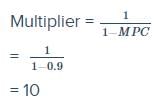All Exams >
CA Foundation >
Mock Tests & Past Year Papers for CA Foundation >
All Questions
All questions of Business Economics Mock Tests for CA Foundation Exam
Assume that when price is Rs. 40 quantity demanded is 9 units, and when price is Rs. 38, quantity demanded is 10 units. Based on this information, what is the marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 9 units to 10 units?- a)Rs. 20
- b)Rs. 40
- c)Rs.38
- d)Rs. 1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assume that when price is Rs. 40 quantity demanded is 9 units, and when price is Rs. 38, quantity demanded is 10 units. Based on this information, what is the marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 9 units to 10 units?
a)
Rs. 20
b)
Rs. 40
c)
Rs.38
d)
Rs. 1

|
Anu Sen answered |
Given information:
Price of one unit = Rs. 40, Quantity demanded at this price = 9 units
Price of one unit = Rs. 38, Quantity demanded at this price = 10 units
To find: Marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 9 units to 10 units
Explanation:
Marginal revenue is the additional revenue earned by selling one additional unit of a product.
To find marginal revenue, we need to calculate the total revenue earned from selling 10 units and subtract it from the total revenue earned from selling 9 units.
Total revenue earned from selling 9 units = Price per unit * Quantity demanded
= Rs. 40 * 9
= Rs. 360
Total revenue earned from selling 10 units = Price per unit * Quantity demanded
= Rs. 38 * 10
= Rs. 380
Marginal revenue = Total revenue earned from selling 10 units - Total revenue earned from selling 9 units
= Rs. 380 - Rs. 360
= Rs. 20
Therefore, the marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 9 units to 10 units is Rs. 20.
Price of one unit = Rs. 40, Quantity demanded at this price = 9 units
Price of one unit = Rs. 38, Quantity demanded at this price = 10 units
To find: Marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 9 units to 10 units
Explanation:
Marginal revenue is the additional revenue earned by selling one additional unit of a product.
To find marginal revenue, we need to calculate the total revenue earned from selling 10 units and subtract it from the total revenue earned from selling 9 units.
Total revenue earned from selling 9 units = Price per unit * Quantity demanded
= Rs. 40 * 9
= Rs. 360
Total revenue earned from selling 10 units = Price per unit * Quantity demanded
= Rs. 38 * 10
= Rs. 380
Marginal revenue = Total revenue earned from selling 10 units - Total revenue earned from selling 9 units
= Rs. 380 - Rs. 360
= Rs. 20
Therefore, the marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 9 units to 10 units is Rs. 20.
When MU is zero, TU is _________.- a)minimum
- b)rising
- c)falling
- d)maximum
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When MU is zero, TU is _________.
a)
minimum
b)
rising
c)
falling
d)
maximum

|
Deepika Nambiar answered |
When marginal utility is zero, then total utility is maximum because any further consumption of that commodity will lead to negative marginal utility and therefore total utility will tend to decrease.
Convex indifferent curve is explained by- a)increasing MRS
- b)diminishing MRS
- c)constant MRS
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Convex indifferent curve is explained by
a)
increasing MRS
b)
diminishing MRS
c)
constant MRS
d)
None of these

|
Simran Pillai answered |
Convexity means slope is decreasing as the marginal rate of substitution goes on diminishing.
Average income increases from INR 20,000 p.m. to INR 22,000 p.m. Quantity demanded per month increases from 5000 to 6000 units. Which of the following is correct?- a)Demand is price inelastic
- b)The good is inferior
- c)Income elasticity is -2
- d)The product has a positive income elasticity of demand
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Average income increases from INR 20,000 p.m. to INR 22,000 p.m. Quantity demanded per month increases from 5000 to 6000 units. Which of the following is correct?
a)
Demand is price inelastic
b)
The good is inferior
c)
Income elasticity is -2
d)
The product has a positive income elasticity of demand

|
Ruchi Mishra answered |
The percentage change in demand is +20%; the percentage change in income is +10%. This means the product is normal because demand rises with more income and has an income elasticity of +2.
When the price of petrol goes up, demand for cars will _____ . - a)rise
- b)fall
- c)not changes
- d)remain unchanged
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When the price of petrol goes up, demand for cars will _____ .
a)
rise
b)
fall
c)
not changes
d)
remain unchanged

|
Niharika Datta answered |
the price of petrol goes up, demand for cars will fall
Which of the following is NOT an input- a)Labour
- b)Entrepreneurship
- c)Natural resources
- d)Production
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT an input
a)
Labour
b)
Entrepreneurship
c)
Natural resources
d)
Production

|
Tanvi Pillai answered |
Production is a process, not an input.
Who is known as father of Economics?- a)Samuelson
- b)Robins
- c)Adam Smith
- d)Marshall
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who is known as father of Economics?
a)
Samuelson
b)
Robins
c)
Adam Smith
d)
Marshall

|
Gaurav Chatterjee answered |
Adam Smith was a Scottish economist who greatly influenced the economic theories of his time and came up with the first definition of economics on wealth generation, thus, he is known as the father of economics.
If the marginal propensity to save decreases, the value of the multiplier will- a)Increase
- b)Decrease
- c)Remain constant
- d)Decrease as much as the decrease in MPS
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the marginal propensity to save decreases, the value of the multiplier will
a)
Increase
b)
Decrease
c)
Remain constant
d)
Decrease as much as the decrease in MPS

|
Divya Dasgupta answered |
If the marginal propensity to save decreases, the value of the multiplier will increase.
Monopoly means ______.- a)single buyer
- b)many sellers
- c)single seller
- d)many buyers
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Monopoly means ______.
a)
single buyer
b)
many sellers
c)
single seller
d)
many buyers

|
Anu Kaur answered |
A market structure characterized by a single seller, selling a unique product in the market. In a monopoly market, the seller faces no competition, as he is the sole seller of goods with no close substitute.
In the case of a straight line demand curve meeting the two axes, the price elasticity of demand at y-axis of the line would be equal to- a)1
- b)infinity
- c)3
- d)1.25
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the case of a straight line demand curve meeting the two axes, the price elasticity of demand at y-axis of the line would be equal to
a)
1
b)
infinity
c)
3
d)
1.25

|
Nitin Kumar answered |
**Price Elasticity of Demand**
Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price. It is calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price.
**Straight Line Demand Curve**
A straight line demand curve is a linear representation of the relationship between price and quantity demanded. It implies a constant slope, which means the percentage change in quantity demanded is proportional to the percentage change in price.
**Elasticity at the Y-Axis**
When the demand curve meets the y-axis, it indicates that the quantity demanded is zero at that price. In other words, the price is so high that no one is willing to purchase the product.
At this point, the demand curve is perfectly elastic because any increase in price will lead to a complete elimination of demand. The demand curve is vertical, indicating an infinite price elasticity of demand.
**Explanation**
The price elasticity of demand at the y-axis of a straight line demand curve is equal to infinity. This is because the percentage change in quantity demanded is infinitely large compared to any percentage change in price.
When the price increases even slightly from zero, the quantity demanded drops to zero. This indicates an infinitely elastic response to any change in price.
Therefore, option B - infinity is the correct answer.
Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price. It is calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price.
**Straight Line Demand Curve**
A straight line demand curve is a linear representation of the relationship between price and quantity demanded. It implies a constant slope, which means the percentage change in quantity demanded is proportional to the percentage change in price.
**Elasticity at the Y-Axis**
When the demand curve meets the y-axis, it indicates that the quantity demanded is zero at that price. In other words, the price is so high that no one is willing to purchase the product.
At this point, the demand curve is perfectly elastic because any increase in price will lead to a complete elimination of demand. The demand curve is vertical, indicating an infinite price elasticity of demand.
**Explanation**
The price elasticity of demand at the y-axis of a straight line demand curve is equal to infinity. This is because the percentage change in quantity demanded is infinitely large compared to any percentage change in price.
When the price increases even slightly from zero, the quantity demanded drops to zero. This indicates an infinitely elastic response to any change in price.
Therefore, option B - infinity is the correct answer.
How much interest is paid by the RBI on the money deposited under the CRR measure?- a)Equal to the rate of CRR
- b)More than the CRR
- c)Less than the CRR
- d)No interest is paid by the RBI
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How much interest is paid by the RBI on the money deposited under the CRR measure?
a)
Equal to the rate of CRR
b)
More than the CRR
c)
Less than the CRR
d)
No interest is paid by the RBI

|
Rutuja Dasgupta answered |
No interest is paid by the RBI on the money deposited under the CRR measure
Who is called the 'father of economics'?- a)Adam Smith
- b)Karl Marx
- c)Max Muller
- d)Amartya Sen
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who is called the 'father of economics'?
a)
Adam Smith
b)
Karl Marx
c)
Max Muller
d)
Amartya Sen

|
Ameya Menon answered |
Adam Smith is called the 'father of economics'.
A quantity measured per unit of time period is known as :- a)Stock variable
- b)Flow variable
- c)Inventory
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A quantity measured per unit of time period is known as :
a)
Stock variable
b)
Flow variable
c)
Inventory
d)
None of these

|
Prashanth Datta answered |
Flow variables are measured per unit time.
Level of savings depends upon __________.- a)ability to save
- b)willingness to saved
- c)willingness to save
- d)willingness save
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Level of savings depends upon __________.
a)
ability to save
b)
willingness to saved
c)
willingness to save
d)
willingness save

|
Lekshmi Mehta answered |
Savings is that part of income which isn't used for consumption and is thus, saved. The level of savings in the economy depends upon the ability of the people to fulfill their consumption needs using a part of their income and the willingness to save, which is driven by the returns on savings and investment.
Human capital increases:- a)Labour in market
- b)Labour Productivity
- c)Trained labour
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Human capital increases:
a)
Labour in market
b)
Labour Productivity
c)
Trained labour
d)
None of the above
|
|
Urvashi Porwal answered |
Correct answer is Option 'b'. Human capital increases labour productivity as human capital means investment in skills , abilities, education, health, expertise so that these factors result in improvement in labour productivity. As every labour works like other but what differentiate one from other is investment in HUMAN CAPITAL . Hence , investment in human capital is very beneficial for our nation.
The shape of transformation curve is changed by- a)opportunity cost
- b)total cost
- c)marginal opportunity cost
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The shape of transformation curve is changed by
a)
opportunity cost
b)
total cost
c)
marginal opportunity cost
d)
none of these

|
Rajveer Yadav answered |
The shape of transformation curve is changed by marginal opportunity cost.
Which economy is now a myth only, as no country in the world is having that type of economy?- a)Capitalist Economy
- b)Socialist Economy
- c)Mixed Economy
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which economy is now a myth only, as no country in the world is having that type of economy?
a)
Capitalist Economy
b)
Socialist Economy
c)
Mixed Economy
d)
None of the above

|
Sameer Sharma answered |
Mythical Economy: Socialist Economy
Socialism is an economic system in which the means of production, distribution, and exchange are owned and controlled by the state or by the community as a whole. However, currently, there is no country in the world that completely practices socialism. While some countries may have socialist policies, they do not have an entirely socialist economy.
Reasons why Socialist Economy is a Myth:
1. The fall of the Soviet Union: The Soviet Union was seen as the epitome of a socialist economy. However, with the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991, the socialist economic model lost its credibility. The failure of the Soviet economy showed that a centrally planned economy could not compete with a market-based economy.
2. The rise of mixed economies: Most countries in the world today practice a mixed economy, which is a combination of socialist and capitalist economic systems. This means that while the government controls some aspects of the economy, there is also room for private enterprise. This has led to the decline of the socialist economic model.
3. Globalization: The rise of globalization has made it difficult for countries to practice a socialist economic system. With the increase in international trade, it is challenging for countries to control their economies entirely.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the socialist economy is now a myth as no country in the world practices it entirely. While some countries may have socialist policies, they also have a market-based economy. The rise of mixed economies and the fall of the Soviet Union have contributed to the decline of the socialist economic model.
Socialism is an economic system in which the means of production, distribution, and exchange are owned and controlled by the state or by the community as a whole. However, currently, there is no country in the world that completely practices socialism. While some countries may have socialist policies, they do not have an entirely socialist economy.
Reasons why Socialist Economy is a Myth:
1. The fall of the Soviet Union: The Soviet Union was seen as the epitome of a socialist economy. However, with the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991, the socialist economic model lost its credibility. The failure of the Soviet economy showed that a centrally planned economy could not compete with a market-based economy.
2. The rise of mixed economies: Most countries in the world today practice a mixed economy, which is a combination of socialist and capitalist economic systems. This means that while the government controls some aspects of the economy, there is also room for private enterprise. This has led to the decline of the socialist economic model.
3. Globalization: The rise of globalization has made it difficult for countries to practice a socialist economic system. With the increase in international trade, it is challenging for countries to control their economies entirely.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the socialist economy is now a myth as no country in the world practices it entirely. While some countries may have socialist policies, they also have a market-based economy. The rise of mixed economies and the fall of the Soviet Union have contributed to the decline of the socialist economic model.
Which of the following rules should be followed by a supplier for profit maximization?- a)Keep producing until the total revenue is equal to total cost.
- b)produce an additional unit of good if the price is greater than the marginal cost
- c)do not produce an additional unit if its marginal cost is higher than the marginal cost of the previously produced units
- d)Always produce an additional unit when the marginal revenue is greater than zero.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following rules should be followed by a supplier for profit maximization?
a)
Keep producing until the total revenue is equal to total cost.
b)
produce an additional unit of good if the price is greater than the marginal cost
c)
do not produce an additional unit if its marginal cost is higher than the marginal cost of the previously produced units
d)
Always produce an additional unit when the marginal revenue is greater than zero.
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
If the price is greater than the marginal cost of the next unit, the firm should continue production as there is a profit on producing the additional unit.
Shalini sells lemonades at Rs 10 per glass. If she sells 300 glasses, what is her total revenue?- a)Rs 1000
- b)Rs 1500
- c)Rs 2000
- d)Rs 3000
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Shalini sells lemonades at Rs 10 per glass. If she sells 300 glasses, what is her total revenue?
a)
Rs 1000
b)
Rs 1500
c)
Rs 2000
d)
Rs 3000
|
|
Jigu Purohit answered |
300 glasses multiply with the price 10 then it is 3000
Total Revenue= Price X quantity
Total Revenue= Price X quantity
Deposits in the banks are:- a)Assets of the bank
- b)Liabilities of the bank
- c)Liabilities of the depositors
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Deposits in the banks are:
a)
Assets of the bank
b)
Liabilities of the bank
c)
Liabilities of the depositors
d)
None of the above

|
Jyoti Nair answered |
Assets and Liabilities in Banking
Assets of the bank:
- Assets are what the bank owns, such as cash, loans, investments, and physical assets like buildings and equipment.
- These are resources that the bank can use to generate revenue and provide services to customers.
- Assets also include the money that customers have deposited in the bank, which the bank can use to lend out to other customers.
Liabilities of the bank:
- Liabilities are what the bank owes, including deposits from customers, loans from other banks, and bonds issued to investors.
- Deposits in the bank are considered liabilities because the bank is obligated to repay these funds to customers on demand.
- When a customer deposits money in the bank, the bank is essentially borrowing that money from the customer.
- The bank must keep a portion of these deposits on reserve and can use the rest to make loans and investments to earn interest.
Therefore, deposits in the banks are classified as liabilities of the bank because they represent funds that the bank owes to its customers. This distinction is important for understanding the balance sheet of a bank and how it manages its assets and liabilities to ensure financial stability and liquidity.
Assets of the bank:
- Assets are what the bank owns, such as cash, loans, investments, and physical assets like buildings and equipment.
- These are resources that the bank can use to generate revenue and provide services to customers.
- Assets also include the money that customers have deposited in the bank, which the bank can use to lend out to other customers.
Liabilities of the bank:
- Liabilities are what the bank owes, including deposits from customers, loans from other banks, and bonds issued to investors.
- Deposits in the bank are considered liabilities because the bank is obligated to repay these funds to customers on demand.
- When a customer deposits money in the bank, the bank is essentially borrowing that money from the customer.
- The bank must keep a portion of these deposits on reserve and can use the rest to make loans and investments to earn interest.
Therefore, deposits in the banks are classified as liabilities of the bank because they represent funds that the bank owes to its customers. This distinction is important for understanding the balance sheet of a bank and how it manages its assets and liabilities to ensure financial stability and liquidity.
Q. If a good is priced at Rs. 180 p.u. and its price is increased to Rs. 240 p.u. Now suppose quantity demanded previously was 100 units and as a result of price increase, the quantity demanded fell to 80 units. What is the price elasticity?- a). 777
- b)1.4
- c)1
- d). 8
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Q. If a good is priced at Rs. 180 p.u. and its price is increased to Rs. 240 p.u. Now suppose quantity demanded previously was 100 units and as a result of price increase, the quantity demanded fell to 80 units. What is the price elasticity?
a)
. 777
b)
1.4
c)
1
d)
. 8

|
Rithika Nair answered |
Price Elasticity of Demand Calculation
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED) is a measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded to the change in price.
PED = (% Change in Quantity Demanded ÷ % Change in Price)
Given:
Initial Price (P1) = Rs. 180
New Price (P2) = Rs. 240
Initial Quantity Demanded (Q1) = 100 units
New Quantity Demanded (Q2) = 80 units
% Change in Quantity Demanded = ((Q2 - Q1) ÷ Q1) × 100
% Change in Quantity Demanded = ((80 - 100) ÷ 100) × 100
% Change in Quantity Demanded = -20%
% Change in Price = ((P2 - P1) ÷ P1) × 100
% Change in Price = ((240 - 180) ÷ 180) × 100
% Change in Price = 33.33%
PED = (% Change in Quantity Demanded ÷ % Change in Price)
PED = (-20% ÷ 33.33%)
PED = -0.6
Absolute Value of PED
The absolute value of PED is taken to represent the elasticity of demand.
|PED| = |-0.6|
|PED| = 0.6
Interpretation
The price elasticity of demand is greater than 1, which means that the good is elastic. A change in price leads to a proportionately larger change in quantity demanded. In this case, the absolute value of PED is 0.6. It means that a 1% increase in price leads to a 0.6% decrease in quantity demanded.
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED) is a measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded to the change in price.
PED = (% Change in Quantity Demanded ÷ % Change in Price)
Given:
Initial Price (P1) = Rs. 180
New Price (P2) = Rs. 240
Initial Quantity Demanded (Q1) = 100 units
New Quantity Demanded (Q2) = 80 units
% Change in Quantity Demanded = ((Q2 - Q1) ÷ Q1) × 100
% Change in Quantity Demanded = ((80 - 100) ÷ 100) × 100
% Change in Quantity Demanded = -20%
% Change in Price = ((P2 - P1) ÷ P1) × 100
% Change in Price = ((240 - 180) ÷ 180) × 100
% Change in Price = 33.33%
PED = (% Change in Quantity Demanded ÷ % Change in Price)
PED = (-20% ÷ 33.33%)
PED = -0.6
Absolute Value of PED
The absolute value of PED is taken to represent the elasticity of demand.
|PED| = |-0.6|
|PED| = 0.6
Interpretation
The price elasticity of demand is greater than 1, which means that the good is elastic. A change in price leads to a proportionately larger change in quantity demanded. In this case, the absolute value of PED is 0.6. It means that a 1% increase in price leads to a 0.6% decrease in quantity demanded.
An isoquant that is- a)further from the origin represents greater output
- b)flatter represents the trade-offs between inputs that are poor substitutes
- c)negatively sloped represents input combinations associated with Stage I of production
- d)All of the above are correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An isoquant that is
a)
further from the origin represents greater output
b)
flatter represents the trade-offs between inputs that are poor substitutes
c)
negatively sloped represents input combinations associated with Stage I of production
d)
All of the above are correct

|
Sanjana Khanna answered |
An isoquant is a graphical representation of all the possible combinations of inputs that can produce a certain level of output. It is similar to an indifference curve in consumer theory, but instead of representing combinations of goods that provide the same level of satisfaction, an isoquant represents combinations of inputs that result in the same level of output.
a) An isoquant that is further from the origin represents greater output:
An isoquant is usually drawn as a curve, and the distance of the curve from the origin represents the level of output. As we move away from the origin along the isoquant curve, we are able to produce higher levels of output. This is because the combinations of inputs represented by points further from the origin are more productive and efficient in generating output. Therefore, option 'A' is correct.
b) A flatter isoquant represents the trade-offs between inputs that are poor substitutes:
The slope of an isoquant represents the rate at which one input can be substituted for another while keeping the level of output constant. If the isoquant is flatter, it means that the inputs are poor substitutes for each other. In other words, a small change in one input can be offset by a larger change in the other input without affecting the level of output. This implies that the firm can easily adjust its input mix without significantly impacting its production. Therefore, option 'B' is incorrect.
c) A negatively sloped isoquant represents input combinations associated with Stage I of production:
The slope of an isoquant is negative because the inputs are assumed to be imperfect substitutes for each other. As a result, as the firm increases the quantity of one input, it needs to decrease the quantity of the other input to maintain the same level of output. This negative slope of the isoquant is associated with the initial stages of production, where increasing the quantity of one input has a significant positive impact on output. Therefore, option 'C' is incorrect.
d) All of the above are correct:
Based on the explanations provided above, it is clear that option 'A' is correct, but options 'B' and 'C' are incorrect. Therefore, option 'D' is incorrect as well.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'A'.
a) An isoquant that is further from the origin represents greater output:
An isoquant is usually drawn as a curve, and the distance of the curve from the origin represents the level of output. As we move away from the origin along the isoquant curve, we are able to produce higher levels of output. This is because the combinations of inputs represented by points further from the origin are more productive and efficient in generating output. Therefore, option 'A' is correct.
b) A flatter isoquant represents the trade-offs between inputs that are poor substitutes:
The slope of an isoquant represents the rate at which one input can be substituted for another while keeping the level of output constant. If the isoquant is flatter, it means that the inputs are poor substitutes for each other. In other words, a small change in one input can be offset by a larger change in the other input without affecting the level of output. This implies that the firm can easily adjust its input mix without significantly impacting its production. Therefore, option 'B' is incorrect.
c) A negatively sloped isoquant represents input combinations associated with Stage I of production:
The slope of an isoquant is negative because the inputs are assumed to be imperfect substitutes for each other. As a result, as the firm increases the quantity of one input, it needs to decrease the quantity of the other input to maintain the same level of output. This negative slope of the isoquant is associated with the initial stages of production, where increasing the quantity of one input has a significant positive impact on output. Therefore, option 'C' is incorrect.
d) All of the above are correct:
Based on the explanations provided above, it is clear that option 'A' is correct, but options 'B' and 'C' are incorrect. Therefore, option 'D' is incorrect as well.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'A'.
Which of the following is not a determinant of a consumer's demand for a commodity?- a)Income
- b)Population
- c)Prices of related goods
- d)Tastes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a determinant of a consumer's demand for a commodity?
a)
Income
b)
Population
c)
Prices of related goods
d)
Tastes

|
Sinjini Gupta answered |
Population is not a determinant of a consumer's demand for a commodity.
When total product is 100 units and units of variable factor are 4, average product will be ____________________.- a)25
- b)400
- c)96
- d)104
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When total product is 100 units and units of variable factor are 4, average product will be ____________________.
a)
25
b)
400
c)
96
d)
104

|
Hrishikesh Pillai answered |
When total product is 100 units and units of variable factor are 4, average product will be 25
Full form of DMU is ______________.- a)Diminishing Marginal Utility
- b)Distributive Marginal Utility
- c)Direct Marginal Utility
- d)Display Marginal Utility
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Full form of DMU is ______________.
a)
Diminishing Marginal Utility
b)
Distributive Marginal Utility
c)
Direct Marginal Utility
d)
Display Marginal Utility

|
Lakshmi Kumar answered |
Diminishing marginal utility states that when a consumer goes on consuming a standard unit of a commodity, the additional utility in every successive unit of consumption keeps on diminishing. It is based on the assumption that the consumer needs to consume a standard unit of the commodity.
If the marginal product of labor is 2, the marginal product of capital is 4, the wage rate is INR 3, the rental price of capital is INR 6, and the price of output is INR 1.50, then the firm should- a)Increase output by hiring more labor, more capital, or both
- b)Hold output constant, but hire more labor and less capital
- c)Decrease output by reducing the quantity of capital, reducing the number of units of labor, or both
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If the marginal product of labor is 2, the marginal product of capital is 4, the wage rate is INR 3, the rental price of capital is INR 6, and the price of output is INR 1.50, then the firm should
a)
Increase output by hiring more labor, more capital, or both
b)
Hold output constant, but hire more labor and less capital
c)
Decrease output by reducing the quantity of capital, reducing the number of units of labor, or both
d)
None of the above

|
Meera Joshi answered |
Cost of hiring one additional unit of labour = Rs 3
Revenue from hiring an additional unit of labour = MP of labour x price = Rs 3
Cost of renting one additional unit of capital = Rs 6
Revenue from renting an additional unit of capital = MP of capital x price = Rs 6
Hence, there is no benefit in increasing labour or capital.
Revenue from hiring an additional unit of labour = MP of labour x price = Rs 3
Cost of renting one additional unit of capital = Rs 6
Revenue from renting an additional unit of capital = MP of capital x price = Rs 6
Hence, there is no benefit in increasing labour or capital.
Suppose that an owner is earning total revenue of Rs. 1,00,000 and is increasing explicit cost of Rs. 60,000. If the owner could work for another company for Rs. 30,000 a year, we would conclude that:- a)The firm is earning economic profit or Rs. 10,000
- b)The firm is earning accounting profit or Rs. 40,000
- c)The firm is earning economic profit of Rs. 40,000
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Suppose that an owner is earning total revenue of Rs. 1,00,000 and is increasing explicit cost of Rs. 60,000. If the owner could work for another company for Rs. 30,000 a year, we would conclude that:
a)
The firm is earning economic profit or Rs. 10,000
b)
The firm is earning accounting profit or Rs. 40,000
c)
The firm is earning economic profit of Rs. 40,000
d)
Both (a) and (b)

|
Disha Joshi answered |
Explanation:
The owner's total revenue is Rs. 1,00,000 and explicit cost is Rs. 60,000. However, if the owner could work for another company for Rs. 30,000 a year, then we need to consider the opportunity cost of the owner's time.
Opportunity cost refers to the cost of the next best alternative foregone. In this case, the opportunity cost of the owner's time is Rs. 30,000, which is the amount the owner could earn by working for another company.
Now, let us consider the two types of profit:
1. Accounting profit: This is the difference between total revenue and explicit costs. In this case, accounting profit is Rs. 40,000 (Rs. 1,00,000 - Rs. 60,000).
2. Economic profit: This is the difference between total revenue and all costs, including both explicit and implicit costs. In this case, the implicit cost is the opportunity cost of the owner's time, which is Rs. 30,000. Therefore, economic profit is Rs. 10,000 (Rs. 1,00,000 - Rs. 60,000 - Rs. 30,000).
Since the owner could earn Rs. 30,000 by working for another company, the economic profit is lower than the accounting profit. Therefore, option (d) is correct as both economic profit and accounting profit are applicable in this case.
The owner's total revenue is Rs. 1,00,000 and explicit cost is Rs. 60,000. However, if the owner could work for another company for Rs. 30,000 a year, then we need to consider the opportunity cost of the owner's time.
Opportunity cost refers to the cost of the next best alternative foregone. In this case, the opportunity cost of the owner's time is Rs. 30,000, which is the amount the owner could earn by working for another company.
Now, let us consider the two types of profit:
1. Accounting profit: This is the difference between total revenue and explicit costs. In this case, accounting profit is Rs. 40,000 (Rs. 1,00,000 - Rs. 60,000).
2. Economic profit: This is the difference between total revenue and all costs, including both explicit and implicit costs. In this case, the implicit cost is the opportunity cost of the owner's time, which is Rs. 30,000. Therefore, economic profit is Rs. 10,000 (Rs. 1,00,000 - Rs. 60,000 - Rs. 30,000).
Since the owner could earn Rs. 30,000 by working for another company, the economic profit is lower than the accounting profit. Therefore, option (d) is correct as both economic profit and accounting profit are applicable in this case.
A firm has variable cost of Rs. 1,000 at 5 units of output. If fixed cost are Rs. 400, what will be the average total cost at 5 units of output?- a)380
- b)280
- c)60
- d)400
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A firm has variable cost of Rs. 1,000 at 5 units of output. If fixed cost are Rs. 400, what will be the average total cost at 5 units of output?
a)
380
b)
280
c)
60
d)
400

|
Amrutha Goyal answered |
Calculating Average Total Cost at 5 Units of Output
Given information:
Variable cost at 5 units of output = Rs. 1,000
Fixed cost = Rs. 400
To calculate the average total cost at 5 units of output, we need to consider both the fixed and variable costs. The formula for average total cost is:
Average total cost = (Fixed cost + Variable cost) / Number of units produced
Substituting the values given in the question, we get:
Average total cost = (400 + 1,000) / 5
Average total cost = 1,400 / 5
Average total cost = 280
Therefore, the average total cost at 5 units of output is Rs. 280.
Given information:
Variable cost at 5 units of output = Rs. 1,000
Fixed cost = Rs. 400
To calculate the average total cost at 5 units of output, we need to consider both the fixed and variable costs. The formula for average total cost is:
Average total cost = (Fixed cost + Variable cost) / Number of units produced
Substituting the values given in the question, we get:
Average total cost = (400 + 1,000) / 5
Average total cost = 1,400 / 5
Average total cost = 280
Therefore, the average total cost at 5 units of output is Rs. 280.
FERA is _________ Exchange Regulation Act.- a)Foreign
- b)Forests
- c)Fiscal
- d)Finance
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
FERA is _________ Exchange Regulation Act.
a)
Foreign
b)
Forests
c)
Fiscal
d)
Finance

|
Tejas Chaudhary answered |
FERA is Foreign Exchange Regulation Act.
Suppose that the following headlines appeared in a newspaper. Which would most clearly represent a macroeconomic issue?- a)"Central Bank Raises Interest Rates
- b)"Auto Dealership to Cut Prices"
- c)"Coffee Bean Crop Falls by 12 Percent"
- d)"Coffee Bean Crop Falls by 10 Percent"
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Suppose that the following headlines appeared in a newspaper. Which would most clearly represent a macroeconomic issue?
a)
"Central Bank Raises Interest Rates
b)
"Auto Dealership to Cut Prices"
c)
"Coffee Bean Crop Falls by 12 Percent"
d)
"Coffee Bean Crop Falls by 10 Percent"
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
Macroeconomics is that branch of Economics, which studies economic problems (or economic issues) relating to economy as a whole. Since Central bank is at the center of the entire banking system, this is an example of Macroeconomic variable.
Marginal Utility curve always- a)rising
- b)parallel to x-axis
- c)parallel to y-axis
- d)falling
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Marginal Utility curve always
a)
rising
b)
parallel to x-axis
c)
parallel to y-axis
d)
falling

|
Srsps answered |
The negative slope of the marginal utility curve reflects the law of diminishing marginal utility. The marginal utility curve also can be used to derived the demand curve.
MRS is determined by- a)satisfaction level of the consumer
- b)income of the consumer
- c)tastes of the consumer
- d)preferences of the consumer
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
MRS is determined by
a)
satisfaction level of the consumer
b)
income of the consumer
c)
tastes of the consumer
d)
preferences of the consumer

|
Aditi Joshi answered |
MRS is always related to the choice and preferences of the consumer.
Calculate Income-elasticity for the household when the income of a household rises by 10% the demand for T.V. rises by 20%- a)+ .5
- b)-.5
- c)+ 2
- d)-2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate Income-elasticity for the household when the income of a household rises by 10% the demand for T.V. rises by 20%
a)
+ .5
b)
-.5
c)
+ 2
d)
-2

|
Freedom Institute answered |
Income elasticity of demand is calculated using the formula: Percentage change in quantity demanded / Percentage change in income. In this case, the demand for T.V. rises by 20% when the income increases by 10%. Therefore, the income elasticity is 20% / 10% = 2. This confirms that the answer is option c, "+ 2".
Which of the following systems is followed by the Reserve Bank of India for issuing currency?- a)Proportionate system
- b)Simple deposit system
- c)Minimum reserve system
- d)Fixed fiduciary issue system
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following systems is followed by the Reserve Bank of India for issuing currency?
a)
Proportionate system
b)
Simple deposit system
c)
Minimum reserve system
d)
Fixed fiduciary issue system

|
Freedom Institute answered |
The RBI follows the minimum reserve system, wherein it has to maintain a minimum quantity of gold bullion as reserves to issue currency.
The positively sloped (i.e. rising) part of the long run average total cost curve is due to which of the following?- a)Diseconomies of scale.
- b)Increasing returns.
- c)The firm being able to take advantage of large-scale production techniques as it expands its output.
- d)The increase in productivity that results from specialization.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The positively sloped (i.e. rising) part of the long run average total cost curve is due to which of the following?
a)
Diseconomies of scale.
b)
Increasing returns.
c)
The firm being able to take advantage of large-scale production techniques as it expands its output.
d)
The increase in productivity that results from specialization.

|
Hrishikesh Mukherjee answered |
The positively sloped (i.e. rising) part of the long run average total cost curve is due to diseconomies of scale
Money that is issued by the authority of the government is called:- a)Full bodied money
- b)Credit money
- c)Fiat money
- d)Fiduciary money
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Money that is issued by the authority of the government is called:
a)
Full bodied money
b)
Credit money
c)
Fiat money
d)
Fiduciary money

|
Rithika Nair answered |
Fiat money refers to money whose value has been decreed by the government.
When the no.of uses of the purchase goods is less price elasticity of demand is- a)High
- b)low
- c)infinity
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When the no.of uses of the purchase goods is less price elasticity of demand is
a)
High
b)
low
c)
infinity
d)
zero

|
Ishan Goyal answered |
When goods whose uses less will have less price elastic because the products can be used for a specific purpose i.e it has no substitutes. The products which have more substitutes will have high elastic demand.
In India, the balance of payments has- a)Regularly been skewed to a surplus
- b)Always been balanced
- c)Remained constant
- d)Regularly been skewed to a deficit
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In India, the balance of payments has
a)
Regularly been skewed to a surplus
b)
Always been balanced
c)
Remained constant
d)
Regularly been skewed to a deficit

|
Sahil Malik answered |
India’s BOP has seen a deficit during most years, as India is a net importer.
Micro economics adopts _________ approach.- a)individualistic
- b)individualistics
- c)comprehensive
- d)superlative
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Micro economics adopts _________ approach.
a)
individualistic
b)
individualistics
c)
comprehensive
d)
superlative

|
Hrishikesh Mukherjee answered |
Where macro economics considers the society as a whole, on the other hand micro economics adopts the factors on individual basis. The approach of micro economics starts with the decisions of an individual about the allocation of time and revenue. The study of micro economics purely involves the study of factors on individual basis.
If the money supply were decreased, what would happen to the price level?- a)Increase
- b)DecreaseCorrect Answer
- c)Remains constant
- d)Either A or B
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the money supply were decreased, what would happen to the price level?
a)
Increase
b)
DecreaseCorrect Answer
c)
Remains constant
d)
Either A or B

|
Dipika Kaur answered |
A decrease in the money supply will lead to a decrease in price levels.
Vysakh is selling samosas. He already sold 250 samosas. His decision on whether or not to sell the 251st samosa is based on the ___- a)MC of the 251st samosa
- b)TC of the 251 samosas
- c)ATC of 251 samosas
- d)AVC of 251 samosas
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Vysakh is selling samosas. He already sold 250 samosas. His decision on whether or not to sell the 251st samosa is based on the ___
a)
MC of the 251st samosa
b)
TC of the 251 samosas
c)
ATC of 251 samosas
d)
AVC of 251 samosas

|
Ankita Mukherjee answered |
On taking any economic decisions, only the marginal quantities are important. In this case, the relevant decision variable is the marginal quantity of the 251st samosa.
If income is distributed evenly, the Gini co-efficient is:- a)Zero
- b)0.5
- c)1
- d)Undefined
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If income is distributed evenly, the Gini co-efficient is:
a)
Zero
b)
0.5
c)
1
d)
Undefined

|
Charvi Roy answered |
A Gini coefficient of zero corresponds to precise equality in income distribution
If MPS is 0.6, what will be ΔS when income increases by Rs 100?- a)Rs 60
- b)Rs 50
- c)Rs 40
- d)Rs 70
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If MPS is 0.6, what will be ΔS when income increases by Rs 100?
a)
Rs 60
b)
Rs 50
c)
Rs 40
d)
Rs 70

|
Sinjini Gupta answered |
Understanding MPS
The Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS) indicates the proportion of additional income that a household saves rather than spends. In this case, an MPS of 0.6 means that for every additional rupee earned, 60% will be saved.
Calculation of ΔS
To find the change in savings (ΔS) when income increases by Rs 100, we can use the formula:
ΔS = MPS × ΔIncome
Here, ΔIncome is the increase in income, which is Rs 100.
Applying the Values
1. MPS = 0.6
2. ΔIncome = Rs 100
Now, substituting the values into the formula:
ΔS = 0.6 × 100
Final Calculation
- ΔS = Rs 60
Thus, when income increases by Rs 100, the change in savings (ΔS) will be Rs 60.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'A' (Rs 60). This indicates that households will save Rs 60 out of every Rs 100 increase in income, reflecting their saving behavior as dictated by the MPS. Understanding this concept is crucial in economics as it helps analyze consumer behavior and the overall economic impact of income changes.
The Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS) indicates the proportion of additional income that a household saves rather than spends. In this case, an MPS of 0.6 means that for every additional rupee earned, 60% will be saved.
Calculation of ΔS
To find the change in savings (ΔS) when income increases by Rs 100, we can use the formula:
ΔS = MPS × ΔIncome
Here, ΔIncome is the increase in income, which is Rs 100.
Applying the Values
1. MPS = 0.6
2. ΔIncome = Rs 100
Now, substituting the values into the formula:
ΔS = 0.6 × 100
Final Calculation
- ΔS = Rs 60
Thus, when income increases by Rs 100, the change in savings (ΔS) will be Rs 60.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'A' (Rs 60). This indicates that households will save Rs 60 out of every Rs 100 increase in income, reflecting their saving behavior as dictated by the MPS. Understanding this concept is crucial in economics as it helps analyze consumer behavior and the overall economic impact of income changes.
Chapter doubts & questions for Business Economics Mock Tests - Mock Tests & Past Year Papers for CA Foundation 2025 is part of CA Foundation exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the CA Foundation exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for CA Foundation 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Business Economics Mock Tests - Mock Tests & Past Year Papers for CA Foundation in English & Hindi are available as part of CA Foundation exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CA Foundation Exam by signing up for free.
Mock Tests & Past Year Papers for CA Foundation
226 docs|19 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup