All Exams >
NEET >
Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Structural Organisation in Animals for NEET Exam
Mineral found in red pigment of vertebrate blood is[1989]- a)magnesium
- b)iron
- c)calcium
- d)copper
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mineral found in red pigment of vertebrate blood is
[1989]
a)
magnesium
b)
iron
c)
calcium
d)
copper
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Red pigment of vertebrate blood is haemoglobin. Haemoglobin is a conjugated protein. It consists of a basic protein globin joined to a nonprotein group heme, hence the name haemoglobin. Heme is an iron-porphyrin ring. A mammalian haemoglobin molecule is a complex of 4 heme molecules joined with 4 globin molecules.
Mucus cells (Goblet cells) :-- a)Unicellular gland
- b)Multicellular glands
- c)Endocrine glands
- d)Parietal cells of gastric glands
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mucus cells (Goblet cells) :-
a)
Unicellular gland
b)
Multicellular glands
c)
Endocrine glands
d)
Parietal cells of gastric glands
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
The main role of goblet cells is to secrete mucus in order to protect the mucous membranes where they are found. Goblet cells accomplish this by secreting mucins, large glycoproteins formed mostly by carbohydrates. ... Secretion may be stimulated by irritants such as dust and smoke, especially in the airway.
Lymph differs from blood in possessing[1989]- a)only WBC
- b)more RBC and WBC
- c)more RBC and few WBC
- d)more WBC and few RBC
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Lymph differs from blood in possessing
[1989]
a)
only WBC
b)
more RBC and WBC
c)
more RBC and few WBC
d)
more WBC and few RBC

|
Ashish Tiwary answered |
Lymph differs from blood in possessing WBCs [and lacking in RBCs].
Which one of the following statements is true for cockroach?- a)They are ureotelic.
- b)Anal styles are absent in females.
- c)The number of ovarioles in each ovary is ten.
- d)The larval stage is called caterpillar.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is true for cockroach?
a)
They are ureotelic.
b)
Anal styles are absent in females.
c)
The number of ovarioles in each ovary is ten.
d)
The larval stage is called caterpillar.

|
Pulicharla Subbareddy answered |
Anal styles are present only in male cockroach
Stratified squamous epithelium found in :-- a)Tonsil
- b)Payer's patch
- c)Appendix
- d)Spleen
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Stratified squamous epithelium found in :-
a)
Tonsil
b)
Payer's patch
c)
Appendix
d)
Spleen
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
The luminal surface of the tonsils are covered with a stratified squamous epithelium (in common with the oral epithelia). ... The epithelial cells are able to phagocytose bacteria, and transfer them to macrophages, which then present the foreign antigens to B-cells, which are activated (with the help of T cells).
Which of the following is not exclusively supplied with involuntary muscles ?[1998]- a)Muscular coats of blood vessels
- b)Muscles of the ducts of glands
- c)Muscles of iris
- d)Muscles of urethra
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not exclusively supplied with involuntary muscles ?
[1998]
a)
Muscular coats of blood vessels
b)
Muscles of the ducts of glands
c)
Muscles of iris
d)
Muscles of urethra

|
Arnab Iyer answered |
Voluntary muscles - under control of our will. Involuntary muscles - Not under control of our will. Muscles of urethra also remain under voluntary control after infancy.
Epithelial tissue with thin flat cells appearing like packed tiles occurs on[1994]- a)inner lining of cheek
- b)inner lining of stomach
- c)inner lining of fallopian tubes
- d)inner lining of ovary
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Epithelial tissue with thin flat cells appearing like packed tiles occurs on
[1994]
a)
inner lining of cheek
b)
inner lining of stomach
c)
inner lining of fallopian tubes
d)
inner lining of ovary

|
Arnab Iyer answered |
Squamous epithelial cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. The shape of the nucleus usually corresponds to the cell form and help to identify the type of epithelium. Squamous cells, for example, tend to have horizontal flattened, elliptical nuclei because of the thin flattened form of the cell. They form the lining of cavities such as the mouth, blood vessels, heart and lungs and make up the outer layers of the skin.
Lining of brain ventricle & central canal of spinal cord is called as:-- a)Ependyma
- b)Endothelium
- c)Mesothelium
- d)Neurosensory
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Lining of brain ventricle & central canal of spinal cord is called as:-
a)
Ependyma
b)
Endothelium
c)
Mesothelium
d)
Neurosensory
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
The ependyma is made up of ependymal cells called ependymocytes, a type of glial cell. These cells line the CSF-filled ventricles in the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. These are nervous tissue cells with a ciliated simple columnar shape much like that of some mucosal epithelial cells.
Inner lining of gut, stomach & liver is made up of :-- a)Simple squamous
- b)Simple cuboidal
- c)Simple columnar
- d)Pseudo stratified epithelium.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Inner lining of gut, stomach & liver is made up of :-
a)
Simple squamous
b)
Simple cuboidal
c)
Simple columnar
d)
Pseudo stratified epithelium.
|
|
Naresh Kumar answered |
Simple columnar cells are found In major organs like stomach as it plays a very important role in secretion and absorption.
Lining of larynx is :-- a)Stratified ciliated columnar Epithelium
- b)Stratified squamous Epithelium
- c)Stratified cuboidal Epithelium
- d)Stratified columnar Epithelium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Lining of larynx is :-
a)
Stratified ciliated columnar Epithelium
b)
Stratified squamous Epithelium
c)
Stratified cuboidal Epithelium
d)
Stratified columnar Epithelium
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Larynx is lined by ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium except vocal cords (lined by stratified squamous epithelium). The wall of larynx is reinforced by cartilage tissue. Large cartilages (cartilago thyroidea, cartilago cricoidea) and part of cartilago arytenoidea are composed of hyaline cartilage.
Term tissue is coined by (for animal anatomy) :-- a)Bichat
- b)Mayer
- c)Malpighi
- d)Hertwig
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Term tissue is coined by (for animal anatomy) :-
a)
Bichat
b)
Mayer
c)
Malpighi
d)
Hertwig
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
The tissue is an ensemble of similar cells from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues.
Marie François Xavier Bichat was a French anatomist and physiologist, who is best remembered as the father of modern histology and descriptive anatomy. Despite working without a microscope, he was the first to introduce the notion of tissues as distinct entities, and maintained that diseases attacked tissues rather than whole organs or the entire body, causing a revolution in anatomical pathology.
Cells of Peritoneum comprise :-- a)Ciliated Epithelium
- b)Glandular Epthelium
- c)Columnar Epithelium
- d)Squamous Epithelium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cells of Peritoneum comprise :-
a)
Ciliated Epithelium
b)
Glandular Epthelium
c)
Columnar Epithelium
d)
Squamous Epithelium
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
- If the epithelium is composed of one layer of cells, it is referred to as simple squamous epithelium and if it possesses multiple layers, it is referred to as stratified squamous epithelium.
- The peritoneum is the serous membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs and is composed of a layer of mesothelium supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. The mesothelium is a membrane composed of simple squamous cells that form the lining of several body cavities like peritoneum.
Hence the correct option is D.
Pseudostratified epithelium is present in :-- a)Nephron & Neuron
- b)Larynx & Pharynx
- c)Trachea & Bronchi
- d)Urinary Bladder & Intestine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Pseudostratified epithelium is present in :-
a)
Nephron & Neuron
b)
Larynx & Pharynx
c)
Trachea & Bronchi
d)
Urinary Bladder & Intestine
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelia are found in the linings of the trachea as well as the upper respiratory tract. Non-ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelia are located in the membranous part of male vas deferens. Most of the respiratory passageways, from the nasal cavity through the bronchi, are lined by ciliated, pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells.
Stratum germinativum is an example of which kind of epithelium?[1997]- a)Cuboidal
- b)Ciliated
- c)Columnar
- d)Squamous
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Stratum germinativum is an example of which kind of epithelium?
[1997]
a)
Cuboidal
b)
Ciliated
c)
Columnar
d)
Squamous

|
Supriya Senapati answered |
Stratum Germinativum is an example of columnar epithelium.
The inner most layer is called stratum germinativum has columnar cells resting upon a common basement membrane.
The inner most layer is called stratum germinativum has columnar cells resting upon a common basement membrane.
Stretchable & Water proof Epithelium :-- a)Simple cuboidal
- b)Simple squamous
- c)Simple Columnar
- d)Transitional
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Stretchable & Water proof Epithelium :-
a)
Simple cuboidal
b)
Simple squamous
c)
Simple Columnar
d)
Transitional
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Transitional epithelium is a type of tissue consisting of multiple layers of epithelial cells that contract and expand. This tissue structure type is found in urothelium, including that of the urinary bladder, the ureters and the superior urethra and gland ducts of the prostate. Transitional epithelium is stretchable and waterproof. The cells of transitional epithelium are highly keratinized and contain tight junctions or virtually impenetrable junctions, that seal together the cellular membranes of neighboring cells. This barrier prevents reabsorption of toxic wastes and pathogens by the bloodstream.
What are cuboidal or columnar cells called when they bear cilia?- a)Ciliated epithelium
- b)Flagellated epithelium
- c)Convoluted epithelium
- d)Brush border epithelium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What are cuboidal or columnar cells called when they bear cilia?
a)
Ciliated epithelium
b)
Flagellated epithelium
c)
Convoluted epithelium
d)
Brush border epithelium
|
|
Advait Das answered |
Ciliated Epithelium
Ciliated epithelium refers to a type of epithelial tissue that consists of cuboidal or columnar cells with cilia. Cilia are hair-like structures present on the surface of these cells that play a crucial role in various physiological processes.
Structure of Ciliated Epithelium
- Cell Shape: The cells of ciliated epithelium are typically cuboidal or columnar in shape.
- Cilia: These cells bear numerous cilia, which are microtubule-based structures extending from the cell surface. Cilia are composed of a central pair of microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of microtubules in a ring-shaped structure called the axoneme.
- Basal Body: Each cilium arises from a basal body, which is a modified centriole located at the base of the cilium.
- Function: The cilia in ciliated epithelium have rhythmic beating movements that facilitate the movement of various substances across the epithelial surface.
Functions of Ciliated Epithelium
Ciliated epithelium serves several important functions in different parts of the body:
- Mucociliary Escalator: In the respiratory tract, ciliated epithelium lines the airways and helps in the clearance of mucus and foreign particles. The coordinated beating of cilia propels the mucus upward, away from the lungs, preventing the accumulation of debris and pathogens.
- Oocyte Transport: In the female reproductive system, ciliated epithelium in the fallopian tubes helps in the transport of oocytes from the ovaries to the uterus. The beating of cilia creates fluid currents that aid in moving the oocytes towards their destination.
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Circulation: Ciliated epithelium lines the ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. The rhythmic beating of cilia in these regions facilitates the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, which helps in maintaining the brain and spinal cord environment.
- Smell and Taste Sensation: Cilia on the olfactory receptor cells in the nasal cavity and taste receptor cells in the taste buds help in detecting and transmitting sensory signals related to smell and taste.
In conclusion, cuboidal or columnar cells with cilia are called ciliated epithelium. These cells play vital roles in various physiological processes such as mucociliary clearance, oocyte transport, cerebrospinal fluid circulation, and sensory perception.
Ciliated epithelium refers to a type of epithelial tissue that consists of cuboidal or columnar cells with cilia. Cilia are hair-like structures present on the surface of these cells that play a crucial role in various physiological processes.
Structure of Ciliated Epithelium
- Cell Shape: The cells of ciliated epithelium are typically cuboidal or columnar in shape.
- Cilia: These cells bear numerous cilia, which are microtubule-based structures extending from the cell surface. Cilia are composed of a central pair of microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of microtubules in a ring-shaped structure called the axoneme.
- Basal Body: Each cilium arises from a basal body, which is a modified centriole located at the base of the cilium.
- Function: The cilia in ciliated epithelium have rhythmic beating movements that facilitate the movement of various substances across the epithelial surface.
Functions of Ciliated Epithelium
Ciliated epithelium serves several important functions in different parts of the body:
- Mucociliary Escalator: In the respiratory tract, ciliated epithelium lines the airways and helps in the clearance of mucus and foreign particles. The coordinated beating of cilia propels the mucus upward, away from the lungs, preventing the accumulation of debris and pathogens.
- Oocyte Transport: In the female reproductive system, ciliated epithelium in the fallopian tubes helps in the transport of oocytes from the ovaries to the uterus. The beating of cilia creates fluid currents that aid in moving the oocytes towards their destination.
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Circulation: Ciliated epithelium lines the ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. The rhythmic beating of cilia in these regions facilitates the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, which helps in maintaining the brain and spinal cord environment.
- Smell and Taste Sensation: Cilia on the olfactory receptor cells in the nasal cavity and taste receptor cells in the taste buds help in detecting and transmitting sensory signals related to smell and taste.
In conclusion, cuboidal or columnar cells with cilia are called ciliated epithelium. These cells play vital roles in various physiological processes such as mucociliary clearance, oocyte transport, cerebrospinal fluid circulation, and sensory perception.
Compound squamous epithelium occurs in :-a)Stomachb)Pharynxc)Intestined)TracheaCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
The compound epithelial tissue consists of two or more layers of cells. They form stratified layers. In the skin, they have a protective function. They do not have much of a role in absorption and secretion. Their function is to provide protection against any form of mechanical or chemical stress. The compound epithelium can be found on the dry surface of the skin, buccal cavity, pharynx, the lining of the salivary glands ducts and pancreatic ducts.
Inner lining of Blood vessels and heart is tesselleted Epithelium. Which is :-- a)Simple squamous due to wavy appearance
- b)Simple squamous due to tile like appearance
- c)Simple cuboidal due to wavy appearance
- d)Simple columnar Epithelium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Inner lining of Blood vessels and heart is tesselleted Epithelium. Which is :-
a)
Simple squamous due to wavy appearance
b)
Simple squamous due to tile like appearance
c)
Simple cuboidal due to wavy appearance
d)
Simple columnar Epithelium
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Tessellated epithelium is another term used for simple squamous epithelium also called as pavement epithelium due to it's flat appearance. It is mainly present in the alveoli and blood capillaries and performs the function of diffusion.
Stereocilia present in :-- a)Epididymis
- b)Seminalvesicle
- c)Ureter
- d)Kidney
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Stereocilia present in :-
a)
Epididymis
b)
Seminalvesicle
c)
Ureter
d)
Kidney
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Epididymitis care involves rest for 1 – 2 days with the scrotum raised if possible. The aim is to get the inflamed area above the level of the heart. This helps blood flow, which lowers swelling and pain, and helps with healing. Putting ice on the scrotum now and then can also help.
If a clean dry bone is kept in dil HCl for about 3 days, it- a)Breaks into pieces
- b) Becomes soft and elastic
- c)Dissolves
- d)Remain unchanged
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a clean dry bone is kept in dil HCl for about 3 days, it
a)
Breaks into pieces
b)
Becomes soft and elastic
c)
Dissolves
d)
Remain unchanged
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
HCl is hydrochloric acid, strong acid. Bone is made of minerals, and the most prominent mineral is calcium. When a bone is dropped in the HCl medium, the calcium of bone slowly starts dissolve due to the action of the strong acid. HCl + Ca --> CaCl2 + H2. Afterward, the bone is depleted of calcium but it does not "melt" because there are other minerals that make up the bone such as potassium, vitamins, and collagen. Since calcium is the main mineral in the bone, the bone becomes brittle and more susceptible to breakage. Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
During an injury nasal septum gets damaged and for its recovery which cartilage is preferred?[2001]- a)Hyaline cartilage
- b)Elastic cartilage
- c)Calcified cartilage
- d)Fibrous cartilage
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During an injury nasal septum gets damaged and for its recovery which cartilage is preferred?
[2001]
a)
Hyaline cartilage
b)
Elastic cartilage
c)
Calcified cartilage
d)
Fibrous cartilage

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
Hyaline cartilage is firm but slightly elastic with clear matrix. It is present in larynx, trachea, bronchi, nose. Elastic cartilage occur in external ear. Calcified cartilage occurs in suprascapula. Fibrous cartilage occurs in intervertebral discs.
Epidermis of skin of vertebrates comprises :-- a)Simple Epithelium
- b)Stratified Epithelium
- c)Transitional Epithelium
- d)Columnar Epithelium
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Epidermis of skin of vertebrates comprises :-
a)
Simple Epithelium
b)
Stratified Epithelium
c)
Transitional Epithelium
d)
Columnar Epithelium
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural integrity.
Covering membrane around muscle fibre is known as- a)Neurilemma
- b)Plasmalemma
- c)Sarcolemma
- d)Myolemma
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Covering membrane around muscle fibre is known as
a)
Neurilemma
b)
Plasmalemma
c)
Sarcolemma
d)
Myolemma
|
|
Rahul answered |
The sarcolemma is the cell membrane of the striated muscle fibre cell. It is also known as the myolemma. The function of the sarcolemma is similar to the function of the plasma membrane of eukaryotic cells. The plasma membrane covering the muscle fibre is known as the sarcolemma.
Germinative layer of Keratinized st. sq. Epithelium :-- a)Cuboidal
- b)Squamous
- c)Pseudo stratified
- d)Transitional
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Germinative layer of Keratinized st. sq. Epithelium :-
a)
Cuboidal
b)
Squamous
c)
Pseudo stratified
d)
Transitional
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
The basal layer of the stratified squamous epithelium is the cuboid layer which forms the other layer known as germinativum layer.
Basement membrane is made up of[1997]- a)epidermal cells only
- b)endodermal cells only
- c)both epidermal and endodermal cells
- d)no cell at all, but is a product of epithelial cells
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Basement membrane is made up of
[1997]
a)
epidermal cells only
b)
endodermal cells only
c)
both epidermal and endodermal cells
d)
no cell at all, but is a product of epithelial cells

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
Basement membrane is a delicate noncellular layer made of extracellular material that lies below the epithelium in contact with its basal surface. Basement membrane is a delicate noncellular layer made of extracellular material that lies below the epithelium in contact with its basal surface. Besides this the basal lamina consists of mucopoly saccharides and very fine fibres.
Transitional Epithelium is found in :-- a)Renal pelvis & Ureter
- b)Urinary bladder
- c)Upper part of male urethra
- d)All of above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Transitional Epithelium is found in :-
a)
Renal pelvis & Ureter
b)
Urinary bladder
c)
Upper part of male urethra
d)
All of above
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Transitional epithelium is a special type of epithelium which has the property of stretchability, it is found in places which requires strechibility as a function such as urinary bladder,ureter etc.
Columnar Epithelium with microvilli or Brush Border is present in :-- a)Intestine
- b)Stomach
- c)Appendix
- d)Pharynx
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Columnar Epithelium with microvilli or Brush Border is present in :-
a)
Intestine
b)
Stomach
c)
Appendix
d)
Pharynx

|
Maheshwar Saini answered |
A brush border (striated border or brush border membrane) is the microvilli-covered surface of simple cuboidal epithelium and simple columnar epithelium cells found in certain locations of the body.
The most important brush border enzymes are dextrinase and glucoamylase, which further break down oligosaccharides. Other brush border enzymes are maltase, sucrase, and lactase. Lactase is absent in most adult humans and for them lactose, like most poly-saccharides, is not digested in the small intestine.
The most important brush border enzymes are dextrinase and glucoamylase, which further break down oligosaccharides. Other brush border enzymes are maltase, sucrase, and lactase. Lactase is absent in most adult humans and for them lactose, like most poly-saccharides, is not digested in the small intestine.
Bone forming cells which secrete ossein protein are called as- a)Chondroblasts
- b)Chondrocytes
- c)Osteoblasts
- d)Osteocytes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Bone forming cells which secrete ossein protein are called as
a)
Chondroblasts
b)
Chondrocytes
c)
Osteoblasts
d)
Osteocytes
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Osteoclasts are large cells which dissolve the bones. They come from bone marrow whereas Osteoblasts help in formation of bones. They make a small bone called 'osteoid' made by some proteins nd collagen.
Membrane of Krause or Z line is a dark membrane which bisects
- a)A band or anisotropic band
- b)Henson's line
- c)I band or isotropic band
- d)Sarcomere
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Membrane of Krause or Z line is a dark membrane which bisects
a)
A band or anisotropic band
b)
Henson's line
c)
I band or isotropic band
d)
Sarcomere
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
Explanation:The Membrane of Krause, also known as the Z line, bisects the I band or isotropic band. Here's a brief explanation of the different components involved:- I band or isotropic band: - The I band is a lighter, less dense region in a sarcomere. - It contains only thin (actin) filaments. - The I band bisected by the Z line, dividing it into two equal halves.- Z line (Membrane of Krause): - The Z line is a dark membrane that appears in the middle of the I band. - It serves as the attachment site for the thin filaments and helps maintain the structure of the sarcomere. - The Z line plays a crucial role in muscle contraction by anchoring the thin filaments and transmitting the force generated during contraction.- A band or anisotropic band: - The A band is a darker, more dense region in a sarcomere. - It contains both thin (actin) and thick (myosin) filaments. - The A band remains constant in length during muscle contraction.- Henson's line: - Henson's line, also known as the M line, is situated in the middle of the A band. - It consists of proteins that help to hold the thick filaments in place and maintain the structure of the sarcomere.- Sarcomere: - The sarcomere is the functional unit of a muscle fiber, responsible for contraction. - It is composed of various bands, lines, and filaments, including the A band, I band, Z line, and Henson's line. - Sarcomeres are organized in series within a muscle fiber, and their coordinated contraction results in the overall shortening of the muscle fiber and generation of force.In summary, the Membrane of Krause or Z line bisects the I band or isotropic band, dividing it into two equal halves and providing attachment sites for the thin filaments within the sarcomere.
Term Epithelium coined by :-- a)Ruysch
- b)Mayer
- c)Bichat
- d)Marcellomalpighi
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Term Epithelium coined by :-
a)
Ruysch
b)
Mayer
c)
Bichat
d)
Marcellomalpighi
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
The term epithelium was introduced in 18th century by Duth Anatomist Ruysch to refer to the fact that these tissue grow upon other tissues.
The cell junctions called tight, adhering and gap junctions are found in[2009]- a)connective tissue
- b)epithelial tissue
- c)neural tissue
- d)muscular tissue
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The cell junctions called tight, adhering and gap junctions are found in
[2009]
a)
connective tissue
b)
epithelial tissue
c)
neural tissue
d)
muscular tissue

|
Pankaj Banerjee answered |
The cell junctions called tight, adhering and gap junctions are found in epithelial tissue. Epithelial tissue covers the whole surface of the body. It is made up of cells closely packed and ranged in one or more layers. This tissue is specialised to form the covering or lining of all internal and external body surfaces. Epithelial tissue that occurs on surfaces of the interior of the body is known as endothelium.
Ciliated Epithelium occurs in frog :-- a)Oviduct & Buccal cavity
- b)Stomach & urinaryBladder
- c)Blood vessels & Lymph vessels
- d)Kidney & stomach
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ciliated Epithelium occurs in frog :-
a)
Oviduct & Buccal cavity
b)
Stomach & urinaryBladder
c)
Blood vessels & Lymph vessels
d)
Kidney & stomach

|
Abhishek Desai answered |
The free surface may have microvilli. They are present in the lining of the stomach and intestine. Its functions include absorption and secretion. Ciliated Epithelium – When the columnar epithelial tissues have cilia, then they are called the ciliated epithelium.
Epithelial lining of cornea is composed of :-- a)Startified squamous nonkeratinised
- b)Transitional
- c)Simple cuboidal
- d)Simple squamous
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Epithelial lining of cornea is composed of :-
a)
Startified squamous nonkeratinised
b)
Transitional
c)
Simple cuboidal
d)
Simple squamous
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
The corneal epithelium is the outermost layer of the cornea. It is composed of a single layer of basal cells and 4-5 cell layers of nonkeratinized, stratified squamous epithelial cells, which are held together by tight junctions, to form an effective barrier against fluid loss and pathogen penetration.
Which of the following are principal cells of areolar connective tissue and secrete maximum amount of matrix - a)Macrophage
- b)Mast cells
- c)Fibroblast
- d)Histiocyte
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are principal cells of areolar connective tissue and secrete maximum amount of matrix
a)
Macrophage
b)
Mast cells
c)
Fibroblast
d)
Histiocyte
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Areolar connective tissue is a loosely arranged connective tissue that is widely distributed in the Body and contains collagen fibres, reticular fibres and a few elastic fibres embedded in a thin, almost fluid-like ground substance.
Fibroblast - responsible for synthesizing (creating) the collagen, elastin, and reticular fibres of the tissue.
Fibroblast - responsible for synthesizing (creating) the collagen, elastin, and reticular fibres of the tissue.
The breakdown of detritus into smaller particles by earthworm is a process called[2011M]- a)humification
- b)fragmentation
- c)mineralisation
- d)catabolism
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The breakdown of detritus into smaller particles by earthworm is a process called
[2011M]
a)
humification
b)
fragmentation
c)
mineralisation
d)
catabolism

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
The break down of detritus into smaller particles by earthworm is known as fragmentation.
Which of the following is not an anticoagulant - a)Histamine
- b)Hirudin
- c)Heparin
- d)Citrate
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an anticoagulant
a)
Histamine
b)
Hirudin
c)
Heparin
d)
Citrate
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Citrate is essentially a regional extracorporeal anticoagulant, with a short systemic half-life of around 5 min, metabolized predominantly by mitochondria in the liver, skeletal muscle and the kidney. Hirudin is the anticoagulant component of the saliva of medicinal leech and inhibits thrombin by formation of irreversible complexes through binding of its active site.
Basophils contain anticoagulant heparin, which prevents blood from clotting too quickly. They also contain the vasodilator histamine, which promotes blood flow to tissues.
Basophils contain anticoagulant heparin, which prevents blood from clotting too quickly. They also contain the vasodilator histamine, which promotes blood flow to tissues.
Basement membrane is absent in :-- a)Transitional Epithelium
- b)Sq. Epithelium
- c)Columnar Epithelium
- d)Simple cuboidal Epithelium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Basement membrane is absent in :-
a)
Transitional Epithelium
b)
Sq. Epithelium
c)
Columnar Epithelium
d)
Simple cuboidal Epithelium
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Transitional epithelium is a stratified tissue made of multiple cell layers, where the cells constituting the tissue can change shape depending on the distention in the organ. When the organ is filled with fluid, cells on the topmost layer of this epithelium can stretch and appear flattened. Alternately, they can also appear cuboidal with a rounded shape when the fluid pressure is low.
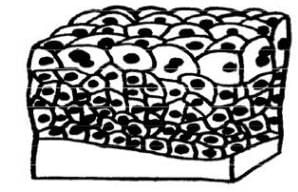
This epithelium is found lining the urinary bladder, ureters and urethra, as well as in the ducts of the prostrate gland.
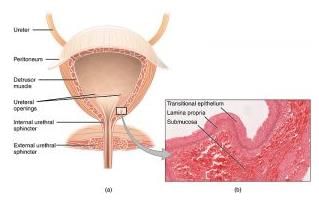
The image shows a cross section of the bladder with an inset displaying the histology of the epithelium, the underlying connective tissue (lamina propria) and submucosa.

This epithelium is found lining the urinary bladder, ureters and urethra, as well as in the ducts of the prostrate gland.

The image shows a cross section of the bladder with an inset displaying the histology of the epithelium, the underlying connective tissue (lamina propria) and submucosa.
Which of the following is not a type of simple epithelial tissue?- a)Squamous epithelium
- b)Cuboidal epithelium
- c)Columnar epithelium
- d)Compound epithelium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a type of simple epithelial tissue?
a)
Squamous epithelium
b)
Cuboidal epithelium
c)
Columnar epithelium
d)
Compound epithelium
|
|
Mayank Gupta answered |
Simple Epithelial Tissue
Simple epithelial tissue is a type of tissue that is composed of a single layer of cells. These cells are tightly packed together and cover a surface or line a cavity. Simple epithelial tissue is classified based on the shape of the cells.
Types of Simple Epithelial Tissue
a) Squamous epithelium - This type of simple epithelial tissue is composed of flat, thin cells that allow for the rapid diffusion of substances. Squamous epithelium is found in areas where rapid diffusion is necessary, such as the alveoli of the lungs.
b) Cuboidal epithelium - This type of simple epithelial tissue is composed of cube-shaped cells that are involved in secretion and absorption. Cuboidal epithelium is found in the glands and tubules of the kidney.
c) Columnar epithelium - This type of simple epithelial tissue is composed of tall, elongated cells that are involved in absorption and secretion. Columnar epithelium is found in the lining of the stomach and intestines.
d) Compound epithelium - This is not a type of simple epithelial tissue. Compound epithelium is composed of multiple layers of cells and is found in areas that require protection, such as the skin.
Conclusion
Simple epithelial tissue is an important type of tissue that plays a crucial role in the functioning of many organs and tissues in the body. It is classified based on the shape of the cells and includes squamous, cuboidal, and columnar epithelium. Compound epithelium is not a type of simple epithelial tissue.
Simple epithelial tissue is a type of tissue that is composed of a single layer of cells. These cells are tightly packed together and cover a surface or line a cavity. Simple epithelial tissue is classified based on the shape of the cells.
Types of Simple Epithelial Tissue
a) Squamous epithelium - This type of simple epithelial tissue is composed of flat, thin cells that allow for the rapid diffusion of substances. Squamous epithelium is found in areas where rapid diffusion is necessary, such as the alveoli of the lungs.
b) Cuboidal epithelium - This type of simple epithelial tissue is composed of cube-shaped cells that are involved in secretion and absorption. Cuboidal epithelium is found in the glands and tubules of the kidney.
c) Columnar epithelium - This type of simple epithelial tissue is composed of tall, elongated cells that are involved in absorption and secretion. Columnar epithelium is found in the lining of the stomach and intestines.
d) Compound epithelium - This is not a type of simple epithelial tissue. Compound epithelium is composed of multiple layers of cells and is found in areas that require protection, such as the skin.
Conclusion
Simple epithelial tissue is an important type of tissue that plays a crucial role in the functioning of many organs and tissues in the body. It is classified based on the shape of the cells and includes squamous, cuboidal, and columnar epithelium. Compound epithelium is not a type of simple epithelial tissue.
Which of the following tissue is present at the joints between skull bones and makes them immovable- a)Cartilage
- b)White fibrous connective tissue
- c)Ligament
- d)Areolar
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following tissue is present at the joints between skull bones and makes them immovable
a)
Cartilage
b)
White fibrous connective tissue
c)
Ligament
d)
Areolar
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Fibrous joints are connected by dense connective tissue, consisting mainly of collagen. These are fixed joints where bones are united by a layer of white fibrous tissue of varying thickness. In the skull the joints between the bones are called sutures. Such immovable joints are also referred to as synarthroses.
Germinal Epithelium of ovary is formed of :-- a)Columnar Epithelium
- b)Squamous Epithelium
- c)Cuboidal Epithelium
- d)Stratified Epithelium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Germinal Epithelium of ovary is formed of :-
a)
Columnar Epithelium
b)
Squamous Epithelium
c)
Cuboidal Epithelium
d)
Stratified Epithelium
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
The cellular covering of internal and external surfaces of the body, including the lining of vessels and other small cavities. It consists of cells joined by small amounts of cementing substances. Epithelium is classified into types on the basis of the number of layers deep and the shape of the superficial cells. Cuboidal epithelium epithelium whose cells are of approximately the same height and width, and appear square in transverse section.
Basement membrane is composed of :-- a)Hyaluronic Acid + glycoproteins
- b)Only mucopoly sacharides
- c)Endodermal cells
- d)Epidermal cells
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Basement membrane is composed of :-
a)
Hyaluronic Acid + glycoproteins
b)
Only mucopoly sacharides
c)
Endodermal cells
d)
Epidermal cells
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
The basement membrane is composed of two layers, the basal lamina and the underlying layer of reticular connective tissue. The clear layer closer to the epithelium is called the lamina lucida, while the dense layer closer to the connective tissue is called the lamina densa.
Histamine secreting cells are found in[1989]- a)connective tissues
- b)lungs
- c)muscular tissue
- d)nervous tissue
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Histamine secreting cells are found in
[1989]
a)
connective tissues
b)
lungs
c)
muscular tissue
d)
nervous tissue

|
Subham Chavan answered |
In connective tissues, histamine is an organic nitrogen compound involved in local immune responses and regulating physiological function in the gut and acts as a neurotransmitter. Histamine is produced by basophils and by mast cells found in nearby connective tissues.
The internal lining of blood vessels is called as :-- a)Mesothelium
- b)Endothelium
- c)Pavement Epithelium
- d)Stratified Epithelium
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The internal lining of blood vessels is called as :-
a)
Mesothelium
b)
Endothelium
c)
Pavement Epithelium
d)
Stratified Epithelium
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Endothelium refers to cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels, forming an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. It is a thin layer of simple, or single-layered, squamous cells called endothelial cells.
The functional unit of contractile system in striated muscle is[1998]- a)myofibril
- b)sarcomere
- c)Z-band
- d)cross bridges
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The functional unit of contractile system in striated muscle is
[1998]
a)
myofibril
b)
sarcomere
c)
Z-band
d)
cross bridges

|
Surbhi Das answered |
A skeletal muscle consists of a bundle of long fibres running the length of the muscle. Each fibre is a single cell with many nuclei. Skeletal muscle is also called striated muscle because the regular arrangement of the myofilaments creates as repeating pattern of light and dark bands. Each repeating unit is a sarcomere, the basic functional unit of the muscle. The borders of the sarcomere the Z lines, are lined up in adjacent myofibrils and contribute to striations visible with a light microscope.
Open circulatory system is not of physiological hinderance in Cockroach because- a)Circulatory and respiratory systems are not connected
- b)Heart is simple but chambered
- c)blood is colourless
- d)Excretion occurs through malpighian tubules
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Open circulatory system is not of physiological hinderance in Cockroach because
a)
Circulatory and respiratory systems are not connected
b)
Heart is simple but chambered
c)
blood is colourless
d)
Excretion occurs through malpighian tubules

|
Sandy Naaz answered |
The open circulatory system is a type of circulatory system in which nutrients and wastes move freely in the body cavity and not blood vessels. This type of circulatory system is found in insects, molluscs etc. In the case of cockroach, the open circulatory system is not of a physiological hindrance as circulatory and respiratory systems are not connected. Respiration mainly takes place by special respiratory organs known as spiracles. So, the correct answer is option A
Epithelial tissue origined from :-- a)Ectoderm
- b)Endoderm
- c)Mesoderm
- d)All of above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Epithelial tissue origined from :-
a)
Ectoderm
b)
Endoderm
c)
Mesoderm
d)
All of above
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
An epithelium is a tissue composed of one or more layers of cells covering the external and internal surfaces of various body parts. Epithelial tissue also forms glands. The term “epithelium” (sing, of epithelia) was given by a Dutch anatomist Ruysch (1638-1731) to refer to the fact that epithelial (Gr. epi- upon, thelio- grows) tissues grow upon other tissues.
The epithelial tissues occur on external and internal exposed surfaces of the body parts where they form protective covering.
Origin of Epithelial Tissue:
Epithelial tissues evolved first and are also formed first in the embryo. The epithelial tissues arise from all the three primary germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, of the embryo. For example the epidermis of the skin from the ectoderm, coelomic epithelium from the mesoderm and epithelial lining of alimentary canal (= gut) from the endoderm.
Features of Epithelial Tissues:
Epithelial tissues consist of variously shaped cells closely arranged in one or more layers. There is little intercellular material between the cells. The cells are held together by intercellular junctions. The epithelial tissues usually rest on a thin non-cellular basement membrane.
Usually blood vessels are absent in epithelial tissues. However the underlying connective tissues are generally well supplied with blood vessels. Nutrients enter epithelial tissues from the underlying connective tissues by diffusing through the basement membrane.
Epithelial lining of bartholins duct is composed of which type of cells :-- a)Transitional
- b)Cuboidal
- c)Columnar
- d)squamous
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Epithelial lining of bartholins duct is composed of which type of cells :-
a)
Transitional
b)
Cuboidal
c)
Columnar
d)
squamous
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
The gland is composed of columnar epithelium, and ducts are lined by stratified squamous epithelium and transitional cell epithelium. ... The Bartholin complex consists of a duct that is lined by squamous epithelium as it enters the distal vagina.
Long refractory period is present in - a)Smooth muscles
- b)Cardiac muscles
- c)Striated muscles
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Long refractory period is present in
a)
Smooth muscles
b)
Cardiac muscles
c)
Striated muscles
d)
None of these
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
The inability of the heart to generate tetanic contractions is the result of the long absolute refractory period of cardiac muscle, defined as the period during and following an action potential when an excitable membrane cannot be re-excited. The refractory period lasts almost as long as the contraction.
Exoskeleton originated form (Eg feathers, nail, horn, hoofs) :-- a)Connective tissue proper
- b)Epithelium tissue
- c)Skeletal tissue
- d)Vascular tissue
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Exoskeleton originated form (Eg feathers, nail, horn, hoofs) :-
a)
Connective tissue proper
b)
Epithelium tissue
c)
Skeletal tissue
d)
Vascular tissue
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissues are thin tissues that cover all the exposed surfaces of the body. They form the external skin, the inner lining of the mouth, digestive tract, secretory glands, the lining of hollow parts of every organ such as the heart, lungs, eyes, ears, the urogenital tract, as well as the ventricular system of the brain and central canals of the spinal cord.
The cells making up epithelia are often closely bound to one another through specialized structures called tight junctions. They are also free from blood vessels and nerves and are supported by a connective tissue called the basement membrane. They have polarity with a distinct basal domain facing the basement membrane and the other apical surface facing the lumen of an organ or the external environment.
Blood brain barrier is formed by - a)Astrocytes
- b)Oligodendrocytes
- c)Glial cells
- d)Microglial cells
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Blood brain barrier is formed by
a)
Astrocytes
b)
Oligodendrocytes
c)
Glial cells
d)
Microglial cells

|
Gopikas S answered |
Astrocytes contribute to induction and maintenance of the blood–brain barrier through paracrine interactions with the pericytes and endothelial cells. Astrocytes secrete classes of factors with either barrier-promoting or barrier-disrupting effects depending on signals received from neurons and/or endothelial cells.
The blood-brain barrier restricts the passage of pathogens, the diffusion of solutes in the blood, and large or hydrophilic molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid, while allowing the diffusion of hydrophobic molecules (O2, CO2, hormones) and small polar molecules.[4] Cells of the barrier actively transport metabolic products such as glucose across the barrier using specific transport proteins
The blood-brain barrier restricts the passage of pathogens, the diffusion of solutes in the blood, and large or hydrophilic molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid, while allowing the diffusion of hydrophobic molecules (O2, CO2, hormones) and small polar molecules.[4] Cells of the barrier actively transport metabolic products such as glucose across the barrier using specific transport proteins
Chapter doubts & questions for Structural Organisation in Animals - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Structural Organisation in Animals - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









