All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT Textbooks, Tests & Solutions >
All Questions
All questions of Plant - Growth & Development for NEET Exam
_________ indudes all the changes that an organism undergoes during its life cycle, from seed germination to senescence.- a)Growth
- b)Differentiation
- c)Dedifferentiation
- d)Development
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
_________ indudes all the changes that an organism undergoes during its life cycle, from seed germination to senescence.
a)
Growth
b)
Differentiation
c)
Dedifferentiation
d)
Development
|
|
Sanskriti Banerjee answered |
Growth:
Growth refers to the increase in size, weight, or volume of an organism over time. It is one of the essential processes in the life cycle of an organism. During growth, cells undergo division and increase in number, leading to an overall increase in the size of the organism. Growth occurs in all living organisms, from plants to animals.
Differentiation:
Differentiation is the process by which cells become specialized and acquire specific functions. It occurs during the development of an organism and is driven by specific genetic programs. Differentiation allows cells to perform specific tasks and contributes to the overall functionality of an organism. For example, in animals, cells differentiate into different types such as nerve cells, muscle cells, and blood cells, each performing a specific function.
Dedifferentiation:
Dedifferentiation is the reverse process of differentiation. It involves the loss of specialized characteristics and the reversion of cells back to a more primitive or undifferentiated state. Dedifferentiation is often observed in plants and certain animals, such as salamanders that can regenerate limbs. It allows for the formation of new cells and tissues, which can then differentiate into specific cell types.
Development:
Development encompasses all the changes that an organism undergoes during its life cycle, from the initial formation of a zygote to the senescence or aging of the organism. It includes processes such as growth, differentiation, and morphogenesis. Development is a highly coordinated and regulated series of events that occur in a precise sequence to form a fully functional organism.
During development, cells divide, differentiate, and organize into tissues and organs. The organism undergoes various developmental stages, such as embryogenesis, organogenesis, and postnatal growth. These stages involve complex interactions between genetic factors, environmental cues, and cellular signaling pathways.
Development is influenced by both intrinsic factors, such as the genetic information encoded in an organism's DNA, and extrinsic factors, such as the availability of nutrients and environmental conditions. It is a dynamic process that ensures the proper formation and functioning of the organism.
In conclusion, development includes all the changes that occur in an organism's life cycle, from seed germination to senescence. It involves processes such as growth, differentiation, and morphogenesis, which contribute to the formation of a fully functional organism.
Growth refers to the increase in size, weight, or volume of an organism over time. It is one of the essential processes in the life cycle of an organism. During growth, cells undergo division and increase in number, leading to an overall increase in the size of the organism. Growth occurs in all living organisms, from plants to animals.
Differentiation:
Differentiation is the process by which cells become specialized and acquire specific functions. It occurs during the development of an organism and is driven by specific genetic programs. Differentiation allows cells to perform specific tasks and contributes to the overall functionality of an organism. For example, in animals, cells differentiate into different types such as nerve cells, muscle cells, and blood cells, each performing a specific function.
Dedifferentiation:
Dedifferentiation is the reverse process of differentiation. It involves the loss of specialized characteristics and the reversion of cells back to a more primitive or undifferentiated state. Dedifferentiation is often observed in plants and certain animals, such as salamanders that can regenerate limbs. It allows for the formation of new cells and tissues, which can then differentiate into specific cell types.
Development:
Development encompasses all the changes that an organism undergoes during its life cycle, from the initial formation of a zygote to the senescence or aging of the organism. It includes processes such as growth, differentiation, and morphogenesis. Development is a highly coordinated and regulated series of events that occur in a precise sequence to form a fully functional organism.
During development, cells divide, differentiate, and organize into tissues and organs. The organism undergoes various developmental stages, such as embryogenesis, organogenesis, and postnatal growth. These stages involve complex interactions between genetic factors, environmental cues, and cellular signaling pathways.
Development is influenced by both intrinsic factors, such as the genetic information encoded in an organism's DNA, and extrinsic factors, such as the availability of nutrients and environmental conditions. It is a dynamic process that ensures the proper formation and functioning of the organism.
In conclusion, development includes all the changes that occur in an organism's life cycle, from seed germination to senescence. It involves processes such as growth, differentiation, and morphogenesis, which contribute to the formation of a fully functional organism.
Cells of tracheary elements (tracheids and vessels) become dead at maturity and lose their protoplasm due to the deposition of lignocellulosic cell wall thickenings. This is an example of- a)Growth
- b)Differentiation
- c)Dedifferentiation
- d)Redifferentiation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cells of tracheary elements (tracheids and vessels) become dead at maturity and lose their protoplasm due to the deposition of lignocellulosic cell wall thickenings. This is an example of
a)
Growth
b)
Differentiation
c)
Dedifferentiation
d)
Redifferentiation
|
|
Srishti Chakraborty answered |
Growth, Differentiation, Dedifferentiation, Redifferentiation
Growth: Growth refers to an increase in size, number, or volume of cells or tissues. It is a fundamental process in living organisms and is crucial for their development and survival. Growth can occur through cell division, cell enlargement, or both.
Differentiation: Differentiation is the process by which cells become specialized and acquire specific functions. During differentiation, cells undergo structural and functional changes that enable them to perform specific tasks in the body. This process is essential for the development and maintenance of tissues and organs.
Dedifferentiation: Dedifferentiation is the reverse process of differentiation, where specialized cells lose their specialized characteristics and revert to a more generic or stem cell-like state. Dedifferentiation is often observed during tissue regeneration or in response to injury, where cells need to regain their ability to divide and differentiate to repair damaged tissues.
Redifferentiation: Redifferentiation is the process by which dedifferentiated cells regain their specialized characteristics and reacquire their specific functions. It involves the reestablishment of cell structures, gene expression patterns, and functional properties that were lost during dedifferentiation.
Explanation:
In the case of tracheary elements such as tracheids and vessels, they undergo a process of differentiation. Initially, these cells are living and contain protoplasm, which includes the nucleus and other cell organelles. However, as these cells mature, they undergo a series of changes that lead to their specialization as water-conducting cells.
During the maturation process, tracheary elements deposit lignocellulosic cell wall thickenings, which provide structural support and help them withstand the mechanical stresses associated with water transport. These thickenings are composed of lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose, which make the cell walls rigid and impermeable to water.
As the thickenings accumulate, the tracheary elements undergo programmed cell death, resulting in the loss of their protoplasm. This cell death is a part of the differentiation process, where the cells sacrifice their living state to become efficient conduits for water transport.
Therefore, the process of tracheary element maturation and the loss of protoplasm due to the deposition of lignocellulosic cell wall thickenings is an example of differentiation. It involves the specialization of cells into a specific cell type with unique characteristics and functions, which in this case is the ability to transport water efficiently.
Growth: Growth refers to an increase in size, number, or volume of cells or tissues. It is a fundamental process in living organisms and is crucial for their development and survival. Growth can occur through cell division, cell enlargement, or both.
Differentiation: Differentiation is the process by which cells become specialized and acquire specific functions. During differentiation, cells undergo structural and functional changes that enable them to perform specific tasks in the body. This process is essential for the development and maintenance of tissues and organs.
Dedifferentiation: Dedifferentiation is the reverse process of differentiation, where specialized cells lose their specialized characteristics and revert to a more generic or stem cell-like state. Dedifferentiation is often observed during tissue regeneration or in response to injury, where cells need to regain their ability to divide and differentiate to repair damaged tissues.
Redifferentiation: Redifferentiation is the process by which dedifferentiated cells regain their specialized characteristics and reacquire their specific functions. It involves the reestablishment of cell structures, gene expression patterns, and functional properties that were lost during dedifferentiation.
Explanation:
In the case of tracheary elements such as tracheids and vessels, they undergo a process of differentiation. Initially, these cells are living and contain protoplasm, which includes the nucleus and other cell organelles. However, as these cells mature, they undergo a series of changes that lead to their specialization as water-conducting cells.
During the maturation process, tracheary elements deposit lignocellulosic cell wall thickenings, which provide structural support and help them withstand the mechanical stresses associated with water transport. These thickenings are composed of lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose, which make the cell walls rigid and impermeable to water.
As the thickenings accumulate, the tracheary elements undergo programmed cell death, resulting in the loss of their protoplasm. This cell death is a part of the differentiation process, where the cells sacrifice their living state to become efficient conduits for water transport.
Therefore, the process of tracheary element maturation and the loss of protoplasm due to the deposition of lignocellulosic cell wall thickenings is an example of differentiation. It involves the specialization of cells into a specific cell type with unique characteristics and functions, which in this case is the ability to transport water efficiently.
Read the following statements regarding arithmetic growth and select the correct answer.
(i) Rate of growth is constant.
(ii) One daughter cell remains meristematic while the other one differentiates and matures.
(iii) Mathematical expression is Lt =L0 +rt.- a)Statements (i) and (ii) are correct.
- b)Statements (ii) and (iii) are correct.
- c)Statements (i) and (ii) are correct.
- d)All statements are correct.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements regarding arithmetic growth and select the correct answer.
(i) Rate of growth is constant.
(ii) One daughter cell remains meristematic while the other one differentiates and matures.
(iii) Mathematical expression is Lt =L0 +rt.
(i) Rate of growth is constant.
(ii) One daughter cell remains meristematic while the other one differentiates and matures.
(iii) Mathematical expression is Lt =L0 +rt.
a)
Statements (i) and (ii) are correct.
b)
Statements (ii) and (iii) are correct.
c)
Statements (i) and (ii) are correct.
d)
All statements are correct.
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
ncrease in growth per unit time is called as growth rate. The growth rate may be arithmetic or geometrical. Arithmetic Growth is a type of growth in which the rate of growth is constant and increase in growth occurs in arithmetic progression-- 2, 4, 6, 8, 10,12. Meristematic cells at the growing point divide in such a fashion that one daughter cell remains meristematic while the other grows and differentiates. the process continues. Mathematically, arithmetic growth is expressed as
Lt =L0 +rt.
where Lt = length after time t, L0 = length at the beginning, and r = growth rate. On plotting growth against time, a linear graph is obtained.
Lt =L0 +rt.
where Lt = length after time t, L0 = length at the beginning, and r = growth rate. On plotting growth against time, a linear graph is obtained.
Which of the following is correct about phytochrome?- a)Pr absorbs red light and becomes
- b)Pr absorbs yellow light and becomes Pfr
- c)Pfr absorbs yellow light and becomes P r
- d)Pfr absorbs red light and becomes Pr
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is correct about phytochrome?
a)
Pr absorbs red light and becomes
b)
Pr absorbs yellow light and becomes Pfr
c)
Pfr absorbs yellow light and becomes P r
d)
Pfr absorbs red light and becomes Pr
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Phytochrome is a bright blue or bluish green pigment which was first of all isolated from plasma membrane of alga Mougeotias. Phytochrome is a photo receptor pigment that controls flowering. It exists in two interconvertible forms: Pfr or P730 (absorbs far red light) and Pr or P660 (absorbs red light).
By absorbing red light, Pr is converted into Pfr repidly. Pfr on absorbing far-red light is converted into Pr rapidly. Pfr is physiologically active form: Pr is inactive.
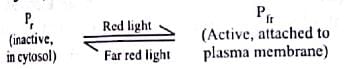
By absorbing red light, Pr is converted into Pfr repidly. Pfr on absorbing far-red light is converted into Pr rapidly. Pfr is physiologically active form: Pr is inactive.

Meristematic cells are characterized by- a)Thin cellulosic cell walls
- b)Dense protoplasm
- c)Prominent nuclei
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Meristematic cells are characterized by
a)
Thin cellulosic cell walls
b)
Dense protoplasm
c)
Prominent nuclei
d)
All of these
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
A meristematic tissue is a group of similar and immature cells that are in continuous state of division. These tissues are found in growing regions of plants. The chief characteristics of these tissues are:
(i) The cells may be round, oval, polygonal or rectangular.
(ii) They have thin cellulosic cell walls.
(iii) They do not have intercellular spaces.
(iv) They have dense cytoplasm with prominent nuclei.
(v) Vacuoles are absent or many small vacuoles may be present. The cells are in active state of metabolism.
(i) The cells may be round, oval, polygonal or rectangular.
(ii) They have thin cellulosic cell walls.
(iii) They do not have intercellular spaces.
(iv) They have dense cytoplasm with prominent nuclei.
(v) Vacuoles are absent or many small vacuoles may be present. The cells are in active state of metabolism.
An irreversible or permanent increase in size, mass or volume of a cell, organ or organism is called as ________.- a)growth
- b)differentiation
- c)dedifferentiation
- d)development
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An irreversible or permanent increase in size, mass or volume of a cell, organ or organism is called as ________.
a)
growth
b)
differentiation
c)
dedifferentiation
d)
development
|
|
Rajesh Banerjee answered |
Understanding Growth
Growth refers to an irreversible increase in the size, mass, or volume of a cell, organ, or organism. It is a fundamental biological process that occurs in all living entities. Here’s a breakdown of the concept:
Characteristics of Growth:
- Irreversibility: Growth results in permanent changes; once an organism or cell has grown, it cannot revert to its previous size or volume.
- Measurement: Growth can be measured in various ways, including increases in cell number (cell division), cell size, or organ size.
- Types of Growth:
- Cellular Growth: Involves cell division and enlargement.
- Organismic Growth: Involves the overall increase in the organism’s size.
Importance of Growth:
- Development: Growth is a crucial aspect of development, leading to more complex structures and functions in multicellular organisms.
- Adaptation: Growth allows organisms to adapt to their environments, increasing their chances of survival.
Distinction from Other Terms:
- Differentiation: This refers to the process by which cells become specialized for specific functions, but it does not necessarily involve size change.
- Dedifferentiation: This is the process where specialized cells revert to a less specialized state, often for regeneration purposes.
- Development: While growth is a component of development, development encompasses a broader range of processes including differentiation and morphogenesis.
In summary, growth is critical for the survival and evolution of organisms, influencing their structure and function throughout their lifecycle.
Growth refers to an irreversible increase in the size, mass, or volume of a cell, organ, or organism. It is a fundamental biological process that occurs in all living entities. Here’s a breakdown of the concept:
Characteristics of Growth:
- Irreversibility: Growth results in permanent changes; once an organism or cell has grown, it cannot revert to its previous size or volume.
- Measurement: Growth can be measured in various ways, including increases in cell number (cell division), cell size, or organ size.
- Types of Growth:
- Cellular Growth: Involves cell division and enlargement.
- Organismic Growth: Involves the overall increase in the organism’s size.
Importance of Growth:
- Development: Growth is a crucial aspect of development, leading to more complex structures and functions in multicellular organisms.
- Adaptation: Growth allows organisms to adapt to their environments, increasing their chances of survival.
Distinction from Other Terms:
- Differentiation: This refers to the process by which cells become specialized for specific functions, but it does not necessarily involve size change.
- Dedifferentiation: This is the process where specialized cells revert to a less specialized state, often for regeneration purposes.
- Development: While growth is a component of development, development encompasses a broader range of processes including differentiation and morphogenesis.
In summary, growth is critical for the survival and evolution of organisms, influencing their structure and function throughout their lifecycle.
Vernalisation can often be replaced by- a)auxin
- b)cytokinins
- c)gibberellins
- d)ethylene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Vernalisation can often be replaced by
a)
auxin
b)
cytokinins
c)
gibberellins
d)
ethylene
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Vernalisation or low temperature treatement of some plants can be replaced by gibberellins.
Different kinds of structures develop in plants in different phases of growth or in response to environment. This ability is called _________.- a)plasticity
- b)elasticity
- c)heterophylly
- d)differentiation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Different kinds of structures develop in plants in different phases of growth or in response to environment. This ability is called _________.
a)
plasticity
b)
elasticity
c)
heterophylly
d)
differentiation
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Different structures develop in different phases of growth as well as in response to environment. The ability to change under the influence of internal or external stimuli is called plasticity.
If a part of pith from the stem of a plant is used as an explant and cultured on nutrient medium, which of the following processes is responsible for the formation of an undifferentiated mass of cells called callus?- a)Growth
- b)Differentiation
- c)Dedifferentitation
- d)Redifferentiation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a part of pith from the stem of a plant is used as an explant and cultured on nutrient medium, which of the following processes is responsible for the formation of an undifferentiated mass of cells called callus?
a)
Growth
b)
Differentiation
c)
Dedifferentitation
d)
Redifferentiation
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The portion of pith taken as an explant comprises of parenchymatous cells (i.e., simple permanent tissue which have lost the capcity to divide). When such cells are cultured on solid culture media, the parenchymatous cells of pith become meristematic and start dividing resulting in a mass of undifferentiated cells called callus. this is an example of dedifferentiation. These cells may be made to divide in different manners in order to produce different organs so that the meristematic cells of callus may become permanent tissues by the process of redifferentiation. for exmaple, treatment of certain hormones may lead to the differentitation of shoot buds or roots.
Vascular cambium and cork cambium are- a)Lateral meristem
- b)Intercalary meristem
- c)Primary meristem
- d)Apical meristem
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Vascular cambium and cork cambium are
a)
Lateral meristem
b)
Intercalary meristem
c)
Primary meristem
d)
Apical meristem
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Lateral meristem occurs on the sides and takes part in increasing girth of the plant. Intra fascicular cambium is the primary lateral meristem which lies in vascular bundles of dicot and gymnosperm stems in between phloem and xylem. Examples of secondary lateral meristems are vascular cambium of the root, inter fascicular cambium of stem,cork cambium etc. that take part in the secondary growth.
Increase in girth (diameter).of plant as a result of the activities of lateral meristems is called _______________.- a)primary growth
- b)secondary growth
- c)open form of growth
- d)diffuse growth
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Increase in girth (diameter).of plant as a result of the activities of lateral meristems is called _______________.
a)
primary growth
b)
secondary growth
c)
open form of growth
d)
diffuse growth
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The Lateral meristem e.g. vascular cambium and cork cambium(in dicotyledons and gymnosperms) are the meristems that cause increase in girth of the organs in which they are active, This is known as secondary growth of the plant.
Growth at cellular level, is principally a consequence of increase in the amount of- a)Protoplasm
- b)DNA
- c)Cell wall
- d)Cell organelles
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Growth at cellular level, is principally a consequence of increase in the amount of
a)
Protoplasm
b)
DNA
c)
Cell wall
d)
Cell organelles
|
|
Akanksha Das answered |
Growth at cellular level, is principally a consequence of increase in the amount of Protoplasm
Growth at the cellular level refers to an increase in the size and mass of individual cells. This growth is primarily attributed to an increase in the amount of protoplasm within the cell. Protoplasm is the living substance within a cell that includes the cytoplasm and the nucleus.
Explanation:
1. Protoplasm as the living substance
Protoplasm is often referred to as the "living substance" because it is responsible for carrying out various cellular functions and processes that are essential for the survival and growth of the cell. It is composed of various organic and inorganic molecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, lipids, and minerals.
2. Increase in protoplasm leads to cell growth
As a cell grows, it requires more protoplasm to accommodate the increased metabolic activities and cellular components. The increase in protoplasm is primarily achieved through the synthesis of various biomolecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids, which are essential for cell growth and division.
3. Role of DNA in cell growth
Although DNA is an important component of the cell, it is not the primary cause of cell growth. DNA contains the genetic information that determines the structure and function of the cell, but it does not directly contribute to the increase in cell size. Instead, DNA replication occurs during the cell cycle to ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic material.
4. Cell wall and organelles
The cell wall is a rigid structure found in plant cells that provides support and protection. While the cell wall may contribute to the overall size of the cell, it is not directly involved in the growth of the protoplasm. Similarly, cell organelles, such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus, play specific roles in cellular processes but do not directly contribute to cell growth.
Conclusion:
In summary, growth at the cellular level is principally a consequence of an increase in the amount of protoplasm within the cell. Protoplasm is the living substance that carries out cellular functions and processes. While DNA, cell wall, and organelles are important components of the cell, they do not directly contribute to cell growth.
Growth at the cellular level refers to an increase in the size and mass of individual cells. This growth is primarily attributed to an increase in the amount of protoplasm within the cell. Protoplasm is the living substance within a cell that includes the cytoplasm and the nucleus.
Explanation:
1. Protoplasm as the living substance
Protoplasm is often referred to as the "living substance" because it is responsible for carrying out various cellular functions and processes that are essential for the survival and growth of the cell. It is composed of various organic and inorganic molecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, lipids, and minerals.
2. Increase in protoplasm leads to cell growth
As a cell grows, it requires more protoplasm to accommodate the increased metabolic activities and cellular components. The increase in protoplasm is primarily achieved through the synthesis of various biomolecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids, which are essential for cell growth and division.
3. Role of DNA in cell growth
Although DNA is an important component of the cell, it is not the primary cause of cell growth. DNA contains the genetic information that determines the structure and function of the cell, but it does not directly contribute to the increase in cell size. Instead, DNA replication occurs during the cell cycle to ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic material.
4. Cell wall and organelles
The cell wall is a rigid structure found in plant cells that provides support and protection. While the cell wall may contribute to the overall size of the cell, it is not directly involved in the growth of the protoplasm. Similarly, cell organelles, such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus, play specific roles in cellular processes but do not directly contribute to cell growth.
Conclusion:
In summary, growth at the cellular level is principally a consequence of an increase in the amount of protoplasm within the cell. Protoplasm is the living substance that carries out cellular functions and processes. While DNA, cell wall, and organelles are important components of the cell, they do not directly contribute to cell growth.
Photoperiod stimulus is perceived by___pigmen- a)cryptochrome
- b)cytochrome
- c)phytochrome
- d)monochrome
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Photoperiod stimulus is perceived by___pigmen
a)
cryptochrome
b)
cytochrome
c)
phytochrome
d)
monochrome
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Experimental evidences have indicated that the photoperiodic stimulus in plants is perceived by pigment phytochrome. Phytochrome is a photoreversible pigment that absorbs light and the flowering is a phytochrome-mediated process.
Growth in plants is- a)Only determinate
- b)Only indeterminate
- c)Mostly determinate
- d)Both determinate and indeterminate
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Growth in plants is
a)
Only determinate
b)
Only indeterminate
c)
Mostly determinate
d)
Both determinate and indeterminate
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
The meristem which is consumed in the formation of an organ is called determinate meristem. The meristem which continues its activity throughout life of the plant is called indeterminate meristem. Root apical meristem, shoot apical meristem, intercalary meristem (e.g., grass) and lateral meristems are all Indeterminate meristems. Plant growth is generally indeterminate, i.e., plants retain the capacity for unlimited growth throughout their life, whereas it is determinate in the meristem which is consumed in the formation of an organ.
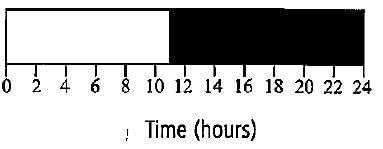
Maryland mammoth tobacco is a short day plant. Its critical duration of darkness is 10 hours. Under which of the following conditions will it not flower?
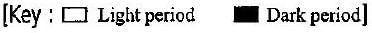
- a)
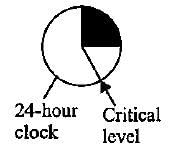
- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Maryland mammoth tobacco is a short day plant. Its critical duration of darkness is 10 hours. Under which of the following conditions will it not flower?
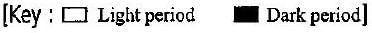
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
A short day plant is the one that flowers on photoperiods shorter than the critical day length. As the critical duration of darkness in the Maryland mammoth tobacco is 10 hours i.e., it requires a minimum period of darkness of 10 hours to flower. Thus under the conditions shown in option (a), the plant will not flower.
Match List - I with List - II.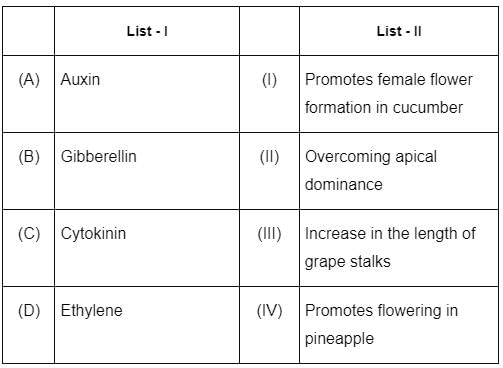 Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :- a)(A)-(II), (B)-(I), (C)-(IV), (D)-(III)
- b)(A)-(IV), (B)-(III), (C)-(II), (D)-(I)
- c)(A)-(I), (B)-(III), (C)-(IV), (D)-(II)
- d)(A)-(III), (B)-(II), (C)-(I), (D)-(IV)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match List - I with List - II.

Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
a)
(A)-(II), (B)-(I), (C)-(IV), (D)-(III)
b)
(A)-(IV), (B)-(III), (C)-(II), (D)-(I)
c)
(A)-(I), (B)-(III), (C)-(IV), (D)-(II)
d)
(A)-(III), (B)-(II), (C)-(I), (D)-(IV)

|
EduRev NEET answered |
(A) Auxin - (IV) Promotes flowering in pineapple: Auxins are a class of plant hormones that influence cell growth by altering cell elongation. However, the role of promoting flowering in pineapple is actually played by Ethylene. Therefore, there's an error in this match.
(B) Gibberellin - (III) Increase in the length of grape stalks: Gibberellins are plant hormones that stimulate stem elongation, seed germination, and flowering. They are known to increase the length of grape stalks.
(C) Cytokinin - (II) Overcoming apical dominance: Cytokinins are plant hormones that promote cell division and delay leaf senescence. They also play a role in overcoming apical dominance, encouraging the growth of lateral buds.
(D) Ethylene - (I) Promotes female flower formation in cucumber: Ethylene is a gaseous plant hormone which regulates a wide range of biological processes. It is known to influence sex determination in certain plants, promoting female flower formation in cucumber.
The plant which requires an exposure to light for a period greater than critical day length is- a)Long day plants
- b)Short day plants
- c)Long-short day plants
- d)Short-long day plants
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The plant which requires an exposure to light for a period greater than critical day length is
a)
Long day plants
b)
Short day plants
c)
Long-short day plants
d)
Short-long day plants
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The effect of photoperiods or daily duration of light hours (and dark periods) on the growth and development of plants, especially flowering, is called photoperiodism. Photoperiodism was first studied by Gamer and Allard (1920) in 'Maryland mammoth' a variety of Tobacco.
Long Day Plants (LDPs) flower when they receive long photoperiods or light hours which are above a critical length, e.g., henbane (Hyoscyamus Nget), wheat oat sugar beet, spinach (Spinacia oleracea), radish, barley, larkspur, lettuce.
Long Day Plants (LDPs) flower when they receive long photoperiods or light hours which are above a critical length, e.g., henbane (Hyoscyamus Nget), wheat oat sugar beet, spinach (Spinacia oleracea), radish, barley, larkspur, lettuce.
Low temperature treatment to speed up the process of flowering is referred to as- a)Photoperiodism
- b)Vernalisation
- c)Thermoperiodism
- d)Hydroponics
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Low temperature treatment to speed up the process of flowering is referred to as
a)
Photoperiodism
b)
Vernalisation
c)
Thermoperiodism
d)
Hydroponics
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Vernalisation is the process of shortening of the juvenile or vegetative phase and hastening flowering by a previous cold treatment. In vernalization by cold treatment, winter varieties are transferred into spring or summer varieties. The site of vernalization is apical meristem or all the meristematic cells e.g., shoot tip, embryo tips, root apex etc. The low temperature required for vernalization is usually 0o − 5oC. As a result of vernalization, a flowering hormone called vernalin is formed (reported by Melchers), but vernalin has never been isolated.
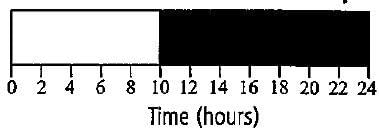
Sedum is a long day plant. Its critical duration of light is 13 hours Under which of the following conditions would it flower?

- a)

- b)
- c)

- d)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Sedum is a long day plant. Its critical duration of light is 13 hours Under which of the following conditions would it flower?


a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
A long day plant (LDP) is the one that flowers on photoperiods longer than critical day length. As the critical duration of light in Sedum is given to be 13 hours i.e., it required a minimum period of light of 13 hours to flower. Thus, the plant will flower only under the conditions shows in option (c).
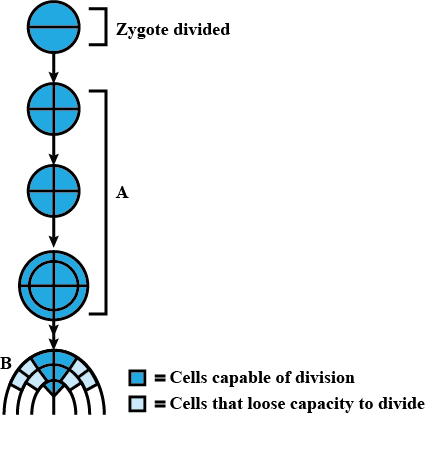
The given figure shows development of an embryo that undergoes two phases A and B. Select the correct option regarding it.
- a)A - Geometric phase, B - Arithmetic phase
- b)A - Arithmetic phase, B - Geometric phase
- c)A - Arithmetic phase, B - Exponential phase
- d)A - Exponential phase, B - Stationary phase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The given figure shows development of an embryo that undergoes two phases A and B. Select the correct option regarding it.


a)
A - Geometric phase, B - Arithmetic phase
b)
A - Arithmetic phase, B - Geometric phase
c)
A - Arithmetic phase, B - Exponential phase
d)
A - Exponential phase, B - Stationary phase
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
An embryo shows geometrical growth initially but later it passes into arithematic phase.
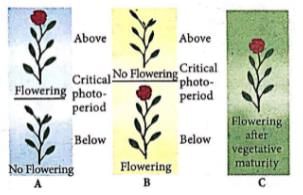
The given figure shows flowering responses of three plants A, B and C to the photoperiod. Select the correct option regarding this.
- a)A-Long day plant, B-Day neutral plant, C-Short day plant
- b)A-Short day plant, B-Day neutral plant, C-Long day plant
- c)A-Long day plant, B-Short day plant, C-Day neutral plant
- d)A-Short day plant, B-Long day plant, C-Day neutral plant
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The given figure shows flowering responses of three plants A, B and C to the photoperiod. Select the correct option regarding this.


a)
A-Long day plant, B-Day neutral plant, C-Short day plant
b)
A-Short day plant, B-Day neutral plant, C-Long day plant
c)
A-Long day plant, B-Short day plant, C-Day neutral plant
d)
A-Short day plant, B-Long day plant, C-Day neutral plant
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Plants which flower after exposure to light above critical photoperiod are called long day plants. Plants which flower when exposed to light below critical photoperiod are called short day plant. Plants which flower after vegetative maturity are called day neutral plant.
Cabbage is a biennial plant which produces flowers in the second year of growth. In an attempt to make it flower in a single year, four potted plants (I, II, III, and IV) of cabbage were subjected to different temperatures for several days given in the table.
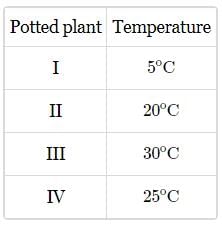
Which potted plant will show flowering?- a)I
- b)II
- c)III
- d)IV
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cabbage is a biennial plant which produces flowers in the second year of growth. In an attempt to make it flower in a single year, four potted plants (I, II, III, and IV) of cabbage were subjected to different temperatures for several days given in the table.

Which potted plant will show flowering?

Which potted plant will show flowering?
a)
I
b)
II
c)
III
d)
IV
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The low temperature required for vernalization is usually 0o − 5oC. In nature, the plants requiring vernalization are commonly biennials (e.g., cabbage, sugar canes), which complete their life cycle in two years. They germinate and grow vegetatively in the first year and produce flowers in the second year of growth. These plants fulfill their cold requirement during winters. However, such-biennial plants can be made to flower in one growing season by providing low-temperature treatment (i.e.,0o − 5oC temperature) to young plants or moistened seeds.
The given figure shows growth of two leaves over the period of one day. If, AG = absolute growth and RGR = relative growth rate, then select the correct option.

- a)AG for leaf A - 1%, RGR for leaf A - 1, AG for leaf B - 2%, RGR for leaf B - 2
- b)AG for leaf A - 100%, RGR for leaf A - 5, AG for leaf B - 10%, RGR for leaf B - 5
- c)AG for leaf A - 5, RGR for leaf A - 100%, AG for leaf B - 5%, RGR for leaf B - 10%
- d)AG for leaf A - 5, RGR for leaf A - 100%, AG for leaf B - 5%, RGR for leaf B - 100%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The given figure shows growth of two leaves over the period of one day. If, AG = absolute growth and RGR = relative growth rate, then select the correct option.


a)
AG for leaf A - 1%, RGR for leaf A - 1, AG for leaf B - 2%, RGR for leaf B - 2
b)
AG for leaf A - 100%, RGR for leaf A - 5, AG for leaf B - 10%, RGR for leaf B - 5
c)
AG for leaf A - 5, RGR for leaf A - 100%, AG for leaf B - 5%, RGR for leaf B - 10%
d)
AG for leaf A - 5, RGR for leaf A - 100%, AG for leaf B - 5%, RGR for leaf B - 100%
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Absolute growth rate (AGR): Increase in total growth of two organs or organisms is measured and comparison of total growth per unit time is called absolute growth. Absolute growth rate is the total growth per unit time. Relative growth rate (RGR) : It is growth per unit time per unit initial growth.
RGR= Growth in given time period / Measurement at start of time period
AG for leaf A = 10cm2 = 5cm2 = 5cm2
RGR for leaf A = 5/5 × 100 = 100%
AG for leaf B = 55cm2 − 50cm2 = 5cm2
RGR for leaf B = 5/50 × 100 = 10%
Though the absolute growth is same for both the leaves (A and B), relative rate of growth is more in leaf A because of its initial small size.
RGR= Growth in given time period / Measurement at start of time period
AG for leaf A = 10cm2 = 5cm2 = 5cm2
RGR for leaf A = 5/5 × 100 = 100%
AG for leaf B = 55cm2 − 50cm2 = 5cm2
RGR for leaf B = 5/50 × 100 = 10%
Though the absolute growth is same for both the leaves (A and B), relative rate of growth is more in leaf A because of its initial small size.
Four potted plants (I, II, Ill, and IV) of a short day plant, which has the critical period of 14 hours; are taken and exposed to light for different time periods. The light periods given are listed in the table.
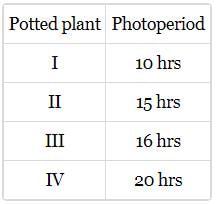
Which potted plant will show flowering after exposure to light?- a)I
- b)II
- c)III
- d)IV
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Four potted plants (I, II, Ill, and IV) of a short day plant, which has the critical period of 14 hours; are taken and exposed to light for different time periods. The light periods given are listed in the table.

Which potted plant will show flowering after exposure to light?

Which potted plant will show flowering after exposure to light?
a)
I
b)
II
c)
III
d)
IV
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
A short day plant (SDP), which has a critical period of 14 hours, will flower only if it is provided a continuous period of darkness of 14 hours; which has been given to the potted plant-I only. In rest of the potted plants, more amounts of light periods are being given and thus the dark periods have been reduced to below 14 hours.
Chapter doubts & questions for Plant - Growth & Development - NCERT Textbooks, Tests & Solutions 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Plant - Growth & Development - NCERT Textbooks, Tests & Solutions in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









