All Exams >
Civil Engineering (CE) >
Engineering Hydrology >
All Questions
All questions of Precipitation & Its Measurement for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam
The percentage of total quantity of water in the world that is saline is about- a)71%
- b)33%
- c)67%
- d)97%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The percentage of total quantity of water in the world that is saline is about
a)
71%
b)
33%
c)
67%
d)
97%

|
Anand Mehta answered |
Explanation:
The world's total quantity of water is about 1.386 billion cubic kilometers. Out of this, only about 2.5% is freshwater, and the remaining 97.5% is saline water.
The percentage of total quantity of water in the world that is saline can be calculated as follows:
Saline water quantity = 97.5% of 1.386 billion cubic kilometers
= 1.3515 billion cubic kilometers
Total water quantity = 1.386 billion cubic kilometers
Percentage of saline water = (Saline water quantity / Total water quantity) x 100
= (1.3515 / 1.386) x 100
= 97.48%
Therefore, the percentage of total quantity of water in the world that is saline is about 97%.
Conclusion:
The world's water resources are mainly composed of saline water, which is not suitable for human consumption or agricultural purposes. The limited freshwater resources need to be conserved and managed sustainably to meet the growing demand for water worldwide.
The world's total quantity of water is about 1.386 billion cubic kilometers. Out of this, only about 2.5% is freshwater, and the remaining 97.5% is saline water.
The percentage of total quantity of water in the world that is saline can be calculated as follows:
Saline water quantity = 97.5% of 1.386 billion cubic kilometers
= 1.3515 billion cubic kilometers
Total water quantity = 1.386 billion cubic kilometers
Percentage of saline water = (Saline water quantity / Total water quantity) x 100
= (1.3515 / 1.386) x 100
= 97.48%
Therefore, the percentage of total quantity of water in the world that is saline is about 97%.
Conclusion:
The world's water resources are mainly composed of saline water, which is not suitable for human consumption or agricultural purposes. The limited freshwater resources need to be conserved and managed sustainably to meet the growing demand for water worldwide.
The mass curve of rainfall of a storm is a plot of- a)rainfall depths for various equal durations plotted in decreasing order
- b)rainfall intensity vs time in chronological order
- c)accumulated rainfall intensity vs time
- d)accumulated precipitation vs time in chronological order
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The mass curve of rainfall of a storm is a plot of
a)
rainfall depths for various equal durations plotted in decreasing order
b)
rainfall intensity vs time in chronological order
c)
accumulated rainfall intensity vs time
d)
accumulated precipitation vs time in chronological order
|
|
Avinash Mehta answered |
The mass curve of rainfall of a storm is a plot of accumulated precipitation against time in chronological order. It shows how the total rainfall changes over time during a storm. It is useful for understanding how much and how quickly rainfall will accumulate during a storm, which can help with flood forecasting and stormwater management. The mass curve can also help to identify how much rainfall is concentrated in a short period of time ( peak rainfall rate) and how much rainfall is spread over the duration of the storm.
Orographic precipitation occurs due to air masses being lifted to higher altitudes by- a)the density difference of air masses
- b)a frontal action
- c)the presence of mountain barriers
- d)extratropical cyclones
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Orographic precipitation occurs due to air masses being lifted to higher altitudes by
a)
the density difference of air masses
b)
a frontal action
c)
the presence of mountain barriers
d)
extratropical cyclones
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The moist air masses may get lifted-up to higher altitudes due to the presence of mountain barriers and consequently undergo cooling, condensation and precipitation, such a precipitation is known as orographic precipitation.
The base of the non-recording type rainfall is permanently fixed in the concrete block.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The base of the non-recording type rainfall is permanently fixed in the concrete block.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
The base of the gauge is permanently fixed into a concrete block at a site where rainfall is to be measured. The precaution is taken during fixing, to level perfectly. The gauge is fixed in the block in such a way that the top of the gauge will be 30 cm above the natural surface level.
What would be the rate of rainfall if the value of N can be given as 2 and the difference in time can be given as 24 sec with the L.C of the instrument as 1m?- a)50m-sec
- b)48m-sec
- c)42m-sec
- d)49m-sec
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What would be the rate of rainfall if the value of N can be given as 2 and the difference in time can be given as 24 sec with the L.C of the instrument as 1m?
a)
50m-sec
b)
48m-sec
c)
42m-sec
d)
49m-sec
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
The rate of rainfall can be determined by using the formula,
R = N*k*δt. On substitution, we get
R = 2*1*24
R = 48m-sec.
R = N*k*δt. On substitution, we get
R = 2*1*24
R = 48m-sec.
Intensity of rainfall is measured by___________- a)Continuously recording gauge
- b)Anemometer
- c)Hydrometer
- d)Seismometer
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Intensity of rainfall is measured by___________
a)
Continuously recording gauge
b)
Anemometer
c)
Hydrometer
d)
Seismometer
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
The intensity of rainfall is expressed as an amount of precipitation in a stead period. During heavy rainstorm the intensity of rainfall varies widely from minute to minute and can be measured only with a continuously recording gauge.
The relation between the area of rainstorm and its average intensity is used in assessing _________- a)Amount of water
- b)Amount of rain
- c)Amount of wind
- d)Amount of duration of rain
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The relation between the area of rainstorm and its average intensity is used in assessing _________
a)
Amount of water
b)
Amount of rain
c)
Amount of wind
d)
Amount of duration of rain

|
Mira Mishra answered |
Relation between Area of Rainstorm and Average Intensity
The relation between the area of a rainstorm and its average intensity is crucial in assessing the amount of rain that is expected to fall during the storm. This relationship helps in predicting the total volume of rainfall that may occur over a specific area.
Area of Rainstorm
The area of a rainstorm refers to the geographical extent over which the storm is affecting. It can vary from a small localized storm to a large-scale storm that covers a wide area.
Average Intensity
Average intensity of a rainstorm refers to the rate at which rainfall is occurring over a specific area. It is usually measured in terms of millimeters per hour or inches per hour.
Assessment of Amount of Rain
By understanding the relation between the area of a rainstorm and its average intensity, experts can assess the amount of rain that is expected to fall during the storm. This information is crucial for flood forecasting, water resource management, and disaster preparedness.
Significance in Civil Engineering
In civil engineering, this information is used in designing stormwater management systems, drainage systems, and infrastructure to handle the expected amount of rainfall. It helps in ensuring that structures are resilient to heavy rainfall events and can effectively manage stormwater runoff.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between the area of a rainstorm and its average intensity is essential for accurately predicting and preparing for the amount of rain that may fall during a storm. This knowledge plays a vital role in various fields, including civil engineering, meteorology, and disaster management.
The relation between the area of a rainstorm and its average intensity is crucial in assessing the amount of rain that is expected to fall during the storm. This relationship helps in predicting the total volume of rainfall that may occur over a specific area.
Area of Rainstorm
The area of a rainstorm refers to the geographical extent over which the storm is affecting. It can vary from a small localized storm to a large-scale storm that covers a wide area.
Average Intensity
Average intensity of a rainstorm refers to the rate at which rainfall is occurring over a specific area. It is usually measured in terms of millimeters per hour or inches per hour.
Assessment of Amount of Rain
By understanding the relation between the area of a rainstorm and its average intensity, experts can assess the amount of rain that is expected to fall during the storm. This information is crucial for flood forecasting, water resource management, and disaster preparedness.
Significance in Civil Engineering
In civil engineering, this information is used in designing stormwater management systems, drainage systems, and infrastructure to handle the expected amount of rainfall. It helps in ensuring that structures are resilient to heavy rainfall events and can effectively manage stormwater runoff.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between the area of a rainstorm and its average intensity is essential for accurately predicting and preparing for the amount of rain that may fall during a storm. This knowledge plays a vital role in various fields, including civil engineering, meteorology, and disaster management.
Which of the following will not come under the classification of rain gauge?- a)Tipping bucket gauge.
- b)Reflective rain gauge
- c)Optical rain gauge
- d)Acoustic rain gauge
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following will not come under the classification of rain gauge?
a)
Tipping bucket gauge.
b)
Reflective rain gauge
c)
Optical rain gauge
d)
Acoustic rain gauge
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Rain gauge has been classified based on the type of work being conducted to adapt the situations. Those include optical rain gauge, acoustic rain gauge and tipping bucket gauge.
The percentage of total quantity of fresh water in the world available in the liquid form is about .- a)30%
- b)70%
- c)11%
- d)51%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The percentage of total quantity of fresh water in the world available in the liquid form is about .
a)
30%
b)
70%
c)
11%
d)
51%

|
Rounak Banerjee answered |
About 71 percent of the Earth's surface is water-covered, and the oceans hold about 96.5 percent of all Earth's water. Also, % of total water available in liquid form out of total quantity of freshwater is 30% and rest is in form of ice and glaciers.
If the average annual rainfall and evaporation over land masses and oceans of the earth are considered it would be found that- a)over the land mass the annual evaporation is the same as the annual precipitation
- b)about 9% more, water evaporates from the oceans than what falls back on them as precipitation
- c)over the oceans about 19% more rain falls than what is evaporated
- d)over the oceans about 19% more water evaporates than what falls back on them as precipitation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the average annual rainfall and evaporation over land masses and oceans of the earth are considered it would be found that
a)
over the land mass the annual evaporation is the same as the annual precipitation
b)
about 9% more, water evaporates from the oceans than what falls back on them as precipitation
c)
over the oceans about 19% more rain falls than what is evaporated
d)
over the oceans about 19% more water evaporates than what falls back on them as precipitation

|
Raghavendra Sengupta answered |
Average Annual Rainfall and Evaporation over Land Masses and Oceans
B. About 9% more water evaporates from the oceans than what falls back on them as precipitation.
Explanation:
Annual rainfall and evaporation are the two most important hydrologic variables that determine the water balance of the earth. The water cycle is an essential process and is responsible for the distribution of freshwater resources across the globe. The average annual rainfall and evaporation over land masses and oceans of the earth are considered to estimate the water balance.
- Water Balance:
The water balance is the relationship between precipitation and evapotranspiration. Precipitation is the amount of water that falls from the atmosphere and reaches the earth's surface. Evapotranspiration is the combined process of evaporation and plant transpiration. It is the amount of water that returns to the atmosphere through the processes of evaporation and transpiration.
- Land Masses:
Over the land mass, the annual evaporation is less than the annual precipitation. This is because the land surface has a lower heat capacity than water and therefore warms up faster. This results in more evaporation from the land surface. The precipitation that falls on the land surface is absorbed by the soil and vegetation or flows into rivers and streams.
- Oceans:
Over the oceans, about 9% more water evaporates than what falls back on them as precipitation. This is because the oceans have a higher heat capacity than land and therefore take longer to warm up. This results in more evaporation from the ocean surface. The precipitation that falls on the ocean surface is absorbed by the ocean or flows into rivers and streams.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the average annual rainfall and evaporation over land masses and oceans of the earth are important hydrologic variables that determine the water balance. Over the land mass, the annual evaporation is less than the annual precipitation, while over the oceans, about 9% more water evaporates than what falls back on them as precipitation.
B. About 9% more water evaporates from the oceans than what falls back on them as precipitation.
Explanation:
Annual rainfall and evaporation are the two most important hydrologic variables that determine the water balance of the earth. The water cycle is an essential process and is responsible for the distribution of freshwater resources across the globe. The average annual rainfall and evaporation over land masses and oceans of the earth are considered to estimate the water balance.
- Water Balance:
The water balance is the relationship between precipitation and evapotranspiration. Precipitation is the amount of water that falls from the atmosphere and reaches the earth's surface. Evapotranspiration is the combined process of evaporation and plant transpiration. It is the amount of water that returns to the atmosphere through the processes of evaporation and transpiration.
- Land Masses:
Over the land mass, the annual evaporation is less than the annual precipitation. This is because the land surface has a lower heat capacity than water and therefore warms up faster. This results in more evaporation from the land surface. The precipitation that falls on the land surface is absorbed by the soil and vegetation or flows into rivers and streams.
- Oceans:
Over the oceans, about 9% more water evaporates than what falls back on them as precipitation. This is because the oceans have a higher heat capacity than land and therefore take longer to warm up. This results in more evaporation from the ocean surface. The precipitation that falls on the ocean surface is absorbed by the ocean or flows into rivers and streams.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the average annual rainfall and evaporation over land masses and oceans of the earth are important hydrologic variables that determine the water balance. Over the land mass, the annual evaporation is less than the annual precipitation, while over the oceans, about 9% more water evaporates than what falls back on them as precipitation.
The intensity of rainfall is given by ______- a)I = R/(T+C)
- b)I = R/(T×C)
- c)I = (T×C)/R
- d)I = (T+R)/C
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The intensity of rainfall is given by ______
a)
I = R/(T+C)
b)
I = R/(T×C)
c)
I = (T×C)/R
d)
I = (T+R)/C
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
The intensity of rainfall is given by,
I = R/(T+C)
Where, I = intensity in inches/hr.
T = Duration of rain storm in hours
R & C = these are constants quoted by different authorities for different areas of world.
The intensity also depends on the area selected for the measurement.
I = R/(T+C)
Where, I = intensity in inches/hr.
T = Duration of rain storm in hours
R & C = these are constants quoted by different authorities for different areas of world.
The intensity also depends on the area selected for the measurement.
The standard Symons' type raingauge has a collecting area of diameter- a)12.7 cm
- b)10 cm
- c)5.08 cm
- d)25.4 cm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard Symons' type raingauge has a collecting area of diameter
a)
12.7 cm
b)
10 cm
c)
5.08 cm
d)
25.4 cm

|
Simran Mukherjee answered |
Collecting Area of Standard Symons Type Raingauge
The standard Symons type raingauge is an instrument used to measure rainfall. It has a cylindrical container with a funnel-shaped top that collects rainwater. The collected water is then measured to determine the amount of rainfall. The collecting area of the standard Symons type raingauge is given as:
a) 12.7 cm
Explanation:
The collecting area of a raingauge is the surface area of the funnel-shaped top that collects rainwater. The standard Symons type raingauge has a diameter of 10 inches (25.4 cm) and a height of 10 inches (25.4 cm). The funnel-shaped top of the raingauge has a diameter of 8 inches (20.32 cm) at the top and a diameter of 5 inches (12.7 cm) at the bottom. Therefore, the collecting area of the raingauge is the area of the circular base with a diameter of 5 inches (12.7 cm).
Hence, the correct answer is option A, i.e., 12.7 cm.
The standard Symons type raingauge is an instrument used to measure rainfall. It has a cylindrical container with a funnel-shaped top that collects rainwater. The collected water is then measured to determine the amount of rainfall. The collecting area of the standard Symons type raingauge is given as:
a) 12.7 cm
Explanation:
The collecting area of a raingauge is the surface area of the funnel-shaped top that collects rainwater. The standard Symons type raingauge has a diameter of 10 inches (25.4 cm) and a height of 10 inches (25.4 cm). The funnel-shaped top of the raingauge has a diameter of 8 inches (20.32 cm) at the top and a diameter of 5 inches (12.7 cm) at the bottom. Therefore, the collecting area of the raingauge is the area of the circular base with a diameter of 5 inches (12.7 cm).
Hence, the correct answer is option A, i.e., 12.7 cm.
Acoustic rain gauge can also be known as__________- a)Hydro gauge
- b)Hydro remote
- c)Hydrophone
- d)Hydro cable
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Acoustic rain gauge can also be known as__________
a)
Hydro gauge
b)
Hydro remote
c)
Hydrophone
d)
Hydro cable

|
Rounak Choudhary answered |
Acoustic Rain Gauge: Introduction
An acoustic rain gauge is a device used to measure rainfall by using sound waves. It is an innovative and non-contact method for measuring precipitation. The gauge is primarily based on the principle that raindrops falling into water create sound waves that can be detected and analyzed to determine the amount of rainfall.
Working Principle of Acoustic Rain Gauge
The acoustic rain gauge consists of a hydrophone, which is a special type of microphone designed to pick up underwater sound signals. The hydrophone is usually placed at the bottom of a water-filled container, such as a bucket or a tank. When raindrops fall into the water, they generate acoustic signals that are sensed by the hydrophone.
Hydrophone as an Alternative Name for Acoustic Rain Gauge
The correct answer, option 'C', states that an acoustic rain gauge can also be known as a "hydrophone." This is because the hydrophone is the main component of the acoustic rain gauge. The hydrophone detects the sound waves produced by the raindrops falling into the water, making it an integral part of the gauge.
Other Options
The other options provided in the question are not correct alternatives for an acoustic rain gauge. Here is a brief explanation of why they are not suitable:
a) Hydro gauge: This term is not commonly used to refer to an acoustic rain gauge. The term "hydro gauge" is more commonly associated with pressure gauges used in hydraulic systems.
b) Hydro remote: This term does not accurately describe an acoustic rain gauge. It may refer to remote sensing techniques used in hydrology, but it is not a specific term for an acoustic rain gauge.
d) Hydro cable: This term is unrelated to an acoustic rain gauge. "Hydro cable" may refer to cables used in hydroelectric power systems or underwater communication systems, but it does not pertain to the measurement of rainfall.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an acoustic rain gauge is a device that utilizes a hydrophone to measure rainfall based on the sound waves produced by raindrops falling into water. The hydrophone is the main component of the gauge, making "hydrophone" an appropriate alternative name for an acoustic rain gauge.
An acoustic rain gauge is a device used to measure rainfall by using sound waves. It is an innovative and non-contact method for measuring precipitation. The gauge is primarily based on the principle that raindrops falling into water create sound waves that can be detected and analyzed to determine the amount of rainfall.
Working Principle of Acoustic Rain Gauge
The acoustic rain gauge consists of a hydrophone, which is a special type of microphone designed to pick up underwater sound signals. The hydrophone is usually placed at the bottom of a water-filled container, such as a bucket or a tank. When raindrops fall into the water, they generate acoustic signals that are sensed by the hydrophone.
Hydrophone as an Alternative Name for Acoustic Rain Gauge
The correct answer, option 'C', states that an acoustic rain gauge can also be known as a "hydrophone." This is because the hydrophone is the main component of the acoustic rain gauge. The hydrophone detects the sound waves produced by the raindrops falling into the water, making it an integral part of the gauge.
Other Options
The other options provided in the question are not correct alternatives for an acoustic rain gauge. Here is a brief explanation of why they are not suitable:
a) Hydro gauge: This term is not commonly used to refer to an acoustic rain gauge. The term "hydro gauge" is more commonly associated with pressure gauges used in hydraulic systems.
b) Hydro remote: This term does not accurately describe an acoustic rain gauge. It may refer to remote sensing techniques used in hydrology, but it is not a specific term for an acoustic rain gauge.
d) Hydro cable: This term is unrelated to an acoustic rain gauge. "Hydro cable" may refer to cables used in hydroelectric power systems or underwater communication systems, but it does not pertain to the measurement of rainfall.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an acoustic rain gauge is a device that utilizes a hydrophone to measure rainfall based on the sound waves produced by raindrops falling into water. The hydrophone is the main component of the gauge, making "hydrophone" an appropriate alternative name for an acoustic rain gauge.
Average annual rainfall ranging to dessert to hilly regions would be _______- a)1100cm
- b)2500cm
- c)845cm
- d)500cm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Average annual rainfall ranging to dessert to hilly regions would be _______
a)
1100cm
b)
2500cm
c)
845cm
d)
500cm
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
The rainfall varies widely from one part of the world to another, ranging from desert regions to the hilly regions where the average annual rainfall may be over 1100cm. in some regions, the seasonal variation is very slight and monthly rainfalls are relatively uniform.
The annual rainfall at any given station varies from _________- a)month to month
- b)weekly basis
- c)year to Year
- d)quarterly
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The annual rainfall at any given station varies from _________
a)
month to month
b)
weekly basis
c)
year to Year
d)
quarterly
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
The annual rainfall at any given station varies irregularly from year to year. The range of this variation marks the reliability of the rainfall and has great importance in the design of storage reservoirs.
The drum situated in recording type makes one rotation for how many hours?- a)4 hours
- b)24 hours
- c)6 hours
- d)12 hours
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The drum situated in recording type makes one rotation for how many hours?
a)
4 hours
b)
24 hours
c)
6 hours
d)
12 hours

|
Raghavendra Sengupta answered |
Understanding the Drum Rotation in Recording Type
The drum in a recording type system, such as a recording drum used in various engineering applications, typically refers to the mechanism that records data or measurements over time. The rotation of this drum is crucial for proper data collection and analysis.
Duration of One Full Rotation
- The drum completes one full rotation in **24 hours**.
- This means that it takes an entire day for the drum to rotate completely around its axis, allowing for continuous recording of data over this time period.
Significance of 24-Hour Rotation
- **Continuous Monitoring**: A 24-hour rotation allows for uninterrupted data collection, which is essential in fields like civil engineering, where conditions may change rapidly over the course of a day.
- **Data Integrity**: A full rotation ensures that all data captured within that timeframe gets recorded accurately, allowing engineers to analyze trends and patterns effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer to how long it takes for the drum to make one rotation in recording type is **24 hours (option B)**. This extended duration is fundamental in ensuring comprehensive and accurate data collection in various engineering applications.
The drum in a recording type system, such as a recording drum used in various engineering applications, typically refers to the mechanism that records data or measurements over time. The rotation of this drum is crucial for proper data collection and analysis.
Duration of One Full Rotation
- The drum completes one full rotation in **24 hours**.
- This means that it takes an entire day for the drum to rotate completely around its axis, allowing for continuous recording of data over this time period.
Significance of 24-Hour Rotation
- **Continuous Monitoring**: A 24-hour rotation allows for uninterrupted data collection, which is essential in fields like civil engineering, where conditions may change rapidly over the course of a day.
- **Data Integrity**: A full rotation ensures that all data captured within that timeframe gets recorded accurately, allowing engineers to analyze trends and patterns effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer to how long it takes for the drum to make one rotation in recording type is **24 hours (option B)**. This extended duration is fundamental in ensuring comprehensive and accurate data collection in various engineering applications.
When specific information about the density of snowfall is not available, the water equivalent -of snowfall is taken as- a)50%
- b)30%
- c)10%
- d)90%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When specific information about the density of snowfall is not available, the water equivalent -of snowfall is taken as
a)
50%
b)
30%
c)
10%
d)
90%
|
|
Vandana Desai answered |
-
The
density of water is 1000 kg/m^3 and
snow density is usually measured as a ratio to this. So
snow which is 100 kg/m^3 is specified as 100/1000, or 10 percent (of the
density of water). The water content divided by the
snow depth also gives the
density of the
snow.
-
When specific information about the density of snowfall is not available, the water equivalent of snowfall is taken as 10%
Thermohygrograph gives a continuous recording of- a)discharge on a thermal sensitive paper
- b)temperature and pressure
- c)temperature and humidity
- d)solar radiation and wind velocity
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Thermohygrograph gives a continuous recording of
a)
discharge on a thermal sensitive paper
b)
temperature and pressure
c)
temperature and humidity
d)
solar radiation and wind velocity

|
Gauri Roy answered |
Thermohygrograph is a device that records continuous data of temperature and humidity. It is commonly used in industries and laboratories where temperature and humidity control is crucial. Here is a detailed explanation of the answer:
Temperature and Humidity Recording:
Thermohygrograph gives a continuous recording of temperature and humidity. It has two sensors, one for temperature and the other for humidity. These sensors record the respective values and plot them on a chart over a period of time. The chart is usually a circular disc that rotates once a day or a week, depending on the model.
Working Principle:
The working principle of a thermohygrograph is based on the expansion and contraction of a special type of paper that is sensitive to temperature and humidity. The paper is coated with a chemical that changes color with the change in temperature and humidity. The paper is wrapped around the rotating disc, and the sensors record the values and plot them on the paper.
Applications:
Thermohygrograph is widely used in industries that require controlled temperature and humidity, such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and storage facilities. It is also used in laboratories to monitor the temperature and humidity during experiments. It is an essential tool for climate studies and weather forecasting.
Advantages:
Thermohygrograph provides a continuous recording of temperature and humidity, which is useful for identifying any fluctuations or variations in the environment. It helps in maintaining the quality and safety of products that are sensitive to temperature and humidity. It also helps in predicting weather patterns and climate changes.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Thermohygrograph is a device that records continuous data of temperature and humidity. It is widely used in industries and laboratories for monitoring and controlling the environment. It provides accurate and reliable data that helps in maintaining the quality and safety of products.
Temperature and Humidity Recording:
Thermohygrograph gives a continuous recording of temperature and humidity. It has two sensors, one for temperature and the other for humidity. These sensors record the respective values and plot them on a chart over a period of time. The chart is usually a circular disc that rotates once a day or a week, depending on the model.
Working Principle:
The working principle of a thermohygrograph is based on the expansion and contraction of a special type of paper that is sensitive to temperature and humidity. The paper is coated with a chemical that changes color with the change in temperature and humidity. The paper is wrapped around the rotating disc, and the sensors record the values and plot them on the paper.
Applications:
Thermohygrograph is widely used in industries that require controlled temperature and humidity, such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and storage facilities. It is also used in laboratories to monitor the temperature and humidity during experiments. It is an essential tool for climate studies and weather forecasting.
Advantages:
Thermohygrograph provides a continuous recording of temperature and humidity, which is useful for identifying any fluctuations or variations in the environment. It helps in maintaining the quality and safety of products that are sensitive to temperature and humidity. It also helps in predicting weather patterns and climate changes.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Thermohygrograph is a device that records continuous data of temperature and humidity. It is widely used in industries and laboratories for monitoring and controlling the environment. It provides accurate and reliable data that helps in maintaining the quality and safety of products.
A precipitation in the form of water droplets of size less than 0.5 mm and intensity less than 1 mm/h is known as - a)Rain
- b)Sleet
- c)Hail
- d)Drizzle
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A precipitation in the form of water droplets of size less than 0.5 mm and intensity less than 1 mm/h is known as
a)
Rain
b)
Sleet
c)
Hail
d)
Drizzle

|
Samridhi Choudhary answered |
The rainfall is used to describe precipitations in the form of water drops of sizes larger than 0.5 mm. Sleet is frozen raindrops of transparent grain which form when rain falls through air at subfreezing temperature. Hail is a showery precipitation in the form of irregular pallets or lumps of size more than 8 mm. Drizzle is a fine sprinkle of numerous water droplets of size less than 0.5 mm and intensity less than 1 mm/h.
A tropical cyclone is a- a)low-pressure zone that occurs in the northern hemisphere only
- b)high-pressure zone with high wind
- c)zone of low pressure with clockwise winds In the northern hemisphere
- d)zone of low pressure with anticlockwise winds in the northern hemispher
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A tropical cyclone is a
a)
low-pressure zone that occurs in the northern hemisphere only
b)
high-pressure zone with high wind
c)
zone of low pressure with clockwise winds In the northern hemisphere
d)
zone of low pressure with anticlockwise winds in the northern hemispher

|
Niharika Yadav answered |
A cyclone is a large low pressure region with circular wind motion. Two types of cyclones are recognized viz., tropical cyclones and extratropical cyclones. A tropical cyclone is a wind system with an intensely strong depression. The normal areal extent of a cyclone is about 100-200 km in diameter. The isobars are closely spaced and the winds are anticlockwise in the Northern hemisphere.
What is ‘Hydrological Cycle’?- a)Processes involved in the transfer of moisture from sea to land
- b)Processes involved in the transfer of moisture from sea back to sea again
- c)Processes involved in the transfer of water from snowmelt in mountains to sea
- d)Processes involved in the transfer of moisture from sea to land and back to sea again
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is ‘Hydrological Cycle’?
a)
Processes involved in the transfer of moisture from sea to land
b)
Processes involved in the transfer of moisture from sea back to sea again
c)
Processes involved in the transfer of water from snowmelt in mountains to sea
d)
Processes involved in the transfer of moisture from sea to land and back to sea again

|
Ashwin Kulkarni answered |
Most of the earth’s water sources such as rivers, fakes, oceans, ground water, etc, get their supplies
from rain, while the rain water in itself is derived from the evaporation from these sources.
Water is intact lost to the atmosphere as vapour from the earth, which is then precipitated back in the form of rain, snow, hail, dew, sleet or frost, etc. This evaporation and precipitation continues forever and thereby, a balance is maintained between the two. This process is known as hydrologic cycle.
from rain, while the rain water in itself is derived from the evaporation from these sources.
Water is intact lost to the atmosphere as vapour from the earth, which is then precipitated back in the form of rain, snow, hail, dew, sleet or frost, etc. This evaporation and precipitation continues forever and thereby, a balance is maintained between the two. This process is known as hydrologic cycle.
Find the least count of the instrument used in case of rainfall determination, if the volume of the bucket is 50cu. m and the area of the funnel is about 21 sq. m.- a)3.38 m
- b)2.83 m
- c)2.38 m
- d)4.38 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the least count of the instrument used in case of rainfall determination, if the volume of the bucket is 50cu. m and the area of the funnel is about 21 sq. m.
a)
3.38 m
b)
2.83 m
c)
2.38 m
d)
4.38 m

|
Sahil Chawla answered |
To determine the least count of an instrument used for rainfall determination, we need to understand the concept of least count and how it is calculated.
What is Least Count?
The least count of an instrument is the smallest value that can be measured using that instrument. It represents the level of accuracy and precision with which measurements can be made.
Formula for Least Count:
The formula to calculate the least count is given by:
Least Count = (Smallest division on the scale) / (Total number of divisions on the scale)
Given Data:
Volume of the bucket (V) = 50 cu. m
Area of the funnel (A) = 21 sq. m
Calculating the Least Count:
1. Volume of water collected in the bucket:
The volume of water collected in the bucket is equal to the volume of rainfall. Therefore, the volume can be calculated as:
Volume = V / A
Volume = 50 cu. m / 21 sq. m
Volume = 2.38 cu. m
2. Smallest division on the scale:
The smallest division on the scale is the smallest increment that can be measured on the instrument. In this case, the smallest division is the smallest increment of volume that can be measured. Since the volume is 2.38 cu. m, the smallest division can be taken as 0.01 cu. m.
3. Total number of divisions on the scale:
The total number of divisions on the scale represents the number of increments that can be measured on the instrument. In this case, since the smallest division is 0.01 cu. m, the total number of divisions can be calculated as:
Total number of divisions = Volume / Smallest division
Total number of divisions = 2.38 cu. m / 0.01 cu. m
Total number of divisions = 238
4. Calculating the Least Count:
Using the formula for least count, we can substitute the values:
Least Count = Smallest division / Total number of divisions
Least Count = 0.01 cu. m / 238
Least Count = 0.000042 cu. m
Answer:
Therefore, the least count of the instrument used for rainfall determination is 2.38 m.
What is Least Count?
The least count of an instrument is the smallest value that can be measured using that instrument. It represents the level of accuracy and precision with which measurements can be made.
Formula for Least Count:
The formula to calculate the least count is given by:
Least Count = (Smallest division on the scale) / (Total number of divisions on the scale)
Given Data:
Volume of the bucket (V) = 50 cu. m
Area of the funnel (A) = 21 sq. m
Calculating the Least Count:
1. Volume of water collected in the bucket:
The volume of water collected in the bucket is equal to the volume of rainfall. Therefore, the volume can be calculated as:
Volume = V / A
Volume = 50 cu. m / 21 sq. m
Volume = 2.38 cu. m
2. Smallest division on the scale:
The smallest division on the scale is the smallest increment that can be measured on the instrument. In this case, the smallest division is the smallest increment of volume that can be measured. Since the volume is 2.38 cu. m, the smallest division can be taken as 0.01 cu. m.
3. Total number of divisions on the scale:
The total number of divisions on the scale represents the number of increments that can be measured on the instrument. In this case, since the smallest division is 0.01 cu. m, the total number of divisions can be calculated as:
Total number of divisions = Volume / Smallest division
Total number of divisions = 2.38 cu. m / 0.01 cu. m
Total number of divisions = 238
4. Calculating the Least Count:
Using the formula for least count, we can substitute the values:
Least Count = Smallest division / Total number of divisions
Least Count = 0.01 cu. m / 238
Least Count = 0.000042 cu. m
Answer:
Therefore, the least count of the instrument used for rainfall determination is 2.38 m.
In which of the following season is evaporation loss from free water is large?- a)Winter
- b)Spring
- c)Autumn
- d)Summer
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following season is evaporation loss from free water is large?
a)
Winter
b)
Spring
c)
Autumn
d)
Summer
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
During summer, the evaporation loss from free water surface is considerably large and this evaporated water finds room in the air mass. The water holding capacity of air in the form of vapor is also considerably large in hot weather.
Movement and filtering of fluid from porous material is called as __________- a)Percolation
- b)Infiltration
- c)Transpiration
- d)Precipitation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Movement and filtering of fluid from porous material is called as __________
a)
Percolation
b)
Infiltration
c)
Transpiration
d)
Precipitation
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Percolation refers to movement and filtering of fluid from porous material. Usually the water which falls on the ground is filtered into the earth surface and is stored under the surface of earth. And this water also improves the ground fertility.
The Double mass curve technique is adopted to- a)check the consistency of raingauge records
- b)to find the average rainfall over a number of years
- c)to find the number of rainguages required
- d)to estimate the missing rainfall data
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Double mass curve technique is adopted to
a)
check the consistency of raingauge records
b)
to find the average rainfall over a number of years
c)
to find the number of rainguages required
d)
to estimate the missing rainfall data

|
Rahul Chauhan answered |
If the conditions relevant to the recording of a raingauge station have undergone a significant change during the period of record, inconsistency would arise in the rainfall data of that station. The checking for inconsistency of record is done by the double mass curve technique. This technique is based on the principal that when each recorded data comes from the same parent population, they are consistent.
The hydrologic cycle states that- a)total inflow - total outflow = constant
- b)subsurface inflow = subsurface outflow
- c)inflow into basin = outflow from the basin .
- d)mass inflow - mass outflow = change in mass storage
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The hydrologic cycle states that
a)
total inflow - total outflow = constant
b)
subsurface inflow = subsurface outflow
c)
inflow into basin = outflow from the basin .
d)
mass inflow - mass outflow = change in mass storage

|
Madhurima Banerjee answered |
The Hydrologic Cycle
The hydrologic cycle is the continuous circulation of water between the earth's surface and the atmosphere. It involves various processes such as evaporation, precipitation, infiltration, and runoff. The balance between the inflow and outflow of water is crucial for the sustainability of water resources.
Mass Inflow and Outflow
The mass inflow and outflow refer to the amount of water that enters and leaves a particular system. The mass inflow includes the amount of water that enters a basin through precipitation, surface runoff, and subsurface flow. The mass outflow includes the amount of water that leaves the basin through evaporation, transpiration, surface runoff, and subsurface flow.
Change in Mass Storage
The change in mass storage refers to the difference between the inflow and outflow of water in a particular system. It is the amount of water that is stored in the basin at a particular time. The change in mass storage can be positive or negative depending on the inflow and outflow of water.
The Correct Answer
The hydrologic cycle states that the mass inflow and outflow are equal, and the change in mass storage is the difference between the inflow and outflow of water. Therefore, the correct answer is option D, "mass inflow - mass outflow = change in mass storage." This equation is important in hydrology as it helps to understand the water balance of a particular system and to manage water resources effectively.
The hydrologic cycle is the continuous circulation of water between the earth's surface and the atmosphere. It involves various processes such as evaporation, precipitation, infiltration, and runoff. The balance between the inflow and outflow of water is crucial for the sustainability of water resources.
Mass Inflow and Outflow
The mass inflow and outflow refer to the amount of water that enters and leaves a particular system. The mass inflow includes the amount of water that enters a basin through precipitation, surface runoff, and subsurface flow. The mass outflow includes the amount of water that leaves the basin through evaporation, transpiration, surface runoff, and subsurface flow.
Change in Mass Storage
The change in mass storage refers to the difference between the inflow and outflow of water in a particular system. It is the amount of water that is stored in the basin at a particular time. The change in mass storage can be positive or negative depending on the inflow and outflow of water.
The Correct Answer
The hydrologic cycle states that the mass inflow and outflow are equal, and the change in mass storage is the difference between the inflow and outflow of water. Therefore, the correct answer is option D, "mass inflow - mass outflow = change in mass storage." This equation is important in hydrology as it helps to understand the water balance of a particular system and to manage water resources effectively.
The % of earth covered by oceans is about- a)31%
- b)51%
- c)71% '
- d)97%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The % of earth covered by oceans is about
a)
31%
b)
51%
c)
71% '
d)
97%

|
Garima Kulkarni answered |
The % of earth covered by oceans is about 71%.
Explanation:
Coverage of the Earth's Surface
The Earth's surface is covered by different types of landmasses such as mountains, valleys, deserts, forests, and water bodies such as oceans, seas, lakes, and rivers.
Percentage of the Earth's Surface Covered by Oceans
The oceans are the largest water bodies on Earth and cover about 71% of the Earth's surface. The remaining 29% of the Earth's surface is covered by landmasses such as continents and islands.
Importance of Oceans
Oceans are important for various reasons such as:
- They regulate the Earth's climate and weather patterns
- They provide a habitat for diverse marine life
- They serve as a source of food and livelihood for millions of people
- They facilitate trade and transportation
- They offer recreational activities such as swimming, surfing, and diving.
Conclusion
In summary, the % of Earth covered by oceans is about 71%, making them a crucial part of the Earth's ecosystem and human activity.
Explanation:
Coverage of the Earth's Surface
The Earth's surface is covered by different types of landmasses such as mountains, valleys, deserts, forests, and water bodies such as oceans, seas, lakes, and rivers.
Percentage of the Earth's Surface Covered by Oceans
The oceans are the largest water bodies on Earth and cover about 71% of the Earth's surface. The remaining 29% of the Earth's surface is covered by landmasses such as continents and islands.
Importance of Oceans
Oceans are important for various reasons such as:
- They regulate the Earth's climate and weather patterns
- They provide a habitat for diverse marine life
- They serve as a source of food and livelihood for millions of people
- They facilitate trade and transportation
- They offer recreational activities such as swimming, surfing, and diving.
Conclusion
In summary, the % of Earth covered by oceans is about 71%, making them a crucial part of the Earth's ecosystem and human activity.
Mean precipitation over an area is best obtained from gauged amounts by- a)Arithmetic mean method
- b)Thiessen method
- c)Linearly interpolated isohyetal method
- d)Orographically weighted isohyetal method
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Mean precipitation over an area is best obtained from gauged amounts by
a)
Arithmetic mean method
b)
Thiessen method
c)
Linearly interpolated isohyetal method
d)
Orographically weighted isohyetal method

|
Gitanjali Menon answered |
Isohyets are contours of equal rainfall. The orographically weighted isohyets are prepared by tracing paper for mountainous areas and therefore they are more accurate than linearly interpolated isohyets.
In the hydrological cycle the average residence time of water in the global- a)atmospheric moisture is larger than that in the global rivers
- b)oceans is smaller than that of the global groundwater
- c)rivers is larger than that of the global groundwater
- d)oceans is larger than that of the global groundwater
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the hydrological cycle the average residence time of water in the global
a)
atmospheric moisture is larger than that in the global rivers
b)
oceans is smaller than that of the global groundwater
c)
rivers is larger than that of the global groundwater
d)
oceans is larger than that of the global groundwater

|
Pallabi Tiwari answered |
Explanation:
The hydrological cycle is the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. It involves the processes of evaporation, transpiration, precipitation, infiltration, and runoff. Water moves through different reservoirs such as the atmosphere, oceans, rivers, lakes, groundwater, and glaciers. The residence time of water refers to the average time that a water molecule spends in a particular reservoir.
Residence time of water in oceans:
- The oceans are the largest reservoir of water on the planet, covering about 70% of the Earth's surface.
- The average residence time of water in the oceans is about 3,000 years.
- This means that a water molecule in the ocean will stay there for an average of 3,000 years before it evaporates into the atmosphere or is transported to another reservoir.
Residence time of water in groundwater:
- Groundwater is the water that is stored in the pores and fractures of rocks beneath the Earth's surface.
- The average residence time of water in groundwater is about 1,400 years.
- This means that a water molecule in groundwater will stay there for an average of 1,400 years before it is discharged into a stream or river, or extracted by a well.
Residence time of water in rivers:
- Rivers are the channels through which water flows from one place to another, eventually reaching the oceans.
- The average residence time of water in rivers is about 16 days.
- This means that a water molecule in a river will stay there for an average of 16 days before it is discharged into the ocean.
Residence time of water in atmospheric moisture:
- Atmospheric moisture refers to the water vapor in the Earth's atmosphere.
- The average residence time of water in atmospheric moisture is about 9 days.
- This means that a water molecule in atmospheric moisture will stay there for an average of 9 days before it either condenses into clouds and precipitates, or is transported to another location by winds.
Conclusion:
From the above explanation, it is clear that the average residence time of water in oceans is larger than that of the global groundwater. Hence, option D is the correct answer.
The hydrological cycle is the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. It involves the processes of evaporation, transpiration, precipitation, infiltration, and runoff. Water moves through different reservoirs such as the atmosphere, oceans, rivers, lakes, groundwater, and glaciers. The residence time of water refers to the average time that a water molecule spends in a particular reservoir.
Residence time of water in oceans:
- The oceans are the largest reservoir of water on the planet, covering about 70% of the Earth's surface.
- The average residence time of water in the oceans is about 3,000 years.
- This means that a water molecule in the ocean will stay there for an average of 3,000 years before it evaporates into the atmosphere or is transported to another reservoir.
Residence time of water in groundwater:
- Groundwater is the water that is stored in the pores and fractures of rocks beneath the Earth's surface.
- The average residence time of water in groundwater is about 1,400 years.
- This means that a water molecule in groundwater will stay there for an average of 1,400 years before it is discharged into a stream or river, or extracted by a well.
Residence time of water in rivers:
- Rivers are the channels through which water flows from one place to another, eventually reaching the oceans.
- The average residence time of water in rivers is about 16 days.
- This means that a water molecule in a river will stay there for an average of 16 days before it is discharged into the ocean.
Residence time of water in atmospheric moisture:
- Atmospheric moisture refers to the water vapor in the Earth's atmosphere.
- The average residence time of water in atmospheric moisture is about 9 days.
- This means that a water molecule in atmospheric moisture will stay there for an average of 9 days before it either condenses into clouds and precipitates, or is transported to another location by winds.
Conclusion:
From the above explanation, it is clear that the average residence time of water in oceans is larger than that of the global groundwater. Hence, option D is the correct answer.
Which one of the following is not a major type of storm precipitation?- a)Frontal storm
- b)Air mass storm
- c)Orographic storm
- d)Continental storm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a major type of storm precipitation?
a)
Frontal storm
b)
Air mass storm
c)
Orographic storm
d)
Continental storm

|
Amar Desai answered |
Major Types of Storm Precipitation
There are three major types of storm precipitation, which are as follows:
1. Frontal Storm: It occurs when two air masses of different temperature and moisture content meet. The warmer and moist air rises over the cooler and drier air, leading to the formation of clouds that produce precipitation.
2. Air Mass Storm: It occurs when a large body of air with uniform temperature and moisture content encounters a region with different temperature and moisture content. The warm air rises and cools, leading to the formation of clouds that produce precipitation.
3. Orographic Storm: It occurs when moist air is forced to rise over a mountain range, leading to the formation of clouds that produce precipitation on the windward side of the range.
Not a Major Type of Storm Precipitation
4. Continental Storm: It is not a major type of storm precipitation. It refers to the precipitation that occurs over land areas due to the heating of the surface. However, this type of precipitation is not caused by any specific weather system or phenomenon. Therefore, it is not considered a major type of storm precipitation.
There are three major types of storm precipitation, which are as follows:
1. Frontal Storm: It occurs when two air masses of different temperature and moisture content meet. The warmer and moist air rises over the cooler and drier air, leading to the formation of clouds that produce precipitation.
2. Air Mass Storm: It occurs when a large body of air with uniform temperature and moisture content encounters a region with different temperature and moisture content. The warm air rises and cools, leading to the formation of clouds that produce precipitation.
3. Orographic Storm: It occurs when moist air is forced to rise over a mountain range, leading to the formation of clouds that produce precipitation on the windward side of the range.
Not a Major Type of Storm Precipitation
4. Continental Storm: It is not a major type of storm precipitation. It refers to the precipitation that occurs over land areas due to the heating of the surface. However, this type of precipitation is not caused by any specific weather system or phenomenon. Therefore, it is not considered a major type of storm precipitation.
Rain gauge is also known as __________- a)Udometer
- b)Opto meter
- c)Luda meter
- d)Rio meter
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rain gauge is also known as __________
a)
Udometer
b)
Opto meter
c)
Luda meter
d)
Rio meter
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
The equipment which involves in the determination of the precipitation levels in the atmosphere is termed as a rain gauge. It is also known as ombro meter or the udometer based on the area it is in use.
A rainfall with an intensity of 5 mm/h is classified as- a)Traces
- b)Light rain
- c)Moderate rain
- d)Heavy rain
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A rainfall with an intensity of 5 mm/h is classified as
a)
Traces
b)
Light rain
c)
Moderate rain
d)
Heavy rain

|
Sai Sarkar answered |
Classification of Rainfall Intensity
Rainfall intensity is classified based on the rate at which rain falls. In this case, a rainfall intensity of 5 mm/h falls under the category of moderate rain.
Explanation
- Traces: Rainfall with an intensity of less than 0.5 mm/h is classified as traces, which is barely noticeable.
- Light rain: Rainfall with an intensity between 0.5 mm/h and 4.9 mm/h is classified as light rain. This type of rain may require windshield wipers on a car but does not cause significant runoff.
- Moderate rain: Rainfall with an intensity between 5 mm/h and 49.9 mm/h is classified as moderate rain. This type of rain can cause some runoff and may lead to localized flooding in areas with poor drainage.
- Heavy rain: Rainfall with an intensity of 50 mm/h or more is classified as heavy rain. This type of rain can cause significant runoff, flash flooding, and potential damage.
Therefore, a rainfall intensity of 5 mm/h falls under the category of moderate rain, which indicates a steady rainfall that can lead to some runoff and localized flooding in certain areas.
Rainfall intensity is classified based on the rate at which rain falls. In this case, a rainfall intensity of 5 mm/h falls under the category of moderate rain.
Explanation
- Traces: Rainfall with an intensity of less than 0.5 mm/h is classified as traces, which is barely noticeable.
- Light rain: Rainfall with an intensity between 0.5 mm/h and 4.9 mm/h is classified as light rain. This type of rain may require windshield wipers on a car but does not cause significant runoff.
- Moderate rain: Rainfall with an intensity between 5 mm/h and 49.9 mm/h is classified as moderate rain. This type of rain can cause some runoff and may lead to localized flooding in areas with poor drainage.
- Heavy rain: Rainfall with an intensity of 50 mm/h or more is classified as heavy rain. This type of rain can cause significant runoff, flash flooding, and potential damage.
Therefore, a rainfall intensity of 5 mm/h falls under the category of moderate rain, which indicates a steady rainfall that can lead to some runoff and localized flooding in certain areas.
The following recording raingauges does not produce the mass curve of precipitation as record:- a)Symons’ raingauge
- b)tipping-bucket type gauge
- c)weighing-bucket type gauge
- d)natural syphon gauge.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The following recording raingauges does not produce the mass curve of precipitation as record:
a)
Symons’ raingauge
b)
tipping-bucket type gauge
c)
weighing-bucket type gauge
d)
natural syphon gauge.

|
Sreemoyee Joshi answered |
The Tipping-bucket type gauge gives data on the intensity of rainfall.
A, B and C are three catchments each having an area of about 10,000 km2 situated in an arid zone, mountainous region of a tropical zone and flat region of a tropical zone respectively. The desirable number of hydrometeorological stations for each of these three areas, NA, NB and NC respectively will be such that- a) NB > NC> NA
- b)NA < NB< NC
- c) NA > NB > NC
- d) NB = NC and NB > NA
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A, B and C are three catchments each having an area of about 10,000 km2 situated in an arid zone, mountainous region of a tropical zone and flat region of a tropical zone respectively. The desirable number of hydrometeorological stations for each of these three areas, NA, NB and NC respectively will be such that
a)
NB > NC> NA
b)
NA < NB< NC
c)
NA > NB > NC
d)
NB = NC and NB > NA

|
Diya Sarkar answered |

A catchment has an area of 150 ha and a runoff/ rainfall ratio of 0.40. If due to a 10 cm rainfall over the catchment a stream flow at the catchment outlet lasts for 10 hours, the average stream flow in the period is- a)1.33 m3/s
- b)16.7 m3/s
- c)100m3/minute
- d)6x104m3/hour
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A catchment has an area of 150 ha and a runoff/ rainfall ratio of 0.40. If due to a 10 cm rainfall over the catchment a stream flow at the catchment outlet lasts for 10 hours, the average stream flow in the period is
a)
1.33 m3/s
b)
16.7 m3/s
c)
100m3/minute
d)
6x104m3/hour

|
Aditi Sarkar answered |
The average stream flow

Which of the following rain gauge equipment is used in case of remote areas?- a)Reflective rain gauge
- b)Acoustic rain gauge
- c)Optical rain gauge
- d)Tipping bucket
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following rain gauge equipment is used in case of remote areas?
a)
Reflective rain gauge
b)
Acoustic rain gauge
c)
Optical rain gauge
d)
Tipping bucket

|
Devanshi Iyer answered |
Remote areas can pose challenges when it comes to collecting accurate rainfall data. In such cases, the most suitable rain gauge equipment is the tipping bucket rain gauge.
What is a Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge?
A tipping bucket rain gauge is an instrument used to measure rainfall. It consists of a funnel-shaped collector that directs the rainwater into a bucket with a small opening at the bottom. The bucket is balanced on a pivot point, allowing it to tip from one side to the other when a certain amount of rainfall is collected.
How does a Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge work?
When rainwater enters the collector, it accumulates and eventually reaches a predetermined volume. Once this volume is reached, the bucket tips, causing the collected water to drain out and a new empty bucket to take its place. The tipping action is detected by a sensor, which records the number of tips. By knowing the volume of each tip, the rainfall amount can be calculated.
Advantages of Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge in Remote Areas:
1. Simplicity: Tipping bucket rain gauges are relatively simple and robust instruments, making them suitable for remote areas where maintenance and repairs may be challenging.
2. Accuracy: Tipping bucket rain gauges provide accurate measurements of rainfall. Since they measure rainfall in discrete volumes, they can capture both light drizzles and heavy downpours accurately.
3. Reliability: These gauges are designed to withstand harsh weather conditions, making them reliable for long-term operation in remote areas.
4. Remote Data Collection: Tipping bucket rain gauges can be equipped with data loggers or telemetry systems, allowing for remote data collection and real-time monitoring even in areas with limited accessibility.
5. Low Maintenance: The tipping bucket rain gauge requires minimal maintenance compared to other rain gauge types. Periodic checks to ensure proper functioning and occasional cleaning are usually sufficient.
Conclusion:
In summary, the tipping bucket rain gauge is the most suitable rain gauge equipment for remote areas. Its simplicity, accuracy, reliability, and ability for remote data collection make it an ideal choice for collecting rainfall data in areas where accessibility and maintenance can be challenging.
What is a Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge?
A tipping bucket rain gauge is an instrument used to measure rainfall. It consists of a funnel-shaped collector that directs the rainwater into a bucket with a small opening at the bottom. The bucket is balanced on a pivot point, allowing it to tip from one side to the other when a certain amount of rainfall is collected.
How does a Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge work?
When rainwater enters the collector, it accumulates and eventually reaches a predetermined volume. Once this volume is reached, the bucket tips, causing the collected water to drain out and a new empty bucket to take its place. The tipping action is detected by a sensor, which records the number of tips. By knowing the volume of each tip, the rainfall amount can be calculated.
Advantages of Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge in Remote Areas:
1. Simplicity: Tipping bucket rain gauges are relatively simple and robust instruments, making them suitable for remote areas where maintenance and repairs may be challenging.
2. Accuracy: Tipping bucket rain gauges provide accurate measurements of rainfall. Since they measure rainfall in discrete volumes, they can capture both light drizzles and heavy downpours accurately.
3. Reliability: These gauges are designed to withstand harsh weather conditions, making them reliable for long-term operation in remote areas.
4. Remote Data Collection: Tipping bucket rain gauges can be equipped with data loggers or telemetry systems, allowing for remote data collection and real-time monitoring even in areas with limited accessibility.
5. Low Maintenance: The tipping bucket rain gauge requires minimal maintenance compared to other rain gauge types. Periodic checks to ensure proper functioning and occasional cleaning are usually sufficient.
Conclusion:
In summary, the tipping bucket rain gauge is the most suitable rain gauge equipment for remote areas. Its simplicity, accuracy, reliability, and ability for remote data collection make it an ideal choice for collecting rainfall data in areas where accessibility and maintenance can be challenging.
Rain gauge is used for ________- a)Hydrological survey
- b)Measuring precipitation
- c)Marine survey
- d)River survey
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rain gauge is used for ________
a)
Hydrological survey
b)
Measuring precipitation
c)
Marine survey
d)
River survey

|
Pallabi Chavan answered |
Measuring precipitation
A rain gauge is a device used to measure the amount of precipitation that falls at a specific location over a specific period of time. It is an essential tool in meteorology and hydrology for monitoring and studying weather patterns and water resources.
What is precipitation?
Precipitation refers to any form of water that falls from the atmosphere to the Earth's surface. This includes rain, snow, sleet, and hail. Precipitation is a vital component of the water cycle and plays a crucial role in maintaining the Earth's ecosystems and providing a fresh water supply.
Why is it important to measure precipitation?
Measuring precipitation is important for several reasons:
1. Weather forecasting: Precipitation data is crucial for accurate weather forecasting. It helps meteorologists predict and track storms, assess the potential for flooding, and issue warnings to the public.
2. Climate studies: Precipitation data is used to analyze long-term climate patterns and trends. By measuring precipitation over time, scientists can understand changes in regional and global climate and assess the impact of climate change.
3. Water resource management: Precipitation measurements are essential for managing water resources. They help determine the availability of freshwater supplies, assess drought conditions, and plan for irrigation, reservoir management, and flood control.
4. Agricultural planning: Farmers rely on precipitation data to make informed decisions about crop planting and irrigation. By understanding the amount and timing of precipitation, farmers can optimize their agricultural practices and minimize water usage.
5. Research and education: Precipitation data is used in various research studies to investigate the Earth's climate system, hydrological processes, and atmospheric dynamics. It is also an important educational tool for teaching students about weather, climate, and the water cycle.
How does a rain gauge work?
A rain gauge typically consists of a cylindrical container with a wide opening at the top to collect rainwater. The gauge is placed in an open area, away from obstructions such as trees or buildings, to ensure accurate measurements. As rain falls, it collects in the container, and the depth of the accumulated water is measured using a scale or ruler.
Modern rain gauges may also include electronic sensors to automatically measure and record precipitation data. These gauges can be connected to weather stations or data loggers for real-time monitoring and analysis.
Conclusion
In summary, a rain gauge is used for measuring precipitation, which is essential for various applications including weather forecasting, climate studies, water resource management, agricultural planning, research, and education. It helps us understand and monitor the Earth's water cycle and its impact on our environment and daily lives.
A rain gauge is a device used to measure the amount of precipitation that falls at a specific location over a specific period of time. It is an essential tool in meteorology and hydrology for monitoring and studying weather patterns and water resources.
What is precipitation?
Precipitation refers to any form of water that falls from the atmosphere to the Earth's surface. This includes rain, snow, sleet, and hail. Precipitation is a vital component of the water cycle and plays a crucial role in maintaining the Earth's ecosystems and providing a fresh water supply.
Why is it important to measure precipitation?
Measuring precipitation is important for several reasons:
1. Weather forecasting: Precipitation data is crucial for accurate weather forecasting. It helps meteorologists predict and track storms, assess the potential for flooding, and issue warnings to the public.
2. Climate studies: Precipitation data is used to analyze long-term climate patterns and trends. By measuring precipitation over time, scientists can understand changes in regional and global climate and assess the impact of climate change.
3. Water resource management: Precipitation measurements are essential for managing water resources. They help determine the availability of freshwater supplies, assess drought conditions, and plan for irrigation, reservoir management, and flood control.
4. Agricultural planning: Farmers rely on precipitation data to make informed decisions about crop planting and irrigation. By understanding the amount and timing of precipitation, farmers can optimize their agricultural practices and minimize water usage.
5. Research and education: Precipitation data is used in various research studies to investigate the Earth's climate system, hydrological processes, and atmospheric dynamics. It is also an important educational tool for teaching students about weather, climate, and the water cycle.
How does a rain gauge work?
A rain gauge typically consists of a cylindrical container with a wide opening at the top to collect rainwater. The gauge is placed in an open area, away from obstructions such as trees or buildings, to ensure accurate measurements. As rain falls, it collects in the container, and the depth of the accumulated water is measured using a scale or ruler.
Modern rain gauges may also include electronic sensors to automatically measure and record precipitation data. These gauges can be connected to weather stations or data loggers for real-time monitoring and analysis.
Conclusion
In summary, a rain gauge is used for measuring precipitation, which is essential for various applications including weather forecasting, climate studies, water resource management, agricultural planning, research, and education. It helps us understand and monitor the Earth's water cycle and its impact on our environment and daily lives.
Where are funnel and receiver in Non-recording type placed?- a)Inside a Metal case
- b)On top of the equipment
- c)Below the base of equipment
- d)In between the metal case
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Where are funnel and receiver in Non-recording type placed?
a)
Inside a Metal case
b)
On top of the equipment
c)
Below the base of equipment
d)
In between the metal case
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The non-recording gauge usually consists of a standard funnel discharging into a receiver large enough to hold the maximum possible day’s rainfall. The funnel and receiver are placed in a metal casing with suitable packing.
The Indian Meteorological department has changed over from Symon’s, gauge to fibreglass raingauges of two sizes. The collector areas of these gauges are:- a)(1000 cm2 and 500 cm2)
- b)(400 cm2 and 20 cm2)
- c)(200 cm2 and 100 cm2)
- d)(100 cm2 and 50 cm2)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The Indian Meteorological department has changed over from Symon’s, gauge to fibreglass raingauges of two sizes. The collector areas of these gauges are:
a)
(1000 cm2 and 500 cm2)
b)
(400 cm2 and 20 cm2)
c)
(200 cm2 and 100 cm2)
d)
(100 cm2 and 50 cm2)

|
Simran Mukherjee answered |
The Indian Meteorological department (IMD) has changed over to the use of fibreglass reinforced polyester raingauges, which is an improvement over the system gauge. These come in different combinations of collector and bottle. The collector in two sizes having areas of 200 and 100 cm2 respectively.
By DAD analysis the maximum average depth over an area of 104 km2 due to one-day storm is found to be 47 cm. For the same area the maximum average depth for a three day storm can be expected to be- a)< 47 cm
- b)> 47 cm
- c)= 47 cm
- d)inadequate information to conclude.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
By DAD analysis the maximum average depth over an area of 104 km2 due to one-day storm is found to be 47 cm. For the same area the maximum average depth for a three day storm can be expected to be
a)
< 47 cm
b)
> 47 cm
c)
= 47 cm
d)
inadequate information to conclude.

|
Dhruba Jain answered |
The maximum depth for a given storm decreases with the area. For a given area the maximum depth increases with the duration.
The standard recording raingauge adopted in India is of- a)weighing bucket type
- b)natural syphon type
- c)tipping bucket type
- d)telemetry type
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard recording raingauge adopted in India is of
a)
weighing bucket type
b)
natural syphon type
c)
tipping bucket type
d)
telemetry type

|
Shilpa Pillai answered |
Natural syphon type is adopted as the standard recording type rainguage in India. It is also known as float-type gauge.
Which gauge gives the permanent record of rainfall?- a)Recording gauge
- b)Non-recoding gauge
- c)Copper daily gauge
- d)Plastic gauge
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which gauge gives the permanent record of rainfall?
a)
Recording gauge
b)
Non-recoding gauge
c)
Copper daily gauge
d)
Plastic gauge
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
These are rain gauges which can give a permanent, automatic rainfall record in the form of a pen mounted on a clock driven chart. From the chart intensity or rate of rainfall in cm per hour. The recording is done by an attached siphon.
Rate of rainfall is expressed in _____________- a)Centimeters
- b)Millimeters
- c)Meters
- d)Kilometers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rate of rainfall is expressed in _____________
a)
Centimeters
b)
Millimeters
c)
Meters
d)
Kilometers
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
The rate of rainfall is expressed in centimeters of water during a given period of time. One centimeter rainfall is the quantity of water collected on a certain area due to rainfall which becomes one centimeter in height.
Instruments for measuring the intensity of incoming radiation are called- a)Pyrheliometers
- b)Sunshine recorders
- c)Hygrometers
- d)Psychrometers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Instruments for measuring the intensity of incoming radiation are called
a)
Pyrheliometers
b)
Sunshine recorders
c)
Hygrometers
d)
Psychrometers

|
Bhargavi Sengupta answered |
Pyheliometers for Measuring Incoming Radiation Intensity
Pyheliometers are instruments specifically designed to measure the intensity of incoming radiation. These instruments are widely used in meteorology, climatology, and solar energy studies to accurately measure solar radiation.
Key Points:
- Pyheliometers are essential tools for determining the amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface.
- These instruments typically consist of a receiver mounted on a stand with a tracking device to ensure it is always facing the sun.
- Pyheliometers are designed to measure direct beam radiation, which is the sunlight that reaches the Earth in a straight line without being scattered by the atmosphere.
- The data collected by pyheliometers is crucial for various applications, such as designing solar energy systems, studying climate patterns, and predicting weather conditions.
- Pyheliometers are calibrated regularly to ensure accurate measurements of solar radiation intensity.
- These instruments play a vital role in understanding the Earth's energy balance and the impact of solar radiation on our planet's climate.
In conclusion, pyheliometers are indispensable tools for measuring the intensity of incoming radiation, providing valuable data for a wide range of scientific studies and applications.
Pyheliometers are instruments specifically designed to measure the intensity of incoming radiation. These instruments are widely used in meteorology, climatology, and solar energy studies to accurately measure solar radiation.
Key Points:
- Pyheliometers are essential tools for determining the amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface.
- These instruments typically consist of a receiver mounted on a stand with a tracking device to ensure it is always facing the sun.
- Pyheliometers are designed to measure direct beam radiation, which is the sunlight that reaches the Earth in a straight line without being scattered by the atmosphere.
- The data collected by pyheliometers is crucial for various applications, such as designing solar energy systems, studying climate patterns, and predicting weather conditions.
- Pyheliometers are calibrated regularly to ensure accurate measurements of solar radiation intensity.
- These instruments play a vital role in understanding the Earth's energy balance and the impact of solar radiation on our planet's climate.
In conclusion, pyheliometers are indispensable tools for measuring the intensity of incoming radiation, providing valuable data for a wide range of scientific studies and applications.
Calculate the total rainfall in an interval, where volume of the bucket is taken as 24cu. m and time interval N = 3.- a)72cu. m
- b)2cu. m
- c)27cu. m
- d)72sq. m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the total rainfall in an interval, where volume of the bucket is taken as 24cu. m and time interval N = 3.
a)
72cu. m
b)
2cu. m
c)
27cu. m
d)
72sq. m
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
The total rainfall in the given interval is determined by using the formula,
Rainfall = N*v. on substitution, we get
Rainfall = 3*24 = 72cu. m.
Rainfall = N*v. on substitution, we get
Rainfall = 3*24 = 72cu. m.
In installing a raingauge network, the relevant Indian standard recommend that- a)The density of gauges should be more in plains than in hills
- b)In regions having an average elevations of 1000 m, at least one station per 130 km2 is desired
- c)At least 50% of raingauge stations should be of recording type
- d)At least 10% of raingauge station should be of recording type
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In installing a raingauge network, the relevant Indian standard recommend that
a)
The density of gauges should be more in plains than in hills
b)
In regions having an average elevations of 1000 m, at least one station per 130 km2 is desired
c)
At least 50% of raingauge stations should be of recording type
d)
At least 10% of raingauge station should be of recording type

|
Sreemoyee Joshi answered |
Indian Standards for Raingauge Network Installation
Density of Gauges
The Indian standard does not recommend a higher density of gauges in plains than in hills.
Average Elevation
The Indian standard recommends at least one station per 130 km2 in regions having an average elevation of 1000 m.
Type of Raingauge Stations
The Indian standard recommends that at least 50% of raingauge stations should be of recording type.
Recording Type Raingauge Stations
Recording type raingauge stations record rainfall data continuously, providing more accurate and detailed information. Therefore, the Indian standard recommends that at least 10% of raingauge stations should be of recording type to improve the accuracy of the data collected.
Density of Gauges
The Indian standard does not recommend a higher density of gauges in plains than in hills.
Average Elevation
The Indian standard recommends at least one station per 130 km2 in regions having an average elevation of 1000 m.
Type of Raingauge Stations
The Indian standard recommends that at least 50% of raingauge stations should be of recording type.
Recording Type Raingauge Stations
Recording type raingauge stations record rainfall data continuously, providing more accurate and detailed information. Therefore, the Indian standard recommends that at least 10% of raingauge stations should be of recording type to improve the accuracy of the data collected.
The probable maximum depth of precipitation over a catchment is given by the relation PMP =- a)
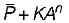
- b)

- c)
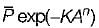
- d)
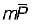
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The probable maximum depth of precipitation over a catchment is given by the relation PMP =
a)
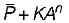
b)

c)
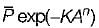
d)
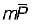

|
Dipika Nambiar answered |
The Probable Maximum Precipitation (PMP) is defined as the greatest or extreme rainfall for a given duration that is physically possible over a station or basin. Statistical studies indicate that PMP can be estimated as,
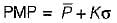
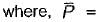 mean of annual maximum rainfall series, σ = standard deviation of the series and K = a frequency factor which depends upon th e statistical distribution of the series, number of years of record and the return period.
mean of annual maximum rainfall series, σ = standard deviation of the series and K = a frequency factor which depends upon th e statistical distribution of the series, number of years of record and the return period.
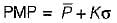
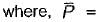 mean of annual maximum rainfall series, σ = standard deviation of the series and K = a frequency factor which depends upon th e statistical distribution of the series, number of years of record and the return period.
mean of annual maximum rainfall series, σ = standard deviation of the series and K = a frequency factor which depends upon th e statistical distribution of the series, number of years of record and the return period.The average annual rainfall over the whole of India is estimated as- a)189 cm
- b)319 cm
- c)89 cm
- d)119 cm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The average annual rainfall over the whole of India is estimated as
a)
189 cm
b)
319 cm
c)
89 cm
d)
119 cm

|
Aditya Jain answered |
The average annual rainfall over the whole of India is estimated as 119 cm.
Factors Affecting Rainfall in India:
- Monsoons: The monsoon winds play a crucial role in determining the rainfall pattern in India. The country experiences two major monsoons: the Southwest Monsoon and the Northeast Monsoon. The Southwest Monsoon, which occurs from June to September, brings the majority of the rainfall to most parts of India.
- Terrain: The diverse topography of India influences the distribution of rainfall. The Western Ghats and the Himalayan mountain ranges act as barriers, causing the winds to rise and cool, resulting in heavy rainfall on the windward side of these ranges.
- Location: Different regions in India receive varying amounts of rainfall based on their geographical location. Coastal regions generally receive more rainfall than inland areas.
- Weather Systems: Weather systems such as cyclones and depressions can bring heavy rainfall to specific regions.
- El Niño and La Niña: These climate phenomena can impact the Indian monsoon and, consequently, the rainfall pattern.
Calculation of Average Annual Rainfall:
To estimate the average annual rainfall over the whole of India, data from various meteorological stations across the country is collected. These stations record the amount of rainfall received in a given year. The data is then combined and averaged to determine the average annual rainfall.
Explanation of Correct Answer:
The correct answer, option 'D' (119 cm), is the estimated average annual rainfall over the whole of India. This value represents the overall average rainfall received in India over a significant period of time, considering the data from various meteorological stations across the country.
It is important to note that the rainfall pattern can vary significantly from year to year. Some years may experience above-average rainfall, while others may experience below-average rainfall. However, the long-term average provides a reliable estimate of the overall rainfall pattern in a specific region or country.
Overall, understanding the factors influencing rainfall and calculating the average annual rainfall is crucial for various sectors such as agriculture, water resource management, and urban planning. It helps in assessing the water availability, planning irrigation systems, and mitigating the impacts of droughts or flood events.
Factors Affecting Rainfall in India:
- Monsoons: The monsoon winds play a crucial role in determining the rainfall pattern in India. The country experiences two major monsoons: the Southwest Monsoon and the Northeast Monsoon. The Southwest Monsoon, which occurs from June to September, brings the majority of the rainfall to most parts of India.
- Terrain: The diverse topography of India influences the distribution of rainfall. The Western Ghats and the Himalayan mountain ranges act as barriers, causing the winds to rise and cool, resulting in heavy rainfall on the windward side of these ranges.
- Location: Different regions in India receive varying amounts of rainfall based on their geographical location. Coastal regions generally receive more rainfall than inland areas.
- Weather Systems: Weather systems such as cyclones and depressions can bring heavy rainfall to specific regions.
- El Niño and La Niña: These climate phenomena can impact the Indian monsoon and, consequently, the rainfall pattern.
Calculation of Average Annual Rainfall:
To estimate the average annual rainfall over the whole of India, data from various meteorological stations across the country is collected. These stations record the amount of rainfall received in a given year. The data is then combined and averaged to determine the average annual rainfall.
Explanation of Correct Answer:
The correct answer, option 'D' (119 cm), is the estimated average annual rainfall over the whole of India. This value represents the overall average rainfall received in India over a significant period of time, considering the data from various meteorological stations across the country.
It is important to note that the rainfall pattern can vary significantly from year to year. Some years may experience above-average rainfall, while others may experience below-average rainfall. However, the long-term average provides a reliable estimate of the overall rainfall pattern in a specific region or country.
Overall, understanding the factors influencing rainfall and calculating the average annual rainfall is crucial for various sectors such as agriculture, water resource management, and urban planning. It helps in assessing the water availability, planning irrigation systems, and mitigating the impacts of droughts or flood events.
Tipping bucket used in the rain gauge will turn under the action of ___________- a)Battery
- b)Hand movement
- c)Gravity
- d)Motor
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Tipping bucket used in the rain gauge will turn under the action of ___________
a)
Battery
b)
Hand movement
c)
Gravity
d)
Motor
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Tipping bucket is provided in the rain gauge for collecting the required amount of rainfall needed for measurement of the precipitation in the atmosphere. After being filled to the maximum level, the tipping bucket will turn under the action of gravity.
Rainfall is also known as ___________- a)Precipitation
- b)Condensation
- c)Infiltration
- d)Down pour
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rainfall is also known as ___________
a)
Precipitation
b)
Condensation
c)
Infiltration
d)
Down pour
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
The rainfall is also known as precipitation, is a natural process of atmospheric vapor into water. Atmospheric vapor are nothing but clouds which are contamination of air and water. When the temperature goes below dew point then precipitation takes place.
Chapter doubts & questions for Precipitation & Its Measurement - Engineering Hydrology 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Precipitation & Its Measurement - Engineering Hydrology in English & Hindi are available as part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Engineering Hydrology
20 videos|53 docs|30 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









