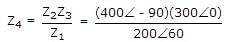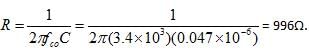All questions of Basic Electrical Components for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam
Where voltage division problem arises- a)Series connected resistors
- b)Parallel connected resistors
- c)When resistors are equal
- d)Both series and parallel resistors
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Where voltage division problem arises
a)
Series connected resistors
b)
Parallel connected resistors
c)
When resistors are equal
d)
Both series and parallel resistors
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
In series, voltage is the difference and current same.
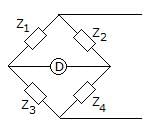
In a Wheatstone bridge, which of the following is used as a null detector?- a)Ammeter
- b)Galvanometer
- c)Voltmeter
- d)Wattmeter
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a Wheatstone bridge, which of the following is used as a null detector?
a)
Ammeter
b)
Galvanometer
c)
Voltmeter
d)
Wattmeter
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
Null detector is used to indicate zero current flow, and the device used is a galvanometer.
The expression for the capacitance (C in pF) of a parallel plate capacitor is given by:C = 6.94 × 10– 3 (d2/S). The diameter (d) of each plate is 20 mm and the spacing between the plates(S) is 0.25 mm. The displacement sensitivity of the capacitor is approximate:- a)44.4 pF/mm
- b)– 44.4 pF/mm
- c)11.1 pF/mm
- d)– 11.1 pF/mm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The expression for the capacitance (C in pF) of a parallel plate capacitor is given by:
C = 6.94 × 10– 3 (d2/S). The diameter (d) of each plate is 20 mm and the spacing between the plates
(S) is 0.25 mm. The displacement sensitivity of the capacitor is approximate:
a)
44.4 pF/mm
b)
– 44.4 pF/mm
c)
11.1 pF/mm
d)
– 11.1 pF/mm
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
C = 6.94 x 10- 3 (d2/S) PF
Displacement sensitivity = dC/dS = -6.94 x 10 - 3 x 20 2 / (0.25)2 = - 44.4 pF/mm
In the simplest form, an AC bridge consists of ____________.- a)arms, source, and a detector
- b)arms and source
- c)source and detector
- d)arms and detector
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the simplest form, an AC bridge consists of ____________.
a)
arms, source, and a detector
b)
arms and source
c)
source and detector
d)
arms and detector
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
In its simplest form, an AC bridge consists of four arms, a source for excitation, and a null detector. The source is connected across a pair of arms while the detector is connected to the team of opposite arms.
Find the application of area where all-pass filters are used?- a)Cathode ray oscilloscope
- b)Television
- c)Telephone wire
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the application of area where all-pass filters are used?
a)
Cathode ray oscilloscope
b)
Television
c)
Telephone wire
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
When signals are transmitted in transmission lines like telephone wire, they undergo change in phase, all-pass filters are used to compensate these phase changes.
A practical voltage source can also be represented as ___________.- a)a resistance in series with an ideal current source
- b)a resistance in series with an ideal voltage source
- c)a resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage source
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A practical voltage source can also be represented as ___________.
a)
a resistance in series with an ideal current source
b)
a resistance in series with an ideal voltage source
c)
a resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage source
d)
none of the mentioned
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
A practical voltage source could be represented with a resistor in series with an ideal voltage source.
Telephone companies make use of the Wheatstone bridge for _________.- a)measuring the telephone resistance
- b)computing the line strength
- c)maintaining Dialtone
- d)locating the cable faults
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Telephone companies make use of the Wheatstone bridge for _________.
a)
measuring the telephone resistance
b)
computing the line strength
c)
maintaining Dialtone
d)
locating the cable faults
|
|
Sinjini Reddy answered |
Explanation:
Wheatstone Bridge:
- The Wheatstone bridge is a circuit used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing two legs of a bridge circuit.
- It consists of four resistors, a voltage source, and a galvanometer.
Locating Cable Faults:
- Telephone companies use the Wheatstone bridge to locate faults in cables.
- When a fault occurs in a cable, it creates an imbalance in the resistance values in the circuit.
- By using the Wheatstone bridge, technicians can determine the exact location of the fault by measuring the resistance values on either side of the fault.
Working Principle:
- The Wheatstone bridge works on the principle of null detection, where the galvanometer reads zero when the bridge is balanced.
- If there is a fault in the cable, the resistance values change, causing the galvanometer to deflect from zero.
- By adjusting the known resistances in the bridge circuit, technicians can bring the bridge back into balance, indicating the location of the fault.
Benefits:
- Using the Wheatstone bridge for locating cable faults is a precise and efficient method.
- It helps in quickly identifying the exact location of the fault without the need for extensive manual testing.
- This method saves time and resources for telephone companies in maintaining and repairing their communication networks.
Wheatstone Bridge:
- The Wheatstone bridge is a circuit used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing two legs of a bridge circuit.
- It consists of four resistors, a voltage source, and a galvanometer.
Locating Cable Faults:
- Telephone companies use the Wheatstone bridge to locate faults in cables.
- When a fault occurs in a cable, it creates an imbalance in the resistance values in the circuit.
- By using the Wheatstone bridge, technicians can determine the exact location of the fault by measuring the resistance values on either side of the fault.
Working Principle:
- The Wheatstone bridge works on the principle of null detection, where the galvanometer reads zero when the bridge is balanced.
- If there is a fault in the cable, the resistance values change, causing the galvanometer to deflect from zero.
- By adjusting the known resistances in the bridge circuit, technicians can bring the bridge back into balance, indicating the location of the fault.
Benefits:
- Using the Wheatstone bridge for locating cable faults is a precise and efficient method.
- It helps in quickly identifying the exact location of the fault without the need for extensive manual testing.
- This method saves time and resources for telephone companies in maintaining and repairing their communication networks.
By using the variations on a Wheatstone bridge we can _________.- a)measure quantities such as voltage, current, and power
- b)measure high resistance values
- c)measure quantities such as complex power
- d)measure quantities such as capacitance, inductance, and impedance
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
By using the variations on a Wheatstone bridge we can _________.
a)
measure quantities such as voltage, current, and power
b)
measure high resistance values
c)
measure quantities such as complex power
d)
measure quantities such as capacitance, inductance, and impedance
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
In its simplest form, a Whetstone bridge consists of resistive arms. A Wheatstone bridge is used to measure quantities such as capacitance, inductance, and impedance by using the variations.
Maxwell’s inductance-capacitance bridge is used for measurement of inductance of :- a)Low Q coils
- b)Medium Q coils
- c)High Q coils
- d)Low and medium Q coils
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Maxwell’s inductance-capacitance bridge is used for measurement of inductance of :
a)
Low Q coils
b)
Medium Q coils
c)
High Q coils
d)
Low and medium Q coils
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
A Maxwell bridge is a modification to a Wheatstone bridge used to measure an unknown inductance (usually of low Q value) in terms of calibrated resistance and inductance or resistance and capacitance. When the calibrated components are a parallel resistor and capacitor, the bridge is known as a Maxwell-Wien bridge.
Voltage source and terminal voltage can be related as ___________.- a)terminal voltage is higher than the source emf
- b)terminal voltage is equal to the source emf
- c)terminal voltage is always lower than source emf
- d)terminal voltage cannot exceed source emf
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Voltage source and terminal voltage can be related as ___________.
a)
terminal voltage is higher than the source emf
b)
terminal voltage is equal to the source emf
c)
terminal voltage is always lower than source emf
d)
terminal voltage cannot exceed source emf
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
A practical voltage source can be represented with a resistance in series with the source. Hence, some voltage drop at the resistor, and the terminal voltage is always lower than the source emf.
Notch filters and band reject filters are the same.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Notch filters and band reject filters are the same.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Notch filters are also referred to as bandstop or band reject filters. Band-reject filters are used to greatly attenuate a narrow range of frequencies around a center point. Notch filters accomplish the same purpose, but for a single frequency.
Frequency can be measured by using:- a)Maxwell’s bridge
- b)Schering bridge
- c)Heavyside Campbell bridge
- d)Wien’s bridge
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Frequency can be measured by using:
a)
Maxwell’s bridge
b)
Schering bridge
c)
Heavyside Campbell bridge
d)
Wien’s bridge
|
|
Aryan Unni answered |
Measuring Frequency using Wien's Bridge
Wien's bridge is a type of AC bridge circuit used to measure the frequency of an unknown alternating current signal. It consists of four resistors, a capacitor, and a variable resistor. The bridge is balanced when the frequency of the unknown signal is equal to the frequency of the reference signal.
Steps involved in measuring frequency using Wien's bridge:
1. Setting up the circuit: The Wien bridge circuit is set up with the unknown signal source connected to one arm of the bridge and the reference signal source connected to the opposite arm. The remaining two arms are filled with resistors.
2. Adjusting the variable resistor: The variable resistor is adjusted until the bridge is balanced, which is indicated by a null detector. At this point, the frequency of the unknown signal is equal to the frequency of the reference signal.
3. Calculating the frequency: The frequency of the unknown signal can be calculated using the following formula:
f = 1 / (2πRC)
Where f is the frequency of the unknown signal, R is the resistance in the arms of the bridge, and C is the capacitance of the capacitor in the bridge.
Advantages of using Wien's bridge to measure frequency:
- The circuit is simple and easy to set up.
- The frequency range can be adjusted by changing the value of the capacitor.
- The accuracy of measurement is high.
Disadvantages of using Wien's bridge to measure frequency:
- The bridge may become unbalanced due to changes in temperature or other environmental factors.
- The circuit may not work well with low-frequency signals.
Wien's bridge is a type of AC bridge circuit used to measure the frequency of an unknown alternating current signal. It consists of four resistors, a capacitor, and a variable resistor. The bridge is balanced when the frequency of the unknown signal is equal to the frequency of the reference signal.
Steps involved in measuring frequency using Wien's bridge:
1. Setting up the circuit: The Wien bridge circuit is set up with the unknown signal source connected to one arm of the bridge and the reference signal source connected to the opposite arm. The remaining two arms are filled with resistors.
2. Adjusting the variable resistor: The variable resistor is adjusted until the bridge is balanced, which is indicated by a null detector. At this point, the frequency of the unknown signal is equal to the frequency of the reference signal.
3. Calculating the frequency: The frequency of the unknown signal can be calculated using the following formula:
f = 1 / (2πRC)
Where f is the frequency of the unknown signal, R is the resistance in the arms of the bridge, and C is the capacitance of the capacitor in the bridge.
Advantages of using Wien's bridge to measure frequency:
- The circuit is simple and easy to set up.
- The frequency range can be adjusted by changing the value of the capacitor.
- The accuracy of measurement is high.
Disadvantages of using Wien's bridge to measure frequency:
- The bridge may become unbalanced due to changes in temperature or other environmental factors.
- The circuit may not work well with low-frequency signals.
Name the filter that has two stop bands?- a)Band-pass filter
- b)Low pass filter
- c)High pass filter
- d)Band-reject filter
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Name the filter that has two stop bands?
a)
Band-pass filter
b)
Low pass filter
c)
High pass filter
d)
Band-reject filter
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
A band-pass filter has two stop bands: 1) 0 < f="" />< />L and 2) f > fH.
The main advantage of Owen’s bridge for measurement of unknown inductance is that- a)it has two independent elements, R and C, for achieving balance
- b)it can be used for the measurement of very high Q coils
- c)it is very inexpensive
- d)it can be used for measurement of unknown capacitance as well
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The main advantage of Owen’s bridge for measurement of unknown inductance is that
a)
it has two independent elements, R and C, for achieving balance
b)
it can be used for the measurement of very high Q coils
c)
it is very inexpensive
d)
it can be used for measurement of unknown capacitance as well
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
The advantages of the Owens bridge are, the unknown inductance measured is independent of frequency and doesn't require any frequency supply. The balance equation can be obtained very quickly and simply. It is used to measure a wide range of inductance in capacitance.
The arm consisting of the standard known resistance R3 is known as __________.- a)standard arm
- b)resistance arm
- c)accurate arm
- d)known arm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The arm consisting of the standard known resistance R3 is known as __________.
a)
standard arm
b)
resistance arm
c)
accurate arm
d)
known arm
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
The arm consisting of the standard known resistance R3 is known as the legal arm. Using this resistance value, the unknown resistance can be determined using the balance condition.
In a certain parallel resonant band-pass filter, the resonant frequency is 14 kHz. If the bandwidth is 4 kHz, the lower frequency is- a)6 kHz
- b)16 kHz
- c)12 kHz
- d)Cannot be determined
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a certain parallel resonant band-pass filter, the resonant frequency is 14 kHz. If the bandwidth is 4 kHz, the lower frequency is
a)
6 kHz
b)
16 kHz
c)
12 kHz
d)
Cannot be determined
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
Given that resonance frequency is 14kHz and the bandwidth is 4kHz We know that bandwidth is equal to twice the frequency of signal
⇒ B = 2 × f
⇒4 = 2 × f
So the signal frequency f = 4 / 2 = 2
Therefore the higher frequency is 14 + 2 = 16kHz and the lower frequency is 14 − 2 = 12kHz.
D.C. bridges are used for _________.- a)measurement of resistance
- b)measurement of capacitance
- c)measurement of current
- d)measurement of inductance
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
D.C. bridges are used for _________.
a)
measurement of resistance
b)
measurement of capacitance
c)
measurement of current
d)
measurement of inductance
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
Resistance measurements are done using a suitable D.C. bridge.
What are filters created by using resistors and capacitors or inductors and capacitors called?- a)Active filters
- b)Passive filters
- c)Continuous filters
- d)Differential filters
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What are filters created by using resistors and capacitors or inductors and capacitors called?
a)
Active filters
b)
Passive filters
c)
Continuous filters
d)
Differential filters
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Simple filters created by using resistors and capacitors or inductors and capacitors are called passive filters because they use passive components that do not amplify. In communication work, many filters are of the passive LC variety, although many other types are used.
The arms consisting of the resistances R1 and R2 are called _________.- a)resistance arms
- b)impedance arms
- c)source arms
- d)ratio arms
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The arms consisting of the resistances R1 and R2 are called _________.
a)
resistance arms
b)
impedance arms
c)
source arms
d)
ratio arms
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
The arms consisting of the two resistances R1 and R2, are known as the resistance arms. Sources do not appear on the arms of the bridge, and they are connected across opposite ends. Wheatstone bridge is purely resistive.
What is the frequency range for a headphone as a detector?- a)20 Hz to 20 kHz
- b)10 kHz to 1 MHz
- c)10 MHz to 1 GHz
- d)250 Hz to 4 kHz
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the frequency range for a headphone as a detector?
a)
20 Hz to 20 kHz
b)
10 kHz to 1 MHz
c)
10 MHz to 1 GHz
d)
250 Hz to 4 kHz
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Headphones can be used as detectors in AC bridges in the low audio frequency range. The common audio frequency range varies from 250 Hz to 4 kHz.
If the gain at center frequency is 10, find the quality factor of narrow band-pass filter- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the gain at center frequency is 10, find the quality factor of narrow band-pass filter
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
The gain of the narrow band-pass filter must satisfy the condition,
AF = 2 × Q2
When Q = 3,
=> 2 × Q2 = 2×(32) = 18.
=> 10 < />
Hence condition is satisfied when Q = 3.
A narrow band-reject filter is commonly called as- a)Notch filter
- b)Band step filter
- c)Delay filter
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A narrow band-reject filter is commonly called as
a)
Notch filter
b)
Band step filter
c)
Delay filter
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
A narrow band-reject filter is also called as notch filter because of its higher quality factor, Q (>10).
Resistance R4 is known as ________.- a)standard resistance
- b)unknown resistance to be measured
- c)resistance arm
- d)input resistance
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Resistance R4 is known as ________.
a)
standard resistance
b)
unknown resistance to be measured
c)
resistance arm
d)
input resistance
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
R4 is the unknown resistance whose value has to be found by comparison with a standard. R3 is known as the standard resistance. The resistance arm comprises four resistances, including R1, R2, R3, and R4.
The attenuation rate is also called?- a)Roll off
- b)Roll in
- c)Envelope delay
- d)Ripple
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The attenuation rate is also called?
a)
Roll off
b)
Roll in
c)
Envelope delay
d)
Ripple
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
Roll off is also called the attenuation rate, roll-off is the rate of change of amplitude with frequency in a filter. The faster the roll-off, or the higher the attenuation rate, the more selective the filter is, i.e., the better able it is to differentiate between two closely spaced signals, one desired and the other not.
At high frequency, source consists of ________.- a)amplifiers
- b)regulators
- c)oscillators
- d)op amps
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
At high frequency, source consists of ________.
a)
amplifiers
b)
regulators
c)
oscillators
d)
op amps
|
|
Pranab Das answered |
At high frequency, source consists of oscillators.
1. Oscillators:
At high frequencies, sources typically consist of oscillators. Oscillators are electronic circuits that generate continuous wave signals without any input. These circuits are designed to produce alternating current signals at a specific frequency. In high-frequency applications, oscillators are crucial for generating precise and stable signals for various electronic systems.
2. Importance of Oscillators:
- In high-frequency communication systems, oscillators are used to generate carrier waves for transmitting information.
- Oscillators are also used in radar systems, electronic test equipment, and other applications where stable and precise frequency signals are required.
- These circuits play a vital role in clock generation for digital systems, ensuring synchronization and timing accuracy.
3. Characteristics of Oscillators:
- Oscillators produce periodic waveforms at a specific frequency.
- They maintain oscillation by providing the required feedback to sustain the signal generation.
- Oscillators can be designed using various circuit configurations such as LC tank circuits, crystal oscillators, and voltage-controlled oscillators.
In conclusion, at high frequencies, sources primarily consist of oscillators due to their ability to generate stable and precise signals required for a wide range of electronic applications.
1. Oscillators:
At high frequencies, sources typically consist of oscillators. Oscillators are electronic circuits that generate continuous wave signals without any input. These circuits are designed to produce alternating current signals at a specific frequency. In high-frequency applications, oscillators are crucial for generating precise and stable signals for various electronic systems.
2. Importance of Oscillators:
- In high-frequency communication systems, oscillators are used to generate carrier waves for transmitting information.
- Oscillators are also used in radar systems, electronic test equipment, and other applications where stable and precise frequency signals are required.
- These circuits play a vital role in clock generation for digital systems, ensuring synchronization and timing accuracy.
3. Characteristics of Oscillators:
- Oscillators produce periodic waveforms at a specific frequency.
- They maintain oscillation by providing the required feedback to sustain the signal generation.
- Oscillators can be designed using various circuit configurations such as LC tank circuits, crystal oscillators, and voltage-controlled oscillators.
In conclusion, at high frequencies, sources primarily consist of oscillators due to their ability to generate stable and precise signals required for a wide range of electronic applications.
Commonly used balance detectors for AC bridges are headphones, tuned amplifiers, and vibration galvanometers.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Commonly used balance detectors for AC bridges are headphones, tuned amplifiers, and vibration galvanometers.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Headphones, tuned amplifier circuits and vibration galvanometers are used for detecting the balance condition in AC bridges.
What is a filter?- a)Frequency selective circuit
- b)Amplitude selective circuit
- c)Frequency damping circuit
- d)Amplitude damping circuit
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is a filter?
a)
Frequency selective circuit
b)
Amplitude selective circuit
c)
Frequency damping circuit
d)
Amplitude damping circuit
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
A filter is a frequency-selective circuit. Filters are designed to pass some frequencies and reject others. Filters are used to reduce noise and increase selectivity.
In D’Sauty’s bridge (unmodified form), it is :- a)Possible to obtain balance even if both the capacitors are imperfect
- b)Possible to obtain balance if one of the capacitors is perfect
- c)Possible to obtain balance only if both the capacitors are perfect
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In D’Sauty’s bridge (unmodified form), it is :
a)
Possible to obtain balance even if both the capacitors are imperfect
b)
Possible to obtain balance if one of the capacitors is perfect
c)
Possible to obtain balance only if both the capacitors are perfect
d)
All the above
|
|
Ujwal Ghoshal answered |
D’Sauty’s bridge is a type of bridge circuit used to measure the unknown value of capacitance. It consists of two identical capacitors (C1 and C2) in parallel, connected to a galvanometer and a variable resistor (R). The bridge is balanced when the galvanometer shows zero deflection, indicating that the unknown capacitance is equal to the known capacitance.
To understand why the correct answer is option 'C', let's examine the possible scenarios:
a) Possible to obtain balance even if both the capacitors are imperfect:
If both capacitors are imperfect, it means that their actual capacitance values are different from their nominal values. In this case, it is not possible to obtain balance because the bridge relies on the assumption that the capacitors are identical. Any difference in capacitance will result in an imbalance and a non-zero deflection on the galvanometer.
b) Possible to obtain balance if one of the capacitors is perfect:
If one of the capacitors is perfect, it means that its actual capacitance value is exactly equal to its nominal value. However, if the other capacitor is imperfect (i.e., its actual capacitance is different from its nominal value), the bridge will still be unbalanced. This is because the bridge requires both capacitors to be identical in order to achieve balance.
c) Possible to obtain balance only if both the capacitors are perfect:
This is the correct answer. In order to obtain balance in D’Sauty’s bridge, both capacitors must be perfect. This means that their actual capacitance values should exactly match their nominal values. When both capacitors are perfect, the bridge is balanced, and the galvanometer shows zero deflection.
d) All the above:
This option is not correct because it includes option 'a' and 'b', which have already been explained as incorrect. The correct answer is option 'C', as explained above.
In summary, D’Sauty’s bridge can only achieve balance if both capacitors are perfect, meaning their actual capacitance values match their nominal values. Any imperfection or difference in capacitance will result in an unbalanced bridge and a non-zero deflection on the galvanometer.
To understand why the correct answer is option 'C', let's examine the possible scenarios:
a) Possible to obtain balance even if both the capacitors are imperfect:
If both capacitors are imperfect, it means that their actual capacitance values are different from their nominal values. In this case, it is not possible to obtain balance because the bridge relies on the assumption that the capacitors are identical. Any difference in capacitance will result in an imbalance and a non-zero deflection on the galvanometer.
b) Possible to obtain balance if one of the capacitors is perfect:
If one of the capacitors is perfect, it means that its actual capacitance value is exactly equal to its nominal value. However, if the other capacitor is imperfect (i.e., its actual capacitance is different from its nominal value), the bridge will still be unbalanced. This is because the bridge requires both capacitors to be identical in order to achieve balance.
c) Possible to obtain balance only if both the capacitors are perfect:
This is the correct answer. In order to obtain balance in D’Sauty’s bridge, both capacitors must be perfect. This means that their actual capacitance values should exactly match their nominal values. When both capacitors are perfect, the bridge is balanced, and the galvanometer shows zero deflection.
d) All the above:
This option is not correct because it includes option 'a' and 'b', which have already been explained as incorrect. The correct answer is option 'C', as explained above.
In summary, D’Sauty’s bridge can only achieve balance if both capacitors are perfect, meaning their actual capacitance values match their nominal values. Any imperfection or difference in capacitance will result in an unbalanced bridge and a non-zero deflection on the galvanometer.
R1 = 1Ω, R2 = 3Ω, R3 = 5Ω and R4 = 7Ω connected in series. Total voltage = 20V, Current I, V2 =?- a)I = 1.23, V2 = 3.75
- b)I = 1.25, V2 = 3.75
- c)I = 1.15, V2 = 3.73
- d)I = 1.16, V2 = 3.72
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
R1 = 1Ω, R2 = 3Ω, R3 = 5Ω and R4 = 7Ω connected in series. Total voltage = 20V, Current I, V2 =?
a)
I = 1.23, V2 = 3.75
b)
I = 1.25, V2 = 3.75
c)
I = 1.15, V2 = 3.73
d)
I = 1.16, V2 = 3.72
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
I = 20 / 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 = 1.25A
V2 = V. R2 / R1 + R2 + R3 + R4
= 20(3) / 16
= 3.75V.
Compute the quality factor of the wide band-pass filter with high and low cut-off frequencies equal to 950Hz and 250Hz.- a)0.278
- b)0.348
- c)0.696
- d)0.994
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Compute the quality factor of the wide band-pass filter with high and low cut-off frequencies equal to 950Hz and 250Hz.
a)
0.278
b)
0.348
c)
0.696
d)
0.994
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
Quality factor Q = √(fh × fL) / (fh - fL) = √(950Hz × 250Hz) / (9950Hz - 250Hz) = 0.696.
Quality factor of the circuit is given by _________- a)Q = ωC1
- b)Q = ωR1
- c)Q = ω
- d)Q = ωR1C1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Quality factor of the circuit is given by _________
a)
Q = ωC1
b)
Q = ωR1
c)
Q = ω
d)
Q = ωR1C1
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
The relation gives the quality factor of a Maxwell inductance capacitance bridge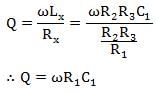
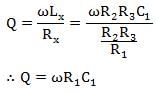
De Sauty’s bridge is used for the measurement of- a)high Q inductances
- b)low Q inductances
- c)lossless capacitors
- d)capacitors with dielectric losses
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
De Sauty’s bridge is used for the measurement of
a)
high Q inductances
b)
low Q inductances
c)
lossless capacitors
d)
capacitors with dielectric losses
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
This bridge provides us the most suitable method for comparing the two values of the capacitor if we neglect dielectric losses in the bridge circuit.
Wheatstone bridge is used to measure the d.c. resistance of various types of wires for _________.- a)determining their effective resistance
- b)computing the power dissipation
- c)quality control of wire
- d)maintaining a source of constant e.m.f
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Wheatstone bridge is used to measure the d.c. resistance of various types of wires for _________.
a)
determining their effective resistance
b)
computing the power dissipation
c)
quality control of wire
d)
maintaining a source of constant e.m.f
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
Wheatstone bridge is used to measure the d.c. resistance of various types of wires for controlling the quality of the cables. The voltage source maintains a constant e.m.f in the bridge circuit.
The advantage of narrow band-pass filter is- a)fc can be changed without changing gain
- b)fc can be changed without changing bandwidth
- c)fc can be changed without changing resistors
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The advantage of narrow band-pass filter is
a)
fc can be changed without changing gain
b)
fc can be changed without changing bandwidth
c)
fc can be changed without changing resistors
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
As the narrow band-pass filter has multiple filters. The center frequency can be changed to a new frequency without changing the gain or bandwidth and is accomplished by changing the resistor to a new value which is given as R’ = R × (fL / fc)2.
Wagner’s Earth devices are used in a.c bridge circuit for :- a)Eliminating the effect of earth capacitances
- b)Eliminating the effect of inter-component capacitances
- c)Eliminating the effect of stray electrostatic fields
- d)Shielding the bridge elements.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Wagner’s Earth devices are used in a.c bridge circuit for :
a)
Eliminating the effect of earth capacitances
b)
Eliminating the effect of inter-component capacitances
c)
Eliminating the effect of stray electrostatic fields
d)
Shielding the bridge elements.
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
The Wagner earthing device is used for removing the earth capacitance from the bridges. It is a type of voltage divider circuit used to reduce the error resulting from stray capacitance. The Wagner Earth device provides high accuracy to the bridge.
Accuracy in a bridge measurement depends on- a)Sensitivity of detector
- b)Applied voltage
- c)Both Sensitivity and applied voltage
- d)Accuracy of indicator
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Accuracy in a bridge measurement depends on
a)
Sensitivity of detector
b)
Applied voltage
c)
Both Sensitivity and applied voltage
d)
Accuracy of indicator
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
Both sensitivity of indicator and applied voltage affects the accuracy in bridge measurement.
The resistive elements in a strain gauge are each 5kΩ. A digital voltmeter with ranges of 10V, 1V, and 0.1V, and a resolution of 0.1% of FSD, is used to measure the output voltage. If R2 is the fixed element and R1 is the element measuring strain, what is the minimum change in R1 that can be detected? Assume a supply of 10V.- a)10 ohms
- b)20 ohms
- c)30 ohms
- d)40 ohms
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The resistive elements in a strain gauge are each 5kΩ. A digital voltmeter with ranges of 10V, 1V, and 0.1V, and a resolution of 0.1% of FSD, is used to measure the output voltage. If R2 is the fixed element and R1 is the element measuring strain, what is the minimum change in R1 that can be detected? Assume a supply of 10V.
a)
10 ohms
b)
20 ohms
c)
30 ohms
d)
40 ohms
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
To measure the output voltage ≈ 5V, the 10V range is required, giving a resolution or sensitivity of 10 mV.
VR = 5.01V = 5,000 × 10/(R1 + 5,000)V
5.01(R1 + 5,000) = 50,000
R1 = (50,000/5.01) − 5,000 = 4,980Ω
Resolution = 5,000 − 4,980 = 20Ω
A variable air gap type capacitor consists of two parallel plates: a fixed plate and a moving plate at a distance x. If a potential V is applied across the two plates, then the force of attraction between the plates is related to x as- a)F is directly proportional to x2
- b)F is inversely proportional to x2
- c)F is inversely proportional to x
- d)F is directly proportional to x
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A variable air gap type capacitor consists of two parallel plates: a fixed plate and a moving plate at a distance x. If a potential V is applied across the two plates, then the force of attraction between the plates is related to x as
a)
F is directly proportional to x2
b)
F is inversely proportional to x2
c)
F is inversely proportional to x
d)
F is directly proportional to x

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
E = ½ CV2. = ½ εA/x V2
F = -δE/δX = ½ εA/xx V2 which is inversely proportional to x2
A metal wire has a uniform cross-section A, length, and resistance R between its two endpoints. It is uniformly stretched so that its length becomes l. The new resistance is- a)αR
- b)α2 R
- c)√αR
- d)eα R
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A metal wire has a uniform cross-section A, length, and resistance R between its two endpoints. It is uniformly stretched so that its length becomes l. The new resistance is
a)
αR
b)
α2 R
c)
√αR
d)
eα R
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
Volume is constant
lA = l’A’
lA = α l A’
A’ = A/α
R’ = ρl'/A' = ρ αlα/A = α2 R
The quality factor of passive twin T-network is increased by using- a)Inverting amplifier
- b)Non-inverting amplifier
- c)Voltage follower
- d)Differential amplifier
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The quality factor of passive twin T-network is increased by using
a)
Inverting amplifier
b)
Non-inverting amplifier
c)
Voltage follower
d)
Differential amplifier
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
The passive twin T-network has a selectively low figure of merit. The Q of the network can be increased significantly, if it is used with the voltage follower.
Maxwell’s bridge can be used for measurement of inductance with- a)high Q factors
- b)very low Q factors
- c)medium Q factors
- d)wide range of Q factor variations
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Maxwell’s bridge can be used for measurement of inductance with
a)
high Q factors
b)
very low Q factors
c)
medium Q factors
d)
wide range of Q factor variations
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
A Maxwell Inductance Capacitance Bridge (known as a Maxwell Bridge) is a modified version of a Wheatstone bridge that is used to measure the self-inductance of a circuit. A Maxwell bridge uses the null deflection method (also known as the “bridge method”) to calculate an unknown inductance in a circuit.
In which filter the output and input voltages are equal in amplitude for all frequencies?- a)All-pass filter
- b)High pass filter
- c)Low pass filter
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In which filter the output and input voltages are equal in amplitude for all frequencies?
a)
All-pass filter
b)
High pass filter
c)
Low pass filter
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
In all-pass filter, the output and input voltages are equal in amplitude for all frequencies. This filter passes all frequencies equally well and with phase shift and between the two function of frequency.
In a first order high pass filter, frequencies higher than low cut-off frequencies are called- a)Stop band frequency
- b)Pass band frequency
- c)Centre band frequency
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a first order high pass filter, frequencies higher than low cut-off frequencies are called
a)
Stop band frequency
b)
Pass band frequency
c)
Centre band frequency
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
Low cut-off frequency, fL is 0.707 times the pass band gain voltage. Therefore, frequencies above fL are pass band frequencies.
The opposite two ends of a Wheatstone bridge consist of _________.- a)voltage and current source
- b)e.m.f and null detector
- c)resistance and capacitance
- d)inductance and impedance
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The opposite two ends of a Wheatstone bridge consist of _________.
a)
voltage and current source
b)
e.m.f and null detector
c)
resistance and capacitance
d)
inductance and impedance
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
The two opposite ends of a Wheatstone bridge circuit consisting of a source of e.m.f and a null detector. Four arms of a Wheatstone bridge consist of resistances. Inductance and capacitance do not appear in a Wheatstone bridge.
Wheatstone bridge is a __________.- a)a.c. bridge
- b)d.c. bridge
- c)high voltage bridge
- d)power dissipation bridge
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Wheatstone bridge is a __________.
a)
a.c. bridge
b)
d.c. bridge
c)
high voltage bridge
d)
power dissipation bridge
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
The Wheatstone bridge is a d.c. Bridge that is used for the measurement of medium resistance. Schering bridge is used for the measurement of high voltages. AC bridges comprise Anderson bridge, Maxwell Bridge, etc.
The use of a capacitor filter in a rectifier circuit- a)Load current is high
- b)Load current is low
- c)Load voltage is high
- d)Load voltage is low
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The use of a capacitor filter in a rectifier circuit
a)
Load current is high
b)
Load current is low
c)
Load voltage is high
d)
Load voltage is low
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
In power supplies, capacitors are used to smooth (filter) the pulsating DC output after rectification so that a nearly constant DC voltage is supplied to the load. The pulsating output of the rectifiers has an average DC value and an AC portion that is called ripple voltage.
Thermal compensation can be provided in a Wheatstone bridge by ________.- a)using more than one resistive sensor
- b)making use of a heat sink
- c)using cooling fans
- d)immersing the circuit into a liquid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Thermal compensation can be provided in a Wheatstone bridge by ________.
a)
using more than one resistive sensor
b)
making use of a heat sink
c)
using cooling fans
d)
immersing the circuit into a liquid
|
|
Madhavan Nair answered |
Thermal compensation in a Wheatstone bridge refers to the ability to compensate for temperature variations that can affect the accuracy of the bridge circuit. This compensation can be achieved by using more than one resistive sensor in the bridge configuration. Let's discuss this in detail below.
The Wheatstone bridge is a circuit arrangement commonly used for measuring resistance or strain. It consists of four resistive elements connected in a bridge configuration, with an excitation voltage applied across the two opposite nodes of the bridge. The output voltage from the bridge is then proportional to the imbalance between the resistive elements.
However, temperature changes can affect the resistance of the elements in the bridge and introduce errors in the measurement. For example, if the temperature increases, the resistive elements may expand, leading to an increase in their resistance values. This change in resistance can result in an unbalanced bridge and inaccurate measurements.
To compensate for these temperature variations, multiple resistive sensors can be used in the Wheatstone bridge. By having more than one sensor, it becomes possible to measure the temperature at different points and adjust the bridge accordingly. This allows for the cancellation of temperature-induced errors by applying appropriate correction techniques.
The use of multiple resistive sensors provides the ability to measure both the desired quantity (e.g., strain) and the temperature at different locations. By simultaneously measuring the temperature, it becomes possible to determine the effect of temperature on the resistance values and compensate for it.
The compensation technique can involve various methods, such as using a reference temperature or employing temperature-dependent resistors. These methods help in adjusting the bridge output based on the temperature measurements, ensuring accurate measurements even in varying thermal conditions.
In summary, by using more than one resistive sensor in a Wheatstone bridge, thermal compensation can be achieved. This compensation allows for the measurement of temperature variations and adjustment of the bridge output accordingly, ensuring accurate and reliable measurements in different thermal conditions.
The Wheatstone bridge is a circuit arrangement commonly used for measuring resistance or strain. It consists of four resistive elements connected in a bridge configuration, with an excitation voltage applied across the two opposite nodes of the bridge. The output voltage from the bridge is then proportional to the imbalance between the resistive elements.
However, temperature changes can affect the resistance of the elements in the bridge and introduce errors in the measurement. For example, if the temperature increases, the resistive elements may expand, leading to an increase in their resistance values. This change in resistance can result in an unbalanced bridge and inaccurate measurements.
To compensate for these temperature variations, multiple resistive sensors can be used in the Wheatstone bridge. By having more than one sensor, it becomes possible to measure the temperature at different points and adjust the bridge accordingly. This allows for the cancellation of temperature-induced errors by applying appropriate correction techniques.
The use of multiple resistive sensors provides the ability to measure both the desired quantity (e.g., strain) and the temperature at different locations. By simultaneously measuring the temperature, it becomes possible to determine the effect of temperature on the resistance values and compensate for it.
The compensation technique can involve various methods, such as using a reference temperature or employing temperature-dependent resistors. These methods help in adjusting the bridge output based on the temperature measurements, ensuring accurate measurements even in varying thermal conditions.
In summary, by using more than one resistive sensor in a Wheatstone bridge, thermal compensation can be achieved. This compensation allows for the measurement of temperature variations and adjustment of the bridge output accordingly, ensuring accurate and reliable measurements in different thermal conditions.
Chapter doubts & questions for Basic Electrical Components - Sensor & Industrial Instrumentation 2025 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Basic Electrical Components - Sensor & Industrial Instrumentation in English & Hindi are available as part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam by signing up for free.
Sensor & Industrial Instrumentation
26 videos|28 docs|29 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup