All Exams >
Class 6 >
GK Olympiad for Class 6 >
All Questions
All questions of Indian Polity for Class 6 Exam
The number of members in the Lok Sabha should not exceed- a)552
- b)545
- c)560
- d)510
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of members in the Lok Sabha should not exceed
a)
552
b)
545
c)
560
d)
510
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
The maximum strength of the Lok Sabha shall not exceed 552. Among 550 representatives, 530 members are directly elected by the people from different states while the remaining 20 are elected from the union territories. The remaining 2 are elected from the Anglo-Indian community.
Choose the correct statements.
(1) Government can make new laws for welfare of state.
(2) Legislative Assembly approves and passes the law.- a)Only 1 is correct
- b)Only 2 is correct
- c)Both are correct
- d)Both are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct statements.
(1) Government can make new laws for welfare of state.
(2) Legislative Assembly approves and passes the law.
(1) Government can make new laws for welfare of state.
(2) Legislative Assembly approves and passes the law.
a)
Only 1 is correct
b)
Only 2 is correct
c)
Both are correct
d)
Both are incorrect

|
Abhineet Kumar answered |
Only 1 is correct
Village Panchayat is the lowest level of the three-tier Panchayat System in India. Which of the following statements is true for Village Panchayat?- a)The President of the Village Panchayat is the Pradhan.
- b)The Gram Panchayats can levy certain taxes and duties to meet their expenses.
- c)The Gram Panchayat must present its budget and annual administrative report before the Gram Sabha.
- d)Both b and c
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Village Panchayat is the lowest level of the three-tier Panchayat System in India. Which of the following statements is true for Village Panchayat?
a)
The President of the Village Panchayat is the Pradhan.
b)
The Gram Panchayats can levy certain taxes and duties to meet their expenses.
c)
The Gram Panchayat must present its budget and annual administrative report before the Gram Sabha.
d)
Both b and c
|
|
Charvi Chauhan answered |
Explanation:
President of the Village Panchayat:
- The President of the Village Panchayat is known as the Pradhan. They are the head of the Panchayat and are responsible for overseeing its functioning.
Gram Panchayat's Powers:
- Gram Panchayats have the authority to levy certain taxes and duties to meet their expenses. This includes taxes like property tax, water tax, etc.
Presenting Budget and Administrative Report:
- The Gram Panchayat is required to present its budget and annual administrative report before the Gram Sabha. This ensures transparency in the functioning of the Panchayat and allows the villagers to be informed about the financial and administrative decisions being made.
Therefore, option 'D' (Both b and c) is the correct answer as both statements about the Village Panchayat are true.
President of the Village Panchayat:
- The President of the Village Panchayat is known as the Pradhan. They are the head of the Panchayat and are responsible for overseeing its functioning.
Gram Panchayat's Powers:
- Gram Panchayats have the authority to levy certain taxes and duties to meet their expenses. This includes taxes like property tax, water tax, etc.
Presenting Budget and Administrative Report:
- The Gram Panchayat is required to present its budget and annual administrative report before the Gram Sabha. This ensures transparency in the functioning of the Panchayat and allows the villagers to be informed about the financial and administrative decisions being made.
Therefore, option 'D' (Both b and c) is the correct answer as both statements about the Village Panchayat are true.
The normal term of Lok Sabha is- a)4 years
- b)6 years
- c)5 years
- d)uncertain
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The normal term of Lok Sabha is
a)
4 years
b)
6 years
c)
5 years
d)
uncertain

|
Praveen Kumar answered |
- Lok Sabha is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament.
- The Hindi name of Lok Sabha was adopted by the house of the people on 14th May 1954.
- The full term of a Lok Sabha is 5 years.
- The fifth Lok Sabha from 1971 to 1977(5 years 10 months and 6 days) is the longest Lok Sabha in India.
- The twelfth Lok Sabha from 1998 to 1999(1 year 1 month and 4 days) is the shortest Lok Sabha in India.
Who among the following persons is acknowledged as the Father of the Indian Constitution?- a)Jawaharlal Nehru
- b)Mahatma Gandhi
- c)Dr.B.R. Ambedkar
- d)Dr. Rajendra Prasad
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who among the following persons is acknowledged as the Father of the Indian Constitution?
a)
Jawaharlal Nehru
b)
Mahatma Gandhi
c)
Dr.B.R. Ambedkar
d)
Dr. Rajendra Prasad
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
Dr.B.R. Ambedkar is acknowledged as the Father of the Indian Constitution.
How much time it took for the Constituent Assembly to finalize the constitution?- a)2 Years 11 Months 18 Days
- b)2 Years 9 Months 8 Days
- c)2 Years 7 Months 18 Days
- d)2 Years 5 Months 20 Days
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How much time it took for the Constituent Assembly to finalize the constitution?
a)
2 Years 11 Months 18 Days
b)
2 Years 9 Months 8 Days
c)
2 Years 7 Months 18 Days
d)
2 Years 5 Months 20 Days
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
In all, the Constituent Assembly took 11 sessions over 2 years, 11 months and 18 days to complete the constitution. The Constitution-makers had gone through the constitutions of about 60 countries, and the Draft Constitution was considered for 114 days. The total expenditure incurred in making the Constitution amounted to 64 lakhs.
The President of India can hold office for a period of- a)5 years
- b)6 years
- c)4 years
- d)7 years
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The President of India can hold office for a period of
a)
5 years
b)
6 years
c)
4 years
d)
7 years
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
- In India, the President holds office for a period of5 years.
- This has been provided inarticle 56 (1) of the Indian Constitution.
- The President is the formal head of the executive, legislature and judiciary of India.
- He is the first citizen of India(Article 53). The idea of the President is taken from England.
Name the body of the Parliament that can be dissolved by the President?- a)Rajya Sabha
- b)Lok Sabha
- c)Both a and b
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Name the body of the Parliament that can be dissolved by the President?
a)
Rajya Sabha
b)
Lok Sabha
c)
Both a and b
d)
None of the above
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
The President can dissolve the Lok Sabha on the advice of the Council of Ministers. As the Prime Minister is head of the Council of Ministers and represents the council of Ministers to the President, then the president can dissolve the Lok Sabha on the advice of the prime minister. Our constitution also states that the president will act on the advice of the Prime minister and his council of ministers. It means he can dissolve Lok Sabha if the Prime minister recommends him to do so.
If fundamental rights are violated then where we can go?- a)Supreme Court
- b)Parliament
- c)Council of Ministers
- d)Election Commission
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If fundamental rights are violated then where we can go?
a)
Supreme Court
b)
Parliament
c)
Council of Ministers
d)
Election Commission
|
|
Freak Artworks answered |
When any of our rights are violated we can seek a remedy through the courts. We can directly approach the Supreme Court or the High Court of a state. The Supreme Court and the High Court have the power to issue directions, orders, or writs for the enforcement of the Fundamental Rights. They can also award compensation to the victims and punishment to the violators.
Which one of the following is a fundamental right?- a)Right to freedom of religion
- b)Right to property
- c)Right to work
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is a fundamental right?
a)
Right to freedom of religion
b)
Right to property
c)
Right to work
d)
All of these
|
|
Harshad Goyal answered |
Understanding Fundamental Rights
Fundamental rights are essential rights guaranteed by the Constitution of a country, designed to protect individual freedoms and promote equality. In the context of India, these rights are enshrined in Part III of the Indian Constitution.
Right to Freedom of Religion
- The Right to Freedom of Religion is indeed a fundamental right.
- It allows individuals to practice, profess, and propagate any religion of their choice.
- This right ensures that people can freely express their beliefs without fear of discrimination or persecution.
Other Options Explained
- Right to Property
- Originally a fundamental right, it was changed to a legal right by the 44th Amendment in 1978.
- While it is still protected, it does not hold the same status as the fundamental rights listed in the Constitution.
- Right to Work
- The Right to Work is not recognized as a fundamental right in India.
- However, it is included as a directive principle of state policy aimed at promoting social welfare.
Conclusion
In summary, while the Right to Freedom of Religion is a fundamental right, the Right to Property and the Right to Work do not hold the same status. Understanding these distinctions is vital for grasping the framework of rights in India. Thus, the correct answer to the question is option 'A'.
Fundamental rights are essential rights guaranteed by the Constitution of a country, designed to protect individual freedoms and promote equality. In the context of India, these rights are enshrined in Part III of the Indian Constitution.
Right to Freedom of Religion
- The Right to Freedom of Religion is indeed a fundamental right.
- It allows individuals to practice, profess, and propagate any religion of their choice.
- This right ensures that people can freely express their beliefs without fear of discrimination or persecution.
Other Options Explained
- Right to Property
- Originally a fundamental right, it was changed to a legal right by the 44th Amendment in 1978.
- While it is still protected, it does not hold the same status as the fundamental rights listed in the Constitution.
- Right to Work
- The Right to Work is not recognized as a fundamental right in India.
- However, it is included as a directive principle of state policy aimed at promoting social welfare.
Conclusion
In summary, while the Right to Freedom of Religion is a fundamental right, the Right to Property and the Right to Work do not hold the same status. Understanding these distinctions is vital for grasping the framework of rights in India. Thus, the correct answer to the question is option 'A'.
_________ appoints the Chief Justice and other judges of the Supreme Court.- a)President
- b)Prime Minister
- c)Vice-President
- d)Governor
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
_________ appoints the Chief Justice and other judges of the Supreme Court.
a)
President
b)
Prime Minister
c)
Vice-President
d)
Governor
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
President appoints the Chief Justice and other judges of the Supreme court.
Which of the following are fundamental duties?- a)Safeguarding public property
- b)Protecting the sovereignty, integrity and unity of India
- c)Developing scientific temper and humanism
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are fundamental duties?
a)
Safeguarding public property
b)
Protecting the sovereignty, integrity and unity of India
c)
Developing scientific temper and humanism
d)
All of the above
|
|
Priyanka Mukherjee answered |
Fundamental duties are the moral obligations that every citizen of India has towards their country. They are enshrined in the Indian Constitution under Part IV-A, Article 51A. These duties serve as a reminder to citizens to be responsible and proactive in contributing to the welfare of the nation.
The correct answer is option 'D' which states that all of the given options – safeguarding public property, protecting the sovereignty, integrity, and unity of India, and developing scientific temper and humanism – are fundamental duties.
1. Safeguarding Public Property:
- Safeguarding public property means taking care of and protecting the assets that belong to the public or the government.
- It includes preventing damage, destruction, or misuse of public property such as government buildings, parks, monuments, etc.
- This duty emphasizes the importance of being responsible citizens and ensuring the welfare of the community as a whole.
2. Protecting the Sovereignty, Integrity, and Unity of India:
- Sovereignty refers to the supreme power or authority of a nation to govern itself without interference from external forces.
- Integrity refers to the adherence to moral and ethical principles, honesty, and uprightness.
- Unity refers to the state of being united or joined as a whole.
- Protecting the sovereignty, integrity, and unity of India means being loyal and committed to the nation, respecting its diverse cultures and religions, and working towards maintaining harmony and unity among the citizens.
- It also involves defending the country against any threats to its independence and ensuring its territorial integrity.
3. Developing Scientific Temper and Humanism:
- Developing scientific temper means promoting a rational and logical approach towards understanding the world and solving problems.
- It encourages citizens to question superstitions, base their beliefs on evidence and reason, and develop a scientific mindset.
- Humanism refers to the belief in the value and dignity of every human being and the importance of compassion, empathy, and social responsibility.
- This duty emphasizes the need for citizens to be open-minded, progressive, and compassionate towards others, promoting equality, justice, and human rights.
In conclusion, all of the given options – safeguarding public property, protecting the sovereignty, integrity, and unity of India, and developing scientific temper and humanism – are fundamental duties that every citizen of India should fulfill. These duties aim to promote responsible citizenship, national unity, and the overall welfare of the nation.
The correct answer is option 'D' which states that all of the given options – safeguarding public property, protecting the sovereignty, integrity, and unity of India, and developing scientific temper and humanism – are fundamental duties.
1. Safeguarding Public Property:
- Safeguarding public property means taking care of and protecting the assets that belong to the public or the government.
- It includes preventing damage, destruction, or misuse of public property such as government buildings, parks, monuments, etc.
- This duty emphasizes the importance of being responsible citizens and ensuring the welfare of the community as a whole.
2. Protecting the Sovereignty, Integrity, and Unity of India:
- Sovereignty refers to the supreme power or authority of a nation to govern itself without interference from external forces.
- Integrity refers to the adherence to moral and ethical principles, honesty, and uprightness.
- Unity refers to the state of being united or joined as a whole.
- Protecting the sovereignty, integrity, and unity of India means being loyal and committed to the nation, respecting its diverse cultures and religions, and working towards maintaining harmony and unity among the citizens.
- It also involves defending the country against any threats to its independence and ensuring its territorial integrity.
3. Developing Scientific Temper and Humanism:
- Developing scientific temper means promoting a rational and logical approach towards understanding the world and solving problems.
- It encourages citizens to question superstitions, base their beliefs on evidence and reason, and develop a scientific mindset.
- Humanism refers to the belief in the value and dignity of every human being and the importance of compassion, empathy, and social responsibility.
- This duty emphasizes the need for citizens to be open-minded, progressive, and compassionate towards others, promoting equality, justice, and human rights.
In conclusion, all of the given options – safeguarding public property, protecting the sovereignty, integrity, and unity of India, and developing scientific temper and humanism – are fundamental duties that every citizen of India should fulfill. These duties aim to promote responsible citizenship, national unity, and the overall welfare of the nation.
Who is the first citizen of the country?- a)The Prime Minister
- b)The wife of the President
- c)The father of the President
- d)The President himself/herself
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Who is the first citizen of the country?
a)
The Prime Minister
b)
The wife of the President
c)
The father of the President
d)
The President himself/herself
|
|
Arjun Yadav answered |
The first citizen of a country is generally considered to be the President or the Head of State. This is because the President holds the highest position in the government and represents the country both domestically and internationally. Let us analyze each option to understand why the correct answer is option 'D' - The President himself/herself.
a) The Prime Minister:
- The Prime Minister is the head of the government, not the head of state.
- The Prime Minister is responsible for running the day-to-day affairs of the country.
- While the Prime Minister is an important figure, they do not hold the highest position in the government.
b) The wife of the President:
- The wife of the President, also known as the First Lady, may hold a ceremonial role but does not have any official powers or responsibilities.
- They are not considered the first citizen of the country.
c) The father of the President:
- The father of the President is a private individual and does not hold any official position within the government.
- They are not considered the first citizen of the country.
d) The President himself/herself:
- The President is the head of state and holds the highest position in the government.
- The President represents the country both domestically and internationally.
- They have various powers and responsibilities, including being the commander-in-chief of the armed forces, signing bills into law, and appointing government officials.
- The President is considered the first citizen as they symbolize the sovereignty and authority of the nation.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'D' - The President himself/herself.
a) The Prime Minister:
- The Prime Minister is the head of the government, not the head of state.
- The Prime Minister is responsible for running the day-to-day affairs of the country.
- While the Prime Minister is an important figure, they do not hold the highest position in the government.
b) The wife of the President:
- The wife of the President, also known as the First Lady, may hold a ceremonial role but does not have any official powers or responsibilities.
- They are not considered the first citizen of the country.
c) The father of the President:
- The father of the President is a private individual and does not hold any official position within the government.
- They are not considered the first citizen of the country.
d) The President himself/herself:
- The President is the head of state and holds the highest position in the government.
- The President represents the country both domestically and internationally.
- They have various powers and responsibilities, including being the commander-in-chief of the armed forces, signing bills into law, and appointing government officials.
- The President is considered the first citizen as they symbolize the sovereignty and authority of the nation.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'D' - The President himself/herself.
Which of the following sentences are true?
(1) In federal government, the constitution is supreme.
(2) In federal government, the constitution may be written or unwritten.
(3) In unitary government, there is no division of powers between Centre and States.
(4) Legislature may be bicameral or unicameral in unitary government. - a)Only 3
- b) 1, 3, 4
- c)1, 2, 3
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following sentences are true?
(1) In federal government, the constitution is supreme.
(2) In federal government, the constitution may be written or unwritten.
(3) In unitary government, there is no division of powers between Centre and States.
(4) Legislature may be bicameral or unicameral in unitary government.
(1) In federal government, the constitution is supreme.
(2) In federal government, the constitution may be written or unwritten.
(3) In unitary government, there is no division of powers between Centre and States.
(4) Legislature may be bicameral or unicameral in unitary government.
a)
Only 3
b)
1, 3, 4
c)
1, 2, 3
d)
All of the above
|
|
Pritam Kulkarni answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option B: 1, 3, 4. Let's analyze each statement to understand why.
Statement 1: In federal government, the constitution is supreme.
This statement is true. In a federal government system, the constitution is considered the supreme law of the land. It establishes the division of powers between the central government and the states or provinces, and it serves as the foundation for the legal framework and governance of the country.
Statement 2: In federal government, the constitution may be written or unwritten.
This statement is not included in the options given, so it cannot be considered as a true statement for this question.
Statement 3: In unitary government, there is no division of powers between Centre and States.
This statement is true. In a unitary government system, the power is concentrated in the central government or the "Centre." There is no division of powers between the Centre and the states or provinces. The central government has the authority to make decisions and govern the entire country.
Statement 4: Legislature may be bicameral or unicameral in unitary government.
This statement is true. In a unitary government system, the legislature can be either bicameral or unicameral. A bicameral legislature consists of two separate chambers, such as an upper house (senate) and a lower house (house of representatives). An example of a unitary government with a bicameral legislature is the United Kingdom. On the other hand, a unicameral legislature consists of a single chamber, and all legislative power is vested in that chamber. Examples of unitary governments with unicameral legislatures include Sweden and New Zealand.
In summary, the correct answer is option B: 1, 3, 4.
The correct answer is option B: 1, 3, 4. Let's analyze each statement to understand why.
Statement 1: In federal government, the constitution is supreme.
This statement is true. In a federal government system, the constitution is considered the supreme law of the land. It establishes the division of powers between the central government and the states or provinces, and it serves as the foundation for the legal framework and governance of the country.
Statement 2: In federal government, the constitution may be written or unwritten.
This statement is not included in the options given, so it cannot be considered as a true statement for this question.
Statement 3: In unitary government, there is no division of powers between Centre and States.
This statement is true. In a unitary government system, the power is concentrated in the central government or the "Centre." There is no division of powers between the Centre and the states or provinces. The central government has the authority to make decisions and govern the entire country.
Statement 4: Legislature may be bicameral or unicameral in unitary government.
This statement is true. In a unitary government system, the legislature can be either bicameral or unicameral. A bicameral legislature consists of two separate chambers, such as an upper house (senate) and a lower house (house of representatives). An example of a unitary government with a bicameral legislature is the United Kingdom. On the other hand, a unicameral legislature consists of a single chamber, and all legislative power is vested in that chamber. Examples of unitary governments with unicameral legislatures include Sweden and New Zealand.
In summary, the correct answer is option B: 1, 3, 4.
Which of the following is the federal features of the Indian constitution?
(1) Rigid constitution
(2) Appointment of Governor
(3) Integrated judiciary
(4) Bicameral legislature- a)1, 2, 3
- b)1, 4
- c)2, 3
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the federal features of the Indian constitution?
(1) Rigid constitution
(2) Appointment of Governor
(3) Integrated judiciary
(4) Bicameral legislature
(1) Rigid constitution
(2) Appointment of Governor
(3) Integrated judiciary
(4) Bicameral legislature
a)
1, 2, 3
b)
1, 4
c)
2, 3
d)
All of the above
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Federal features of the Indian Constitution are:
- Bicameralism at the Federal level
- Independent and Impartial Judiciary
- Division of powers
- Written Constitution
- Rigid feature
- Supremacy of the Constitution.
Our unity lines in our- a)diversity
- b)castism
- c)religions
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Our unity lines in our
a)
diversity
b)
castism
c)
religions
d)
none of these
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Unity in Diversity is a concept that signifies unity among individuals who have certain differences among them. These differences can be on the basis of culture, language, ideology, religion, sect, class, ethnicity, etc.
Match column I with Column II and select the correct answer from the codes given below.
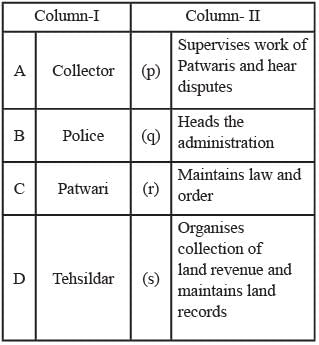
- a)(A-p), (B-q), (C-r), (D-s)
- b)(A-s), (B-r), (C-p), (D-q)
- c)(A-q), (B-s), (C-p), (D-r)
- d)(A-q), (B-r), (C-s), (D-p)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match column I with Column II and select the correct answer from the codes given below.


a)
(A-p), (B-q), (C-r), (D-s)
b)
(A-s), (B-r), (C-p), (D-q)
c)
(A-q), (B-s), (C-p), (D-r)
d)
(A-q), (B-r), (C-s), (D-p)
|
|
Varun Kapoor answered |
A. Collector: A District Magistrate is an Indian Administrative Service officer who is in charge of a district, the basic unit of administration, in India.
B. Police: The police maintain law and order to establish peace in society.
C. Patwari: Patwari is the village account or the administrative officer in a village who is responsible for maintaining land records of the village.
D. Tehsildar: Tehsildar or Mamlatdar is a tax officer accompanied by revenue inspectors.
B. Police: The police maintain law and order to establish peace in society.
C. Patwari: Patwari is the village account or the administrative officer in a village who is responsible for maintaining land records of the village.
D. Tehsildar: Tehsildar or Mamlatdar is a tax officer accompanied by revenue inspectors.
Political party that runs government is- a)Ruling party
- b)Rajya Sabha
- c)Opposition party
- d)Lok Sabha
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Political party that runs government is
a)
Ruling party
b)
Rajya Sabha
c)
Opposition party
d)
Lok Sabha
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
In a democratic setup, ruling party is the party or coalition of the majority in the House which administers the affairs of the state. It controls the executive branch of the government. As of 2016, BJP is the country's largest political party in terms of representation in the parliament.
Which fundamental right ensures that no person can be forced to work against their wish. It prohibits employing children below 14 years of age.- a)Right to Constitutional Remedies
- b)Right to Freedom
- c)Right against exploitation
- d)Right to expressions
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which fundamental right ensures that no person can be forced to work against their wish. It prohibits employing children below 14 years of age.
a)
Right to Constitutional Remedies
b)
Right to Freedom
c)
Right against exploitation
d)
Right to expressions
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
It is the right against exploitation.
Which of the following is are included in Right to Freedom of Religion?- a)Right to freedom of conscience
- b)Freedom Against religious instructions
- c)Practice and propagation of religion
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is are included in Right to Freedom of Religion?
a)
Right to freedom of conscience
b)
Freedom Against religious instructions
c)
Practice and propagation of religion
d)
All of these
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Article 25 gives every person the right to freedom of conscience and the right to freely profess, practice, and propagate religion subject to public order, morality, and health. Article 26 also gives all denominations the right to manage their own affairs in matters of religion.
When did Right to Information Act come into force in India?- a)10th October, 2005
- b)11th October, 2005
- c)12th October, 2005
- d)13th October, 2005
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When did Right to Information Act come into force in India?
a)
10th October, 2005
b)
11th October, 2005
c)
12th October, 2005
d)
13th October, 2005
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
The Right to Information Act will come into force w.e.f. 12th October, 2005. The Act extends to the whole of India except Jammu & Kashmir. It provides a very definite day for its commencement i.e. 120 days from enactment.
Under which constitutional amendment, 30% seats in village panchayats have been reserved for women in India?- a)70
- b)71
- c)73
- d)74
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Under which constitutional amendment, 30% seats in village panchayats have been reserved for women in India?
a)
70
b)
71
c)
73
d)
74
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
The 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992 provided for the Reservation for women in rural local body Panchayat. Article 243D in Part IX of the constitution provides for the reservation of not more than One-third of the total number of seats shall be reserved for women including the number of seats reserved for women belonging to scheduled castes and scheduled tribes.
Which of the following states was the first to establish the Panchayat Raj institutions in India?- a)Rajasthan
- b)Maharashtra
- c)Bihar
- d)UP
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following states was the first to establish the Panchayat Raj institutions in India?
a)
Rajasthan
b)
Maharashtra
c)
Bihar
d)
UP
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Rajasthan is the state in which first Panchayat Raj Institute was established in Independent India. Panchayat Raj system or local self-governing institutions was inaugurated by Jawaharlal Nehru on 2 October 1959 at Nagaur in Rajasthan.
_______ has the power to give or withhold his assent for a bill passed by the parliament.- a)Prime Minister
- b)President
- c)Members of the House
- d)Minister
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
_______ has the power to give or withhold his assent for a bill passed by the parliament.
a)
Prime Minister
b)
President
c)
Members of the House
d)
Minister
|
|
Varun Kapoor answered |
The President shall not withhold constitutional amendment bill duly passed by Parliament per Article 368. If the President gives his assent, the bill is published in The Gazette of India and becomes an act from the date of his assent. If he withholds his assent, the bill is dropped, which is known as an absolute veto.
Find out which the following statements are true and select the correct alternative accordingly.
(1) The RTI Act guarantees people right to hold meetings and public gatherings.
(2) Those who approach a controversial law may approach the parliament.
(3) NREGA is a scheme for mass scale employment of the rural people.
(4) Civil cases begin with the lodging of the FIR with the police.- a)Statements 1 and 2 are true.
- b)Statements 3 and 4 are true.
- c)Statements 1, 2 and 4 are true.
- d)All of the above are true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find out which the following statements are true and select the correct alternative accordingly.
(1) The RTI Act guarantees people right to hold meetings and public gatherings.
(2) Those who approach a controversial law may approach the parliament.
(3) NREGA is a scheme for mass scale employment of the rural people.
(4) Civil cases begin with the lodging of the FIR with the police.
(1) The RTI Act guarantees people right to hold meetings and public gatherings.
(2) Those who approach a controversial law may approach the parliament.
(3) NREGA is a scheme for mass scale employment of the rural people.
(4) Civil cases begin with the lodging of the FIR with the police.
a)
Statements 1 and 2 are true.
b)
Statements 3 and 4 are true.
c)
Statements 1, 2 and 4 are true.
d)
All of the above are true.
|
|
Varun Kapoor answered |
- The RTI Act mandates that any Indian citizen is free to seek any information from any public or government authority and the authority is under liability to respond to such a request within a period of 30 days from the date of receiving such an application.
- Legislative proposals are brought before either house of the Parliament of India in the form of a bill. A bill is the draft of a legislative proposal, which, when passed by both houses of Parliament and assented to by the President, becomes an act of Parliament.
Which is the smallest parliamentary constituency in India?- a)Malkajgiri
- b)Lakshwadeep
- c)Sikkim
- d)Goa
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the smallest parliamentary constituency in India?
a)
Malkajgiri
b)
Lakshwadeep
c)
Sikkim
d)
Goa
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Lakshadweep Lok Sabha constituency is a Lok Sabha (lower house of the Indian parliament) constituency, which covers the entire area of the Union Territory of Lakshadweep in India. This seat is reserved for Scheduled Tribes. As of 2014, it is the smallest Lok Sabha constituency by number of voters.
In India, the judges of High Court of a State are appointed by- a)President
- b)Vice- President
- c)Chief Justice of India
- d)Governor
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In India, the judges of High Court of a State are appointed by
a)
President
b)
Vice- President
c)
Chief Justice of India
d)
Governor
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
In India, the judges of High Court of a State are appointed by the President.
How many members are nominated by the President for Rajya Sabha?- a)12
- b)18
- c)20
- d)15
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How many members are nominated by the President for Rajya Sabha?
a)
12
b)
18
c)
20
d)
15
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
12 members are nominated by the President.
Who is the constitutional head of the Indian Union?- a)Vice President
- b)Prime Minister
- c)President
- d)Governor
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who is the constitutional head of the Indian Union?
a)
Vice President
b)
Prime Minister
c)
President
d)
Governor
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
President is the constitutional head of the Indian Union.
Is India a secularist country?- a)Yes
- b)No
- c)Can’t say
- d)May be
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Is India a secularist country?
a)
Yes
b)
No
c)
Can’t say
d)
May be
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
With the Forty-second Amendment of the Constitution of India enacted in 1976, the Preamble to the Constitution asserted that India is a secular nation.
_______ number of members are nominated by President for Lok Sabha.- a)4
- b)2
- c)10
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
_______ number of members are nominated by President for Lok Sabha.
a)
4
b)
2
c)
10
d)
5
|
|
Varun Kapoor answered |
The President nominates two members to the Lok Sabha from the Anglo-Indian Community and twelve members to the Rajya Sabha from among the persons who have acquired special knowledge in art, science, literature and social service.
Who among the following is the leader of the ruling party in Lok Sabha?- a)President
- b)Speaker of the Lok Sabha
- c)Prime Minister
- d)Vice-President
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who among the following is the leader of the ruling party in Lok Sabha?
a)
President
b)
Speaker of the Lok Sabha
c)
Prime Minister
d)
Vice-President
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
Prime minister is the leader of the ruling party in Lok Sabha.
Who among the following may provogue house or either house of Parliament?- a)Lok Sabha Speaker
- b)President
- c)Vice President
- d)Prime Minister
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who among the following may provogue house or either house of Parliament?
a)
Lok Sabha Speaker
b)
President
c)
Vice President
d)
Prime Minister
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
President may either provogue house of Parliament.
Which among the following is/are NOT a requirement to be a judge of the High Court?- a)He should be a citizen of India.
- b)He should have held a judicial office in India for minimum 10 years.
- c)He should have been an advocate of a high court for atleast 10 years.
- d)He should be over 40 years of age.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is/are NOT a requirement to be a judge of the High Court?
a)
He should be a citizen of India.
b)
He should have held a judicial office in India for minimum 10 years.
c)
He should have been an advocate of a high court for atleast 10 years.
d)
He should be over 40 years of age.
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
There is no specification of a minimum age limit for the judge of a High Court.
The members of Rajya Sabha are elected- a)directly
- b)indirectly
- c)both (a) & (b)
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The members of Rajya Sabha are elected
a)
directly
b)
indirectly
c)
both (a) & (b)
d)
none of these
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Its members are elected by the Legislative Assembly of States and Union territories by means of Single transferable vote through Proportional representation. It also has 12 members who are nominated by the President of India. A member of the Rajya Sabha must be a citizen of India.
An individual member of Rajya Sabha has a tenure of- a)3 years
- b)5 years
- c)6 years
- d)4 years
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An individual member of Rajya Sabha has a tenure of
a)
3 years
b)
5 years
c)
6 years
d)
4 years
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Rajya Sabha has an indefinite term and is not subject to dissolution (Article 83.1). The term of an Individual Rajya Sabha member is 6 years and one-third of its members retire every two years, in accordance with the rules as prescribed by the parliament of India.
_________ is the only constitutional body which has the supreme power of making law.- a)Only Lok Sabha
- b)Parliament
- c)Both President and Prime Minister
- d)Rajya Sabha
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
_________ is the only constitutional body which has the supreme power of making law.
a)
Only Lok Sabha
b)
Parliament
c)
Both President and Prime Minister
d)
Rajya Sabha
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
While both the Union and the States have the power to legislate on matters enumerated in the Concurrent List, only Parliament has the power to make laws on matters not included in the State List or the Concurrent List.
Who appoints chief minister?- a)President
- b)Governor
- c)Prime Minister
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who appoints chief minister?
a)
President
b)
Governor
c)
Prime Minister
d)
None of these
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
The Chief Minister is appointed by the Governor who also appoints other ministers on the advice of the Chief Minister. The Council of Ministers is collectively responsible for the legislative assembly of the State.
The Universal adult franchise mean- a)Right to freedom
- b)Right to equality
- c)Right to vote
- d)Right to adult freedom
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The Universal adult franchise mean
a)
Right to freedom
b)
Right to equality
c)
Right to vote
d)
Right to adult freedom
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
Universal Adult Franchise means that the right to vote should be given to all adult citizens without the discrimination of caste, class, colour, religion, or gender. It is based on equality, which is a basic principle of democracy.
Members of legislative Assembly are called- a)MLA
- b)MLC
- c)MP
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Members of legislative Assembly are called
a)
MLA
b)
MLC
c)
MP
d)
None of these
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Those elected or appointed to a Legislative Assembly (Vidhan Sabha) are referred to as Members of the Legislative Assembly or MLAs. Each legislative constituency of the State or UT is represented by only one MLA.
The right provided by constitution are called- a)Governmental Rights
- b)Fundamental Rights
- c)Economic Rights
- d)Optional Rights
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The right provided by constitution are called
a)
Governmental Rights
b)
Fundamental Rights
c)
Economic Rights
d)
Optional Rights
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
- The rights provided by the constitution are called fundamental rights.
- Fundamental rights are the basic human rights enshrined in the Constitution of India which are guaranteed to all citizens. They are applied without discrimination on the basis of race, religion, gender, etc. Significantly, fundamental rights are enforceable by the courts, subject to certain conditions.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
(i) India has a single unified and integrated judicial system.
(ii) High courts have jurisdiction over states and union territories.
(iii) Supreme court is the guardian of the constitution.
(iv) Police can keep a person in custody as long as they wish.- a)(i) only
- b)(i), (ii) and (iii)
- c)(iii) only
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
(i) India has a single unified and integrated judicial system.
(ii) High courts have jurisdiction over states and union territories.
(iii) Supreme court is the guardian of the constitution.
(iv) Police can keep a person in custody as long as they wish.
(i) India has a single unified and integrated judicial system.
(ii) High courts have jurisdiction over states and union territories.
(iii) Supreme court is the guardian of the constitution.
(iv) Police can keep a person in custody as long as they wish.
a)
(i) only
b)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
c)
(iii) only
d)
(i) and (iv)
|
|
Varun Kapoor answered |
India has a single unified and integrated judicial system for the entire nation because:
- Supreme Court decisions are binding precedent for lower subordinate courts. At the apex of country's judicial system is the Supreme Court which is supreme guardian of the law of the land, comprising of chief justice and other 30 judges.
- There are High Courts at the state level which have jurisdiction over a state, or a Union territory or a group of states or union Territories.
Who was the first Chief Election Commissioner of India ?- a)Sukumar Sen
- b)K.V.K. Sundaram
- c)S.P. Sen Verma
- d)T.N. Seshan
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who was the first Chief Election Commissioner of India ?
a)
Sukumar Sen
b)
K.V.K. Sundaram
c)
S.P. Sen Verma
d)
T.N. Seshan
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
Sukumar Sen was the first Chief Election Commissioner of India from 21st March, 1950 - 19th December, 1958.
Which among the following is not among the six fundamental rights provided by Constitution ?- a)Right to Equality
- b)Right to Protest
- c)Right against Exploitation
- d)Right to freedom of Religion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is not among the six fundamental rights provided by Constitution ?
a)
Right to Equality
b)
Right to Protest
c)
Right against Exploitation
d)
Right to freedom of Religion
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
Six fundamental rights provided by Constitution are :
1. Right to equality
2. Right to liberty
3. Right against exploitation
4. Right to freedom of religion
5. Cultural and Educational rights
6. Right to constitutional remedy
1. Right to equality
2. Right to liberty
3. Right against exploitation
4. Right to freedom of religion
5. Cultural and Educational rights
6. Right to constitutional remedy
Democracy means:- a)Rule of people
- b)Rule of minister
- c)Rule of speaker
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Democracy means:
a)
Rule of people
b)
Rule of minister
c)
Rule of speaker
d)
All of these
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Abraham Lincoln said, "Democracy is a rule of the people, for the people and by the people". It means that democracy is a form of government in which the rulers are elected by the people. The citizens of the country elect the Government to rule the country and the elected government work for the welfare of the people.
How many members were there in the Constitutent Assembly?- a)389
- b)380
- c)240
- d)385
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How many members were there in the Constitutent Assembly?
a)
389
b)
380
c)
240
d)
385
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
There were 389 members in the Constituent Assembly. The members of the Constituent Assembly were taken from different regions, castes, genders, and sections. It also consisted of different experts and political representatives.
Who is the head of the Legislative Assembly?- a)Minister
- b)MLA
- c)Chief Minister
- d)All of them
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who is the head of the Legislative Assembly?
a)
Minister
b)
MLA
c)
Chief Minister
d)
All of them
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
The Chief Minister is the leader of the majority party in the legislative assembly. He and most of the other ministers are taken from among its member of the legislative assembly.
Rajya Sabha is also known as- a)house of people
- b)council of states
- c)Parliament
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rajya Sabha is also known as
a)
house of people
b)
council of states
c)
Parliament
d)
none of these
|
|
Sarita Singh answered |
It is also known as council of states.
What kind of feeling does the ballot box provide at the time of voting?- a)Feeling of equality
- b)Feeling of freedom
- c)Feeling of choice
- d)Feeling of self- importance
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What kind of feeling does the ballot box provide at the time of voting?
a)
Feeling of equality
b)
Feeling of freedom
c)
Feeling of choice
d)
Feeling of self- importance
|
|
Varun Kapoor answered |
All adults in India have the equal right to vote during elections and this "power over the ballot box" has been used by people to elect or replace their representatives. But this feeling of equality that the ballot box provides does not extend to most people's lives.
Chapter doubts & questions for Indian Polity - GK Olympiad for Class 6 2025 is part of Class 6 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 6 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 6 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Indian Polity - GK Olympiad for Class 6 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 6 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 6 Exam by signing up for free.
GK Olympiad for Class 6
39 videos|80 docs|102 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









