All Exams >
NEET >
NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions >
All Questions
All questions of Animal Kingdom for NEET Exam
Diploblastic and triplo blastic are terms that describe- a)the number of in vaginations during embryonic development
- b)the number of heads during embryonic development
- c)the number of germinal layers during embryonic development
- d)the number of cell types during development
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Diploblastic and triplo blastic are terms that describe
a)
the number of in vaginations during embryonic development
b)
the number of heads during embryonic development
c)
the number of germinal layers during embryonic development
d)
the number of cell types during development
|
|
Pooja Mukherjee answered |
Germinal Layers in Embryonic Development and Diploblastic/Triploblastic Classification
Embryonic development is a complex process that involves the formation of various tissues and organs from a single cell. During this process, the embryo undergoes several stages of development that are marked by the formation of germinal layers. Germinal layers are the layers of cells that differentiate into specific tissues and organs during embryonic development. These layers form the basis of the body plan of an organism and are classified as either diploblastic or triploblastic.
Diploblastic Organisms
Diploblastic organisms are those that have only two germinal layers: the ectoderm and endoderm. These layers are formed during gastrulation, which is the process by which the embryo folds in on itself to form a hollow ball of cells called the gastrula. In diploblastic organisms, the ectoderm gives rise to the outer layer of the body and the nervous system, while the endoderm gives rise to the inner layer of the body.
Examples of diploblastic organisms include cnidarians (e.g. jellyfish, corals, sea anemones) and ctenophores (comb jellies).
Triploblastic Organisms
Triploblastic organisms are those that have three germinal layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. These layers are formed during gastrulation, but unlike in diploblastic organisms, the mesoderm layer is also formed. The mesoderm gives rise to the muscles, circulatory system, and other internal organs.
Examples of triploblastic organisms include most animals, including humans.
Conclusion
The diploblastic/triploblastic classification is based on the number of germinal layers that are present during embryonic development. Diploblastic organisms have two germinal layers (ectoderm and endoderm), while triploblastic organisms have three germinal layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm). This classification is important for understanding the basic body plan of organisms and how different tissues and organs are formed during embryonic development.
Embryonic development is a complex process that involves the formation of various tissues and organs from a single cell. During this process, the embryo undergoes several stages of development that are marked by the formation of germinal layers. Germinal layers are the layers of cells that differentiate into specific tissues and organs during embryonic development. These layers form the basis of the body plan of an organism and are classified as either diploblastic or triploblastic.
Diploblastic Organisms
Diploblastic organisms are those that have only two germinal layers: the ectoderm and endoderm. These layers are formed during gastrulation, which is the process by which the embryo folds in on itself to form a hollow ball of cells called the gastrula. In diploblastic organisms, the ectoderm gives rise to the outer layer of the body and the nervous system, while the endoderm gives rise to the inner layer of the body.
Examples of diploblastic organisms include cnidarians (e.g. jellyfish, corals, sea anemones) and ctenophores (comb jellies).
Triploblastic Organisms
Triploblastic organisms are those that have three germinal layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. These layers are formed during gastrulation, but unlike in diploblastic organisms, the mesoderm layer is also formed. The mesoderm gives rise to the muscles, circulatory system, and other internal organs.
Examples of triploblastic organisms include most animals, including humans.
Conclusion
The diploblastic/triploblastic classification is based on the number of germinal layers that are present during embryonic development. Diploblastic organisms have two germinal layers (ectoderm and endoderm), while triploblastic organisms have three germinal layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm). This classification is important for understanding the basic body plan of organisms and how different tissues and organs are formed during embryonic development.
Which of the following statements is incorrect with regard to bilateral symmetry?
- a)Body can be divided into two equal halves by a single plane only.
- b)The organisms that show bilateral symmetry have paired body organs that occur on the two sides of a central axis.
- c)It is found in all invertebrates and few vertebrates.
- d)Spider and crab show bilateral symmetry.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is incorrect with regard to bilateral symmetry?
a)
Body can be divided into two equal halves by a single plane only.
b)
The organisms that show bilateral symmetry have paired body organs that occur on the two sides of a central axis.
c)
It is found in all invertebrates and few vertebrates.
d)
Spider and crab show bilateral symmetry.
|
|
Poulomi Roy answered |
Bilateral Symmetry
Bilateral symmetry refers to the arrangement of body parts in such a way that an organism can be divided into two equal halves by a single plane passing through the central axis of the body. This type of symmetry is found in many animals, especially invertebrates and some vertebrates.
Incorrect statement
The incorrect statement is option C, which states that bilateral symmetry is found in all invertebrates and few vertebrates. This statement is incorrect because bilateral symmetry is actually found in the majority of animals, both invertebrates, and vertebrates. Almost all animals belonging to the phyla Chordata, Arthropoda, Mollusca, and Annelida exhibit bilateral symmetry.
Examples of animals with bilateral symmetry
- Invertebrates like insects, crustaceans, spiders, and worms exhibit bilateral symmetry.
- Vertebrates like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals exhibit bilateral symmetry.
Advantages of bilateral symmetry
Bilateral symmetry provides several advantages to animals:
- It allows for more efficient movement and coordination since paired limbs and muscles can work together to produce more precise movements.
- It facilitates the development of specialized organs and structures, such as eyes and ears, that are paired and located on opposite sides of the body.
- It enables animals to have directional movement, since paired limbs can be used to move forward or backward, up or down, and left or right.
Conclusion
Bilateral symmetry is a common type of symmetry found in the majority of animals, both invertebrates, and vertebrates. It allows for more efficient movement and coordination, facilitates the development of specialized organs and structures, and enables directional movement.
Bilateral symmetry refers to the arrangement of body parts in such a way that an organism can be divided into two equal halves by a single plane passing through the central axis of the body. This type of symmetry is found in many animals, especially invertebrates and some vertebrates.
Incorrect statement
The incorrect statement is option C, which states that bilateral symmetry is found in all invertebrates and few vertebrates. This statement is incorrect because bilateral symmetry is actually found in the majority of animals, both invertebrates, and vertebrates. Almost all animals belonging to the phyla Chordata, Arthropoda, Mollusca, and Annelida exhibit bilateral symmetry.
Examples of animals with bilateral symmetry
- Invertebrates like insects, crustaceans, spiders, and worms exhibit bilateral symmetry.
- Vertebrates like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals exhibit bilateral symmetry.
Advantages of bilateral symmetry
Bilateral symmetry provides several advantages to animals:
- It allows for more efficient movement and coordination since paired limbs and muscles can work together to produce more precise movements.
- It facilitates the development of specialized organs and structures, such as eyes and ears, that are paired and located on opposite sides of the body.
- It enables animals to have directional movement, since paired limbs can be used to move forward or backward, up or down, and left or right.
Conclusion
Bilateral symmetry is a common type of symmetry found in the majority of animals, both invertebrates, and vertebrates. It allows for more efficient movement and coordination, facilitates the development of specialized organs and structures, and enables directional movement.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: All triploblastic animals are eucoelomates.
Statement 2: They have a false coelom.
- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
- c)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: All triploblastic animals are eucoelomates.
Statement 2: They have a false coelom.
Statement 1: All triploblastic animals are eucoelomates.
Statement 2: They have a false coelom.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
c)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
- Animals that belong to the phylum Platyhelminthes to Chordata are all triploblastic.
- But Platyhelminthes and aschelminthes belong to pseudocoelomates.
- Annelids, arthropods, echinoderms and chordates are under eucoelomates. This means not all triploblastic animals are eucoelomates.
- Pseudocoelomates have false coelom while eucoelomate animals only have the true coelom.
Hence, both statement 1 and statement 2 are incorrect.
Select the correct matching of animals, their symmetry, organisation and coelom type.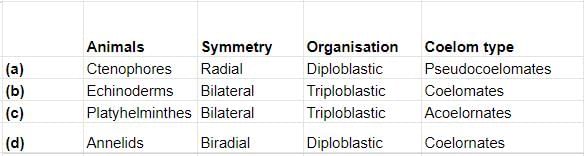
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct matching of animals, their symmetry, organisation and coelom type.

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Yashvi Khanna answered |
Correct Matching Explained
The correct answer is option 'C', as it accurately matches the animals with their corresponding symmetry, organization, and coelom type.
Animal Categories and Their Characteristics
- Ctenophores
- Symmetry: Radial
- Organisation: Diploblastic
- Coelom Type: Coelomates (not Pseudocoelomates)
- Echinoderms
- Symmetry: Bilateral (larval stage) and Radial (adult stage)
- Organisation: Triploblastic
- Coelom Type: Coelomates
- Platyhelminthes
- Symmetry: Bilateral
- Organisation: Triploblastic
- Coelom Type: Acoelomates
- Annelids
- Symmetry: Bilateral
- Organisation: Triploblastic
- Coelom Type: Coelomates (not Diploblastic)
Detailed Breakdown of Option 'C'
- Platyhelminthes
- These organisms, commonly known as flatworms, exhibit bilateral symmetry which allows for more complex movement and organization.
- They are triploblastic, meaning they have three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
- Importantly, they are classified as acoelomates, lacking a true coelom, which differentiates them from other triploblastic groups.
Conclusion
The other options provided contain inaccuracies regarding the animals' symmetry, organization, or coelom type. Thus, option 'C' is indeed the correct choice, effectively aligning Platyhelminthes with bilateral symmetry, triploblastic organization, and acoelomate structure.
The correct answer is option 'C', as it accurately matches the animals with their corresponding symmetry, organization, and coelom type.
Animal Categories and Their Characteristics
- Ctenophores
- Symmetry: Radial
- Organisation: Diploblastic
- Coelom Type: Coelomates (not Pseudocoelomates)
- Echinoderms
- Symmetry: Bilateral (larval stage) and Radial (adult stage)
- Organisation: Triploblastic
- Coelom Type: Coelomates
- Platyhelminthes
- Symmetry: Bilateral
- Organisation: Triploblastic
- Coelom Type: Acoelomates
- Annelids
- Symmetry: Bilateral
- Organisation: Triploblastic
- Coelom Type: Coelomates (not Diploblastic)
Detailed Breakdown of Option 'C'
- Platyhelminthes
- These organisms, commonly known as flatworms, exhibit bilateral symmetry which allows for more complex movement and organization.
- They are triploblastic, meaning they have three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
- Importantly, they are classified as acoelomates, lacking a true coelom, which differentiates them from other triploblastic groups.
Conclusion
The other options provided contain inaccuracies regarding the animals' symmetry, organization, or coelom type. Thus, option 'C' is indeed the correct choice, effectively aligning Platyhelminthes with bilateral symmetry, triploblastic organization, and acoelomate structure.
Which one of the following statements is incorrect about the occurrence of notochord? - a)It is present only in larval tail in ascidian.
- b)It is replaced by a vertebral column in adult frog.
- c)It is absent throughout life in humans from the very beginning.
- d)It is present throughout life in Amphioxus.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is incorrect about the occurrence of notochord?
a)
It is present only in larval tail in ascidian.
b)
It is replaced by a vertebral column in adult frog.
c)
It is absent throughout life in humans from the very beginning.
d)
It is present throughout life in Amphioxus.
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Humans belong to the phylum Chordata. Animals belonging to the phylum Chordata possess a notochord either during early embryonic life or throughout the embryonic life. In some, it is replaced by vertebral column. In humans, notochord is present only in the embryonic stage, it is replaced by vertebral column in the adult form.
Which one of the following is a matching pair of a body feature and the animal possessing it?- a)Ventral central nervous system - Leech
- b)Pharyngeal gill slits absent in embryo - Chameleon
- c)Ventral heart - Scorpion
- d)Post-anal tail - Octopus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is a matching pair of a body feature and the animal possessing it?
a)
Ventral central nervous system - Leech
b)
Pharyngeal gill slits absent in embryo - Chameleon
c)
Ventral heart - Scorpion
d)
Post-anal tail - Octopus
|
|
Janhavi Desai answered |
Matching Body Feature and Animal Possessing It
Body features are specific characteristics that distinguish one animal from another. Here, we are identifying the correct matching pair of body features and the animal possessing it.
Ventral Central Nervous System - Leech
- The ventral central nervous system is a characteristic feature of the leech.
- The leech belongs to the phylum Annelida, which is characterized by segmented bodies.
- The nervous system of the leech is ventral, which means that it is located on the underside of the body.
- The ventral nerve cord of the leech runs the length of the body and is composed of ganglia (clusters of nerve cells) connected by nerves.
- The ventral central nervous system of the leech is responsible for coordinating movement and other bodily functions.
Pharyngeal Gill Slits Absent in Embryo - Chameleon
- The chameleon belongs to the class Reptilia, which is characterized by the absence of pharyngeal gill slits in the embryo.
- Pharyngeal gill slits are a characteristic feature of chordates, which includes vertebrates.
- In the embryo of chordates, pharyngeal gill slits develop into structures such as gills, jaws, and ears.
- However, in reptiles such as chameleons, these structures do not develop from pharyngeal gill slits.
Ventral Heart - Scorpion
- The ventral heart is a characteristic feature of the scorpion.
- The scorpion belongs to the class Arachnida, which is characterized by the presence of a ventral heart.
- The ventral heart of the scorpion is located on the underside of the body, between the cephalothorax and the abdomen.
- The ventral heart of the scorpion is made up of a series of muscular chambers that pump blood throughout the body.
Post-Anal Tail - Octopus
- The post-anal tail is a characteristic feature of some animals, such as fish and amphibians, but not of octopuses.
- Octopuses belong to the class Cephalopoda, which is characterized by the absence of a post-anal tail.
- Octopuses are marine animals with eight arms and no tail.
- The lack of a post-anal tail in octopuses is related to their mode of movement, which involves jet propulsion through water using a muscular mantle cavity.
Therefore, the correct matching pair of body feature and animal possessing it is:
a) Ventral central nervous system - Leech.
Body features are specific characteristics that distinguish one animal from another. Here, we are identifying the correct matching pair of body features and the animal possessing it.
Ventral Central Nervous System - Leech
- The ventral central nervous system is a characteristic feature of the leech.
- The leech belongs to the phylum Annelida, which is characterized by segmented bodies.
- The nervous system of the leech is ventral, which means that it is located on the underside of the body.
- The ventral nerve cord of the leech runs the length of the body and is composed of ganglia (clusters of nerve cells) connected by nerves.
- The ventral central nervous system of the leech is responsible for coordinating movement and other bodily functions.
Pharyngeal Gill Slits Absent in Embryo - Chameleon
- The chameleon belongs to the class Reptilia, which is characterized by the absence of pharyngeal gill slits in the embryo.
- Pharyngeal gill slits are a characteristic feature of chordates, which includes vertebrates.
- In the embryo of chordates, pharyngeal gill slits develop into structures such as gills, jaws, and ears.
- However, in reptiles such as chameleons, these structures do not develop from pharyngeal gill slits.
Ventral Heart - Scorpion
- The ventral heart is a characteristic feature of the scorpion.
- The scorpion belongs to the class Arachnida, which is characterized by the presence of a ventral heart.
- The ventral heart of the scorpion is located on the underside of the body, between the cephalothorax and the abdomen.
- The ventral heart of the scorpion is made up of a series of muscular chambers that pump blood throughout the body.
Post-Anal Tail - Octopus
- The post-anal tail is a characteristic feature of some animals, such as fish and amphibians, but not of octopuses.
- Octopuses belong to the class Cephalopoda, which is characterized by the absence of a post-anal tail.
- Octopuses are marine animals with eight arms and no tail.
- The lack of a post-anal tail in octopuses is related to their mode of movement, which involves jet propulsion through water using a muscular mantle cavity.
Therefore, the correct matching pair of body feature and animal possessing it is:
a) Ventral central nervous system - Leech.
What is common between parrot, platypus and kangaroo?- a)Toothless jaws
- b)Functional postanal tail
- c)Oviparity
- d)Homoiothermy
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is common between parrot, platypus and kangaroo?
a)
Toothless jaws
b)
Functional postanal tail
c)
Oviparity
d)
Homoiothermy
|
|
Nisha Datta answered |
Common Features of Parrot, Platypus, and Kangaroo
Homoiothermy
- All three animals are homoiothermic or warm-blooded.
- They are able to maintain a constant body temperature regardless of the external temperature.
- This allows them to live in a variety of environments and adapt to changing conditions.
Differences among Parrot, Platypus, and Kangaroo
Toothless Jaws
- Parrots have a toothless beak that is adapted for cracking seeds and nuts.
- Platypuses have a toothless bill that is used to detect prey in the water.
- Kangaroos have teeth that are adapted for grazing on grass and plants.
Functional Postanal Tail
- Platypuses have a flat, broad tail that is used for swimming.
- Kangaroos have a long, muscular tail that helps them balance and jump.
- Parrots do not have a postanal tail.
Oviparity
- Platypuses are oviparous, which means they lay eggs.
- Kangaroos are marsupials and give birth to relatively undeveloped young that continue to develop in the mother's pouch.
- Parrots lay eggs and incubate them until they hatch.
In conclusion, although parrots, platypuses, and kangaroos share the common feature of homoiothermy, they differ in terms of their toothless jaws, functional postanal tail, and method of reproduction.
Homoiothermy
- All three animals are homoiothermic or warm-blooded.
- They are able to maintain a constant body temperature regardless of the external temperature.
- This allows them to live in a variety of environments and adapt to changing conditions.
Differences among Parrot, Platypus, and Kangaroo
Toothless Jaws
- Parrots have a toothless beak that is adapted for cracking seeds and nuts.
- Platypuses have a toothless bill that is used to detect prey in the water.
- Kangaroos have teeth that are adapted for grazing on grass and plants.
Functional Postanal Tail
- Platypuses have a flat, broad tail that is used for swimming.
- Kangaroos have a long, muscular tail that helps them balance and jump.
- Parrots do not have a postanal tail.
Oviparity
- Platypuses are oviparous, which means they lay eggs.
- Kangaroos are marsupials and give birth to relatively undeveloped young that continue to develop in the mother's pouch.
- Parrots lay eggs and incubate them until they hatch.
In conclusion, although parrots, platypuses, and kangaroos share the common feature of homoiothermy, they differ in terms of their toothless jaws, functional postanal tail, and method of reproduction.
Which one of the following statements about all the four of Spongila, leech, dolphin and penguin is correct?- a)Penguin is homeothermic while the remaining three are poikilothermic.
- b)Leech is a fresh water form while all others are marine.
- c)Spongilla has special collared cells called choanocytes, not found in the remaining three.
- d)All are bilaterally symmetrical.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements about all the four of Spongila, leech, dolphin and penguin is correct?
a)
Penguin is homeothermic while the remaining three are poikilothermic.
b)
Leech is a fresh water form while all others are marine.
c)
Spongilla has special collared cells called choanocytes, not found in the remaining three.
d)
All are bilaterally symmetrical.
|
|
Kunal Nambiar answered |
The correct answer is option 'C': Spongilla has special collared cells called choanocytes, not found in the remaining three.
Explanation:
- Spongilla is a genus of freshwater sponge, while leech, dolphin, and penguin belong to different animal groups.
- The statement mentions that Spongilla has special collared cells called choanocytes, which are not found in the remaining three organisms.
- Choanocytes: Choanocytes are specialized cells found in sponges. They have a collar-like structure with a flagellum projecting from the center. These cells help in creating water currents and capturing food particles.
- Spongilla, being a freshwater sponge, relies on choanocytes for filter-feeding.
- In contrast, leeches are segmented worms, dolphins are marine mammals, and penguins are flightless birds. These organisms do not possess choanocytes.
- The other statements in the options are incorrect:
- Option 'A': Penguins are not homeothermic; they are actually endothermic, meaning they can generate and regulate their own body heat. The remaining three organisms (Spongilla, leech, and dolphin) are poikilothermic, meaning their body temperature is dependent on external factors.
- Option 'B': Leeches can be found in both freshwater and marine environments. Dolphins are marine mammals, penguins inhabit marine and terrestrial habitats, while Spongilla is a freshwater sponge.
- Option 'D': Although all the mentioned organisms are bilaterally symmetrical, this statement is not specific to only these four organisms and can be true for many other animals as well.
In summary, the correct statement is that Spongilla has special collared cells called choanocytes, which are not found in leech, dolphin, and penguin.
Explanation:
- Spongilla is a genus of freshwater sponge, while leech, dolphin, and penguin belong to different animal groups.
- The statement mentions that Spongilla has special collared cells called choanocytes, which are not found in the remaining three organisms.
- Choanocytes: Choanocytes are specialized cells found in sponges. They have a collar-like structure with a flagellum projecting from the center. These cells help in creating water currents and capturing food particles.
- Spongilla, being a freshwater sponge, relies on choanocytes for filter-feeding.
- In contrast, leeches are segmented worms, dolphins are marine mammals, and penguins are flightless birds. These organisms do not possess choanocytes.
- The other statements in the options are incorrect:
- Option 'A': Penguins are not homeothermic; they are actually endothermic, meaning they can generate and regulate their own body heat. The remaining three organisms (Spongilla, leech, and dolphin) are poikilothermic, meaning their body temperature is dependent on external factors.
- Option 'B': Leeches can be found in both freshwater and marine environments. Dolphins are marine mammals, penguins inhabit marine and terrestrial habitats, while Spongilla is a freshwater sponge.
- Option 'D': Although all the mentioned organisms are bilaterally symmetrical, this statement is not specific to only these four organisms and can be true for many other animals as well.
In summary, the correct statement is that Spongilla has special collared cells called choanocytes, which are not found in leech, dolphin, and penguin.
Which of the following is correctly matched?- a)Radial symmetry - Coelenterates
- b)Coelomates - Aschelminthes
- c)Metamerism - Molluscs
- d)Triploblastic - Sponges
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is correctly matched?
a)
Radial symmetry - Coelenterates
b)
Coelomates - Aschelminthes
c)
Metamerism - Molluscs
d)
Triploblastic - Sponges
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Coelenterates have radial symmetry. Aschelminth are pseudocoelomates. Molluscs do not show metamerit Sponges are diploblastic.
Which one of the following pairs of animals are similar to each other for the feature stated against them?- a)Pteropus and Ornithorhyncus - viviparity
- b)Garden lizard and crocodile - three chambered heart
- c)Ascaris and Ancylostoma - metameric segmentation
- d)Sea horse and flying fish - cold blooded (poikilothermal)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs of animals are similar to each other for the feature stated against them?
a)
Pteropus and Ornithorhyncus - viviparity
b)
Garden lizard and crocodile - three chambered heart
c)
Ascaris and Ancylostoma - metameric segmentation
d)
Sea horse and flying fish - cold blooded (poikilothermal)
|
|
Sonal Reddy answered |
Answer:
Similarity between animal pairs based on features:
a) Pteropus and Ornithorhyncus - viviparity
Both Pteropus (fruit bats) and Ornithorhyncus (platypus) are mammals that exhibit viviparity, which means giving birth to live young ones instead of laying eggs.
b) Garden lizard and crocodile - three chambered heart
Both Garden lizard and crocodile have a three-chambered heart, which consists of two atria and one ventricle. This type of heart is less efficient than a four-chambered heart found in mammals and birds, as it causes mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
c) Ascaris and Ancylostoma - metameric segmentation
Both Ascaris (roundworm) and Ancylostoma (hookworm) exhibit metameric segmentation, which means their body is divided into repeating segments that have similar structures and functions.
d) Sea horse and flying fish - cold-blooded (poikilothermal)
Both Sea horse and flying fish are cold-blooded (poikilothermal) animals, which means their body temperature fluctuates with the surrounding environment. They cannot regulate their body temperature internally like warm-blooded (homeothermic) animals such as mammals and birds.
Conclusion:
In summary, the pairs of animals that are similar to each other for the feature stated against them are Pteropus and Ornithorhyncus for viviparity, Garden lizard and crocodile for a three-chambered heart, Ascaris and Ancylostoma for metameric segmentation, and Sea horse and flying fish for being cold-blooded (poikilothermal).
Similarity between animal pairs based on features:
a) Pteropus and Ornithorhyncus - viviparity
Both Pteropus (fruit bats) and Ornithorhyncus (platypus) are mammals that exhibit viviparity, which means giving birth to live young ones instead of laying eggs.
b) Garden lizard and crocodile - three chambered heart
Both Garden lizard and crocodile have a three-chambered heart, which consists of two atria and one ventricle. This type of heart is less efficient than a four-chambered heart found in mammals and birds, as it causes mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
c) Ascaris and Ancylostoma - metameric segmentation
Both Ascaris (roundworm) and Ancylostoma (hookworm) exhibit metameric segmentation, which means their body is divided into repeating segments that have similar structures and functions.
d) Sea horse and flying fish - cold-blooded (poikilothermal)
Both Sea horse and flying fish are cold-blooded (poikilothermal) animals, which means their body temperature fluctuates with the surrounding environment. They cannot regulate their body temperature internally like warm-blooded (homeothermic) animals such as mammals and birds.
Conclusion:
In summary, the pairs of animals that are similar to each other for the feature stated against them are Pteropus and Ornithorhyncus for viviparity, Garden lizard and crocodile for a three-chambered heart, Ascaris and Ancylostoma for metameric segmentation, and Sea horse and flying fish for being cold-blooded (poikilothermal).
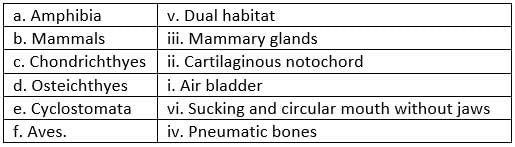
Match Column-I with Column-II and select the correct option from the codes given below.
Column-I
(A) Amphibia
(B) Mammals
(C) Chondrichthyes
(D) Osteichthyes
(E) Cyclostomata
(F) Aves
Column-II
(i) Air bladder
(ii) Cartilaginous notochord
(iii) Mammary glands
(iv) Pneumatic bones
(v) Dual habitat
(vi) Sucking and circular mouth without jaws- a)A-(i), B-(iii), C-(iv), D-(v), E-(ii), F-(vi)
- b)A-(ii), B-(v), C-(iv), D-(vi), E-(iii), F-(i)
- c)A-(v), B-(iii), C-(ii), D-(i), E-(vi), F-(iv)
- d)A-(v), B-(ii), C-(iii), D-(i), E-(iv), F-(v)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Match Column-I with Column-II and select the correct option from the codes given below.
Column-I
(A) Amphibia
(B) Mammals
(C) Chondrichthyes
(D) Osteichthyes
(E) Cyclostomata
(F) Aves
Column-II
(i) Air bladder
(ii) Cartilaginous notochord
(iii) Mammary glands
(iv) Pneumatic bones
(v) Dual habitat
(vi) Sucking and circular mouth without jaws
Column-I
(A) Amphibia
(B) Mammals
(C) Chondrichthyes
(D) Osteichthyes
(E) Cyclostomata
(F) Aves
Column-II
(i) Air bladder
(ii) Cartilaginous notochord
(iii) Mammary glands
(iv) Pneumatic bones
(v) Dual habitat
(vi) Sucking and circular mouth without jaws
a)
A-(i), B-(iii), C-(iv), D-(v), E-(ii), F-(vi)
b)
A-(ii), B-(v), C-(iv), D-(vi), E-(iii), F-(i)
c)
A-(v), B-(iii), C-(ii), D-(i), E-(vi), F-(iv)
d)
A-(v), B-(ii), C-(iii), D-(i), E-(iv), F-(v)
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Which of the following is an exclusive character of class mammalia?- a)Internal fertilization
- b)Presence of a completely 4-chambered heart
- c)Homoiothermy
- d)Presence of a muscular diaphragm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an exclusive character of class mammalia?
a)
Internal fertilization
b)
Presence of a completely 4-chambered heart
c)
Homoiothermy
d)
Presence of a muscular diaphragm
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Presence of a muscular diaphragm is an exclusive character of class Mammalia. Diaphragm is a complex muscular partition that separates the thoracic cavity from fix abdominal cavity. It increases the efficiency of breathing.
Which of the following is a correct match?- a)Cray fish - Elasmobranch
- b)Cuttle fish - Osteichthyes
- c)Jelly fish - Echinodermata
- d)Silver fish - Arthropod
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a correct match?
a)
Cray fish - Elasmobranch
b)
Cuttle fish - Osteichthyes
c)
Jelly fish - Echinodermata
d)
Silver fish - Arthropod
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Silver fish and cray fish belong to the phylum Arthropoda. Cuttle fish belongs to the phylum Mollusca and jelly fish belongs to the phylum Coelenterata.
Which one of the following is a matching pair of an animal and a certein phenomenon it exhibits?
- a)Pheretime - Sexual dimorphism
- b)Musca - Complete metamorphosis
- c)Chameleon - Mimicry
- d)Taenia - Polymorphism
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is a matching pair of an animal and a certein phenomenon it exhibits?
a)
Pheretime - Sexual dimorphism
b)
Musca - Complete metamorphosis
c)
Chameleon - Mimicry
d)
Taenia - Polymorphism
|
|
Aditi Datta answered |
Possible Answer:
Understanding the Matching Pair:
In this question, we are given a set of animal and phenomenon pairs and we need to identify the correct matching pair. Let's analyze each option to determine the correct answer.
Option A: Pheretime - Sexual Dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism refers to the physical differences between males and females of the same species. However, "Pheretime" is not a recognized animal name or term related to sexual dimorphism. Therefore, option A is incorrect.
Option B: Musca - Complete Metamorphosis
Complete metamorphosis is a biological process where an animal undergoes distinct stages of development, including egg, larva, pupa, and adult. "Musca" is the scientific name for the common housefly, which is a well-known example of an animal that exhibits complete metamorphosis. Therefore, option B is the correct matching pair.
Option C: Chameleon - Mimicry
Mimicry is a phenomenon where an animal imitates the appearance or behavior of another organism to gain some advantage, such as protection from predators. While chameleons are known for their remarkable ability to change color, this is not an example of mimicry. Therefore, option C is incorrect.
Option D: Taenia - Polymorphism
Polymorphism refers to the occurrence of multiple forms or variations within a single species. Taenia is a genus of parasitic flatworms, commonly known as tapeworms. While some tapeworms might exhibit variations in their morphology, they are not typically considered polymorphic. Therefore, option D is incorrect.
Conclusion:
After analyzing all the options, we can conclude that the correct matching pair of an animal and a phenomenon it exhibits is option B: Musca - Complete Metamorphosis. The common housefly (Musca) undergoes complete metamorphosis during its life cycle, which includes the stages of egg, larva (maggot), pupa, and adult.
Understanding the Matching Pair:
In this question, we are given a set of animal and phenomenon pairs and we need to identify the correct matching pair. Let's analyze each option to determine the correct answer.
Option A: Pheretime - Sexual Dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism refers to the physical differences between males and females of the same species. However, "Pheretime" is not a recognized animal name or term related to sexual dimorphism. Therefore, option A is incorrect.
Option B: Musca - Complete Metamorphosis
Complete metamorphosis is a biological process where an animal undergoes distinct stages of development, including egg, larva, pupa, and adult. "Musca" is the scientific name for the common housefly, which is a well-known example of an animal that exhibits complete metamorphosis. Therefore, option B is the correct matching pair.
Option C: Chameleon - Mimicry
Mimicry is a phenomenon where an animal imitates the appearance or behavior of another organism to gain some advantage, such as protection from predators. While chameleons are known for their remarkable ability to change color, this is not an example of mimicry. Therefore, option C is incorrect.
Option D: Taenia - Polymorphism
Polymorphism refers to the occurrence of multiple forms or variations within a single species. Taenia is a genus of parasitic flatworms, commonly known as tapeworms. While some tapeworms might exhibit variations in their morphology, they are not typically considered polymorphic. Therefore, option D is incorrect.
Conclusion:
After analyzing all the options, we can conclude that the correct matching pair of an animal and a phenomenon it exhibits is option B: Musca - Complete Metamorphosis. The common housefly (Musca) undergoes complete metamorphosis during its life cycle, which includes the stages of egg, larva (maggot), pupa, and adult.
Mark the incorrect statement:- a)Radial symmetry is advantageous to sedentary mode of life
- b)Notochord is mesodermal in origin placed between dorsal hollow nerve cord and alimentary canal in some animals
- c)Pseudocoel (false coelom) derived from blastocoel of the embryo and is bounded by ectoderm and mesoderm
- d)Cephalization is the concentration of sense organs, nervous tissue (brain), and food capturing organs at the anterior end
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Radial symmetry is advantageous to sedentary mode of life
b)
Notochord is mesodermal in origin placed between dorsal hollow nerve cord and alimentary canal in some animals
c)
Pseudocoel (false coelom) derived from blastocoel of the embryo and is bounded by ectoderm and mesoderm
d)
Cephalization is the concentration of sense organs, nervous tissue (brain), and food capturing organs at the anterior end
|
|
Arnav Unni answered |
Incorrect Statement Explanation:
Explanation of Option C:
- Pseudocoel (false coelom) is not derived from the blastocoel of the embryo.
- It is actually derived from the blastocoel of the embryo in some animals.
- The pseudocoel is a fluid-filled body cavity that is not completely lined by mesoderm.
- It is found in organisms like roundworms (nematodes) and rotifers.
- The true coelom, on the other hand, is derived from mesoderm and is completely lined by mesoderm.
Therefore, option C is the incorrect statement as it misrepresents the origin and structure of the pseudocoel in certain organisms.
Explanation of Option C:
- Pseudocoel (false coelom) is not derived from the blastocoel of the embryo.
- It is actually derived from the blastocoel of the embryo in some animals.
- The pseudocoel is a fluid-filled body cavity that is not completely lined by mesoderm.
- It is found in organisms like roundworms (nematodes) and rotifers.
- The true coelom, on the other hand, is derived from mesoderm and is completely lined by mesoderm.
Therefore, option C is the incorrect statement as it misrepresents the origin and structure of the pseudocoel in certain organisms.
Which of the following is/are not the characteristics of the class Osteichthyes?
(i) Body is streamlined and mouth is terminal.
(ii) Gills are covered by operculum.
(iii) Skin covered with cycloid and placoid scales.
(iv) Many of them are viviparous. - a)(iv) only
- b)(iii) and (iv)
- c)(i), (iii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are not the characteristics of the class Osteichthyes?
(i) Body is streamlined and mouth is terminal.
(ii) Gills are covered by operculum.
(iii) Skin covered with cycloid and placoid scales.
(iv) Many of them are viviparous.
(i) Body is streamlined and mouth is terminal.
(ii) Gills are covered by operculum.
(iii) Skin covered with cycloid and placoid scales.
(iv) Many of them are viviparous.
a)
(iv) only
b)
(iii) and (iv)
c)
(i), (iii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iv)
|
|
Mahi Mehta answered |
Not Characteristics of Osteichthyes
(i) Body is streamlined and mouth is terminal:
This characteristic is actually a defining feature of Osteichthyes. They are bony fish that have a streamlined body shape and terminal mouth position.
(ii) Gills are covered by operculum:
This is another defining feature of Osteichthyes. They have a bony plate, called an operculum, that covers and protects the gills.
Characteristics of Osteichthyes
(iii) Skin covered with cycloid and placoid scales:
Osteichthyes do have scales covering their skin, but they are not both cycloid and placoid. Cycloid scales are found in some fish, but not Osteichthyes. Instead, Osteichthyes have ganoid or ctenoid scales.
(iv) Many of them are viviparous:
Osteichthyes are mostly oviparous, which means they lay eggs that hatch outside of the mother's body. There are some viviparous species within Osteichthyes, but this is not a characteristic of the entire class.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer is option (c) (i), (iii), and (iv), as these characteristics are not accurate descriptions of Osteichthyes.
(i) Body is streamlined and mouth is terminal:
This characteristic is actually a defining feature of Osteichthyes. They are bony fish that have a streamlined body shape and terminal mouth position.
(ii) Gills are covered by operculum:
This is another defining feature of Osteichthyes. They have a bony plate, called an operculum, that covers and protects the gills.
Characteristics of Osteichthyes
(iii) Skin covered with cycloid and placoid scales:
Osteichthyes do have scales covering their skin, but they are not both cycloid and placoid. Cycloid scales are found in some fish, but not Osteichthyes. Instead, Osteichthyes have ganoid or ctenoid scales.
(iv) Many of them are viviparous:
Osteichthyes are mostly oviparous, which means they lay eggs that hatch outside of the mother's body. There are some viviparous species within Osteichthyes, but this is not a characteristic of the entire class.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer is option (c) (i), (iii), and (iv), as these characteristics are not accurate descriptions of Osteichthyes.
Which of the following groups of animals are uricotelic?- a)Reptiles, birds, land snails, insects
- b)Reptiles, birds, land snails
- c)Aquatic amphibians, birds, land snails, insects
- d)Amphibians, reptiles, birds, insects
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following groups of animals are uricotelic?
a)
Reptiles, birds, land snails, insects
b)
Reptiles, birds, land snails
c)
Aquatic amphibians, birds, land snails, insects
d)
Amphibians, reptiles, birds, insects
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Uricotelic animals are those animals that excrete their waste matter in the form of uric acid. Reptiles, birds, lard snals and insects are uricotelic animals.
Which of the following are correct?
(i)Diploblastic:Poriferans, Coelenterates
(ii)Triploblastic:Platyheliminthes to Chorodates
(iii)Acoelomate:Poriferans,Coelenterates,Platyhelminthes
(iv)Pseudocoelomate:Aschelminthes /Roundworms
(v)Eucoelomate:Annelids to Chordates
- a)(iv) and (v) are correct
- b)(i), (ii), (iii) ,(iv) and (v) are correct
- c)(i), (ii) and (v) are correct
- d)(iii) and (v) are correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are correct?
(i)Diploblastic:Poriferans, Coelenterates
(ii)Triploblastic:Platyheliminthes to Chorodates
(iii)Acoelomate:Poriferans,Coelenterates,Platyhelminthes
(iv)Pseudocoelomate:Aschelminthes /Roundworms
(v)Eucoelomate:Annelids to Chordates
(i)Diploblastic:Poriferans, Coelenterates
(ii)Triploblastic:Platyheliminthes to Chorodates
(iii)Acoelomate:Poriferans,Coelenterates,Platyhelminthes
(iv)Pseudocoelomate:Aschelminthes /Roundworms
(v)Eucoelomate:Annelids to Chordates
a)
(iv) and (v) are correct
b)
(i), (ii), (iii) ,(iv) and (v) are correct
c)
(i), (ii) and (v) are correct
d)
(iii) and (v) are correct
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
(i) Diploblastic - Poriferans, Coelenterates
(ii) Triploblastic - Platyhelminthes to Chordates
(iii) Acoelomate - Poriferans, Coelenterates, Platyhelminthes
(iv) Pseudocoelomate - Aschelminthes/Roundworms
(v) Eucoelomate - Annelids to Chordates
So, the correct answer is '(i), (ii), (iii), (iv) and (v)'.
Which one of the following groups of animals is correctly matched with its characteristic feature without any exception?- a)Reptilia: possess 3 -chambered heart with an incompletely divided ventricle
- b)Chordata: possess a mouth with an upper and a lower jaw
- c)Chondrichthyes: possess cartilaginous endoskeleton
- d)Mammalia : give birth to young ones
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following groups of animals is correctly matched with its characteristic feature without any exception?
a)
Reptilia: possess 3 -chambered heart with an incompletely divided ventricle
b)
Chordata: possess a mouth with an upper and a lower jaw
c)
Chondrichthyes: possess cartilaginous endoskeleton
d)
Mammalia : give birth to young ones
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Reptiles usually posses 3-chambered heart but crocodiles are an exception with 4-chambered heart. Not all chordates have a mouth with upper and lower jaw. Egg laying mammals include duck-billed platypus. Chondrichtlyes (cartilaginous fishes) are the fishes that have cartilaginous endoskeleton. There is no exception to this.
In some chordates, the notochord is modified as the vertebral column. Such animals are called vertebrates. Which one of the following statements makes sense?- a)All chordates are vertebrates but all vertebrates ate not chordates.
- b)All vertebrates are chordates and all chordates are vertebrates.
- c)All vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates.
- d)Chordates are not vertebrates and vertebrates are not chordates.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In some chordates, the notochord is modified as the vertebral column. Such animals are called vertebrates. Which one of the following statements makes sense?
a)
All chordates are vertebrates but all vertebrates ate not chordates.
b)
All vertebrates are chordates and all chordates are vertebrates.
c)
All vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates.
d)
Chordates are not vertebrates and vertebrates are not chordates.
|
|
Neha Dasgupta answered |
Answer:
The correct answer is option 'C': All vertebrates are chordates, but not all chordates are vertebrates.
Explanation:
To understand why option 'C' is the correct answer, let's break down the definitions of chordates and vertebrates and examine their relationship.
Chordates:
- Chordates are a phylum of animals that belong to the animal kingdom.
- They are characterized by certain key features, including a notochord (a flexible rod-like structure) at some point during their development.
- The notochord is usually present in the early embryonic stages and may or may not persist into adulthood.
- Chordates also possess other characteristics like a dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail.
Vertebrates:
- Vertebrates are a subphylum of chordates that have a backbone or vertebral column.
- They possess a notochord during their embryonic stage, but this notochord is subsequently replaced by the development of bones or cartilage forming the vertebral column.
- The vertebral column provides support and protection to the spinal cord in vertebrates.
- Vertebrates include animals like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals.
Relationship between Chordates and Vertebrates:
- All vertebrates are chordates because they possess the defining characteristics of chordates, including the presence of a notochord during their embryonic stage.
- However, not all chordates are vertebrates. Some chordates, like tunicates and lancelets, possess a notochord throughout their entire life but do not develop a vertebral column.
- These non-vertebrate chordates retain the notochord as their primary supportive structure.
Therefore, option 'C' makes sense because it correctly states that all vertebrates are chordates, but not all chordates are vertebrates.
The correct answer is option 'C': All vertebrates are chordates, but not all chordates are vertebrates.
Explanation:
To understand why option 'C' is the correct answer, let's break down the definitions of chordates and vertebrates and examine their relationship.
Chordates:
- Chordates are a phylum of animals that belong to the animal kingdom.
- They are characterized by certain key features, including a notochord (a flexible rod-like structure) at some point during their development.
- The notochord is usually present in the early embryonic stages and may or may not persist into adulthood.
- Chordates also possess other characteristics like a dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail.
Vertebrates:
- Vertebrates are a subphylum of chordates that have a backbone or vertebral column.
- They possess a notochord during their embryonic stage, but this notochord is subsequently replaced by the development of bones or cartilage forming the vertebral column.
- The vertebral column provides support and protection to the spinal cord in vertebrates.
- Vertebrates include animals like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals.
Relationship between Chordates and Vertebrates:
- All vertebrates are chordates because they possess the defining characteristics of chordates, including the presence of a notochord during their embryonic stage.
- However, not all chordates are vertebrates. Some chordates, like tunicates and lancelets, possess a notochord throughout their entire life but do not develop a vertebral column.
- These non-vertebrate chordates retain the notochord as their primary supportive structure.
Therefore, option 'C' makes sense because it correctly states that all vertebrates are chordates, but not all chordates are vertebrates.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Cephalochordata bears notochord all along the body throughout life.
Statement 2: Urochordate bears vertebral column only in tail region throughout the life.- a)Botht statements 1 and 2 are correct.
- b)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
- c)Statement 1 is incorrect and statement 2 is correct.
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Cephalochordata bears notochord all along the body throughout life.
Statement 2: Urochordate bears vertebral column only in tail region throughout the life.
Statement 1: Cephalochordata bears notochord all along the body throughout life.
Statement 2: Urochordate bears vertebral column only in tail region throughout the life.
a)
Botht statements 1 and 2 are correct.
b)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
c)
Statement 1 is incorrect and statement 2 is correct.
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
|
|
Avantika Chavan answered |
Understanding the Statements
To analyze the statements regarding Cephalochordata and Urochordata, we need to clarify the characteristics of these two groups of organisms.
Cephalochordata Characteristics
- Cephalochordates, such as lancelets, possess a notochord that extends the entire length of their body throughout their life.
- This notochord provides structural support and is characteristic of the phylum Chordata.
Urochordata Characteristics
- Urochordates, commonly known as tunicates, have a notochord only during their larval stage.
- In the adult stage, most Urochordates do not have a vertebral column; instead, they lose the notochord and are primarily composed of a tunic.
Analysis of the Statements
- Statement 1: "Cephalochordata bears notochord all along the body throughout life."
- This statement is correct as Cephalochordates retain their notochord from larval stages into adulthood.
- Statement 2: "Urochordate bears vertebral column only in tail region throughout the life."
- This statement is incorrect. Urochordates do not possess a vertebral column in their adult form; they lose the notochord and develop a tunic.
Conclusion
- Given that Statement 1 is correct and Statement 2 is incorrect, the correct answer is option B.
By understanding the characteristics of these two groups, we can see why the statements hold their truth values as described.
To analyze the statements regarding Cephalochordata and Urochordata, we need to clarify the characteristics of these two groups of organisms.
Cephalochordata Characteristics
- Cephalochordates, such as lancelets, possess a notochord that extends the entire length of their body throughout their life.
- This notochord provides structural support and is characteristic of the phylum Chordata.
Urochordata Characteristics
- Urochordates, commonly known as tunicates, have a notochord only during their larval stage.
- In the adult stage, most Urochordates do not have a vertebral column; instead, they lose the notochord and are primarily composed of a tunic.
Analysis of the Statements
- Statement 1: "Cephalochordata bears notochord all along the body throughout life."
- This statement is correct as Cephalochordates retain their notochord from larval stages into adulthood.
- Statement 2: "Urochordate bears vertebral column only in tail region throughout the life."
- This statement is incorrect. Urochordates do not possess a vertebral column in their adult form; they lose the notochord and develop a tunic.
Conclusion
- Given that Statement 1 is correct and Statement 2 is incorrect, the correct answer is option B.
By understanding the characteristics of these two groups, we can see why the statements hold their truth values as described.
Which of the following statements are incorrect regarding class Amphibia?
(i) Has body divisible into head and trunk. Tail is present in some amphibians.
(ii) Show respiration by gills, lungs and through skin.
(iii) Has scales in all its members.
(iv) Can lead dual life (aquatic and terrestrial).
(v) Has eyelids.
- a)All are correct
- b)(i) and (iv) are correct
- c)Only (iii) is incorrect
- d)Only (ii) is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements are incorrect regarding class Amphibia?
(i) Has body divisible into head and trunk. Tail is present in some amphibians.
(ii) Show respiration by gills, lungs and through skin.
(iii) Has scales in all its members.
(iv) Can lead dual life (aquatic and terrestrial).
(v) Has eyelids.
(i) Has body divisible into head and trunk. Tail is present in some amphibians.
(ii) Show respiration by gills, lungs and through skin.
(iii) Has scales in all its members.
(iv) Can lead dual life (aquatic and terrestrial).
(v) Has eyelids.
a)
All are correct
b)
(i) and (iv) are correct
c)
Only (iii) is incorrect
d)
Only (ii) is incorrect
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Amphibians do not have scales.
A common characteristic of all vertebrates without exception is- a)the division of body into head, neck, trunk and tail
- b)their body covered with an exoskeleton
- c)the possession of two pairs of functional appendage
- d)the presence of well-developed skull
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A common characteristic of all vertebrates without exception is
a)
the division of body into head, neck, trunk and tail
b)
their body covered with an exoskeleton
c)
the possession of two pairs of functional appendage
d)
the presence of well-developed skull
|
|
Ishani Nair answered |
Introduction:
Vertebrates are a group of animals that possess a vertebral column or backbone. They include fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. These animals share certain characteristics that distinguish them from other groups of animals.
Main Body:
Characteristic of vertebrates without exception:
The correct answer to the given question is option 'D', which states that the common characteristic of all vertebrates without exception is the presence of a well-developed skull.
1. Presence of a well-developed skull:
- All vertebrates possess a well-developed skull, which is a bony structure that encloses and protects the brain.
- The skull is made up of several bones and provides a rigid framework for the protection of the brain and sensory organs such as the eyes, ears, and nasal passages.
- The skull also plays a crucial role in the attachment of muscles responsible for chewing, biting, and other movements of the head.
2. Importance of a well-developed skull:
- The presence of a well-developed skull is essential for vertebrates as it protects the delicate brain from injury.
- The skull also provides support and protection to the sensory organs, which are vital for survival and adaptation to the environment.
- Additionally, the attachment points for muscles on the skull allow for the complex movements of the head and jaw, enabling various functions such as feeding, communication, and defense.
3. Differences in skull structure:
- While all vertebrates possess a well-developed skull, there are variations in its structure among different groups.
- Fish have a relatively simple skull, consisting of several bony plates and a cartilaginous framework.
- Amphibians and reptiles have more complex skulls, with additional bones and structures to accommodate their specific adaptations.
- Birds have a highly specialized skull, designed for lightweight and efficient flight.
- Mammals have the most diverse and complex skulls, reflecting their wide range of adaptations and lifestyles.
Conclusion:
The presence of a well-developed skull is a common characteristic of all vertebrates without exception. This structure protects the brain, supports sensory organs, and allows for various head and jaw movements. While the overall structure of the skull may vary among different groups of vertebrates, its importance in providing protection and facilitating essential functions remains constant.
Vertebrates are a group of animals that possess a vertebral column or backbone. They include fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. These animals share certain characteristics that distinguish them from other groups of animals.
Main Body:
Characteristic of vertebrates without exception:
The correct answer to the given question is option 'D', which states that the common characteristic of all vertebrates without exception is the presence of a well-developed skull.
1. Presence of a well-developed skull:
- All vertebrates possess a well-developed skull, which is a bony structure that encloses and protects the brain.
- The skull is made up of several bones and provides a rigid framework for the protection of the brain and sensory organs such as the eyes, ears, and nasal passages.
- The skull also plays a crucial role in the attachment of muscles responsible for chewing, biting, and other movements of the head.
2. Importance of a well-developed skull:
- The presence of a well-developed skull is essential for vertebrates as it protects the delicate brain from injury.
- The skull also provides support and protection to the sensory organs, which are vital for survival and adaptation to the environment.
- Additionally, the attachment points for muscles on the skull allow for the complex movements of the head and jaw, enabling various functions such as feeding, communication, and defense.
3. Differences in skull structure:
- While all vertebrates possess a well-developed skull, there are variations in its structure among different groups.
- Fish have a relatively simple skull, consisting of several bony plates and a cartilaginous framework.
- Amphibians and reptiles have more complex skulls, with additional bones and structures to accommodate their specific adaptations.
- Birds have a highly specialized skull, designed for lightweight and efficient flight.
- Mammals have the most diverse and complex skulls, reflecting their wide range of adaptations and lifestyles.
Conclusion:
The presence of a well-developed skull is a common characteristic of all vertebrates without exception. This structure protects the brain, supports sensory organs, and allows for various head and jaw movements. While the overall structure of the skull may vary among different groups of vertebrates, its importance in providing protection and facilitating essential functions remains constant.
In which one of the following, the genus name, its two characters and its class/phylum are correctly matched?

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which one of the following, the genus name, its two characters and its class/phylum are correctly matched?


a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Salamandra belonging to the class Amphibia has a tympanum that represents ear and in it fertilization is external. Ascaris has unsegmented body and it Belongs to the phylum Aschelminthes. Pteropus is viviparous. Aurelia has tissue level of organization.
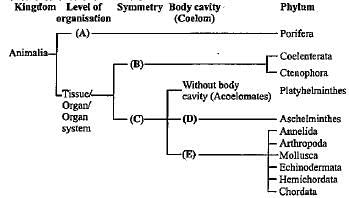
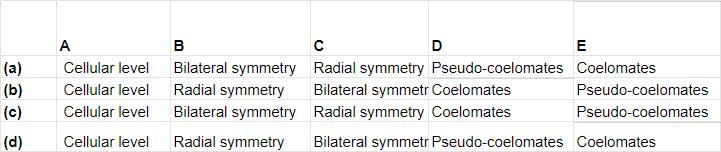
Study carefully the given flow chart and fill in the blanks (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E).
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Study carefully the given flow chart and fill in the blanks (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E).



a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
(A) Cellular level
(B) Radial symmetry
(C) Bilateral symmetry
(D) Pseudocoelomates
(E) Coelomates
(B) Radial symmetry
(C) Bilateral symmetry
(D) Pseudocoelomates
(E) Coelomates
Which of the following are correct?
(i) Sponges: Cellular level of organization
(ii) Cnidaria : Tissue level of organization
(iii) Platyhelminthes: Organ level of organization
(iv) Annelids, Arthropods, Molluscs, Echinoderms and Chordates: Organ system level of organization.- a)All are correct
- b)(ii) and (iv) only
- c)(ii) and (iii) only
- d)(i) and (ii) only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are correct?
(i) Sponges: Cellular level of organization
(ii) Cnidaria : Tissue level of organization
(iii) Platyhelminthes: Organ level of organization
(iv) Annelids, Arthropods, Molluscs, Echinoderms and Chordates: Organ system level of organization.
(i) Sponges: Cellular level of organization
(ii) Cnidaria : Tissue level of organization
(iii) Platyhelminthes: Organ level of organization
(iv) Annelids, Arthropods, Molluscs, Echinoderms and Chordates: Organ system level of organization.
a)
All are correct
b)
(ii) and (iv) only
c)
(ii) and (iii) only
d)
(i) and (ii) only
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Animals show four different grades of organization, (i) Protoplasmic grade found in protozoans. (ii) cellular grade is the characteristic of sponges and mesozoans because in a sponge, cells exhibit division of labour for performing specialized functions. (iii) Tissue grade is of two types : Cell-tissue grade is seen in coelenterates as there are cells not only specialized for different functions but also certain similar cells gather together to form tissue as well. Tissue - organ grade appears in flatworms (Platyhelminthes) with arrangement of tissues to form organs, (iv) In organ system level of organisation, organs are joined in a system to perform basic functions. It is found in higher invertebrates and all vertebrates.
Identify the animal (A) and name the phylum to which its belongs (B).

- a)A-Balanoglossus, B-Hemichordata
- b)A-Balanoglossus, B-Cephalochordata
- c)N-Nereis, B-Urochordata
- d)N-Nereis, B-Annelida
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the animal (A) and name the phylum to which its belongs (B).


a)
A-Balanoglossus, B-Hemichordata
b)
A-Balanoglossus, B-Cephalochordata
c)
N-Nereis, B-Urochordata
d)
N-Nereis, B-Annelida
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
The given animal belongs to subphylum hemichordata. The name of the animal is Balanoglossus or acorn worm. In it, true notochord is absent but gill slits are present.
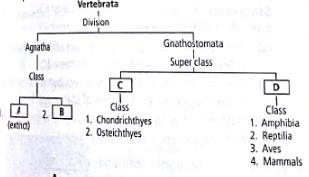
Go through the following flowchart for division of subphylum vertebrata. Fill the gaps A, B, C and D and select the correct option.

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Go through the following flowchart for division of subphylum vertebrata. Fill the gaps A, B, C and D and select the correct option.



a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Subphylum Vertebrata is divided into two divisions. They are agnatha (jawless) and gnathostomata (with jaw). Agnatha are further divided into two classes-Ostracodermi, which is extinct and Cydostomata (e.g., hag fish). Jawed vertebrates are divided into two superdasses-Pisces (true fish) and Tetrapoda (four limbs).
You have discovered an animal having characters like, triploblastic, bilateral symmetry, coelomate, chitinous exoskeleton, head, thorax and abdomen as body parts, and jointed appendages.
You should place the animal under- a)Tetrapoda
- b)Arthropoda
- c)Annelida
- d)Hemichordata.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
You have discovered an animal having characters like, triploblastic, bilateral symmetry, coelomate, chitinous exoskeleton, head, thorax and abdomen as body parts, and jointed appendages.
You should place the animal under
You should place the animal under
a)
Tetrapoda
b)
Arthropoda
c)
Annelida
d)
Hemichordata.
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
An animal having characters like triploblastic, bilateral symmetry, coelomate, chitinous exoskeleton, head, thorax, abdomen as body parts, and jointed appendages is placed under 'Arthropoda'.
Which among these is not a homeotherm?- a)Aptenodytes
- b)Testudo
- c)Delphinus
- d)Neophron
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among these is not a homeotherm?
a)
Aptenodytes
b)
Testudo
c)
Delphinus
d)
Neophron
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Testudo (tortoise) belonging to class Reptilia is a poikilotherm.
Which of the following group is formed of only the hermaphrodite organisms?- a)Earthworm, tapeworm, housefly, frog
- b)Earthworm, tapeworm, sea horse, housefly
- c)Earthworm, leech, sponge, roundworm
- d)Earthworm, tapeworm, leech, sponge
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following group is formed of only the hermaphrodite organisms?
a)
Earthworm, tapeworm, housefly, frog
b)
Earthworm, tapeworm, sea horse, housefly
c)
Earthworm, leech, sponge, roundworm
d)
Earthworm, tapeworm, leech, sponge
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Hermaphrodite organisms are those organisms in which both male and female sex organs are present in a single individual. Earthworm, tapeworm, leech and sponge are hermaphroditic organisms.
The limbless amphibian is- a)Ichthyophis
- b)Hyla
- c)Rana
- d)Salamandra
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The limbless amphibian is
a)
Ichthyophis
b)
Hyla
c)
Rana
d)
Salamandra
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Lchthyophis (Blind worm) is a limbless amphibian.
Identify the aquatic mammal(s) from the following.
(i) Bataenoptera
(ii) Equus
(iii) Delphinus
(iv) Pteropus
(v) Felis- a)(i) and (iii)
- b)(ii) and (iv)
- c)(v) only
- d)(iv) and (v)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the aquatic mammal(s) from the following.
(i) Bataenoptera
(ii) Equus
(iii) Delphinus
(iv) Pteropus
(v) Felis
(i) Bataenoptera
(ii) Equus
(iii) Delphinus
(iv) Pteropus
(v) Felis
a)
(i) and (iii)
b)
(ii) and (iv)
c)
(v) only
d)
(iv) and (v)
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Balaenoptera (Whale) and Delphinus (Dolphin) are auatic mammals. Equus (Horse) is terrestrial and Pteroous (Bat) is a flying mammal.
Which one of the folowing phyla is correctly matched with its two general characteristics?- a)Echinodermata - pentamerous radial symmetry and mostly internal fertilization
- b)Mollusca - normally oviparous and development through a trochophore or veliger larva
- c)Arthropoda - body divided into head, thorax and abdome and respiration by mouth
- d)Chordata - notochord persists throughout and separate anal and urinary openings to the outside
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the folowing phyla is correctly matched with its two general characteristics?
a)
Echinodermata - pentamerous radial symmetry and mostly internal fertilization
b)
Mollusca - normally oviparous and development through a trochophore or veliger larva
c)
Arthropoda - body divided into head, thorax and abdome and respiration by mouth
d)
Chordata - notochord persists throughout and separate anal and urinary openings to the outside
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Mollusca is normally oviparous and its development may be direct or indirect. If development is indirect then a occurs through trochophore or veliger larva. Echinoder show bilateral symmetry in larvae but pentamerous rafers symmetry in adult. Fertilization is external. In arthropods body is divided into head thorax and abdomen. Respiratory organs consists of book gills, book lungs and tracheae Notochord is present in chordates at some stage of their lives. Urinary and anal openings, may or may not be separate.
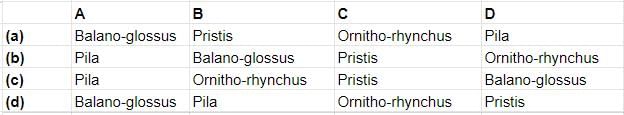
Examine the figures given below and identify the option which represents correct grouping of the labelled figures A, B, C and D.

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Examine the figures given below and identify the option which represents correct grouping of the labelled figures A, B, C and D.




a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
A - Pila
B - Balanoglossus
C - Pristis
D - Ornithorhynchus
B - Balanoglossus
C - Pristis
D - Ornithorhynchus
Select the correct option that represents examples of the following types of animals.
(i) Cold blooded animal
(ii) Warm blooded animal
(iii) Animal possessing dry and cornified skin
(iv) Dioecious animal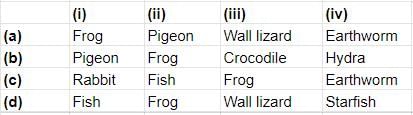
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct option that represents examples of the following types of animals.
(i) Cold blooded animal
(ii) Warm blooded animal
(iii) Animal possessing dry and cornified skin
(iv) Dioecious animal
(i) Cold blooded animal
(ii) Warm blooded animal
(iii) Animal possessing dry and cornified skin
(iv) Dioecious animal

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Frog (Amphibian) is a cold blooded animal i.e. its body temperature varies with the temperatue of the environment. Pigeon (Aves) is a warm blooded animal i.e. its body temperature remains constant irrespective of the temperature of the environment. Wall lizard (Reptile) possesses dry and cornified skin. Earthworm (Annelid) is a dioecious animal i.e. both male and female sex organs are present in the Single individual.
Which of the following pairs are correctly matched?

- a)(ii), (iii) and (iv)
- b)(i) and (iv)
- c)(i) and (ii)
- d)(i), (iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pairs are correctly matched?


a)
(ii), (iii) and (iv)
b)
(i) and (iv)
c)
(i) and (ii)
d)
(i), (iii) and (iv)
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Parapodia are locomotory structures present in some annelids. Sea urchin belongs to phylum Echinodermata.
Examine the figures of diploblastic (i) and triploblastic (ii) organization in animals given below and identify the labelled parts A to D.
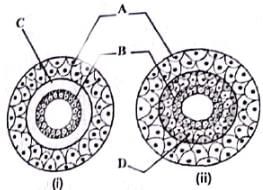
- a)A - Mesoglea, B - Ectoderm, C - Endoderm, D - Mesoderm
- b)A - Endocdern, B - Mesoderm, C - Mesoglea, D - Ectodderm
- c)A - Mesoderm, B - Mesoglea, C - Ectoderm, D - Endoderm
- d)A - Ectoderm, B - Endoderm, C - Mesoglea, D - Mesoderm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Examine the figures of diploblastic (i) and triploblastic (ii) organization in animals given below and identify the labelled parts A to D.


a)
A - Mesoglea, B - Ectoderm, C - Endoderm, D - Mesoderm
b)
A - Endocdern, B - Mesoderm, C - Mesoglea, D - Ectodderm
c)
A - Mesoderm, B - Mesoglea, C - Ectoderm, D - Endoderm
d)
A - Ectoderm, B - Endoderm, C - Mesoglea, D - Mesoderm
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
A - Ectoderm
B - Endoderm
C - Mesoglea
D - Mesoderm
So, the correct answer is 'A - Ectoderm, B - Endoderm, C - Mesoglea, D - Mesoderm'.
B - Endoderm
C - Mesoglea
D - Mesoderm
So, the correct answer is 'A - Ectoderm, B - Endoderm, C - Mesoglea, D - Mesoderm'.
The given figure shows a cross section of the body of an invertebrate. Identify the animal which has such body plan.
- a)Cochrooch (Artfiropoda)
- b)Round worm (Aschelminthes)
- c)PIanarla (Platyhelrninthes)
- d)Earthworm (Annelida)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The given figure shows a cross section of the body of an invertebrate. Identify the animal which has such body plan.


a)
Cochrooch (Artfiropoda)
b)
Round worm (Aschelminthes)
c)
PIanarla (Platyhelrninthes)
d)
Earthworm (Annelida)
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
The animals in which the coelom is absent are called acoelomates, for example flatworms (Planaria). In them the space between ectoderm and endodorm is filled with parenchyma derived from mesoderm.
Chapter doubts & questions for Animal Kingdom - NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Animal Kingdom - NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









