All Exams >
Class 9 >
Social Studies (SST) Class 9 >
All Questions
All questions of Sample Papers with Solutions for Class 9 Exam
Whom did Louis XVI get married?- a)Olympe de Gouges
- b)Marie Antoinette
- c)Marie de Medicis
- d)Nanine Vallain
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Whom did Louis XVI get married?
a)
Olympe de Gouges
b)
Marie Antoinette
c)
Marie de Medicis
d)
Nanine Vallain
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
In 1774, Louis XVI of the Bourbon family of kings ascended the throne of France. He was 20 years old and married to the Austrian princess Marie Antoinette.
On the physical map of India, A and B are marked as two parallel ranges of central India. Identify it from the following options.
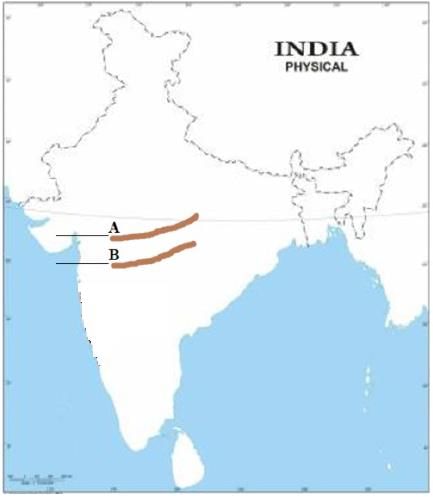
- a)Aravali Hills and Vindhya range
- b)Satpura range and Shiwaliks
- c)Vindhya Range and Satpura range
- d)Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
On the physical map of India, A and B are marked as two parallel ranges of central India. Identify it from the following options.


a)
Aravali Hills and Vindhya range
b)
Satpura range and Shiwaliks
c)
Vindhya Range and Satpura range
d)
Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
The Vindhyan range is bounded by the Satpura range on the south and the Aravalis on the northwest.
Question No. 47 to 52 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
India is one of the ancient civilisations in the world. It has achieved multifaceted socio-economic progress during the last five decades. It has moved forward displaying remarkable progress in the field of agriculture, industry, technology, and overall economic development. India has also contributed significantly to the making of world history. India is a vast country. Lying entirely in the Northern hemisphere the mainland extends between latitudes 8°4'N and 37°6'N and longitudes 68°7'E and 97°25'E. The Tropic of Cancer divides the country into almost two equal parts. To the southeast and southwest of the mainland, lie the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and the Lakshadweep Islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea respectively. The southernmost point of the Indian Union was submerged under the seawater in 2004 during the Tsunami.Q. Find the relation between A and B in each group and fill in the blank accordingly.
A: Arabian Sea: Lakshadweep islands
B: Bay of Bengal: ________.- a)Majuli Island
- b)None of these
- c)Kavaratti islands
- d)Andaman and Nicobar islands
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question No. 47 to 52 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
India is one of the ancient civilisations in the world. It has achieved multifaceted socio-economic progress during the last five decades. It has moved forward displaying remarkable progress in the field of agriculture, industry, technology, and overall economic development. India has also contributed significantly to the making of world history. India is a vast country. Lying entirely in the Northern hemisphere the mainland extends between latitudes 8°4'N and 37°6'N and longitudes 68°7'E and 97°25'E. The Tropic of Cancer divides the country into almost two equal parts. To the southeast and southwest of the mainland, lie the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and the Lakshadweep Islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea respectively. The southernmost point of the Indian Union was submerged under the seawater in 2004 during the Tsunami.
India is one of the ancient civilisations in the world. It has achieved multifaceted socio-economic progress during the last five decades. It has moved forward displaying remarkable progress in the field of agriculture, industry, technology, and overall economic development. India has also contributed significantly to the making of world history. India is a vast country. Lying entirely in the Northern hemisphere the mainland extends between latitudes 8°4'N and 37°6'N and longitudes 68°7'E and 97°25'E. The Tropic of Cancer divides the country into almost two equal parts. To the southeast and southwest of the mainland, lie the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and the Lakshadweep Islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea respectively. The southernmost point of the Indian Union was submerged under the seawater in 2004 during the Tsunami.
Q. Find the relation between A and B in each group and fill in the blank accordingly.
A: Arabian Sea: Lakshadweep islands
B: Bay of Bengal: ________.
A: Arabian Sea: Lakshadweep islands
B: Bay of Bengal: ________.
a)
Majuli Island
b)
None of these
c)
Kavaratti islands
d)
Andaman and Nicobar islands
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
To the southeast and southwest of the mainland, lie the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and the Lakshadweep Islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea respectively.
Question No. 53 to 58 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
Zimbabwe attained independence from White minority rule in 1980. Since then the country has been ruled by ZANU-PF, the party that led the freedom struggle. Its leader, Robert Mugabe, ruled the country since independence. Elections were held regularly and always won by ZANU-PF. President Mugabe was popular but also used unfair practices in elections. Over the years his government changed the constitution several times to increase the powers of the President and make him less accountable.
Opposition party workers were harassed and their meetings disrupted. Public protests and demonstrations against the government were declared illegal. There was a law that limited the right to criticise the President. Television and radio were controlled by the government and gave only the ruling party’s version. There were independent newspapers but the government harassed those journalists who went against it. The government ignored some court judgments that went against it and pressurised judges. He was forced out of office in 2017. The example of Zimbabwe shows that popular approval of the rulers is necessary for a democracy, but it is not sufficient. Popular governments can be undemocratic. Popular leaders can be autocratic. If we wish to assess a democracy, it is important to look at the elections. But it is equally important to look before and after the elections. There should be sufficient room for normal political activity, including political opposition, in the period before elections. This requires that the state should respect some basic rights of the citizen. They should be free to think, to have opinions, to express these in public, to form associations, to protest and take other political actions. Everyone should be equal in the eyes of law. These rights must be protected by an independent judiciary whose orders are obeyed by everyone.Q. Assertion (A): The media was not independent in Zimbabwe.
Reason (R): Television and radio had freedom of the press and gave fair and equitable version.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true but R is false.
- d)A is false but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question No. 53 to 58 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
Zimbabwe attained independence from White minority rule in 1980. Since then the country has been ruled by ZANU-PF, the party that led the freedom struggle. Its leader, Robert Mugabe, ruled the country since independence. Elections were held regularly and always won by ZANU-PF. President Mugabe was popular but also used unfair practices in elections. Over the years his government changed the constitution several times to increase the powers of the President and make him less accountable.
Opposition party workers were harassed and their meetings disrupted. Public protests and demonstrations against the government were declared illegal. There was a law that limited the right to criticise the President. Television and radio were controlled by the government and gave only the ruling party’s version. There were independent newspapers but the government harassed those journalists who went against it. The government ignored some court judgments that went against it and pressurised judges. He was forced out of office in 2017. The example of Zimbabwe shows that popular approval of the rulers is necessary for a democracy, but it is not sufficient. Popular governments can be undemocratic. Popular leaders can be autocratic. If we wish to assess a democracy, it is important to look at the elections. But it is equally important to look before and after the elections. There should be sufficient room for normal political activity, including political opposition, in the period before elections. This requires that the state should respect some basic rights of the citizen. They should be free to think, to have opinions, to express these in public, to form associations, to protest and take other political actions. Everyone should be equal in the eyes of law. These rights must be protected by an independent judiciary whose orders are obeyed by everyone.
Zimbabwe attained independence from White minority rule in 1980. Since then the country has been ruled by ZANU-PF, the party that led the freedom struggle. Its leader, Robert Mugabe, ruled the country since independence. Elections were held regularly and always won by ZANU-PF. President Mugabe was popular but also used unfair practices in elections. Over the years his government changed the constitution several times to increase the powers of the President and make him less accountable.
Opposition party workers were harassed and their meetings disrupted. Public protests and demonstrations against the government were declared illegal. There was a law that limited the right to criticise the President. Television and radio were controlled by the government and gave only the ruling party’s version. There were independent newspapers but the government harassed those journalists who went against it. The government ignored some court judgments that went against it and pressurised judges. He was forced out of office in 2017. The example of Zimbabwe shows that popular approval of the rulers is necessary for a democracy, but it is not sufficient. Popular governments can be undemocratic. Popular leaders can be autocratic. If we wish to assess a democracy, it is important to look at the elections. But it is equally important to look before and after the elections. There should be sufficient room for normal political activity, including political opposition, in the period before elections. This requires that the state should respect some basic rights of the citizen. They should be free to think, to have opinions, to express these in public, to form associations, to protest and take other political actions. Everyone should be equal in the eyes of law. These rights must be protected by an independent judiciary whose orders are obeyed by everyone.
Q. Assertion (A): The media was not independent in Zimbabwe.
Reason (R): Television and radio had freedom of the press and gave fair and equitable version.
Reason (R): Television and radio had freedom of the press and gave fair and equitable version.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true but R is false.
d)
A is false but R is true.

|
Crafty Classes answered |
A is true but R is false.
Democracy originated:- a)in the US after freeing itself from British tyranny.
- b)in the UK, after the signing of Magna Carta.
- c)in France after the Revolution.
- d)in ancient Greece.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Democracy originated:
a)
in the US after freeing itself from British tyranny.
b)
in the UK, after the signing of Magna Carta.
c)
in France after the Revolution.
d)
in ancient Greece.
|
|
Aditi Sharma answered |
Full democracy was not established in the US, the UK, or France until the twentieth century.
In the secondary sector which of the following is the most labour absorbing?- a)Mining
- b)Quarrying
- c)Trade
- d)Small scale manufacturing
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the secondary sector which of the following is the most labour absorbing?
a)
Mining
b)
Quarrying
c)
Trade
d)
Small scale manufacturing
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
Small scale manufacturing is the most labour absorbing sector of the secondary sector.
The famous political party of Mexico was:- a)Revolutionary party
- b)Chinese Communist party
- c)Institutional Revolutionary party
- d)People’s party
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The famous political party of Mexico was:
a)
Revolutionary party
b)
Chinese Communist party
c)
Institutional Revolutionary party
d)
People’s party
|
|
Avinash Patel answered |
In Mexico, until 2000 every election was won by a party called PRI (Institutional Revolutionary Party)
Which Kharif crop is grown during the rainy season?
- a)Millets
- b)Jawar
- c)Sugar
- d)Wheat
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which Kharif crop is grown during the rainy season?
a)
Millets
b)
Jawar
c)
Sugar
d)
Wheat
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Jawar Kharif crop is grown during the rainy season.
Question No. 47 to 52 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
India is one of the ancient civilisations in the world. It has achieved multifaceted socio-economic progress during the last five decades. It has moved forward displaying remarkable progress in the field of agriculture, industry, technology, and overall economic development. India has also contributed significantly to the making of world history. India is a vast country. Lying entirely in the Northern hemisphere the mainland extends between latitudes 8°4'N and 37°6'N and longitudes 68°7'E and 97°25'E. The Tropic of Cancer divides the country into almost two equal parts. To the southeast and southwest of the mainland, lie the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and the Lakshadweep Islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea respectively. The southernmost point of the Indian Union was submerged under the seawater in 2004 during the Tsunami.Q. Tropic of Cancer divides the country into almost two equal parts. What is the latitudinal value of the Tropic of Cancer?- a)0° N
- b)68°7' E
- c)23° 30' N
- d)8°4' N
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question No. 47 to 52 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
India is one of the ancient civilisations in the world. It has achieved multifaceted socio-economic progress during the last five decades. It has moved forward displaying remarkable progress in the field of agriculture, industry, technology, and overall economic development. India has also contributed significantly to the making of world history. India is a vast country. Lying entirely in the Northern hemisphere the mainland extends between latitudes 8°4'N and 37°6'N and longitudes 68°7'E and 97°25'E. The Tropic of Cancer divides the country into almost two equal parts. To the southeast and southwest of the mainland, lie the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and the Lakshadweep Islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea respectively. The southernmost point of the Indian Union was submerged under the seawater in 2004 during the Tsunami.
India is one of the ancient civilisations in the world. It has achieved multifaceted socio-economic progress during the last five decades. It has moved forward displaying remarkable progress in the field of agriculture, industry, technology, and overall economic development. India has also contributed significantly to the making of world history. India is a vast country. Lying entirely in the Northern hemisphere the mainland extends between latitudes 8°4'N and 37°6'N and longitudes 68°7'E and 97°25'E. The Tropic of Cancer divides the country into almost two equal parts. To the southeast and southwest of the mainland, lie the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and the Lakshadweep Islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea respectively. The southernmost point of the Indian Union was submerged under the seawater in 2004 during the Tsunami.
Q. Tropic of Cancer divides the country into almost two equal parts. What is the latitudinal value of the Tropic of Cancer?
a)
0° N
b)
68°7' E
c)
23° 30' N
d)
8°4' N
|
|
Aditi Sharma answered |
23° 30' N
What capital is needed to set up a jaggery manufacturing unit?- a)Physical capital
- b)Working capital
- c)Fixed Capital
- d)Recurring capital
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What capital is needed to set up a jaggery manufacturing unit?
a)
Physical capital
b)
Working capital
c)
Fixed Capital
d)
Recurring capital
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Working capital is needed to set up a jaggery manufacturing unit.
1st estate comprised of which group?- a)Monarchs
- b)Big businessmen
- c)Nobility
- d)Clergy
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
1st estate comprised of which group?
a)
Monarchs
b)
Big businessmen
c)
Nobility
d)
Clergy
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
1st estate comprised of Clergy.
What was the unit of currency in France, that discontinued in 1794?- a)Livre
- b)Taille
- c)Pound
- d)Tithe
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What was the unit of currency in France, that discontinued in 1794?
a)
Livre
b)
Taille
c)
Pound
d)
Tithe
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Livre was the unit of currency in France, discontinued in 1794
Which of the following parallel ranges are known as Lesser Himalayas?- a)Himachal
- b)Purvanchal
- c)Himadri
- d)Shiwaliks
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following parallel ranges are known as Lesser Himalayas?
a)
Himachal
b)
Purvanchal
c)
Himadri
d)
Shiwaliks
|
|
Abhay Yadav answered |
Lesser Himalayas - Himachal
The Lesser Himalayas, also known as the Himachal or Lower Himalayas, are a parallel range in the Himalayan mountain system. This range is situated to the south of the Greater Himalayas and north of the Shiwalik range. The Lesser Himalayas are characterized by lower elevations compared to the Greater Himalayas, but they still feature rugged terrain and high peaks.
Features of the Lesser Himalayas - Himachal
- The Lesser Himalayas are known for their forested slopes, rich biodiversity, and picturesque landscapes.
- This range is famous for its hill stations like Shimla, Manali, and Mussoorie, which attract tourists from around the world.
- The Lesser Himalayas are also home to several important rivers like the Beas, Chenab, and Sutlej, which originate from the glaciers in this region.
- The climate in the Lesser Himalayas is generally milder than that of the Greater Himalayas, making it a popular destination for trekking, mountaineering, and other outdoor activities.
- The Himachal range is an important source of water, timber, and other natural resources for the surrounding regions.
Significance of the Lesser Himalayas - Himachal
- The Lesser Himalayas play a crucial role in the ecological balance of the region, providing habitats for diverse flora and fauna.
- These mountains also have cultural and spiritual significance for the local communities, with many temples, monasteries, and sacred sites located in the region.
- The Lesser Himalayas are an important part of India's natural heritage, attracting researchers, conservationists, and nature enthusiasts.
The Lesser Himalayas, also known as the Himachal or Lower Himalayas, are a parallel range in the Himalayan mountain system. This range is situated to the south of the Greater Himalayas and north of the Shiwalik range. The Lesser Himalayas are characterized by lower elevations compared to the Greater Himalayas, but they still feature rugged terrain and high peaks.
Features of the Lesser Himalayas - Himachal
- The Lesser Himalayas are known for their forested slopes, rich biodiversity, and picturesque landscapes.
- This range is famous for its hill stations like Shimla, Manali, and Mussoorie, which attract tourists from around the world.
- The Lesser Himalayas are also home to several important rivers like the Beas, Chenab, and Sutlej, which originate from the glaciers in this region.
- The climate in the Lesser Himalayas is generally milder than that of the Greater Himalayas, making it a popular destination for trekking, mountaineering, and other outdoor activities.
- The Himachal range is an important source of water, timber, and other natural resources for the surrounding regions.
Significance of the Lesser Himalayas - Himachal
- The Lesser Himalayas play a crucial role in the ecological balance of the region, providing habitats for diverse flora and fauna.
- These mountains also have cultural and spiritual significance for the local communities, with many temples, monasteries, and sacred sites located in the region.
- The Lesser Himalayas are an important part of India's natural heritage, attracting researchers, conservationists, and nature enthusiasts.
Question No. 47 to 52 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
In the past, peasants and workers had participated in revolts against increasing taxes and food scarcity.
But they lacked the means and programmes to carry out full-scale measures that would bring about a change in the social and economic order. This was left to those groups within the third estate who had become prosperous and had access to education and new ideas. The eighteenth-century witnessed the emergence of social groups, termed the middle class, who earned their wealth through expanding overseas trade and from the manufacture of goods such as woollen and silk textiles that were either exported or bought by the richer members of society. In addition to merchants and manufacturers, the third estate included professions such as lawyers or administrative officials. All of these were educated and believed that no group in society should be privileged by birth. Rather, a person’s social position must depend on his merit. These ideas envisaging a society based on freedom and equal laws and opportunities for all were put forward by philosophers such as John Locke and Jean Jacques Rousseau.
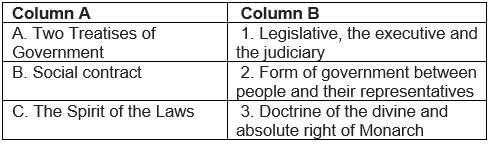
In his Two Treatises of Government, Locke sought to refute the doctrine of the divine and absolute right of the monarch. Rousseau carried the idea forward, proposing a form of government based on a social contract between people and their representatives. In The Spirit of the Laws, Montesquieu proposed a division of power within the government between the legislative, the executive and the judiciary. This model of government was put into force in the USA after the thirteen colonies declared their independence from Britain. The American constitution and its guarantee of individual rights was an important example for political thinkers in France.Q. Match the following:
- a)A-1, B-1, C-2
- b)A-3, B-2, C-1
- c)A-1, B-3, C-2
- d)A-2, B-1, C-3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question No. 47 to 52 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
In the past, peasants and workers had participated in revolts against increasing taxes and food scarcity.
But they lacked the means and programmes to carry out full-scale measures that would bring about a change in the social and economic order. This was left to those groups within the third estate who had become prosperous and had access to education and new ideas. The eighteenth-century witnessed the emergence of social groups, termed the middle class, who earned their wealth through expanding overseas trade and from the manufacture of goods such as woollen and silk textiles that were either exported or bought by the richer members of society. In addition to merchants and manufacturers, the third estate included professions such as lawyers or administrative officials. All of these were educated and believed that no group in society should be privileged by birth. Rather, a person’s social position must depend on his merit. These ideas envisaging a society based on freedom and equal laws and opportunities for all were put forward by philosophers such as John Locke and Jean Jacques Rousseau.
In his Two Treatises of Government, Locke sought to refute the doctrine of the divine and absolute right of the monarch. Rousseau carried the idea forward, proposing a form of government based on a social contract between people and their representatives. In The Spirit of the Laws, Montesquieu proposed a division of power within the government between the legislative, the executive and the judiciary. This model of government was put into force in the USA after the thirteen colonies declared their independence from Britain. The American constitution and its guarantee of individual rights was an important example for political thinkers in France.
In the past, peasants and workers had participated in revolts against increasing taxes and food scarcity.
But they lacked the means and programmes to carry out full-scale measures that would bring about a change in the social and economic order. This was left to those groups within the third estate who had become prosperous and had access to education and new ideas. The eighteenth-century witnessed the emergence of social groups, termed the middle class, who earned their wealth through expanding overseas trade and from the manufacture of goods such as woollen and silk textiles that were either exported or bought by the richer members of society. In addition to merchants and manufacturers, the third estate included professions such as lawyers or administrative officials. All of these were educated and believed that no group in society should be privileged by birth. Rather, a person’s social position must depend on his merit. These ideas envisaging a society based on freedom and equal laws and opportunities for all were put forward by philosophers such as John Locke and Jean Jacques Rousseau.
In his Two Treatises of Government, Locke sought to refute the doctrine of the divine and absolute right of the monarch. Rousseau carried the idea forward, proposing a form of government based on a social contract between people and their representatives. In The Spirit of the Laws, Montesquieu proposed a division of power within the government between the legislative, the executive and the judiciary. This model of government was put into force in the USA after the thirteen colonies declared their independence from Britain. The American constitution and its guarantee of individual rights was an important example for political thinkers in France.
Q. Match the following:


a)
A-1, B-1, C-2
b)
A-3, B-2, C-1
c)
A-1, B-3, C-2
d)
A-2, B-1, C-3
|
|
Meera Rana answered |
What is the name of Chinese parliament?- a)National Congress
- b)National People's Congress
- c)Congress
- d)Communist Congress
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the name of Chinese parliament?
a)
National Congress
b)
National People's Congress
c)
Congress
d)
Communist Congress
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
Chinese parliament is called Quanguo Renmin Daibiao Dahui(National People's Congress).
Question No. 47 to 52 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
In the past, peasants and workers had participated in revolts against increasing taxes and food scarcity.
But they lacked the means and programmes to carry out full-scale measures that would bring about a change in the social and economic order. This was left to those groups within the third estate who had become prosperous and had access to education and new ideas. The eighteenth-century witnessed the emergence of social groups, termed the middle class, who earned their wealth through expanding overseas trade and from the manufacture of goods such as woollen and silk textiles that were either exported or bought by the richer members of society. In addition to merchants and manufacturers, the third estate included professions such as lawyers or administrative officials. All of these were educated and believed that no group in society should be privileged by birth. Rather, a person’s social position must depend on his merit. These ideas envisaging a society based on freedom and equal laws and opportunities for all were put forward by philosophers such as John Locke and Jean Jacques Rousseau.
In his Two Treatises of Government, Locke sought to refute the doctrine of the divine and absolute right of the monarch. Rousseau carried the idea forward, proposing a form of government based on a social contract between people and their representatives. In The Spirit of the Laws, Montesquieu proposed a division of power within the government between the legislative, the executive and the judiciary. This model of government was put into force in the USA after the thirteen colonies declared their independence from Britain. The American constitution and its guarantee of individual rights was an important example for political thinkers in France.Q. Which social group emerged in France in the 18th century?- a)Middle class
- b)Nobility
- c)Clergy
- d)Philosophers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question No. 47 to 52 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
In the past, peasants and workers had participated in revolts against increasing taxes and food scarcity.
But they lacked the means and programmes to carry out full-scale measures that would bring about a change in the social and economic order. This was left to those groups within the third estate who had become prosperous and had access to education and new ideas. The eighteenth-century witnessed the emergence of social groups, termed the middle class, who earned their wealth through expanding overseas trade and from the manufacture of goods such as woollen and silk textiles that were either exported or bought by the richer members of society. In addition to merchants and manufacturers, the third estate included professions such as lawyers or administrative officials. All of these were educated and believed that no group in society should be privileged by birth. Rather, a person’s social position must depend on his merit. These ideas envisaging a society based on freedom and equal laws and opportunities for all were put forward by philosophers such as John Locke and Jean Jacques Rousseau.
In his Two Treatises of Government, Locke sought to refute the doctrine of the divine and absolute right of the monarch. Rousseau carried the idea forward, proposing a form of government based on a social contract between people and their representatives. In The Spirit of the Laws, Montesquieu proposed a division of power within the government between the legislative, the executive and the judiciary. This model of government was put into force in the USA after the thirteen colonies declared their independence from Britain. The American constitution and its guarantee of individual rights was an important example for political thinkers in France.
In the past, peasants and workers had participated in revolts against increasing taxes and food scarcity.
But they lacked the means and programmes to carry out full-scale measures that would bring about a change in the social and economic order. This was left to those groups within the third estate who had become prosperous and had access to education and new ideas. The eighteenth-century witnessed the emergence of social groups, termed the middle class, who earned their wealth through expanding overseas trade and from the manufacture of goods such as woollen and silk textiles that were either exported or bought by the richer members of society. In addition to merchants and manufacturers, the third estate included professions such as lawyers or administrative officials. All of these were educated and believed that no group in society should be privileged by birth. Rather, a person’s social position must depend on his merit. These ideas envisaging a society based on freedom and equal laws and opportunities for all were put forward by philosophers such as John Locke and Jean Jacques Rousseau.
In his Two Treatises of Government, Locke sought to refute the doctrine of the divine and absolute right of the monarch. Rousseau carried the idea forward, proposing a form of government based on a social contract between people and their representatives. In The Spirit of the Laws, Montesquieu proposed a division of power within the government between the legislative, the executive and the judiciary. This model of government was put into force in the USA after the thirteen colonies declared their independence from Britain. The American constitution and its guarantee of individual rights was an important example for political thinkers in France.
Q. Which social group emerged in France in the 18th century?
a)
Middle class
b)
Nobility
c)
Clergy
d)
Philosophers
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Middle class
In the secondary sector which of the following is the most labour absorbing?- a)Mining
- b)Quarrying
- c)Trade
- d)Small scale manufacturing
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the secondary sector which of the following is the most labour absorbing?
a)
Mining
b)
Quarrying
c)
Trade
d)
Small scale manufacturing

|
Priya Nair answered |
Small scale manufacturing is the most labor absorbing in the secondary sector.
Explanation:
Secondary sector refers to the sector of the economy that involves the processing of raw materials into finished goods. It includes activities such as manufacturing, construction, mining, and quarrying. In this sector, small scale manufacturing stands out as the most labor absorbing option due to the following reasons:
1. Labor-intensive nature: Small scale manufacturing typically involves the use of a significant amount of manual labor. This is because small scale industries often have limited funds and resources, which means they rely heavily on human labor to carry out various tasks. As a result, these industries tend to employ a large number of workers.
2. Diverse job opportunities: Small scale manufacturing encompasses a wide range of industries, such as textiles, food processing, handicrafts, and electronics. Each of these industries requires different types of skills and expertise. As a result, small scale manufacturing provides diverse job opportunities for individuals with varying educational backgrounds and skill sets.
3. Local employment generation: Small scale manufacturing units are often located in rural or semi-urban areas where unemployment rates may be high. By setting up these industries, local employment opportunities are created, allowing individuals in these areas to earn a livelihood without having to migrate to cities in search of work.
4. Potential for entrepreneurship: Small scale manufacturing also offers opportunities for entrepreneurship. Individuals with innovative ideas and skills can start their own small businesses and contribute to the growth of the economy. This promotes self-employment and fosters a culture of innovation and creativity.
5. Economic development: Small scale manufacturing plays a crucial role in the economic development of a country. It contributes to GDP growth, generates income for individuals, and promotes industrialization. Additionally, the labor-intensive nature of small scale manufacturing helps reduce unemployment rates, alleviate poverty, and improve living standards.
In conclusion, small scale manufacturing is the most labor absorbing in the secondary sector due to its labor-intensive nature, diverse job opportunities, local employment generation, potential for entrepreneurship, and its contribution to economic development.
Explanation:
Secondary sector refers to the sector of the economy that involves the processing of raw materials into finished goods. It includes activities such as manufacturing, construction, mining, and quarrying. In this sector, small scale manufacturing stands out as the most labor absorbing option due to the following reasons:
1. Labor-intensive nature: Small scale manufacturing typically involves the use of a significant amount of manual labor. This is because small scale industries often have limited funds and resources, which means they rely heavily on human labor to carry out various tasks. As a result, these industries tend to employ a large number of workers.
2. Diverse job opportunities: Small scale manufacturing encompasses a wide range of industries, such as textiles, food processing, handicrafts, and electronics. Each of these industries requires different types of skills and expertise. As a result, small scale manufacturing provides diverse job opportunities for individuals with varying educational backgrounds and skill sets.
3. Local employment generation: Small scale manufacturing units are often located in rural or semi-urban areas where unemployment rates may be high. By setting up these industries, local employment opportunities are created, allowing individuals in these areas to earn a livelihood without having to migrate to cities in search of work.
4. Potential for entrepreneurship: Small scale manufacturing also offers opportunities for entrepreneurship. Individuals with innovative ideas and skills can start their own small businesses and contribute to the growth of the economy. This promotes self-employment and fosters a culture of innovation and creativity.
5. Economic development: Small scale manufacturing plays a crucial role in the economic development of a country. It contributes to GDP growth, generates income for individuals, and promotes industrialization. Additionally, the labor-intensive nature of small scale manufacturing helps reduce unemployment rates, alleviate poverty, and improve living standards.
In conclusion, small scale manufacturing is the most labor absorbing in the secondary sector due to its labor-intensive nature, diverse job opportunities, local employment generation, potential for entrepreneurship, and its contribution to economic development.
Arrange the following events in chronological order:
i. A constitution is framed to limit the powers of the king.
ii. Louis XVI becomes king of France.
iii. Convocation of Estates General.
iv. France becomes a republic.- a)iii, i, ii, iv
- b)ii, iii, i, iv
- c)iv, iii, ii, i
- d)ii, i, iv, iii
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following events in chronological order:
i. A constitution is framed to limit the powers of the king.
ii. Louis XVI becomes king of France.
iii. Convocation of Estates General.
iv. France becomes a republic.
i. A constitution is framed to limit the powers of the king.
ii. Louis XVI becomes king of France.
iii. Convocation of Estates General.
iv. France becomes a republic.
a)
iii, i, ii, iv
b)
ii, iii, i, iv
c)
iv, iii, ii, i
d)
ii, i, iv, iii
|
|
Aditi Sharma answered |
ii. 1774: Louis XVI becomes king of France.
iii. 1789: Convocation of Estates General.
i. 1791: A constitution is framed to limit the powers of the king.
iv. 1792-93: France becomes a republic.
iii. 1789: Convocation of Estates General.
i. 1791: A constitution is framed to limit the powers of the king.
iv. 1792-93: France becomes a republic.
Democracy improves the quality of decision-making because:- a)Decisions are taken over a long period of time
- b)Decisions are taken by educated people
- c)Decisions are taken by consultation and discussion
- d)All decisions are approved by judiciary
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Democracy improves the quality of decision-making because:
a)
Decisions are taken over a long period of time
b)
Decisions are taken by educated people
c)
Decisions are taken by consultation and discussion
d)
All decisions are approved by judiciary
|
|
Niharika Kapoor answered |
Understanding Democracy and Decision-Making
Democracy plays a crucial role in enhancing the quality of decision-making processes in a society. The correct answer to the question is option 'C', which emphasizes the importance of consultation and discussion.
Importance of Consultation and Discussion
- Collective Wisdom: In a democratic setup, decisions are made through the input of various stakeholders. This collective approach brings together diverse perspectives, experiences, and knowledge, leading to more informed and balanced outcomes.
- Public Participation: Democracy encourages active participation from citizens. When individuals voice their opinions and concerns, it leads to decisions that reflect the needs and aspirations of the broader population, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility.
- Accountability: Through consultation and discussion, decision-makers are held accountable for their choices. This transparency ensures that decisions are not made in isolation but are subject to scrutiny by the public, which can lead to more responsible governance.
Comparison with Other Options
- Long Decision-making Periods: While lengthy discussions can be beneficial, they can also lead to indecisiveness and missed opportunities. Quick, effective decisions are sometimes necessary.
- Educated Decision-makers: Although education is important, it does not guarantee better decisions. Relying solely on a select group of educated individuals may exclude valuable insights from the general populace.
- Judicial Approval: While the judiciary plays a vital role in upholding laws and protecting rights, it is not the primary mechanism for decision-making in a democracy. Judicial review is essential but does not directly enhance the quality of decisions made by elected officials.
In summary, option 'C' highlights the essence of democratic decision-making where consultation and discussion lead to better, more inclusive outcomes.
Democracy plays a crucial role in enhancing the quality of decision-making processes in a society. The correct answer to the question is option 'C', which emphasizes the importance of consultation and discussion.
Importance of Consultation and Discussion
- Collective Wisdom: In a democratic setup, decisions are made through the input of various stakeholders. This collective approach brings together diverse perspectives, experiences, and knowledge, leading to more informed and balanced outcomes.
- Public Participation: Democracy encourages active participation from citizens. When individuals voice their opinions and concerns, it leads to decisions that reflect the needs and aspirations of the broader population, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility.
- Accountability: Through consultation and discussion, decision-makers are held accountable for their choices. This transparency ensures that decisions are not made in isolation but are subject to scrutiny by the public, which can lead to more responsible governance.
Comparison with Other Options
- Long Decision-making Periods: While lengthy discussions can be beneficial, they can also lead to indecisiveness and missed opportunities. Quick, effective decisions are sometimes necessary.
- Educated Decision-makers: Although education is important, it does not guarantee better decisions. Relying solely on a select group of educated individuals may exclude valuable insights from the general populace.
- Judicial Approval: While the judiciary plays a vital role in upholding laws and protecting rights, it is not the primary mechanism for decision-making in a democracy. Judicial review is essential but does not directly enhance the quality of decisions made by elected officials.
In summary, option 'C' highlights the essence of democratic decision-making where consultation and discussion lead to better, more inclusive outcomes.
Which Pakistan General led a military coup in October 1999?- a)Nawaz Sharif
- b)None of these
- c)Ayub Khan
- d)Parvez Musharraf
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which Pakistan General led a military coup in October 1999?
a)
Nawaz Sharif
b)
None of these
c)
Ayub Khan
d)
Parvez Musharraf
|
|
Raveena Patel answered |
Overview of the 1999 Coup
In October 1999, Pakistan experienced a significant political shift when General Pervez Musharraf led a military coup, deposing the elected Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif. This event marked a critical moment in Pakistan's political history.
Key Events Leading to the Coup
- Background Tensions: Nawaz Sharif's government faced multiple challenges, including economic instability and rising tensions with the military.
- Kargil Conflict: The Kargil conflict with India in 1999 strained relations between the military and the government. Sharif's decision to withdraw troops from Kargil angered military leaders.
- Dismissal of the Army Chief: In a controversial move, Nawaz Sharif attempted to dismiss General Musharraf as the Chief of Army Staff, which was a decisive turning point.
The Coup Execution
- Seizure of Power: On October 12, 1999, as Nawaz Sharif was trying to replace Musharraf, the military took control of key installations in Karachi and Islamabad.
- Arrest of Sharif: Musharraf's forces arrested Nawaz Sharif, effectively ending his government. The coup was met with little resistance from the civilian population.
Musharraf's Rule
- Military Government: Following the coup, Musharraf assumed power and declared a state of emergency, positioning himself as the Chief Executive of Pakistan.
- Political Reforms: Musharraf's regime introduced various reforms, but also faced criticism for human rights abuses and lack of democratic processes.
Conclusion
General Pervez Musharraf's coup in 1999 was a pivotal moment in Pakistan's history, emphasizing the ongoing struggle between civilian governance and military power in the country.
In October 1999, Pakistan experienced a significant political shift when General Pervez Musharraf led a military coup, deposing the elected Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif. This event marked a critical moment in Pakistan's political history.
Key Events Leading to the Coup
- Background Tensions: Nawaz Sharif's government faced multiple challenges, including economic instability and rising tensions with the military.
- Kargil Conflict: The Kargil conflict with India in 1999 strained relations between the military and the government. Sharif's decision to withdraw troops from Kargil angered military leaders.
- Dismissal of the Army Chief: In a controversial move, Nawaz Sharif attempted to dismiss General Musharraf as the Chief of Army Staff, which was a decisive turning point.
The Coup Execution
- Seizure of Power: On October 12, 1999, as Nawaz Sharif was trying to replace Musharraf, the military took control of key installations in Karachi and Islamabad.
- Arrest of Sharif: Musharraf's forces arrested Nawaz Sharif, effectively ending his government. The coup was met with little resistance from the civilian population.
Musharraf's Rule
- Military Government: Following the coup, Musharraf assumed power and declared a state of emergency, positioning himself as the Chief Executive of Pakistan.
- Political Reforms: Musharraf's regime introduced various reforms, but also faced criticism for human rights abuses and lack of democratic processes.
Conclusion
General Pervez Musharraf's coup in 1999 was a pivotal moment in Pakistan's history, emphasizing the ongoing struggle between civilian governance and military power in the country.
Which of the following is not the reason of empty treasure?- a)Food supplies to the ordinary citizens.
- b)The cost of maintaining an extravagant court.
- c)To meet its regular expenses.
- d)Long years of war.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not the reason of empty treasure?
a)
Food supplies to the ordinary citizens.
b)
The cost of maintaining an extravagant court.
c)
To meet its regular expenses.
d)
Long years of war.
|
|
Meera Rana answered |
Long years of war had drained the financial resources of France. Added to this was the cost of maintaining an extravagant court at the immense palace of Versailles. To meet its regular expenses, such as the cost of maintaining an army, the court, running government offices or universities, the state was forced to increase taxes.
During which period did China record its worst famines in the world's history?- a)1935-39
- b)1952-55
- c)1958-61
- d)1943-46
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During which period did China record its worst famines in the world's history?
a)
1935-39
b)
1952-55
c)
1958-61
d)
1943-46
|
|
Arpita Rane answered |
The Great Chinese Famine (1958-1961)
The correct answer is option 'C', which refers to the period of 1958-1961, during which China experienced the worst famines in world history. This period is known as the Great Chinese Famine or the Great Leap Forward famine.
Background
The Great Chinese Famine was a direct consequence of Chairman Mao Zedong's policies and the implementation of the Great Leap Forward. This economic and social campaign aimed to transform China from an agrarian society into an industrialized socialist country. However, the policies implemented during this period had disastrous consequences for the Chinese population and resulted in widespread famine.
Causes of the Famine
There were several factors that contributed to the severity of the Great Chinese Famine:
1. Communes and Collectivization: As part of the Great Leap Forward, Mao introduced the system of communes and collectivization, which involved pooling land, labor, and resources into large collective farms. This forced farmers to abandon traditional agricultural practices and focus on backyard steel furnaces and communal dining halls. The collectivization process disrupted traditional farming methods, leading to a decline in agricultural productivity.
2. Steel Production Targets: Mao's emphasis on steel production led to the diversion of resources and manpower from agriculture to backyard steel furnaces. This diversion severely impacted agricultural output and further contributed to the famine.
3. Poor Harvests and Natural Disasters: The Great Chinese Famine was exacerbated by a series of poor harvests and natural disasters, including floods, droughts, and pest infestations. These factors significantly reduced crop yields and further worsened the food shortage.
4. Misreporting and Central Planning: The government's centralized planning system and misreporting of agricultural output created a false sense of abundance, leading to inadequate distribution of food resources. Local officials were incentivized to overreport grain production to meet unrealistic targets, resulting in a severe misallocation of resources.
Consequences and Impact
The Great Chinese Famine had devastating consequences for the Chinese population. It is estimated that tens of millions of people died from starvation, malnutrition, and related diseases during this period. The exact death toll remains a subject of debate due to limited access to data and government suppression of information.
The famine also had long-lasting social, economic, and political impacts on China. It shattered people's faith in the communist government and led to widespread disillusionment. It also highlighted the flaws of central planning and forced the Chinese government to reassess its policies.
Conclusion
The Great Chinese Famine, which occurred during the period of 1958-1961, was the worst famine in world history. It was caused by a combination of factors, including the implementation of the Great Leap Forward policies, collectivization, poor harvests, and misreporting. The consequences of the famine were severe, resulting in the death of millions and significant social and political repercussions for China.
The correct answer is option 'C', which refers to the period of 1958-1961, during which China experienced the worst famines in world history. This period is known as the Great Chinese Famine or the Great Leap Forward famine.
Background
The Great Chinese Famine was a direct consequence of Chairman Mao Zedong's policies and the implementation of the Great Leap Forward. This economic and social campaign aimed to transform China from an agrarian society into an industrialized socialist country. However, the policies implemented during this period had disastrous consequences for the Chinese population and resulted in widespread famine.
Causes of the Famine
There were several factors that contributed to the severity of the Great Chinese Famine:
1. Communes and Collectivization: As part of the Great Leap Forward, Mao introduced the system of communes and collectivization, which involved pooling land, labor, and resources into large collective farms. This forced farmers to abandon traditional agricultural practices and focus on backyard steel furnaces and communal dining halls. The collectivization process disrupted traditional farming methods, leading to a decline in agricultural productivity.
2. Steel Production Targets: Mao's emphasis on steel production led to the diversion of resources and manpower from agriculture to backyard steel furnaces. This diversion severely impacted agricultural output and further contributed to the famine.
3. Poor Harvests and Natural Disasters: The Great Chinese Famine was exacerbated by a series of poor harvests and natural disasters, including floods, droughts, and pest infestations. These factors significantly reduced crop yields and further worsened the food shortage.
4. Misreporting and Central Planning: The government's centralized planning system and misreporting of agricultural output created a false sense of abundance, leading to inadequate distribution of food resources. Local officials were incentivized to overreport grain production to meet unrealistic targets, resulting in a severe misallocation of resources.
Consequences and Impact
The Great Chinese Famine had devastating consequences for the Chinese population. It is estimated that tens of millions of people died from starvation, malnutrition, and related diseases during this period. The exact death toll remains a subject of debate due to limited access to data and government suppression of information.
The famine also had long-lasting social, economic, and political impacts on China. It shattered people's faith in the communist government and led to widespread disillusionment. It also highlighted the flaws of central planning and forced the Chinese government to reassess its policies.
Conclusion
The Great Chinese Famine, which occurred during the period of 1958-1961, was the worst famine in world history. It was caused by a combination of factors, including the implementation of the Great Leap Forward policies, collectivization, poor harvests, and misreporting. The consequences of the famine were severe, resulting in the death of millions and significant social and political repercussions for China.
The full form of GNP is:- a)Gross National Performance
- b)Green National Project
- c)Gross National Product
- d)Green Nation People
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The full form of GNP is:
a)
Gross National Performance
b)
Green National Project
c)
Gross National Product
d)
Green Nation People
|
|
Aditi Sharma answered |
Full form of GNP is Gross National Product. Gross national product is the market value of all the products and services produced in one year by labour and property supplied by the citizens of a country.
Who did not have the right to vote in Saudi Arabia?- a)Non-residents
- b)Propertied men
- c)Non-propertied men
- d)Women
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Who did not have the right to vote in Saudi Arabia?
a)
Non-residents
b)
Propertied men
c)
Non-propertied men
d)
Women
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
There are many instances of denial of equal right to vote. For example: In Saudi Arabia, women did not have the right to vote. Women were previously forbidden from voting in all elections or being elected to any political office, but in 2011 King Abdullah allowed women to vote in the 2015 local municipal elections and be appointed to the Consultative Assembly.
Question No. 53 to 58 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
The northern plain has been formed by the interplay of the three major river systems. This plain is formed of alluvial soil. The deposition of alluvium in a vast basin lying at the foothills of the Himalaya over millions of years formed this fertile plain. It spreads over an area of 7 lakh sq. km. The plain being about 2400 km long and 240 to 320 km broad, is a densely populated physiographic division. With a rich soil cover combined with an adequate water supply and favourable climate it is agriculturally a productive part of India The Northern Plain is broadly divided into three sections. The Western part of the Northern Plain is referred to as the Punjab Plains. Formed by the Indus and its tributaries, the larger part of this plain lies in Pakistan. The Indus and its tributaries - the Jhelum, the Chenab, the Ravi, the Beas and the Satluj originate in the Himalaya. This section of the plain is dominated by the doabs.
The Ganga plain extends between Ghaggar and Teesta rivers. It is spread over the states of North India, Haryana, Delhi, U.P., Bihar, partly Jharkhand and West Bengal to its East, particularly in Assam lies the Brahmaputra plain. The northern plains are generally described as flat land with no variations in its relief. It is not true. These vast plains also have diverse relief features. According to the variations in relief features, the Northern plains can be divided into four regions. The rivers, after descending from the mountains deposit pebbles in a narrow belt of about 8 to 16 km in width lying parallel to the slopes of the Shiwaliks. It is known as bhabar. All the streams disappear in this bhabar belt. South of this belt, the streams and rivers re-emerge and create a wet, swampy and marshy region known as terai. This was a thickly forested region full of wildlife. The forests have been cleared to create agricultural land and to settle migrants from Pakistan after partition.Q. Assertion (A): The rivers of northern mountains are involved in depositional work causing the formation of riverine islands.
Reason (R): Due to the gentle slopes in the lower course of the river its velocity decreases resulting in the formation of riverine islands.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true but R is false.
- d)A is false but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question No. 53 to 58 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
The northern plain has been formed by the interplay of the three major river systems. This plain is formed of alluvial soil. The deposition of alluvium in a vast basin lying at the foothills of the Himalaya over millions of years formed this fertile plain. It spreads over an area of 7 lakh sq. km. The plain being about 2400 km long and 240 to 320 km broad, is a densely populated physiographic division. With a rich soil cover combined with an adequate water supply and favourable climate it is agriculturally a productive part of India The Northern Plain is broadly divided into three sections. The Western part of the Northern Plain is referred to as the Punjab Plains. Formed by the Indus and its tributaries, the larger part of this plain lies in Pakistan. The Indus and its tributaries - the Jhelum, the Chenab, the Ravi, the Beas and the Satluj originate in the Himalaya. This section of the plain is dominated by the doabs.
The Ganga plain extends between Ghaggar and Teesta rivers. It is spread over the states of North India, Haryana, Delhi, U.P., Bihar, partly Jharkhand and West Bengal to its East, particularly in Assam lies the Brahmaputra plain. The northern plains are generally described as flat land with no variations in its relief. It is not true. These vast plains also have diverse relief features. According to the variations in relief features, the Northern plains can be divided into four regions. The rivers, after descending from the mountains deposit pebbles in a narrow belt of about 8 to 16 km in width lying parallel to the slopes of the Shiwaliks. It is known as bhabar. All the streams disappear in this bhabar belt. South of this belt, the streams and rivers re-emerge and create a wet, swampy and marshy region known as terai. This was a thickly forested region full of wildlife. The forests have been cleared to create agricultural land and to settle migrants from Pakistan after partition.
The northern plain has been formed by the interplay of the three major river systems. This plain is formed of alluvial soil. The deposition of alluvium in a vast basin lying at the foothills of the Himalaya over millions of years formed this fertile plain. It spreads over an area of 7 lakh sq. km. The plain being about 2400 km long and 240 to 320 km broad, is a densely populated physiographic division. With a rich soil cover combined with an adequate water supply and favourable climate it is agriculturally a productive part of India The Northern Plain is broadly divided into three sections. The Western part of the Northern Plain is referred to as the Punjab Plains. Formed by the Indus and its tributaries, the larger part of this plain lies in Pakistan. The Indus and its tributaries - the Jhelum, the Chenab, the Ravi, the Beas and the Satluj originate in the Himalaya. This section of the plain is dominated by the doabs.
The Ganga plain extends between Ghaggar and Teesta rivers. It is spread over the states of North India, Haryana, Delhi, U.P., Bihar, partly Jharkhand and West Bengal to its East, particularly in Assam lies the Brahmaputra plain. The northern plains are generally described as flat land with no variations in its relief. It is not true. These vast plains also have diverse relief features. According to the variations in relief features, the Northern plains can be divided into four regions. The rivers, after descending from the mountains deposit pebbles in a narrow belt of about 8 to 16 km in width lying parallel to the slopes of the Shiwaliks. It is known as bhabar. All the streams disappear in this bhabar belt. South of this belt, the streams and rivers re-emerge and create a wet, swampy and marshy region known as terai. This was a thickly forested region full of wildlife. The forests have been cleared to create agricultural land and to settle migrants from Pakistan after partition.
Q. Assertion (A): The rivers of northern mountains are involved in depositional work causing the formation of riverine islands.
Reason (R): Due to the gentle slopes in the lower course of the river its velocity decreases resulting in the formation of riverine islands.
Reason (R): Due to the gentle slopes in the lower course of the river its velocity decreases resulting in the formation of riverine islands.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true but R is false.
d)
A is false but R is true.

|
Rahul Rane answered |
Explanation:
Assertion (A):
- The rivers of northern mountains are involved in depositional work causing the formation of riverine islands.
Reason (R):
- Due to the gentle slopes in the lower course of the river, its velocity decreases resulting in the formation of riverine islands.
Explanation:
- The assertion is true because the rivers in the northern mountains undergo depositional work due to the decrease in velocity in their lower course, leading to the formation of riverine islands. This process occurs as the rivers carry sediments downstream and deposit them, creating landforms like riverine islands.
- The reason is also true as the gentle slopes in the lower course of the river reduce its velocity, allowing for the deposition of sediments and the formation of riverine islands. This process is a natural consequence of the river's flow dynamics.
Therefore, both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason correctly explains why the rivers of the northern mountains are involved in depositional work, leading to the formation of riverine islands.
Assertion (A):
- The rivers of northern mountains are involved in depositional work causing the formation of riverine islands.
Reason (R):
- Due to the gentle slopes in the lower course of the river, its velocity decreases resulting in the formation of riverine islands.
Explanation:
- The assertion is true because the rivers in the northern mountains undergo depositional work due to the decrease in velocity in their lower course, leading to the formation of riverine islands. This process occurs as the rivers carry sediments downstream and deposit them, creating landforms like riverine islands.
- The reason is also true as the gentle slopes in the lower course of the river reduce its velocity, allowing for the deposition of sediments and the formation of riverine islands. This process is a natural consequence of the river's flow dynamics.
Therefore, both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason correctly explains why the rivers of the northern mountains are involved in depositional work, leading to the formation of riverine islands.
Which party of Zimbabwe helped its country to gain independence?- a)None of these
- b)Zimbabwe party
- c)Popular party
- d)ZANU-PF
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which party of Zimbabwe helped its country to gain independence?
a)
None of these
b)
Zimbabwe party
c)
Popular party
d)
ZANU-PF
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Zimbabwe attained independence from White minority rule in 1980. Since then the country has been ruled by ZANU-PF, the party that led the freedom struggle.
2nd estate comprised of which group?- a)Clergy
- b)Lawyers
- c)Big businessmen
- d)Nobility
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
2nd estate comprised of which group?
a)
Clergy
b)
Lawyers
c)
Big businessmen
d)
Nobility
|
|
Mihika Iyer answered |
The 2nd estate comprised of Nobility.
- Nobility: The second estate in pre-revolutionary France was made up of the nobility. This group included individuals who held titles of nobility, such as dukes, counts, and barons. The nobility enjoyed privileges such as exemption from certain taxes and the right to hold positions of power and influence in society.
The nobility played a crucial role in the social and political structure of pre-revolutionary France. They held significant power and wealth, often owning large estates and controlling vast resources. Despite their small numbers, the nobility wielded considerable influence over the monarchy and were able to maintain their privileged position in society.
Overall, the nobility represented a small but powerful segment of French society, and their interests often conflicted with those of the common people. This tension between the nobility and the lower classes would eventually contribute to the outbreak of the French Revolution, as the oppressed masses sought to overthrow the entrenched power structures that kept them in poverty and servitude.
When people appear to be employed, this kind of unemployment is called:- a)Seasonal unemployment
- b)Disguised unemployment
- c)Educated unemployment
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When people appear to be employed, this kind of unemployment is called:
a)
Seasonal unemployment
b)
Disguised unemployment
c)
Educated unemployment
d)
All of these
|
|
Vedika Kapoor answered |
Understanding Disguised Unemployment
Disguised unemployment refers to a situation where individuals appear to be employed but are, in fact, not contributing significantly to the productivity of the economy. This type of unemployment often goes unnoticed because people are technically working, yet their roles do not utilize their skills or capacities fully.
Characteristics of Disguised Unemployment
- Underemployment: Individuals may have jobs that do not utilize their skills, education, or experience. For example, a highly qualified engineer working as a manual laborer.
- Low Productivity: The contributions of these workers are minimal. Despite being employed, they do not add value to production, leading to inefficiencies in the labor market.
- Hidden Nature: This form of unemployment is often hidden because it doesn't show up in traditional unemployment statistics. People are counted as employed, even when they are not fully engaged in productive work.
Examples of Disguised Unemployment
- Family Businesses: Many family-run businesses employ family members who may not be actively involved in work, yet they are considered employed.
- Agricultural Sector: In rural areas, farmers may have more workers than needed for their land, leading to many being employed but not effectively contributing to agricultural productivity.
Importance of Addressing Disguised Unemployment
- Economic Growth: Reducing disguised unemployment can lead to increased productivity and economic growth.
- Skill Utilization: It is crucial to match workers with appropriate jobs to ensure that their skills are effectively utilized.
Disguised unemployment highlights the complexity of labor markets and the importance of addressing inefficiencies to enhance overall economic health. Understanding this concept is vital for students studying economics and labor dynamics.
Disguised unemployment refers to a situation where individuals appear to be employed but are, in fact, not contributing significantly to the productivity of the economy. This type of unemployment often goes unnoticed because people are technically working, yet their roles do not utilize their skills or capacities fully.
Characteristics of Disguised Unemployment
- Underemployment: Individuals may have jobs that do not utilize their skills, education, or experience. For example, a highly qualified engineer working as a manual laborer.
- Low Productivity: The contributions of these workers are minimal. Despite being employed, they do not add value to production, leading to inefficiencies in the labor market.
- Hidden Nature: This form of unemployment is often hidden because it doesn't show up in traditional unemployment statistics. People are counted as employed, even when they are not fully engaged in productive work.
Examples of Disguised Unemployment
- Family Businesses: Many family-run businesses employ family members who may not be actively involved in work, yet they are considered employed.
- Agricultural Sector: In rural areas, farmers may have more workers than needed for their land, leading to many being employed but not effectively contributing to agricultural productivity.
Importance of Addressing Disguised Unemployment
- Economic Growth: Reducing disguised unemployment can lead to increased productivity and economic growth.
- Skill Utilization: It is crucial to match workers with appropriate jobs to ensure that their skills are effectively utilized.
Disguised unemployment highlights the complexity of labor markets and the importance of addressing inefficiencies to enhance overall economic health. Understanding this concept is vital for students studying economics and labor dynamics.
Which of the following landmass is a part of Peninsular Plateau?- a)Tethys
- b)Gondwana land
- c)Angara land
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following landmass is a part of Peninsular Plateau?
a)
Tethys
b)
Gondwana land
c)
Angara land
d)
None of these
|
|
Sadhana Patel answered |
Tethys Ocean
- The Tethys is an ancient ocean that existed during the Mesozoic era.
- It is not a landmass but a body of water that contributed to the geological history of the region.
Gondwana Land
- Gondwana was a supercontinent that included present-day South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia, and the Indian subcontinent.
- It played a crucial role in the formation of the Peninsular Plateau.
- The Peninsular Plateau is primarily made up of ancient crystalline rocks, which are remnants of the Gondwana landmass.
- The breakup of Gondwana led to the uplift of the Peninsular Plateau, making it a significant geological feature of India.
Angara Land
- Angara land refers to a landmass that existed in the northern hemisphere, primarily encompassing parts of what are now North America, Europe, and Asia.
- It is not associated with the Peninsular Plateau of India.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' (Gondwana land) as it is directly related to the formation and composition of the Peninsular Plateau in India.
- Understanding the geological history of these landmasses helps explain the current topography and mineral wealth of the region.
- The Tethys is an ancient ocean that existed during the Mesozoic era.
- It is not a landmass but a body of water that contributed to the geological history of the region.
Gondwana Land
- Gondwana was a supercontinent that included present-day South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia, and the Indian subcontinent.
- It played a crucial role in the formation of the Peninsular Plateau.
- The Peninsular Plateau is primarily made up of ancient crystalline rocks, which are remnants of the Gondwana landmass.
- The breakup of Gondwana led to the uplift of the Peninsular Plateau, making it a significant geological feature of India.
Angara Land
- Angara land refers to a landmass that existed in the northern hemisphere, primarily encompassing parts of what are now North America, Europe, and Asia.
- It is not associated with the Peninsular Plateau of India.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' (Gondwana land) as it is directly related to the formation and composition of the Peninsular Plateau in India.
- Understanding the geological history of these landmasses helps explain the current topography and mineral wealth of the region.
Whom did Louis XVI get married?- a)Olympe de Gouges
- b)Marie Antoinette
- c)Marie de Medicis
- d)Nanine Vallain
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Whom did Louis XVI get married?
a)
Olympe de Gouges
b)
Marie Antoinette
c)
Marie de Medicis
d)
Nanine Vallain
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
In 1774, Louis XVI of the Bourbon family of kings ascended the throne of France. He was 20 years old and married to the Austrian princess Marie Antoinette.
What is the Old Regime?- a)The society and institutions of France before 1789.
- b)The period when the storming of the Bastille occurred.
- c)The period when the French society divided into a different estate.
- d)The society and institutions of France after 1789.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the Old Regime?
a)
The society and institutions of France before 1789.
b)
The period when the storming of the Bastille occurred.
c)
The period when the French society divided into a different estate.
d)
The society and institutions of France after 1789.
|
|
Aditya Shah answered |
The term Old Regime is usually used to describe the society and institutions of France before 1789.
What is the Old Regime?- a)The society and institutions of France before 1789.
- b)The period when the storming of the Bastille occurred.
- c)The period when the French society divided into a different estate.
- d)The society and institutions of France after 1789.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the Old Regime?
a)
The society and institutions of France before 1789.
b)
The period when the storming of the Bastille occurred.
c)
The period when the French society divided into a different estate.
d)
The society and institutions of France after 1789.
|
|
Rajnandini Singh answered |
The Old Regime Explained
The term "Old Regime" refers to the societal structure and institutions of France prior to the French Revolution, specifically before 1789. This period was characterized by a feudal system and a distinct social hierarchy.
Key Features of the Old Regime
- Social Structure
- The Old Regime was divided into three estates:
- **First Estate**: The clergy, who held significant power and wealth.
- **Second Estate**: The nobility, enjoying privileges and tax exemptions.
- **Third Estate**: Comprised the vast majority of the population, including peasants, urban workers, and the bourgeoisie, who bore the tax burden.
- Political Authority
- The monarchy held absolute power, with King Louis XVI as a prominent figure. The king was seen as the divine right ruler, and his authority was unquestioned.
- Economic Conditions
- Economic disparity was rampant. The Third Estate faced heavy taxation while the First and Second Estates were largely exempt, leading to widespread discontent and resentment.
- Cultural Aspects
- The Old Regime maintained traditional values and customs, heavily influenced by religion, which played a central role in daily life and governance.
Impact Leading to Revolution
The injustices and inequalities of the Old Regime ultimately fueled the desire for reform and equality among the Third Estate. This discontent culminated in the French Revolution, which sought to dismantle the old feudal structures and establish a new order based on liberty, equality, and fraternity.
Understanding the Old Regime is crucial for grasping the motivations behind the revolutionary changes that transformed French society and influenced the modern world.
The term "Old Regime" refers to the societal structure and institutions of France prior to the French Revolution, specifically before 1789. This period was characterized by a feudal system and a distinct social hierarchy.
Key Features of the Old Regime
- Social Structure
- The Old Regime was divided into three estates:
- **First Estate**: The clergy, who held significant power and wealth.
- **Second Estate**: The nobility, enjoying privileges and tax exemptions.
- **Third Estate**: Comprised the vast majority of the population, including peasants, urban workers, and the bourgeoisie, who bore the tax burden.
- Political Authority
- The monarchy held absolute power, with King Louis XVI as a prominent figure. The king was seen as the divine right ruler, and his authority was unquestioned.
- Economic Conditions
- Economic disparity was rampant. The Third Estate faced heavy taxation while the First and Second Estates were largely exempt, leading to widespread discontent and resentment.
- Cultural Aspects
- The Old Regime maintained traditional values and customs, heavily influenced by religion, which played a central role in daily life and governance.
Impact Leading to Revolution
The injustices and inequalities of the Old Regime ultimately fueled the desire for reform and equality among the Third Estate. This discontent culminated in the French Revolution, which sought to dismantle the old feudal structures and establish a new order based on liberty, equality, and fraternity.
Understanding the Old Regime is crucial for grasping the motivations behind the revolutionary changes that transformed French society and influenced the modern world.
Quarrying and mining are included in the:- a)Government sector
- b)Secondary sector
- c)Tertiary sector
- d)Primary sector
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Quarrying and mining are included in the:
a)
Government sector
b)
Secondary sector
c)
Tertiary sector
d)
Primary sector
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Quarrying and mining are included in the primary sector.
Raw material and money in hand are called:- a)Fixed Capital
- b)Human Capital
- c)Working Capital
- d)Variable Capital
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Raw material and money in hand are called:
a)
Fixed Capital
b)
Human Capital
c)
Working Capital
d)
Variable Capital
|
|
Abhijeet Dasgupta answered |
Working Capital refers to the capital required for day-to-day operations of a business. It is the amount of money or resources that a company has readily available to fund its daily operations, cover its short-term liabilities, and invest in its ongoing projects. Working capital is essential for the smooth functioning of a business and helps in meeting its short-term financial obligations.
Raw materials and money in hand are both components of working capital. Raw materials are the basic materials used in the production process to create finished goods. These can include items such as metals, chemicals, textiles, or agricultural products, depending on the nature of the business. Having an adequate supply of raw materials is crucial for uninterrupted production and timely delivery of goods to customers.
Money in hand, on the other hand, refers to the cash or cash equivalents that a company possesses at a given point in time. It includes physical currency, as well as funds held in bank accounts or other liquid assets that can be readily converted into cash. Money in hand is necessary to meet various day-to-day expenses, such as paying wages to employees, purchasing supplies, and covering other operational costs.
Having both raw materials and money in hand ensures that a business can continue its operations smoothly without any disruptions. It allows the company to fulfill customer orders on time, maintain a steady production process, and meet its financial obligations.
In summary, working capital is the capital required for the day-to-day functioning of a business. It includes raw materials and money in hand, which are both essential for the smooth operation of a company. Raw materials are necessary for production, while money in hand is required to meet daily expenses and financial obligations.
Raw materials and money in hand are both components of working capital. Raw materials are the basic materials used in the production process to create finished goods. These can include items such as metals, chemicals, textiles, or agricultural products, depending on the nature of the business. Having an adequate supply of raw materials is crucial for uninterrupted production and timely delivery of goods to customers.
Money in hand, on the other hand, refers to the cash or cash equivalents that a company possesses at a given point in time. It includes physical currency, as well as funds held in bank accounts or other liquid assets that can be readily converted into cash. Money in hand is necessary to meet various day-to-day expenses, such as paying wages to employees, purchasing supplies, and covering other operational costs.
Having both raw materials and money in hand ensures that a business can continue its operations smoothly without any disruptions. It allows the company to fulfill customer orders on time, maintain a steady production process, and meet its financial obligations.
In summary, working capital is the capital required for the day-to-day functioning of a business. It includes raw materials and money in hand, which are both essential for the smooth operation of a company. Raw materials are necessary for production, while money in hand is required to meet daily expenses and financial obligations.
Which one of these is the most labour absorbing sector of the economy?- a)Transportation
- b)Agriculture
- c)Service
- d)Industries
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of these is the most labour absorbing sector of the economy?
a)
Transportation
b)
Agriculture
c)
Service
d)
Industries
|
|
Aditi Sharma answered |
Agriculture is the most labour absorbing sector of the economy.
Which work, done mostly by woman, is not considered in the National Income?- a)Household work
- b)Work done in a private company
- c)Teaching work in schools
- d)Own business work
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which work, done mostly by woman, is not considered in the National Income?
a)
Household work
b)
Work done in a private company
c)
Teaching work in schools
d)
Own business work
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Women are not paid for the services or household work delivered in the family. So, household work is not considered in the National Income.
Assertion (A): People in the Jacobin group started wearing striped trousers like dock workers.
Reason (R): It was their way of presenting themselves differently from other sections of society.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true but R is false.
- d)A is false but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): People in the Jacobin group started wearing striped trousers like dock workers.
Reason (R): It was their way of presenting themselves differently from other sections of society.
Reason (R): It was their way of presenting themselves differently from other sections of society.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true but R is false.
d)
A is false but R is true.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The Jacobin club was the most successful political club in Paris. Its members belonged mainly to the less prosperous sections of society. They included small shopkeepers, artisans such as shoemakers, pastry cooks, watch-makers, printers, as well as servants, and daily-wage workers. A large group among the Jacobins decided to start wearing long striped trousers similar to those worn by dockworkers. This was to set themselves apart from the fashionable sections of society, especially nobles, who wore knee-breeches.
2nd estate comprised of which group?- a)Clergy
- b)Lawyers
- c)Big businessmen
- d)Nobility
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
2nd estate comprised of which group?
a)
Clergy
b)
Lawyers
c)
Big businessmen
d)
Nobility
|
|
Dhwani Shah answered |
2nd Estate - Nobility
The 2nd estate in the traditional feudal system comprised of the nobility. This group consisted of individuals who held hereditary titles and land, often passed down through generations. Nobles were typically granted their titles by the monarch in exchange for their loyalty, military service, or other forms of support.
Characteristics of the Nobility
- The nobility held significant power and influence in society, often controlling vast amounts of land and resources.
- They were exempt from many taxes and had special privileges, such as the right to hunt on their land or hold court.
- Nobles often served as advisors to the monarch and held positions of authority within the government, military, and church.
Role of the Nobility
- The nobility played a crucial role in maintaining social order and stability, as they were responsible for governing their lands and providing protection for their subjects.
- They also played a key role in the feudal system, where they swore loyalty to the monarch in exchange for land and protection.
Decline of the Nobility
- The power and influence of the nobility began to decline with the rise of centralized monarchies and the emergence of a more modern, merit-based society.
- The French Revolution in 1789 marked a significant turning point for the nobility, as many nobles lost their privileges and titles during the upheaval.
In conclusion, the 2nd estate, comprised of the nobility, played a significant role in medieval society but eventually saw its power diminish over time.
Assertion (A): Constituent Assembly Debates has been recorded and preserved.
Reason (R): It is used to interpret the meaning of the Constitution.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true but R is false.
- d)A is false but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Constituent Assembly Debates has been recorded and preserved.
Reason (R): It is used to interpret the meaning of the Constitution.
Reason (R): It is used to interpret the meaning of the Constitution.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true but R is false.
d)
A is false but R is true.
|
|
Sanjivani Iyer answered |
Assertion (A): Constituent Assembly Debates has been recorded and preserved.
Reason (R): It is used to interpret the meaning of the Constitution.
The correct answer is option 'A': Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
The Constituent Assembly Debates refer to the discussions and deliberations that took place during the framing of the Indian Constitution by the Constituent Assembly of India. These debates were recorded and preserved for future reference and have played a crucial role in interpreting the meaning and intent of the Constitution.
Importance of Recording and Preservation:
The recording and preservation of the Constituent Assembly Debates have several important implications:
1. Historical Reference: The debates provide a historical record of the thought processes, discussions, and arguments that went into the making of the Constitution. They serve as an invaluable resource for understanding the context in which different provisions were framed.
2. Intent of the Framers: The debates help in understanding the intent and vision of the framers of the Constitution. They shed light on the objectives, principles, and ideals that guided them during the drafting process.
3. Interpretation of the Constitution: The Constituent Assembly Debates are often referred to by the judiciary, scholars, and legal experts to interpret the meaning and scope of various provisions of the Constitution. When there is ambiguity or a need for clarification, the debates provide insight into the framers' intentions and help in arriving at an informed interpretation.
4. Democratic Process: The recording and preservation of the debates reflect the commitment to transparency and accountability in the democratic process. It allows for public access to the discussions that shaped the Constitution and promotes a better understanding of the principles and values it upholds.
Overall, the preservation of the Constituent Assembly Debates ensures that the constitutional framework is not only a static document but a living one, capable of evolving with changing times while remaining true to its original spirit. It enables a deeper understanding of the Constitution and its significance in shaping the democratic fabric of India.
Therefore, both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) correctly explains Assertion (A).
Reason (R): It is used to interpret the meaning of the Constitution.
The correct answer is option 'A': Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
The Constituent Assembly Debates refer to the discussions and deliberations that took place during the framing of the Indian Constitution by the Constituent Assembly of India. These debates were recorded and preserved for future reference and have played a crucial role in interpreting the meaning and intent of the Constitution.
Importance of Recording and Preservation:
The recording and preservation of the Constituent Assembly Debates have several important implications:
1. Historical Reference: The debates provide a historical record of the thought processes, discussions, and arguments that went into the making of the Constitution. They serve as an invaluable resource for understanding the context in which different provisions were framed.
2. Intent of the Framers: The debates help in understanding the intent and vision of the framers of the Constitution. They shed light on the objectives, principles, and ideals that guided them during the drafting process.
3. Interpretation of the Constitution: The Constituent Assembly Debates are often referred to by the judiciary, scholars, and legal experts to interpret the meaning and scope of various provisions of the Constitution. When there is ambiguity or a need for clarification, the debates provide insight into the framers' intentions and help in arriving at an informed interpretation.
4. Democratic Process: The recording and preservation of the debates reflect the commitment to transparency and accountability in the democratic process. It allows for public access to the discussions that shaped the Constitution and promotes a better understanding of the principles and values it upholds.
Overall, the preservation of the Constituent Assembly Debates ensures that the constitutional framework is not only a static document but a living one, capable of evolving with changing times while remaining true to its original spirit. It enables a deeper understanding of the Constitution and its significance in shaping the democratic fabric of India.
Therefore, both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) correctly explains Assertion (A).
Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan is a significant step towards providing education to all children in the age group:- a)6-14 years
- b)5-10 years
- c)10-15 years
- d)5-14 years
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan is a significant step towards providing education to all children in the age group:
a)
6-14 years
b)
5-10 years
c)
10-15 years
d)
5-14 years
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
It aims to provide compulsory and free elementary education to all children between the age of 6-14 years.
Question No. 53 to 58 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
The northern plain has been formed by the interplay of the three major river systems. This plain is formed of alluvial soil. The deposition of alluvium in a vast basin lying at the foothills of the Himalaya over millions of years formed this fertile plain. It spreads over an area of 7 lakh sq. km. The plain being about 2400 km long and 240 to 320 km broad, is a densely populated physiographic division. With a rich soil cover combined with an adequate water supply and favourable climate it is agriculturally a productive part of India The Northern Plain is broadly divided into three sections. The Western part of the Northern Plain is referred to as the Punjab Plains. Formed by the Indus and its tributaries, the larger part of this plain lies in Pakistan. The Indus and its tributaries - the Jhelum, the Chenab, the Ravi, the Beas and the Satluj originate in the Himalaya. This section of the plain is dominated by the doabs.
The Ganga plain extends between Ghaggar and Teesta rivers. It is spread over the states of North India, Haryana, Delhi, U.P., Bihar, partly Jharkhand and West Bengal to its East, particularly in Assam lies the Brahmaputra plain. The northern plains are generally described as flat land with no variations in its relief. It is not true. These vast plains also have diverse relief features. According to the variations in relief features, the Northern plains can be divided into four regions. The rivers, after descending from the mountains deposit pebbles in a narrow belt of about 8 to 16 km in width lying parallel to the slopes of the Shiwaliks. It is known as bhabar. All the streams disappear in this bhabar belt. South of this belt, the streams and rivers re-emerge and create a wet, swampy and marshy region known as terai. This was a thickly forested region full of wildlife. The forests have been cleared to create agricultural land and to settle migrants from Pakistan after partition.Q. The northern plain has been formed by the interplay of the three major river systems. Name the rivers.- a)Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi
- b)Indus, Ganga, Brahmaputra
- c)Narmada, Tapi, Sabarmati
- d)Godavari, Ganga, Narmada
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question No. 53 to 58 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
The northern plain has been formed by the interplay of the three major river systems. This plain is formed of alluvial soil. The deposition of alluvium in a vast basin lying at the foothills of the Himalaya over millions of years formed this fertile plain. It spreads over an area of 7 lakh sq. km. The plain being about 2400 km long and 240 to 320 km broad, is a densely populated physiographic division. With a rich soil cover combined with an adequate water supply and favourable climate it is agriculturally a productive part of India The Northern Plain is broadly divided into three sections. The Western part of the Northern Plain is referred to as the Punjab Plains. Formed by the Indus and its tributaries, the larger part of this plain lies in Pakistan. The Indus and its tributaries - the Jhelum, the Chenab, the Ravi, the Beas and the Satluj originate in the Himalaya. This section of the plain is dominated by the doabs.
The Ganga plain extends between Ghaggar and Teesta rivers. It is spread over the states of North India, Haryana, Delhi, U.P., Bihar, partly Jharkhand and West Bengal to its East, particularly in Assam lies the Brahmaputra plain. The northern plains are generally described as flat land with no variations in its relief. It is not true. These vast plains also have diverse relief features. According to the variations in relief features, the Northern plains can be divided into four regions. The rivers, after descending from the mountains deposit pebbles in a narrow belt of about 8 to 16 km in width lying parallel to the slopes of the Shiwaliks. It is known as bhabar. All the streams disappear in this bhabar belt. South of this belt, the streams and rivers re-emerge and create a wet, swampy and marshy region known as terai. This was a thickly forested region full of wildlife. The forests have been cleared to create agricultural land and to settle migrants from Pakistan after partition.
The northern plain has been formed by the interplay of the three major river systems. This plain is formed of alluvial soil. The deposition of alluvium in a vast basin lying at the foothills of the Himalaya over millions of years formed this fertile plain. It spreads over an area of 7 lakh sq. km. The plain being about 2400 km long and 240 to 320 km broad, is a densely populated physiographic division. With a rich soil cover combined with an adequate water supply and favourable climate it is agriculturally a productive part of India The Northern Plain is broadly divided into three sections. The Western part of the Northern Plain is referred to as the Punjab Plains. Formed by the Indus and its tributaries, the larger part of this plain lies in Pakistan. The Indus and its tributaries - the Jhelum, the Chenab, the Ravi, the Beas and the Satluj originate in the Himalaya. This section of the plain is dominated by the doabs.
The Ganga plain extends between Ghaggar and Teesta rivers. It is spread over the states of North India, Haryana, Delhi, U.P., Bihar, partly Jharkhand and West Bengal to its East, particularly in Assam lies the Brahmaputra plain. The northern plains are generally described as flat land with no variations in its relief. It is not true. These vast plains also have diverse relief features. According to the variations in relief features, the Northern plains can be divided into four regions. The rivers, after descending from the mountains deposit pebbles in a narrow belt of about 8 to 16 km in width lying parallel to the slopes of the Shiwaliks. It is known as bhabar. All the streams disappear in this bhabar belt. South of this belt, the streams and rivers re-emerge and create a wet, swampy and marshy region known as terai. This was a thickly forested region full of wildlife. The forests have been cleared to create agricultural land and to settle migrants from Pakistan after partition.
Q. The northern plain has been formed by the interplay of the three major river systems. Name the rivers.
a)
Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi
b)
Indus, Ganga, Brahmaputra
c)
Narmada, Tapi, Sabarmati
d)
Godavari, Ganga, Narmada
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The rivers are Indus, Ganga, Brahmaputra.
Nelson Mandela remained in prison for treason for about:- a)26 years
- b)20 years
- c)27 years
- d)25 years
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Nelson Mandela remained in prison for treason for about:
a)
26 years
b)
20 years
c)
27 years
d)
25 years
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
Nelson Mandela spent the next 27 years in South Africa’s most dreaded prison, Robben Island.
Which of the following is not the reason of empty treasure?
- a)Food supplies to the ordinary citizens.
- b)The cost of maintaining an extravagant court.
- c)To meet its regular expenses.
- d)Long years of war.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not the reason of empty treasure?
a)
Food supplies to the ordinary citizens.
b)
The cost of maintaining an extravagant court.
c)
To meet its regular expenses.
d)
Long years of war.

|
Bhargavi Mehta answered |
Food supplies to the ordinary citizens
The reason "Food supplies to the ordinary citizens" is not a cause of empty treasure is because providing food supplies to the ordinary citizens is a basic necessity that a government should fulfill. It is essential for the well-being of the population and is not a luxury or extravagance that would lead to a depletion of the treasury.
The cost of maintaining an extravagant court
Maintaining an extravagant court can be a significant drain on the treasury. This includes expenses related to the royal family, courtiers, ceremonies, and luxury items. The cost of maintaining such a lavish lifestyle can quickly deplete the treasury and lead to empty coffers.
To meet its regular expenses
Meeting regular expenses such as salaries of government officials, infrastructure maintenance, and other essential services can also contribute to emptying the treasury. If the government is unable to manage its finances efficiently or if there is widespread corruption, it can lead to a situation where regular expenses exceed the revenue generated.
Long years of war
Engaging in long years of war can be extremely costly for a government. War expenses include funding the military, purchasing weapons, providing healthcare for soldiers, and rebuilding infrastructure post-war. The financial burden of sustained military conflicts can drain the treasury and lead to financial difficulties for the government.
In conclusion, providing food supplies to the ordinary citizens is not a reason for empty treasure as it is a basic necessity. However, maintaining an extravagant court, meeting regular expenses, and engaging in long years of war can all contribute to depleting the treasury.
How many members were there in the Constituent Assembly that wrote the Indian Constitution?- a)101 members
- b)206 members
- c)299 members
- d)36 members
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many members were there in the Constituent Assembly that wrote the Indian Constitution?
a)
101 members
b)
206 members
c)
299 members
d)
36 members
|
|
Alok Majumdar answered |
There were 299 members in the Constituent Assembly that wrote the Indian Constitution.
- **Formation of the Constituent Assembly**
The Constituent Assembly of India was formed in 1946 to draft the Constitution of India.
- **Composition of the Constituent Assembly**
The Constituent Assembly consisted of a total of 299 members. Out of these, 284 members were representatives of the provinces, while the rest were from the princely states.
- **Representation**
The members of the Constituent Assembly were representatives of various communities, regions, and interest groups in India, ensuring a diverse and inclusive approach to constitution-making.
- **Leadership**
Dr. Rajendra Prasad was elected as the President of the Constituent Assembly, while Dr. B.R. Ambedkar served as the Chairman of the Drafting Committee.
- **Work of the Constituent Assembly**
The Constituent Assembly held numerous sessions over a period of nearly three years to discuss, debate, and finalize the provisions of the Indian Constitution.
- **Adoption of the Constitution**
The Indian Constitution was finally adopted on January 26, 1950, marking the beginning of a new era for independent India.
In conclusion, the Constituent Assembly of India, with its 299 members, played a crucial role in shaping the Constitution of India, a document that continues to guide the country's governance and uphold its democratic values.
- **Formation of the Constituent Assembly**
The Constituent Assembly of India was formed in 1946 to draft the Constitution of India.
- **Composition of the Constituent Assembly**
The Constituent Assembly consisted of a total of 299 members. Out of these, 284 members were representatives of the provinces, while the rest were from the princely states.
- **Representation**
The members of the Constituent Assembly were representatives of various communities, regions, and interest groups in India, ensuring a diverse and inclusive approach to constitution-making.
- **Leadership**
Dr. Rajendra Prasad was elected as the President of the Constituent Assembly, while Dr. B.R. Ambedkar served as the Chairman of the Drafting Committee.
- **Work of the Constituent Assembly**
The Constituent Assembly held numerous sessions over a period of nearly three years to discuss, debate, and finalize the provisions of the Indian Constitution.
- **Adoption of the Constitution**
The Indian Constitution was finally adopted on January 26, 1950, marking the beginning of a new era for independent India.
In conclusion, the Constituent Assembly of India, with its 299 members, played a crucial role in shaping the Constitution of India, a document that continues to guide the country's governance and uphold its democratic values.
Question No. 53 to 58 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
The northern plain has been formed by the interplay of the three major river systems. This plain is formed of alluvial soil. The deposition of alluvium in a vast basin lying at the foothills of the Himalaya over millions of years formed this fertile plain. It spreads over an area of 7 lakh sq. km. The plain being about 2400 km long and 240 to 320 km broad, is a densely populated physiographic division. With a rich soil cover combined with an adequate water supply and favourable climate it is agriculturally a productive part of India The Northern Plain is broadly divided into three sections. The Western part of the Northern Plain is referred to as the Punjab Plains. Formed by the Indus and its tributaries, the larger part of this plain lies in Pakistan. The Indus and its tributaries - the Jhelum, the Chenab, the Ravi, the Beas and the Satluj originate in the Himalaya. This section of the plain is dominated by the doabs.
The Ganga plain extends between Ghaggar and Teesta rivers. It is spread over the states of North India, Haryana, Delhi, U.P., Bihar, partly Jharkhand and West Bengal to its East, particularly in Assam lies the Brahmaputra plain. The northern plains are generally described as flat land with no variations in its relief. It is not true. These vast plains also have diverse relief features. According to the variations in relief features, the Northern plains can be divided into four regions. The rivers, after descending from the mountains deposit pebbles in a narrow belt of about 8 to 16 km in width lying parallel to the slopes of the Shiwaliks. It is known as bhabar. All the streams disappear in this bhabar belt. South of this belt, the streams and rivers re-emerge and create a wet, swampy and marshy region known as terai. This was a thickly forested region full of wildlife. The forests have been cleared to create agricultural land and to settle migrants from Pakistan after partition.Q. The Northern plain is formed due to alluvial deposits brought by the Himalayan river(s) such as ________.- a)Indus
- b)All of these
- c)Brahmaputra
- d)Ganga
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question No. 53 to 58 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
The northern plain has been formed by the interplay of the three major river systems. This plain is formed of alluvial soil. The deposition of alluvium in a vast basin lying at the foothills of the Himalaya over millions of years formed this fertile plain. It spreads over an area of 7 lakh sq. km. The plain being about 2400 km long and 240 to 320 km broad, is a densely populated physiographic division. With a rich soil cover combined with an adequate water supply and favourable climate it is agriculturally a productive part of India The Northern Plain is broadly divided into three sections. The Western part of the Northern Plain is referred to as the Punjab Plains. Formed by the Indus and its tributaries, the larger part of this plain lies in Pakistan. The Indus and its tributaries - the Jhelum, the Chenab, the Ravi, the Beas and the Satluj originate in the Himalaya. This section of the plain is dominated by the doabs.
The Ganga plain extends between Ghaggar and Teesta rivers. It is spread over the states of North India, Haryana, Delhi, U.P., Bihar, partly Jharkhand and West Bengal to its East, particularly in Assam lies the Brahmaputra plain. The northern plains are generally described as flat land with no variations in its relief. It is not true. These vast plains also have diverse relief features. According to the variations in relief features, the Northern plains can be divided into four regions. The rivers, after descending from the mountains deposit pebbles in a narrow belt of about 8 to 16 km in width lying parallel to the slopes of the Shiwaliks. It is known as bhabar. All the streams disappear in this bhabar belt. South of this belt, the streams and rivers re-emerge and create a wet, swampy and marshy region known as terai. This was a thickly forested region full of wildlife. The forests have been cleared to create agricultural land and to settle migrants from Pakistan after partition.
The northern plain has been formed by the interplay of the three major river systems. This plain is formed of alluvial soil. The deposition of alluvium in a vast basin lying at the foothills of the Himalaya over millions of years formed this fertile plain. It spreads over an area of 7 lakh sq. km. The plain being about 2400 km long and 240 to 320 km broad, is a densely populated physiographic division. With a rich soil cover combined with an adequate water supply and favourable climate it is agriculturally a productive part of India The Northern Plain is broadly divided into three sections. The Western part of the Northern Plain is referred to as the Punjab Plains. Formed by the Indus and its tributaries, the larger part of this plain lies in Pakistan. The Indus and its tributaries - the Jhelum, the Chenab, the Ravi, the Beas and the Satluj originate in the Himalaya. This section of the plain is dominated by the doabs.
The Ganga plain extends between Ghaggar and Teesta rivers. It is spread over the states of North India, Haryana, Delhi, U.P., Bihar, partly Jharkhand and West Bengal to its East, particularly in Assam lies the Brahmaputra plain. The northern plains are generally described as flat land with no variations in its relief. It is not true. These vast plains also have diverse relief features. According to the variations in relief features, the Northern plains can be divided into four regions. The rivers, after descending from the mountains deposit pebbles in a narrow belt of about 8 to 16 km in width lying parallel to the slopes of the Shiwaliks. It is known as bhabar. All the streams disappear in this bhabar belt. South of this belt, the streams and rivers re-emerge and create a wet, swampy and marshy region known as terai. This was a thickly forested region full of wildlife. The forests have been cleared to create agricultural land and to settle migrants from Pakistan after partition.
Q. The Northern plain is formed due to alluvial deposits brought by the Himalayan river(s) such as ________.
a)
Indus
b)
All of these
c)
Brahmaputra
d)
Ganga
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
The Northern plain is formed due to alluvial deposits brought by the Himalayan river(s) such as Indus, Brahmaputra and Ganga.
Chapter doubts & questions for Sample Papers with Solutions - Social Studies (SST) Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Sample Papers with Solutions - Social Studies (SST) Class 9 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Social Studies (SST) Class 9
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









