Let's say the bank balance as per the bank statement is $10,000, and there are unpresented cheques of $3,000. When preparing the bank reconciliation statement, the unpresented cheques of $3,000 will be added to the bank balance, resulting in a reconciled balance of $13,000.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when starting with a debit balance as per the bank statement, the unpresented cheques should be added to the bank balance to reconcile the difference between the bank balance as per the company's records and the bank statement. This adjustment ensures that both balances are in agreement and reflects the correct financial position of the business.
The balance as per Cash Book (overdraft ) is 1,500. Cheques for Rs. 400 were deposited but were not collected. The cheques issued but not presented were Rs. 100, Rs. 125, Rs. 50. Balance as per Pass Book is :
- a)Rs. 1,100
- b)Rs. 1,625
- c)Rs. 12,000
- d)Rs. 1,375
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
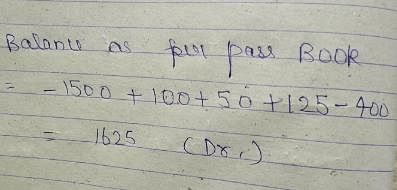
Which of these types of errors are not detected during Bank Reconciliation’ :- a)Cash embezzlement by cashier
- b)Cheques deposited but not credited by bank
- c)Casting mistakes in bank column of cash book
- d)Interest or commission charged by the bank not accounted in cash book
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Raghavendra Choudhury answered |
Bank column of a cash book of a trader shows a credit balance of Rs. 7,900 and the bank statement shows a debit balance of Rs. 10,300 on a particular date after payments made by the bank as per the standing orders. In the statement of affairs, the bank balance will be shown on:- a)Assets side Rs. 7,900
- b)Liabilities side Rs. 10,300
- c)Liabilities side Rs. 2,400
- d)Assets side Rs. 10,300
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Ritika Iyer answered |
The bank column of a cash book shows the balance of the trader's account with the bank. On a particular date, the bank column of the cash book shows a credit balance of Rs. 7,900. This means that the trader has deposited Rs. 7,900 in the bank account.
However, the bank statement shows a debit balance of Rs. 10,300. This means that the bank has paid out Rs. 10,300 from the trader's account as per the standing orders.
Therefore, the actual balance of the trader's account with the bank on that particular date is a debit balance of Rs. 10,300. This balance will be shown on the liabilities side of the statement of affairs because it represents an amount that the trader owes to the bank.
Hence, the correct answer is option B, i.e., the bank balance will be shown on the liabilities side of the statement of affairs as Rs. 10,300.
When the balance as per Cash Book is the starting point, direct deposits by customers are:- a)added
- b)subtracted;
- c)not required to be adjusted
- d)neither of the two
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Rajveer Jain answered |
Direct deposits by customers are added when the balance as per Cash Book is the starting point. This is because direct deposits by customers are an inflow of cash into the business, which increases the cash balance. Adding these deposits to the starting balance of the Cash Book reflects the actual cash position of the business.
To understand this concept in detail, let's break down the answer:
**1. Cash Book:**
The Cash Book is a subsidiary book that records all cash and bank transactions of a business. It serves as a record of all cash inflows and outflows, including cash received from customers and cash paid to suppliers, employees, etc.
**2. Starting Point:**
The starting point refers to the opening balance of the Cash Book. It is the balance of cash on hand or in the bank at the beginning of a particular accounting period. This balance is carried forward from the previous period's closing balance.
**3. Direct Deposits by Customers:**
Direct deposits by customers refer to cash payments made directly into the business's bank account by its customers. These deposits could be in the form of payments for goods or services, loan repayments, or any other form of cash inflow from customers.
**4. Adding Direct Deposits:**
When the balance as per Cash Book is the starting point, direct deposits by customers are added. This means that the amount of direct deposits made by customers is added to the starting balance of the Cash Book.
Adding these deposits increases the cash balance in the Cash Book, reflecting the actual inflow of cash into the business. It ensures that the Cash Book accurately represents the cash position of the business at the beginning of the accounting period.
**5. Purpose of Adjustment:**
The purpose of this adjustment is to reconcile the Cash Book balance with the bank statement balance. By adding the direct deposits made by customers, the Cash Book balance will match the bank statement balance, which also includes these deposits.
**Conclusion:**
In summary, when the balance as per Cash Book is the starting point, direct deposits by customers are added. This adjustment ensures that the Cash Book accurately reflects the cash position of the business and reconciles it with the bank statement balance.
Balance as per Cash Book is Rs. 5,000. Cheques issued but not presented for payment Rs. 2,000 and Cheques sent for collection but not collected Rs. 1,500. The Bank had wrongly debited the account of firm by Rs. 20. Balance as per pass book will be:- a)Rs. 5,580
- b)Rs. 5,480
- c)Rs. 4,520
- d)Rs. 5,520
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
User12742372 answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:When overdraft as per Cash Book is the starting point, a cheque of Rs. 500 deposited into bank but not recorded in cash book will be :
- A:
Added by Rs. 500
- B:
Deducted by Rs. 500
- C:
Added by Rs. 1,000
- D:
Deducted by Rs. 1,000
The answer is b.
When overdraft as per Cash Book is the starting point, a cheque of Rs. 500 deposited into bank but not recorded in cash book will be :
Added by Rs. 500
Deducted by Rs. 500
Added by Rs. 1,000
Deducted by Rs. 1,000
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:If balance as per Pass Book is the starting point, then uncollected cheques are:
- A:
Added in BRS
- B:
Subtracted in BRS
- C:
Ignored while preparing BRS
- D:
None of these
The answer is a.
If balance as per Pass Book is the starting point, then uncollected cheques are:
Added in BRS
Subtracted in BRS
Ignored while preparing BRS
None of these

|
Jyoti Nair answered |
When preparing a Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS), the starting point is the balance as per Pass Book, which is the balance shown in the bank statement. However, this balance may not be the same as the balance in the company's Cash Book due to various reasons, such as outstanding cheques, bank charges, interest, etc.
One of the reasons for the difference between the balances is uncollected cheques, which are cheques issued by the company but have not yet been presented for payment by the recipients. These cheques are also known as outstanding cheques or uncleared cheques.
When preparing a BRS, uncollected cheques are added to the balance as per Pass Book because they have already been recorded in the company's Cash Book but have not yet been debited by the bank. Therefore, they are part of the company's bank balance that is not reflected in the bank statement.
For example, if the balance as per Pass Book is Rs. 50,000 and there are uncollected cheques worth Rs. 10,000, the adjusted bank balance would be Rs. 60,000 (Rs. 50,000 + Rs. 10,000).
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A', i.e., uncollected cheques are added in BRS.
The bank charged Rs. 1,000 as bank charges to a client and communicates the same to him. The accountant records it in the bank account in books. Later on the bank realizes that the charges were wrongly charged and reverses the same, but forgot to communicate the same to the client. If the accountant is starting with the bank balance as per bank account in books, what will be the treatment in Bank Reconciliation statement to arrive at balance as per Bank statement:- a)Reduce Rs. 1,000
- b)Add Rs. 1,000
- c)Add Rs. 2,000
- d)No treatment
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Mihir Banerjee answered |
When preparing a Bank Reconciliation Statement, the accountant must reconcile the bank balance as per the bank statement with the bank balance as per the books of accounts. In this scenario, the bank charged Rs. 1,000 as bank charges to a client, which was recorded in the books. However, the bank later realized the error and reversed the charges without informing the client.
To arrive at the balance as per the bank statement, the following treatment must be applied:
Add Rs. 1,000
- The bank charges were reversed by the bank, which means that the bank balance as per the bank statement will be higher by Rs. 1,000.
- However, since the reversal was not communicated to the client, the bank balance as per the books of accounts will not reflect this change.
- Therefore, to reconcile the two balances, the accountant must add Rs. 1,000 to the bank balance as per the books of accounts.
- This will result in the balance as per the bank statement and the balance as per the books of accounts being reconciled.
In summary, when bank charges are reversed but not communicated to the client, the accountant must add the amount of the reversal to the bank balance as per the books of accounts to arrive at the balance as per the bank statement.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Balance as per Cash Book is Rs. 5,000. Cheques issued but not presented for payment Rs. 2,000 and Cheques sent for collection but not collected Rs. 1,500. The Bank had wrongly debited the account of firm by Rs. 20. Balance as per pass book will be:
- A:
Rs. 5,580
- B:
Rs. 5,480
- C:
Rs. 4,520
- D:
Rs. 5,520
The answer is b.
Balance as per Cash Book is Rs. 5,000. Cheques issued but not presented for payment Rs. 2,000 and Cheques sent for collection but not collected Rs. 1,500. The Bank had wrongly debited the account of firm by Rs. 20. Balance as per pass book will be:
Rs. 5,580
Rs. 5,480
Rs. 4,520
Rs. 5,520

|
Sai Joshi answered |
The cash book showed an overdraft of Rs. 2,000 as cash at bank but the pass book upto the same date showed that cheques of Rs. 100, Rs. 150 and Rs. 175 have not been presented for payments; and the cheque of Rs. 600 deposited into account has not been cleared. The overdraft as per pass book will be:- a)Rs. 2,150
- b)Rs. 2,175
- c)Rs. 1,475
- d)Rs. 1,925
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Puja Singh answered |
The balance as per Cash Book is Rs. 10,000 Cheques for Rs. 2,000 were issued but not presented for payment. What would be the balance as per Pass Book?- a)Rs. 10,000
- b)Rs. 2,000
- c)Rs. 12,000
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Monica D answered |
Add: cheques issued but not presented =2,000
.•. bal. as per passbook = 12,000
Debit balance as per Cash Book of ABC Enterprises as on 31.3.2011 is Rs. 1,500. Cheques deposited but not cleared amounts to Rs. 100 and Cheques issued but not presented of Rs. 150. The bank allowed interest amounting Rs. 50 and collected dividend Rs. 50 on behalf of ABC Enterprises. Balance as per pass book should be- a)Rs.1,600.
- b)Rs.1,450.
- c)Rs.1,850.
- d)Rs.1,650.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
If the balance as per Pass Book is the starting point, so the treatment of undercasting of receipt side of Cash Book will be :- a)Added
- b)Deducted
- c)No treatment
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Prasenjit Kapoor answered |
When the balance as per Pass Book is the starting point, the treatment of undercasting of receipt side of Cash Book will be deducted from the balance as per Pass Book. This is because undercasting of receipt side of Cash Book means that some of the cash received has not been recorded in the Cash Book, resulting in a lower balance as per Cash Book. As a result, when we start with the balance as per Pass Book, we need to adjust it for the undercast amount so that the correct balance is reflected.
Steps for Deducting Undercasting of Receipt Side of Cash Book
The following steps can be followed to deduct the undercasting of receipt side of Cash Book:
Step 1: Identify the undercast amount
The first step is to identify the undercast amount on the receipt side of the Cash Book. This can be done by comparing the entries in the Cash Book with the bank statement or Pass Book.
Step 2: Deduct the undercast amount from the balance as per Pass Book
Once the undercast amount has been identified, it should be deducted from the balance as per Pass Book. This will give us the correct balance as per Cash Book.
Step 3: Record the adjustment in the Cash Book
The adjustment for the undercast amount should be recorded in the Cash Book. This can be done by writing a narration explaining the adjustment and the reason for it.
Example
Suppose the balance as per Pass Book is Rs. 50,000. On comparing the Cash Book with the Pass Book, it is found that a receipt of Rs. 5,000 has been undercast in the Cash Book. The treatment of undercasting of receipt side of Cash Book will be as follows:
- Deduct the undercast amount of Rs. 5,000 from the balance as per Pass Book:
Balance as per Pass Book = Rs. 50,000 - Rs. 5,000 = Rs. 45,000
- Record the adjustment in the Cash Book with a narration:
Cash Book:
Receipt side
To adjust undercast of Rs. 5,000
By deducting the undercast amount, the correct balance as per Cash Book of Rs. 45,000 is reflected, and the adjustment is recorded in the Cash Book.
If we take balance as per Pass book which of the following will be deducted to get balance as per cash book :
- a)Interest given by bank
- b)Interest charged by Bank
- c)Cheque deposited but not cleared
- d)payment made by bank under standing instructions
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Rajveer Yadav answered |
a) Interest given by the bank
Interest given by the bank is an income for the account holder and needs to be deducted from the balance as per the passbook to get the correct balance as per the cash book. When the bank pays interest on the account holder's savings or fixed deposit, it increases the balance as per the passbook. However, since this interest is not recorded in the cash book, it needs to be deducted.
Example: If the passbook shows a balance of $10,000 and the bank has credited $500 as interest, the balance as per the cash book would be $9,500 ($10,000 - $500).
b) Interest charged by the bank
Interest charged by the bank is an expense for the account holder and is not recorded in the cash book. Therefore, it does not affect the balance as per the cash book and should not be deducted.
c) Cheque deposited but not cleared
Cheques deposited but not cleared are already recorded in the cash book as receipts. Therefore, they do not need to be deducted again to get the balance as per the cash book.
d) Payment made by the bank under standing instructions
Payments made by the bank under standing instructions are already recorded in the cash book as payments. Therefore, they do not need to be deducted again to get the balance as per the cash book.
In summary, to get the balance as per the cash book, only interest given by the bank needs to be deducted from the balance as per the passbook. Other items such as interest charged by the bank, cheques deposited but not cleared, and payments made by the bank under standing instructions do not affect the balance as per the cash book.
The cashbook showed an overdraft of Rs. 2,000 as cash at bank, but the pass book,made up tothe same date showed that cheques of Rs. 200, Rs. 150 and Rs. 175 respectively had not been presented for payments; and the cheque of Rs. 600 paid into account had not been cleared. The balance as per the pass book will be- a)Rs. 2,150
- b)Rs. 2,175
- c)Rs. 1,475
- d)Rs. 2,075
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Freedom Institute answered |
2000-(200+150+175)+600=2075
Which of the following is not salient feature of bank reconciliation statement?- a)Any undue delay in the in the clearance of cheques will be shown up by the reconciliation
- b)Reconciliation statement will help in finding the person doing any fraud
- c)Reconciliation is done by the bankers
- d)It helps in finding out the actual position of the bank balance.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Maheshwar Goyal answered |
Bank reconciliation statement is a process of matching the bank balance as per the company's books with the bank statement. It helps in identifying any discrepancies or errors in the bank statement or the company's books. The salient features of bank reconciliation statement are:
• Timely Identification of Delayed Clearances: Any undue delay in the clearance of cheques will be shown up by the reconciliation. This means that if the company has issued a cheque and it has not been cleared by the bank for a long time, the bank reconciliation statement will identify this delay, allowing the company to follow up with the bank.
• Fraud Detection: Reconciliation statement will help in finding the person doing any fraud. The bank reconciliation statement is an essential tool for detecting any fraudulent activities related to the company's bank accounts. It helps in identifying any suspicious transactions that may have occurred and allows the company to take appropriate action.
• Actual Position of Bank Balance: It helps in finding out the actual position of the bank balance. The bank reconciliation statement is an important document that helps in determining the actual balance of the company's bank account. It takes into account all the transactions that have taken place and ensures that the balance as per the company's books matches with the bank statement.
• Prepared by the Company: Bank reconciliation is done by the company and not the bankers. The bank reconciliation statement is a document prepared by the company's accountant or finance team. It is not done by the bankers as they only provide the bank statement.
Conclusion
Bank reconciliation statement is a vital tool for any company to ensure that its bank accounts are accurate and up-to-date. It helps in identifying any discrepancies or errors in the bank statement or the company's books and ensures that the actual bank balance is known. While the bankers provide the bank statement, the reconciliation is done by the company's accountant or finance team.
A debit balance in the depositor’s Cash Book will be shown as:- a)A debit balance in the Bank Statement.
- b)A credit balance in the Bank Statement.
- c)An overdrawn balance in the Bank Statement.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Utsav answered |
A Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared by - a)The Bank
- b)The Government
- c)The Bank Account holder
- d)The user of financial statements
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Nipun Tuteja answered |
- It is a tool used to match the account holder’s records against the bank statement.
- The goal is to identify discrepancies due to outstanding checks, deposits in transit, or bank errors.
- This process ensures that the financial records are accurate and complete.
- It helps the account holder maintain accurate financial records and detect any unauthorized transactions.
ABC Co. has issued a cheque to its suppliers for an amount of Rs. 10,000 but the accountant of the company by error has recorded the payment as Rs. 1,000 This error can be primarily identified on preparing ___________.- a)Profit and Loss Account
- b)Trial Balance
- c)Bank Book
- d)Bank Reconciliation Statement
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Anuj Roy answered |
Explanation:
Bank Reconciliation Statement is a statement prepared to reconcile the balance as per company's cash book with the balance as per bank statement. It helps in identifying the differences between the two balances and also helps in identifying any errors or omissions made in the cash book or bank statement.
In the given scenario, the accountant of ABC Co. has recorded the payment as Rs. 1,000 instead of Rs. 10,000. This error can be identified on preparing the Bank Reconciliation Statement as follows:
Step 1: Compare the closing balance as per cash book with the closing balance as per bank statement.
Step 2: Identify any differences between the two balances, such as uncleared cheques, deposits in transit, bank charges, interest earned, etc.
Step 3: Reconcile the differences by making necessary adjustments in the cash book or bank statement.
In this case, the error made by the accountant can be identified as a difference between the payment recorded in the cash book and the payment actually made by the bank. The correct amount of Rs. 10,000 should have been recorded in the cash book, but only Rs. 1,000 was recorded. This difference can be reconciled by adjusting the cash book balance with the correct amount of Rs. 10,000.
Therefore, it can be concluded that the error made by the accountant can be primarily identified on preparing the Bank Reconciliation Statement.
The overdraft as per cash book of Mr. X is Rs. 20,500. One of the customer of Mr. X residing in Mumbai directly remitted Rs. 50,000 into Mr. X’s account, about which Mr. X was not aware. One of the cheques deposited into bank for Rs. 25,000 was returned unpaid and the advice in this regard is yet to be received by Mr. X. The balance as per Pass book was:- a)Rs. 4,500 credit
- b)Rs. 4,500 overdraft
- c)Rs. 45,500 credit
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Srsps answered |
The Cash book showed an overdraft of Rs.1,500 but the pass book made up to same date should that cheques of Rs. 100, Rs. 50 and Rs. 125 had not been presented for payment and a cheque of Rs. 400 had not been cleared. The balance as per the Cash Book will be:- a)Rs. 1,100
- b)Rs. 1,625
- c)Rs. 2,175
- d)Rs. 1,375
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Akshay Saini answered |
Step 1: Overdraft as per Cash Book = Rs. 1,500 (Given)
Step 2: Add uncleared cheques:
- Cheque of Rs. 100 not presented for payment = Rs. 100
- Cheque of Rs. 50 not presented for payment = Rs. 50
- Cheque of Rs. 125 not presented for payment = Rs. 125
- Cheque of Rs. 400 not cleared = Rs. 400
Total = Rs. 675
Step 3: Adjust the balance as per Pass Book:
- Overdraft as per Cash Book = Rs. 1,500
- Add: Cheques not presented for payment = Rs. 275 (Rs. 100 + Rs. 50 + Rs. 125)
- Deduct: Cheque not cleared = Rs. 400
Balance as per Pass Book = Rs. 1,375
Step 4: Calculation of Corrected Balance:
- Overdraft as per Cash Book = Rs. 1,500
- Add: Uncleared cheques = Rs. 675
- Less: Adjusted balance as per Pass Book = Rs. 1,375
Corrected Balance as per Cash Book = Rs. 1,625
Hence, the correct answer is option B, Rs. 1,625.
On 31.3.09 the balance of the cash book is Rs. 7,074 (credit) and Balance as per Bank statement is Rs. 3,159 (debit). On scrutiny it was found that the difference was due to cheques issued but yet not presented for payment. The Bank Balance as on 31.3.09 to be shown in Balance Sheet as :-- a)As Bank Overdraft Rs. 3,159
- b)As Cash at Bank Rs. 7,074
- c)As Bank Overdraft Rs. 7,074
- d)As Cash at Bank Rs. 3,159
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
A Bank Statement is a copy of - a)Cash column of the cash book
- b)Bank column of the cash book
- c)A Customer account in the bank book
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Maheshwar Sharma answered |
**Explanation:**
**1. Definition of a Bank Statement:**
A bank statement is a summary of all the transactions that have occurred in a bank account during a specific period of time. It is typically issued by the bank at the end of each month, but can also be obtained on demand.
**2. Purpose of a Bank Statement:**
The main purpose of a bank statement is to provide the account holder with an accurate record of all the transactions that have taken place in their bank account. It allows them to verify the accuracy of their own records and ensure that there are no discrepancies or errors.
**3. Contents of a Bank Statement:**
A bank statement typically includes the following information:
- Account holder's name and address
- Account number
- Statement period (start and end date)
- Opening and closing balances
- Individual transaction details (debit and credit)
- Cheque numbers (if applicable)
- Bank charges and fees (if applicable)
- Interest earned (if applicable)
**4. Relationship with the Bank Book:**
The bank statement is a copy of the customer account in the bank book. The bank book is a record maintained by the bank, which contains all the transactions related to the customer's account. It includes deposits, withdrawals, cheques issued, cheques deposited, and other relevant information.
The bank statement provides a summarized version of the bank book, highlighting the opening and closing balances, as well as the individual transaction details. It acts as a proof of the transactions that have taken place and serves as a reference for the account holder to reconcile their own records with the bank's records.
**Conclusion:**
In conclusion, a bank statement is a copy of a customer account in the bank book. It provides a summary of all the transactions that have occurred in the customer's bank account over a specific period of time. It is an important document for account reconciliation and helps ensure the accuracy of the customer's financial records.
When the balance as per Pass Book is the starting point, uncollected cheques are: - a)Added in the bank reconciliation statement
- b)Subtracted in the bank reconciliation statement
- c)Not required to be adjusted in the bank reconciliation statement.
- d)Neither of the above.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Vanshika Gupta answered |
When balance as per Cash Book is the starting point, uncollected cheques are: - a)Added in the bank reconciliation statement
- b)Subtracted in the bank reconciliation statement
- c)Not required to be adjusted in the bank reconciliation statement
- d)Neither of the above.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Srsps answered |
When balance as per Pass Book is the starting point, interest allowed by Bank is- a)added
- b)subtracted
- c)not required to be adjusted.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
From the following particulars, ascertain the balance as per Cash Book as on 30th April 2014:
a. Bank Overdraft as per Pass Book Rs. 26,500
b. Cheques recorded in Cash Book but not sent to bank for collection Rs. 11,000
c. Payment received from customers directly by bank Rs. 4,700
d. Bills of Rs. 4,000 (discounted with the bank) dishonoured on 20th April and Noting charges paid by bank Rs. 200 - a)Rs. 28,600 Overdraft
- b)Rs. 6,600 Overdraft
- c)Rs. 16,600 Overdraft
- d)Rs. 46,400 Overdraft
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a. Bank Overdraft as per Pass Book Rs. 26,500
b. Cheques recorded in Cash Book but not sent to bank for collection Rs. 11,000
c. Payment received from customers directly by bank Rs. 4,700
d. Bills of Rs. 4,000 (discounted with the bank) dishonoured on 20th April and Noting charges paid by bank Rs. 200

|
Taha Merchant answered |
When the balance as per Pass Book is the starting point, direct payment by bank are:- a)added in the bank reconciliation statement
- b)subtracted in the bank reconciliation statement
- c)Not required to be adjusted in the bank reconciliation statement.
- d)Neither of the above.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Anand Dasgupta answered |
Bank reconciliation statement is a statement that reconciles the bank balance as per the cash book with the bank balance as per the pass book. It helps in identifying the differences between the two balances and ensures that the records of the company and the bank are in agreement.
Direct Payments by Bank
Direct payments by bank refer to the payments made by the bank on behalf of the company. These payments are directly made by the bank without the involvement of the company. Examples of direct payments include payment of bank charges, interest charges, direct debits, etc.
Treatment of Direct Payments by Bank in the Bank Reconciliation Statement
When the balance as per the pass book is taken as the starting point in the bank reconciliation statement, direct payments by bank need to be added.
Reason for Adding Direct Payments by Bank
The reason for adding direct payments by bank is to adjust the balance as per the pass book to reflect the correct balance as per the cash book. Since these payments are made by the bank on behalf of the company, they have not been recorded in the cash book. Therefore, they need to be added to the balance as per the pass book to account for these payments.
Example
Let's understand this with an example. Suppose the balance as per the pass book is $10,000 and there are direct payments made by the bank of $500 for bank charges and $200 for interest charges. In this case, the balance as per the cash book will be $10,000 - $500 - $200 = $9,300.
Therefore, in the bank reconciliation statement, the direct payments by bank of $500 and $200 will be added to the balance as per the pass book to arrive at the balance as per the cash book.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when the balance as per the pass book is the starting point in the bank reconciliation statement, direct payments by bank are added to adjust the balance as per the pass book to reflect the correct balance as per the cash book. This ensures that the records of the company and the bank are in agreement.
