All Exams >
CA Foundation >
Accounting for CA Foundation >
All Questions
All questions of Unit 7: Accounting as a Measurement Discipline — Valuation Principles, Accounting Estimates for CA Foundation Exam
Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2000. On 31st March, 2006 The similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 but the realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2000) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
Q.
The realizable value of machinery is
- a)Rs. 10,00,000.
- b)Rs. 20,00,000.
- c)Rs. 12,00,000
- d)Rs. 15,00,000.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2000. On 31st March, 2006 The similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 but the realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2000) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
Q.
The realizable value of machinery is
The realizable value of machinery is
a)
Rs. 10,00,000.
b)
Rs. 20,00,000.
c)
Rs. 12,00,000
d)
Rs. 15,00,000.

|
Srestha Shah answered |
Realizable value of machinery
The realizable value of the machinery purchased by Mohan on 1st April 2000 was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000 on 31st March 2006.
Explanation:
Realizable value refers to the amount that can be obtained by selling an asset in the market. In this case, the machinery purchased by Mohan had a realizable value of Rs. 15,00,000 on 31st March 2006. This means that if Mohan were to sell the machinery at that point in time, he could have obtained Rs. 15,00,000 for it.
Calculation of realizable value:
The question states that a similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 on 31st March 2006. This means that the market value of the machinery purchased by Mohan had increased over time.
However, the realizable value of the machinery is not the same as its market value. Realizable value takes into account the condition of the asset, its age, and other relevant factors that might affect its resale value.
Therefore, the realizable value of the machinery purchased by Mohan was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000, which is less than its market value of Rs. 20,00,000.
Conclusion:
The realizable value of an asset refers to the amount that can be obtained by selling it in the market. In this case, the realizable value of the machinery purchased by Mohan was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000 on 31st March 2006, which is less than its market value of Rs. 20,00,000.
The realizable value of the machinery purchased by Mohan on 1st April 2000 was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000 on 31st March 2006.
Explanation:
Realizable value refers to the amount that can be obtained by selling an asset in the market. In this case, the machinery purchased by Mohan had a realizable value of Rs. 15,00,000 on 31st March 2006. This means that if Mohan were to sell the machinery at that point in time, he could have obtained Rs. 15,00,000 for it.
Calculation of realizable value:
The question states that a similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 on 31st March 2006. This means that the market value of the machinery purchased by Mohan had increased over time.
However, the realizable value of the machinery is not the same as its market value. Realizable value takes into account the condition of the asset, its age, and other relevant factors that might affect its resale value.
Therefore, the realizable value of the machinery purchased by Mohan was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000, which is less than its market value of Rs. 20,00,000.
Conclusion:
The realizable value of an asset refers to the amount that can be obtained by selling it in the market. In this case, the realizable value of the machinery purchased by Mohan was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000 on 31st March 2006, which is less than its market value of Rs. 20,00,000.
Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2001. On 31st March, 2011, similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 but the realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2001) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
Q. The historical cost of machinery is:- a)Rs. 10,00,000
- b)Rs. 20,00,000
- c)Rs. 15,00,000
- d)Rs. 12,00,000
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2001. On 31st March, 2011, similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 but the realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2001) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
Q. The historical cost of machinery is:
Q. The historical cost of machinery is:
a)
Rs. 10,00,000
b)
Rs. 20,00,000
c)
Rs. 15,00,000
d)
Rs. 12,00,000

|
Rajveer Jain answered |
Answer:
Historical Cost of Machinery
The historical cost of machinery is the amount paid to acquire the machinery. In this case, Mohan purchased the machinery for Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April 2001. Hence, the historical cost of machinery is Rs. 10,00,000.
Explanation:
The question provides the following information:
- Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2001.
- On 31st March, 2011, similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000.
- The realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2001) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000.
- The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
From the above information, we can calculate the following:
- The machinery purchased on 1st April, 2001 has a historical cost of Rs. 10,00,000.
- The machinery purchased on 31st March, 2011 has a cost of Rs. 20,00,000.
- The realizable value of the machinery purchased on 1st April, 2001 is Rs. 15,00,000.
- The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business is Rs. 12,00,000.
Based on the above information, we can conclude that the historical cost of machinery is Rs. 10,00,000. This is because the historical cost is the amount paid to acquire the machinery, which in this case is Rs. 10,00,000.
Historical Cost of Machinery
The historical cost of machinery is the amount paid to acquire the machinery. In this case, Mohan purchased the machinery for Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April 2001. Hence, the historical cost of machinery is Rs. 10,00,000.
Explanation:
The question provides the following information:
- Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2001.
- On 31st March, 2011, similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000.
- The realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2001) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000.
- The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
From the above information, we can calculate the following:
- The machinery purchased on 1st April, 2001 has a historical cost of Rs. 10,00,000.
- The machinery purchased on 31st March, 2011 has a cost of Rs. 20,00,000.
- The realizable value of the machinery purchased on 1st April, 2001 is Rs. 15,00,000.
- The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business is Rs. 12,00,000.
Based on the above information, we can conclude that the historical cost of machinery is Rs. 10,00,000. This is because the historical cost is the amount paid to acquire the machinery, which in this case is Rs. 10,00,000.
Book value of machinery on 31st March, 2011 10,00,000
Market value as on 31st March, 2011 11,00,000
As on 31st March, 2011, if the company values the machinery
At Rs. 11,00,000 which of the following valuation principle is being followed?- a)Historical Cost.
- b)Present value.
- c)Reaslisable Value.
- d)Current Cost.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Book value of machinery on 31st March, 2011 10,00,000
Market value as on 31st March, 2011 11,00,000
As on 31st March, 2011, if the company values the machinery
At Rs. 11,00,000 which of the following valuation principle is being followed?
Market value as on 31st March, 2011 11,00,000
As on 31st March, 2011, if the company values the machinery
At Rs. 11,00,000 which of the following valuation principle is being followed?
a)
Historical Cost.
b)
Present value.
c)
Reaslisable Value.
d)
Current Cost.

|
Ameya Menon answered |
Explanation:
Current Cost Valuation Principle:
The current cost valuation principle refers to the valuation of assets and liabilities at their current market value. Under this principle, the assets are valued at the price that they would fetch if they were to be sold in the market at the time of valuation.
Explanation of the Given Question:
In the given question, the book value of machinery as on 31st March 2011 is Rs.10,00,000 and the market value of the machinery as on the same date is Rs.11,00,000. If the company values the machinery at Rs.11,00,000 as on 31st March 2011, then it is following the current cost valuation principle.
Reasoning:
The market value of an asset represents the current cost of the asset. The company has valued the machinery at its current market value of Rs.11,00,000, which means that it is following the current cost valuation principle. The historical cost principle refers to the valuation of assets at their original cost, i.e., the cost at which they were acquired. The present value principle refers to the valuation of assets and liabilities at their present value, which is calculated by discounting the future cash flows. The realizable value principle refers to the valuation of assets at the amount that they are expected to realize from their sale or use.
Hence, the correct answer is option 'D' - Current Cost.
Current Cost Valuation Principle:
The current cost valuation principle refers to the valuation of assets and liabilities at their current market value. Under this principle, the assets are valued at the price that they would fetch if they were to be sold in the market at the time of valuation.
Explanation of the Given Question:
In the given question, the book value of machinery as on 31st March 2011 is Rs.10,00,000 and the market value of the machinery as on the same date is Rs.11,00,000. If the company values the machinery at Rs.11,00,000 as on 31st March 2011, then it is following the current cost valuation principle.
Reasoning:
The market value of an asset represents the current cost of the asset. The company has valued the machinery at its current market value of Rs.11,00,000, which means that it is following the current cost valuation principle. The historical cost principle refers to the valuation of assets at their original cost, i.e., the cost at which they were acquired. The present value principle refers to the valuation of assets and liabilities at their present value, which is calculated by discounting the future cash flows. The realizable value principle refers to the valuation of assets at the amount that they are expected to realize from their sale or use.
Hence, the correct answer is option 'D' - Current Cost.
Measurement discipline deals with- a)Identification of objects and events.
- b)Selection of scale.
- c)Evaluation of dimension of measurement scale.
- d)All of the above.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Measurement discipline deals with
a)
Identification of objects and events.
b)
Selection of scale.
c)
Evaluation of dimension of measurement scale.
d)
All of the above.
|
|
Anjali Kapoor answered |
Measurement is vital aspect of accounting. Primarily transactions and events are measured in terms of money. According to Prof. R.J. Chambers ‘To measure is to assign numbers to objects and events according to rules specifying the property to be measured, the scale to be used and the dimension of the unit’.
On analyzing this definition, we can understand any measurement discipline deals with three basic elements of measurement:
1. Identification of an object and the event to be measured.
2. Selection of standard or scale to be measured.
3. Evaluation of dimension of measurement standard or scale.
Measurement discipline deals with:- a)Identification of objects and events.
- b)Selection of scale.
- c)Evaluation of dimension of measurement scale.
- d)All of the above.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Measurement discipline deals with:
a)
Identification of objects and events.
b)
Selection of scale.
c)
Evaluation of dimension of measurement scale.
d)
All of the above.
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
Measurement is vital aspect of accounting. Primarily ily transactions and events are measured in terms of money. According to Prof. R.J. Chambers 'To measure is to assign numbers to objects and events according to rules specifying the property to be measured, the scale to be used and the dimension of the unit'.
On analyzing this definition, we can under stand any measurement discipline deals with three basic elements of measurement
• Identification of an object and the event to be measured
• Selection of standard or scale to be measured
• Evaluation of dimension of measurement standard or scale
All of the following are valuation principles except- a)Historical cost.
- b)Present value.
- c)Future value.
- d)Realisable value.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
All of the following are valuation principles except
a)
Historical cost.
b)
Present value.
c)
Future value.
d)
Realisable value.

|
Rishika Kumar answered |
Valuation Principles
Valuation principles are the set of rules and guidelines used for determining the value of an asset or a liability. The following are the commonly used valuation principles:
1. Historical cost
Historical cost is the original cost of an asset or liability at the time of acquisition. It is used to measure the value of an asset or liability based on the actual amount paid for it. It is not adjusted for inflation or changes in market conditions.
2. Present value
Present value is the current value of an asset or liability based on its expected future cash flows. It is calculated by discounting the future cash flows using a discount rate that reflects the time value of money and the risk associated with the asset or liability.
3. Realisable value
Realisable value is the value of an asset if it is sold in the market. It is used when the value of an asset cannot be determined using historical cost or present value.
Valuation Principles - Exclusion
The option 'C' - Future value is incorrect because it is not a valuation principle. Future value refers to the value of an asset or liability at a future date based on its expected future cash flows. It is not a commonly used valuation principle because it does not provide a current value of an asset or liability. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C'.
Valuation principles are the set of rules and guidelines used for determining the value of an asset or a liability. The following are the commonly used valuation principles:
1. Historical cost
Historical cost is the original cost of an asset or liability at the time of acquisition. It is used to measure the value of an asset or liability based on the actual amount paid for it. It is not adjusted for inflation or changes in market conditions.
2. Present value
Present value is the current value of an asset or liability based on its expected future cash flows. It is calculated by discounting the future cash flows using a discount rate that reflects the time value of money and the risk associated with the asset or liability.
3. Realisable value
Realisable value is the value of an asset if it is sold in the market. It is used when the value of an asset cannot be determined using historical cost or present value.
Valuation Principles - Exclusion
The option 'C' - Future value is incorrect because it is not a valuation principle. Future value refers to the value of an asset or liability at a future date based on its expected future cash flows. It is not a commonly used valuation principle because it does not provide a current value of an asset or liability. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C'.
Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2001. On 31st March, 2011, similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 but the realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2001) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
Q. The realizable value of machinery is:- a)Rs. 10,00,000
- b)Rs. 20,00,000
- c)Rs. 15,00,000
- d)Rs. 12,00,000
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2001. On 31st March, 2011, similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 but the realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2001) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
Q. The realizable value of machinery is:
Q. The realizable value of machinery is:
a)
Rs. 10,00,000
b)
Rs. 20,00,000
c)
Rs. 15,00,000
d)
Rs. 12,00,000

|
Himaja Honey answered |
Since the realizable value of the machinery is Rs. 15,00,000 as on purchase date (1.4.2001) hence the realizable value will be Rs. 15,00,000.
Therefore option (c) is correct.
Therefore option (c) is correct.
There are ________generally accepted measurement bases or valuation principles : - a)Two
- b)Three
- c)Four
- d)Five
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
There are ________generally accepted measurement bases or valuation principles :
a)
Two
b)
Three
c)
Four
d)
Five
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
There are four generally accepted measurement basis or valuation principles. There are:
(1) Historical Cost
(2) Current Cost
(3) Realizable Value
(4) Present Cost
Gross Book value of a Fixed Asset is its: - a)Cost less depreciation
- b)Historical Cost
- c)Fair Market Value
- d)Realizable value
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Gross Book value of a Fixed Asset is its:
a)
Cost less depreciation
b)
Historical Cost
c)
Fair Market Value
d)
Realizable value
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
Gross book value of a fixed asset is its historical cost or other amount substituted for historical cost in the books of account or financial statements. When this amount is shown net of accumulated depreciation, it is termed as net book value.
Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2000. On 31st March, 2006 The similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 but the realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2000) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000. Q.The historical cost of machinery is- a)Rs. 10,00,000.
- b)Rs. 20,00,000.
- c)Rs. 15,00,000.
- d)Rs. 12,00,000.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2000. On 31st March, 2006 The similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 but the realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2000) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
Q.The historical cost of machinery is
a)
Rs. 10,00,000.
b)
Rs. 20,00,000.
c)
Rs. 15,00,000.
d)
Rs. 12,00,000.

|
Khushbu answered |

In Accounting Money is the : - a)Measurement Value
- b)Scale of Measurement
- c)Scale of Social Measurement
- d)Store of Value
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In Accounting Money is the :
a)
Measurement Value
b)
Scale of Measurement
c)
Scale of Social Measurement
d)
Store of Value

|
Ruchi Mishra answered |
The Scale of Measurement in Accounting
In accounting, the term "scale of measurement" refers to the different levels of measurement that are used to categorize financial data. There are four scales of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. Each scale of measurement has its own unique characteristics and uses.
The Correct Answer
The correct answer to the question is option "B," which states that money is the scale of measurement in accounting. This is because money is used as a unit of measure to quantify financial transactions and events. Accounting is the process of recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions in monetary terms. Thus, money is the scale of measurement in accounting.
Explanation
Money is used in accounting as a unit of measure to quantify financial transactions and events. For example, when a company sells a product, the amount of money received from the sale is recorded as revenue. When a company pays for an expense, the amount of money paid is recorded as an expense. Money is also used to measure assets, liabilities, and equity.
Money is considered to be the most reliable and consistent scale of measurement in accounting. It is universally accepted and easily convertible into other currencies. Additionally, money is a stable measure of value over time, which makes it an ideal scale of measurement for financial reporting.
Conclusion
In conclusion, money is the scale of measurement in accounting. It is used as a unit of measure to quantify financial transactions and events. Accounting is the process of recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions in monetary terms. Money is considered to be the most reliable and consistent scale of measurement in accounting because it is universally accepted, easily convertible, and a stable measure of value over time.
In accounting, the term "scale of measurement" refers to the different levels of measurement that are used to categorize financial data. There are four scales of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. Each scale of measurement has its own unique characteristics and uses.
The Correct Answer
The correct answer to the question is option "B," which states that money is the scale of measurement in accounting. This is because money is used as a unit of measure to quantify financial transactions and events. Accounting is the process of recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions in monetary terms. Thus, money is the scale of measurement in accounting.
Explanation
Money is used in accounting as a unit of measure to quantify financial transactions and events. For example, when a company sells a product, the amount of money received from the sale is recorded as revenue. When a company pays for an expense, the amount of money paid is recorded as an expense. Money is also used to measure assets, liabilities, and equity.
Money is considered to be the most reliable and consistent scale of measurement in accounting. It is universally accepted and easily convertible into other currencies. Additionally, money is a stable measure of value over time, which makes it an ideal scale of measurement for financial reporting.
Conclusion
In conclusion, money is the scale of measurement in accounting. It is used as a unit of measure to quantify financial transactions and events. Accounting is the process of recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions in monetary terms. Money is considered to be the most reliable and consistent scale of measurement in accounting because it is universally accepted, easily convertible, and a stable measure of value over time.
Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2000. On 31st March, 2006 The similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 but the realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2000) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
Q. The current cost of the machinery is
- a)Rs. 10,00,000.
- b)Rs. 15,00,000.
- c)Rs. 20,00,000.
- d)Rs. 12,00,000.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2000. On 31st March, 2006 The similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 but the realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2000) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
Q. The current cost of the machinery is
a)
Rs. 10,00,000.
b)
Rs. 15,00,000.
c)
Rs. 20,00,000.
d)
Rs. 12,00,000.

|
Majji Rajesh answered |
Market value or net realizable value which ever is lower. Future. Value cannot be taken so option c
ABC Ltd. purchased a building by paying Rs 50,00,000 as on 1st April, 2000. On 1st April, 2007 it found that it would cost Rs. 1,50,00,000 to purchase the similar building. This value of Rs. 1,50,00,000 is known as : - a)Historical Cost
- b)Realizable value
- c)Current Cost
- d)Present Cost
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
ABC Ltd. purchased a building by paying Rs 50,00,000 as on 1st April, 2000. On 1st April, 2007 it found that it would cost Rs. 1,50,00,000 to purchase the similar building. This value of Rs. 1,50,00,000 is known as :
a)
Historical Cost
b)
Realizable value
c)
Current Cost
d)
Present Cost

|
Anu Sen answered |
Explanation:
Current Cost refers to the amount of money that is required to replace an asset with the similar asset in the current market conditions. In the given question, ABC Ltd. purchased a building by paying Rs 50,00,000 on 1st April 2000. On 1st April 2007, it found that it would cost Rs. 1,50,00,000 to purchase the similar building. This value of Rs. 1,50,00,000 is known as the current cost.
The other options are:
- Historical Cost: It is the cost of an asset when it was purchased or acquired by the company. In this case, the historical cost of the building is Rs. 50,00,000.
- Realizable Value: It is the amount of money that a company can receive by selling an asset in the market. In this case, the realizable value of the building is not given.
- Present Cost: It is the cost of an asset at the present time. In this case, the present cost of the building is Rs. 1,50,00,000.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C, i.e., Current Cost.
Current Cost refers to the amount of money that is required to replace an asset with the similar asset in the current market conditions. In the given question, ABC Ltd. purchased a building by paying Rs 50,00,000 on 1st April 2000. On 1st April 2007, it found that it would cost Rs. 1,50,00,000 to purchase the similar building. This value of Rs. 1,50,00,000 is known as the current cost.
The other options are:
- Historical Cost: It is the cost of an asset when it was purchased or acquired by the company. In this case, the historical cost of the building is Rs. 50,00,000.
- Realizable Value: It is the amount of money that a company can receive by selling an asset in the market. In this case, the realizable value of the building is not given.
- Present Cost: It is the cost of an asset at the present time. In this case, the present cost of the building is Rs. 1,50,00,000.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C, i.e., Current Cost.
Change in accounting estimate means : - a)Differences arising between certain parameters re-estimated during the current period and actual results achieved during the current period
- b)Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and re-estimated during the current period
- c)Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and actual results achieved during the current period
- d)Both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Change in accounting estimate means :
a)
Differences arising between certain parameters re-estimated during the current period and actual results achieved during the current period
b)
Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and re-estimated during the current period
c)
Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and actual results achieved during the current period
d)
Both (b) and (c)

|
Subhankar Sen answered |
**Change in accounting estimate**
Change in accounting estimate refers to the revision of an estimated amount or the revision of an estimated useful life or depreciation method for an asset.
**Option D: Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and re-estimated during the current period AND Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and actual results achieved during the current period**
Option D is the correct answer because change in accounting estimate can occur in two situations:
1. Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and re-estimated during the current period: Sometimes, due to changes in circumstances or new information, it becomes necessary to revise an estimated amount. For example, if a company initially estimated that it will receive $10,000 as bad debt expense, but during the current period, it revises this estimate to $15,000 based on new information, it is considered a change in accounting estimate.
2. Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and actual results achieved during the current period: Another situation where a change in accounting estimate can occur is when the actual results achieved during the current period differ from the earlier estimated amounts. For example, if a company estimated that it will incur $50,000 as repair and maintenance expenses, but during the current period, it actually incurs $60,000, it is considered a change in accounting estimate.
**Importance of change in accounting estimate**
Change in accounting estimate is important because it ensures that financial statements reflect the most accurate and reliable information. It allows companies to adjust their estimates based on new information or changes in circumstances, thereby providing more relevant and useful financial information to users of financial statements.
**Disclosure and accounting treatment**
When a change in accounting estimate occurs, it is important for a company to disclose the nature of the change and its impact on the financial statements. This can be done through footnotes or in the management discussion and analysis section of the financial statements. The change in accounting estimate should be applied prospectively, meaning that it should be implemented from the current period onwards and should not be applied retrospectively to prior periods.
**Conclusion**
In conclusion, change in accounting estimate refers to the revision of an estimated amount or the revision of an estimated useful life or depreciation method for an asset. It can occur when there are differences between the earlier estimates and the re-estimated amounts or between the earlier estimates and the actual results achieved during the current period. Option D is the correct answer as it encompasses both situations where change in accounting estimate can occur.
Change in accounting estimate refers to the revision of an estimated amount or the revision of an estimated useful life or depreciation method for an asset.
**Option D: Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and re-estimated during the current period AND Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and actual results achieved during the current period**
Option D is the correct answer because change in accounting estimate can occur in two situations:
1. Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and re-estimated during the current period: Sometimes, due to changes in circumstances or new information, it becomes necessary to revise an estimated amount. For example, if a company initially estimated that it will receive $10,000 as bad debt expense, but during the current period, it revises this estimate to $15,000 based on new information, it is considered a change in accounting estimate.
2. Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and actual results achieved during the current period: Another situation where a change in accounting estimate can occur is when the actual results achieved during the current period differ from the earlier estimated amounts. For example, if a company estimated that it will incur $50,000 as repair and maintenance expenses, but during the current period, it actually incurs $60,000, it is considered a change in accounting estimate.
**Importance of change in accounting estimate**
Change in accounting estimate is important because it ensures that financial statements reflect the most accurate and reliable information. It allows companies to adjust their estimates based on new information or changes in circumstances, thereby providing more relevant and useful financial information to users of financial statements.
**Disclosure and accounting treatment**
When a change in accounting estimate occurs, it is important for a company to disclose the nature of the change and its impact on the financial statements. This can be done through footnotes or in the management discussion and analysis section of the financial statements. The change in accounting estimate should be applied prospectively, meaning that it should be implemented from the current period onwards and should not be applied retrospectively to prior periods.
**Conclusion**
In conclusion, change in accounting estimate refers to the revision of an estimated amount or the revision of an estimated useful life or depreciation method for an asset. It can occur when there are differences between the earlier estimates and the re-estimated amounts or between the earlier estimates and the actual results achieved during the current period. Option D is the correct answer as it encompasses both situations where change in accounting estimate can occur.
Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2000. On 31st March, 2006 The similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 but the realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2000) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000. Q.The present value of machinery is- a)Rs. 10,00,000.
- b)Rs. 20,00,000.
- c)Rs. 15,00,000.
- d)Rs. 12,00,000.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2000. On 31st March, 2006 The similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 but the realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2000) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
Q.The present value of machinery is
a)
Rs. 10,00,000.
b)
Rs. 20,00,000.
c)
Rs. 15,00,000.
d)
Rs. 12,00,000.
|
|
Subodh Deshmukh answered |
Option D is correct beacouse it is calculated by the business. According to the conservatism concept we calculate maximum loss not profit.
All of the following are valuation principles except: - a)Historical Cost
- b)Present value
- c)Future value
- d)Realizable value
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
All of the following are valuation principles except:
a)
Historical Cost
b)
Present value
c)
Future value
d)
Realizable value

|
Madhavan Malik answered |
The correct answer is option 'C' - Future value.
Valuation Principles:
Valuation principles are important concepts used in accounting and finance to determine the value of assets, liabilities, investments, and various financial transactions. These principles help in accurately measuring and reporting the financial position of a business or entity. Some commonly used valuation principles include:
1. Historical Cost:
- Historical cost is a valuation principle that states that assets should be recorded on the balance sheet at their original purchase price.
- According to this principle, the value of an asset is determined based on its cost at the time of acquisition.
- This principle provides a reliable and objective basis for valuing assets.
2. Present Value:
- Present value is a valuation principle that takes into account the time value of money.
- It is the concept that the value of money today is worth more than the same amount of money in the future.
- Present value calculations involve discounting future cash flows to their equivalent value in today's dollars.
- This principle helps in making investment decisions and determining the fair value of financial instruments.
3. Future Value:
- Future value is the value that an investment or cash flow will have in the future.
- It is the principle that the value of money today will increase over time due to earning interest or returns.
- Future value calculations involve compounding the present value of cash flows to determine their value at a future date.
- This principle is used for financial planning, retirement savings, and investment analysis.
4. Realizable Value:
- Realizable value is a valuation principle that determines the value of an asset based on its estimated selling price in the market.
- It is the amount that can be realized from the sale of an asset under normal market conditions.
- Realizable value takes into account factors such as market demand, supply, and other relevant conditions.
- This principle is used to determine the value of inventory, accounts receivable, and other assets that are expected to be sold.
Explanation:
The correct answer is option 'C' - Future value. This is because future value is indeed a valuation principle and is used to determine the value of an investment or cash flow at a future date. The other options, historical cost, present value, and realizable value are all valid valuation principles used in accounting and finance.
Valuation Principles:
Valuation principles are important concepts used in accounting and finance to determine the value of assets, liabilities, investments, and various financial transactions. These principles help in accurately measuring and reporting the financial position of a business or entity. Some commonly used valuation principles include:
1. Historical Cost:
- Historical cost is a valuation principle that states that assets should be recorded on the balance sheet at their original purchase price.
- According to this principle, the value of an asset is determined based on its cost at the time of acquisition.
- This principle provides a reliable and objective basis for valuing assets.
2. Present Value:
- Present value is a valuation principle that takes into account the time value of money.
- It is the concept that the value of money today is worth more than the same amount of money in the future.
- Present value calculations involve discounting future cash flows to their equivalent value in today's dollars.
- This principle helps in making investment decisions and determining the fair value of financial instruments.
3. Future Value:
- Future value is the value that an investment or cash flow will have in the future.
- It is the principle that the value of money today will increase over time due to earning interest or returns.
- Future value calculations involve compounding the present value of cash flows to determine their value at a future date.
- This principle is used for financial planning, retirement savings, and investment analysis.
4. Realizable Value:
- Realizable value is a valuation principle that determines the value of an asset based on its estimated selling price in the market.
- It is the amount that can be realized from the sale of an asset under normal market conditions.
- Realizable value takes into account factors such as market demand, supply, and other relevant conditions.
- This principle is used to determine the value of inventory, accounts receivable, and other assets that are expected to be sold.
Explanation:
The correct answer is option 'C' - Future value. This is because future value is indeed a valuation principle and is used to determine the value of an investment or cash flow at a future date. The other options, historical cost, present value, and realizable value are all valid valuation principles used in accounting and finance.
Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2001. On 31st March, 2011, similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 but the realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2001) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
Q. The current cost of the machinery is:- a)Rs. 10,00,000
- b)Rs. 20,00,000
- c)Rs. 15,00,000
- d)Rs. 12,00,000
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2001. On 31st March, 2011, similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 but the realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2001) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
Q. The current cost of the machinery is:
Q. The current cost of the machinery is:
a)
Rs. 10,00,000
b)
Rs. 20,00,000
c)
Rs. 15,00,000
d)
Rs. 12,00,000

|
Deepika Desai answered |
Understanding Current Cost of Machinery
Mohan purchased a machinery for Rs. 10,00,000 in 2001. To determine the current cost of the machinery in 2011, we need to evaluate the information provided.
Key Information
- Original Purchase Price: Rs. 10,00,000 (1st April 2001)
- Cost of Similar Machinery (2011): Rs. 20,00,000
- Realizable Value of Existing Machinery: Rs. 15,00,000
- Present Discounted Value of Future Net Cash Inflows: Rs. 12,00,000
Analysis of Current Cost
The current cost of the machinery is determined by assessing the replacement cost, which is the cost to acquire a similar asset at current market prices. The significant factors for consideration include:
- Replacement Cost: The cost of a similar machinery in 2011 is Rs. 20,00,000. This indicates that, in today's market, this is the amount required to replace the machinery.
- Realizable Value: The estimated realizable value of Rs. 15,00,000 is lower than the replacement cost, showing that the current market value does not reflect the price of similar machinery.
- Future Cash Inflows: The present discounted value of Rs. 12,00,000 suggests potential future earnings but does not directly indicate the current cost.
Conclusion
Given that the replacement cost of similar machinery is Rs. 20,00,000, this figure represents the current cost necessary to replace the asset. Therefore, the correct answer is:
Current Cost of Machinery: Rs. 20,00,000 (Option B).
Mohan purchased a machinery for Rs. 10,00,000 in 2001. To determine the current cost of the machinery in 2011, we need to evaluate the information provided.
Key Information
- Original Purchase Price: Rs. 10,00,000 (1st April 2001)
- Cost of Similar Machinery (2011): Rs. 20,00,000
- Realizable Value of Existing Machinery: Rs. 15,00,000
- Present Discounted Value of Future Net Cash Inflows: Rs. 12,00,000
Analysis of Current Cost
The current cost of the machinery is determined by assessing the replacement cost, which is the cost to acquire a similar asset at current market prices. The significant factors for consideration include:
- Replacement Cost: The cost of a similar machinery in 2011 is Rs. 20,00,000. This indicates that, in today's market, this is the amount required to replace the machinery.
- Realizable Value: The estimated realizable value of Rs. 15,00,000 is lower than the replacement cost, showing that the current market value does not reflect the price of similar machinery.
- Future Cash Inflows: The present discounted value of Rs. 12,00,000 suggests potential future earnings but does not directly indicate the current cost.
Conclusion
Given that the replacement cost of similar machinery is Rs. 20,00,000, this figure represents the current cost necessary to replace the asset. Therefore, the correct answer is:
Current Cost of Machinery: Rs. 20,00,000 (Option B).
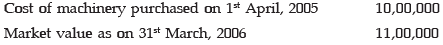 As on 31st March, 2006, if the company values the machineryAt Rs. 11,00,000, which of the following valuation principle is being followed?
As on 31st March, 2006, if the company values the machineryAt Rs. 11,00,000, which of the following valuation principle is being followed?- a)Historical Cost.
- b)Present Value..
- c)Realisable Value.
- d)Current Cost.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
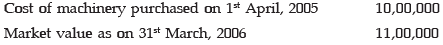
As on 31st March, 2006, if the company values the machinery
At Rs. 11,00,000, which of the following valuation principle is being followed?
a)
Historical Cost.
b)
Present Value..
c)
Realisable Value.
d)
Current Cost.
|
|
Majji Rajesh answered |
Reliasable value or market value which ever is lower market value is not given so answer is option c
Change in accounting estimate means- a)Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and re-estimated during the current period.
- b)Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and actual results achieved during the current period.
- c)Differences arising between certain parameters re-estimated during the current period and actual results achieved during the current period.
- d)Both (a) and (b).
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Change in accounting estimate means
a)
Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and re-estimated during the current period.
b)
Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and actual results achieved during the current period.
c)
Differences arising between certain parameters re-estimated during the current period and actual results achieved during the current period.
d)
Both (a) and (b).

|
Siddharth Sen answered |
The correct answer is option 'A', which states that a change in accounting estimate means differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and re-estimated during the current period.
Explanation:
A change in accounting estimate refers to a revision made to an accounting estimate, which is an approximation of a future event or transaction's financial impact. Accounting estimates are necessary because some items cannot be measured with precision, and they require management's judgment or expertise. These estimates are reviewed periodically to ensure they remain relevant and accurate.
The key points to understand about a change in accounting estimate are as follows:
1. Definition:
- A change in accounting estimate occurs when there is a revision to an estimate made in a prior period.
- It is not a correction of an error, but rather a change in judgment or new information that leads to a revision of the estimate.
2. Parameters Estimated Earlier:
- A change in accounting estimate refers to differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier.
- Parameters can include items like useful life, depreciation rate, bad debt provision, inventory obsolescence, etc.
3. Re-Estimated During Current Period:
- The change in accounting estimate occurs when these parameters are re-estimated during the current period.
- The re-estimation can be due to new information, changes in circumstances, or improved estimation techniques.
4. Examples:
- For example, if a company estimates the useful life of its machinery as 10 years but later determines that it should be 8 years based on new information or technological advancements, it would result in a change in accounting estimate.
- Similarly, if a company estimates the provision for bad debts at 5% of accounts receivable but later determines that it should be 7% based on historical trends or economic conditions, it would also be a change in accounting estimate.
In summary, a change in accounting estimate occurs when there are differences between certain parameters estimated earlier and re-estimated during the current period. It reflects a revision in judgment or new information that leads to a more accurate estimation of future financial impacts.
Explanation:
A change in accounting estimate refers to a revision made to an accounting estimate, which is an approximation of a future event or transaction's financial impact. Accounting estimates are necessary because some items cannot be measured with precision, and they require management's judgment or expertise. These estimates are reviewed periodically to ensure they remain relevant and accurate.
The key points to understand about a change in accounting estimate are as follows:
1. Definition:
- A change in accounting estimate occurs when there is a revision to an estimate made in a prior period.
- It is not a correction of an error, but rather a change in judgment or new information that leads to a revision of the estimate.
2. Parameters Estimated Earlier:
- A change in accounting estimate refers to differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier.
- Parameters can include items like useful life, depreciation rate, bad debt provision, inventory obsolescence, etc.
3. Re-Estimated During Current Period:
- The change in accounting estimate occurs when these parameters are re-estimated during the current period.
- The re-estimation can be due to new information, changes in circumstances, or improved estimation techniques.
4. Examples:
- For example, if a company estimates the useful life of its machinery as 10 years but later determines that it should be 8 years based on new information or technological advancements, it would result in a change in accounting estimate.
- Similarly, if a company estimates the provision for bad debts at 5% of accounts receivable but later determines that it should be 7% based on historical trends or economic conditions, it would also be a change in accounting estimate.
In summary, a change in accounting estimate occurs when there are differences between certain parameters estimated earlier and re-estimated during the current period. It reflects a revision in judgment or new information that leads to a more accurate estimation of future financial impacts.
The long term assets that have no physical existence but are rights that have value is known as- a)Current assets
- b)Fixed assets
- c)Intangible assets
- d)Investments
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The long term assets that have no physical existence but are rights that have value is known as
a)
Current assets
b)
Fixed assets
c)
Intangible assets
d)
Investments

|
Ritu Majhi Majhi answered |
Option C intangible assets have no physical existence but are rights that have value for example goodwill, patent, copyright etc.
Change in accounting estimate means:- a)Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and re- estimated during the current period.
- b)Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and actual results achieved during the current period.
- c)Differences arising between certain parameters re-estimated during the current period and actual results achieved during the current period.
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Change in accounting estimate means:
a)
Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and re- estimated during the current period.
b)
Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and actual results achieved during the current period.
c)
Differences arising between certain parameters re-estimated during the current period and actual results achieved during the current period.
d)
Both (a) and (b)

|
Maheshwar Sharma answered |
Change in accounting estimate means:
A change in accounting estimate refers to a revision in the estimated value of certain parameters used in the preparation of financial statements. These changes occur when new information becomes available or when the circumstances related to the estimate change. The correct answer to the question is option 'D', which states that a change in accounting estimate involves differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier (option 'a') and differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and actual results achieved during the current period (option 'b').
Explaining the answer:
To understand the answer in detail, let's break it down into two parts:
Part 1: Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier
- When preparing financial statements, certain estimates are made for various parameters such as useful life of an asset, allowance for doubtful accounts, inventory obsolescence, warranty expenses, etc.
- These estimates are based on management's judgment, historical data, industry trends, and other relevant information available at the time.
- However, due to the inherent uncertainty involved in estimating future events, there may be a need to revise these estimates as new information becomes available or circumstances change.
- For example, if a company estimated the useful life of its machinery to be 10 years but later realizes that it should be revised to 8 years based on the current condition and usage patterns, it represents a change in accounting estimate.
- Therefore, option 'a' correctly states that a change in accounting estimate involves differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier.
Part 2: Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and actual results achieved during the current period
- In addition to the revision of estimates, a change in accounting estimate also takes into account the differences that arise between the estimated value and the actual results achieved during the current period.
- For example, a company may estimate that its bad debt expense for the year will be $10,000 based on historical data and industry trends. However, at the end of the year, it determines that the actual bad debt expense is $12,000. This represents a difference between the estimated value and the actual result achieved.
- Therefore, option 'b' correctly states that a change in accounting estimate involves differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and actual results achieved during the current period.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a change in accounting estimate occurs when there are differences between certain parameters estimated earlier and when there are differences between those estimates and the actual results achieved during the current period. These changes are necessary to ensure that the financial statements reflect the most accurate and reliable information available.
A change in accounting estimate refers to a revision in the estimated value of certain parameters used in the preparation of financial statements. These changes occur when new information becomes available or when the circumstances related to the estimate change. The correct answer to the question is option 'D', which states that a change in accounting estimate involves differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier (option 'a') and differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and actual results achieved during the current period (option 'b').
Explaining the answer:
To understand the answer in detail, let's break it down into two parts:
Part 1: Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier
- When preparing financial statements, certain estimates are made for various parameters such as useful life of an asset, allowance for doubtful accounts, inventory obsolescence, warranty expenses, etc.
- These estimates are based on management's judgment, historical data, industry trends, and other relevant information available at the time.
- However, due to the inherent uncertainty involved in estimating future events, there may be a need to revise these estimates as new information becomes available or circumstances change.
- For example, if a company estimated the useful life of its machinery to be 10 years but later realizes that it should be revised to 8 years based on the current condition and usage patterns, it represents a change in accounting estimate.
- Therefore, option 'a' correctly states that a change in accounting estimate involves differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier.
Part 2: Differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and actual results achieved during the current period
- In addition to the revision of estimates, a change in accounting estimate also takes into account the differences that arise between the estimated value and the actual results achieved during the current period.
- For example, a company may estimate that its bad debt expense for the year will be $10,000 based on historical data and industry trends. However, at the end of the year, it determines that the actual bad debt expense is $12,000. This represents a difference between the estimated value and the actual result achieved.
- Therefore, option 'b' correctly states that a change in accounting estimate involves differences arising between certain parameters estimated earlier and actual results achieved during the current period.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a change in accounting estimate occurs when there are differences between certain parameters estimated earlier and when there are differences between those estimates and the actual results achieved during the current period. These changes are necessary to ensure that the financial statements reflect the most accurate and reliable information available.
Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2001. On 31st March, 2011, similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 but the realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2001) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
Q. The present value of machinery is - a)Rs. 10,00,000.
- b)Rs.20,00,000.
- c)Rs.15,00,000.
- d)Rs.12,00,000.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Mohan purchased a machinery amounting Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2001. On 31st March, 2011, similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000 but the realizable value of the machinery (purchased on 1.4.2001) was estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business, was calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
Q. The present value of machinery is
Q. The present value of machinery is
a)
Rs. 10,00,000.
b)
Rs.20,00,000.
c)
Rs.15,00,000.
d)
Rs.12,00,000.

|
Saumya Khanna answered |
To calculate the present value of the machinery, we need to consider the cash flows it is expected to generate in the future.
Given information:
- Mohan purchased the machinery for Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2001.
- On 31st March, 2011, similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000.
- The realizable value of the machinery purchased on 1st April, 2001 is estimated at Rs. 15,00,000.
- The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business is calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
To calculate the present value, we need to discount the future cash flows to the present using an appropriate discount rate. In this case, the discount rate is not given, so we cannot calculate the exact present value. However, we can analyze the given information to understand the concept.
Explanation:
1. Machinery Cost: Mohan purchased the machinery for Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2001. This is the historical cost of the machinery.
2. Replacement Cost: On 31st March, 2011, similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000. This indicates the cost of acquiring a similar machinery at a later date.
3. Realizable Value: The realizable value of the machinery purchased on 1st April, 2001 is estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. This indicates the expected value that can be realized by selling the machinery at a later date.
4. Present Discounted Value: The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business is calculated as Rs. 12,00,000. This indicates the present value of the expected cash flows from the machinery.
Based on the given information, it can be inferred that the present value of the machinery is Rs. 12,00,000. This is the present discounted value of the expected cash inflows from the machinery.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - Rs. 12,00,000.
Given information:
- Mohan purchased the machinery for Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2001.
- On 31st March, 2011, similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000.
- The realizable value of the machinery purchased on 1st April, 2001 is estimated at Rs. 15,00,000.
- The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business is calculated as Rs. 12,00,000.
To calculate the present value, we need to discount the future cash flows to the present using an appropriate discount rate. In this case, the discount rate is not given, so we cannot calculate the exact present value. However, we can analyze the given information to understand the concept.
Explanation:
1. Machinery Cost: Mohan purchased the machinery for Rs. 10,00,000 on 1st April, 2001. This is the historical cost of the machinery.
2. Replacement Cost: On 31st March, 2011, similar machinery could be purchased for Rs. 20,00,000. This indicates the cost of acquiring a similar machinery at a later date.
3. Realizable Value: The realizable value of the machinery purchased on 1st April, 2001 is estimated at Rs. 15,00,000. This indicates the expected value that can be realized by selling the machinery at a later date.
4. Present Discounted Value: The present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the machinery was expected to generate in the normal course of business is calculated as Rs. 12,00,000. This indicates the present value of the expected cash flows from the machinery.
Based on the given information, it can be inferred that the present value of the machinery is Rs. 12,00,000. This is the present discounted value of the expected cash inflows from the machinery.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - Rs. 12,00,000.
Chapter doubts & questions for Unit 7: Accounting as a Measurement Discipline — Valuation Principles, Accounting Estimates - Accounting for CA Foundation 2025 is part of CA Foundation exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the CA Foundation exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for CA Foundation 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Unit 7: Accounting as a Measurement Discipline — Valuation Principles, Accounting Estimates - Accounting for CA Foundation in English & Hindi are available as part of CA Foundation exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CA Foundation Exam by signing up for free.
Accounting for CA Foundation
68 videos|265 docs|83 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









