All Exams >
NEET >
Inorganic Chemistry for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Environmental Chemistry for NEET Exam
The greenhouse effect is because of the [1996]- a)presence of gases, which in general are strong infrared absorbers, in the atmosphere
- b)presence of CO2 only in the atmosphere
- c)pressure of O3 and CH4 in the atmosphere
- d)N2O and chlorofluorohydrocarbons in the atmosphere
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The greenhouse effect is because of the [1996]
a)
presence of gases, which in general are strong infrared absorbers, in the atmosphere
b)
presence of CO2 only in the atmosphere
c)
pressure of O3 and CH4 in the atmosphere
d)
N2O and chlorofluorohydrocarbons in the atmosphere

|
Nayanika Reddy answered |
Green house gases such as CO2, ozone, methane, the chlorofluoro carbon compounds and water vapour form a thick cover around the earth which prevents the IR rays emitted by the earth to escape. It gradually leads to increase in temperature of atmosphere.
Lead emitted by vehicles interferes with development of:- a)Platelets
- b)Red blood cell
- c)Kidney
- d)White blood cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Lead emitted by vehicles interferes with development of:
a)
Platelets
b)
Red blood cell
c)
Kidney
d)
White blood cells
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Lead does affect the kidney and CNS but its first target is RBC and through that onlt it travels inside the body to CNS and kidneys.
Atmosphere traps the sun’s heat near the earth’s surface. This is called:- a)Acid rain
- b)Biosphere
- c)Global warming
- d)Natural green house effect
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Atmosphere traps the sun’s heat near the earth’s surface. This is called:
a)
Acid rain
b)
Biosphere
c)
Global warming
d)
Natural green house effect
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
A greenhouse is a house made of glass. It has glass walls and a glass roof. People grow tomatoes and flowers and other plants in them. A greenhouse stays warm inside, even during winter. Sunlight shines in and warms the plants and air inside. But the heat is trapped by the glass and can't escape. So during the daylight hours, it gets warmer and warmer inside a greenhouse, and stays pretty warm at night too.
A synthetic toxic chemical with ecological repercussions is:- a)Protium
- b)Tritium
- c)SO2 and NO2
- d)Pesticides
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A synthetic toxic chemical with ecological repercussions is:
a)
Protium
b)
Tritium
c)
SO2 and NO2
d)
Pesticides
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Pesticides are poisons and, unfortunately, they can harm more than just the “pests” at which they are targeted. They are toxic, and exposure to pesticides can not only cause a number of health effects, but is linked to a range of serious illnesses and diseases in humans, from respiratory problems to cancer.
Stratospheric Pollution is caused due to:- a)Break down of Ozone
- b)Oxides of nitrogen
- c)Photochemical smog
- d)Particulate
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Stratospheric Pollution is caused due to:
a)
Break down of Ozone
b)
Oxides of nitrogen
c)
Photochemical smog
d)
Particulate
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
A physical, biological or chemical alteration to the air in the atmosphere can be termed as pollution. It occurs when any harmful gases, dust, smoke enters into the atmosphere and makes it difficult for plants, animals and humans to survive as the air becomes dirty.
Presence of undesirable solid or gaseous particles in the air promotes:- a)Tropospheric pollution
- b)Statospheric pollution
- c)Ozone depletion
- d)Sulphur pollution
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Presence of undesirable solid or gaseous particles in the air promotes:
a)
Tropospheric pollution
b)
Statospheric pollution
c)
Ozone depletion
d)
Sulphur pollution
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Tropospheric pollution occurs due to the presence of undesirable solid or gaseous particles in the air.
The lowest region of atmosphere in which the human being along with other organisms live is known as:- a)Ionosphere
- b)Stratosphere
- c)Lithosphere
- d)Troposphere
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The lowest region of atmosphere in which the human being along with other organisms live is known as:
a)
Ionosphere
b)
Stratosphere
c)
Lithosphere
d)
Troposphere
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
The layer above the troposphere is called the stratosphere. Nearly all of the water vapor and dust particles in the atmosphere are in the troposphere. That is why most clouds are found in this lowest layer, too. The bottom of the troposphere, right next to the surface of Earth, is called the "boundary layer".
Major contributors to acid rain are:- a)SO2 and NO2
- b)HD
- c)Tritium
- d)Protium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Major contributors to acid rain are:
a)
SO2 and NO2
b)
HD
c)
Tritium
d)
Protium
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
The main chemicals in air pollution that create acid rain are sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen (NOx). Acid rain usually forms high in the clouds where sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides react with water, oxygen, and oxidants. this mixture forms a mild solution of sulfuric acid and nitric acid.
Oxidation of ethene in the presence of ionic catalyst in aqueous medium produces:- a)Ethanal
- b)Methanal
- c)Hydrogen peroxide
- d)Ethyne
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxidation of ethene in the presence of ionic catalyst in aqueous medium produces:
a)
Ethanal
b)
Methanal
c)
Hydrogen peroxide
d)
Ethyne
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The correct answer is option A Ethanal is commercially prepared by one step oxidation of ethene in the presence of ionic catalyst in aqueous medium with a yield of 90%
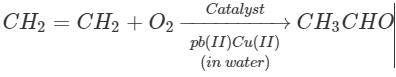
Human excreta contains bacteria which causes gastrointestinal diseases are:- a)Staphylococcus
- b)Lactic acid bacillus
- c)Escherichia coli
- d)Listeria
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Human excreta contains bacteria which causes gastrointestinal diseases are:
a)
Staphylococcus
b)
Lactic acid bacillus
c)
Escherichia coli
d)
Listeria
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option C.
Escherichia coli ; E. coli bacteria, which causes gastrointestinal infections with symptoms including bloody diarrhea and vomiting.
Roasting of sulphides gives the gas X as a by product. This is colorless gas with choking smell of burnt sulphur and caused great damage to respiratory organs as a result of acid rain. Its aqueous solution is acidic, acts as a reducing agent and its acid has never been isolated. The gas X is : [NEET 2013]- a)SO2
- b)CO2
- c)SO3
- d)H2S
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Roasting of sulphides gives the gas X as a by product. This is colorless gas with choking smell of burnt sulphur and caused great damage to respiratory organs as a result of acid rain. Its aqueous solution is acidic, acts as a reducing agent and its acid has never been isolated. The gas X is : [NEET 2013]
a)
SO2
b)
CO2
c)
SO3
d)
H2S

|
Krish Saha answered |
Based on the features given above the gas must be SO2
Which one of the following statement is not true ?[2011]- a)pH of drinking water should be between 5.5 – 9.5.
- b)Concentration of DO below 6 ppm is good for the growth of fish.
- c)Clean water would have a BOD value of less than 5 ppm.
- d)Oxides of sulphur, nitrogen and carbon are the most widespread air pollutant.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statement is not true ?[2011]
a)
pH of drinking water should be between 5.5 – 9.5.
b)
Concentration of DO below 6 ppm is good for the growth of fish.
c)
Clean water would have a BOD value of less than 5 ppm.
d)
Oxides of sulphur, nitrogen and carbon are the most widespread air pollutant.
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The ideal value of D.O for growth of fishes is 8 mg/ℓ . 7mgℓ is desirable range, below this value fishes get susceptible to desease. A value of 2 mg/ℓ or below is lethal for fishes.
Tropospheric pollution is basically due to- a)region of less air movement and cloud formation.
- b)various oxides of sulphur, nitrogen, carbon, halogens
- c)dinitrogen, dioxygen
- d)it is 10 km from sea level.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Tropospheric pollution is basically due to
a)
region of less air movement and cloud formation.
b)
various oxides of sulphur, nitrogen, carbon, halogens
c)
dinitrogen, dioxygen
d)
it is 10 km from sea level.

|
Moumita Chakraborty answered |
various oxides of sulphur, nitrogen, carbon, halogens causes Tropospheric pollution
Vehicles emit a major air pollution consisting of:- a)Lead
- b)Ammonia
- c)Iron
- d)Sulphur
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Vehicles emit a major air pollution consisting of:
a)
Lead
b)
Ammonia
c)
Iron
d)
Sulphur
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Historic major sources of lead air emissions were motor vehicles and industrial sources. Motor-vehicle emissions have been reduced by the phasing out of leaded gasoline, but lead is still used in general-aviation gasoline for piston-engine aircraft.
Which one of the following statements is not true? [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)Dissolved oxygen (DO) in cold water can reach a concentration upto 10 ppm.
- b)Clean water would have a BOD value of 5 ppm.
- c)Fluoride deficiency in drinking water is harmful. Soluble fluoride is often used to bring its concentration upto 1 ppm.
- d)When the pH of rain water is higher than 6.5, it is called acid rain.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is not true? [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
Dissolved oxygen (DO) in cold water can reach a concentration upto 10 ppm.
b)
Clean water would have a BOD value of 5 ppm.
c)
Fluoride deficiency in drinking water is harmful. Soluble fluoride is often used to bring its concentration upto 1 ppm.
d)
When the pH of rain water is higher than 6.5, it is called acid rain.
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
Acid rain is the rain water containing sulphuric acid and nitric acid which are formed from the oxides of sulphur and nitrogen present in the air as pollutants and rain water has a pH of 4-5.
Global warming will not result in:- a)Melting of the ice caps
- b)Increasing the size of the hole in the ozone layer
- c)Increasing sea levels
- d)Unpredictable climate patterns
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Global warming will not result in:
a)
Melting of the ice caps
b)
Increasing the size of the hole in the ozone layer
c)
Increasing sea levels
d)
Unpredictable climate patterns

|
Gowri Nambiar answered |
Global warming will not increasing the size of the hole in the ozone layer
Reducing potentially hazardous waste through smarter productions is called
- a)Green Chemistry
- b)Metathesis
- c)waste water management
- d) chemistry
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Reducing potentially hazardous waste through smarter productions is called
a)
Green Chemistry
b)
Metathesis
c)
waste water management
d)
chemistry

|
Priyanka Roy answered |
‘Green Chemistry’ is defined as reducing potentially hazardous waste through smarter productions.
The gas emitted during volcanic eruptions is- a)hydrogen peroxide
- b)carbonmonoxide
- c)carbondioxide
- d)nitric oxide
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The gas emitted during volcanic eruptions is
a)
hydrogen peroxide
b)
carbonmonoxide
c)
carbondioxide
d)
nitric oxide

|
Mansi Chopra answered |
CO2 is the gas emitted during volcanic eruptions
Clean water and highly polluted water have BOD:- a)7ppm and 6ppm respectively
- b)5ppm and 17ppm respectively
- c)6ppm and 12ppm respectively
- d)7ppm and 5ppm respectively
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Clean water and highly polluted water have BOD:
a)
7ppm and 6ppm respectively
b)
5ppm and 17ppm respectively
c)
6ppm and 12ppm respectively
d)
7ppm and 5ppm respectively
|
|
Sanchita Mukherjee answered |
Explanation:
BOD stands for Biological Oxygen Demand, which is the amount of dissolved oxygen required by microorganisms to decompose the organic matter present in water. The higher the BOD, the more organic matter is present, and the more polluted the water is.
Clean water has a lower BOD compared to highly polluted water because it contains less organic matter. Therefore, the correct answer is option B, which states that:
- Clean water has a BOD of 5ppm
- Highly polluted water has a BOD of 17ppm
It is important to note that different bodies of water have different BOD levels, and some may even have BOD levels below 5ppm. However, a BOD level of 17ppm is considered highly polluted and can have negative impacts on aquatic life and human health.
BOD stands for Biological Oxygen Demand, which is the amount of dissolved oxygen required by microorganisms to decompose the organic matter present in water. The higher the BOD, the more organic matter is present, and the more polluted the water is.
Clean water has a lower BOD compared to highly polluted water because it contains less organic matter. Therefore, the correct answer is option B, which states that:
- Clean water has a BOD of 5ppm
- Highly polluted water has a BOD of 17ppm
It is important to note that different bodies of water have different BOD levels, and some may even have BOD levels below 5ppm. However, a BOD level of 17ppm is considered highly polluted and can have negative impacts on aquatic life and human health.
Earth is protected from UV radiation by a layer of:- a)Oxygen
- b)Ozone
- c)Carbon dioxide
- d)Nitrogen
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Earth is protected from UV radiation by a layer of:
a)
Oxygen
b)
Ozone
c)
Carbon dioxide
d)
Nitrogen
|
|
Rashi Sharma answered |
Explanation:
- The Earth is surrounded by a layer of gases known as the atmosphere, which protects it from harmful radiation from the sun and space.
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than visible light. It is harmful to living organisms, causing skin cancer, cataracts, and other health problems.
- The ozone layer is a region of the Earth's stratosphere that contains a high concentration of ozone molecules (O3).
- Ozone absorbs most of the UV radiation from the sun, preventing it from reaching the Earth's surface.
- If the ozone layer were to disappear, the amount of UV radiation reaching the Earth's surface would increase significantly, causing widespread damage to plants, animals, and humans.
- Human activities, such as the use of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) in refrigerants and aerosol sprays, have been responsible for the depletion of the ozone layer in recent decades.
- International efforts, such as the Montreal Protocol, have been successful in reducing the production and use of CFCs, and the ozone layer is slowly recovering.
Acid rain is- a)The gaseous pollutants come down to the earth
- b)much water vapour
- c)organic wastes come down to the earth
- d)water polluted by toxic heavy metal residues come down to the earth
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Acid rain is
a)
The gaseous pollutants come down to the earth
b)
much water vapour
c)
organic wastes come down to the earth
d)
water polluted by toxic heavy metal residues come down to the earth

|
Kritika Bajaj answered |
The gaseous pollutants come down to the earth in form of rain forms acid rain.
Presence of particulate matter in polluted air catalyses the oxidation of sulphur dioxide to:- a)Nitric oxide
- b)Dioxygen
- c)Hydrogen peroxide
- d)Sulphur trioxide
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Presence of particulate matter in polluted air catalyses the oxidation of sulphur dioxide to:
a)
Nitric oxide
b)
Dioxygen
c)
Hydrogen peroxide
d)
Sulphur trioxide
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The presence of particulate matter in polluted air catalyses the oxidation of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide. Oxides of Nitrogen: Di-nitrogen and di-oxygen are the main constituents of air. These gases do not react with each other at a normal temperature.
The greenhouse effect is where:- a)Heat energy is trapped by the atmosphere
- b)Solar panels are attached to the roofs of houses
- c)You take gardening too seriously
- d)Too many buildings are built from glass
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The greenhouse effect is where:
a)
Heat energy is trapped by the atmosphere
b)
Solar panels are attached to the roofs of houses
c)
You take gardening too seriously
d)
Too many buildings are built from glass

|
Tanvi Roy answered |
The greenhouse effect is where heat energy is trapped by the atmosphere
Residence time of methane in the atmosphere is- a)2 - 3 years
- b)5 - 7 days
- c)4 -9 days
- d)3 - 7 years
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Residence time of methane in the atmosphere is
a)
2 - 3 years
b)
5 - 7 days
c)
4 -9 days
d)
3 - 7 years

|
Surbhi Mishra answered |
Residence time of methane in the atmosphere is 3 - 7 years
The main reason of ozone layer depletion is the release of:- a)Smoke and fog
- b)fire
- c)Chlorofluorocarbons
- d)water
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The main reason of ozone layer depletion is the release of:
a)
Smoke and fog
b)
fire
c)
Chlorofluorocarbons
d)
water
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Man-made causes of depletion of ozone layer: The main cause for the depletion of ozone is determined as excessive release of chlorine and bromine from man-made compounds such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
Requirement of macronutrient per acre of the land is- a)30-400 kg
- b)5 to 200 kg
- c)200-400 kg
- d)20-200 kg
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Requirement of macronutrient per acre of the land is
a)
30-400 kg
b)
5 to 200 kg
c)
200-400 kg
d)
20-200 kg

|
Gowri Kulkarni answered |
Requirement of macronutrient per acre of the land is 5 to 200 kg
Which of these is not released from burning fossil fuels?- a)Nitrogen oxides
- b)Carbon dioxide
- c)Copper oxide
- d)Sulphur dioxide
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these is not released from burning fossil fuels?
a)
Nitrogen oxides
b)
Carbon dioxide
c)
Copper oxide
d)
Sulphur dioxide

|
Aditya Sengupta answered |
Currently, oil burning is responsible for about 30% of all carbon dioxide emissions to air. Natural gas does not release as much carbon,cooper dioxide because of its methane structure. The largest emissions are cause by coal combustion. Coal may result in underground fires that are virtually impossible to extinguish
Three elements needed for the healthy growth of plants are- a)N S P
- b)N K C
- c)N P K
- d)N Ca P
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Three elements needed for the healthy growth of plants are
a)
N S P
b)
N K C
c)
N P K
d)
N Ca P

|
Aditya Sengupta answered |
Plant nutrition
1 The macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg), carbon (C), oxygen(O), hydrogen (H)
2 The micronutrients (or trace minerals): iron (Fe), boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)
This process in which nutrient enriched water bodies support a dense plant population, which kills animal life by depriving it of oxygen and results in subsequent loss of biodiversity, is called- a)mesosphere effect
- b)Eutrophication
- c)troposphere effect
- d)increase in green house gas
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
This process in which nutrient enriched water bodies support a dense plant population, which kills animal life by depriving it of oxygen and results in subsequent loss of biodiversity, is called
a)
mesosphere effect
b)
Eutrophication
c)
troposphere effect
d)
increase in green house gas
|
|
Rajeev Nair answered |
Eutrophication
Eutrophication is the process in which nutrient-enriched water bodies support a dense plant population, leading to the death of animal life due to oxygen deprivation and subsequent loss of biodiversity. It is an environmental issue that can have significant ecological and economic impacts.
Causes of Eutrophication
There are several factors that contribute to eutrophication:
1. Excessive Nutrient Inputs: The primary cause of eutrophication is the excessive input of nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus, into water bodies. These nutrients can come from various sources such as agricultural runoff, sewage discharge, and industrial activities.
2. Fertilizer Use: The use of fertilizers in agriculture can lead to nutrient runoff into nearby water bodies. When rain or irrigation water carries these nutrients into rivers, lakes, or oceans, it can result in eutrophication.
3. Sewage and Wastewater Discharge: Untreated or poorly treated sewage and wastewater discharge can introduce high levels of nutrients into water bodies, promoting the growth of algae and other aquatic plants.
4. Deforestation and Urbanization: Land-use practices such as deforestation and urbanization can increase the amount of sediment and nutrients entering water bodies. This sediment can contribute to the buildup of organic matter, further promoting eutrophication.
Process of Eutrophication
The process of eutrophication typically involves the following steps:
1. Nutrient Enrichment: Excessive nutrients, mainly nitrogen and phosphorus, enter the water body through various sources.
2. Algal Bloom: These nutrients stimulate the rapid growth of algae and other aquatic plants, leading to the formation of dense algal blooms. These blooms can turn the water green or brown and reduce water clarity.
3. Reduced Oxygen Levels: As the algae die and decompose, bacteria break down the organic matter, consuming oxygen in the process. This causes a decrease in the dissolved oxygen levels in the water.
4. Oxygen Depletion: The high oxygen demand from the decomposition of organic matter can deplete the available oxygen in the water, leading to hypoxic or anoxic conditions. This lack of oxygen can be detrimental to fish and other aquatic organisms, often resulting in their death.
5. Loss of Biodiversity: The depletion of oxygen and subsequent death of animal life can result in a loss of biodiversity in the affected water body. Fish, shellfish, and other organisms that rely on oxygen-rich water may not be able to survive in such conditions, leading to a decline in their populations.
Impacts of Eutrophication
Eutrophication can have several negative impacts on aquatic ecosystems:
1. Fish Kills: The oxygen depletion caused by eutrophication can lead to fish kills, especially in shallow water bodies where oxygen levels can drop rapidly.
2. Harmful Algal Blooms: Some algal blooms can produce toxins that are harmful to humans and marine life. These harmful algal blooms (HABs) can contaminate drinking water supplies and cause health issues in animals and humans.
3. Loss of Biodiversity: Eutrophication can result in the loss of biodiversity as fish and other aquatic organisms die off due to oxygen deprivation. This can disrupt the food chain and have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem.
4. Economic Losses: Eutrophication can have economic consequences, particularly for industries dependent on
Eutrophication is the process in which nutrient-enriched water bodies support a dense plant population, leading to the death of animal life due to oxygen deprivation and subsequent loss of biodiversity. It is an environmental issue that can have significant ecological and economic impacts.
Causes of Eutrophication
There are several factors that contribute to eutrophication:
1. Excessive Nutrient Inputs: The primary cause of eutrophication is the excessive input of nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus, into water bodies. These nutrients can come from various sources such as agricultural runoff, sewage discharge, and industrial activities.
2. Fertilizer Use: The use of fertilizers in agriculture can lead to nutrient runoff into nearby water bodies. When rain or irrigation water carries these nutrients into rivers, lakes, or oceans, it can result in eutrophication.
3. Sewage and Wastewater Discharge: Untreated or poorly treated sewage and wastewater discharge can introduce high levels of nutrients into water bodies, promoting the growth of algae and other aquatic plants.
4. Deforestation and Urbanization: Land-use practices such as deforestation and urbanization can increase the amount of sediment and nutrients entering water bodies. This sediment can contribute to the buildup of organic matter, further promoting eutrophication.
Process of Eutrophication
The process of eutrophication typically involves the following steps:
1. Nutrient Enrichment: Excessive nutrients, mainly nitrogen and phosphorus, enter the water body through various sources.
2. Algal Bloom: These nutrients stimulate the rapid growth of algae and other aquatic plants, leading to the formation of dense algal blooms. These blooms can turn the water green or brown and reduce water clarity.
3. Reduced Oxygen Levels: As the algae die and decompose, bacteria break down the organic matter, consuming oxygen in the process. This causes a decrease in the dissolved oxygen levels in the water.
4. Oxygen Depletion: The high oxygen demand from the decomposition of organic matter can deplete the available oxygen in the water, leading to hypoxic or anoxic conditions. This lack of oxygen can be detrimental to fish and other aquatic organisms, often resulting in their death.
5. Loss of Biodiversity: The depletion of oxygen and subsequent death of animal life can result in a loss of biodiversity in the affected water body. Fish, shellfish, and other organisms that rely on oxygen-rich water may not be able to survive in such conditions, leading to a decline in their populations.
Impacts of Eutrophication
Eutrophication can have several negative impacts on aquatic ecosystems:
1. Fish Kills: The oxygen depletion caused by eutrophication can lead to fish kills, especially in shallow water bodies where oxygen levels can drop rapidly.
2. Harmful Algal Blooms: Some algal blooms can produce toxins that are harmful to humans and marine life. These harmful algal blooms (HABs) can contaminate drinking water supplies and cause health issues in animals and humans.
3. Loss of Biodiversity: Eutrophication can result in the loss of biodiversity as fish and other aquatic organisms die off due to oxygen deprivation. This can disrupt the food chain and have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem.
4. Economic Losses: Eutrophication can have economic consequences, particularly for industries dependent on
The gaseous envelope around the earth is known as atmosphere. The lowest layer of this is extended upto 10 km from sea level, this layer is _________.- a)Mesosphere
- b)Hydrosphere
- c)Troposphere
- d)Stratosphere
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The gaseous envelope around the earth is known as atmosphere. The lowest layer of this is extended upto 10 km from sea level, this layer is _________.
a)
Mesosphere
b)
Hydrosphere
c)
Troposphere
d)
Stratosphere

|
Ishani Mehta answered |
this is troposphere
Biochemical Oxygen Demand, (BOD) is a measure of organic material present in water. BOD value less than 5 ppm indicates a water sample to be __________.- a)highly polluted.
- b)rich in dissolved oxygen.
- c)poor in dissolved oxygen.
- d)not suitable for aquatic life.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Biochemical Oxygen Demand, (BOD) is a measure of organic material present in water. BOD value less than 5 ppm indicates a water sample to be __________.
a)
highly polluted.
b)
rich in dissolved oxygen.
c)
poor in dissolved oxygen.
d)
not suitable for aquatic life.

|
Simran Mishra answered |
This means water sample is rich in dissolved oxygen.
Ozone in the stratosphere is a product of UV radiations acting on:- a)CFCs
- b)Chlorine atoms
- c)Dioxygen molecule
- d)Free oxygen atoms
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ozone in the stratosphere is a product of UV radiations acting on:
a)
CFCs
b)
Chlorine atoms
c)
Dioxygen molecule
d)
Free oxygen atoms
|
|
Bhargavi Bajaj answered |
Explanation:
Ozone in the stratosphere is formed by the action of UV radiation on dioxygen molecules. The process of ozone formation can be explained as follows:
1. Absorption of UV radiation: The ozone layer in the stratosphere absorbs high-energy UV radiation from the sun.
2. Dissociation of dioxygen molecules: The UV radiation dissociates (breaks apart) dioxygen molecules (O2) into two oxygen atoms (O).
3. Formation of ozone: The oxygen atoms then combine with other dioxygen molecules to form ozone (O3).
O2 + UV radiation → 2O
O + O2 → O3
4. Destruction of ozone: The ozone molecules can also be destroyed by UV radiation, which breaks them apart into oxygen molecules and oxygen atoms.
O3 + UV radiation → O2 + O
Therefore, the concentration of ozone in the stratosphere is determined by a balance between its formation and destruction.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, ozone in the stratosphere is formed by the action of UV radiation on dioxygen molecules, not on CFCs or chlorine atoms. The formation of ozone is an important process that helps to protect the earth from harmful UV radiation. However, human-made chemicals such as CFCs can destroy the ozone layer in the stratosphere, leading to an increase in UV radiation reaching the earth's surface.
Ozone in the stratosphere is formed by the action of UV radiation on dioxygen molecules. The process of ozone formation can be explained as follows:
1. Absorption of UV radiation: The ozone layer in the stratosphere absorbs high-energy UV radiation from the sun.
2. Dissociation of dioxygen molecules: The UV radiation dissociates (breaks apart) dioxygen molecules (O2) into two oxygen atoms (O).
3. Formation of ozone: The oxygen atoms then combine with other dioxygen molecules to form ozone (O3).
O2 + UV radiation → 2O
O + O2 → O3
4. Destruction of ozone: The ozone molecules can also be destroyed by UV radiation, which breaks them apart into oxygen molecules and oxygen atoms.
O3 + UV radiation → O2 + O
Therefore, the concentration of ozone in the stratosphere is determined by a balance between its formation and destruction.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, ozone in the stratosphere is formed by the action of UV radiation on dioxygen molecules, not on CFCs or chlorine atoms. The formation of ozone is an important process that helps to protect the earth from harmful UV radiation. However, human-made chemicals such as CFCs can destroy the ozone layer in the stratosphere, leading to an increase in UV radiation reaching the earth's surface.
Unleaded paint and petrol were introduced because:- a)Lead was proven to affect the brain and cause mental impairment
- b)Unleaded petrol made cars go faster
- c)It was cheaper to produce than leaded products
- d)European Parliament told us to
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Unleaded paint and petrol were introduced because:
a)
Lead was proven to affect the brain and cause mental impairment
b)
Unleaded petrol made cars go faster
c)
It was cheaper to produce than leaded products
d)
European Parliament told us to
|
|
Sandeep Chawla answered |
Introduction
Unleaded paint and petrol were introduced as a replacement for leaded products due to the harmful effects of lead on human health and the environment.
Impact of Lead on Brain
Lead is a toxic metal that can have devastating effects on the human body, especially the brain. Research has shown that exposure to lead can cause mental impairment, including decreased IQ, poor attention span, and behavior problems.
Leaded Paint
Leaded paint was commonly used in the past as a pigment for coloring paint. However, as the harmful effects of lead on human health became apparent, leaded paint was phased out in many countries, including the US and Europe. Unleaded paint, which uses alternative pigments, is now widely used in the painting industry.
Leaded Petrol
Leaded petrol was introduced in the early 20th century as a way to improve engine performance. However, it was later discovered that leaded petrol releases toxic lead particles into the air when burned, leading to serious health problems. Unleaded petrol was introduced as a replacement, which is now widely used in many countries.
Conclusion
Unleaded paint and petrol were introduced primarily to reduce the harmful effects of lead on human health and the environment. The use of these alternative products has significantly improved public health and reduced environmental pollution.
Unleaded paint and petrol were introduced as a replacement for leaded products due to the harmful effects of lead on human health and the environment.
Impact of Lead on Brain
Lead is a toxic metal that can have devastating effects on the human body, especially the brain. Research has shown that exposure to lead can cause mental impairment, including decreased IQ, poor attention span, and behavior problems.
Leaded Paint
Leaded paint was commonly used in the past as a pigment for coloring paint. However, as the harmful effects of lead on human health became apparent, leaded paint was phased out in many countries, including the US and Europe. Unleaded paint, which uses alternative pigments, is now widely used in the painting industry.
Leaded Petrol
Leaded petrol was introduced in the early 20th century as a way to improve engine performance. However, it was later discovered that leaded petrol releases toxic lead particles into the air when burned, leading to serious health problems. Unleaded petrol was introduced as a replacement, which is now widely used in many countries.
Conclusion
Unleaded paint and petrol were introduced primarily to reduce the harmful effects of lead on human health and the environment. The use of these alternative products has significantly improved public health and reduced environmental pollution.
Which of the following statements about photochemical smog is wrong?- a)It can be controlled by controlling the release of NO2, hydrocarbons, ozone etc.
- b)It has high concentration of oxidising agents.
- c)It has low concentration of oxidising agent.
- d)Plantation of some plants like pinus helps in controlling photochemical smog.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about photochemical smog is wrong?
a)
It can be controlled by controlling the release of NO2, hydrocarbons, ozone etc.
b)
It has high concentration of oxidising agents.
c)
It has low concentration of oxidising agent.
d)
Plantation of some plants like pinus helps in controlling photochemical smog.

|
Arya Reddy answered |
photochemical smog has high concentration of oxidising agent.
Industrial solid wastes are sorted out as:- a)Classified and non-classified wastes
- b)Proportion ans improportion wastes
- c)Chemical and non-chemical wastes
- d)Biodegradable and non-degradable wastes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Industrial solid wastes are sorted out as:
a)
Classified and non-classified wastes
b)
Proportion ans improportion wastes
c)
Chemical and non-chemical wastes
d)
Biodegradable and non-degradable wastes
|
|
Ananya Sharma answered |
Definition
A biodegradable material can be defined as a material which can be decomposed by b bacteria or other natural organisms and not be adding to pollution.
Biodegradable wastes are such waste materials which are and can be degraded by natural factors like microbes (e.g. bacteria, fungi and few more), abiotic elements like temperature, UV, oxygen, etc. Some examples of such wastes are food materials, kitchen wastes, and other natural wastes. Microorganisms and other abiotic factors together break down complex substances into simpler organic matters which eventually suspend and fade into the soil. The whole process is natural which can be rapid or slow. Therefore the environmental issues and risks caused by biodegradable wastes are low.
Examples
But the huge dumping of waste can raise some threats to life sooner or later. To avoid this, some people practice composting. In composting, the biodegradable wastes are dumped into a pit and covered for a period. Due to the action of microbes, they will decompose and will be used as manure for cultivation purpose. This will reduce the amount of waste at landfills.
Biodegradable Waste
Biodegradable waste is a type of waste, typically originating from plant or animal sources, which may be degraded by other living organisms.
Biodegradable waste can be commonly found in municipal solid waste as green waste, food waste, paper waste, and biodegradable plastics. Other biodegradable wastes include human waste, manure, sewage, slaughterhouse waste.
Non-Biodegradable
A Non-Biodegradable material can be defined as a kind of substance which cannot be broken down by natural organisms and acts as a source of pollution.
Unlike biodegradable wastes, non-biodegradable cannot be easily handled. Non-biodegradable wastes are those who cannot be decomposed or dissolved by natural agents. They remain on earth for thousands of years without any degradation. Hence the threat caused by them is also more critical. A notable example is the plastics which are a commonly used material in almost every field. To give these plastics a long lasting effect, improved quality plastics are being put to use. This made them more temperature resistant and more durable even after use. Other examples are cans, metals, and chemicals for agricultural and industrial purposes. They are the main causes of air, water and soil pollution and diseases like cancer.
Since non-biodegradable wastes are not Eco-friendly, they need to be replaced. As a part of a development of alternatives, scientists have brought forward many ides like biodegradable plastics, etc. They incorporated some biodegradable materials with plastics and made them easily and rapidly degradable. But this is quite an expensive procedure.
Non-Biodegradable waste
Waste which cannot be decomposed by biological process is known as “Non-biodegradable wastes”. Most of the inorganic waste is non-biodegradable. Non-biodegradable wastes which can be recycled are known as “Recyclable waste” and those which cannot be recycled are known as “Non-recyclable waste”.
The greenhouse effect is thought to be the cause of:- a)Huge tomatoes
- b)Skin cancer
- c)An increase in global temperature
- d)An increase in asthma sufferers
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The greenhouse effect is thought to be the cause of:
a)
Huge tomatoes
b)
Skin cancer
c)
An increase in global temperature
d)
An increase in asthma sufferers

|
Bhavana Chavan answered |
The greenhouse effect increases the global temperature
Green chemistry means such reactions which :- a)produce colour during reactions [2008]
- b)reduce the use and production of hazardous chemicals
- c)are related to the depletion of ozone layer
- d)study the reactions in plants
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Green chemistry means such reactions which :
a)
produce colour during reactions [2008]
b)
reduce the use and production of hazardous chemicals
c)
are related to the depletion of ozone layer
d)
study the reactions in plants

|
Prashanth Dasgupta answered |
Green chemistry may be defined as the programme of developing new chemical products and chemical processes or making improvements in the already existing compounds and processes so as to make less harmful to human health and environment. This means the same as to reduce the use and production of hazardous chemicals. i.e. correct answer is option (b).
Photochemical smog occurs in:- a)Warm,dry and sunny climate
- b)Winter climate
- c)Rainy climate
- d)Frozen time
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Photochemical smog occurs in:
a)
Warm,dry and sunny climate
b)
Winter climate
c)
Rainy climate
d)
Frozen time
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
Photochemical smog occurs in warm, dry and sunny climate. It is formed by the action of sunlight on unsaturated hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides. Chemically, it is an oxidising mixture. It does not involve any smoke or fog.
Recycling of materials and energy will lead to- a)inssen the trapped solar energy
- b)increase in soil pollution
- c)decrease in environmental pollution
- d)increase in green house gas
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Recycling of materials and energy will lead to
a)
inssen the trapped solar energy
b)
increase in soil pollution
c)
decrease in environmental pollution
d)
increase in green house gas

|
Puja Kaur answered |
Recycling of materials and energy will lead to decrease in environmental pollution
The amount of oxygen required by bacteria to break down the organic matter present in a certain volume of a sample of water is called:- a)Sulphur
- b)Ammonia
- c)BOD
- d)Iron
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The amount of oxygen required by bacteria to break down the organic matter present in a certain volume of a sample of water is called:
a)
Sulphur
b)
Ammonia
c)
BOD
d)
Iron

|
Naveen Choudhary answered |
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD, also called Biological Oxygen Demand) is the amount of dissolved oxygen needed (i.e. demanded) by aerobic biological organisms to break down organic material present in a given water sample at certain temperature over a specific time period.
Chemical species present in the environment are either naturally occurring or generated by human activities. Their interrelation with the surroundings is called:- a)environmental pollution
- b)environmental chemical interactions
- c)environmental chemistry
- d)environmental studies
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Chemical species present in the environment are either naturally occurring or generated by human activities. Their interrelation with the surroundings is called:
a)
environmental pollution
b)
environmental chemical interactions
c)
environmental chemistry
d)
environmental studies

|
Srishti Roy answered |
environmental chemistry basically deals with the interrelationship between chemical species generated by human activities or naturally.
In winter polar Stratospheric clouds provide surface on which chlorine nitrate formed get hydrolysed to form:- a)Molecular chlorine
- b)Nitrate free radical
- c)Chlorine free radical
- d)Hypochlorous acid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In winter polar Stratospheric clouds provide surface on which chlorine nitrate formed get hydrolysed to form:
a)
Molecular chlorine
b)
Nitrate free radical
c)
Chlorine free radical
d)
Hypochlorous acid

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
In summer season, nitrogen dioxide and methane react with chlorine monoxide and chlorine free radicals forming chlorine sinks, preventing much ozone depletion, whereas in winters, special type of clouds, called the polar stratospheric clouds are formed over Antarctica.These polar stratospheric clouds provide surface on which chlorine nitrate gets hydrolysed to form hypochlorous acid. It also reacts with hydrogen chloride to give molecular chlorine.
Acid rain is harmful for:- a)human beings
- b)Agriculture
- c)aquatic animals
- d)all of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Acid rain is harmful for:
a)
human beings
b)
Agriculture
c)
aquatic animals
d)
all of the above
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
Air pollution like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides can cause respiratory diseases, or can make these diseases worse. Respiratory diseases like asthma or chronic bronchitis make it hard for people to breathe. The pollution that causes acid rain can also create tiny particles.
SO D IS CORRECT.
Measure of the amount of organic material in the water, in terms of how much oxygen will be required to break it down biologically is termed as- a)hydrosphere measure
- b)measure of polluted water
- c)Eutrophication value
- d)Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Measure of the amount of organic material in the water, in terms of how much oxygen will be required to break it down biologically is termed as
a)
hydrosphere measure
b)
measure of polluted water
c)
Eutrophication value
d)
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)

|
Rithika Mukherjee answered |
Measure of the amount of organic material in the water, in terms of how much oxygen will be required to break it down biologically is termed as Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
Catalytic converters must be used in cars to reduce the to reduce the effect of exhaust fumes on the atmosphere. The converter should contain one of the main components- a)ceramic honeycomb coated with precious metals
- b)plastic comb coated with Pd, Pt
- c)ceramic honeycomb coated with nonmetals
- d)plastic comb coated with Rh
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Catalytic converters must be used in cars to reduce the to reduce the effect of exhaust fumes on the atmosphere. The converter should contain one of the main components
a)
ceramic honeycomb coated with precious metals
b)
plastic comb coated with Pd, Pt
c)
ceramic honeycomb coated with nonmetals
d)
plastic comb coated with Rh

|
Vaishnavi Bajaj answered |
The converter should contain ceramic honeycomb coated with precious metals
Stratosphere is a region of the atmosphere which contains- a)air
- b)plants
- c)much water vapour and clouds
- d)Ozone layer
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Stratosphere is a region of the atmosphere which contains
a)
air
b)
plants
c)
much water vapour and clouds
d)
Ozone layer
|
|
Anirban Shah answered |
The correct answer is option 'D' - Ozone layer. Let's delve into the details to understand why.
The Stratosphere:
The stratosphere is a layer of the Earth's atmosphere that lies above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. It is situated roughly between 10 and 50 kilometers (6-30 miles) above the Earth's surface. The stratosphere plays a crucial role in protecting life on Earth by containing the ozone layer, which absorbs harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun.
The Ozone Layer:
The ozone layer is a region within the stratosphere that contains a higher concentration of ozone (O3) molecules. Ozone is a molecule made up of three oxygen atoms bonded together. This layer is located between approximately 10 and 50 kilometers (6-30 miles) above the Earth's surface.
Importance of the Ozone Layer:
The ozone layer is vital because it acts as a shield, absorbing most of the sun's harmful UV radiation. UV radiation can cause various health issues, including skin cancer, cataracts, and weakened immune systems. It can also harm ecosystems, including marine life, crops, and phytoplankton.
Formation and Stability of the Ozone Layer:
The ozone layer is formed and maintained by a balance of chemical reactions involving oxygen molecules (O2) and ozone (O3). Solar UV radiation breaks apart some oxygen molecules into individual oxygen atoms. These free oxygen atoms then react with other oxygen molecules to form ozone. The ozone molecules, in turn, absorb UV radiation and prevent it from reaching the Earth's surface.
Depletion of the Ozone Layer:
Human activities have led to the release of certain chemicals, called ozone-depleting substances (ODS), into the atmosphere. The most well-known ODS are chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and halons, which were commonly used in refrigerants, aerosol propellants, and fire extinguishing systems. ODS can reach the stratosphere and disrupt the balance of ozone formation and destruction, leading to ozone depletion.
Consequences of Ozone Depletion:
Ozone depletion allows more UV radiation to reach the Earth's surface, which can have adverse effects. Increased UV radiation can cause skin cancer, damage to the eyes, suppression of the immune system, and harm to marine ecosystems, agriculture, and the overall environment. To mitigate ozone depletion, the international community developed the Montreal Protocol in 1987, which regulates the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances.
In conclusion, the stratosphere is a region of the atmosphere that contains the ozone layer. The ozone layer is crucial for protecting life on Earth by absorbing harmful UV radiation from the sun. Ozone depletion caused by human activities can have severe consequences, highlighting the importance of preserving and safeguarding the ozone layer.
The Stratosphere:
The stratosphere is a layer of the Earth's atmosphere that lies above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. It is situated roughly between 10 and 50 kilometers (6-30 miles) above the Earth's surface. The stratosphere plays a crucial role in protecting life on Earth by containing the ozone layer, which absorbs harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun.
The Ozone Layer:
The ozone layer is a region within the stratosphere that contains a higher concentration of ozone (O3) molecules. Ozone is a molecule made up of three oxygen atoms bonded together. This layer is located between approximately 10 and 50 kilometers (6-30 miles) above the Earth's surface.
Importance of the Ozone Layer:
The ozone layer is vital because it acts as a shield, absorbing most of the sun's harmful UV radiation. UV radiation can cause various health issues, including skin cancer, cataracts, and weakened immune systems. It can also harm ecosystems, including marine life, crops, and phytoplankton.
Formation and Stability of the Ozone Layer:
The ozone layer is formed and maintained by a balance of chemical reactions involving oxygen molecules (O2) and ozone (O3). Solar UV radiation breaks apart some oxygen molecules into individual oxygen atoms. These free oxygen atoms then react with other oxygen molecules to form ozone. The ozone molecules, in turn, absorb UV radiation and prevent it from reaching the Earth's surface.
Depletion of the Ozone Layer:
Human activities have led to the release of certain chemicals, called ozone-depleting substances (ODS), into the atmosphere. The most well-known ODS are chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and halons, which were commonly used in refrigerants, aerosol propellants, and fire extinguishing systems. ODS can reach the stratosphere and disrupt the balance of ozone formation and destruction, leading to ozone depletion.
Consequences of Ozone Depletion:
Ozone depletion allows more UV radiation to reach the Earth's surface, which can have adverse effects. Increased UV radiation can cause skin cancer, damage to the eyes, suppression of the immune system, and harm to marine ecosystems, agriculture, and the overall environment. To mitigate ozone depletion, the international community developed the Montreal Protocol in 1987, which regulates the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances.
In conclusion, the stratosphere is a region of the atmosphere that contains the ozone layer. The ozone layer is crucial for protecting life on Earth by absorbing harmful UV radiation from the sun. Ozone depletion caused by human activities can have severe consequences, highlighting the importance of preserving and safeguarding the ozone layer.
Which of the following statements is wrong?- a)Ozone is produced in upper stratosphere by the action of UV rays on oxygen.
- b)Ozone is not responsible for green house effect.
- c)Ozone can oxidise sulphur dioxide present in the atmosphere to sulphur trioxide.
- d)Ozone hole is thinning of ozone layer present in stratosphere.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is wrong?
a)
Ozone is produced in upper stratosphere by the action of UV rays on oxygen.
b)
Ozone is not responsible for green house effect.
c)
Ozone can oxidise sulphur dioxide present in the atmosphere to sulphur trioxide.
d)
Ozone hole is thinning of ozone layer present in stratosphere.

|
Anjana Desai answered |
Depleation of Ozone is responsible for green house effect.
Sewage containing organic waste should not be disposed in water bodies because it causes major water pollution. Fishes in such a polluted water die because of- a)Decrease in the amount of dissolved oxygen in water.
- b)Increase in the amount of dissolved oxygen.
- c)Large number of mosquitoes.
- d)becomeClogging of gills by mud.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Sewage containing organic waste should not be disposed in water bodies because it causes major water pollution. Fishes in such a polluted water die because of
a)
Decrease in the amount of dissolved oxygen in water.
b)
Increase in the amount of dissolved oxygen.
c)
Large number of mosquitoes.
d)
becomeClogging of gills by mud.

|
Rhea Choudhary answered |
water pollution causes the death of fishes because of decrease in amount of dissolved oxygen.
Which of the following is/are the hazardous pollutant(s) present in automobile exhaust gases? (i)N2 (ii) CO (iii) CH4 (iv) Oxides of nitrogen
- a)(ii) and (iii)
- b)(i) and (ii) [1996]
- c)(ii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are the hazardous pollutant(s) present in automobile exhaust gases? (i)N2 (ii) CO (iii) CH4 (iv) Oxides of nitrogen
a)
(ii) and (iii)
b)
(i) and (ii) [1996]
c)
(ii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iii)

|
Dipanjan Mehta answered |
CO and oxides of Nitr ogen ar e poisnous gases present in automobile exhaust gases.
Chapter doubts & questions for Environmental Chemistry - Inorganic Chemistry for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Environmental Chemistry - Inorganic Chemistry for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