When the balance as per Pass Book is the starting point, uncollected cheques are:- a)added in the bank reconciliation statement
- b)subtracted in the bank reconciliation statement
- c)not required to be adjusted in the bank reconciliation statement.
- d)neither of the above.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
R D S Ramanan answered |
A debit balance in the depositor’s Cash Book will be shown as:- a)a debit balance on the Bank Statement.
- b)a credit balance on the Bank Statement.
- c)an overdrawn balance on Bank Statement.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Debit balance as per cash book of ABC Enterprises as on 31st March, 2012 was Rs. 1,500. Cheques deposited but not cleared amount to Rs. 100. Cheques issued but not presented amount to Rs. 150. The bank allowed interest amounting to Rs. 50 and collected dividend Rs. 50 on behalf of ABC Enterprises. Balance as per Pass Book as on 31st March 2012, should be:
- a)Rs. 1,600
- b)Rs. 1,450
- c)Rs. 1,850
- d)Rs. 1,650
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Disha Joshi answered |
Given Information:
- Debit balance as per cash book on 31st March 2012 = Rs. 1,500
- Cheques deposited but not cleared = Rs. 100
- Cheques issued but not presented = Rs. 150
- Bank interest allowed = Rs. 50
- Dividend collected on behalf of ABC Enterprises = Rs. 50
To find the balance as per the pass book, we need to consider the adjustments required to reconcile the cash book balance with the pass book balance.
Adjustments for Reconciliation:
1. Cheques deposited but not cleared:
- These cheques have been recorded in the cash book but have not yet been cleared by the bank.
- As per the cash book, the balance is higher by the amount of these cheques.
- Therefore, we need to deduct the amount of these cheques from the cash book balance.
- Deduct: Rs. 100
2. Cheques issued but not presented:
- These cheques have been issued by ABC Enterprises but have not yet been presented to the bank for payment.
- As per the cash book, the balance is lower by the amount of these cheques.
- Therefore, we need to add the amount of these cheques to the cash book balance.
- Add: Rs. 150
3. Bank interest allowed:
- This is an income for ABC Enterprises and has been collected by the bank on their behalf.
- As per the cash book, this income has not been recorded.
- Therefore, we need to add the amount of bank interest to the cash book balance.
- Add: Rs. 50
4. Dividend collected on behalf of ABC Enterprises:
- This is an income for ABC Enterprises and has been collected by the bank on their behalf.
- As per the cash book, this income has not been recorded.
- Therefore, we need to add the amount of dividend collected to the cash book balance.
- Add: Rs. 50
Calculation:
Debit balance as per cash book on 31st March 2012 = Rs. 1,500
Less: Cheques deposited but not cleared (Rs. 100)
Add: Cheques issued but not presented (Rs. 150)
Add: Bank interest allowed (Rs. 50)
Add: Dividend collected (Rs. 50)
Balance as per pass book on 31st March 2012 = Rs. 1,550
Therefore, the correct answer is option (d) Rs. 1,650.
Bank overdraft as per Cash Book on 31st May, 2011 was Rs. 8,720. Cheques deposited on 28th May but not credited until 31st May amounted to Rs. 690. These were credited on 4th June, 2011. Bank overdraft as per Pass Book is ________- a)Rs. 8,054
- b)Rs. 8,030
- c)Rs. 9,410
- d)Rs. 9,366
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Gaurav Chatterjee answered |
Step 1: Bank overdraft as per Cash Book on 31st May, 2011 = Rs. 8,720
Step 2: Cheques deposited on 28th May but not credited until 31st May = Rs. 690
Step 3: Add Step 1 and Step 2 = Rs. 9,410
Step 4: Cheques credited on 4th June, 2011 are not considered in Cash Book as on 31st May, 2011
Step 5: Deduct the amount of cheques credited on 4th June from Step 3 = Rs. 9,410 - Rs. 690 = Rs. 8,720
Therefore, the Bank overdraft as per Pass Book is Rs. 9,410.
Chapter doubts & questions for Chapter 3: Bank Reconciliation Statement - Accounting for CA Foundation 2025 is part of CA Foundation exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the CA Foundation exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for CA Foundation 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Accounting for CA Foundation
68 videos|160 docs|83 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!

Contact Support
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|










