All Exams >
Humanities/Arts >
Legal Studies for Class 11 >
All Questions
All questions of Jurisprudence, Nature and Meaning of Law for Humanities/Arts Exam
_____ was a social utilitarian.- a)Haurion
- b)Ihering
- c)Duguit
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
_____ was a social utilitarian.
a)
Haurion
b)
Ihering
c)
Duguit
d)
None of the above
|
|
Prashanth Goyal answered |
Understanding Social Utilitarianism
Social utilitarianism is an ethical theory that evaluates actions based on their consequences, particularly in terms of the overall happiness or utility they produce. Among the prominent figures associated with this concept is Rudolf von Jhering, often referred to simply as Ihering.
Who was Ihering?
- Ihering was a German jurist and legal scholar active in the 19th century.
- He is best known for his work in legal philosophy and for advocating that law should serve social purposes.
Ihering's Contribution to Social Utilitarianism
- Ihering argued that the law is not merely a set of rules but must serve the interests of society as a whole.
- He believed that laws should be designed to promote social welfare and the greatest happiness for the greatest number.
Key Concepts in Ihering's Philosophy
- Purpose of Law: According to Ihering, the purpose of law is to protect social interests and enhance communal well-being.
- Social Utility: His theories emphasize that legal norms should be evaluated based on their contribution to societal happiness.
- Conflict of Interests: Ihering acknowledged that laws often mediate between conflicting interests, aiming for a balance that serves the common good.
Conclusion
In summary, Ihering's contributions to social utilitarianism highlight the importance of viewing law as a tool for promoting societal welfare rather than merely a system of punishment or regulation. His work has had a lasting impact on legal theory, making option B the correct answer in the context of social utilitarianism.
Social utilitarianism is an ethical theory that evaluates actions based on their consequences, particularly in terms of the overall happiness or utility they produce. Among the prominent figures associated with this concept is Rudolf von Jhering, often referred to simply as Ihering.
Who was Ihering?
- Ihering was a German jurist and legal scholar active in the 19th century.
- He is best known for his work in legal philosophy and for advocating that law should serve social purposes.
Ihering's Contribution to Social Utilitarianism
- Ihering argued that the law is not merely a set of rules but must serve the interests of society as a whole.
- He believed that laws should be designed to promote social welfare and the greatest happiness for the greatest number.
Key Concepts in Ihering's Philosophy
- Purpose of Law: According to Ihering, the purpose of law is to protect social interests and enhance communal well-being.
- Social Utility: His theories emphasize that legal norms should be evaluated based on their contribution to societal happiness.
- Conflict of Interests: Ihering acknowledged that laws often mediate between conflicting interests, aiming for a balance that serves the common good.
Conclusion
In summary, Ihering's contributions to social utilitarianism highlight the importance of viewing law as a tool for promoting societal welfare rather than merely a system of punishment or regulation. His work has had a lasting impact on legal theory, making option B the correct answer in the context of social utilitarianism.
Who is considered to be father of analytical thought?- a)Bentham
- b)Austin
- c)Pound
- d)Salmond
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who is considered to be father of analytical thought?
a)
Bentham
b)
Austin
c)
Pound
d)
Salmond

|
Ss Study Center answered |
John Austin is the founder of the Analytical School. He is considered as the 'father of English Jurisprudence.
Principle One of the principles of natural justice is Nemo judex in causa sua, which means that no one should be a judge in his own cause. In other words, no person can judge a case in which he has an interest.Facts 'X', a member of the selection board for a government service, was also a candidate for selection for the same service. 'X' did not take part in the deliberations of the board when his name was considered and approved.- a)Selection of 'X' is against the principle of natural justice.
- b)Selection of 'X' is not against the principle of natural justice.
- c)Non-selection of 'X' will be against the principles of natural justice.
- d)Non-participation of 'X' in the board deliberations will render his selection valid.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Principle One of the principles of natural justice is Nemo judex in causa sua, which means that no one should be a judge in his own cause. In other words, no person can judge a case in which he has an interest.
Facts 'X', a member of the selection board for a government service, was also a candidate for selection for the same service. 'X' did not take part in the deliberations of the board when his name was considered and approved.
a)
Selection of 'X' is against the principle of natural justice.
b)
Selection of 'X' is not against the principle of natural justice.
c)
Non-selection of 'X' will be against the principles of natural justice.
d)
Non-participation of 'X' in the board deliberations will render his selection valid.

|
Learning Educators answered |
In the given scenario, selection of X is not against the principle of natural justice, as X did not take part in the deliberations of the board when his name was considered and approved.
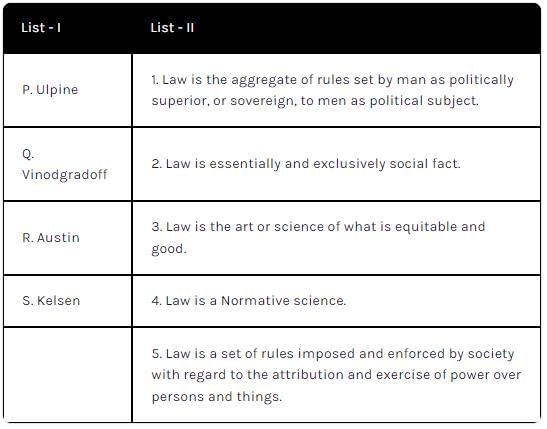
Law is the art or science of what is equitable or good. Who said this?- a)Salmond
- b)Ulpine
- c)Kelsen
- d)Holmes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Law is the art or science of what is equitable or good. Who said this?
a)
Salmond
b)
Ulpine
c)
Kelsen
d)
Holmes
|
|
Sahana Choudhury answered |
Introduction
The quote "Law is the art or science of what is equitable or good" is attributed to Ulpian, a prominent Roman jurist. Understanding this definition requires a deeper exploration of Ulpian's contributions to legal thought.
Who was Ulpian?
- Ulpian (c. 170 – 223 AD) was a renowned Roman lawyer and jurist.
- He played a significant role in the development of Roman law, particularly in the realm of legal principles and ethics.
Meaning of the Quote
- The phrase emphasizes that law is not merely a set of rules but also embodies principles of equity and morality.
- It underlines the idea that law should serve justice and reflect societal values of what is considered good.
Importance of Equity
- Equity in law refers to fairness and justice, addressing situations where rigid application of law may lead to unjust outcomes.
- Ulpian’s perspective encourages a legal system that adapts to the nuances of individual cases, promoting a sense of justice.
Influence on Modern Legal Systems
- Ulpian’s thoughts have influenced many contemporary legal systems, encouraging a balance between strict legal rules and moral considerations.
- His ideas resonate in the principles of equity and fairness that are foundational to many legal frameworks today.
Conclusion
Ulpian's definition of law as the "art or science of what is equitable or good" reflects a profound understanding of the law's purpose. It highlights the importance of justice and moral considerations in legal practice, making it a timeless assertion in the field of law.
The quote "Law is the art or science of what is equitable or good" is attributed to Ulpian, a prominent Roman jurist. Understanding this definition requires a deeper exploration of Ulpian's contributions to legal thought.
Who was Ulpian?
- Ulpian (c. 170 – 223 AD) was a renowned Roman lawyer and jurist.
- He played a significant role in the development of Roman law, particularly in the realm of legal principles and ethics.
Meaning of the Quote
- The phrase emphasizes that law is not merely a set of rules but also embodies principles of equity and morality.
- It underlines the idea that law should serve justice and reflect societal values of what is considered good.
Importance of Equity
- Equity in law refers to fairness and justice, addressing situations where rigid application of law may lead to unjust outcomes.
- Ulpian’s perspective encourages a legal system that adapts to the nuances of individual cases, promoting a sense of justice.
Influence on Modern Legal Systems
- Ulpian’s thoughts have influenced many contemporary legal systems, encouraging a balance between strict legal rules and moral considerations.
- His ideas resonate in the principles of equity and fairness that are foundational to many legal frameworks today.
Conclusion
Ulpian's definition of law as the "art or science of what is equitable or good" reflects a profound understanding of the law's purpose. It highlights the importance of justice and moral considerations in legal practice, making it a timeless assertion in the field of law.
According to Kelsen, law is a '____________'.- a)Positive science
- b)Normative science
- c)Positive art
- d)Normative art
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Kelsen, law is a '____________'.
a)
Positive science
b)
Normative science
c)
Positive art
d)
Normative art

|
Curiosity Classes answered |
Kelsen believed that law is a science that deals not with the actual events of the world (what is) but with norms (what ought to be). The legal relation contains the threat of a sanction from an authority in response to a certain act.
Who defines Jurisprudence as the formal science of positive law?- a)Ulpain
- b)Austin
- c)Holland
- d)Allen
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who defines Jurisprudence as the formal science of positive law?
a)
Ulpain
b)
Austin
c)
Holland
d)
Allen
|
|
Pj Commerce Academy answered |
An English Jurist Sir Thomas Erskine Holland defines, Jurisprudence as, " Jurisprudence is the formal science of positive law'" According to him jurisprudence should only concern itself with the basic principles of concepts underlying in any natural system of law.
LEGAL PRINCIPLE: The concept of natural justice is against bias and for the right to a fair hearing. While the term natural justice is often retained as a general concept, and it has largely been replaced and extended by the general 'duty to act fairly'.FACTUAL SITUATION: 'X', a male employee of a company was dismissed by the employer just on the basis of a complaint by 'Y', a female employee of the company that 'X' was trying to be too friendly with her and often requested her to accompany him to the canteen. Is the dismissal of X valid?- a)No, because the employer did not give a chance to 'X' to explain his side, thereby violated the principles of natural justice.
- b)Yes, moral law is antique and therefore, not applicable in modern times, therefore the termination is valid and not violations of the principles of natural justice occurred.
- c)Yes, because men are not supposed to behave improperly with women and hence there is no violation of any principles of law.
- d)No, because in the modern times this type of behaviour is common.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
LEGAL PRINCIPLE: The concept of natural justice is against bias and for the right to a fair hearing. While the term natural justice is often retained as a general concept, and it has largely been replaced and extended by the general 'duty to act fairly'.
FACTUAL SITUATION: 'X', a male employee of a company was dismissed by the employer just on the basis of a complaint by 'Y', a female employee of the company that 'X' was trying to be too friendly with her and often requested her to accompany him to the canteen. Is the dismissal of X valid?
a)
No, because the employer did not give a chance to 'X' to explain his side, thereby violated the principles of natural justice.
b)
Yes, moral law is antique and therefore, not applicable in modern times, therefore the termination is valid and not violations of the principles of natural justice occurred.
c)
Yes, because men are not supposed to behave improperly with women and hence there is no violation of any principles of law.
d)
No, because in the modern times this type of behaviour is common.
|
|
Pj Commerce Academy answered |
Principles of natural justice constitute one of the most important concepts of Administrative law. The expression 'natural justice' has been interpreted to cover several rules of equity and fair play and is sometimes also referred to as 'substantial justice', 'fundamental justice', 'Universal justice' and 'fair play in action'. The underlying object of natural justice is not only to secure justice, but also to prevent miscarriage of justice, thus ensuring that fundamental liberties and rights of citizens are well protected.
Two basic pillars of principles of natural justice
1. Nemo debet esse judex in propria causa: no man can be a judge in his own cause
2. Audi alteram partem: A person cannot be condemned without being heard
Considering the above given situation the dismissal of X is against the principles of natural justice, considering the second basic pillar of natural justice i.e. Audi alteram partem
Two basic pillars of principles of natural justice
1. Nemo debet esse judex in propria causa: no man can be a judge in his own cause
2. Audi alteram partem: A person cannot be condemned without being heard
Considering the above given situation the dismissal of X is against the principles of natural justice, considering the second basic pillar of natural justice i.e. Audi alteram partem
Who described Law as, " a set of rules imposed and enforced by society with regard to the attribution and exercise of power over persons and things"?- a)Vinogradoff
- b)Austin
- c)Kelsen
- d)Salmond
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who described Law as, " a set of rules imposed and enforced by society with regard to the attribution and exercise of power over persons and things"?
a)
Vinogradoff
b)
Austin
c)
Kelsen
d)
Salmond

|
Learning Educators answered |
Vinogradoff described Law as, " a set of rules imposed and enforced by society with regard to the attribution and exercise of power over persons and things"
According to whom, jurisprudence is a part of history, a part of economics and sociology, a part of ethics and a philosophy of life ?- a)Pound
- b)Keeton
- c)Radclifle
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to whom, jurisprudence is a part of history, a part of economics and sociology, a part of ethics and a philosophy of life ?
a)
Pound
b)
Keeton
c)
Radclifle
d)
None of the above

|
Learning Educators answered |
Dr. M.J.Sethna : Strongest exponent of Sythetic Jurisprudence . According to him jurisprudence is study of legal principles ,including their philosophical ,historical and sociological basis and analysis of legal concepts.
The nature and meaning of law may be defined through _____ school.- a)Modern
- b)Artificial
- c)Realistic
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The nature and meaning of law may be defined through _____ school.
a)
Modern
b)
Artificial
c)
Realistic
d)
None of the above

|
Curiosity Classes answered |
The nature and meaning of law may be defined through realistic school.
Bentham's legal philosophy is known as ______.- a)Utilitarian individualism
- b)Rationalism
- c)Both of the above
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bentham's legal philosophy is known as ______.
a)
Utilitarian individualism
b)
Rationalism
c)
Both of the above
d)
None of the above

|
Curiosity Classes answered |
Bentham's legal philosophy is known as Utilitarian individualism
Which of the following is/are the main characteristics of law? - Law pre-supposes a State.
- Authorization from State to make, or recognizes or sanction rules.
- Laws are made to serve some purpose.
Select the correct answer from the options given below -- a)1 only
- b)1 and 2 only
- c)2 and 3 only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are the main characteristics of law?
- Law pre-supposes a State.
- Authorization from State to make, or recognizes or sanction rules.
- Laws are made to serve some purpose.
Select the correct answer from the options given below -
a)
1 only
b)
1 and 2 only
c)
2 and 3 only
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Prashanth Das answered |
Main Characteristics of Law
Law is a structured system of rules created and enforced through social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior. The characteristics listed in the question reflect the foundational aspects of law.
1. Law Pre-supposes a State
- Laws are inherently linked to the existence of a state or governing body.
- A state provides the necessary framework for the establishment and enforcement of laws, ensuring order and resolution of conflicts within society.
2. Authorization from State to Make, Recognize, or Sanction Rules
- The legitimacy of laws stems from the authority of the state.
- Only entities recognized by the state have the power to create, modify, or enforce rules. This ensures that the laws are binding and upheld by the state’s institutions.
3. Laws are Made to Serve Some Purpose
- Laws are not arbitrary; they serve specific functions such as maintaining order, protecting individual rights, and promoting social justice.
- They are designed to address societal needs and challenges, supporting the welfare of the community and ensuring the smooth functioning of society.
Conclusion
Given these points, it is clear that all three characteristics are integral to understanding the nature and role of law. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' (1, 2, and 3), as they collectively encapsulate the essence of what law represents in a societal context.
Law is a structured system of rules created and enforced through social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior. The characteristics listed in the question reflect the foundational aspects of law.
1. Law Pre-supposes a State
- Laws are inherently linked to the existence of a state or governing body.
- A state provides the necessary framework for the establishment and enforcement of laws, ensuring order and resolution of conflicts within society.
2. Authorization from State to Make, Recognize, or Sanction Rules
- The legitimacy of laws stems from the authority of the state.
- Only entities recognized by the state have the power to create, modify, or enforce rules. This ensures that the laws are binding and upheld by the state’s institutions.
3. Laws are Made to Serve Some Purpose
- Laws are not arbitrary; they serve specific functions such as maintaining order, protecting individual rights, and promoting social justice.
- They are designed to address societal needs and challenges, supporting the welfare of the community and ensuring the smooth functioning of society.
Conclusion
Given these points, it is clear that all three characteristics are integral to understanding the nature and role of law. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' (1, 2, and 3), as they collectively encapsulate the essence of what law represents in a societal context.
Laws are:- a)informal norms
- b)formal norms enforced by the state
- c)casual folkways
- d)less important than folkways
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Laws are:
a)
informal norms
b)
formal norms enforced by the state
c)
casual folkways
d)
less important than folkways
|
|
Aravind Chawla answered |
Understanding Laws
Laws are critical components of society that govern behavior and maintain order. They differ from other social norms in significant ways.
Definition of Laws
- Laws are formal norms established by a governing body, typically the state.
- They are codified rules that dictate what is permissible and what is not within a society.
Enforcement Mechanism
- Unlike informal norms or folkways, laws are enforced by the state.
- This enforcement can involve various institutions, such as police, courts, and regulatory agencies, which ensure compliance and impose penalties for violations.
Comparison with Other Norms
- Informal norms (option a) are unwritten and based on social customs, lacking formal enforcement mechanisms.
- Casual folkways (option c) are minor norms that guide everyday behavior but do not carry significant consequences if violated.
- Laws (option b) hold a higher importance and authority, as they are vital for maintaining social order and protecting individual rights.
Significance of Laws
- Laws serve to establish clear standards of behavior, thereby reducing uncertainty in social interactions.
- They protect the welfare of individuals and communities by deterring harmful actions.
In conclusion, option 'B' is correct because laws are formal norms enforced by the state, distinguishing them from informal norms and folkways, which lack formal enforcement and are less critical in maintaining societal order.
Laws are critical components of society that govern behavior and maintain order. They differ from other social norms in significant ways.
Definition of Laws
- Laws are formal norms established by a governing body, typically the state.
- They are codified rules that dictate what is permissible and what is not within a society.
Enforcement Mechanism
- Unlike informal norms or folkways, laws are enforced by the state.
- This enforcement can involve various institutions, such as police, courts, and regulatory agencies, which ensure compliance and impose penalties for violations.
Comparison with Other Norms
- Informal norms (option a) are unwritten and based on social customs, lacking formal enforcement mechanisms.
- Casual folkways (option c) are minor norms that guide everyday behavior but do not carry significant consequences if violated.
- Laws (option b) hold a higher importance and authority, as they are vital for maintaining social order and protecting individual rights.
Significance of Laws
- Laws serve to establish clear standards of behavior, thereby reducing uncertainty in social interactions.
- They protect the welfare of individuals and communities by deterring harmful actions.
In conclusion, option 'B' is correct because laws are formal norms enforced by the state, distinguishing them from informal norms and folkways, which lack formal enforcement and are less critical in maintaining societal order.
According to whom, law is command in Jurisprudence?- a)Austin
- b)Pound
- c)Bentham
- d)Ulpian
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
According to whom, law is command in Jurisprudence?
a)
Austin
b)
Pound
c)
Bentham
d)
Ulpian

|
Curiosity Classes answered |
The proponent of analytical school of jurisprudence reflected that the utmost significant facet of law is its relation to the State. They see law as a command stemming from the sovereign, namely the State
According to Salmond, a __________ is one which is merely the application of an already existing rule of law.- a)Absolutely authoritative precedents
- b)Persuasive precedents
- c)Declaratory precedent
- d)Conditionally authoritative precedents
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Salmond, a __________ is one which is merely the application of an already existing rule of law.
a)
Absolutely authoritative precedents
b)
Persuasive precedents
c)
Declaratory precedent
d)
Conditionally authoritative precedents
|
|
Mayank Goyal answered |
Understanding Declaratory Precedents
Declaratory precedents are a crucial concept in legal theory, particularly as articulated by legal scholar H.L.A. Hart and further discussed by others, including Salmond. Here’s a detailed breakdown of why a declaratory precedent is defined as the mere application of an already existing rule of law.
Definition of Declaratory Precedent
- **Nature of Declaratory Precedents**: These precedents do not create new laws; instead, they clarify, confirm, or illuminate existing legal principles.
- **Function in Law**: Their primary role is to ensure consistency and predictability in legal interpretations, thereby reinforcing the stability of the legal system.
Characteristics of Declaratory Precedents
- **Application of Existing Rules**: Declaratory precedents affirm that a particular legal rule has always existed but may not have been previously articulated in that context.
- **Judicial Interpretation**: They often arise in cases where courts interpret statutory provisions or previous rulings, elucidating the scope and application of the law without altering its substance.
Importance in Legal System
- **Promotes Legal Certainty**: By relying on declaratory precedents, courts can maintain uniformity in legal decisions, fostering trust in the legal system.
- **Guidance for Future Cases**: They serve as a reliable reference for future cases, ensuring that similar facts lead to similar outcomes.
In conclusion, declaratory precedents play a vital role in the legal landscape by applying established rules of law and reinforcing legal consistency. Their significance lies in their ability to provide clarity and stability within the judicial system.
Declaratory precedents are a crucial concept in legal theory, particularly as articulated by legal scholar H.L.A. Hart and further discussed by others, including Salmond. Here’s a detailed breakdown of why a declaratory precedent is defined as the mere application of an already existing rule of law.
Definition of Declaratory Precedent
- **Nature of Declaratory Precedents**: These precedents do not create new laws; instead, they clarify, confirm, or illuminate existing legal principles.
- **Function in Law**: Their primary role is to ensure consistency and predictability in legal interpretations, thereby reinforcing the stability of the legal system.
Characteristics of Declaratory Precedents
- **Application of Existing Rules**: Declaratory precedents affirm that a particular legal rule has always existed but may not have been previously articulated in that context.
- **Judicial Interpretation**: They often arise in cases where courts interpret statutory provisions or previous rulings, elucidating the scope and application of the law without altering its substance.
Importance in Legal System
- **Promotes Legal Certainty**: By relying on declaratory precedents, courts can maintain uniformity in legal decisions, fostering trust in the legal system.
- **Guidance for Future Cases**: They serve as a reliable reference for future cases, ensuring that similar facts lead to similar outcomes.
In conclusion, declaratory precedents play a vital role in the legal landscape by applying established rules of law and reinforcing legal consistency. Their significance lies in their ability to provide clarity and stability within the judicial system.
Principle: The concept of natural justice is against bias and for the right to a fair hearing. While the term natural justice is often retained as a general concept, and it had largely been replaced and extended by the general duty to act fairly'.Fact: 'X' a male employee of a company was dismissed by the employer just on the basis of a complaint by 'Y', a female employee of the company that 'X' was trying to be too friendly with her and often requested her to accompany him to the canteen.Is the dismissal of 'X' valid?- a)No, because in the modern times this type of behavior is common.
- b)Yes, because men are not supposed to behave improperly with women and hence there is no violation of any principles of law
- c)Yes, moral law is antique and therefore, not applicable in modern times, therefore the termination is valid and no violations of the principles of natural justice occurred.
- d)No, because the employer did not give a chance to 'X' to explain his side, thereby violated the principles of natural justice.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Principle: The concept of natural justice is against bias and for the right to a fair hearing. While the term natural justice is often retained as a general concept, and it had largely been replaced and extended by the general duty to act fairly'.
Fact: 'X' a male employee of a company was dismissed by the employer just on the basis of a complaint by 'Y', a female employee of the company that 'X' was trying to be too friendly with her and often requested her to accompany him to the canteen.Is the dismissal of 'X' valid?
a)
No, because in the modern times this type of behavior is common.
b)
Yes, because men are not supposed to behave improperly with women and hence there is no violation of any principles of law
c)
Yes, moral law is antique and therefore, not applicable in modern times, therefore the termination is valid and no violations of the principles of natural justice occurred.
d)
No, because the employer did not give a chance to 'X' to explain his side, thereby violated the principles of natural justice.

|
Ss Study Center answered |
No, because the employer did not give a chance to 'X' to explain his side, thereby violated the principles of natural justice.
Natural justice mandates that X should have been given a fair chance to explain his side before a decision was taken and was dismissed by his employer. There was no 'duty to act fairly' and the principle of natural justice has been violated.
Natural justice mandates that X should have been given a fair chance to explain his side before a decision was taken and was dismissed by his employer. There was no 'duty to act fairly' and the principle of natural justice has been violated.
The book of Hart is ______.- a)Concept of Law
- b)Volksgeist
- c)Constitution
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The book of Hart is ______.
a)
Concept of Law
b)
Volksgeist
c)
Constitution
d)
None of the above
|
|
Devansh Choudhary answered |
Introduction
The book of Hart referred to in the question is "The Concept of Law," written by H.L.A. Hart. This influential work is a cornerstone in legal philosophy and jurisprudence.
Overview of "The Concept of Law"
- "The Concept of Law," published in 1961, explores the nature of law, its relationship with morality, and the structure of legal systems.
- Hart argues against the natural law tradition and the positivist views of earlier theorists, particularly challenging the ideas of legal positivism propagated by figures like John Austin.
Key Themes
- **Law as a System of Rules**: Hart introduces the idea that law is best understood as a system of rules, which includes primary rules (obligations) and secondary rules (rules about rules).
- **Separation of Law and Morality**: He emphasizes that law should be viewed independently of moral considerations, although he acknowledges that moral principles can influence legal frameworks.
- **The Role of Society**: Hart discusses how law operates within social contexts and its dependence on social practices and public acceptance.
Significance
- Hart's work has had a profound impact on legal theory, shaping discussions in legal philosophy and influencing contemporary debates.
- It serves as a pivotal text for students, scholars, and practitioners in understanding the complexities of legal systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, "The Concept of Law" is a fundamental text that provides insights into the nature of law and its function in society, making option 'A' the correct answer to the question posed.
The book of Hart referred to in the question is "The Concept of Law," written by H.L.A. Hart. This influential work is a cornerstone in legal philosophy and jurisprudence.
Overview of "The Concept of Law"
- "The Concept of Law," published in 1961, explores the nature of law, its relationship with morality, and the structure of legal systems.
- Hart argues against the natural law tradition and the positivist views of earlier theorists, particularly challenging the ideas of legal positivism propagated by figures like John Austin.
Key Themes
- **Law as a System of Rules**: Hart introduces the idea that law is best understood as a system of rules, which includes primary rules (obligations) and secondary rules (rules about rules).
- **Separation of Law and Morality**: He emphasizes that law should be viewed independently of moral considerations, although he acknowledges that moral principles can influence legal frameworks.
- **The Role of Society**: Hart discusses how law operates within social contexts and its dependence on social practices and public acceptance.
Significance
- Hart's work has had a profound impact on legal theory, shaping discussions in legal philosophy and influencing contemporary debates.
- It serves as a pivotal text for students, scholars, and practitioners in understanding the complexities of legal systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, "The Concept of Law" is a fundamental text that provides insights into the nature of law and its function in society, making option 'A' the correct answer to the question posed.
The method which Austin applied is known as ______.- a)Analytical
- b)Conception
- c)Practical
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The method which Austin applied is known as ______.
a)
Analytical
b)
Conception
c)
Practical
d)
All of the above

|
Ss Study Center answered |
he method which Austin applied is known as Analytical.
Chapter doubts & questions for Jurisprudence, Nature and Meaning of Law - Legal Studies for Class 11 2025 is part of Humanities/Arts exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Humanities/Arts exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Humanities/Arts 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Jurisprudence, Nature and Meaning of Law - Legal Studies for Class 11 in English & Hindi are available as part of Humanities/Arts exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Humanities/Arts Exam by signing up for free.
Legal Studies for Class 11
67 videos|81 docs|25 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup