All Exams >
NEET >
NEET Past Year Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Neural Control and Coordination for NEET Exam
The most abundant intracellular cation is : [NEET 2013]- a)Ca++
- b)H+
- c)K+
- d)Na+
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The most abundant intracellular cation is : [NEET 2013]
a)
Ca++
b)
H+
c)
K+
d)
Na+

|
Shalini Saha answered |
The most abundant intracellular cation is K+.
During the transmission of nerve impulse through a nerve fibre, the potential on the inner side of the plasma membrane has which type of electric change? [2007]- a)First positive, then negative and continue to be positive
- b)First negative, then positive and continue to be positive.
- c)First positive, then negative and again back to positive
- d)First negative, then positive and again back to negative
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
During the transmission of nerve impulse through a nerve fibre, the potential on the inner side of the plasma membrane has which type of electric change? [2007]
a)
First positive, then negative and continue to be positive
b)
First negative, then positive and continue to be positive.
c)
First positive, then negative and again back to positive
d)
First negative, then positive and again back to negative

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
Once the events of depolarization have occurred, a nerve impulse or spike is initiated. Action potential is another name of nerve impulse. It lasts about 1 msec (millisecond). The stimulalted, negatively charged point on the outside of the membrane sends out an electrical current to the positive point (still polarized adjacent to it). This local current causes the adjacent inner part of the membrane to reverse its potential from –70 mV to +30 mV. The reversal repeats itself over and over until the nerve impulse is conducted through the length of the neuron
During the propagation of a nerve impulse, the action potential results from the movement of : [2008]- a)K+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
- b)Na+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
- c)K+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
- d)Na+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
During the propagation of a nerve impulse, the action potential results from the movement of : [2008]
a)
K+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
b)
Na+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
c)
K+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
d)
Na+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid

|
Anjana Dasgupta answered |
Total sum of physio-electrochemical changes that takes place along the length of nerve fibre is known as nerve impulse. Change in potential due to stimulation of nerve fibre is called action potential. During propagation of nerve impulse, Na⁺ enters inside so(+ve) change is formed inside the membrane. K⁺ ions come out.
In the resting state of the neural membrane, diffusion due to concentration gradients, if allowed, would drive [2004]- a)K+ into the cell
- b)K+ and Na+ out of the cell
- c)Na+ into the cell
- d)Na+ out of the cell
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the resting state of the neural membrane, diffusion due to concentration gradients, if allowed, would drive [2004]
a)
K+ into the cell
b)
K+ and Na+ out of the cell
c)
Na+ into the cell
d)
Na+ out of the cell

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
In a resting state of the neural membrane, Na+ concentration is higher on the outer side and K+ concentration is more within the cell. This concentration gradient is maintained by voltage gated channels. Hence if diffusion is allowed Na+ would enter the cell and K+ would leave.
Which of the following statements is correct for ‘nodes of Ranvier’ of nerve? [2002]- a)Neurilemma is discontinuous
- b)Myelin sheath is discontinuous
- c)Both neurilemma and myelin sheath are discontinuous
- d)Covered by myelin sheath
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct for ‘nodes of Ranvier’ of nerve? [2002]
a)
Neurilemma is discontinuous
b)
Myelin sheath is discontinuous
c)
Both neurilemma and myelin sheath are discontinuous
d)
Covered by myelin sheath
|
|
Srestha Bose answered |
Understanding Nodes of Ranvier
The nodes of Ranvier are critical components in the structure of myelinated nerve fibers. They play a significant role in the propagation of nerve impulses through a process known as saltatory conduction.
Discontinuity of Myelin Sheath
- The myelin sheath is a protective covering that surrounds the axons of many neurons.
- At the nodes of Ranvier, this myelin sheath is interrupted.
- This discontinuity allows for the rapid transmission of electrical signals along the nerve fiber.
Role of Neurilemma
- Neurilemma, also known as the Schwann cell sheath, is present in myelinated fibers.
- While the neurilemma is found at the nodes, it is primarily the myelin sheath that is discontinuous at these points.
- Neurilemma does not contribute to the discontinuity of the myelin sheath but rather supports the axon.
Importance of Myelin Discontinuity
- The gaps created by the nodes of Ranvier facilitate the jumping of action potentials from one node to the next.
- This process significantly increases the speed of nerve impulse conduction compared to unmyelinated fibers.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct statement regarding the nodes of Ranvier is that the myelin sheath is discontinuous at these points. This structural feature is essential for efficient nerve signal transmission, making option 'B' the accurate choice.
The nodes of Ranvier are critical components in the structure of myelinated nerve fibers. They play a significant role in the propagation of nerve impulses through a process known as saltatory conduction.
Discontinuity of Myelin Sheath
- The myelin sheath is a protective covering that surrounds the axons of many neurons.
- At the nodes of Ranvier, this myelin sheath is interrupted.
- This discontinuity allows for the rapid transmission of electrical signals along the nerve fiber.
Role of Neurilemma
- Neurilemma, also known as the Schwann cell sheath, is present in myelinated fibers.
- While the neurilemma is found at the nodes, it is primarily the myelin sheath that is discontinuous at these points.
- Neurilemma does not contribute to the discontinuity of the myelin sheath but rather supports the axon.
Importance of Myelin Discontinuity
- The gaps created by the nodes of Ranvier facilitate the jumping of action potentials from one node to the next.
- This process significantly increases the speed of nerve impulse conduction compared to unmyelinated fibers.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct statement regarding the nodes of Ranvier is that the myelin sheath is discontinuous at these points. This structural feature is essential for efficient nerve signal transmission, making option 'B' the accurate choice.
When a neuron is in resting state I not conducting any impulse, the axonal membrane is: [2011]- a)comparatively more permeable to Na+ ions and nearly impermeable to K+ ions
- b)equally permeable to both Na+ and K+ ions
- c)impermeable to both Na+ and K+ ions
- d)comparatively more permeable to K+ ions and nearly impermeable to Na+ ions
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When a neuron is in resting state I not conducting any impulse, the axonal membrane is: [2011]
a)
comparatively more permeable to Na+ ions and nearly impermeable to K+ ions
b)
equally permeable to both Na+ and K+ ions
c)
impermeable to both Na+ and K+ ions
d)
comparatively more permeable to K+ ions and nearly impermeable to Na+ ions

|
Pallabi Reddy answered |
When a neurone is in resting state i.e., not conducting any impulse, the axonal membrane is comparatively more permeable to K+ ion and nearly impermeable to Na+ ions.
CNS is mostly made of [1993]- a)motor neurons and sensory neurons
- b)sensory neurons and association neurons
- c)association neurons
- d)motor neurons and association neurons
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
motor neurons and sensory neurons
b)
sensory neurons and association neurons
c)
association neurons
d)
motor neurons and association neurons

|
Top Rankers answered |
The central nervous system (CNS) primarily consists of association neurons (interneurons), which connect sensory neurons to motor neurons and process information within the brain and spinal cord.
Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: The cerebral hemispheres are connected by nerve tract known as corpus callosum.
Statement II: The brain stem consists of the medulla oblongata, pons and cerebrum.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect.
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
- d)Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: The cerebral hemispheres are connected by nerve tract known as corpus callosum.
Statement II: The brain stem consists of the medulla oblongata, pons and cerebrum.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Statement I: The cerebral hemispheres are connected by nerve tract known as corpus callosum.
Statement II: The brain stem consists of the medulla oblongata, pons and cerebrum.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect.
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
d)
Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
|
|
Sagar Choudhary answered |
Explanation of Statement I
- Statement I: The cerebral hemispheres are connected by a nerve tract known as corpus callosum.
- This statement is correct. The corpus callosum is a thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres, facilitating communication between them.
Explanation of Statement II
- Statement II: The brain stem consists of the medulla oblongata, pons, and cerebrum.
- This statement is incorrect. The brain stem is made up of the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain, not the cerebrum. The cerebrum is actually a separate structure that is responsible for higher brain functions, including thought and action.
Conclusion
- Given the evaluations of both statements:
- Statement I is correct.
- Statement II is incorrect.
Thus, the correct answer is option C: Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
- Statement I: The cerebral hemispheres are connected by a nerve tract known as corpus callosum.
- This statement is correct. The corpus callosum is a thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres, facilitating communication between them.
Explanation of Statement II
- Statement II: The brain stem consists of the medulla oblongata, pons, and cerebrum.
- This statement is incorrect. The brain stem is made up of the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain, not the cerebrum. The cerebrum is actually a separate structure that is responsible for higher brain functions, including thought and action.
Conclusion
- Given the evaluations of both statements:
- Statement I is correct.
- Statement II is incorrect.
Thus, the correct answer is option C: Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
In which animal nerve cell is present but brain is absent? [2002]- a)Sponge
- b)Earthworm
- c)Cockroach
- d)Hydra
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which animal nerve cell is present but brain is absent? [2002]
a)
Sponge
b)
Earthworm
c)
Cockroach
d)
Hydra

|
Shalini Saha answered |
A primitive type of nervous system, without brain is found in the form of intra epidermal nerve net. However, there is no brain in Hydra to coordinate the response.
A sagittal section of human-brain is shown here. Identify at least two labels from A-D. [NEET Kar. 2013]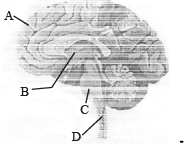
- a)A – Cerebral hemispheres; B – Cerebellum
- b)C – Mid brain; D – Cerebellum
- c)A – Cerebrum; C – Pons
- d)B – Corpus callosum; D – Medulla
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A sagittal section of human-brain is shown here. Identify at least two labels from A-D. [NEET Kar. 2013]

a)
A – Cerebral hemispheres; B – Cerebellum
b)
C – Mid brain; D – Cerebellum
c)
A – Cerebrum; C – Pons
d)
B – Corpus callosum; D – Medulla

|
Aashna Mukherjee answered |
Cerebrum is the first and most developed part of fore brain. It makes 2/3 part of total brain. Pons is a small spherical projection, which is situated below the midbrain and upper side of the medulla oblongata. It acts as a relay centre among different parts of brain. B and D are thalamus and spinal cord respectively.
Afferent nerve fibres carry impulses from [1992]- a)effector organs to CNS
- b)receptors to CNS
- c)CNS to receptors
- d)CNS to muscles
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
effector organs to CNS
b)
receptors to CNS
c)
CNS to receptors
d)
CNS to muscles

|
Lead Academy answered |
Afferent nerve fibres are sensory nerve fibres that carry sensory information from receptors (e.g., in skin, eyes, ears) to the central nervous system (CNS). Conversely, efferent nerve fibres carry motor commands from the CNS to muscles or glands (effectors).
A diagram showing axon terminal and synapse is given. Identify correctly at least two of A-D. [NEET 2013]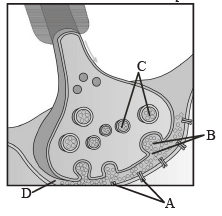
- a)B-Synaptic connection, D-K+
- b)A-Neurotransmitter, B-Synaptic cleft
- c)C- Neurotransmitter, D-Ca++
- d)A-Receptor, C-Synaptic vesicles
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A diagram showing axon terminal and synapse is given. Identify correctly at least two of A-D. [NEET 2013]

a)
B-Synaptic connection, D-K+
b)
A-Neurotransmitter, B-Synaptic cleft
c)
C- Neurotransmitter, D-Ca++
d)
A-Receptor, C-Synaptic vesicles

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
A-Receptor, C-Synaptic vesicles B is synaptic cleft. A synapse is formed by the membranes of a synaptic neuron and post synaptic neuron, which may or may not separated by a gap called synaptic cleft. It is filled by fluid called neurotransmitter which are involved in transmission of impulse at these synapses.
Which part of the brain is responsible for thermoregulation? [2019]- a)Medulla oblongata
- b)Cerebrum
- c)Hypothalamus
- d)Corpus callosum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of the brain is responsible for thermoregulation? [2019]
a)
Medulla oblongata
b)
Cerebrum
c)
Hypothalamus
d)
Corpus callosum
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Hypothalamus is thermoregulatory centre. Hence it is called “thermostat” of the body. It keeps body temperature at roughly 37°C by means of a complex thermostat system.
The nerve centres which control the body temperature and the urge for eating are contained in: [2010]- a)hypothalamus
- b)pons
- c)cerebellum
- d)thalamus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The nerve centres which control the body temperature and the urge for eating are contained in: [2010]
a)
hypothalamus
b)
pons
c)
cerebellum
d)
thalamus

|
Surbhi Das answered |
Hypothalamus contains important nerve centres that controls the body temperature, thirst, hunger and eating, water balance and sexual function.
Which part of human brain is concerned with the regulation of body temperature? [2009]- a)Cerebellum
- b)Cerebrum
- c)Hypothalamus
- d)Medulla Oblongata
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of human brain is concerned with the regulation of body temperature? [2009]
a)
Cerebellum
b)
Cerebrum
c)
Hypothalamus
d)
Medulla Oblongata

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
Hypothalamus part of human brain is concerned with the regulation of body temperature. The hypothalamus is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. The hypothalamus is small cone-shaped structure, projects downward, ending in the pituitary.
Chapter doubts & questions for Neural Control and Coordination - NEET Past Year Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Neural Control and Coordination - NEET Past Year Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









