All Exams >
JEE >
Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced >
All Questions
All questions of General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals for JEE Exam
Only One Option Correct TypeThis section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctQ. Which represents the correct abundance order of elements in the earth crust?- a)O > Si > Fe > Al
- b)O > Si > AI > Fe
- c)O > C > Si > AI
- d)AI > Fe > 0 > Si
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
Q.
Which represents the correct abundance order of elements in the earth crust?
a)
O > Si > Fe > Al
b)
O > Si > AI > Fe
c)
O > C > Si > AI
d)
AI > Fe > 0 > Si
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The mass-abundance of the nine most abundant elements in the Earth's crust is approximately: oxygen 46%, silicon 28%, aluminum 8.3%, iron 5.6%, calcium 4.2%, sodium 2.5%, magnesium 2.4%, potassium 2.0%, and titanium 0.61%.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Which of the following contains both copper and iron?
- A:
Cuprite
- B:
Chalcocite
- C:
Chalcopyrite
- D:
Malachite
The answer is c.
Which of the following contains both copper and iron?
Cuprite
Chalcocite
Chalcopyrite
Malachite
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Chalcopyrite is a brass-yellow mineral with a chemical composition of CuFeS2. It occurs in most sulfide mineral deposits throughout the world and has been the most important ore of copper for thousands of years.
› Chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) is the ore contains both copper and iron.
› The largest deposit of nearly pure chalcopyrite ever discovered in Canada was at the southern end of the Temagami Greenstone Belt where Copperfield Mine extracted the high-grade copper.
Regarding cryolite incorrect statement is
- a)It is an ore of Al
- b)The non-metal is fluorine
- c)It is used in aluminium extraction from bauxite
- d)Its formula is 3NaF. AIF3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Regarding cryolite incorrect statement is
a)
It is an ore of Al
b)
The non-metal is fluorine
c)
It is used in aluminium extraction from bauxite
d)
Its formula is 3NaF. AIF3
|
|
Anisha Bose answered |
Cryolite is an important ore of aluminum that is used in the extraction of aluminum from bauxite. It is a rare mineral that occurs in small quantities in Greenland, and its chemical formula is Na3AlF6.
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 5 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q. Which of the following is the correct combination?
- a)Borax = Na2B4O7 . 5H2O
- b)Colemanite = Ca2Br6O11 . 5H2O
- c)Anglesite = PbCO3
- d)Chile saltpeter = NaNO3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 5 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q. Which of the following is the correct combination?
a)
Borax = Na2B4O7 . 5H2O
b)
Colemanite = Ca2Br6O11 . 5H2O
c)
Anglesite = PbCO3
d)
Chile saltpeter = NaNO3
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Sodium nitrate is the chemical compound with the formula NaNO3. This alkali metal nitrate salt is also known as Chile saltpeter (large deposits of which were historically mined in Chile) to distinguish it from ordinary saltpeter, potassium nitrate. The mineral form is also known as nitratine, nitratite or soda niter.
Comprehension TypeThis section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
PassageThe natural substances in which metals occur in the earth are called minerals. A mineral has a definite composition. It may be a single compound or a complex mixture . It is usually associated with number of impurities. The minerals from which the metals can be conveniently extracted are called ores .Thus, all ores are minerals but all minerals are not ores. Depending on the composition ores are classified into different types such as oxides, sulphides, carbonates, halides, silicates etc.Q. The impurities associated with minerals are called.- a)Gangue
- b)Flux
- c)Slag
- d)Depressant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Comprehension Type
This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Passage
Passage
The natural substances in which metals occur in the earth are called minerals. A mineral has a definite composition. It may be a single compound or a complex mixture . It is usually associated with number of impurities. The minerals from which the metals can be conveniently extracted are called ores .Thus, all ores are minerals but all minerals are not ores. Depending on the composition ores are classified into different types such as oxides, sulphides, carbonates, halides, silicates etc.
Q. The impurities associated with minerals are called.
a)
Gangue
b)
Flux
c)
Slag
d)
Depressant
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
The correct answer is option A
The impurities associated with minerals used in metallurgy are collectively called Gangue.
The impurities associated with minerals used in metallurgy are collectively called Gangue.
2CuCO3 . Cu(OH)2 is the formula of- a)Malachite
- b)Azurite
- c)Siderite
- d)Chalcopyrite
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
2CuCO3 . Cu(OH)2 is the formula of
a)
Malachite
b)
Azurite
c)
Siderite
d)
Chalcopyrite
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Azurite is an copper Ore [2CuCO3⋅Cu(OH)2]
One Integer Value Correct TypeThis section contains 5 questions, when worked out will result in an integer value from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)Q. The number of carbonate minerals among the followingCassiterite , Siderite , Anglesite , Azurite , Calamine , Cryolite ,Calcite ,Magnetite, Magnesite
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
One Integer Value Correct Type
This section contains 5 questions, when worked out will result in an integer value from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. The number of carbonate minerals among the following
Cassiterite , Siderite , Anglesite , Azurite , Calamine , Cryolite ,Calcite ,Magnetite, Magnesite
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The carbonate ores are siderite, azurite. calamine, calcite, magnesite.
Which of the following is the correct combination?- a)Calamine, siderite
- b)Magnesite , dolomite
- c)Malachite , azurite
- d)Calcite , witherite
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct combination?
a)
Calamine, siderite
b)
Magnesite , dolomite
c)
Malachite , azurite
d)
Calcite , witherite

|
Naani Mahesh answered |
B becoz they have same carbonates MAGNESITE IS MgCO3 and DOLOMITE is CaCO3.MgCO3.......
For which oxide formation ΔG° is more negative than Gr2O3?- a)FeO
- b)ZnO
- c)Al2O3
- d)MgO
Correct answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
For which oxide formation ΔG° is more negative than Gr2O3?
a)
FeO
b)
ZnO
c)
Al2O3
d)
MgO
|
|
Anuj Unni answered |
Introduction:
The question asks us to determine which oxide formation has a more negative value of standard Gibbs free energy of formation (ΔG°f) compared to Gr2O3. The standard Gibbs free energy of formation is a measure of the thermodynamic stability of a compound, with more negative values indicating greater stability.
Analysis:
To compare the ΔG°f values of different oxides, we need to refer to the standard Gibbs free energy of formation data. By comparing the values, we can determine which oxide formation is more stable (i.e., has a more negative ΔG°f value) than Gr2O3.
Options:
a) FeO:
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation for FeO is -272.8 kJ/mol. Since FeO has a more negative ΔG°f value than Gr2O3, it is more stable.
b) ZnO:
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation for ZnO is -318.3 kJ/mol. Since ZnO has a more negative ΔG°f value than Gr2O3, it is more stable.
c) Al2O3:
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation for Al2O3 is -1582.3 kJ/mol. Since Al2O3 has a more negative ΔG°f value than Gr2O3, it is more stable.
d) MgO:
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation for MgO is -601.6 kJ/mol. Since MgO has a more negative ΔG°f value than Gr2O3, it is more stable.
Conclusion:
Based on the comparison of the standard Gibbs free energy of formation values, the oxide formations with more negative ΔG°f values than Gr2O3 are Al2O3 and MgO. Therefore, the correct answer is option C and D.
The question asks us to determine which oxide formation has a more negative value of standard Gibbs free energy of formation (ΔG°f) compared to Gr2O3. The standard Gibbs free energy of formation is a measure of the thermodynamic stability of a compound, with more negative values indicating greater stability.
Analysis:
To compare the ΔG°f values of different oxides, we need to refer to the standard Gibbs free energy of formation data. By comparing the values, we can determine which oxide formation is more stable (i.e., has a more negative ΔG°f value) than Gr2O3.
Options:
a) FeO:
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation for FeO is -272.8 kJ/mol. Since FeO has a more negative ΔG°f value than Gr2O3, it is more stable.
b) ZnO:
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation for ZnO is -318.3 kJ/mol. Since ZnO has a more negative ΔG°f value than Gr2O3, it is more stable.
c) Al2O3:
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation for Al2O3 is -1582.3 kJ/mol. Since Al2O3 has a more negative ΔG°f value than Gr2O3, it is more stable.
d) MgO:
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation for MgO is -601.6 kJ/mol. Since MgO has a more negative ΔG°f value than Gr2O3, it is more stable.
Conclusion:
Based on the comparison of the standard Gibbs free energy of formation values, the oxide formations with more negative ΔG°f values than Gr2O3 are Al2O3 and MgO. Therefore, the correct answer is option C and D.
Statement TypeThis section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct anser from the codes given below.Q. Statement I : The copper pyrite (CuFeS2) is the ore of copper.Statement II : The clay (Al2O3 . 2SiO2 . 2H2O) is the ore of aluminium.- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement Type
This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct anser from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : The copper pyrite (CuFeS2) is the ore of copper.
Statement II : The clay (Al2O3 . 2SiO2 . 2H2O) is the ore of aluminium.
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
Aluminium cannot be extracted from clay profitably.
The different number of non-metals present in fluorapatite are
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
The different number of non-metals present in fluorapatite are
|
|
Sankar Singh answered |
Fluorapatite is a mineral that belongs to the apatite group. It has the chemical formula Ca5(PO4)3F and is composed of calcium, phosphorus, oxygen, and fluorine. The number of non-metals present in fluorapatite can be determined by analyzing its chemical formula.
Chemical Formula of Fluorapatite
- The chemical formula of fluorapatite is Ca5(PO4)3F.
- The formula can be broken down into its constituent elements as follows:
- Calcium (Ca)
- Phosphorus (P)
- Oxygen (O)
- Fluorine (F)
Non-Metals Present in Fluorapatite
- Non-metals are elements that lack metallic properties such as malleability, ductility, and conductivity.
- In the chemical formula of fluorapatite, the non-metals present are phosphorus, oxygen, and fluorine.
- Calcium is a metal, and therefore, it is not considered a non-metal.
Conclusion
- Fluorapatite contains three non-metals, which are phosphorus, oxygen, and fluorine.
Chemical Formula of Fluorapatite
- The chemical formula of fluorapatite is Ca5(PO4)3F.
- The formula can be broken down into its constituent elements as follows:
- Calcium (Ca)
- Phosphorus (P)
- Oxygen (O)
- Fluorine (F)
Non-Metals Present in Fluorapatite
- Non-metals are elements that lack metallic properties such as malleability, ductility, and conductivity.
- In the chemical formula of fluorapatite, the non-metals present are phosphorus, oxygen, and fluorine.
- Calcium is a metal, and therefore, it is not considered a non-metal.
Conclusion
- Fluorapatite contains three non-metals, which are phosphorus, oxygen, and fluorine.
Which of the following is a halide ore?- a)Feldspar
- b)Fluorspar
- c)Sylvine
- d)Carnallite
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a halide ore?
a)
Feldspar
b)
Fluorspar
c)
Sylvine
d)
Carnallite

|
Aditya Sen answered |
Feldspar = KAISi3O8, Fluorspar = CaF2
Sylvine= KCI, Carnallite = KCI.MgCI2 . 6H2O
Sylvine= KCI, Carnallite = KCI.MgCI2 . 6H2O
In the froth floatation process for benefaction of the ores, the ore particles float because- a)They are light
- b)Their surface is not easily wetted by water
- c)They are insoluble
- d)They bear electric charge
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the froth floatation process for benefaction of the ores, the ore particles float because
a)
They are light
b)
Their surface is not easily wetted by water
c)
They are insoluble
d)
They bear electric charge

|
Rishika Chauhan answered |
The ore particles preferentially wetted by the oil become lighter and thus rise to the surface along with the froth while the gangue particle wetted by wated become heavier and thus settle down at the bottom.
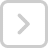
In the leaching of Ag2S with NaCN the equation isAg2S + 4NaCN → 2Na[Ag(CN)2] + Na2S. In this change in oxidation state of silver.
Correct answer is '0'. Can you explain this answer?
In the leaching of Ag2S with NaCN the equation is
Ag2S + 4NaCN → 2Na[Ag(CN)2] + Na2S. In this change in oxidation state of silver.

|
Anjana Sen answered |
The Leaching of Ag2S with NaCN: Change in Oxidation State of Silver
The leaching process involves the extraction of a metal from its ore by using a suitable solvent. In the case of the leaching of Ag2S (silver sulfide) with NaCN (sodium cyanide), the reaction equation is as follows:
Ag2S + 4NaCN → 2Na[Ag(CN)2] + Na2S
In this reaction, the silver sulfide (Ag2S) reacts with sodium cyanide (NaCN) to form sodium dicyanoargentate(I) (Na[Ag(CN)2]) and sodium sulfide (Na2S). Let's analyze the change in the oxidation state of silver in this reaction.
The Oxidation State of Silver in Ag2S
In Ag2S, silver exists as a +1 oxidation state. This is because sulfide (S2-) has an oxidation state of -2, and since Ag2S is a neutral compound, the oxidation state of silver must balance the charge, resulting in a +1 oxidation state.
The Oxidation State of Silver in Na[Ag(CN)2]
In Na[Ag(CN)2], the sodium ion (Na+) has a fixed oxidation state of +1. The cyanide ion (CN-) has a -1 oxidation state. Therefore, to maintain charge neutrality in the compound, the oxidation state of silver must be +1. This is the same as the oxidation state of silver in Ag2S.
Conclusion
The change in oxidation state of silver during the leaching of Ag2S with NaCN is zero. The silver starts with a +1 oxidation state in Ag2S and remains in the +1 oxidation state in Na[Ag(CN)2]. This is because the cyanide ions in NaCN act as a ligand, forming a coordination compound with the silver ion, but do not cause a change in its oxidation state.
Overall, the leaching of Ag2S with NaCN is a redox-neutral process, where the silver ions do not undergo any change in their oxidation state.
The leaching process involves the extraction of a metal from its ore by using a suitable solvent. In the case of the leaching of Ag2S (silver sulfide) with NaCN (sodium cyanide), the reaction equation is as follows:
Ag2S + 4NaCN → 2Na[Ag(CN)2] + Na2S
In this reaction, the silver sulfide (Ag2S) reacts with sodium cyanide (NaCN) to form sodium dicyanoargentate(I) (Na[Ag(CN)2]) and sodium sulfide (Na2S). Let's analyze the change in the oxidation state of silver in this reaction.
The Oxidation State of Silver in Ag2S
In Ag2S, silver exists as a +1 oxidation state. This is because sulfide (S2-) has an oxidation state of -2, and since Ag2S is a neutral compound, the oxidation state of silver must balance the charge, resulting in a +1 oxidation state.
The Oxidation State of Silver in Na[Ag(CN)2]
In Na[Ag(CN)2], the sodium ion (Na+) has a fixed oxidation state of +1. The cyanide ion (CN-) has a -1 oxidation state. Therefore, to maintain charge neutrality in the compound, the oxidation state of silver must be +1. This is the same as the oxidation state of silver in Ag2S.
Conclusion
The change in oxidation state of silver during the leaching of Ag2S with NaCN is zero. The silver starts with a +1 oxidation state in Ag2S and remains in the +1 oxidation state in Na[Ag(CN)2]. This is because the cyanide ions in NaCN act as a ligand, forming a coordination compound with the silver ion, but do not cause a change in its oxidation state.
Overall, the leaching of Ag2S with NaCN is a redox-neutral process, where the silver ions do not undergo any change in their oxidation state.
When compared to ΔG° for the formation of Al2O3 the ΔG° for the formation of Cr2O3 is- a)higher
- b)Lower
- c)Same
- d)Unpredicted
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When compared to ΔG° for the formation of Al2O3 the ΔG° for the formation of Cr2O3 is
a)
higher
b)
Lower
c)
Same
d)
Unpredicted

|
Ameya Basu answered |
ΔG° is higher for the formation of Cr2O3.
Which of the following chemicals are involved in froth floatation process?- a)Collectors
- b)Depressant
- c)Flux
- d)Activators
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following chemicals are involved in froth floatation process?
a)
Collectors
b)
Depressant
c)
Flux
d)
Activators
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
In froth flotation the effectiveness of an air bubble to adhere to a particle is based on how hydrophobic the particle is. Hydrophobic particles have an affinity to air bubbles, leading to adsorption. Collectors are the main additives used to improve particle surfaces.
The reaction 3CaO + 2AI → Al2O3 + 3Ca is non-spontaneous. The number of electrons involved are
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction 3CaO + 2AI → Al2O3 + 3Ca is non-spontaneous. The number of electrons involved are
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
3CaO + 2Al Al2O3 + 3Ca
At anode: 2Al(s) 2Al3+ + 6e-
At cathode: 3Ca2+ + 6e- 3Ca(s)
Hence, number of e- involved = 6
At anode: 2Al(s) 2Al3+ + 6e-
At cathode: 3Ca2+ + 6e- 3Ca(s)
Hence, number of e- involved = 6
One or More than One Options Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. Purification of alumina is called- a)Baeyer’s proces
- b)Hall process
- c)Mond’s proces
- d)Hoope’s proces
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Purification of alumina is called
a)
Baeyer’s proces
b)
Hall process
c)
Mond’s proces
d)
Hoope’s proces

|
Universe Mystery answered |
Baeyer's process is used to obtain pure alumina. as sodium silicate, leaving behind the impurities. The resulting solution is filtered, and cooled and neutralized with carbon dioxide to get aluminium hydroxide as precipitate leaving sodium silicate in the solution.
Molecular formula of Glauber salt's- a)MgSO4 . 7H2O
- b)FeSO4 . 7H2O
- c)CuSO4 . 5H2O
- d)Na2SO4 . 10H2O
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Molecular formula of Glauber salt's
a)
MgSO4 . 7H2O
b)
FeSO4 . 7H2O
c)
CuSO4 . 5H2O
d)
Na2SO4 . 10H2O
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Glauber's salt, common name for sodium sulfate decahydrate, Na2SO4.10H2O. It occurs as white or colorless monoclinic crystals. Upon exposure to fairly dry air, it effloresces, forming powdery anhydrous sodium sulfate.
Which one of the following ores is concentrated by chemical leaching method?- a)Galena
- b)Copper pyrite
- c)CaO + SiO3
- d)SiO2 and CaSiO3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following ores is concentrated by chemical leaching method?
a)
Galena
b)
Copper pyrite
c)
CaO + SiO3
d)
SiO2 and CaSiO3
|
|
Sreemoyee Choudhury answered |
In this process the finely divided powdered argentite or the native silver or gold is treated with a dilute solution (0.5%) of sodium or potassium cyanide while a current of air is continuously passed. As a result silver pass into solution forming their respective soluble complex cyanides while the impurities remain unaffected which are filtered off.
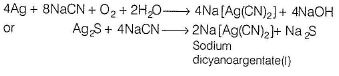
The main reaction occurring in blast furnace during the extraction of iron from haematite is- a)Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
- b)FeO + SiO2 → FeSiO3
- c)Fe2O3 + 3C → 2Fe + 3CO
- d)CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The main reaction occurring in blast furnace during the extraction of iron from haematite is
a)
Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
b)
FeO + SiO2 → FeSiO3
c)
Fe2O3 + 3C → 2Fe + 3CO
d)
CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3

|
Muskaan Chhikara answered |
3Fe2O3 + CO → 2Fe3O4 + CO2
Fe3O4 + CO → 3FeO + CO2
FeO + CO → Fe + CO2
Fe3O4 + CO → 3FeO + CO2
FeO + CO → Fe + CO2
A mineral is called an ore if- a)the percentage of metal content is more than 50 %
- b)it is possible to isolate metal from it
- c)a metal can be profitably extracted from it
- d)if it is free from any earthly impurities
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A mineral is called an ore if
a)
the percentage of metal content is more than 50 %
b)
it is possible to isolate metal from it
c)
a metal can be profitably extracted from it
d)
if it is free from any earthly impurities

|
Anisha Deshpande answered |
The Definition of an Ore
An ore is a type of mineral that contains a valuable metal or metal compound. It is a naturally occurring solid material from which a metal or valuable mineral can be profitably extracted. The classification of a mineral as an ore depends on certain criteria.
Criteria for Classifying a Mineral as an Ore
To be classified as an ore, a mineral must meet the following criteria:
1. Metal Content Percentage
The percentage of metal content in a mineral does not determine whether it is classified as an ore. Some ores may have a metal content of less than 50%, while some non-ores may have a higher metal content. Therefore, option A is incorrect.
2. Ability to Isolate Metal
For a mineral to be classified as an ore, it must be possible to isolate the metal from it. This means that the metal should be extractable from the mineral in a relatively straightforward manner. If it is not possible to isolate the metal from the mineral, it cannot be classified as an ore. Therefore, option B is correct.
3. Profitable Extraction
The extraction of metal from an ore should be economically viable. This means that the cost of extracting the metal should be lower than the value of the metal obtained. If the extraction process is not profitable, the mineral cannot be classified as an ore. Therefore, option C is correct.
4. Absence of Earthly Impurities
The presence of earthly impurities does not determine whether a mineral is classified as an ore. Ores often contain impurities that need to be removed during the extraction process. Therefore, option D is incorrect.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a mineral is called an ore if it is possible to isolate a metal from it, and if the extraction of the metal is economically viable. The percentage of metal content or the absence of earthly impurities are not determining factors for classifying a mineral as an ore.
An ore is a type of mineral that contains a valuable metal or metal compound. It is a naturally occurring solid material from which a metal or valuable mineral can be profitably extracted. The classification of a mineral as an ore depends on certain criteria.
Criteria for Classifying a Mineral as an Ore
To be classified as an ore, a mineral must meet the following criteria:
1. Metal Content Percentage
The percentage of metal content in a mineral does not determine whether it is classified as an ore. Some ores may have a metal content of less than 50%, while some non-ores may have a higher metal content. Therefore, option A is incorrect.
2. Ability to Isolate Metal
For a mineral to be classified as an ore, it must be possible to isolate the metal from it. This means that the metal should be extractable from the mineral in a relatively straightforward manner. If it is not possible to isolate the metal from the mineral, it cannot be classified as an ore. Therefore, option B is correct.
3. Profitable Extraction
The extraction of metal from an ore should be economically viable. This means that the cost of extracting the metal should be lower than the value of the metal obtained. If the extraction process is not profitable, the mineral cannot be classified as an ore. Therefore, option C is correct.
4. Absence of Earthly Impurities
The presence of earthly impurities does not determine whether a mineral is classified as an ore. Ores often contain impurities that need to be removed during the extraction process. Therefore, option D is incorrect.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a mineral is called an ore if it is possible to isolate a metal from it, and if the extraction of the metal is economically viable. The percentage of metal content or the absence of earthly impurities are not determining factors for classifying a mineral as an ore.
In chromite ore, the oxidation state of iron and chromium respectively are- a)+3, + 6
- b)+3, + 2
- c)+2, + 3
- d)+2, + 6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In chromite ore, the oxidation state of iron and chromium respectively are
a)
+3, + 6
b)
+3, + 2
c)
+2, + 3
d)
+2, + 6
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
Chromite ore is FeCr2O4
Oxidation state of Fe is +2 and Cr is +3
The processes used in the refining of aluminium and zinc metals respectively are- a)Hoope’s process and fractional distillation
- b)Hoope’s process and cupellation
- c)Poling and fractional distillation
- d)cupellation and fractional distillation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The processes used in the refining of aluminium and zinc metals respectively are
a)
Hoope’s process and fractional distillation
b)
Hoope’s process and cupellation
c)
Poling and fractional distillation
d)
cupellation and fractional distillation

|
Aravind Mehra answered |
The processes used in the refining of aluminium and zinc metals are Hoope's process and fractional distillation.
How many of the given mineral contain silicon in them? Pyrargyrite (Ruby silver), Kaolinite (China clay) .Feldspar, Willemite, Limonite, Mica, Beryl
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
How many of the given mineral contain silicon in them? Pyrargyrite (Ruby silver), Kaolinite (China clay) .Feldspar, Willemite, Limonite, Mica, Beryl

|
Dishani Kulkarni answered |
Silicon is present in Beryl = 3 BeO . AI2O3 . 6SiO2;
Mica = K2O . 3AI2O3 . 6SiO2 . 2H2O
Zn2SiO4 = Willemite; Feldspar = KAISi3O8.
China clay = Al2O3 . 2SiO2 . 2H2O (or) [AI2(OH)4 Si2O5]
Silicon is not present in
Limonite = 2Fe2O3 . 3H2O; Pyrargyrite (Ruby silver)
= 3Ag2S3Sb2S3.
Mica = K2O . 3AI2O3 . 6SiO2 . 2H2O
Zn2SiO4 = Willemite; Feldspar = KAISi3O8.
China clay = Al2O3 . 2SiO2 . 2H2O (or) [AI2(OH)4 Si2O5]
Silicon is not present in
Limonite = 2Fe2O3 . 3H2O; Pyrargyrite (Ruby silver)
= 3Ag2S3Sb2S3.
Among the following statements the incorrect one is- a)Calamine and siderite are carbonate ores
- b)Argentite and cuprite are oxides
- c)Zinc blende and pyrites are sulphide ores
- d)Malachite and azurite are ores of copper
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following statements the incorrect one is
a)
Calamine and siderite are carbonate ores
b)
Argentite and cuprite are oxides
c)
Zinc blende and pyrites are sulphide ores
d)
Malachite and azurite are ores of copper

|
Sanjana Bajaj answered |
Statement: Argentite and cuprite are oxides.
Explanation:
- Argentite is a silver ore, which is a sulfide mineral composed of silver sulfide (Ag2S). It is not an oxide.
- Cuprite is a copper ore, which is an oxide mineral composed of copper(I) oxide (Cu2O). It is an oxide.
Conclusion:
The given statement that "Argentite and cuprite are oxides" is incorrect. Argentite is a sulfide ore, not an oxide ore.
Explanation:
- Argentite is a silver ore, which is a sulfide mineral composed of silver sulfide (Ag2S). It is not an oxide.
- Cuprite is a copper ore, which is an oxide mineral composed of copper(I) oxide (Cu2O). It is an oxide.
Conclusion:
The given statement that "Argentite and cuprite are oxides" is incorrect. Argentite is a sulfide ore, not an oxide ore.
Sulphide ores are common for metalsa)Ag, Cu and Pbb)Ag, Cu and Snc)Ag, Mg and Pbd)Al, Cu and PbCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Ag, Cu and Pb
Ag →→ Ag22S
Cu →→ CuFeS22
Pb →→ PbS
Which is not an example of ore?- a)Ruby silver
- b)Horn Silver
- c)German Silver
- d)Quick Silver
Correct answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is not an example of ore?
a)
Ruby silver
b)
Horn Silver
c)
German Silver
d)
Quick Silver
|
|
Advait Ghosh answered |
Not an example of ore
- German Silver and Quick Silver are not examples of ore.
German Silver:
- German Silver, also known as nickel silver, is a type of alloy made from copper, zinc, and nickel.
- It does not occur naturally as an ore.
- German Silver is primarily used in the manufacturing of coins, musical instruments, and silverware.
Quick Silver:
- Quick Silver, also known as mercury, is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80.
- It is a heavy, silvery liquid at room temperature.
- Quick Silver does not occur naturally as an ore.
- It is primarily used in thermometers, barometers, dental amalgams, and various industrial processes.
Ruby Silver and Horn Silver:
Ruby Silver:
- Ruby Silver is a mineral that consists of silver sulfide (Ag2S).
- It is commonly found in hydrothermal veins associated with silver deposits.
- Ruby Silver is an important ore of silver.
Horn Silver:
- Horn Silver, also known as silver chloride (AgCl), is a secondary mineral that forms in oxidized silver ore deposits.
- It is typically found as a powdery or granular material.
- Horn Silver is an important ore of silver.
Conclusion:
- German Silver and Quick Silver are not ores because they are not naturally occurring minerals.
- Ruby Silver and Horn Silver, on the other hand, are examples of ores as they are naturally occurring minerals that contain valuable amounts of silver.
- German Silver and Quick Silver are not examples of ore.
German Silver:
- German Silver, also known as nickel silver, is a type of alloy made from copper, zinc, and nickel.
- It does not occur naturally as an ore.
- German Silver is primarily used in the manufacturing of coins, musical instruments, and silverware.
Quick Silver:
- Quick Silver, also known as mercury, is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80.
- It is a heavy, silvery liquid at room temperature.
- Quick Silver does not occur naturally as an ore.
- It is primarily used in thermometers, barometers, dental amalgams, and various industrial processes.
Ruby Silver and Horn Silver:
Ruby Silver:
- Ruby Silver is a mineral that consists of silver sulfide (Ag2S).
- It is commonly found in hydrothermal veins associated with silver deposits.
- Ruby Silver is an important ore of silver.
Horn Silver:
- Horn Silver, also known as silver chloride (AgCl), is a secondary mineral that forms in oxidized silver ore deposits.
- It is typically found as a powdery or granular material.
- Horn Silver is an important ore of silver.
Conclusion:
- German Silver and Quick Silver are not ores because they are not naturally occurring minerals.
- Ruby Silver and Horn Silver, on the other hand, are examples of ores as they are naturally occurring minerals that contain valuable amounts of silver.
Which of the following has lowest carbon content?- a)Cast iron
- b)Wrought Iron
- c)Stainless steel
- d)Chrome steel
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following has lowest carbon content?
a)
Cast iron
b)
Wrought Iron
c)
Stainless steel
d)
Chrome steel

|
Sanchita Iyer answered |
Wrought Iron has the lowest carbon content among the given options.
Wrought Iron:
Wrought iron is a form of iron that has very low carbon content, typically less than 0.08%. It is produced by refining pig iron and removing impurities like sulfur and excess carbon through a process called puddling. Wrought iron is known for its malleability, ductility, and resistance to corrosion. It is often used in decorative applications, such as gates, fences, and railings.
Cast Iron:
Cast iron, on the other hand, has a higher carbon content compared to wrought iron. It typically contains around 2-4% carbon, which gives it its characteristic hardness and brittleness. Cast iron is produced by melting iron and adding carbon-rich materials, such as coke or charcoal, to the molten metal. It is commonly used in applications where strength and wear resistance are important, such as engine blocks, pipes, and cookware.
Stainless Steel:
Stainless steel is an alloy that contains iron, chromium, and other elements. It has a minimum of 10.5% chromium content, which helps to form a protective layer of chromium oxide on the surface, making it resistant to corrosion. The carbon content in stainless steel can vary depending on the type and grade, but it is typically less than 1%. Stainless steel is widely used in various industries, including construction, automotive, and food processing, due to its strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
Chrome Steel:
Chrome steel, also known as chrome alloy or chrome-moly steel, is a type of steel that contains chromium and molybdenum as alloying elements. It has excellent strength, hardness, and high-temperature resistance. The carbon content in chrome steel is usually higher than stainless steel but lower than cast iron. It is commonly used in applications that require high strength, such as automotive components, power generation equipment, and industrial machinery.
In conclusion, wrought iron has the lowest carbon content among the given options. It is known for its low carbon content, malleability, and resistance to corrosion.
Wrought Iron:
Wrought iron is a form of iron that has very low carbon content, typically less than 0.08%. It is produced by refining pig iron and removing impurities like sulfur and excess carbon through a process called puddling. Wrought iron is known for its malleability, ductility, and resistance to corrosion. It is often used in decorative applications, such as gates, fences, and railings.
Cast Iron:
Cast iron, on the other hand, has a higher carbon content compared to wrought iron. It typically contains around 2-4% carbon, which gives it its characteristic hardness and brittleness. Cast iron is produced by melting iron and adding carbon-rich materials, such as coke or charcoal, to the molten metal. It is commonly used in applications where strength and wear resistance are important, such as engine blocks, pipes, and cookware.
Stainless Steel:
Stainless steel is an alloy that contains iron, chromium, and other elements. It has a minimum of 10.5% chromium content, which helps to form a protective layer of chromium oxide on the surface, making it resistant to corrosion. The carbon content in stainless steel can vary depending on the type and grade, but it is typically less than 1%. Stainless steel is widely used in various industries, including construction, automotive, and food processing, due to its strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
Chrome Steel:
Chrome steel, also known as chrome alloy or chrome-moly steel, is a type of steel that contains chromium and molybdenum as alloying elements. It has excellent strength, hardness, and high-temperature resistance. The carbon content in chrome steel is usually higher than stainless steel but lower than cast iron. It is commonly used in applications that require high strength, such as automotive components, power generation equipment, and industrial machinery.
In conclusion, wrought iron has the lowest carbon content among the given options. It is known for its low carbon content, malleability, and resistance to corrosion.
One or More than One Options Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. Which one of the following reactions, take place during the extraction of iron?- a)FeO + SiO2 → FeSiO3
- b)Fe2O3 + 3O2 → 2Fe + 3CO
- c)FeO + CO → Fe + CO2
- d)CO2 + C → 2CO
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Which one of the following reactions, take place during the extraction of iron?
a)
FeO + SiO2 → FeSiO3
b)
Fe2O3 + 3O2 → 2Fe + 3CO
c)
FeO + CO → Fe + CO2
d)
CO2 + C → 2CO
|
|
Ritika Sengupta answered |
B)Fe2O3 CO
c)FeO CO
d)Fe3O4 CO
c)FeO CO
d)Fe3O4 CO
One Integer Value Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 20-24) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result is an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. The percentage of copper in duralumin is
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 20-24) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result is an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
The percentage of copper in duralumin is

|
Sankar Chakraborty answered |
Duralumin is an alloy having Al (95%), Cu(4%) and Mg (1%).
Gravity method of ore concentration depends on- a)Preferential wetting properties of particles
- b)Difference in the the specific gravity of ore and gangue particles
- c)Fusion temperature of gangue and ore particles
- d)Magnetic properties of gangue and ore particles
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Gravity method of ore concentration depends on
a)
Preferential wetting properties of particles
b)
Difference in the the specific gravity of ore and gangue particles
c)
Fusion temperature of gangue and ore particles
d)
Magnetic properties of gangue and ore particles

|
Amrutha Pillai answered |
The mineral particle becom es wet by oils while the gangue particles by water. A rotating paddle agitates the mixtures and draws air in it. As a result froth is formed which carrier the mineral particles. The froth is light and is skimmed of. If is then dried for recovery of the ore particles.
Number of ores concentrated by Levigation (hydraulic washing) among pitche blende, tinstone, chromite, galena, copper pyrites, argentite.
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of ores concentrated by Levigation (hydraulic washing) among pitche blende, tinstone, chromite, galena, copper pyrites, argentite.

|
Amrutha Pillai answered |
Pitche blende, tinstone, chromite are purified by levigation.
In sulphatizing roasting of ZnS products are- a)ZnO + SO2
- b)ZnO + ZnSO4 + SO2
- c)ZnCI2
- d)Zn + SO2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In sulphatizing roasting of ZnS products are
a)
ZnO + SO2
b)
ZnO + ZnSO4 + SO2
c)
ZnCI2
d)
Zn + SO2

|
Ashish Nambiar answered |
Due to incomplete roasting ZnSO4 is formed.
Number of oxide ores among Galena, Pyrolusite, Rutile, Cinnabar, Cassiterite, Haematite, Sphalerite, Salt petre, Cuprite
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of oxide ores among Galena, Pyrolusite, Rutile, Cinnabar, Cassiterite, Haematite, Sphalerite, Salt petre, Cuprite
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The oxide ores are pyrolusite, rutile, cassiterite, haematite and cuprite.
According to Ellingham diagrams the oxidation reaction of carbon and carbon monoxide may be used to reduce which one of the following oxides at the lowest temperature?- a)Al2O3
- b)ZnO
- c)MgO
- d)Cu2O
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Ellingham diagrams the oxidation reaction of carbon and carbon monoxide may be used to reduce which one of the following oxides at the lowest temperature?
a)
Al2O3
b)
ZnO
c)
MgO
d)
Cu2O

|
Pooja Pillai answered |
Because ΔG° for reductions of rest three oxides [Al2O3, ZnO and MgO] are less negative than that of Cu2O at lower temperature.
In the extraction of copper, the metal formed in the Bessemers convertor is due to the reaction- a)Cu2S → 2Cu + S
- b)2Cu2O → 4Cu + O2
- c)2Cu2S + 3O2 → 2Cu2O + 2SO2
- d)2Cu2O + Cu2S → 6Cu + SO2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the extraction of copper, the metal formed in the Bessemers convertor is due to the reaction
a)
Cu2S → 2Cu + S
b)
2Cu2O → 4Cu + O2
c)
2Cu2S + 3O2 → 2Cu2O + 2SO2
d)
2Cu2O + Cu2S → 6Cu + SO2

|
Anjana Sen answered |
Extraction of Copper
Copper is one of the most important metals used in various industries due to its excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. The extraction of copper from its ore involves several steps, including smelting and refining. One of the key processes in this extraction is the use of a Bessemer converter.
Bessemer Converter
The Bessemer converter is a type of furnace used in the extraction of copper and other metals. It is a large, cylindrical vessel made of steel, lined with a refractory material. The converter is equipped with a series of tuyeres (nozzles) through which air or oxygen is blown into the molten copper matte.
Reaction in Bessemer Converter
The reaction that takes place in the Bessemer converter is as follows:
2Cu2O + Cu2S → 6Cu + SO2
Let's break down this reaction and understand it step by step:
1. Cu2O and Cu2S are the main components of the copper matte, which is a mixture of copper oxide and copper sulfide.
2. When the copper matte is heated in the Bessemer converter, the following reactions occur:
a) Cu2O is reduced to copper (Cu) by the reaction:
2Cu2O → 4Cu + O2
b) Cu2S is also reduced to copper (Cu) by the reaction:
2Cu2S → 4Cu + S
3. Both the reactions mentioned above result in the formation of molten copper (Cu) in the converter.
4. The molten copper is then collected and further purified through processes like electrolysis to obtain pure copper metal.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the correct reaction in the Bessemer converter during the extraction of copper is 2Cu2O + Cu2S → 6Cu + SO2. This reaction involves the reduction of copper oxide (Cu2O) and copper sulfide (Cu2S) to copper metal (Cu) and the release of sulfur dioxide (SO2) gas. The molten copper obtained from this reaction is further processed to obtain pure copper.
Copper is one of the most important metals used in various industries due to its excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. The extraction of copper from its ore involves several steps, including smelting and refining. One of the key processes in this extraction is the use of a Bessemer converter.
Bessemer Converter
The Bessemer converter is a type of furnace used in the extraction of copper and other metals. It is a large, cylindrical vessel made of steel, lined with a refractory material. The converter is equipped with a series of tuyeres (nozzles) through which air or oxygen is blown into the molten copper matte.
Reaction in Bessemer Converter
The reaction that takes place in the Bessemer converter is as follows:
2Cu2O + Cu2S → 6Cu + SO2
Let's break down this reaction and understand it step by step:
1. Cu2O and Cu2S are the main components of the copper matte, which is a mixture of copper oxide and copper sulfide.
2. When the copper matte is heated in the Bessemer converter, the following reactions occur:
a) Cu2O is reduced to copper (Cu) by the reaction:
2Cu2O → 4Cu + O2
b) Cu2S is also reduced to copper (Cu) by the reaction:
2Cu2S → 4Cu + S
3. Both the reactions mentioned above result in the formation of molten copper (Cu) in the converter.
4. The molten copper is then collected and further purified through processes like electrolysis to obtain pure copper metal.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the correct reaction in the Bessemer converter during the extraction of copper is 2Cu2O + Cu2S → 6Cu + SO2. This reaction involves the reduction of copper oxide (Cu2O) and copper sulfide (Cu2S) to copper metal (Cu) and the release of sulfur dioxide (SO2) gas. The molten copper obtained from this reaction is further processed to obtain pure copper.
Number of unpaired electrons in the complex [Ag(CN)2]- are
Correct answer is '0'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of unpaired electrons in the complex [Ag(CN)2]- are
|
|
Rajesh Chauhan answered |
Number of unpaired electrons in the complex [Ag(CN)2]- are '0'
Explanation:
1. Coordination Complex:
A coordination complex consists of a central metal ion or atom surrounded by ligands, which are typically ions or molecules that donate electron pairs to the metal ion to form coordinate bonds.
2. Structure of [Ag(CN)2]-:
The complex [Ag(CN)2]- consists of a central silver ion (Ag+) surrounded by two cyanide ligands (CN-). The cyanide ligands act as monodentate ligands, meaning they donate one electron pair to the metal ion.
3. Ligand Field Theory:
In the context of coordination complexes, Ligand Field Theory is used to describe the splitting of d orbitals of the central metal ion in the presence of ligands. This splitting leads to the formation of energy levels known as d-orbitals.
4. Crystal Field Theory:
Crystal Field Theory is a simplified version of Ligand Field Theory that assumes point charges instead of molecular orbitals. According to Crystal Field Theory, the d-orbitals of the central metal ion are split into two sets of different energies: the lower energy set, or the t2g set (dxy, dxz, dyz), and the higher energy set, or the eg set (dx2-y2, dz2).
5. Electron Configuration of Ag+:
The electron configuration of Ag+ is [Kr] 4d10. Since Ag+ loses one electron to form the complex, the electron configuration of the central silver ion in [Ag(CN)2]- becomes [Kr] 4d9.
6. Hund's Rule:
Hund's Rule states that electrons occupy degenerate orbitals singly before pairing up. This means that in the presence of ligands, the electrons will first fill the lower energy t2g set before occupying the higher energy eg set.
7. Filling of d-orbitals in [Ag(CN)2]-:
In [Ag(CN)2]-, the 4d orbitals of the central silver ion are split into t2g and eg sets. Since Ag+ has 9 electrons in its 4d orbitals, they will occupy all three t2g orbitals singly before pairing up. Therefore, there are no unpaired electrons in the complex [Ag(CN)2]-.
Conclusion:
The complex [Ag(CN)2]- has '0' unpaired electrons.
Explanation:
1. Coordination Complex:
A coordination complex consists of a central metal ion or atom surrounded by ligands, which are typically ions or molecules that donate electron pairs to the metal ion to form coordinate bonds.
2. Structure of [Ag(CN)2]-:
The complex [Ag(CN)2]- consists of a central silver ion (Ag+) surrounded by two cyanide ligands (CN-). The cyanide ligands act as monodentate ligands, meaning they donate one electron pair to the metal ion.
3. Ligand Field Theory:
In the context of coordination complexes, Ligand Field Theory is used to describe the splitting of d orbitals of the central metal ion in the presence of ligands. This splitting leads to the formation of energy levels known as d-orbitals.
4. Crystal Field Theory:
Crystal Field Theory is a simplified version of Ligand Field Theory that assumes point charges instead of molecular orbitals. According to Crystal Field Theory, the d-orbitals of the central metal ion are split into two sets of different energies: the lower energy set, or the t2g set (dxy, dxz, dyz), and the higher energy set, or the eg set (dx2-y2, dz2).
5. Electron Configuration of Ag+:
The electron configuration of Ag+ is [Kr] 4d10. Since Ag+ loses one electron to form the complex, the electron configuration of the central silver ion in [Ag(CN)2]- becomes [Kr] 4d9.
6. Hund's Rule:
Hund's Rule states that electrons occupy degenerate orbitals singly before pairing up. This means that in the presence of ligands, the electrons will first fill the lower energy t2g set before occupying the higher energy eg set.
7. Filling of d-orbitals in [Ag(CN)2]-:
In [Ag(CN)2]-, the 4d orbitals of the central silver ion are split into t2g and eg sets. Since Ag+ has 9 electrons in its 4d orbitals, they will occupy all three t2g orbitals singly before pairing up. Therefore, there are no unpaired electrons in the complex [Ag(CN)2]-.
Conclusion:
The complex [Ag(CN)2]- has '0' unpaired electrons.
One Integer Value Correct TypeThis section contains 5 questions, when worked out will result in an integer value from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. The number of ores concentrated by froth floatation process among cassiterite, galena, zinc blende, chromite, haematite, copper iron pyrites
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
One Integer Value Correct Type
This section contains 5 questions, when worked out will result in an integer value from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
The number of ores concentrated by froth floatation process among cassiterite, galena, zinc blende, chromite, haematite, copper iron pyrites

|
Anuj Iyer answered |
Galena, zinc blende and copper iron pyrites are concentrated by froth floatation method.
The number of ores concentrated by leaching or wet process among calamine, tinstone, bauxite, argentite, horn silver, galena, cinnabar, native gold
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of ores concentrated by leaching or wet process among calamine, tinstone, bauxite, argentite, horn silver, galena, cinnabar, native gold
|
|
Rutuja Mehta answered |
Leaching or Wet Process
Leaching or wet process is a method of extracting metals from their ores by using chemicals such as acid or alkali. This process is used when the ore is soluble in a particular chemical and can be easily separated from the impurities.
Ores Concentrated by Leaching or Wet Process
The following ores are concentrated by leaching or wet process:
1. Bauxite - It is an ore of aluminium and is concentrated by leaching with a solution of sodium hydroxide.
2. Argentite - It is an ore of silver and is concentrated by leaching with a solution of sodium cyanide.
3. Cinnabar - It is an ore of mercury and is concentrated by leaching with a solution of sodium hydroxide.
4. Native Gold - It is an ore of gold and is concentrated by leaching with a solution of cyanide.
The Correct Answer
Out of the given options, four ores are concentrated by leaching or wet process. These are:
1. Bauxite
2. Argentite
3. Cinnabar
4. Native Gold
Therefore, the correct answer is '4'.
Leaching or wet process is a method of extracting metals from their ores by using chemicals such as acid or alkali. This process is used when the ore is soluble in a particular chemical and can be easily separated from the impurities.
Ores Concentrated by Leaching or Wet Process
The following ores are concentrated by leaching or wet process:
1. Bauxite - It is an ore of aluminium and is concentrated by leaching with a solution of sodium hydroxide.
2. Argentite - It is an ore of silver and is concentrated by leaching with a solution of sodium cyanide.
3. Cinnabar - It is an ore of mercury and is concentrated by leaching with a solution of sodium hydroxide.
4. Native Gold - It is an ore of gold and is concentrated by leaching with a solution of cyanide.
The Correct Answer
Out of the given options, four ores are concentrated by leaching or wet process. These are:
1. Bauxite
2. Argentite
3. Cinnabar
4. Native Gold
Therefore, the correct answer is '4'.
In froth floatation process the particles of the ore come on the froth because- a)They become water repellent
- b)They are light
- c)They have lower molecular weight
- d)Impurities are more polar nature
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
In froth floatation process the particles of the ore come on the froth because
a)
They become water repellent
b)
They are light
c)
They have lower molecular weight
d)
Impurities are more polar nature
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
In froth floatation process, advantage is taken of prefferential wetting of ore particles by oil and gangue particles by water. ... Only sulphide ores are concentrated by froth flotation process because pine oil selectively wets the sulphide ore and hence brings it to the froth.
Sulphide ores of metals are usually concentrated by froth floatation process.Which one of the following sulphide ores offers an exception and is concentrated by leaching?- a)Sphalerite
- b)Argentite
- c)Galena
- d)Copper pyrites
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Sulphide ores of metals are usually concentrated by froth floatation process.Which one of the following sulphide ores offers an exception and is concentrated by leaching?
a)
Sphalerite
b)
Argentite
c)
Galena
d)
Copper pyrites

|
Ashwin Yadav answered |
Leaching This process consists in treating the powdered ore with a suitable reagent (such as acids, bases or other chemicals) which can selectively dissolves the ore but not the impuritier. It is used to extract silver metals.
Which is not a mineral of Al?- a)Spinel
- b)Feldspar
- c)Corundum
- d)Magnalium
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is not a mineral of Al?
a)
Spinel
b)
Feldspar
c)
Corundum
d)
Magnalium
|
|
Abhijeet Menon answered |
Explanation:
Introduction:
In this question, we are asked to identify the mineral that does not belong to the group of minerals of Al. We are given four options: Spinel, Feldspar, Corundum, and Magnalium. We need to determine which mineral is not related to Al.
Explanation:
To answer this question, we need to analyze each option and understand whether it is a mineral of Al or not.
Spinel:
Spinel is a mineral composed of magnesium, aluminum, and oxygen. Its chemical formula is (Mg,Al)₂O₄. As it contains aluminum, Spinel is considered a mineral of Al.
Feldspar:
Feldspar is a group of rock-forming minerals that are composed of aluminum, silicon, and oxygen. They are the most abundant minerals in the Earth's crust. Feldspar is also a mineral of Al.
Corundum:
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminum oxide. Its chemical formula is Al₂O₃. Corundum is considered a mineral of Al.
Magnalium:
Magnalium is an alloy composed of aluminum and magnesium. It is not a mineral but a man-made material. Therefore, Magnalium is not a mineral of Al.
Conclusion:
Based on the analysis above, we can determine that the mineral which does not belong to the group of minerals of Al is Magnalium. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A, B', as both Spinel and Feldspar are minerals of Al.
Introduction:
In this question, we are asked to identify the mineral that does not belong to the group of minerals of Al. We are given four options: Spinel, Feldspar, Corundum, and Magnalium. We need to determine which mineral is not related to Al.
Explanation:
To answer this question, we need to analyze each option and understand whether it is a mineral of Al or not.
Spinel:
Spinel is a mineral composed of magnesium, aluminum, and oxygen. Its chemical formula is (Mg,Al)₂O₄. As it contains aluminum, Spinel is considered a mineral of Al.
Feldspar:
Feldspar is a group of rock-forming minerals that are composed of aluminum, silicon, and oxygen. They are the most abundant minerals in the Earth's crust. Feldspar is also a mineral of Al.
Corundum:
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminum oxide. Its chemical formula is Al₂O₃. Corundum is considered a mineral of Al.
Magnalium:
Magnalium is an alloy composed of aluminum and magnesium. It is not a mineral but a man-made material. Therefore, Magnalium is not a mineral of Al.
Conclusion:
Based on the analysis above, we can determine that the mineral which does not belong to the group of minerals of Al is Magnalium. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A, B', as both Spinel and Feldspar are minerals of Al.
The number of silver containing compounds among Nessler’s reagent, Tollen’s reagent, Baeyer’s reagent, Corrosive sublimate, Horn silver, Ruby silver, Calomel.
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of silver containing compounds among Nessler’s reagent, Tollen’s reagent, Baeyer’s reagent, Corrosive sublimate, Horn silver, Ruby silver, Calomel.

|
Aditya Sen answered |
Nessler’s reagent (K2[HgI4]), Tollen's reagent [Ag(NH3)2]+ , Baeyer's reagent AIk. KMnO4, Corrosive sublimate (HgCI2), Horn silver (AgCI), Ruby silver (3Ag2SSb2S3), Calomel (Hg2CI2).
Only One Option Correct TypeDirection : This section contains 9 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Ellingham diagram represents a graph of - a)ΔG vsT
- b)ΔG° vs T
- c)ΔS° vs T
- d)ΔG vs P
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction : This section contains 9 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Ellingham diagram represents a graph of
a)
ΔG vsT
b)
ΔG° vs T
c)
ΔS° vs T
d)
ΔG vs P

|
Srestha Choudhury answered |
Eilingham diagram represents a graph of ΔG° vs T.
One Integer Value Correct TypeDirection (Q, Nos. 20-24) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. Gibbsite formula is Al2O3 . xH2O. Here, value of x is
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q, Nos. 20-24) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
Gibbsite formula is Al2O3 . xH2O. Here, value of x is

|
Pranjal Pillai answered |
Gibbsite is AI2O3.3H2O.
In the extraction of iron from haematite in blast furnace reducing agent- a)At low temperature CO is effective
- b)At high temperature carbon is more effective
- c)Both carbon and CO are effective at any temperature
- d)Carbon is effective at low temperature and CO at high temperature
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the extraction of iron from haematite in blast furnace reducing agent
a)
At low temperature CO is effective
b)
At high temperature carbon is more effective
c)
Both carbon and CO are effective at any temperature
d)
Carbon is effective at low temperature and CO at high temperature
|
|
Geetika Tiwari answered |
The correct answer is option
Carbon monoxide is the actual reducing agent of haematite in blast furnace.
Carbon monoxide is the actual reducing agent of haematite in blast furnace.
C + O2 → CO2↑
CO2 + C → 2CO↑
Fe2O3 + CO → 2FeO + CO2↑
FeO + CO → Fe + CO2↑
CO2 + C → 2CO↑
Fe2O3 + CO → 2FeO + CO2↑
FeO + CO → Fe + CO2↑
Cu2+ + Fe → Cu + Fe2+ for this reaction to calculate ΔG° the formula ΔG° = - nFE° is used. Here, value of n is
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
Cu2+ + Fe → Cu + Fe2+ for this reaction to calculate ΔG° the formula ΔG° = - nFE° is used. Here, value of n is

|
Keerthana Mehta answered |
ΔG°= -nFE°, n = number of electrons involved
Chapter doubts & questions for General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
353 videos|587 docs|309 tests
|
Related JEE Content
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup