All Exams >
Commerce >
Entrepreneurship Class 12 >
All Questions
All questions of Business Arithmetic for Commerce Exam
Joseph invested ₹ 1,000 in a pizza restaurant in 2018 and sold the shares for a total of ₹ 1,200 one year later. While looking at the accounts, he wanted to calculate the return on investment for his restaurant. To calculate it, he divided the net profits by the investment cost. Calculate and confirm how much would be the return on investment for Joseph’s restaurant. - a)10%
- b)20%
- c)15%
- d)25%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Joseph invested ₹ 1,000 in a pizza restaurant in 2018 and sold the shares for a total of ₹ 1,200 one year later. While looking at the accounts, he wanted to calculate the return on investment for his restaurant. To calculate it, he divided the net profits by the investment cost. Calculate and confirm how much would be the return on investment for Joseph’s restaurant.
a)
10%
b)
20%
c)
15%
d)
25%
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Formula Return on Investment (ROI)
- First method:
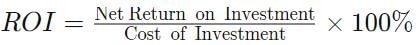
- Second method:

A company uses 300 units of an item per day and the order lead time is 5 days. What should be the level of inventory when a new order is to be placed?- a)1500 units
- b)1000 units
- c)500 units
- d)2000 units
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A company uses 300 units of an item per day and the order lead time is 5 days. What should be the level of inventory when a new order is to be placed?
a)
1500 units
b)
1000 units
c)
500 units
d)
2000 units
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The basic formula for calculating ending inventory is: Beginning inventory + net purchases – COGS = ending inventory.
Your beginning inventory is the last period's ending inventory.
The net purchases are the items you've bought and added to your inventory count.
Your beginning inventory is the last period's ending inventory.
The net purchases are the items you've bought and added to your inventory count.
Amul Milk Pvt. Ltd. is conducting campus placement to hire new workforce for their new branch in Patiala, Punjab. The HR team went to a college campus nearby to select around 20 candidates. While conducting the personal interviews of selected 25 candidates, the HR asked one of them to explain what does he understand by the term ‘Production Cycle’. He responded confidently by saying that it is the time period between receiving the raw material and converting them into final finished goods.
Considering the candidate’s response, state whether his statement is true or false. - a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Amul Milk Pvt. Ltd. is conducting campus placement to hire new workforce for their new branch in Patiala, Punjab. The HR team went to a college campus nearby to select around 20 candidates. While conducting the personal interviews of selected 25 candidates, the HR asked one of them to explain what does he understand by the term ‘Production Cycle’. He responded confidently by saying that it is the time period between receiving the raw material and converting them into final finished goods.
Considering the candidate’s response, state whether his statement is true or false.
Considering the candidate’s response, state whether his statement is true or false.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Production Cycle: The production cycle is comprised of all activities related to the conversion of raw materials into finished goods. The cycle has several distinct components, involving the design of products, their incorporation into a production schedule, manufacturing activities, and a cost accounting feedback loop.
For example, the production cycle for the windows manufacturing enterprise would be much shorter, than for the automobile manufacturers.
For example, the production cycle for the windows manufacturing enterprise would be much shorter, than for the automobile manufacturers.
Which of the following is an examples of carrying costs for inventories?- a)Money tied up in inventory
- b)Storage of inventories
- c)Obsolescence cost
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an examples of carrying costs for inventories?
a)
Money tied up in inventory
b)
Storage of inventories
c)
Obsolescence cost
d)
All of the above

|
Rhea Choudhary answered |
Examples of carrying costs for inventories:
Carrying costs refer to the expenses incurred by a business in holding and storing inventory. These costs can significantly impact a company's profitability and should be carefully managed. The examples of carrying costs for inventories are:
1. Money tied up in inventory:
- The cost of purchasing inventory ties up a significant amount of a company's capital. This capital could be used for other purposes such as investing in new projects or paying off debts.
- The longer inventory is held, the more money is tied up in it, leading to an opportunity cost for the business.
2. Storage of inventories:
- Businesses need to allocate space for storing their inventory, which incurs costs.
- Renting or owning warehouse space, maintaining the warehouse, and ensuring proper security measures all contribute to the carrying costs.
- Additionally, utilities like electricity and heating/cooling expenses are required to keep the inventory in good condition.
3. Obsolescence cost:
- Over time, inventory can become obsolete or outdated, particularly in industries with rapidly changing technology or fashion trends.
- Obsolescence costs occur when inventory loses its value or utility due to changes in market demand, product design, or technological advancements.
- These costs can include markdowns, write-offs, or potential losses if the inventory cannot be sold.
4. Insurance and taxes:
- Carrying costs also include expenses such as property and inventory insurance, as well as property taxes.
- Insurance protects against losses due to theft, fire, or damage to inventory, while property taxes are levied on the value of the inventory and the storage facilities.
5. Costs of capital:
- The cost of financing inventory through loans or lines of credit adds to the carrying costs.
- Interest charges, loan fees, and other financial costs are incurred when borrowing money to purchase or maintain inventory.
Conclusion:
Carrying costs for inventories encompass various expenses that a business incurs while holding and storing inventory. These costs include the money tied up in inventory, storage expenses, obsolescence costs, insurance and taxes, as well as the costs of capital. Proper management of these carrying costs is essential for optimizing profitability and maintaining a healthy inventory turnover.
Carrying costs refer to the expenses incurred by a business in holding and storing inventory. These costs can significantly impact a company's profitability and should be carefully managed. The examples of carrying costs for inventories are:
1. Money tied up in inventory:
- The cost of purchasing inventory ties up a significant amount of a company's capital. This capital could be used for other purposes such as investing in new projects or paying off debts.
- The longer inventory is held, the more money is tied up in it, leading to an opportunity cost for the business.
2. Storage of inventories:
- Businesses need to allocate space for storing their inventory, which incurs costs.
- Renting or owning warehouse space, maintaining the warehouse, and ensuring proper security measures all contribute to the carrying costs.
- Additionally, utilities like electricity and heating/cooling expenses are required to keep the inventory in good condition.
3. Obsolescence cost:
- Over time, inventory can become obsolete or outdated, particularly in industries with rapidly changing technology or fashion trends.
- Obsolescence costs occur when inventory loses its value or utility due to changes in market demand, product design, or technological advancements.
- These costs can include markdowns, write-offs, or potential losses if the inventory cannot be sold.
4. Insurance and taxes:
- Carrying costs also include expenses such as property and inventory insurance, as well as property taxes.
- Insurance protects against losses due to theft, fire, or damage to inventory, while property taxes are levied on the value of the inventory and the storage facilities.
5. Costs of capital:
- The cost of financing inventory through loans or lines of credit adds to the carrying costs.
- Interest charges, loan fees, and other financial costs are incurred when borrowing money to purchase or maintain inventory.
Conclusion:
Carrying costs for inventories encompass various expenses that a business incurs while holding and storing inventory. These costs include the money tied up in inventory, storage expenses, obsolescence costs, insurance and taxes, as well as the costs of capital. Proper management of these carrying costs is essential for optimizing profitability and maintaining a healthy inventory turnover.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. ROE represents the quantity of an item which is most economical to order when fresh supplies are required.
- a)False
- b)True
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. ROE represents the quantity of an item which is most economical to order when fresh supplies are required.
Q. ROE represents the quantity of an item which is most economical to order when fresh supplies are required.
a)
False
b)
True
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Return on equity ratio can be described as a financial ratio that helps measure a company's proficiency to generate profits from its shareholders' investments. This profitability helps to gauge a company's effectiveness when it comes to using equity funding to run its daily operations.
How is ‘Unit of Sale’ determined in a restaurant providing dinner?- a)Unit of sale will be the number of dinners offered.
- b)Unit of sale will be the average amount billed per dinner.
- c)Both (a) and (b).
- d)None of these.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How is ‘Unit of Sale’ determined in a restaurant providing dinner?
a)
Unit of sale will be the number of dinners offered.
b)
Unit of sale will be the average amount billed per dinner.
c)
Both (a) and (b).
d)
None of these.
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Unit of sale: A unit of sale is what a customer actually buys from you. It's the amount of product (or service) you use to figure your operations and profitability. The unit of sale is really the basic building block of your business. If you were a retailer who sold athletic shoes, your unit of sale would be a single pair of shoes.
Harshdeep is the stock keeper of Neha Textiles Ltd. The company is into converting cotton yarn into fabric and then further computerised printing on the same to add value to the fabric. He wants to know the ideal quantity of yarn to be ordered so that the production process does not stop. How can he know the correct time to place an order?- a)By calculating Break-even point
- b)By calculating Re-order point
- c)By calculating Economic order quantity
- d)By calculating Lead time
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Harshdeep is the stock keeper of Neha Textiles Ltd. The company is into converting cotton yarn into fabric and then further computerised printing on the same to add value to the fabric. He wants to know the ideal quantity of yarn to be ordered so that the production process does not stop. How can he know the correct time to place an order?
a)
By calculating Break-even point
b)
By calculating Re-order point
c)
By calculating Economic order quantity
d)
By calculating Lead time
|
|
Amita Das answered |
The basic formula for the reorder point is to multiply the average daily usage rate for an inventory item by the lead time in days to replenish it. This formula alteration means that replenishment stock will be ordered sooner, which greatly reduces the risk that there will be a stockout condition.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Gross margin and gross profit are one and the same. - a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Gross margin and gross profit are one and the same.
Q. Gross margin and gross profit are one and the same.
a)
True
b)
False

|
Akshay Shah answered |
Understanding Gross Margin and Gross Profit
Gross margin and gross profit are often used interchangeably, leading to some confusion. However, it’s essential to understand their definitions and how they relate to each other.
Definitions
- Gross Profit: This is the revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from total sales. It reflects the efficiency of production and sales operations.
- Gross Margin: This is a percentage that represents the gross profit as a proportion of total sales. It is calculated using the formula:
Gross Margin (%) = (Gross Profit / Total Sales) x 100.
Relationship Between Gross Margin and Gross Profit
- While gross profit is a monetary value, gross margin provides insight into profitability in percentage terms.
- They are related but represent different aspects of financial performance. For instance, a company can have a high gross profit but a low gross margin if its sales volume is very high relative to its costs.
Conclusion
The statement that gross margin and gross profit are one and the same is technically False. While they are related concepts, they convey different information about a company's financial health. Understanding both is crucial for evaluating a business's profitability and making informed decisions.
Gross margin and gross profit are often used interchangeably, leading to some confusion. However, it’s essential to understand their definitions and how they relate to each other.
Definitions
- Gross Profit: This is the revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from total sales. It reflects the efficiency of production and sales operations.
- Gross Margin: This is a percentage that represents the gross profit as a proportion of total sales. It is calculated using the formula:
Gross Margin (%) = (Gross Profit / Total Sales) x 100.
Relationship Between Gross Margin and Gross Profit
- While gross profit is a monetary value, gross margin provides insight into profitability in percentage terms.
- They are related but represent different aspects of financial performance. For instance, a company can have a high gross profit but a low gross margin if its sales volume is very high relative to its costs.
Conclusion
The statement that gross margin and gross profit are one and the same is technically False. While they are related concepts, they convey different information about a company's financial health. Understanding both is crucial for evaluating a business's profitability and making informed decisions.
In a sugar mill in UP, jaggery is produced using cane. The mill owner is unable to decide whether to continue with his subsidiary or not. The monthly output of the subsidiary is 2,500/kg. Sale price ₹ 100/ kg, Variable cost ₹ 30/kg, Fixed expenses ₹ 70,000. The mill owner is trying to find out the break-even point in units. It will be?- a)7,500 units
- b)10,000 units
- c)1,500 units
- d)1,000 units
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a sugar mill in UP, jaggery is produced using cane. The mill owner is unable to decide whether to continue with his subsidiary or not. The monthly output of the subsidiary is 2,500/kg. Sale price ₹ 100/ kg, Variable cost ₹ 30/kg, Fixed expenses ₹ 70,000. The mill owner is trying to find out the break-even point in units. It will be?
a)
7,500 units
b)
10,000 units
c)
1,500 units
d)
1,000 units
|
|
Amita Das answered |
To calculate the break-even point in units use the formula: Break-Even point (units) = Fixed Costs ÷ (Sales price per unit – Variable costs per unit) or in sales dollars using the formula: Break-Even point (sales dollars) = Fixed Costs ÷ Contribution Margin.
Which of the following statement is false with respect to ABC analysis?- a)‘A’ includes the items whose annual consumption value is the highest
- b)‘B’ includes the items with a lower consumption value
- c)ABC analysis can help you control you inventory better
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is false with respect to ABC analysis?
a)
‘A’ includes the items whose annual consumption value is the highest
b)
‘B’ includes the items with a lower consumption value
c)
ABC analysis can help you control you inventory better
d)
All of the above

|
Nilanjan Malik answered |
ABC analysis is a technique used for inventory management and categorizes items into three categories based on their value and importance.
b) It helps in identifying the items that contribute the most to the overall inventory value and should be given more attention.
c) It is also known as Pareto analysis.
d) It is only applicable for companies that sell physical products.
b) It helps in identifying the items that contribute the most to the overall inventory value and should be given more attention.
c) It is also known as Pareto analysis.
d) It is only applicable for companies that sell physical products.
Sohan’s firm has a capital of ₹ 10,00,000; Sales of ₹ 5,00,000; Gross profit of ₹ 2,00,000 and Expenses of ₹ 1,00,000. He has hired a chartered account to work and manage his accounts. The CA, while working on the sales and profits, etc. found that the return on investment for the firm will be 10%. Sohan doubted the calculation of the CA. Keeping in view the above scenario, state whether the CA’s calculation was true or false.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Sohan’s firm has a capital of ₹ 10,00,000; Sales of ₹ 5,00,000; Gross profit of ₹ 2,00,000 and Expenses of ₹ 1,00,000. He has hired a chartered account to work and manage his accounts. The CA, while working on the sales and profits, etc. found that the return on investment for the firm will be 10%. Sohan doubted the calculation of the CA. Keeping in view the above scenario, state whether the CA’s calculation was true or false.
a)
True
b)
False

|
Dishani Kulkarni answered |
Can you please provide more context or clarify your question?
Pintu runs a company that sells ball pens. They first determined the fixed costs, which included Property tax, salaries, etc, which sums up to 1,00,000. The variable cost for manufacturing a pen is ₹ 2 per unit. Hence, they sell the pen at a price of ₹ 10. If one has to determine the break-even point, that would come up to:- a)5,000
- b)20,000
- c)12,500
- d)15,000
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Pintu runs a company that sells ball pens. They first determined the fixed costs, which included Property tax, salaries, etc, which sums up to 1,00,000. The variable cost for manufacturing a pen is ₹ 2 per unit. Hence, they sell the pen at a price of ₹ 10. If one has to determine the break-even point, that would come up to:
a)
5,000
b)
20,000
c)
12,500
d)
15,000

|
Kalyan Desai answered |
Break-even point refers to the level of sales at which a company neither makes a profit nor incurs a loss. It is the point where total revenue equals total costs. In order to determine the break-even point, we need to calculate the number of units that need to be sold to cover both fixed and variable costs.
1. Calculate the Contribution Margin per unit:
The contribution margin is the difference between the selling price per unit and the variable cost per unit. In this case, the selling price is Rs. 10 and the variable cost is Rs. 2. Therefore, the contribution margin per unit is Rs. 10 - Rs. 2 = Rs. 8.
2. Calculate the Break-even Point in units:
The break-even point in units can be calculated by dividing the total fixed costs by the contribution margin per unit.
Break-even Point (in units) = Total Fixed Costs / Contribution Margin per unit
Break-even Point (in units) = Rs. 1,00,000 / Rs. 8 = 12,500 units
3. Determine the correct option:
The correct answer is option 'C' which states that the break-even point is 12,500 units.
Explanation:
To break-even, Pintu needs to sell 12,500 units of ball pens. At this level, the total revenue generated from selling 12,500 units at a price of Rs. 10 per unit would be Rs. 1,25,000 (12,500 units x Rs. 10). This revenue would cover both the fixed costs of Rs. 1,00,000 and the variable costs of Rs. 2 per unit for the 12,500 units (12,500 units x Rs. 2). Thus, there would be no profit or loss at the break-even point.
It is important for businesses to determine their break-even point as it helps them understand the level of sales needed to cover their costs. It also provides insights into the profitability of the business and helps in making pricing and production decisions.
1. Calculate the Contribution Margin per unit:
The contribution margin is the difference between the selling price per unit and the variable cost per unit. In this case, the selling price is Rs. 10 and the variable cost is Rs. 2. Therefore, the contribution margin per unit is Rs. 10 - Rs. 2 = Rs. 8.
2. Calculate the Break-even Point in units:
The break-even point in units can be calculated by dividing the total fixed costs by the contribution margin per unit.
Break-even Point (in units) = Total Fixed Costs / Contribution Margin per unit
Break-even Point (in units) = Rs. 1,00,000 / Rs. 8 = 12,500 units
3. Determine the correct option:
The correct answer is option 'C' which states that the break-even point is 12,500 units.
Explanation:
To break-even, Pintu needs to sell 12,500 units of ball pens. At this level, the total revenue generated from selling 12,500 units at a price of Rs. 10 per unit would be Rs. 1,25,000 (12,500 units x Rs. 10). This revenue would cover both the fixed costs of Rs. 1,00,000 and the variable costs of Rs. 2 per unit for the 12,500 units (12,500 units x Rs. 2). Thus, there would be no profit or loss at the break-even point.
It is important for businesses to determine their break-even point as it helps them understand the level of sales needed to cover their costs. It also provides insights into the profitability of the business and helps in making pricing and production decisions.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Sales mix is the proportion in which two or more products are sold.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Sales mix is the proportion in which two or more products are sold.
Q. Sales mix is the proportion in which two or more products are sold.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
Sales mix is the proportion in which two or more products are sold.
For the calculation of break-even point for sales mix, following assumptions are made in addition to those already made for CVP analysis:
For the calculation of break-even point for sales mix, following assumptions are made in addition to those already made for CVP analysis:
- The proportion of sales mix must be predetermined.
- The sales mix must not change within the relevant time period.
The calculation method for the break-even point of sales mix is based on the contribution approach method. Since we have multiple products in sales mix therefore it is most likely that we will be dealing with products with different contribution margin per unit and contribution margin ratios. This problem is overcome by calculating weighted average contribution margin per unit and contribution margin ratio. These are then used to calculate the break-even point for sales mix.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Working capital is required to meet day-to-day expenses and to facilitate smooth functioning of the business.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Working capital is required to meet day-to-day expenses and to facilitate smooth functioning of the business.
Q. Working capital is required to meet day-to-day expenses and to facilitate smooth functioning of the business.
a)
True
b)
False

|
Shail Chakraborty answered |
Explanation:
Working capital refers to the funds that are used to cover the day-to-day operational expenses of a business. It is the difference between a company's current assets and its current liabilities. The statement given in the question is true, and it can be explained as follows:
Importance of Working Capital:
Working capital is essential for the smooth functioning of a business. It is required to meet the day-to-day expenses and to ensure that the business operations run smoothly. Without sufficient working capital, a company may face difficulties in paying its bills, buying inventory, and meeting other short-term obligations.
Meeting Day-to-Day Expenses:
One of the primary purposes of working capital is to cover the day-to-day expenses of a business. These expenses include salaries and wages, rent, utilities, raw materials, and other operating costs. Having enough working capital ensures that these expenses can be paid on time, allowing the business to operate smoothly.
Facilitating Smooth Functioning:
Working capital also plays a crucial role in facilitating the smooth functioning of the business. It provides the necessary funds to maintain inventory levels, fulfill customer orders, and manage the cash flow. For example, if a company does not have enough working capital to purchase inventory, it may face stockouts and lose potential sales.
Seasonal Fluctuations:
Working capital is particularly important for businesses that experience seasonal fluctuations in sales. During the low season, when sales are slow, working capital helps cover the expenses and keep the business running until the high season arrives. It provides the necessary cushion to bridge the gap between sales and expenses.
Dealing with Unexpected Events:
Having sufficient working capital also enables a business to deal with unexpected events or emergencies. For instance, if a major piece of equipment breaks down, working capital can be used to repair or replace it. This ensures that the business can continue its operations without major disruptions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, working capital is indeed required to meet day-to-day expenses and facilitate the smooth functioning of a business. It ensures that operational expenses can be met, inventory can be maintained, and cash flow remains healthy. Without sufficient working capital, a business may struggle to operate effectively and face various financial challenges.
Working capital refers to the funds that are used to cover the day-to-day operational expenses of a business. It is the difference between a company's current assets and its current liabilities. The statement given in the question is true, and it can be explained as follows:
Importance of Working Capital:
Working capital is essential for the smooth functioning of a business. It is required to meet the day-to-day expenses and to ensure that the business operations run smoothly. Without sufficient working capital, a company may face difficulties in paying its bills, buying inventory, and meeting other short-term obligations.
Meeting Day-to-Day Expenses:
One of the primary purposes of working capital is to cover the day-to-day expenses of a business. These expenses include salaries and wages, rent, utilities, raw materials, and other operating costs. Having enough working capital ensures that these expenses can be paid on time, allowing the business to operate smoothly.
Facilitating Smooth Functioning:
Working capital also plays a crucial role in facilitating the smooth functioning of the business. It provides the necessary funds to maintain inventory levels, fulfill customer orders, and manage the cash flow. For example, if a company does not have enough working capital to purchase inventory, it may face stockouts and lose potential sales.
Seasonal Fluctuations:
Working capital is particularly important for businesses that experience seasonal fluctuations in sales. During the low season, when sales are slow, working capital helps cover the expenses and keep the business running until the high season arrives. It provides the necessary cushion to bridge the gap between sales and expenses.
Dealing with Unexpected Events:
Having sufficient working capital also enables a business to deal with unexpected events or emergencies. For instance, if a major piece of equipment breaks down, working capital can be used to repair or replace it. This ensures that the business can continue its operations without major disruptions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, working capital is indeed required to meet day-to-day expenses and facilitate the smooth functioning of a business. It ensures that operational expenses can be met, inventory can be maintained, and cash flow remains healthy. Without sufficient working capital, a business may struggle to operate effectively and face various financial challenges.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Longer the operating cycle, working capital quantum is more.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Longer the operating cycle, working capital quantum is more.
Q. Longer the operating cycle, working capital quantum is more.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
- Longer the operating cycle time, the more is the working capital required. Thus, it follows that depending upon the length of working cycle, the requirement for working capital varies from enterprise to enterprise.
- Operating cycle is an important concept in management of cash and management of working capital.
- The operating cycle reveals the time that elapses between outlay of cash and inflow of cash.
- Quicker the operating cycle less amount of investment in working capital is needed and it improves the profitability.
Which of the following is an example of variable cost?- a)Raw material
- b)Commission on sales
- c)Packing material
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of variable cost?
a)
Raw material
b)
Commission on sales
c)
Packing material
d)
All of the above
|
|
Amita Das answered |
Variable cost: A variable cost is a corporate expense that changes in proportion to how much a company produces or sells. Variable costs increase or decrease depending on a company's production or sales volume, they rise as production increases and fall as production decreases. A variable cost can be contrasted with a fixed cost.
Common examples of variable costs include costs of goods sold (COGS), raw materials and inputs to production, packaging, wages and commissions, and certain utilities (for example, electricity or gas that increases with production capacity).
Common examples of variable costs include costs of goods sold (COGS), raw materials and inputs to production, packaging, wages and commissions, and certain utilities (for example, electricity or gas that increases with production capacity).
Annual quantity of jeans sold by a shop is 1,200 at the rate of ₹ 100/- per month. Cost of placing an order and receiving goods is ₹ 500/- per order. Inventory holding cost is ₹ 30/- per annum. What is the economic order quantity for the shopkeeper?- a)500 jeans
- b)200 jeans
- c)630 jeans
- d)800 jeans
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Annual quantity of jeans sold by a shop is 1,200 at the rate of ₹ 100/- per month. Cost of placing an order and receiving goods is ₹ 500/- per order. Inventory holding cost is ₹ 30/- per annum. What is the economic order quantity for the shopkeeper?
a)
500 jeans
b)
200 jeans
c)
630 jeans
d)
800 jeans
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
The economic order quantity, or EOQ, is a calculation designed to find the optimal order quantity for businesses to minimize logistics costs, warehousing space, stockouts, and overstock costs.
The formula is: EOQ = square root of: [2(setup costs)(demand rate)] / holding costs.
The formula is: EOQ = square root of: [2(setup costs)(demand rate)] / holding costs.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Gross working capital is the sum total of all current liabilities of the business.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Gross working capital is the sum total of all current liabilities of the business.
Q. Gross working capital is the sum total of all current liabilities of the business.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Gross working capital is the sum total of all the current assets of a company, whereas net working capital is the difference between the current assets and the current liabilities of a company.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Reorder point = Average daily usage rate × Lead time in days.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Reorder point = Average daily usage rate × Lead time in days.
Q. Reorder point = Average daily usage rate × Lead time in days.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Reorder point = Average daily usage rate × Lead time in days.
Multiply the maximum number of daily orders by the maximum lead time that may be required in case of supplier delays. Multiply the average number of daily orders by the average lead time. Subtract the result of Step 2 from the result of Step 1.
Multiply the maximum number of daily orders by the maximum lead time that may be required in case of supplier delays. Multiply the average number of daily orders by the average lead time. Subtract the result of Step 2 from the result of Step 1.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Rent is an example of variable cost.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Rent is an example of variable cost.
Q. Rent is an example of variable cost.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
- Variable costs may include Commission on sales, credit card fees, wages of part-time staff, etc.
- Fixed costs may include Depreciation, interest paid on capital, rent, salary, property taxes, insurance premium, etc.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. The Cash Conversion Cycle is the length of time between a firm’s purchase of inventory and the receipt of cash from accounts receivable.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. The Cash Conversion Cycle is the length of time between a firm’s purchase of inventory and the receipt of cash from accounts receivable.
Q. The Cash Conversion Cycle is the length of time between a firm’s purchase of inventory and the receipt of cash from accounts receivable.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
- The cash conversion cycle (CCC) is a formula in management accounting that measures how efficiently a company's managers are managing its working capital.
- The CCC measures the length of time between a company's purchase of inventory and the receipts of cash from its accounts receivable.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Usage rate is the average rate at which the inventory is drawn over a period.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Usage rate is the average rate at which the inventory is drawn over a period.
Q. Usage rate is the average rate at which the inventory is drawn over a period.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Inventory usage is how much inventory a business has used over a specific time frame. It's similar to COGS, but it speaks to the number of units sold and not their monetary value. It's also called inventory consumption. That's called the inventory usage rate.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Operating Cycle is also referred to as the Cash Community Cycle.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Operating Cycle is also referred to as the Cash Community Cycle.
Q. Operating Cycle is also referred to as the Cash Community Cycle.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
The cash operating cycle (also known as the working capital cycle or the cash conversion cycle) is the number of days between paying suppliers and receiving cash from sales.
Cash operating cycle = Inventory days + Receivables days – Payables days.
Cash operating cycle = Inventory days + Receivables days – Payables days.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Order lead time is an average time that elapses between placing an order and receiving the goods.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Order lead time is an average time that elapses between placing an order and receiving the goods.
Q. Order lead time is an average time that elapses between placing an order and receiving the goods.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Priyanka Khatri answered |
A lead time is the latency between the initiation and completion of a process.
For example, the lead time between the placement of an order and delivery of new cars by a given manufacturer might be between 2 weeks and 6 months, depending on various particularities.
For example, the lead time between the placement of an order and delivery of new cars by a given manufacturer might be between 2 weeks and 6 months, depending on various particularities.
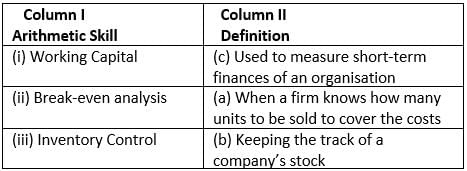
Given are the arithmetic skills in Column 1. Match them with their correct definition in Column 2.
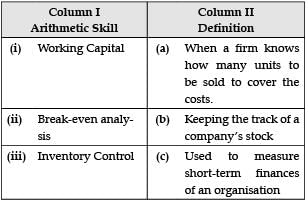
- a)(i) - c, (ii) - a, (iii) - b
- b)(i) - b, (ii) - a, (iii) -c
- c)(i) - c, (ii) -b, (iii) - a
- d)(i) - b, (ii) -c, (iii) - a
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Given are the arithmetic skills in Column 1. Match them with their correct definition in Column 2.


a)
(i) - c, (ii) - a, (iii) - b
b)
(i) - b, (ii) - a, (iii) -c
c)
(i) - c, (ii) -b, (iii) - a
d)
(i) - b, (ii) -c, (iii) - a
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
Correct Match:

State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Low ROI indicates more efficient management and utilization of total funds invested.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Low ROI indicates more efficient management and utilization of total funds invested.
Q. Low ROI indicates more efficient management and utilization of total funds invested.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
- Return on investment (ROI) is a performance measure used to evaluate the efficiency or profitability of an investment or compare the efficiency of a number of different investments.
- ROI tries to directly measure the amount of return on a particular investment, relative to the investment's cost.
- A low Return on Investment Ratio (ROI) indicates Improper utilization of resources and Over investment in assets.
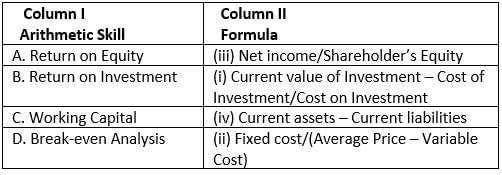
Given are the arithmetic skills in Column 1. Match them with their correct formulae in Column 2.
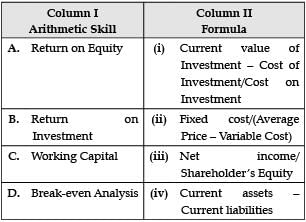
- a)A. (ii), B. (i), C. (iv), D. (iii)
- b)A. (iii), B. (i), C. (iv), D. (ii)
- c)A. (ii), B. (iii), C. (iv), D. (i)
- d)A. (iv), B. (iii), C. (i), D. (ii)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Given are the arithmetic skills in Column 1. Match them with their correct formulae in Column 2.


a)
A. (ii), B. (i), C. (iv), D. (iii)
b)
A. (iii), B. (i), C. (iv), D. (ii)
c)
A. (ii), B. (iii), C. (iv), D. (i)
d)
A. (iv), B. (iii), C. (i), D. (ii)
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Correct Formula Match:

State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Current liabilities represent short-term source of funds.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Current liabilities represent short-term source of funds.
Q. Current liabilities represent short-term source of funds.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Priyanka Khatri answered |
Current liabilities are a company's short-term financial obligations that are due within one year or within a normal operating cycle. An operating cycle, also referred to as the cash conversion cycle, is the time it takes a company to purchase inventory and convert it to cash from sales.
What does total cost include?- a)Only variable cost
- b)Only fixed cost
- c)Both variable and fixed cost
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What does total cost include?
a)
Only variable cost
b)
Only fixed cost
c)
Both variable and fixed cost
d)
None of these
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
- The Total Cost is the actual cost incurred in the production of a given level of output.
- The total cost includes both the variable cost (that varies with the change in the total output) and the fixed cost (that remains fixed irrespective of the change in the total output).
Chapter doubts & questions for Business Arithmetic - Entrepreneurship Class 12 2025 is part of Commerce exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Commerce 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Business Arithmetic - Entrepreneurship Class 12 in English & Hindi are available as part of Commerce exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Commerce Exam by signing up for free.
Entrepreneurship Class 12
19 videos|70 docs|12 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










