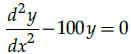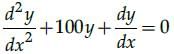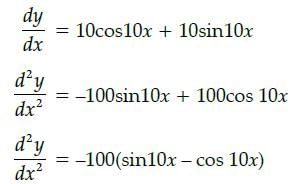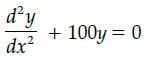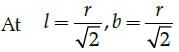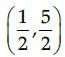All Exams >
JEE >
Mathematics (Maths) Class 12 >
All Questions
All questions of CBSE Sample Papers with Solutions for JEE Exam
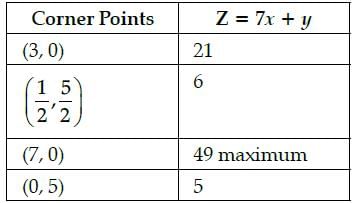
Z = 30x1 + 30x2, subject to x1 ≥ 0, x2 ≥ 0, x1 + 3x2 ≤ 6, 4x1 + 8x2 ≥ 16, x1 + x2 ≤ 4. The minimum value of Z occurs at- a)(3, 0)
- b)(2, 1)
- c)(0, 2)
- d)(4, 0)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Z = 30x1 + 30x2, subject to x1 ≥ 0, x2 ≥ 0, x1 + 3x2 ≤ 6, 4x1 + 8x2 ≥ 16, x1 + x2 ≤ 4. The minimum value of Z occurs at
a)
(3, 0)
b)
(2, 1)
c)
(0, 2)
d)
(4, 0)
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Corner Points are (0, 2), (2, 1), (4, 0) and (3, 1).
The objective function for (x, y) is 30x1 + 30x2.
After putting the corner points in the objective function, we get the minimum value of Z.
The objective function for (x, y) is 30x1 + 30x2.
After putting the corner points in the objective function, we get the minimum value of Z.
What is the equation of the normal to the curve y = 3x2 – 7x + 5 at (0, 5)?- a)x – 7y + 35 = 0
- b)7x – 3y + 35 = 0
- c)3x + 7y + 35 = 0
- d)3x + 7y + 21 = 0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the equation of the normal to the curve y = 3x2 – 7x + 5 at (0, 5)?
a)
x – 7y + 35 = 0
b)
7x – 3y + 35 = 0
c)
3x + 7y + 35 = 0
d)
3x + 7y + 21 = 0

|
New Words answered |
Tangent and normal are perpendicular to each other
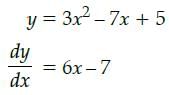
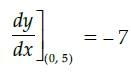
∴ Slope of normal = 1/7
Equation of normal is
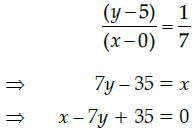
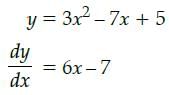
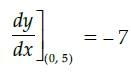
∴ Slope of normal = 1/7
Equation of normal is
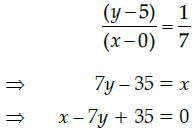
Consider the function 3x4 +20x3 −36x2 +44 in the interval [−5,10] , function is maximum at- a)1
- b)0
- c)2
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the function 3x4 +20x3 −36x2 +44 in the interval [−5,10] , function is maximum at
a)
1
b)
0
c)
2
d)
3

