All Exams >
Electrical Engineering (EE) >
Electrical and Electronic Measurements >
All Questions
All questions of Digital Voltmeter (DVM) for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam
A voltmeter connected across 15 kΩ resistor reads 10 V in the circuit given. Voltmeter is rated at 500 Ω / volt and has a full- scale reading of 20 V. The supply voltage is:
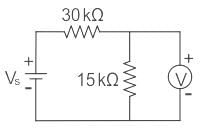
- a)60 V
- b)45 V
- c)30 V
- d)90 V
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A voltmeter connected across 15 kΩ resistor reads 10 V in the circuit given. Voltmeter is rated at 500 Ω / volt and has a full- scale reading of 20 V. The supply voltage is:


a)
60 V
b)
45 V
c)
30 V
d)
90 V

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
Concept:
The voltmeter sensitivity (Sv) is determined by dividing the sum of the resistance of the meter (Rm)
Mathematically, sensitivity is expressed as:
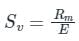
E = Rated Voltage or Full scale Reading
Voltmeter sensitivity is expressed in Ohm/Volt
Rm = Sv × E
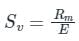
E = Rated Voltage or Full scale Reading
Voltmeter sensitivity is expressed in Ohm/Volt
Rm = Sv × E
Calculation:
Sensitivity of voltmeter = 500 Ω/V
Internal resistance of voltmeter = 500 ×
20 = 10 kΩ
Effective resistance across A – B is
= 10 || 15 = 6 kΩ
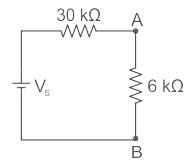
The voltmeter reading is 10 V
⇒ VAB = 10 V
By voltage division,
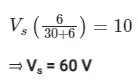
Sensitivity of voltmeter = 500 Ω/V
Internal resistance of voltmeter = 500 ×
20 = 10 kΩ
Effective resistance across A – B is
= 10 || 15 = 6 kΩ

The voltmeter reading is 10 V
⇒ VAB = 10 V
By voltage division,
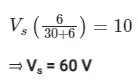
In a dual slope integrating type DVM, the accuracy of measured voltage ________ on the integrating time constant and ______ of frequency of oscillation.- a)depends, independent
- b)doesn't depend, function
- c)doesn't depend, independent
- d)depends, function
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a dual slope integrating type DVM, the accuracy of measured voltage ________ on the integrating time constant and ______ of frequency of oscillation.
a)
depends, independent
b)
doesn't depend, function
c)
doesn't depend, independent
d)
depends, function
|
|
Samridhi Bose answered |
Accuracy of Measured Voltage in a Dual Slope Integrating Type DVM
The accuracy of a measured voltage in a dual slope integrating type digital voltmeter (DVM) is independent of the integrating time constant and the frequency of oscillation.
Explanation:
Dual Slope Integrating Type DVM:
A dual slope integrating type DVM is a type of digital voltmeter that uses an integrating technique to measure the voltage. The voltage to be measured is integrated over a known time period and then compared with a reference voltage. The time taken for the integration process is measured and converted into a digital display.
Accuracy of Measured Voltage:
The accuracy of a measured voltage refers to how close the measured value is to the true value. In a dual slope integrating type DVM, the accuracy is determined by various factors, such as the resolution of the instrument, noise levels, and linearity of the integrating circuit.
Independence of Accuracy on Integrating Time Constant and Frequency of Oscillation:
The accuracy of a measured voltage in a dual slope integrating type DVM is independent of the integrating time constant and the frequency of oscillation due to the following reasons:
1. Integrating Time Constant (T):
The integrating time constant determines the length of time over which the voltage is integrated. It is usually selected based on the range of the input voltage. However, the accuracy of the measurement is not affected by the integrating time constant as long as it is within the specified range. The accuracy is primarily dependent on the resolution and linearity of the integrating circuit.
2. Frequency of Oscillation:
The frequency of oscillation is the frequency at which the integrating capacitor is discharged during the measurement process. The frequency affects the time taken for the voltage to reach the reference level and also influences the noise levels in the system. However, the accuracy of the measurement is not affected by the frequency of oscillation as long as it is within the specified range. The accuracy is primarily dependent on the resolution and linearity of the integrating circuit.
Conclusion:
In a dual slope integrating type DVM, the accuracy of the measured voltage is independent of the integrating time constant and the frequency of oscillation. The accuracy is primarily determined by the resolution and linearity of the integrating circuit.
The accuracy of a measured voltage in a dual slope integrating type digital voltmeter (DVM) is independent of the integrating time constant and the frequency of oscillation.
Explanation:
Dual Slope Integrating Type DVM:
A dual slope integrating type DVM is a type of digital voltmeter that uses an integrating technique to measure the voltage. The voltage to be measured is integrated over a known time period and then compared with a reference voltage. The time taken for the integration process is measured and converted into a digital display.
Accuracy of Measured Voltage:
The accuracy of a measured voltage refers to how close the measured value is to the true value. In a dual slope integrating type DVM, the accuracy is determined by various factors, such as the resolution of the instrument, noise levels, and linearity of the integrating circuit.
Independence of Accuracy on Integrating Time Constant and Frequency of Oscillation:
The accuracy of a measured voltage in a dual slope integrating type DVM is independent of the integrating time constant and the frequency of oscillation due to the following reasons:
1. Integrating Time Constant (T):
The integrating time constant determines the length of time over which the voltage is integrated. It is usually selected based on the range of the input voltage. However, the accuracy of the measurement is not affected by the integrating time constant as long as it is within the specified range. The accuracy is primarily dependent on the resolution and linearity of the integrating circuit.
2. Frequency of Oscillation:
The frequency of oscillation is the frequency at which the integrating capacitor is discharged during the measurement process. The frequency affects the time taken for the voltage to reach the reference level and also influences the noise levels in the system. However, the accuracy of the measurement is not affected by the frequency of oscillation as long as it is within the specified range. The accuracy is primarily dependent on the resolution and linearity of the integrating circuit.
Conclusion:
In a dual slope integrating type DVM, the accuracy of the measured voltage is independent of the integrating time constant and the frequency of oscillation. The accuracy is primarily determined by the resolution and linearity of the integrating circuit.
Multiplication features are incorporated in an ohmmeter to enable the meter to ________.- a)measure very high resistance values
- b)measure values with the least error
- c)be multipurpose in its application
- d)has less power consumption
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Multiplication features are incorporated in an ohmmeter to enable the meter to ________.
a)
measure very high resistance values
b)
measure values with the least error
c)
be multipurpose in its application
d)
has less power consumption
|
|
Mahesh Singh answered |
Introduction:
An ohmmeter is a device used to measure the resistance of an electrical component. It typically consists of a galvanometer and a series resistor. However, to enhance its functionality and accuracy, multiplication features are incorporated in an ohmmeter.
Explanation:
The multiplication features in an ohmmeter enable the meter to measure values with the least error. Let's understand this in detail:
1. Measurement Accuracy:
- When measuring resistance using an ohmmeter, it is important to minimize errors. The multiplication feature helps in achieving higher accuracy by reducing the impact of various factors that can affect the measurement, such as galvanometer sensitivity, internal resistance, and lead resistance.
- By incorporating multiplication features, the ohmmeter can compensate for these factors and provide more accurate resistance measurements.
2. Range Selection:
- An ohmmeter typically has multiple ranges to measure different resistance values. The multiplication feature allows the ohmmeter to automatically select the appropriate range based on the resistance being measured.
- For example, if a high resistance value is being measured, the ohmmeter can switch to a higher range by multiplying the reading to provide a more precise measurement.
3. Error Reduction:
- When measuring low resistance values, the internal resistance of the ohmmeter can introduce errors in the measurement. The multiplication feature in the ohmmeter helps in reducing these errors by compensating for the internal resistance.
- By multiplying the measured resistance value, the ohmmeter provides a corrected reading that accounts for the internal resistance, resulting in a more accurate measurement.
4. Enhanced Functionality:
- Multiplication features in an ohmmeter make it more versatile and multipurpose in its application. It can be used to measure a wide range of resistance values, including both high and low resistance values.
- This versatility allows the ohmmeter to be used in various electrical engineering applications, such as testing circuits, troubleshooting faults, and verifying component values.
Conclusion:
Incorporating multiplication features in an ohmmeter enhances its accuracy, reduces errors, enables range selection, and makes it more versatile in its application. By multiplying the measured resistance values, the ohmmeter provides more precise readings, making it a valuable tool for electrical engineers and technicians.
An ohmmeter is a device used to measure the resistance of an electrical component. It typically consists of a galvanometer and a series resistor. However, to enhance its functionality and accuracy, multiplication features are incorporated in an ohmmeter.
Explanation:
The multiplication features in an ohmmeter enable the meter to measure values with the least error. Let's understand this in detail:
1. Measurement Accuracy:
- When measuring resistance using an ohmmeter, it is important to minimize errors. The multiplication feature helps in achieving higher accuracy by reducing the impact of various factors that can affect the measurement, such as galvanometer sensitivity, internal resistance, and lead resistance.
- By incorporating multiplication features, the ohmmeter can compensate for these factors and provide more accurate resistance measurements.
2. Range Selection:
- An ohmmeter typically has multiple ranges to measure different resistance values. The multiplication feature allows the ohmmeter to automatically select the appropriate range based on the resistance being measured.
- For example, if a high resistance value is being measured, the ohmmeter can switch to a higher range by multiplying the reading to provide a more precise measurement.
3. Error Reduction:
- When measuring low resistance values, the internal resistance of the ohmmeter can introduce errors in the measurement. The multiplication feature in the ohmmeter helps in reducing these errors by compensating for the internal resistance.
- By multiplying the measured resistance value, the ohmmeter provides a corrected reading that accounts for the internal resistance, resulting in a more accurate measurement.
4. Enhanced Functionality:
- Multiplication features in an ohmmeter make it more versatile and multipurpose in its application. It can be used to measure a wide range of resistance values, including both high and low resistance values.
- This versatility allows the ohmmeter to be used in various electrical engineering applications, such as testing circuits, troubleshooting faults, and verifying component values.
Conclusion:
Incorporating multiplication features in an ohmmeter enhances its accuracy, reduces errors, enables range selection, and makes it more versatile in its application. By multiplying the measured resistance values, the ohmmeter provides more precise readings, making it a valuable tool for electrical engineers and technicians.
Which of the following is an advantage of the analog multimeter over the digital multimeter?- a)No loading effect
- b)High accuracy
- c)Smaller size
- d)Less electric noise
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an advantage of the analog multimeter over the digital multimeter?
a)
No loading effect
b)
High accuracy
c)
Smaller size
d)
Less electric noise
|
|
Aman Jain answered |
Advantage of Analog Multimeter over Digital Multimeter:
Advantage: Less electric noise
The analog multimeter has an advantage over the digital multimeter in terms of generating less electric noise. This is a significant advantage in certain situations where precise measurements are required without interference from external electrical noise.
Explanation:
Electric Noise:
- Electric noise refers to unwanted electrical signals that can interfere with the accuracy of measurements taken by a multimeter.
- Digital multimeters are more susceptible to electric noise because of the sensitive electronic components used in their design.
- Analog multimeters, on the other hand, are less prone to picking up electric noise due to their simpler design and the use of analog components.
Less Susceptibility to Noise:
- Analog multimeters use analog circuits and moving pointers to display measurements, which are less affected by electric noise compared to digital displays.
- The analog nature of these multimeters allows for smoother readings without the presence of digital artifacts caused by electric noise.
Advantages of Less Electric Noise:
- Accurate measurements: With less electric noise interference, analog multimeters can provide more accurate readings in noisy environments.
- Reliable readings: The absence of electric noise ensures that the measurements displayed on an analog multimeter are more reliable and consistent.
- Better performance: In critical applications where precise measurements are essential, the lower susceptibility to electric noise gives analog multimeters an edge over digital ones.
In conclusion, the advantage of less electric noise makes analog multimeters a preferred choice in certain scenarios where accurate and reliable measurements are crucial.
Advantage: Less electric noise
The analog multimeter has an advantage over the digital multimeter in terms of generating less electric noise. This is a significant advantage in certain situations where precise measurements are required without interference from external electrical noise.
Explanation:
Electric Noise:
- Electric noise refers to unwanted electrical signals that can interfere with the accuracy of measurements taken by a multimeter.
- Digital multimeters are more susceptible to electric noise because of the sensitive electronic components used in their design.
- Analog multimeters, on the other hand, are less prone to picking up electric noise due to their simpler design and the use of analog components.
Less Susceptibility to Noise:
- Analog multimeters use analog circuits and moving pointers to display measurements, which are less affected by electric noise compared to digital displays.
- The analog nature of these multimeters allows for smoother readings without the presence of digital artifacts caused by electric noise.
Advantages of Less Electric Noise:
- Accurate measurements: With less electric noise interference, analog multimeters can provide more accurate readings in noisy environments.
- Reliable readings: The absence of electric noise ensures that the measurements displayed on an analog multimeter are more reliable and consistent.
- Better performance: In critical applications where precise measurements are essential, the lower susceptibility to electric noise gives analog multimeters an edge over digital ones.
In conclusion, the advantage of less electric noise makes analog multimeters a preferred choice in certain scenarios where accurate and reliable measurements are crucial.
What is the resolution of 4-digit digital measuring instrument? - a)0.002%
- b)0.005%
- c)0.1%
- d)0.01%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the resolution of 4-digit digital measuring instrument?
a)
0.002%
b)
0.005%
c)
0.1%
d)
0.01%
|
|
Pooja Patel answered |
Concept:
Resolution: It is the smallest increment an instrument can detect and display.
- The resolution for the 'N' bit digital voltmeter is given by:
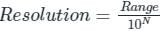
- The range of an instrument is the sum of the smallest and the largest number it can display.
For 4-digit, the smallest and the largest number that can be displayed is:
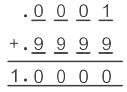
Range = 1
Resolution = 1/104
Resolution = 10-4 = 0.0001
In percentage, the resolution is 0.01%

Range = 1
Resolution = 1/104
Resolution = 10-4 = 0.0001
In percentage, the resolution is 0.01%
A DVM has a 3½ digit display. The 1-volt range can read upon- a)9999
- b)9.99
- c)1.999
- d)0.19999
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A DVM has a 3½ digit display. The 1-volt range can read upon
a)
9999
b)
9.99
c)
1.999
d)
0.19999
|
|
Jyoti Basak answered |
A DVM (Doctor of Veterinary Medicine) has a 3-year professional degree program at an accredited veterinary school.
In a digital multi-meter, AC voltage, DC current, AC current and resistance are first converted into equivalent ________ by a device and then measured with the help of a digital voltmeter.- a)DC voltage
- b)Resistance
- c)Inductance
- d)Capacitance
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a digital multi-meter, AC voltage, DC current, AC current and resistance are first converted into equivalent ________ by a device and then measured with the help of a digital voltmeter.
a)
DC voltage
b)
Resistance
c)
Inductance
d)
Capacitance
|
|
Pooja Patel answered |
Digital Multimeter:
- A digital multimeter is an electronic instrument that can measure very precisely the dc and ac voltage, current (dc and ac), and resistance.
- All quantities other than dc voltage are first converted into an equivalent dc voltage by some device and then measured with the help of a digital voltmeter.
- Multimeters measure resistance by injecting a small current into the circuit and then measuring the voltage drop across those points in the circuit.
- The known current and the resulting voltage drop are then used to calculate the resistance using Ohm's Law.
In a digital voltmeter, during start of conversion, zero indication is displayed and is called auto zeroing. This is achieved by - a)Using a positive reference voltage
- b)Using a negative reference voltage
- c)Properly charging the differentiator circuit capacitance to ground
- d)Properly discharging the integrator circuit capacitance to ground
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a digital voltmeter, during start of conversion, zero indication is displayed and is called auto zeroing. This is achieved by
a)
Using a positive reference voltage
b)
Using a negative reference voltage
c)
Properly charging the differentiator circuit capacitance to ground
d)
Properly discharging the integrator circuit capacitance to ground
|
|
Pooja Patel answered |
In a digital voltmeter, during start of conversion, zero indication is displayed. This is known as auto zeroing.
The circuit is used for this purpose is shown below.
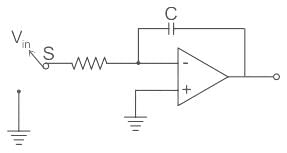
It consists of an integrator. To achieve auto zeroing, the switch S is connected from Vin to the ground potential and the capacitor C of the dual-slope integrator discharges to the ground.
The circuit is used for this purpose is shown below.

It consists of an integrator. To achieve auto zeroing, the switch S is connected from Vin to the ground potential and the capacitor C of the dual-slope integrator discharges to the ground.
A 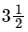 digit voltmeter has the resolution of
digit voltmeter has the resolution of- a)0.01% of the full range
- b)0.05% of the full range
- c)0.1% of the full range
- d)0.5% of the full range
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A 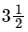 digit voltmeter has the resolution of
digit voltmeter has the resolution of
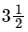 digit voltmeter has the resolution of
digit voltmeter has the resolution ofa)
0.01% of the full range
b)
0.05% of the full range
c)
0.1% of the full range
d)
0.5% of the full range
|
|
Pooja Patel answered |
Concept:
The resolution (R) in an N bit DVM is given by:

Where N is the number of full digits.
In a DVM, a full digit counts 0 to 9 and a half digit counts from 0 to 1.
For N and half DVM resolution (R) is given by:

The resolution (R) in an N bit DVM is given by:

Where N is the number of full digits.
In a DVM, a full digit counts 0 to 9 and a half digit counts from 0 to 1.
For N and half DVM resolution (R) is given by:

Calculation:
Given that,
N = 3(1/2)

%R = (1/2000) × 100 × of full range
%R = 0.05 % of full range
Given that,
N = 3(1/2)

%R = (1/2000) × 100 × of full range
%R = 0.05 % of full range
A reading of 100V on a digital multimeter ranges from 97V to 103V. Compute the accuracy.- a)±0.3%
- b)±6%
- c)±1.5%
- d)±3%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A reading of 100V on a digital multimeter ranges from 97V to 103V. Compute the accuracy.
a)
±0.3%
b)
±6%
c)
±1.5%
d)
±3%
|
|
Pooja Patel answered |
Digital multimeter:
- Digital multimeter present measurement data in a direct format that does not require calculating the exact value, and they are free from the parallax error of analog meters.
- Unlike meter movements in analog meters, digital multimeter displays have no moving parts, and they are free from wear and shock failures.
- Digital multimeters automatically detect polarity, show positive and negative values, have much better overload protection, and offer automatic as well as manual range selection options.
Calculation:
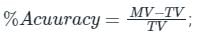
Here, MV = Measured value
TV = True value
Given, Lowest range of Measured Value(ML) = 97
Highest range of Measured Value(MH) = 103
True Value = 100
therefore,
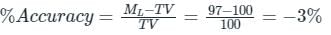
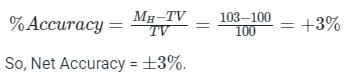
Chapter doubts & questions for Digital Voltmeter (DVM) - Electrical and Electronic Measurements 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Digital Voltmeter (DVM) - Electrical and Electronic Measurements in English & Hindi are available as part of Electrical Engineering (EE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Electrical and Electronic Measurements
48 videos|48 docs|23 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









