All Exams >
NEET >
Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Anatomy of Flowering Plants for NEET Exam
The function of root cap is- a)Protection of root tip and control of geotropic movement
- b)Storage of food products
- c)Absorption of nutrients
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The function of root cap is
a)
Protection of root tip and control of geotropic movement
b)
Storage of food products
c)
Absorption of nutrients
d)
None of the above
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
In plants having a taproot system, the trunk-like primary root develops directly from the embryonic root called radicle and grows downward into the soil. From this taproot, lateral roots develop which may initially grow horizontally then turn downward. These roots repeatedly form finer roots which terminate in a root tip with a minute, dome-shaped, protective root cap at the tipmost part. As the root grows, it pushes its root cap forward, probing the soil and absorbing water and nutrients mainly through fine root hairs. The root hairs are extensions of the epidermis which develop in the region of differentiation. These plant organs are short-lived and constantly replaced.
Branch of Botany which deals with the study of internal organization of plants is- a)Physiology
- b)Ecology
- c)Anatomy
- d)Cytology
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Branch of Botany which deals with the study of internal organization of plants is
a)
Physiology
b)
Ecology
c)
Anatomy
d)
Cytology

|
Jeeshan Ahmed answered |
Study of internal organization of plants is called anatomy. Plant anatomy is basically a branch of botany that is all about the study of internal structure of plants and it is also called as Phytotomy
Main function of lenticel is[2002]- a)transpiration
- b)guttation
- c)gaseous exchange
- d)bleeding
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Main function of lenticel is
[2002]
a)
transpiration
b)
guttation
c)
gaseous exchange
d)
bleeding

|
Shivani Tiwari answered |
Lenticels are pores present in woody stem through which transpiration or loss of water vapour takes place. Lenticel formation begins during the development of the first periderm. In the stem, they usually appear below a stoma or group of stomata. It should also be noted that lenticels can be present on fruits such as apples and pears.
A meristem may be defined as the group of cells which -- a)Add to the bulk of the Plants.
- b)Conserve food
- c)Divide continuously to give rise to new cells.
- d)Elongate and add to the group of cells.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A meristem may be defined as the group of cells which -
a)
Add to the bulk of the Plants.
b)
Conserve food
c)
Divide continuously to give rise to new cells.
d)
Elongate and add to the group of cells.

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
- A meristem may be defined as the group of cells which divide continuously to give rise to new cells.
- A meristem is the tissue in most plants containing undifferentiated cells, found in zones of the plant where growth can take place.
- Meristematic cells give rise to various organs of the plant and keep the plant growing.
- Meristematic cells are incompletely or not at all differentiated and are capable of continued cellular division. Furthermore, the cells are small and protoplasm fills the cell completely. The vacuoles are extremely small.
- The cytoplasm does not contain differentiated plastids, although they are present in rudimentary form- proplastids.
- Meristematic cells are packed closely together without intercellular cavities.
- The cell wall is a very thin primary cell wall.
Thus, the correct answer is option C.
The secondary meristem originates froma)Promeristemb)Permanent tissuec)Primary meristemd)Secretory tissueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Impact Learning answered |
On the basis of origin and development, meristem is grouped as promeristem, primary and secondary meristem. Promeristem includes undifferentiated, actively dividing apical initials which are derived from embryonic tissues and give rise to primary meristem. Primary meristem is derived from promeristem or embryonic meristem and produce primary permanent tissues of primary plant body. Secondary meristem develops from permanent tissues during secondary growth and gives rise to secondary tissues. Secretory tissues are the permanent primary tissues, which are derived from promeristem.
Thus, the correct answer is option B
Maximum growth in root occurs -- a)At its tip
- b)Towards light
- c)Behind the apex
- d)Towards apex
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Maximum growth in root occurs -
a)
At its tip
b)
Towards light
c)
Behind the apex
d)
Towards apex
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
Maximum growth of root takes place in the back side portion of the root apex. Apex portion is made up of root cap and then follows the region of cell division where meristematic tissues are present.
Bamboo, grass and mint stem elongate by the activity of -- a)Primary meristem
- b)Secondary meristem
- c)Intercalary meristems
- d)Apical meristems
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Bamboo, grass and mint stem elongate by the activity of -
a)
Primary meristem
b)
Secondary meristem
c)
Intercalary meristems
d)
Apical meristems

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
Bamboo, grass and mint stem elongate by the activity of Intercalary meristems. Intercalary meristem at base of leaves or nodes of grasses is responsible for primary growth. Meristems are classified by their location as apical located at root and shoot tips, lateral in the vascular and cork cambia, and intercalary at internodes, or stem regions between the places at which leaves attach and leaf bases. Intercalary meristem cells possess the ability to divide and produce new cells, as do apical and lateral meristems. They differ, however, in being situated between regions of mature tissue, such as at the base of grass leaves, which are themselves located on mature stem tissue.
Thus, the correct answer is option C.
Thus, the correct answer is option C.
In plants, during embryonic condition- a)All cells of the embryo divide
- b)Meristematic activity is confined to single apical cell
- c)Meristematic activity is confined to a group of apical cells.
- d)Apical & lateral cells only divide
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In plants, during embryonic condition
a)
All cells of the embryo divide
b)
Meristematic activity is confined to single apical cell
c)
Meristematic activity is confined to a group of apical cells.
d)
Apical & lateral cells only divide
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Plant embryogenesis is a process that occurs after the fertilization of an ovule to produce a fully developed plant embryo. This is a pertinent stage in the plant life cycle that is followed by dormancy and germination.The zygote produced after fertilization, must undergo various cellular divisions and differentiations to become a mature embryo.An end stage embryo has five major components including the shoot apical meristem, hypocotyl, root meristem, root cap, and cotyledons.Unlike animal embryogenesis, plant embryogenesis results in an immature form of the plant, lacking most structures like leaves, stems, and reproductive structures.
Mechanical tissue consisting of living cells is -- a)Sclerenchyma
- b)Collenchyma
- c)Chlorenchyma
- d)Parenchyma
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Mechanical tissue consisting of living cells is -
a)
Sclerenchyma
b)
Collenchyma
c)
Chlorenchyma
d)
Parenchyma
|
|
Saumya Dey answered |
Collenchyma cells are mechanical tissue, they possess thickening of corners of cells.
Meristems are not found in -
a) Cycas stem
b) Fern leaf
c) Fern rhizome
d) Pollen of pinus
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
b) Fern leaf
c) Fern rhizome
d) Pollen of pinus
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Lohit Matani answered |
Pollen of Pinus do not have meristems. A meristem is the tissue in most plants containing undifferentiated cells, found in zones of the plant where growth can take place. Meristematic cells give rise to various organs of the plant and keep the plant growing. Meristematic cells are incompletely or not at all differentiated, and are capable of continued cellular division.
Thus, the correct answer is option D.
Which of the following do not undergo anysecondary growth?
- a)Dicotyledonous stem
- b)Monocotyledonous root
- c)Monocotyledonous stem
- d)Both (B) and (C)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following do not undergo anysecondary growth?
a)
Dicotyledonous stem
b)
Monocotyledonous root
c)
Monocotyledonous stem
d)
Both (B) and (C)

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
Monocotyledonous roots and stems generally do not undergo secondary growth:
-
Monocotyledonous rootsMonocot roots do not undergo secondary growth because they lack vascular cambium, which is found in the vascular bundle between the xylem and phloem.
-
Monocotyledonous stemsMonocot stems do not undergo secondary growth, but they can increase in girth. This is called anomalous thickening and does not result in the development of secondary xylem and phloem
Which of the following tissues form the main bulk of storage organ- a)Parenchyma
- b)Collenchyma
- c)Sclerenchyma
- d)Aerenchyma
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following tissues form the main bulk of storage organ
a)
Parenchyma
b)
Collenchyma
c)
Sclerenchyma
d)
Aerenchyma

|
Virat answered |
Main function of parenchyma is storage of food.
A meristematic region present between the xylem and the phloem of open vascular bundles is called- a)Pericycle
- b)Pith
- c)Intrafascicular cambium
- d)Medullary ray
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A meristematic region present between the xylem and the phloem of open vascular bundles is called
a)
Pericycle
b)
Pith
c)
Intrafascicular cambium
d)
Medullary ray
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Intrafascicular cambium is present between xylem and phloem in dicot stem and roots. It is also termed as fascicular cambium. This meristematic area spreads laterally from each bundle and eventually becomes continuous, forming a complete vascular cambium.
A simple mechanical tissue devoid of lignin is -- a)Parenchyma
- b)Collenchyma
- c)Sclerenchyma
- d)Chlorenchyma
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A simple mechanical tissue devoid of lignin is -
a)
Parenchyma
b)
Collenchyma
c)
Sclerenchyma
d)
Chlorenchyma
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
The question is asking for "mechanical tissue". Both sclerenchyma and collenchyma are mechanical tissues, but sclerenchyma contains lignin. Hence the simple mechanical tissue without lignin is chollenchyma.
The tissue not having specifically thickened walls are- a)Parenchyma
- b)Collenchyma
- c)Fibres
- d)Sclereids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The tissue not having specifically thickened walls are
a)
Parenchyma
b)
Collenchyma
c)
Fibres
d)
Sclereids

|
Notes Wala answered |
- Parenchyma cells are thin-walled and are not specifically thickened, making them different from the other tissues mentioned.
- Collenchyma cells have thickened cell walls at the corners, providing mechanical support.
- Fibres and sclereids are types of sclerenchyma, which are characterized by having thick, lignified cell walls.
- Therefore, parenchyma is the tissue that does not have specifically thickened walls.
In grasses, certain adaxial epidermal cells along the veins modify themselves into large empty, colourless cells called- a)Guard cells
- b)Subsidiary cells
- c)Companion cells
- d)Bulliform cells
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In grasses, certain adaxial epidermal cells along the veins modify themselves into large empty, colourless cells called
a)
Guard cells
b)
Subsidiary cells
c)
Companion cells
d)
Bulliform cells
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
In grasses, certain adaxial epidermal cells along the veins modify themselves into large, empty, colourless cells. These are called bulliform cells or motor cells. Bulliform cells help in folding and unfolding of grass leaves.
When the bulliform cells in the leaves have absorbed water and are turgid, the leaf surface is exposed. When they are flaccid due to water stress, they make the leaves curl inwards (inrolling) to minimise water loss (transpiration).
Phloem of angiosperm is different from that of pteridophytes and gymnosperm in -
a) The absence of enzymes
b) Presence of endocytosis
c) Presence of companion cells
d) None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Harsh Sharma answered |
I think the answer should be c because pteridophytes and gymnosperms contains albuminous cells in place of companion cell
Which one of the following is wrongly matched?[2011]- a)Root pressure - Guttation
- b)Puccinia - Smut
- c)Root - Exarch protoxylem
- d)Cassia - Imbricate aestivation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is wrongly matched?
[2011]
a)
Root pressure - Guttation
b)
Puccinia - Smut
c)
Root - Exarch protoxylem
d)
Cassia - Imbricate aestivation

|
Prisha Singh answered |
Smut is a disease of cereals, corn, grasses and sorghum caused by many species of fungi.
Bordered pits are very common among tracheids of -
- a)Gymnosperm
- b)Dicotyledons
- c)Pteridophytes
- d)Monocotyledons
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bordered pits are very common among tracheids of -
a)
Gymnosperm
b)
Dicotyledons
c)
Pteridophytes
d)
Monocotyledons
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Tracheids are the chief water-conducting elements in gymnosperms and seedless vascular plants. They can also be found in angiosperms. Tracheids are elongated cells, closed at both ends. The walls are opened by numerous pits that are, depending on their origin, either round, oval, gap- or groove-shaped. Bordered pits are especially common in the tracheids of some gymnosperms.
Correct option is A.
Correct option is A.
A tissue is a group of cells which are -- a)Similar in origin, but dissimilar in form and function.
- b)Dissimilar in origin, form and function.
- c)Dissimilar in origin, but similar in form and function.
- d)Similar in origin, form and function.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A tissue is a group of cells which are -
a)
Similar in origin, but dissimilar in form and function.
b)
Dissimilar in origin, form and function.
c)
Dissimilar in origin, but similar in form and function.
d)
Similar in origin, form and function.
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Tissues are large groups of cells all doing the same job. The different kinds of tissues are classified into four groups, epithelial tissue, connective tissue, nerve tissue, and muscle tissue. Within each group are many kinds of tissue, but they are similar in the job they do.
Ectophloic siphonostele is found in- a)Osmunda and Equisetum
- b)Marsilea and Botrychium
- c)Adiantum and Cucurbitaceae
- d)Dicksonia and Maidenhair fern
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ectophloic siphonostele is found in
a)
Osmunda and Equisetum
b)
Marsilea and Botrychium
c)
Adiantum and Cucurbitaceae
d)
Dicksonia and Maidenhair fern

|
Pooja Saha answered |
The central pith is surrounded by xylem, phloem, pericycle and endodermis . The phloem occurs only outside the xylem e.g Equisetum, Osmunda.
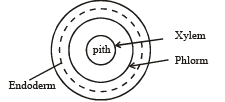
The lateral roots originate from- a)Endodermis cells
- b)Cortical cells below root hair
- c)Pericycle cells
- d)Epiblema
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The lateral roots originate from
a)
Endodermis cells
b)
Cortical cells below root hair
c)
Pericycle cells
d)
Epiblema
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Lateral roots start to develop in the pericycle cells, which is the outermost cell layer in the vascular cylinder. Remember that the xylem and phloem make up the vascular cylinder and that it is found in the center of the root.
Which of the following plant organs do not contain collenchyma
a)Leaf basesb)Monocot stemc)Rootsd)All of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Collenchyma is simple living tissue with thick non-lignified walls and uneven deposition of cellulose and pectin. They are derived from parenchyma and are present in groups under epidermis to provide flexible support to the growing plant's organs and thus are present in young dicot stem, pedicel, and petioles, not in leaf base and roots, which are not the growing part. It is not present in monocots.
As the secondary growth takes place (proceeds) in a tree, thickness of [1994]- a)heart wood increases
- b)sap-wood increases
- c)both increase
- d)both remain the same
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
As the secondary growth takes place (proceeds) in a tree, thickness of
[1994]
a)
heart wood increases
b)
sap-wood increases
c)
both increase
d)
both remain the same

|
Dipika Das answered |
Heartwood is the central wood of mature dicot stem and is the nonfunctional part of secondary xylem.
The casparian thickening occurs in the cells of
- a)Pericycle of root
- b)Endodermis of stem
- c)Endodermis of root
- d)Pericycle of stem
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The casparian thickening occurs in the cells of
a)
Pericycle of root
b)
Endodermis of stem
c)
Endodermis of root
d)
Pericycle of stem

|
Aniket Chawla answered |
Casparian strips occur in the Endodermis. It is a cell wall material that is deposited in the radial and transverse walls of the endodermis of roots.
Collenchyma differs from sclerenchyma in -- a)Retaining protoplasm at maturity
- b)Having thick walls
- c)Having a wide lumen
- d)Being meristematic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Collenchyma differs from sclerenchyma in -
a)
Retaining protoplasm at maturity
b)
Having thick walls
c)
Having a wide lumen
d)
Being meristematic
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
Collenchyma tissue is composed of elongated cells with irregularly thickened walls. They provide structural support and flexibility to the growing stems.
Sclerenchyma is the supporting tissue in plants. It is composed of dead cells which is completely devoid of protoplasm.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A.
Casparian thickenings are found in the cells of- a)Endodermis of the root
- b)Pericycle of the root
- c)Endodermis of the stem
- d)Pericycle of the stem
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Casparian thickenings are found in the cells of
a)
Endodermis of the root
b)
Pericycle of the root
c)
Endodermis of the stem
d)
Pericycle of the stem
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
In plant anatomy, the Casparian strip is a band of cell wall material deposited in the radial and tranverse walls of the endodermis, and is chemically different from the rest of the cell wall - the cell wall being made of lignin and without suberin - whereas the Casparian strip is made of suberin and sometimes lignin.
In a woody dicotyledonous tree, which of the following parts will mainly consist of primary tissues?[2005]- a)Shoot tips and root tips
- b)Stem and root
- c)Flowers, fruits and leaves
- d)All parts
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a woody dicotyledonous tree, which of the following parts will mainly consist of primary tissues?
[2005]
a)
Shoot tips and root tips
b)
Stem and root
c)
Flowers, fruits and leaves
d)
All parts

|
Shanaya Rane answered |
Primary Meristems : They are those meristematic tissues which are dervied directly from the meristems of the embryo and retain their meristematic activity. They are present at root, shoot tip and leaf primordia.
Which of the following is a primary meristem- a)Intra fascicular cambium
- b)Cork cambium
- c)Vascular cambium in roots
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a primary meristem
a)
Intra fascicular cambium
b)
Cork cambium
c)
Vascular cambium in roots
d)
None of the above
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
The cork cambium is a lateral meristem and is responsible for secondary growth that replaces the epidermis in roots and stems. It is found in woody and many herbaceous dicots, gymnosperms and some monocots (monocots usually lack secondary growth).
Fibre (longest plant cell), belongs to which tissue -
a) Parenchyma
b) Collenchyma
c) Aerenchyma
d) Sclerenchyma
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Sclerenchyma is a simple permanent tissue which is mainly composed of dead cells. The walls consist of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin. These are the principal supporting cells in plant tissues that have ceased elongation.
Sclerenchyma fibres are of great economical importance, since they constitute the source material for many fabrics (flax, hemp, jute, ramie).
So, the correct answer is option D.
Sclerenchyma fibres are of great economical importance, since they constitute the source material for many fabrics (flax, hemp, jute, ramie).
So, the correct answer is option D.
Reduction in vascular tissue, mechanical tissue and cuticle is characteristic of: [2009]- a)mesophytes
- b)epiphytes
- c)hydrophytes
- d)xerophytes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Reduction in vascular tissue, mechanical tissue and cuticle is characteristic of:
[2009]
a)
mesophytes
b)
epiphytes
c)
hydrophytes
d)
xerophytes

|
Prisha Singh answered |
Reduction in vascular tissue, mechanical tissue and cuticle is characteristic of hydrophytes.
Tracheids and vessels are present in all except - a)Marselia
- b)Equisetum
- c)Gnetum
- d)Cycas
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Tracheids and vessels are present in all except
a)
Marselia
b)
Equisetum
c)
Gnetum
d)
Cycas

|
Abhishek Desai answered |
Tracheids are elongated cells in the xylem of vascular plants that serve in the transport of water and mineral salts. Tracheids are Cycas one of two types of tracheary elements, vessel elements being the other. Tracheids, unlike vessel elements, do not have perforation plates.
In Kranz anatomy, the bundle sheath cells have[2011M]- a)thin walls, many intercellular spaces and no chloroplasts
- b)thick walls, no intercellular spaces and large number of chloroplasts
- c)thin walls, no intercellular spaces and several chloroplasts
- d)thick walls, many intercellular spaces and few chloroplasts
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In Kranz anatomy, the bundle sheath cells have
[2011M]
a)
thin walls, many intercellular spaces and no chloroplasts
b)
thick walls, no intercellular spaces and large number of chloroplasts
c)
thin walls, no intercellular spaces and several chloroplasts
d)
thick walls, many intercellular spaces and few chloroplasts

|
Naveen Menon answered |
In Kranz anatomy, the bundle sheath cells have thick wall, no intracellular spaces and large number of chloroplasts.
Gymnosperms are also called soft wood spermatophytes because they lack :[2012]- a)Cambium
- b)Phloem fibres
- c)Thick-walled tracheids
- d)Xylem fibres
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Gymnosperms are also called soft wood spermatophytes because they lack :
[2012]
a)
Cambium
b)
Phloem fibres
c)
Thick-walled tracheids
d)
Xylem fibres

|
Shivani Tiwari answered |
Gymnosperms lack xylem fibres. Large amount of parenchymatous cells are present with secondary xylem tracheids. So, these are also known as softwood spermatophytes.
A mature sieve tube differs from a vessel -- a)In lacking a functional nucleus
- b)Absence of lignified walls
- c)Being nearly dead
- d)Lacking cytoplasm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A mature sieve tube differs from a vessel -
a)
In lacking a functional nucleus
b)
Absence of lignified walls
c)
Being nearly dead
d)
Lacking cytoplasm

|
Abhishek Desai answered |
Solution :
The walls of vessels are lignified and hard and not very thick. Sieve tubes have thin cellulose walls.
The tissue responsible for translocation of food material is -- a)Parenchyma
- b)Phloem
- c)Vessels
- d)Fibres
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The tissue responsible for translocation of food material is -
a)
Parenchyma
b)
Phloem
c)
Vessels
d)
Fibres

|
Abhishek Desai answered |
Translocation occurs within a series of cells known as the phloem pathway, or phloem transport system, with phloem being the principal food-conducting tissue in vascular plants. Nutrients are translocated in the phloem as solutes in a solution called phloem sap.
Procambium forms[1994]- a)only primary vascular bundles
- b)only vascular cambium
- c)only cork cambium
- d)primary vascular bundles and vascular cambium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Procambium forms
[1994]
a)
only primary vascular bundles
b)
only vascular cambium
c)
only cork cambium
d)
primary vascular bundles and vascular cambium

|
Shivani Tiwari answered |
Procambium is the derivative of shoot apical meristem and forms vascular strand.
For a critical study of secondary growth in plants. Which one of the following pairs is suitable?[2007]- a)teak and pine
- b)deodar and fern
- c)wheat and maiden hair fern
- d)sugarcane and sunflower.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For a critical study of secondary growth in plants. Which one of the following pairs is suitable?
[2007]
a)
teak and pine
b)
deodar and fern
c)
wheat and maiden hair fern
d)
sugarcane and sunflower.

|
Aman Sharma answered |
Teak and pine is most suitable for the study of critical secondary growth because in secondary growth, secondary tissues are formed from lateral meristem which is well developed in these two cases and secondary growth occurs in gymnosperms and dicots.
The annular and spirally thickened conducting elements generally develop in the protoxylem when the root or stem is: [2009]
- a)elongating
- b)widening
- c)differentiating
- d)maturing
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The annular and spirally thickened conducting elements generally develop in the protoxylem when the root or stem is: [2009]
a)
elongating
b)
widening
c)
differentiating
d)
maturing

|
Arindam Khanna answered |
The annular and spirally thickened conducting elements generally develop in the protoxylem when the root or stem is maturing.This is the time when protoxylem develops or produces annular and spiral thick carrier elements. They also grow plants to provide mechanical support.
Collenchyma is found in -- a)Herbaceous climbers
- b)Hydrophytes
- c)Climbing stems
- d)Xerophytes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Collenchyma is found in -
a)
Herbaceous climbers
b)
Hydrophytes
c)
Climbing stems
d)
Xerophytes
|
|
Mahesh Mahajan answered |
Collenchyma occurs in climbing stems. Collenchyma occurs in the stem and petioles of dicot herbs. Due to deposition of pectin, it has high water retaining capacity. Since pectin appears at the angles, it becomes a spongy tissues.
The length of different internodes in a culm of sugarcane is variable because of[2008]- a)shoot apical meristem
- b)position of axillary buds
- c)size of leaf lamina at the node below each internode
- d)intercalary meristem
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The length of different internodes in a culm of sugarcane is variable because of
[2008]
a)
shoot apical meristem
b)
position of axillary buds
c)
size of leaf lamina at the node below each internode
d)
intercalary meristem

|
Dipanjan Mehta answered |
The length of different internodes in a culm of sugarcane is variable because of intercalary meristem. Intercalary meristem is not a part of apical meristem, occurs in the internodes of grasses (sugarcane) between leaf nodes and enables longitudinal growth of the stem.
Vascular tissues in flowering plants develop from:[2008]- a)phellogen
- b)plerome
- c)periblem
- d)dermatogen
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Vascular tissues in flowering plants develop from:
[2008]
a)
phellogen
b)
plerome
c)
periblem
d)
dermatogen

|
Sushant Goyal answered |
Vascular tissues in flowering plants develop from plerome. Plerome is a central core of primary meristem which gives rise to all cells of the stele from the pericycle inward.
As compared to a dicot root, a monocot root has[2012M]- a)many xylem bundles.
- b)relatively thicker periderm.
- c)inconspicuous annual rings.
- d)more abundant secondary xylem.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
As compared to a dicot root, a monocot root has
[2012M]
a)
many xylem bundles.
b)
relatively thicker periderm.
c)
inconspicuous annual rings.
d)
more abundant secondary xylem.

|
Prisha Singh answered |
The vascular bundles are arranged in a loose circle inside the endodermis of a monocot root. In a monocot root, more than six vascular bundles are present. It shows polyarch condition.
In land plants, the guard cells differ from other epidermal cells in having :[2011]- a)cytoskeleton
- b)mitochondria
- c)endoplasmic reticulum
- d)chloroplasts
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In land plants, the guard cells differ from other epidermal cells in having :
[2011]
a)
cytoskeleton
b)
mitochondria
c)
endoplasmic reticulum
d)
chloroplasts

|
Sarthak Saini answered |
Guard cells differ from epidermal cells in having chloroplast. The cell wall of guard cells are not uniform, inner walls are thicker than the outer walls, epidermal cells are uniformly thin.
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Anatomically, all the tissues present on the inner side of endodermis such as pericyde, vascular bundles and pith constitute the stele.
Statement 2 : Eustele is the stele in which vascular bundles are arranged in the form of a ring as present in dicot stems.
- a)Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- c)Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Anatomically, all the tissues present on the inner side of endodermis such as pericyde, vascular bundles and pith constitute the stele.
Statement 2 : Eustele is the stele in which vascular bundles are arranged in the form of a ring as present in dicot stems.
Statement 1 : Anatomically, all the tissues present on the inner side of endodermis such as pericyde, vascular bundles and pith constitute the stele.
Statement 2 : Eustele is the stele in which vascular bundles are arranged in the form of a ring as present in dicot stems.
a)
Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
c)
Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
The term stele was coined by Van Tiegham and Dauliot (1886). It is the axial portion of plant axis. Anatomically, all the tissues on the innerside of endodermis such as pericyde, vascular bundles and pith constitute the stele. Eustele is the type of stele in which a ring of vascular bundles is present around the central pith and inner to the pericyde e.g., dicot stem. Stele containing irregularly scattered vascular bundles is called atactostele, e.g., monocot stem. Pteridophytes are the first plants possenssing stele.
The only plant cells without nuclei among the following are
- a)Cambium cells
- b)Cells of pericycle
- c)Xylem parenchyma
- d)Sieve tubes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The only plant cells without nuclei among the following are
a)
Cambium cells
b)
Cells of pericycle
c)
Xylem parenchyma
d)
Sieve tubes
|
|
Manisha Sarkar answered |
The correct answer is option 'D', which states that the only plant cells without nuclei among the given options are sieve tubes. Let's understand why this is the correct answer.
Plant Cells and Nuclei:
Plant cells are the fundamental units of plants and possess various specialized structures that perform specific functions. One of the essential organelles found in plant cells is the nucleus. The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the genetic material of the cell, including DNA and RNA. It plays a crucial role in regulating the activities of the cell, including protein synthesis, cell division, and gene expression.
Explanation of the Options:
a) Cambium Cells:
Cambium cells are meristematic cells found in the stem and root of a plant. They are responsible for secondary growth, which leads to an increase in the diameter of the stem or root. Cambium cells actively divide and differentiate into secondary xylem and phloem cells. These cells contain nuclei as they are actively involved in cellular processes.
b) Cells of Pericycle:
The pericycle is a layer of cells located just inside the endodermis in the root. It is responsible for lateral root formation and the initiation of secondary growth. The cells of the pericycle also contain nuclei, as they actively participate in various cellular processes such as cell division and differentiation.
c) Xylem Parenchyma:
Xylem parenchyma cells are a type of parenchyma cells found in the xylem tissue of plants. They are involved in storage and transportation of water and minerals. Xylem parenchyma cells, like other plant cells, contain nuclei. The nuclei are essential for the regulation of cellular activities and the synthesis of proteins and enzymes required for cell function.
d) Sieve Tubes:
Sieve tubes are specialized cells found in the phloem tissue of plants. They are responsible for the transport of organic substances, such as sugars, from the leaves to other parts of the plant. Sieve tubes are unique in that they lack nuclei at maturity. During their development, the sieve tube elements lose their nuclei, allowing for a more efficient flow of materials through the phloem. The absence of nuclei in sieve tubes is an adaptation to facilitate the rapid and uninterrupted transport of organic solutes.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, sieve tubes are the only plant cells without nuclei. The absence of nuclei in sieve tubes allows for more efficient movement of organic substances through the phloem. The other options - cambium cells, cells of pericycle, and xylem parenchyma cells - all contain nuclei, which are essential for their cellular functions.
Plant Cells and Nuclei:
Plant cells are the fundamental units of plants and possess various specialized structures that perform specific functions. One of the essential organelles found in plant cells is the nucleus. The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the genetic material of the cell, including DNA and RNA. It plays a crucial role in regulating the activities of the cell, including protein synthesis, cell division, and gene expression.
Explanation of the Options:
a) Cambium Cells:
Cambium cells are meristematic cells found in the stem and root of a plant. They are responsible for secondary growth, which leads to an increase in the diameter of the stem or root. Cambium cells actively divide and differentiate into secondary xylem and phloem cells. These cells contain nuclei as they are actively involved in cellular processes.
b) Cells of Pericycle:
The pericycle is a layer of cells located just inside the endodermis in the root. It is responsible for lateral root formation and the initiation of secondary growth. The cells of the pericycle also contain nuclei, as they actively participate in various cellular processes such as cell division and differentiation.
c) Xylem Parenchyma:
Xylem parenchyma cells are a type of parenchyma cells found in the xylem tissue of plants. They are involved in storage and transportation of water and minerals. Xylem parenchyma cells, like other plant cells, contain nuclei. The nuclei are essential for the regulation of cellular activities and the synthesis of proteins and enzymes required for cell function.
d) Sieve Tubes:
Sieve tubes are specialized cells found in the phloem tissue of plants. They are responsible for the transport of organic substances, such as sugars, from the leaves to other parts of the plant. Sieve tubes are unique in that they lack nuclei at maturity. During their development, the sieve tube elements lose their nuclei, allowing for a more efficient flow of materials through the phloem. The absence of nuclei in sieve tubes is an adaptation to facilitate the rapid and uninterrupted transport of organic solutes.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, sieve tubes are the only plant cells without nuclei. The absence of nuclei in sieve tubes allows for more efficient movement of organic substances through the phloem. The other options - cambium cells, cells of pericycle, and xylem parenchyma cells - all contain nuclei, which are essential for their cellular functions.
Aerating pores in the bark of plants is known as- a)Lenticels
- b)Stomata
- c)Air pore
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Aerating pores in the bark of plants is known as
a)
Lenticels
b)
Stomata
c)
Air pore
d)
None of these

|
Kunal Rane answered |
In plants respiratory organs in stem is called lenticels. They are located as pores in the bark of plants.
What is not true about sclereids?[1996]- a)These are parenchyma cells with thickened lignified walls
- b)These are elongated and flexible with tapered ends
- c)These are commonly found in the shells of nuts and in the pulp of guava, pear, etc
- d) These are also called the stone cells
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is not true about sclereids?
[1996]
a)
These are parenchyma cells with thickened lignified walls
b)
These are elongated and flexible with tapered ends
c)
These are commonly found in the shells of nuts and in the pulp of guava, pear, etc
d)
These are also called the stone cells

|
Palak Khanna answered |
Sclereids are small bundles of sclerenchyma tissue in plants that form durable layers, such as the cores of apples and the gritty texture of pears. Sclereids are variable in shape. The cells can be isodiametric, prosenchymatic, forked or fantastically branched. The cell walls fill nearly all the cell’s volume. The shell of many seeds like those of nuts as well as the stones of drupes like cherries or plums are made up from sclereid.
A common structural feature of vessel elements and sieve tube elements are[2006]- a)pores on lateral walls
- b)presence of p-protein
- c)enucleate condition
- d)thick secondary walls
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A common structural feature of vessel elements and sieve tube elements are
[2006]
a)
pores on lateral walls
b)
presence of p-protein
c)
enucleate condition
d)
thick secondary walls

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
In plant conducting tissue xylem has an important integral cell as xylem vessel which is without nucleus. The phloem on other hand has a row of sieve tubes which are also without nucleus at maturity.
Chapter doubts & questions for Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily