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Let f(x) = 3x4 + 20x3 – 36x2 + 44
f '(x) = 12x3 + 60x2 – 72x
f'(x) = 0
12x3 + 60x2 – 72x = 0
12x (x2 + 5x – 6) = 0
12x (x – 3) (x – 2) = 0
x = 0, 2, 3
f''(x) = 36x2 + 120x – 72
f''(0) = –72 < 0
f''(2) = 312 > 0
f''(3) = 612 > 0
∴ function has a maxima at x = 0
f '(x) = 12x3 + 60x2 – 72x
f'(x) = 0
12x3 + 60x2 – 72x = 0
12x (x2 + 5x – 6) = 0
12x (x – 3) (x – 2) = 0
x = 0, 2, 3
f''(x) = 36x2 + 120x – 72
f''(0) = –72 < 0
f''(2) = 312 > 0
f''(3) = 612 > 0
∴ function has a maxima at x = 0
What is the equation of the tangent to the curve y – 5x2 = 0 and parallel to line 5x + y + 1 = 0 ?- a)20x + 7y + 5 =0
- b)20x – 3y + = 0
- c)20x + 4y + 5 = 0
- d)20x – 9y + 5 = 0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the equation of the tangent to the curve y – 5x2 = 0 and parallel to line 5x + y + 1 = 0 ?
a)
20x + 7y + 5 =0
b)
20x – 3y + = 0
c)
20x + 4y + 5 = 0
d)
20x – 9y + 5 = 0
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Given equation of the curve is y – 5x2 = 0
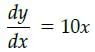
Slope of the line 5x + y + 1 = 0 is – 5 slope of the tangent = slope of the parallel line
i.e., 10x = – 5
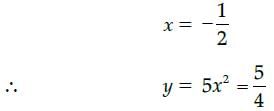
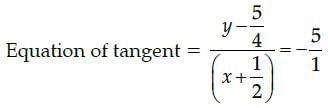
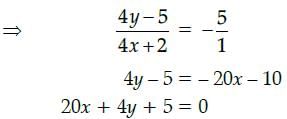
Let T be the set of all triangles in a plane with R is a relation in T given by R = {(T1, T2) : T1 is congruent to T2}. Then R is- a)Non commutative relation
- b)A universal relation
- c)An equivalence relation
- d)An empty relation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Let T be the set of all triangles in a plane with R is a relation in T given by R = {(T1, T2) : T1 is congruent to T2}. Then R is
a)
Non commutative relation
b)
A universal relation
c)
An equivalence relation
d)
An empty relation
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
For reflexive, T1 is congruent to T1
⇒ (T1,T1) Î R For symmetric, (T1,T2) ∈ R ⇒ T1 is congruent to T2 ⇒ T2 is congruent to T1 ⇒ (T2,T1) ∈ R. Hence it is symmetric.
For transitive, (T1, T2) ∈ R ⇒ T1 is congruent to T2 and (T2,T3) ∈ R ⇒ T2 is congruent to T3 which implies T1 is congruent to T3 ⇒ (T1,T3) ∈ R. Hence, it is transitive.
Hence, R is an equivalence relation.
⇒ (T1,T1) Î R For symmetric, (T1,T2) ∈ R ⇒ T1 is congruent to T2 ⇒ T2 is congruent to T1 ⇒ (T2,T1) ∈ R. Hence it is symmetric.
For transitive, (T1, T2) ∈ R ⇒ T1 is congruent to T2 and (T2,T3) ∈ R ⇒ T2 is congruent to T3 which implies T1 is congruent to T3 ⇒ (T1,T3) ∈ R. Hence, it is transitive.
Hence, R is an equivalence relation.
The maximum value of (1/x)x is:- a)e
- b)ee
- c)e1/e
- d)(1/e)1/e
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The maximum value of (1/x)x is:
a)
e
b)
ee
c)
e1/e
d)
(1/e)1/e
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
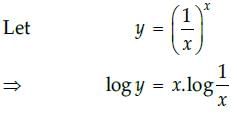
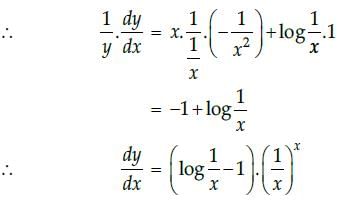
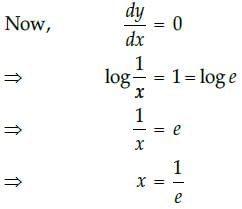 Hence, the maximum value of
Hence, the maximum value of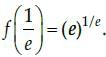
If A is a square matrix of order 3, such that A(adj A) = 10I, then |adj A| is equal to- a)1
- b)10
- c)100
- d)101
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If A is a square matrix of order 3, such that A(adj A) = 10I, then |adj A| is equal to
a)
1
b)
10
c)
100
d)
101
|
|
Ameya Pillai answered |
Given: A is a square matrix of order 3, such that A(adj A) = 10I
To find: |adj A|
Solution:
1. Using the property of adjoint of a matrix
We know that, adj(A) = (Cofactor of A)T
where Cofactor of A is the matrix obtained by taking the determinant of each minor of A and multiplying it by (-1)^(i+j), where i and j are the row and column indices of the element.
So, A(adj A) = A((Cofactor of A)T) = (ACofactor of A)T
2. Using the given condition
We are given that A(adj A) = 10I
Substituting this in the above equation, we get:
(ACofactor of A)T = 10I
Taking determinant on both sides, we get:
|ACofactor of A|T = 10^3
|ACofactor of A| = 10^3 (since determinant of a matrix is equal to the determinant of its transpose)
3. Using the property of determinant
We know that, |AB| = |A||B|
Substituting A = adj(A), we get:
|adj(A)Cofactor of A| = |adj(A)||Cofactor of A|
Since adj(A)Cofactor of A = |A|I (where I is the identity matrix), we get:
|A||Cofactor of A| = |adj(A)||Cofactor of A|
|A| = |adj(A)|
Substituting this in the previous equation, we get:
|adj(A)| |Cofactor of A| = 10^3
|adj(A)| = (10^3)/|Cofactor of A|
4. Finding the value of |Cofactor of A|
Since A is a square matrix of order 3, its adjoint matrix adj(A) is of order 3. Therefore, the Cofactor of A will be a matrix of order 3 as well.
Using the formula for finding the Cofactor of a matrix, we get:
Cofactor of A = (−1)^{i+j} M_{ij}
where M_{ij} is the determinant of the matrix obtained by deleting the i-th row and j-th column of A.
So, we need to find the determinant of 9 matrices (3x3) to find the Cofactor of A. However, we can simplify this process by using the property of symmetry of the Cofactor matrix.
We know that the Cofactor matrix is symmetric, i.e., Cofactor of A = (Cofactor of A)T
Therefore, we can find the determinant of only 4 matrices and use them to find the determinant of the remaining 5 matrices.
The 4 matrices are:
M_{11} = det\begin{pmatrix}a_{22} & a_{23}\\a_{32} & a_{33}\end{pmatrix}
M_{22} = det\begin{pmatrix}a_{11} & a_{13}\\a_{31} & a_{33}\end{pmatrix}
M_{33} = det\begin{pmatrix}a_{11} & a_{12}\\a_{21} &
To find: |adj A|
Solution:
1. Using the property of adjoint of a matrix
We know that, adj(A) = (Cofactor of A)T
where Cofactor of A is the matrix obtained by taking the determinant of each minor of A and multiplying it by (-1)^(i+j), where i and j are the row and column indices of the element.
So, A(adj A) = A((Cofactor of A)T) = (ACofactor of A)T
2. Using the given condition
We are given that A(adj A) = 10I
Substituting this in the above equation, we get:
(ACofactor of A)T = 10I
Taking determinant on both sides, we get:
|ACofactor of A|T = 10^3
|ACofactor of A| = 10^3 (since determinant of a matrix is equal to the determinant of its transpose)
3. Using the property of determinant
We know that, |AB| = |A||B|
Substituting A = adj(A), we get:
|adj(A)Cofactor of A| = |adj(A)||Cofactor of A|
Since adj(A)Cofactor of A = |A|I (where I is the identity matrix), we get:
|A||Cofactor of A| = |adj(A)||Cofactor of A|
|A| = |adj(A)|
Substituting this in the previous equation, we get:
|adj(A)| |Cofactor of A| = 10^3
|adj(A)| = (10^3)/|Cofactor of A|
4. Finding the value of |Cofactor of A|
Since A is a square matrix of order 3, its adjoint matrix adj(A) is of order 3. Therefore, the Cofactor of A will be a matrix of order 3 as well.
Using the formula for finding the Cofactor of a matrix, we get:
Cofactor of A = (−1)^{i+j} M_{ij}
where M_{ij} is the determinant of the matrix obtained by deleting the i-th row and j-th column of A.
So, we need to find the determinant of 9 matrices (3x3) to find the Cofactor of A. However, we can simplify this process by using the property of symmetry of the Cofactor matrix.
We know that the Cofactor matrix is symmetric, i.e., Cofactor of A = (Cofactor of A)T
Therefore, we can find the determinant of only 4 matrices and use them to find the determinant of the remaining 5 matrices.
The 4 matrices are:
M_{11} = det\begin{pmatrix}a_{22} & a_{23}\\a_{32} & a_{33}\end{pmatrix}
M_{22} = det\begin{pmatrix}a_{11} & a_{13}\\a_{31} & a_{33}\end{pmatrix}
M_{33} = det\begin{pmatrix}a_{11} & a_{12}\\a_{21} &
The function y = 5x2 – 32x has a local minimum in the interval (0,10).- a)x = 1
- b)x = 2
- c)x = 3.2
- d)No local minimum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The function y = 5x2 – 32x has a local minimum in the interval (0,10).
a)
x = 1
b)
x = 2
c)
x = 3.2
d)
No local minimum

|
Vaishnavi Dasgupta answered |
The function y = 5x² represents a quadratic function. The variable x represents the input or independent variable, and the variable y represents the output or dependent variable. This function describes a parabola that opens upward and has a vertical stretch factor of 5. The exponent of 2 indicates that the variable x is squared, meaning that the function is quadratic.
Let R be the relation in the set {5, 6, 7, 8} given by R = {(5, 6), (6, 6), (5, 5), (8, 8), (5, 7), (7, 7), (7, 6)}.
Choose the correct answer:- a)R is reflexive and symmetric but not transitive
- b)R is reflexive and transitive but not symmetric
- c)R is symmetric and transitive but not reflexive
- d)R is an equivalence relation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Let R be the relation in the set {5, 6, 7, 8} given by R = {(5, 6), (6, 6), (5, 5), (8, 8), (5, 7), (7, 7), (7, 6)}.
Choose the correct answer:
Choose the correct answer:
a)
R is reflexive and symmetric but not transitive
b)
R is reflexive and transitive but not symmetric
c)
R is symmetric and transitive but not reflexive
d)
R is an equivalence relation
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Let R be the relation in the set {1, 2,3, 4} is given by:
R = {(5,6), (6,6), (5,5), (8,8), (5,7), (7,7), (7,6)}
(a) (5,5), (6,6), (7,7), (8,8) ∈ R Therefore, R is reflexive.
(b) (5,6) ∈ R but (6,5) ∈ R. Therefore, R is not symmetric.
(c) If (5, 7) ∈ R and (7, 6) ∈ R then (5, 6) ∈ R. Therefore, R is transitive.
R = {(5,6), (6,6), (5,5), (8,8), (5,7), (7,7), (7,6)}
(a) (5,5), (6,6), (7,7), (8,8) ∈ R Therefore, R is reflexive.
(b) (5,6) ∈ R but (6,5) ∈ R. Therefore, R is not symmetric.
(c) If (5, 7) ∈ R and (7, 6) ∈ R then (5, 6) ∈ R. Therefore, R is transitive.
If A is a 3 × 3 matrix such that |A| = 8, then |3A| equals- a)8
- b)24
- c)72
- d)216
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If A is a 3 × 3 matrix such that |A| = 8, then |3A| equals
a)
8
b)
24
c)
72
d)
216
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Here |A| = 8
Then |3A| = 33|A| = 27 × 8 = 216
Then |3A| = 33|A| = 27 × 8 = 216
If a matrix has 4 rows and 3 columns then how many elements will be there in this matrix?- a)4
- b)3
- c)1
- d)12
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If a matrix has 4 rows and 3 columns then how many elements will be there in this matrix?
a)
4
b)
3
c)
1
d)
12
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Matrix is represented by m × n
Where m = no. of rows & n = no. of column
And number of total elements = mn
If a matrix has 4 rows and 3 columns hen the number of elements in the matrix is 12.
Where m = no. of rows & n = no. of column
And number of total elements = mn
If a matrix has 4 rows and 3 columns hen the number of elements in the matrix is 12.
What is the domain of the cot–1 x ?- a)[∞,-∞]
- b)(-∞, ∞)
- c)(–∞, –1] ∪ [1, ∞)
- d)[–1,1]
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the domain of the cot–1 x ?
a)
[∞,-∞]
b)
(-∞, ∞)
c)
(–∞, –1] ∪ [1, ∞)
d)
[–1,1]
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
The cot function is periodic so to calculate its inverse function we need to make the function bijective. For that we have to consider an interval in which all values of the function exist and do not repeat. Now for the inverse of a function the domain becomes range and the range becomes domain. Thus the range of cot function, that is, (-∞, ∞) becomes the domain of inverse function.
If A is skew symmetric matrix of order 3, then the value of |A| is- a)3
- b)0
- c)9
- d)27
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If A is skew symmetric matrix of order 3, then the value of |A| is
a)
3
b)
0
c)
9
d)
27
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Determinant value of skew symmetric matrix is always '0'.
For a square matrix A = [aij] the quantity calculated for any element aij in A as the determinant of thesquare sub-matrix of order (n – 1) obtained by leaving the ith row and jth column of A is known as:- a)Cofactor
- b)Minor
- c)Coefficient
- d)Elements
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For a square matrix A = [aij] the quantity calculated for any element aij in A as the determinant of thesquare sub-matrix of order (n – 1) obtained by leaving the ith row and jth column of A is known as:
a)
Cofactor
b)
Minor
c)
Coefficient
d)
Elements
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
The minor of an element aij in A is calculated as the determinant of the square sub-matrix of order (n-1) obtained by leaving the ith row and jth column of A.
Which of the following functions is decreasing on 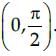
- a)sin 2x
- b)tan x
- c)cos x
- d)cos 3x
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following functions is decreasing on 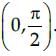
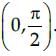
a)
sin 2x
b)
tan x
c)
cos x
d)
cos 3x
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
In the given interval 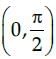
f(x) = cos x
On differentiating with respect to x, we get f´(x) = – sin x
which gives
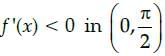
Hence, f(x) = cosx is decreasing in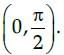
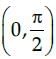
f(x) = cos x
On differentiating with respect to x, we get f´(x) = – sin x
which gives
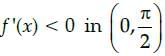
Hence, f(x) = cosx is decreasing in
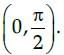
The function f(x) = 4sin3x – 6 sin2x + 12 sinx + 100 is strictly- a)

- b)
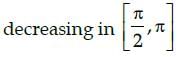
- c)
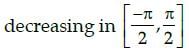
- d)
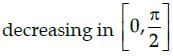
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The function f(x) = 4sin3x – 6 sin2x + 12 sinx + 100 is strictly
a)

b)
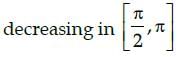
c)
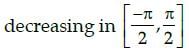
d)
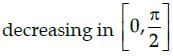
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Given that, f(x) = 4sin3x – 6 sin2x + 12 sinx 100
On differentiating with respect to x, we get
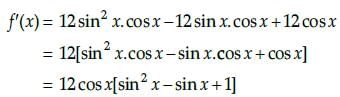
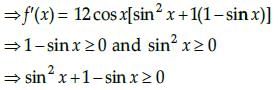
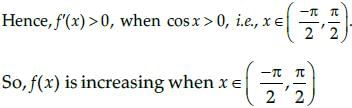
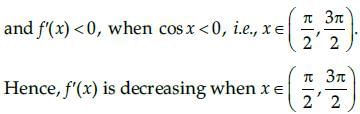
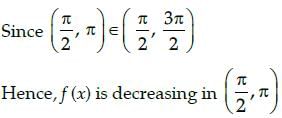
On differentiating with respect to x, we get
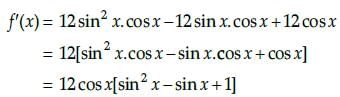
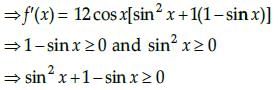
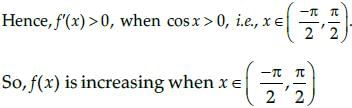
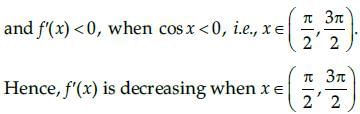
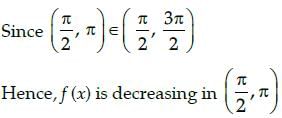
Evaluate the determinant of the matrix 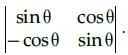
- a)sin θ
- b)cos θ
- c)1
- d)0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate the determinant of the matrix 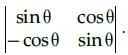
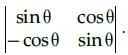
a)
sin θ
b)
cos θ
c)
1
d)
0
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |
The determinant of a square matrix of order 2 is given by the difference of the product of diagonal elements and the product of the offdiagonal elements.
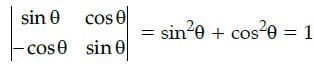
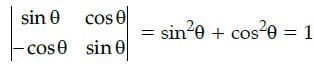
Case - StudyThe Relation between the height of the plant (y in cm) with respect to exposure to sunlight is governed
by the following equation y = 4x -1/2x2 . where x is the number of days exposed to sunlight.
 The rate of growth of the plant with respect to sunlight is ______ .
The rate of growth of the plant with respect to sunlight is ______ .- a)
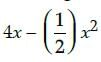
- b)4-x
- c)x-4
- d)
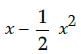
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Case - Study
The Relation between the height of the plant (y in cm) with respect to exposure to sunlight is governed
by the following equation y = 4x -1/2x2 . where x is the number of days exposed to sunlight.

by the following equation y = 4x -1/2x2 . where x is the number of days exposed to sunlight.

The rate of growth of the plant with respect to sunlight is ______ .
a)
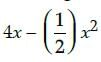
b)
4-x
c)
x-4
d)
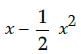
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
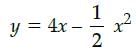
∴ rate of growth of the plant with respect
to sunlight
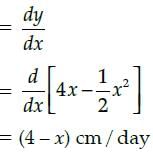
to sunlight
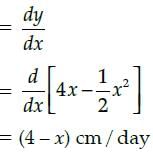
Which of the given values of x and y make the following pair of matrices equal
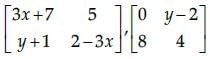
- a)x=-1/3 , y = 7
- b)Not possible to find
- c)y = 7, x = -2/3
- d)x = -1/3, y = -2/3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the given values of x and y make the following pair of matrices equal
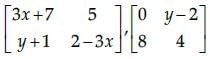
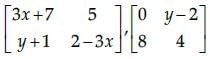
a)
x=-1/3 , y = 7
b)
Not possible to find
c)
y = 7, x = -2/3
d)
x = -1/3, y = -2/3
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
It is given that
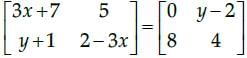
Equating the corresponding elements, we get
3x + 7 = 0
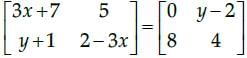
Equating the corresponding elements, we get
3x + 7 = 0
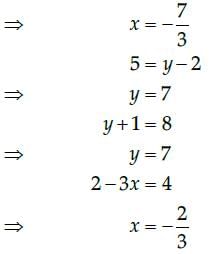
We find that on comparing the corresponding elements of the two matrices, we get two different values of x, which is not possible.
Hence, it is not possible to find the values of x and y for which the given matrices are equal.
Which of the function is not differentiable everywhere in R?- a)log x
- b)sin x
- c)|x|
- d)3x3 + 5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the function is not differentiable everywhere in R?
a)
log x
b)
sin x
c)
|x|
d)
3x3 + 5
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |
|x| is not differentiable at x=0
The matrix
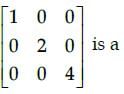
- a)identity matrix
- b)symmetric matrix
- c)skew-symmetric matrix
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The matrix
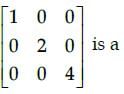
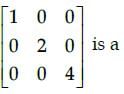
a)
identity matrix
b)
symmetric matrix
c)
skew-symmetric matrix
d)
None of these
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
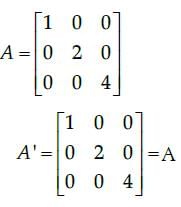
So, the given matrix is a symmetric matrix. [Since, in a square matrix A, if A’ = A, then A is called symmetric matrix.]
What is the value of l in the function 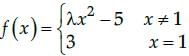 provided function is continuous at x = 1?
provided function is continuous at x = 1?- a)2
- b)4
- c)8
- d)16
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the value of l in the function 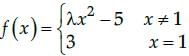 provided function is continuous at x = 1?
provided function is continuous at x = 1?
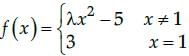 provided function is continuous at x = 1?
provided function is continuous at x = 1?a)
2
b)
4
c)
8
d)
16
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
For a function to be continuous L.H. L=R.H. L= f (x)
The function f(x) = e|x| is- a)continuous everywhere but not differentiable at x = 0
- b)continuous and differentiable everywhere
- c)not continuous at x = 0
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The function f(x) = e|x| is
a)
continuous everywhere but not differentiable at x = 0
b)
continuous and differentiable everywhere
c)
not continuous at x = 0
d)
none of these
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
Given that,
f (x) = e|x|
f (x) = e|x|
The functions ex and |x| are continuous functions for all real value of x. Since ex is differentiable everywhere but |x| is non-differentiable at x = 0.
Thus, the given functions f(x) = e|x| is continuous everywhere but not differentiable at x = 0.
Thus, the given functions f(x) = e|x| is continuous everywhere but not differentiable at x = 0.
What is the principal value branch of cot–1x ?- a)(–1, 1)
- b)[–1, 1]
- c)(0, π)
- d)[0, π]
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the principal value branch of cot–1x ?
a)
(–1, 1)
b)
[–1, 1]
c)
(0, π)
d)
[0, π]
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The cotangent function is periodic so to calculate its inverse function we need to make the function bijective. For that we have to consider an interval in which all values of the function exist and do not repeat. For cotangent function this interval is considered as (0, π).
Thus when we take the inverse of the function the domain becomes range and the range becomes domain. Hence the principal value branch is the range of cot–1 x that is (0, π).
The principal value of 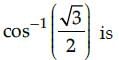
- a)3π/4
- b)π/4
- c)π/2
- d)π/6
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The principal value of 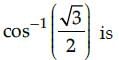
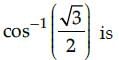
a)
3π/4
b)
π/4
c)
π/2
d)
π/6
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The principal value of 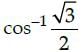 means that we need to find an angle in the principal branch of the function where the cosine function is equal to √3/2 . Hence the required value
means that we need to find an angle in the principal branch of the function where the cosine function is equal to √3/2 . Hence the required value
is π/6
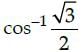 means that we need to find an angle in the principal branch of the function where the cosine function is equal to √3/2 . Hence the required value
means that we need to find an angle in the principal branch of the function where the cosine function is equal to √3/2 . Hence the required valueis π/6
The matrix 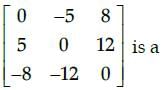
- a)diagonal matrix
- b)symmetric matrix
- c)skew symmetric matrix
- d)scalar matrix
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The matrix 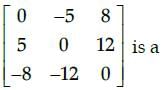
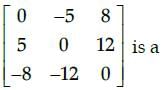
a)
diagonal matrix
b)
symmetric matrix
c)
skew symmetric matrix
d)
scalar matrix
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |
We know that, in a square matrix, if bij = 0 when i ≠ j then it is said to be a diagonal matrix. Here, b12, b13…. ≠ 0
so the given matrix is not a diagonal matrix.
Now,
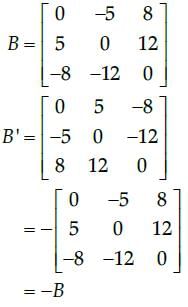
So, the given matrix is a skew-symmetric matrix, since we know that in a square matrix B, if B’ = − B, then it is called skew-symmetric matrix.
so the given matrix is not a diagonal matrix.
Now,
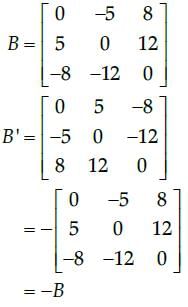
So, the given matrix is a skew-symmetric matrix, since we know that in a square matrix B, if B’ = − B, then it is called skew-symmetric matrix.
Case - StudyThe Relation between the height of the plant (y in cm) with respect to exposure to sunlight is governed
by the following equation y = 4x -1/2x2 . where x is the number of days exposed to sunlight.
 What is the number of days it will take for the plant to grow to the maximum height?
What is the number of days it will take for the plant to grow to the maximum height?- a)4
- b)6
- c)7
- d)10
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Case - Study
The Relation between the height of the plant (y in cm) with respect to exposure to sunlight is governed
by the following equation y = 4x -1/2x2 . where x is the number of days exposed to sunlight.

by the following equation y = 4x -1/2x2 . where x is the number of days exposed to sunlight.

What is the number of days it will take for the plant to grow to the maximum height?
a)
4
b)
6
c)
7
d)
10
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
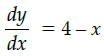
The number of days it will take for the plant to grow to the maximum height,
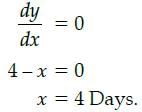
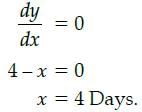
Case - StudyThe Relation between the height of the plant (y in cm) with respect to exposure to sunlight is governed
by the following equation y = 4x -1/2x2 . where x is the number of days exposed to sunlight.
 If the height of the plant is 7/2 cm, the number of days it has been exposed to the sunlight is _____ .
If the height of the plant is 7/2 cm, the number of days it has been exposed to the sunlight is _____ .- a)2
- b)3
- c)4
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Case - Study
The Relation between the height of the plant (y in cm) with respect to exposure to sunlight is governed
by the following equation y = 4x -1/2x2 . where x is the number of days exposed to sunlight.

by the following equation y = 4x -1/2x2 . where x is the number of days exposed to sunlight.

If the height of the plant is 7/2 cm, the number of days it has been exposed to the sunlight is _____ .
a)
2
b)
3
c)
4
d)
1
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
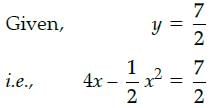
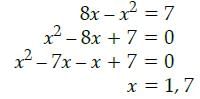
We will take x = 1, because it will take 4 days for the plant to grow to the maximum height i.e. 8 cm and 7/2 cm is not maximum height so, it will take less than 4 days. i.e., 1 Day.
All the trigonometric functions have inverse functions irrespective of the domain.- a)True
- b)False
- c)True but for only sine, cos and tan
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
All the trigonometric functions have inverse functions irrespective of the domain.
a)
True
b)
False
c)
True but for only sine, cos and tan
d)
None of the above
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
For the inverse of a function to exist the function should be bijective which none of the trigonometric function is as they are periodic functions.
If A and B are symmetric matrices of same order, then AB – BA is a:- a)Skew-symmetric matrix
- b)Symmetric matrix
- c)Zero matrix
- d)Identity matrix
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If A and B are symmetric matrices of same order, then AB – BA is a:
a)
Skew-symmetric matrix
b)
Symmetric matrix
c)
Zero matrix
d)
Identity matrix
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |
A and B are symmetric matrices.
⇒ A = A’ and B = B’
Now, (AB – BA)’ = (AB)’ – (BA)’ ...(i)
⇒ (AB – BA)’=B’A’ – A’B’ [By reversal law]
⇒ (AB – BA)’ = BA – AB [From Eq. (i)]
⇒ (AB – BA)’ = –(AB – BA)
⇒ (AB – BA) is a skew-symmetric matrix.
⇒ A = A’ and B = B’
Now, (AB – BA)’ = (AB)’ – (BA)’ ...(i)
⇒ (AB – BA)’=B’A’ – A’B’ [By reversal law]
⇒ (AB – BA)’ = BA – AB [From Eq. (i)]
⇒ (AB – BA)’ = –(AB – BA)
⇒ (AB – BA) is a skew-symmetric matrix.
Case - StudyThe Relation between the height of the plant (y in cm) with respect to exposure to sunlight is governed
by the following equation y = 4x -1/2x2 . where x is the number of days exposed to sunlight.
 What is the maximum height of the plant?
What is the maximum height of the plant?- a)12 cm
- b)10 cm
- c)8 cm
- d)6 cm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Case - Study
The Relation between the height of the plant (y in cm) with respect to exposure to sunlight is governed
by the following equation y = 4x -1/2x2 . where x is the number of days exposed to sunlight.

by the following equation y = 4x -1/2x2 . where x is the number of days exposed to sunlight.

What is the maximum height of the plant?
a)
12 cm
b)
10 cm
c)
8 cm
d)
6 cm
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
We have, number of days for maximum height of plant = 4 Days
∴ Maximum height of plant
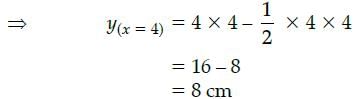
∴ Maximum height of plant
If A = {1, 2}, B = {3,4, 5} and f = {(1, 3), (2, 5)} is a function from A to B, then f(x) is- a)onto
- b)bijective
- c)one-one
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If A = {1, 2}, B = {3,4, 5} and f = {(1, 3), (2, 5)} is a function from A to B, then f(x) is
a)
onto
b)
bijective
c)
one-one
d)
None of these
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Given, A = {1, 2}, B = {3,4, 5} and f : A → B is defined as f = {(1, 3), (2, 5)} i.e., f(1) = 3, f(2) = 5.
We can see that the images of distinct elements of A under f are distinct. So, f is one-one.
We can see that the images of distinct elements of A under f are distinct. So, f is one-one.
The domain of sin–1 x is :- a)[0, 1]
- b)[–1, ∞]
- c)(– ∞, ∞)
- d)[–1, 1]
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The domain of sin–1 x is :
a)
[0, 1]
b)
[–1, ∞]
c)
(– ∞, ∞)
d)
[–1, 1]
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The domain of sin-1 x is [-1, 1].
The contentment obtained after eating x units of a new dish at a trial function is given by the functionf(x) = x3 + 6x2 + 5x + 3. The marginal contentment when 3 units of dish are consumed is ____________.- a)60
- b)68
- c)24
- d)48
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The contentment obtained after eating x units of a new dish at a trial function is given by the functionf(x) = x3 + 6x2 + 5x + 3. The marginal contentment when 3 units of dish are consumed is ____________.
a)
60
b)
68
c)
24
d)
48
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
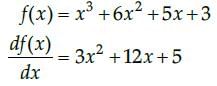
At x = 3,
Marginal contentment
= 3x (3)2 + 12 x 3 + 5
= 27+ 36 +5
68 units.
Choose the correct option for the given matrix.
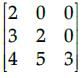
- a)Lower triangular matrix
- b)Upper triangular matrix
- c)Diagonal matrix
- d)Unit matrix
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct option for the given matrix.
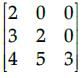
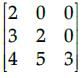
a)
Lower triangular matrix
b)
Upper triangular matrix
c)
Diagonal matrix
d)
Unit matrix
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
A square matrix is called lower triangular if all the entries above the main diagonal are zero. Similarly, a square matrix is called upper triangular if all the entries below the main diagonal is zero.
Hence, given matrix is lower triangular matrix.
Hence, given matrix is lower triangular matrix.
The function f(x) = tan x – x- a)always increases
- b)always decreases
- c)never increases
- d)sometimes increases and sometimes decreases
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The function f(x) = tan x – x
a)
always increases
b)
always decreases
c)
never increases
d)
sometimes increases and sometimes decreases
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
We have
f(x) = tan x – x
On differentiating with respect to x, we
get
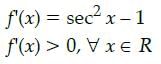
So, f(x) always increases.
f(x) = tan x – x
On differentiating with respect to x, we
get
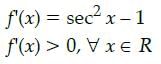
So, f(x) always increases.
Case - StudyThe Relation between the height of the plant (y in cm) with respect to exposure to sunlight is governed
by the following equation y = 4x -1/2x2 . where x is the number of days exposed to sunlight.
 What will be the height of the plant after 2 days?
What will be the height of the plant after 2 days?- a)4 cm
- b)6 cm
- c)8 cm
- d)10 cm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Case - Study
The Relation between the height of the plant (y in cm) with respect to exposure to sunlight is governed
by the following equation y = 4x -1/2x2 . where x is the number of days exposed to sunlight.

by the following equation y = 4x -1/2x2 . where x is the number of days exposed to sunlight.

What will be the height of the plant after 2 days?
a)
4 cm
b)
6 cm
c)
8 cm
d)
10 cm
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Height of plant after 2 days
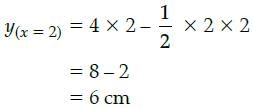
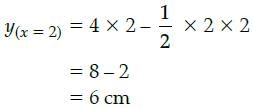
if 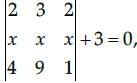 then the value of x is
then the value of x is- a)3
- b)0
- c)– 1
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
if 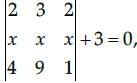 then the value of x is
then the value of x is
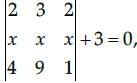 then the value of x is
then the value of x isa)
3
b)
0
c)
– 1
d)
1
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
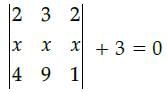
On expanding along R1
2(x – 9x) – 3(x – 4x)+ 2(9x – 4x) + 3 = 0
2(–8x) – 3(–3x) + 2(5x) + 3 = 0
– 16x + 9x + 10x + 3 = 0
3x + 3 = 0
3x = –3
x = - 3/3
x = –1
if 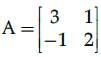 then A2−5A + 7I2 is equal to :
then A2−5A + 7I2 is equal to :- a)0
- b)1
- c)-1
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
if 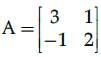 then A2−5A + 7I2 is equal to :
then A2−5A + 7I2 is equal to :
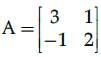 then A2−5A + 7I2 is equal to :
then A2−5A + 7I2 is equal to :a)
0
b)
1
c)
-1
d)
2
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
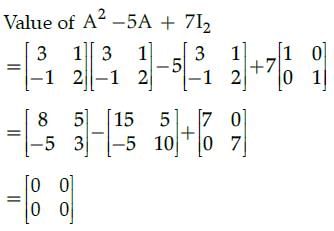
Since, all the elements of matrix are zero. So, given matrix is null/zero matrix.
The maximum value of sin x. cos x is- a)1/4
- b)1/2
- c)√2
- d)2√2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The maximum value of sin x. cos x is
a)
1/4
b)
1/2
c)
√2
d)
2√2
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
Let us assume that,
f(x) = sin x cos x
Now, we know that
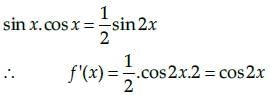
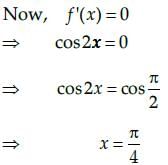
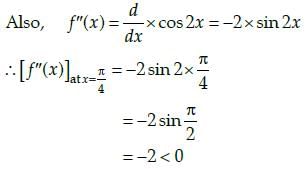
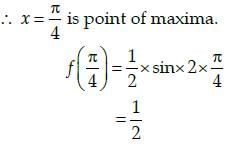
f(x) = sin x cos x
Now, we know that
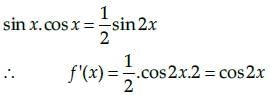
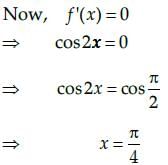
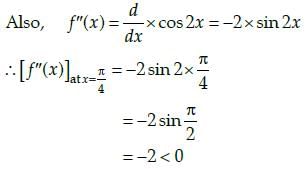
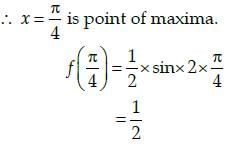
Chapter doubts & questions for CBSE Sample Papers with Solutions - Mathematics (Maths) Class 12 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of CBSE Sample Papers with Solutions - Mathematics (Maths) Class 12 in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup