All Exams >
Commerce >
Sample Papers for Class 12 Commerce >
All Questions
All questions of Economics for Commerce Exam
Two friends Mira and Sindhu were discussing the exchange rate systems. ‘Under this system, the exchange rates are determined by the market forces of demand and supply. However, deliberate efforts are made by the competent authority to keep the exchange rates within a specific range’.
The above-mentioned statement was given by Sindhu, identify the type of exchange rate system was she talking about?- a)Fixed Exchange Rate
- b)Floating Exchange Rate
- c)Managed Floating Exchange Rate
- d)Managed Fixed Exchange Rate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Two friends Mira and Sindhu were discussing the exchange rate systems. ‘Under this system, the exchange rates are determined by the market forces of demand and supply. However, deliberate efforts are made by the competent authority to keep the exchange rates within a specific range’.
The above-mentioned statement was given by Sindhu, identify the type of exchange rate system was she talking about?
The above-mentioned statement was given by Sindhu, identify the type of exchange rate system was she talking about?
a)
Fixed Exchange Rate
b)
Floating Exchange Rate
c)
Managed Floating Exchange Rate
d)
Managed Fixed Exchange Rate
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
The type of exchange rate that Sindhu is talking about is ‘Managed floating exchange rate’. In this type of exchange rate, with the help of market forces of demand and supply, exchange rate is determined. And competent authority, i.e., country’s central bank intervenes so as to maintain the exchange rate within a specific range. Central bank also keeps reserves of foreign exchange within the targeted value. Managed floating exchange rate is also called as ‘Dirty floating’.
Arrange the following events in the correct chronological order:
(i) ‘Expert group’ was formed.
(ii) ‘Study group’ was formed by Planning Commission.
(iii) ‘Jail cost of living’ criteria used by Dadabhai Naoroji to estimate poverty line.
(iv) Task force on projection of minimum needs and effective consumption demand was formed.- a)(iv),(i),(iii),(ii)
- b)(i),(ii),(iii),(iv)
- c)(iii),(ii),(iv),(i)
- d)(iii),(iv),(ii),(i)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following events in the correct chronological order:
(i) ‘Expert group’ was formed.
(ii) ‘Study group’ was formed by Planning Commission.
(iii) ‘Jail cost of living’ criteria used by Dadabhai Naoroji to estimate poverty line.
(iv) Task force on projection of minimum needs and effective consumption demand was formed.
(i) ‘Expert group’ was formed.
(ii) ‘Study group’ was formed by Planning Commission.
(iii) ‘Jail cost of living’ criteria used by Dadabhai Naoroji to estimate poverty line.
(iv) Task force on projection of minimum needs and effective consumption demand was formed.
a)
(iv),(i),(iii),(ii)
b)
(i),(ii),(iii),(iv)
c)
(iii),(ii),(iv),(i)
d)
(iii),(iv),(ii),(i)
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Expert group was formed. – 1989
Study group was formed by Planning Commission – 1962
‘Jail cost of living’ criteria by Dadabhai Naoroji to reduce poverty – Preindependent India
Taskforce on Projection of minimum needs and effective consumption demand was formed – 1979
Study group was formed by Planning Commission – 1962
‘Jail cost of living’ criteria by Dadabhai Naoroji to reduce poverty – Preindependent India
Taskforce on Projection of minimum needs and effective consumption demand was formed – 1979
Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and for Reason (R) :
Assertion (A): India became an exporter of primary products and an importer of finished consumer and capital goods produced in Britain.
Reason (R): Restrictive policies of commodity production, trade and tariff pursued by the colonial government adversely affected the structure, composition and volume of India’s foreign trade.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and for Reason (R) :
Assertion (A): India became an exporter of primary products and an importer of finished consumer and capital goods produced in Britain.
Reason (R): Restrictive policies of commodity production, trade and tariff pursued by the colonial government adversely affected the structure, composition and volume of India’s foreign trade.
Assertion (A): India became an exporter of primary products and an importer of finished consumer and capital goods produced in Britain.
Reason (R): Restrictive policies of commodity production, trade and tariff pursued by the colonial government adversely affected the structure, composition and volume of India’s foreign trade.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Britain exploited India by making India an exporter of primary products like raw silk, cotton etc and importer of finished goods like cotton and woollen clothes.
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternatives given below:
Statement 1: India is often called as the ‘outsourcing hub’ of the world.
Statement 2: Availability of skilled manpower is one of the prime factors responsible for the status gained by India at the international platform.- a)Both the statements are true.
- b)Both the statements are false.
- c)Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
- d)Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternatives given below:
Statement 1: India is often called as the ‘outsourcing hub’ of the world.
Statement 2: Availability of skilled manpower is one of the prime factors responsible for the status gained by India at the international platform.
Statement 1: India is often called as the ‘outsourcing hub’ of the world.
Statement 2: Availability of skilled manpower is one of the prime factors responsible for the status gained by India at the international platform.
a)
Both the statements are true.
b)
Both the statements are false.
c)
Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
d)
Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.

|
Bhavya Joshi answered |
A) Land of Diversity
b) Land of Opportunities
c) Land of Culture
d) None of the above
The correct answer is a) Land of Diversity.
b) Land of Opportunities
c) Land of Culture
d) None of the above
The correct answer is a) Land of Diversity.
The Government of India has decided to vaccinate the adult population of India (with Covaxin/ Covishield), without any charge. This would be categorized as ____________.- a)revenue nature income
- b)capital nature expenditure
- c)revenue nature expenditure
- d)capital nature income
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The Government of India has decided to vaccinate the adult population of India (with Covaxin/ Covishield), without any charge. This would be categorized as ____________.
a)
revenue nature income
b)
capital nature expenditure
c)
revenue nature expenditure
d)
capital nature income
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Vaccinating the adult population of the country with Covaxin /Covishield without any charge would mean that this type of expenditure by government is neither creating any asset nor causing any fall in liability. Hence, it is categorized as revenue nature expenditure.
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative:
Statement 1: Payment of salaries and interest is a revenue expenditure.
Statement 2: Revenue expenditure can be defined as the expenditure which leads to neither creation of asset nor reduction in liability of the government. - a)Both the statements are true.
- b)Both the statements are false.
- c)Statement 1 is true but statement 2 is false.
- d)Statement 1 is false but statement 2 is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative:
Statement 1: Payment of salaries and interest is a revenue expenditure.
Statement 2: Revenue expenditure can be defined as the expenditure which leads to neither creation of asset nor reduction in liability of the government.
Statement 1: Payment of salaries and interest is a revenue expenditure.
Statement 2: Revenue expenditure can be defined as the expenditure which leads to neither creation of asset nor reduction in liability of the government.
a)
Both the statements are true.
b)
Both the statements are false.
c)
Statement 1 is true but statement 2 is false.
d)
Statement 1 is false but statement 2 is true.
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Revenue expenditure like salaries, pensions, interest, etc. is a revenue expenditure because it leads to neither creation of asset nor reduces liability.
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternatives given below:
Statement 1 : Poverty line in India is defined in terms of monetary value of the minimum nutritional (calorific) requirements of an individual in a day.
Statement 2 : The definition of poverty line in monetary terms has not changed over the years.- a)Both the statements are true.
- b)Both the statements are false.
- c)Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
- d)Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternatives given below:
Statement 1 : Poverty line in India is defined in terms of monetary value of the minimum nutritional (calorific) requirements of an individual in a day.
Statement 2 : The definition of poverty line in monetary terms has not changed over the years.
Statement 1 : Poverty line in India is defined in terms of monetary value of the minimum nutritional (calorific) requirements of an individual in a day.
Statement 2 : The definition of poverty line in monetary terms has not changed over the years.
a)
Both the statements are true.
b)
Both the statements are false.
c)
Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
d)
Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |
Poverty line in India can be defined as the minimum nutritional requirements of an individual in a day measured in monetary value. Also, the statement 2 is false because the definition of poverty line in monetary terms has changed over the years.
Balance of Payments of an economy records_____________ for a fiscal year.- a)income and expenditure of the government
- b)inflow and outflow of funds of the government
- c)inflow and outflow of foreign exchange to/from the economy
- d)inflow and outflow of loans to/from the rest of the world
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Balance of Payments of an economy records_____________ for a fiscal year.
a)
income and expenditure of the government
b)
inflow and outflow of funds of the government
c)
inflow and outflow of foreign exchange to/from the economy
d)
inflow and outflow of loans to/from the rest of the world

|
Bhargavi Banerjee answered |
Balance of Payments (BoP) is a systematic record of all economic transactions between residents of a country and the rest of the world during a specific period, typically a fiscal year. It is divided into two main accounts: the current account and the capital and financial account. The correct answer for what the Balance of Payments records for a fiscal year is option 'C', which is the inflow and outflow of foreign exchange to/from the economy.
Below is a detailed explanation of why option 'C' is the correct answer:
1. Balance of Payments (BoP):
The BoP is a comprehensive accounting record of all economic transactions between a country and the rest of the world. It includes both visible and invisible transactions, such as exports, imports, services, income, and financial flows.
2. Current Account:
The current account is a major component of the BoP, and it records transactions related to the exchange of goods and services, income flows, and unilateral transfers.
3. Inflow and Outflow of Foreign Exchange:
The current account of the BoP records the inflow and outflow of foreign exchange to/from the economy. Inflows of foreign exchange include earnings from exports of goods and services, income from investments abroad, and unilateral transfers like foreign aid or remittances. Outflows of foreign exchange include payments for imports of goods and services, income paid to foreign investors, and unilateral transfers sent abroad.
4. Components of the Current Account:
The current account of the BoP includes various components that contribute to the inflow and outflow of foreign exchange. These components are:
- Trade Balance: Records the difference between exports and imports of goods.
- Services Balance: Records the difference between exports and imports of services (e.g., tourism, transportation, financial services).
- Income Balance: Records income flows such as wages, salaries, and profits earned from investments abroad.
- Current Transfers: Records unilateral transfers, such as foreign aid, remittances, and grants.
5. Capital and Financial Account:
The capital and financial account is the other major component of the BoP, which records transactions related to capital transfers, financial investments, and loans between the domestic economy and the rest of the world. However, the BoP does not record the income and expenditure of the government or the inflow and outflow of loans to/from the rest of the world.
In conclusion, the Balance of Payments of an economy records the inflow and outflow of foreign exchange to/from the economy during a fiscal year. It is a comprehensive record that includes various components such as the trade balance, services balance, income balance, and current transfers.
Below is a detailed explanation of why option 'C' is the correct answer:
1. Balance of Payments (BoP):
The BoP is a comprehensive accounting record of all economic transactions between a country and the rest of the world. It includes both visible and invisible transactions, such as exports, imports, services, income, and financial flows.
2. Current Account:
The current account is a major component of the BoP, and it records transactions related to the exchange of goods and services, income flows, and unilateral transfers.
3. Inflow and Outflow of Foreign Exchange:
The current account of the BoP records the inflow and outflow of foreign exchange to/from the economy. Inflows of foreign exchange include earnings from exports of goods and services, income from investments abroad, and unilateral transfers like foreign aid or remittances. Outflows of foreign exchange include payments for imports of goods and services, income paid to foreign investors, and unilateral transfers sent abroad.
4. Components of the Current Account:
The current account of the BoP includes various components that contribute to the inflow and outflow of foreign exchange. These components are:
- Trade Balance: Records the difference between exports and imports of goods.
- Services Balance: Records the difference between exports and imports of services (e.g., tourism, transportation, financial services).
- Income Balance: Records income flows such as wages, salaries, and profits earned from investments abroad.
- Current Transfers: Records unilateral transfers, such as foreign aid, remittances, and grants.
5. Capital and Financial Account:
The capital and financial account is the other major component of the BoP, which records transactions related to capital transfers, financial investments, and loans between the domestic economy and the rest of the world. However, the BoP does not record the income and expenditure of the government or the inflow and outflow of loans to/from the rest of the world.
In conclusion, the Balance of Payments of an economy records the inflow and outflow of foreign exchange to/from the economy during a fiscal year. It is a comprehensive record that includes various components such as the trade balance, services balance, income balance, and current transfers.
Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): In rural India, horticulture plays a vital role in providing food and nutrition to the rural population.
Reason (R): Various horticultural activities in Indian villages have improved the economic conditions of many farmers. Such activities have become a lucrative source of livelihood for many people in rural India.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): In rural India, horticulture plays a vital role in providing food and nutrition to the rural population.
Reason (R): Various horticultural activities in Indian villages have improved the economic conditions of many farmers. Such activities have become a lucrative source of livelihood for many people in rural India.
Assertion (A): In rural India, horticulture plays a vital role in providing food and nutrition to the rural population.
Reason (R): Various horticultural activities in Indian villages have improved the economic conditions of many farmers. Such activities have become a lucrative source of livelihood for many people in rural India.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Nisha Kulkarni answered |
Explanation:
Assertion (A) and Reason (R) Analysis:
- Assertion (A): In rural India, horticulture plays a vital role in providing food and nutrition to the rural population.
- Reason (R): Various horticultural activities in Indian villages have improved the economic conditions of many farmers. Such activities have become a lucrative source of livelihood for many people in rural India.
Evaluation of Options:
- Option A: Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A). This option correctly interprets the relationship between the two statements.
- Option B: Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A). This option is not accurate as the reason provided indeed explains why horticulture is essential in rural India.
- Option C: Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false. This option is incorrect as both statements are true.
- Option D: Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true. This option is incorrect as the assertion is true.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A', where both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason correctly explains why horticulture is significant in rural India.
Assertion (A) and Reason (R) Analysis:
- Assertion (A): In rural India, horticulture plays a vital role in providing food and nutrition to the rural population.
- Reason (R): Various horticultural activities in Indian villages have improved the economic conditions of many farmers. Such activities have become a lucrative source of livelihood for many people in rural India.
Evaluation of Options:
- Option A: Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A). This option correctly interprets the relationship between the two statements.
- Option B: Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A). This option is not accurate as the reason provided indeed explains why horticulture is essential in rural India.
- Option C: Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false. This option is incorrect as both statements are true.
- Option D: Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true. This option is incorrect as the assertion is true.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A', where both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason correctly explains why horticulture is significant in rural India.
Human development is a _________ of human welfare.- a)A parameter
- b)An index
- c)An attribute
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Human development is a _________ of human welfare.
a)
A parameter
b)
An index
c)
An attribute
d)
None of these
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
HDI was developed to track as a development indicator of human welfare.
Occupational structure refers to___________.- a)size of labour force in a country
- b)number of people living in a country
- c)distribution of workforce among different sectors of an economy
- d)nature of different occupations
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Occupational structure refers to___________.
a)
size of labour force in a country
b)
number of people living in a country
c)
distribution of workforce among different sectors of an economy
d)
nature of different occupations
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Occupational structure can be defined as distribution of workforce among various different sectors of the economy such as primary, secondary and tertiary sectors.
Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): In cottage industries, machines are not used whereas these are used in small sector.
Reason (R): Cottage industries are smaller industries than the small sector industries. - a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion(A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but Reason(R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): In cottage industries, machines are not used whereas these are used in small sector.
Reason (R): Cottage industries are smaller industries than the small sector industries.
Assertion (A): In cottage industries, machines are not used whereas these are used in small sector.
Reason (R): Cottage industries are smaller industries than the small sector industries.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion(A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but Reason(R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Krish Kapoor answered |
Unfortunately, the provided statements are missing.
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: Demonetization was the step taken by the Government of India in order to tackle the problems of corruption, black money, terrorism and circulation of fake currency in the Indian Economy.
Statement 2: Demonetization has ensured improved tax compliance in India over the period of time.- a)Both the statements are true.
- b)Both the statements are false.
- c)Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
- d)Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: Demonetization was the step taken by the Government of India in order to tackle the problems of corruption, black money, terrorism and circulation of fake currency in the Indian Economy.
Statement 2: Demonetization has ensured improved tax compliance in India over the period of time.
Statement 1: Demonetization was the step taken by the Government of India in order to tackle the problems of corruption, black money, terrorism and circulation of fake currency in the Indian Economy.
Statement 2: Demonetization has ensured improved tax compliance in India over the period of time.
a)
Both the statements are true.
b)
Both the statements are false.
c)
Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
d)
Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Demonetization means taking away notes or coin from its status as legal tender. Both the statements are true as demonetization is a step taken by the government to deal with the problem of corruption, black money, terrorism and circulation of fake currency in the Indian economy. Also, it has improved tax compliance over a period of time.
Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): It is essential to develop proper storage facilities in rural areas.
Reason (R): Farmers can wait for better prices for their products in the market.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): It is essential to develop proper storage facilities in rural areas.
Reason (R): Farmers can wait for better prices for their products in the market.
Assertion (A): It is essential to develop proper storage facilities in rural areas.
Reason (R): Farmers can wait for better prices for their products in the market.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Farmers are forced to sell their crops at very low prices to traders because of the fear of getting damage from fire, rodents or pests due to lack of proper storage facilities.
Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): Current account is a part of Balance of Trade.
Reason (R): Current account records exports and imports of goods and services and transfer payments.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion(A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but Reason(R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): Current account is a part of Balance of Trade.
Reason (R): Current account records exports and imports of goods and services and transfer payments.
Assertion (A): Current account is a part of Balance of Trade.
Reason (R): Current account records exports and imports of goods and services and transfer payments.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion(A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but Reason(R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Balance of Trade is a part of current account.
Balance on Current Account =Trade balance + Invisibles balance
Balance on Current Account =Trade balance + Invisibles balance
The Government can achieve its budget objective of ‘Redistribution of Income’ by____________.- a)managing the General Price Level in the economy to the desired level.
- b)increasing the Gross Domestic Products (GDP) of the economy.
- c)bringing the production of goods and services under its direct and absolute control.
- d)rationalisation of taxes in pro-poor direction.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Government can achieve its budget objective of ‘Redistribution of Income’ by____________.
a)
managing the General Price Level in the economy to the desired level.
b)
increasing the Gross Domestic Products (GDP) of the economy.
c)
bringing the production of goods and services under its direct and absolute control.
d)
rationalisation of taxes in pro-poor direction.
|
|
Kalyan Joshi answered |
Reducing the deficit by implementing several strategies:
1. Increasing revenue: The government can increase revenue by implementing tax reforms, closing loopholes, and reducing tax evasion. This can be achieved by ensuring a fair and progressive tax system that encourages compliance.
2. Cutting expenditure: The government can reduce unnecessary expenditure by reviewing and cutting down on non-essential programs and projects. This includes reducing subsidies, eliminating duplication of services, and improving efficiency in government operations.
3. Controlling public debt: The government can manage its debt more effectively by implementing measures such as refinancing debt at lower interest rates, reducing reliance on external borrowing, and negotiating favorable terms with creditors.
4. Stimulating economic growth: The government can implement policies that promote economic growth, such as investing in infrastructure projects, supporting small and medium-sized enterprises, and attracting foreign direct investment. A growing economy can lead to increased tax revenue and reduced reliance on borrowing.
5. Implementing fiscal discipline: The government can enforce fiscal discipline by setting realistic budget targets, monitoring spending, and implementing measures to prevent overspending. This includes enforcing strict financial controls and accountability measures.
6. Prioritizing spending: The government can allocate resources to priority areas such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure. By focusing on essential services and investments, the government can ensure efficient use of funds and achieve its budget objectives.
7. Encouraging public participation: The government can engage citizens in the budget process by seeking their input and feedback. This can help identify areas of inefficiency and wasteful expenditure, leading to better budget management.
Overall, a combination of these strategies can help the government achieve its budget objective of reducing the deficit and maintaining fiscal stability.
1. Increasing revenue: The government can increase revenue by implementing tax reforms, closing loopholes, and reducing tax evasion. This can be achieved by ensuring a fair and progressive tax system that encourages compliance.
2. Cutting expenditure: The government can reduce unnecessary expenditure by reviewing and cutting down on non-essential programs and projects. This includes reducing subsidies, eliminating duplication of services, and improving efficiency in government operations.
3. Controlling public debt: The government can manage its debt more effectively by implementing measures such as refinancing debt at lower interest rates, reducing reliance on external borrowing, and negotiating favorable terms with creditors.
4. Stimulating economic growth: The government can implement policies that promote economic growth, such as investing in infrastructure projects, supporting small and medium-sized enterprises, and attracting foreign direct investment. A growing economy can lead to increased tax revenue and reduced reliance on borrowing.
5. Implementing fiscal discipline: The government can enforce fiscal discipline by setting realistic budget targets, monitoring spending, and implementing measures to prevent overspending. This includes enforcing strict financial controls and accountability measures.
6. Prioritizing spending: The government can allocate resources to priority areas such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure. By focusing on essential services and investments, the government can ensure efficient use of funds and achieve its budget objectives.
7. Encouraging public participation: The government can engage citizens in the budget process by seeking their input and feedback. This can help identify areas of inefficiency and wasteful expenditure, leading to better budget management.
Overall, a combination of these strategies can help the government achieve its budget objective of reducing the deficit and maintaining fiscal stability.
Aid provided by a country to another country will come in which of the following accounts of the second country?- a)Official reserves account
- b)Errors and omissions
- c)Capital account
- d)Current account
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Aid provided by a country to another country will come in which of the following accounts of the second country?
a)
Official reserves account
b)
Errors and omissions
c)
Capital account
d)
Current account
|
|
Anisha Bose answered |
Current Account:
The aid provided by a country to another country will come in the current account of the second country. The current account of a country's balance of payments includes the flow of goods, services, investment income, and unilateral transfers (such as aid) between the country and the rest of the world.
Types of Transactions in Current Account:
- Goods: Includes imports and exports of physical goods.
- Services: Includes transactions for services like tourism, transportation, and financial services.
- Investment Income: Includes income earned from investments abroad.
- Unilateral Transfers: Includes aid, grants, and gifts between countries.
Role of Aid in Current Account:
- Aid provided by one country to another is recorded as a unilateral transfer in the current account.
- It represents a one-way transfer of resources without anything in return.
- Aid can help improve the recipient country's balance of payments by providing much-needed financial support.
Importance of Current Account:
- The current account is a key component of a country's balance of payments, reflecting its economic interactions with the rest of the world.
- Aid received through the current account can help address deficits and support economic development in the recipient country.
In conclusion, aid provided by a country to another country will be recorded in the current account of the recipient country, reflecting the flow of resources and financial assistance between nations.
Which of the following should not be included in the balance of payments account?- a)Import of automobile parts
- b)Interest payment on the loan to the IMF
- c)Dividend payment to home-country investors from a foreign investor
- d)Bonus shares to equity shareholders
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following should not be included in the balance of payments account?
a)
Import of automobile parts
b)
Interest payment on the loan to the IMF
c)
Dividend payment to home-country investors from a foreign investor
d)
Bonus shares to equity shareholders
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Bonus shares to equity shareholders does not involve provision of new resources and no transaction is recorded.
Agriculture sector appears to be _________ affected by the economic reform process.- a)adversely
- b)positively
- c)not
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Agriculture sector appears to be _________ affected by the economic reform process.
a)
adversely
b)
positively
c)
not
d)
none of the above

|
Sanchita Reddy answered |
The agriculture sector is adversely affected by the economic reform process. This means that the reforms have had a negative impact on the agriculture sector.
Reasons for the adverse effect on the agriculture sector can be attributed to various factors:
1. Reduced government support: Economic reforms often involve a reduction in government subsidies and support for the agriculture sector. This can result in a decrease in financial assistance for farmers, leading to a decline in their income and overall agricultural productivity.
2. Market liberalization: Economic reforms typically aim to liberalize markets and promote competition. While this can benefit some sectors, it can be detrimental to the agriculture sector. Farmers may struggle to compete with cheaper imports, leading to a decline in domestic agricultural production.
3. Shift of focus: Economic reforms often prioritize industrialization and urban development. As a result, resources and investments may be redirected away from the agriculture sector, leading to a lack of infrastructure development, technological advancements, and research and development in agriculture.
4. Inadequate access to credit: Economic reforms may result in financial sector reforms, which can make it more difficult for farmers to access credit. Limited access to credit can hinder farmers' ability to invest in modern agricultural techniques, purchase high-quality inputs, and expand their operations.
5. Inequality and displacement: Economic reforms can exacerbate income disparities and lead to the displacement of small-scale farmers. Large corporations and agribusinesses may benefit from the reforms, while small-scale farmers struggle to compete and are forced to abandon their agricultural activities.
Overall, the adverse impact of economic reforms on the agriculture sector can lead to a decline in agricultural production, food security concerns, and increased rural poverty. It is crucial for policymakers to consider the specific needs and challenges of the agriculture sector when implementing economic reforms to ensure sustainable and equitable development.
Reasons for the adverse effect on the agriculture sector can be attributed to various factors:
1. Reduced government support: Economic reforms often involve a reduction in government subsidies and support for the agriculture sector. This can result in a decrease in financial assistance for farmers, leading to a decline in their income and overall agricultural productivity.
2. Market liberalization: Economic reforms typically aim to liberalize markets and promote competition. While this can benefit some sectors, it can be detrimental to the agriculture sector. Farmers may struggle to compete with cheaper imports, leading to a decline in domestic agricultural production.
3. Shift of focus: Economic reforms often prioritize industrialization and urban development. As a result, resources and investments may be redirected away from the agriculture sector, leading to a lack of infrastructure development, technological advancements, and research and development in agriculture.
4. Inadequate access to credit: Economic reforms may result in financial sector reforms, which can make it more difficult for farmers to access credit. Limited access to credit can hinder farmers' ability to invest in modern agricultural techniques, purchase high-quality inputs, and expand their operations.
5. Inequality and displacement: Economic reforms can exacerbate income disparities and lead to the displacement of small-scale farmers. Large corporations and agribusinesses may benefit from the reforms, while small-scale farmers struggle to compete and are forced to abandon their agricultural activities.
Overall, the adverse impact of economic reforms on the agriculture sector can lead to a decline in agricultural production, food security concerns, and increased rural poverty. It is crucial for policymakers to consider the specific needs and challenges of the agriculture sector when implementing economic reforms to ensure sustainable and equitable development.
What is the term used for the policy, which promote setting up an upper limit of the land that could be owned by a landowner?- a)Land Fragmentation
- b)Land Ceiling
- c)Land Cultivation
- d)Land Tilling
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the term used for the policy, which promote setting up an upper limit of the land that could be owned by a landowner?
a)
Land Fragmentation
b)
Land Ceiling
c)
Land Cultivation
d)
Land Tilling
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |
Land Ceiling means fixing the maximum size of land which could be owned by an individual. The purpose of land ceiling was to reduce the concentration of land ownership in a few hands.
Before the advent of Green Revolution in 1960’s, India was primarily dependent on _________for the supply of food grains.- a)United States of America (USA)
- b)Britain (United Kingdom)
- c)Mexico
- d)Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Before the advent of Green Revolution in 1960’s, India was primarily dependent on _________for the supply of food grains.
a)
United States of America (USA)
b)
Britain (United Kingdom)
c)
Mexico
d)
Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR)

|
Shreya Gupta answered |
, agriculture was largely dependent on traditional farming methods and techniques. Farmers relied on natural rainfall for irrigation, used traditional seeds, and practiced extensive farming methods. This resulted in low crop yields and frequent famines due to crop failures.
The Green Revolution, which began in the 1960s, introduced technological advancements and practices that significantly increased agricultural productivity. Key components of the Green Revolution included the development and distribution of high-yielding varieties (HYVs) of seeds, increased use of chemical fertilizers, and improved irrigation techniques.
The introduction of HYVs of seeds, particularly in wheat and rice, led to substantial increases in crop yields. These new varieties were bred to have shorter growing cycles, resistance to pests and diseases, and higher responsiveness to chemical fertilizers. As a result, farmers achieved higher yields per unit of land, thus increasing food production.
Chemical fertilizers, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, were also widely adopted during the Green Revolution. These fertilizers provided essential nutrients to the crops, promoting faster and healthier growth. Additionally, pesticides and herbicides were introduced to control pests and weeds, further protecting the crops and enhancing yields.
Improved irrigation techniques, including the use of tube wells and pumps, allowed farmers to provide water to their fields even in areas with limited rainfall. This enabled them to cultivate their land throughout the year, reducing dependence on monsoon rains.
Overall, the Green Revolution transformed agriculture by increasing crop yields and ensuring food security. It played a crucial role in alleviating hunger and poverty in many parts of the world. However, it also had some negative consequences, such as environmental degradation, increased reliance on chemical inputs, and disparities in access to resources between small and large farmers.
The Green Revolution, which began in the 1960s, introduced technological advancements and practices that significantly increased agricultural productivity. Key components of the Green Revolution included the development and distribution of high-yielding varieties (HYVs) of seeds, increased use of chemical fertilizers, and improved irrigation techniques.
The introduction of HYVs of seeds, particularly in wheat and rice, led to substantial increases in crop yields. These new varieties were bred to have shorter growing cycles, resistance to pests and diseases, and higher responsiveness to chemical fertilizers. As a result, farmers achieved higher yields per unit of land, thus increasing food production.
Chemical fertilizers, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, were also widely adopted during the Green Revolution. These fertilizers provided essential nutrients to the crops, promoting faster and healthier growth. Additionally, pesticides and herbicides were introduced to control pests and weeds, further protecting the crops and enhancing yields.
Improved irrigation techniques, including the use of tube wells and pumps, allowed farmers to provide water to their fields even in areas with limited rainfall. This enabled them to cultivate their land throughout the year, reducing dependence on monsoon rains.
Overall, the Green Revolution transformed agriculture by increasing crop yields and ensuring food security. It played a crucial role in alleviating hunger and poverty in many parts of the world. However, it also had some negative consequences, such as environmental degradation, increased reliance on chemical inputs, and disparities in access to resources between small and large farmers.
Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): India adopted the import substitution policy during the first seven Five-year plans precisely.
Reason (R): Import substitution was to substitute the imports of our economy with domestic production.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion(A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but Reason(R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): India adopted the import substitution policy during the first seven Five-year plans precisely.
Reason (R): Import substitution was to substitute the imports of our economy with domestic production.
Assertion (A): India adopted the import substitution policy during the first seven Five-year plans precisely.
Reason (R): Import substitution was to substitute the imports of our economy with domestic production.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion(A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but Reason(R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
India adopted import substitution policy during the first seven Five-year plans precisely to protect domestic industries.
‘Since independence, India has witnessed a considerable fall in the Infant Mortality Rate in India’ Identify which of the following may not be one of the reasons for the fall in the Infant Mortality Rate?- a)Improvement in health facilities over the years
- b)Improvement in educational standards over the years
- c)Fall in standard of living of the population of the nation over the years
- d)Technological expansion over the years
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
‘Since independence, India has witnessed a considerable fall in the Infant Mortality Rate in India’ Identify which of the following may not be one of the reasons for the fall in the Infant Mortality Rate?
a)
Improvement in health facilities over the years
b)
Improvement in educational standards over the years
c)
Fall in standard of living of the population of the nation over the years
d)
Technological expansion over the years
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Infant mortality rate can be defined as number of deaths per 1000 live births of children below one year of age in a year. All these reasons, improvement in health facilities, improvement in educational standards, and technological expansion over the years can lead to fall in infant mortality rate but option (c) fall in standard of living of people increases the infant mortality rate.
Industrial Policy Resolution (IPR) 1956 formed the basis of the_________ Five Year Plan.- a)First
- b)Fourth
- c)Second
- d)Third
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Industrial Policy Resolution (IPR) 1956 formed the basis of the_________ Five Year Plan.
a)
First
b)
Fourth
c)
Second
d)
Third
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Industrial policy Resolution (IPR), 1956 was introduced in second five-year plan. It covered various issues related to the industrial enterprises of the country. In this, industries were divided into three types: Schedule A, Schedule B and Schedule C.
Ms. Sakshi, an economics teacher, was explaining the concept of ‘minimum percentage of the total deposits to be kept by any commercial bank with the Central Bank of the country, as per norms and statute prevailing in the country’.
From the following, choose the correct alternative which specifies towards the concept explained by her?- a)Cash Reserve Ratio
- b)Repo Rate
- c)Bank Rate
- d)Statutory Liquidity Ratio
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ms. Sakshi, an economics teacher, was explaining the concept of ‘minimum percentage of the total deposits to be kept by any commercial bank with the Central Bank of the country, as per norms and statute prevailing in the country’.
From the following, choose the correct alternative which specifies towards the concept explained by her?
From the following, choose the correct alternative which specifies towards the concept explained by her?
a)
Cash Reserve Ratio
b)
Repo Rate
c)
Bank Rate
d)
Statutory Liquidity Ratio
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Ms. Sakshi, an economics teacher explained the concept of ‘cash reserve ratio’ by saying that minimum percentage of the total deposits (net demand and time deposits) which is kept by any commercial bank with the central bank. Because through Cash reserve ratio, Central bank is able to control the money supply.
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternatives given below:
Statement 1: Subsidies do not add any burden on the financial health of a nation.
Statement 2: Complete removal of subsidies may violate the aim of equitable distribution of income.- a)Both the statements are true.
- b)Both the statements are false.
- c)Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
- d)Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternatives given below:
Statement 1: Subsidies do not add any burden on the financial health of a nation.
Statement 2: Complete removal of subsidies may violate the aim of equitable distribution of income.
Statement 1: Subsidies do not add any burden on the financial health of a nation.
Statement 2: Complete removal of subsidies may violate the aim of equitable distribution of income.
a)
Both the statements are true.
b)
Both the statements are false.
c)
Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
d)
Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Subsidies are given to the farmers so that they get inputs at prices which are lesser than the market price. As the statement 1 is false, subsidies do add burden on the financial health of a nation. If with the help of subsidies, government tries to remove the gap between rich and poor, hence aim of equitable distribution of income may be violated if subsidies is removed.
In a hypothetical economy, Mr. Neeraj has deposited ₹100 in the bank. If it is assumed that there is no other currency circulation in the economy, then the total money supply in the economy will be ________________.- a)zero
- b)₹100
- c)not defined
- d)₹120
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a hypothetical economy, Mr. Neeraj has deposited ₹100 in the bank. If it is assumed that there is no other currency circulation in the economy, then the total money supply in the economy will be ________________.
a)
zero
b)
₹100
c)
not defined
d)
₹120
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
If money deposited in the bank is `100, and no other money is circulating in the economy, then the total money supply in the economy is ₹100 because money supply can be defined as total stock of money available in the economy at a given point of time in the form of currency and demand deposits.
National Bank for Agricultural and Rural Development (NABARD) was set up in 1982 as a/ the_________body to coordinate the activities of all institutions involved in the rural financing system.- a)Cooperative
- b)Apex
- c)micro credit
- d)private credit
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
National Bank for Agricultural and Rural Development (NABARD) was set up in 1982 as a/ the_________body to coordinate the activities of all institutions involved in the rural financing system.
a)
Cooperative
b)
Apex
c)
micro credit
d)
private credit
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
NABARD is an apex body or organisation which helps in promoting the strength of various credit institutions, like, cooperatives, commercial banks and regional rural banks. Also, it provides financial help to the non-farm sector.
_____________ is the portion of agricultural produce which is sold in the market by the farmers, after meeting their self-consumption requirements.- a)Trade Surplus
- b)Marketable Surplus
- c)Producer Surplus
- d)Consumer Surplus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
_____________ is the portion of agricultural produce which is sold in the market by the farmers, after meeting their self-consumption requirements.
a)
Trade Surplus
b)
Marketable Surplus
c)
Producer Surplus
d)
Consumer Surplus
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Due to green revolution, ‘marketable surplus’ could be generated. Marketable surplus can be defined as that portion of agricultural produce which farmers sell in the market after fulfilling their selfconsumption requirements.
Identify which of the following is not an example of ‘invisible item’ under Current Account of the Balance of Payments transactions:- a)Air and sea transport
- b)Postal and courier services
- c)Education-related travel
- d)Merchandise linked transactions
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify which of the following is not an example of ‘invisible item’ under Current Account of the Balance of Payments transactions:
a)
Air and sea transport
b)
Postal and courier services
c)
Education-related travel
d)
Merchandise linked transactions

|
Bhavya Joshi answered |
You have not provided the options to choose from. Please provide the options so that I can identify which one is not an example of something.
Which of the following doesn’t highlight the status of industrial sector during the colonial period?- a)Capital goods industries were lacking.
- b)Bristish followed equi-proportional tariff policy.
- c)Conversion of India as a sprawing market for British finished goods.
- d)India handicraft industries declined.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following doesn’t highlight the status of industrial sector during the colonial period?
a)
Capital goods industries were lacking.
b)
Bristish followed equi-proportional tariff policy.
c)
Conversion of India as a sprawing market for British finished goods.
d)
India handicraft industries declined.
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The restrictive policies of commodity production, trade and tariff pursued by the colonial government adversely affected the structure, composition and volume of India’s foreign trade.
Choose the correct statement from the following:- a)Poverty line does not distinguish between the poor and non-poor.
- b)There was unequal distribution of assets due to which non-poor received the benefits.
- c)Fall in population is one of the cause of poverty.
- d)Reason for rise in poverty is high level of economic development.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct statement from the following:
a)
Poverty line does not distinguish between the poor and non-poor.
b)
There was unequal distribution of assets due to which non-poor received the benefits.
c)
Fall in population is one of the cause of poverty.
d)
Reason for rise in poverty is high level of economic development.
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Poverty alleviation programmes were criticized on the basis that there was unequal distribution of assets and benefits of poverty alleviation programmes have made non-poor more rich and poor more vulnerable.
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: Public goods are those goods and services that are collectively consumed by the public.
Statement 2: Public goods are excludable and rivalrous in nature.- a)Both the statements are true.
- b)Both the statements are false.
- c)Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
- d)Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: Public goods are those goods and services that are collectively consumed by the public.
Statement 2: Public goods are excludable and rivalrous in nature.
Statement 1: Public goods are those goods and services that are collectively consumed by the public.
Statement 2: Public goods are excludable and rivalrous in nature.
a)
Both the statements are true.
b)
Both the statements are false.
c)
Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
d)
Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
Public goods are those goods which are collectively consumed by the public. The given statement 1 is true. For example, air. But the statement 2 is false as public goods are non-excludable and non-rival in nature. Taking the example of air, no one can be excluded from consuming it and also if one group of people consumes the public good, here, air then the consumption of air for other people do not fall.
Identify which of the following bank does not interact directly with the general public?- a)Bank of India
- b)State Bank of India
- c)Central Bank of India
- d)Reserve Bank of India
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify which of the following bank does not interact directly with the general public?
a)
Bank of India
b)
State Bank of India
c)
Central Bank of India
d)
Reserve Bank of India
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Reserve bank of India does not interact directly with the public. As Central bank deals with commercial banks and commercial banks deal with the public. Deposits are made by public with the commercial banks and central bank deal with commercial banks in controlling money supply and credit through various instruments or policies.
Identify which of the following is not a function of the Reserve Bank of India?- a)To act as the banker to the Government of India.
- b)To act as the custodian of the gold reserve of India
- c)To act as the financial advisor to the Government of India
- d)To issue coins and one rupee note
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify which of the following is not a function of the Reserve Bank of India?
a)
To act as the banker to the Government of India.
b)
To act as the custodian of the gold reserve of India
c)
To act as the financial advisor to the Government of India
d)
To issue coins and one rupee note
|
|
Mihir Yadav answered |
Not a Function of the Reserve Bank of India
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central banking institution of India, responsible for regulating the country's monetary policy and currency. It performs several important functions to ensure the stability and efficiency of the financial system. However, one of the options mentioned in the question is not a function of the RBI. Let's analyze each option to identify the correct answer.
a) To act as the banker to the Government of India
The RBI acts as the banker to the Government of India, which means it manages the government's accounts, provides banking services, and handles the collection and payment of funds on behalf of the government. This includes managing the government's receipts and payments, maintaining the Consolidated Fund of India, and conducting government transactions.
b) To act as the custodian of the gold reserve of India
Another important function of the RBI is to act as the custodian of the gold reserve of India. It holds and safeguards the country's gold reserves, which play a crucial role in maintaining financial stability and supporting the value of the Indian rupee. The RBI manages the gold reserves to protect against economic uncertainties and provide a sense of security.
c) To act as the financial advisor to the Government of India
The RBI also acts as the financial advisor to the Government of India. It provides expert advice on various financial matters, including fiscal policies, budgetary allocations, and economic reforms. The RBI's expertise and insights help the government in making informed decisions to promote economic growth, manage inflation, and address financial challenges.
d) To issue coins and one rupee note
This is the correct answer. The RBI is not responsible for issuing coins and one rupee notes. The responsibility for coinage rests with the Government of India, specifically the Ministry of Finance. The government's Minting Presses produce coins of various denominations, including one rupee. Similarly, the printing of one rupee notes is carried out by the Government of India's Security Printing and Minting Corporation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, among the given options, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) does not have the function of issuing coins and one rupee notes. This responsibility lies with the Government of India, specifically the Ministry of Finance. The RBI's primary functions include acting as the banker to the government, custodian of the gold reserve, and financial advisor to the government.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central banking institution of India, responsible for regulating the country's monetary policy and currency. It performs several important functions to ensure the stability and efficiency of the financial system. However, one of the options mentioned in the question is not a function of the RBI. Let's analyze each option to identify the correct answer.
a) To act as the banker to the Government of India
The RBI acts as the banker to the Government of India, which means it manages the government's accounts, provides banking services, and handles the collection and payment of funds on behalf of the government. This includes managing the government's receipts and payments, maintaining the Consolidated Fund of India, and conducting government transactions.
b) To act as the custodian of the gold reserve of India
Another important function of the RBI is to act as the custodian of the gold reserve of India. It holds and safeguards the country's gold reserves, which play a crucial role in maintaining financial stability and supporting the value of the Indian rupee. The RBI manages the gold reserves to protect against economic uncertainties and provide a sense of security.
c) To act as the financial advisor to the Government of India
The RBI also acts as the financial advisor to the Government of India. It provides expert advice on various financial matters, including fiscal policies, budgetary allocations, and economic reforms. The RBI's expertise and insights help the government in making informed decisions to promote economic growth, manage inflation, and address financial challenges.
d) To issue coins and one rupee note
This is the correct answer. The RBI is not responsible for issuing coins and one rupee notes. The responsibility for coinage rests with the Government of India, specifically the Ministry of Finance. The government's Minting Presses produce coins of various denominations, including one rupee. Similarly, the printing of one rupee notes is carried out by the Government of India's Security Printing and Minting Corporation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, among the given options, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) does not have the function of issuing coins and one rupee notes. This responsibility lies with the Government of India, specifically the Ministry of Finance. The RBI's primary functions include acting as the banker to the government, custodian of the gold reserve, and financial advisor to the government.
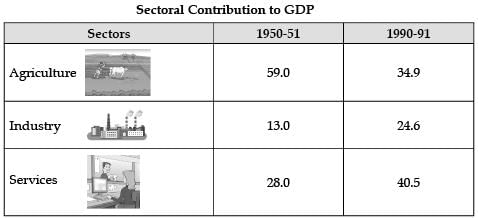 Q. Contribution of service sector has increased due to:
Q. Contribution of service sector has increased due to:- a)Self-reliance
- b)Modernisation
- c)Globalisation
- d)Privatisation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

Q. Contribution of service sector has increased due to:
a)
Self-reliance
b)
Modernisation
c)
Globalisation
d)
Privatisation
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Contribution of service sector to GDP has increased due to Globalisation as many of the services such as voice-based business processes (popularly known as BPO or call centres), record keeping, accountancy, banking services, music recording, film editing, book transcription, clinical advice or even teaching are being outsourced by companies in developed countries to India.
_________ is an example of capital receipt.- a)Interest
- b)Escheats
- c)Borrowings
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
_________ is an example of capital receipt.
a)
Interest
b)
Escheats
c)
Borrowings
d)
All of these
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Borrowings is a capital receipt as it creates a liability.
Agriculture in India has not reached its total potential. It is observed that the following measures can be undertaken to reach the maximum potential of the agricultural production:
(I) The supply of finance should be fully institutionalised and dependence on private sources for credit should be eliminated.
(II) The interest rate should be low in general. The banks should charge different rates for different uses.
(III)The basis of credit should not be mortgage of any security. Production or productivity of land should be the basis for the approval of loans.
(IV)The conditions of repayment of loans should be different so as to suit different circumstances.
(V) It should be ensured that finance is used for production. Loans can be given in the form of goods like seeds, fertilisers, etc.
(VI)There should be adequately trained and devoted personnel to manage the financial institutions. The persons should have full knowledge of agriculture and interest of farmers. The person should be able to guide the farmers on how to use the loan systematically.Q. The conditions of loans and their repayment needs to be _________.- a)Same
- b)Different
- c)Without Conditions
- d)Personal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Agriculture in India has not reached its total potential. It is observed that the following measures can be undertaken to reach the maximum potential of the agricultural production:
(I) The supply of finance should be fully institutionalised and dependence on private sources for credit should be eliminated.
(II) The interest rate should be low in general. The banks should charge different rates for different uses.
(III)The basis of credit should not be mortgage of any security. Production or productivity of land should be the basis for the approval of loans.
(IV)The conditions of repayment of loans should be different so as to suit different circumstances.
(V) It should be ensured that finance is used for production. Loans can be given in the form of goods like seeds, fertilisers, etc.
(VI)There should be adequately trained and devoted personnel to manage the financial institutions. The persons should have full knowledge of agriculture and interest of farmers. The person should be able to guide the farmers on how to use the loan systematically.
(I) The supply of finance should be fully institutionalised and dependence on private sources for credit should be eliminated.
(II) The interest rate should be low in general. The banks should charge different rates for different uses.
(III)The basis of credit should not be mortgage of any security. Production or productivity of land should be the basis for the approval of loans.
(IV)The conditions of repayment of loans should be different so as to suit different circumstances.
(V) It should be ensured that finance is used for production. Loans can be given in the form of goods like seeds, fertilisers, etc.
(VI)There should be adequately trained and devoted personnel to manage the financial institutions. The persons should have full knowledge of agriculture and interest of farmers. The person should be able to guide the farmers on how to use the loan systematically.
Q. The conditions of loans and their repayment needs to be _________.
a)
Same
b)
Different
c)
Without Conditions
d)
Personal
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The conditions of loans and their repayment should be different so that it can suit different circumstances.
Operation flood is related to _________ revolution.- a)Green
- b)White
- c)Blue
- d)Golden
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Operation flood is related to _________ revolution.
a)
Green
b)
White
c)
Blue
d)
Golden
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Operation flood is related to White Revolution. It increased production of milk in the country and also increased employment for the poor farmers.
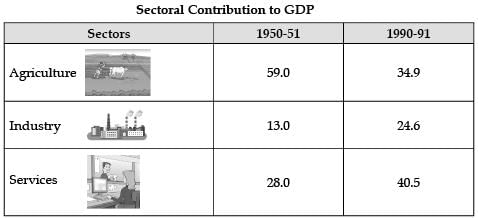 Q. All the three sectors, i.e. agriculture, industry and service sectors are _________ on each other.
Q. All the three sectors, i.e. agriculture, industry and service sectors are _________ on each other.- a)Independent
- b)Interdependent
- c)not related to each other
- d)Both (A) and (B)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

Q. All the three sectors, i.e. agriculture, industry and service sectors are _________ on each other.
a)
Independent
b)
Interdependent
c)
not related to each other
d)
Both (A) and (B)
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
All the three sectors i.e., agriculture, industry and service sector are interdependent on each other. All that is produced in the primary sector is if no use until it undergoes a change into finished product which is also not possible without transportation.
Which type of poor has been represented by the above diagram?- a)Churning poor
- b)Occasionally poor
- c)Always poor
- d)Usually poor
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

Which type of poor has been represented by the above diagram?
a)
Churning poor
b)
Occasionally poor
c)
Always poor
d)
Usually poor
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The occasionally poor are those who are rich most of the time but may sometimes have a patch of bad luck.
Agriculture in India has not reached its total potential. It is observed that the following measures can be undertaken to reach the maximum potential of the agricultural production:
(I) The supply of finance should be fully institutionalised and dependence on private sources for credit should be eliminated.
(II) The interest rate should be low in general. The banks should charge different rates for different uses.
(III)The basis of credit should not be mortgage of any security. Production or productivity of land should be the basis for the approval of loans.
(IV)The conditions of repayment of loans should be different so as to suit different circumstances.
(V) It should be ensured that finance is used for production. Loans can be given in the form of goods like seeds, fertilisers, etc.
(VI)There should be adequately trained and devoted personnel to manage the financial institutions. The persons should have full knowledge of agriculture and interest of farmers. The person should be able to guide the farmers on how to use the loan systematically.Q. Which among the following are the institutional sources of finance for agriculture?- a)Commercial Bank
- b)Land development Banks
- c)Traders and Commission agents
- d)Both (A) and (B)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Agriculture in India has not reached its total potential. It is observed that the following measures can be undertaken to reach the maximum potential of the agricultural production:
(I) The supply of finance should be fully institutionalised and dependence on private sources for credit should be eliminated.
(II) The interest rate should be low in general. The banks should charge different rates for different uses.
(III)The basis of credit should not be mortgage of any security. Production or productivity of land should be the basis for the approval of loans.
(IV)The conditions of repayment of loans should be different so as to suit different circumstances.
(V) It should be ensured that finance is used for production. Loans can be given in the form of goods like seeds, fertilisers, etc.
(VI)There should be adequately trained and devoted personnel to manage the financial institutions. The persons should have full knowledge of agriculture and interest of farmers. The person should be able to guide the farmers on how to use the loan systematically.
(I) The supply of finance should be fully institutionalised and dependence on private sources for credit should be eliminated.
(II) The interest rate should be low in general. The banks should charge different rates for different uses.
(III)The basis of credit should not be mortgage of any security. Production or productivity of land should be the basis for the approval of loans.
(IV)The conditions of repayment of loans should be different so as to suit different circumstances.
(V) It should be ensured that finance is used for production. Loans can be given in the form of goods like seeds, fertilisers, etc.
(VI)There should be adequately trained and devoted personnel to manage the financial institutions. The persons should have full knowledge of agriculture and interest of farmers. The person should be able to guide the farmers on how to use the loan systematically.
Q. Which among the following are the institutional sources of finance for agriculture?
a)
Commercial Bank
b)
Land development Banks
c)
Traders and Commission agents
d)
Both (A) and (B)
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Institutional sources are those credit sources that are formal and involves the formalities of providing or proving the means to pay back the loan.
_________ accepts deposits from the public and lend out this money to interest earning investment projects.- a)Commercial Bank
- b)Central Bank
- c)RBI
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
_________ accepts deposits from the public and lend out this money to interest earning investment projects.
a)
Commercial Bank
b)
Central Bank
c)
RBI
d)
All of these
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
When a commercial bank receives deposits, it keeps a part of it with the Central bank and a part with itself. These are called legal reserves. The money lent comes back to it as deposits. Again it keeps a part of it with the central bank and a part with itself and lends the rest. This process continues. In this way bank gives loans which is many a times the original deposit.
The objective of government budget is to achieve _________.- a)Economic stability
- b)Inflation
- c)Deflation
- d)Poverty
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The objective of government budget is to achieve _________.
a)
Economic stability
b)
Inflation
c)
Deflation
d)
Poverty
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
The objective of government budget is maintaining economic stability in the economy. During inflation, government should reduce its expenditure and increase tax rate and during deflation, it should its expenditure and reduce tax rate.
Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and reason (R):
Assertion (A): Import substitution leads to saving of foreign exchange.
Reason (R): Import substitution leads the goods to be produced in the country itself. - a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and reason (R):
Assertion (A): Import substitution leads to saving of foreign exchange.
Reason (R): Import substitution leads the goods to be produced in the country itself.
Assertion (A): Import substitution leads to saving of foreign exchange.
Reason (R): Import substitution leads the goods to be produced in the country itself.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Import substitution leads to restricting imported foreign goods but producing those goods in the domestic country. Import substitution helps in saving foreign exchange in the country by importing less through restrictions like tariffs and quotas.
Agriculture in India has not reached its total potential. It is observed that the following measures can be undertaken to reach the maximum potential of the agricultural production:
(I) The supply of finance should be fully institutionalised and dependence on private sources for credit should be eliminated.
(II) The interest rate should be low in general. The banks should charge different rates for different uses.
(III)The basis of credit should not be mortgage of any security. Production or productivity of land should be the basis for the approval of loans.
(IV)The conditions of repayment of loans should be different so as to suit different circumstances.
(V) It should be ensured that finance is used for production. Loans can be given in the form of goods like seeds, fertilisers, etc.
(VI)There should be adequately trained and devoted personnel to manage the financial institutions. The persons should have full knowledge of agriculture and interest of farmers. The person should be able to guide the farmers on how to use the loan systematically.Q. Read the following statements and select the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: The financial institutes need to have trained staff and devoted personnel.
Statement 2: There should be full knowledge of agriculture with the financial institutes.- a)Both the statements are true.
- b)Both the statements are false.
- c)Statement 1 is true but Statement 2 is false.
- d)Statement 1 is false but statement 2 is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Agriculture in India has not reached its total potential. It is observed that the following measures can be undertaken to reach the maximum potential of the agricultural production:
(I) The supply of finance should be fully institutionalised and dependence on private sources for credit should be eliminated.
(II) The interest rate should be low in general. The banks should charge different rates for different uses.
(III)The basis of credit should not be mortgage of any security. Production or productivity of land should be the basis for the approval of loans.
(IV)The conditions of repayment of loans should be different so as to suit different circumstances.
(V) It should be ensured that finance is used for production. Loans can be given in the form of goods like seeds, fertilisers, etc.
(VI)There should be adequately trained and devoted personnel to manage the financial institutions. The persons should have full knowledge of agriculture and interest of farmers. The person should be able to guide the farmers on how to use the loan systematically.
(I) The supply of finance should be fully institutionalised and dependence on private sources for credit should be eliminated.
(II) The interest rate should be low in general. The banks should charge different rates for different uses.
(III)The basis of credit should not be mortgage of any security. Production or productivity of land should be the basis for the approval of loans.
(IV)The conditions of repayment of loans should be different so as to suit different circumstances.
(V) It should be ensured that finance is used for production. Loans can be given in the form of goods like seeds, fertilisers, etc.
(VI)There should be adequately trained and devoted personnel to manage the financial institutions. The persons should have full knowledge of agriculture and interest of farmers. The person should be able to guide the farmers on how to use the loan systematically.
Q. Read the following statements and select the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: The financial institutes need to have trained staff and devoted personnel.
Statement 2: There should be full knowledge of agriculture with the financial institutes.
Statement 1: The financial institutes need to have trained staff and devoted personnel.
Statement 2: There should be full knowledge of agriculture with the financial institutes.
a)
Both the statements are true.
b)
Both the statements are false.
c)
Statement 1 is true but Statement 2 is false.
d)
Statement 1 is false but statement 2 is true.
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The financial institutes need to have adequately trained and devoted personnel to manage the financial institutions and persons should have full knowledge of agriculture.
Under the Balance of Payments structure of a nation, the two main categories of accounts for the classification of the transactions are ________ and ________.
i. current account
ii. unilateral transfer account
iii. capital account
iv. loan account
Identify the correct alternatives from the following:- a)i and ii
- b)i and iii
- c)iii and iv
- d)iv and i
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Under the Balance of Payments structure of a nation, the two main categories of accounts for the classification of the transactions are ________ and ________.
i. current account
ii. unilateral transfer account
iii. capital account
iv. loan account
Identify the correct alternatives from the following:
i. current account
ii. unilateral transfer account
iii. capital account
iv. loan account
Identify the correct alternatives from the following:
a)
i and ii
b)
i and iii
c)
iii and iv
d)
iv and i
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Balance of payment of a country comprises of two accounts: (a) Current account, and (b) Capital account. Current account records transactions related to export and import of goods and services, unilateral transfers received and paid to and from rest of the world and capital account records transactions related to Borrowings and loans given, Investment made to and from rest of the world, and change in foreign exchange reserves.
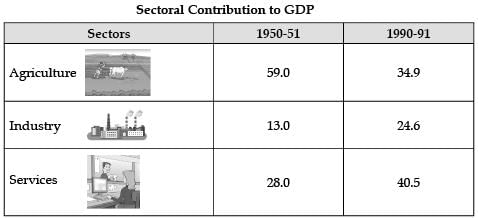 Q. Choose the correct alternative given below from the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R)
Q. Choose the correct alternative given below from the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R)
Assertion (A): The share of agriculture sector to GDP has fallen from 1950-51 (59%) to 1990-91 (34.9%).
Reason (R): The agriculture sector accounts for the largest share of workforce.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion(A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

Q. Choose the correct alternative given below from the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R)
Assertion (A): The share of agriculture sector to GDP has fallen from 1950-51 (59%) to 1990-91 (34.9%).
Reason (R): The agriculture sector accounts for the largest share of workforce.
Assertion (A): The share of agriculture sector to GDP has fallen from 1950-51 (59%) to 1990-91 (34.9%).
Reason (R): The agriculture sector accounts for the largest share of workforce.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion(A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
The share of agriculture sector to GDP has fallen from 1950 to 1991 because industrial sector became well diversified by 1990, largely due to the public sector.
____________ is not a reason for poverty in India. - a)population explosion
- b)rise in per capita GDP
- c)low capital formation
- d)socio-economic exclusion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
____________ is not a reason for poverty in India.
a)
population explosion
b)
rise in per capita GDP
c)
low capital formation
d)
socio-economic exclusion
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
Poverty in India arises due to various reasons such as population explosion, low capital formation, higher unemployment, inequalities in income, etc. But ‘rise in per capita GDP’ is not the reason for poverty in India. Rather, it reduces poverty.
 Q. The market value of all the final goods and services produced in the country during a period of one year is called as:
Q. The market value of all the final goods and services produced in the country during a period of one year is called as:- a)Gross National Product
- b)Gross Domestic Product
- c)Both (A) and (B)
- d)Neither (A) nor (B)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

Q. The market value of all the final goods and services produced in the country during a period of one year is called as:
a)
Gross National Product
b)
Gross Domestic Product
c)
Both (A) and (B)
d)
Neither (A) nor (B)
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
Gross domestic product (GDP) measures the economic growth of a country. It measures the market value of all final goods and services produced in the country during a period of one year.
Chapter doubts & questions for Economics - Sample Papers for Class 12 Commerce 2025 is part of Commerce exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Commerce 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Economics - Sample Papers for Class 12 Commerce in English & Hindi are available as part of Commerce exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Commerce Exam by signing up for free.
Sample Papers for Class 12 Commerce
130 docs|5 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









