All Exams >
NEET >
Physical Chemistry for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure for NEET Exam
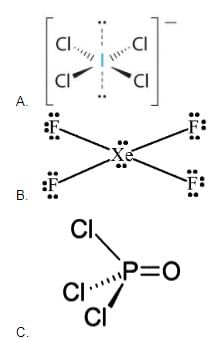
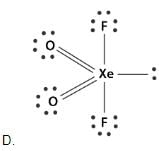
Which of the following shows the Lewis dot formula for CO2?- a)

- b)
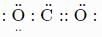
- c)
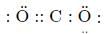
- d)
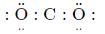
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following shows the Lewis dot formula for CO2?
a)

b)
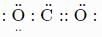
c)
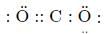
d)
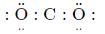
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Step I: Skeleton OCO
Step II: A = 1 x 4 for C + 2 x 6 for O = 4 + 12 = 16 electrons
Step III : Total no. of electrons needed to achieve noble gas configuration (N)
N= 1 x 8 + 2 x 8 = 24
N= 1 x 8 + 2 x 8 = 24
Step IV : Shared electrons, S = N- A = 24-16 = 8 electrons
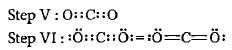
Hybridisation of Acetylene is- a)sp
- b)sp2
- c)sp3
- d)dsp2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Hybridisation of Acetylene is
a)
sp
b)
sp2
c)
sp3
d)
dsp2
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Since acetylene is made up of triple bond. So the hybridization of carbon in acetylene is sp.
In allene (C3H4), the type(s) of hybridisation of the carbon atoms is (are)
- a)sp and sp3
- b)sp and sp2
- c)Only sp2
- d)sp2 and sp3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In allene (C3H4), the type(s) of hybridisation of the carbon atoms is (are)
a)
sp and sp3
b)
sp and sp2
c)
Only sp2
d)
sp2 and sp3
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
The type(s) of hybridization of the carbon atoms in Allene (C3H4) is sp and sp2.
Which of the following is/are correct statement(s)?a)s + py→ two sp-hybrid orbitals lying in the yz planeb)s + px → two sp-hybrid orbitals lying in xz planec)(s + px + pz) → three sp2-hybrid orbitals lying in xz planed)(s + py) → two sp-hybrid orbitals lying along y-axisCorrect answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Incorrect (b)
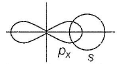
two sp-hybrid orbitals are along x-axis.
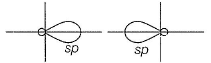
two sp-hybrid orbitals are along x-axis.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-11) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Assuming that Hund's rule is violated, the bond order and magnetic nature of the diatomic molecule B2 is
- a)1 and diamagnetic
- b)0 and diamagnetic
- c)1 and paramagnetic
- d)0 and paramagnetic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-11) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Assuming that Hund's rule is violated, the bond order and magnetic nature of the diatomic molecule B2 is
a)
1 and diamagnetic
b)
0 and diamagnetic
c)
1 and paramagnetic
d)
0 and paramagnetic
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |

Different kinds of bonds and interaction present within CuSO4 • 5H2O. They can beI. σ-bond
II. π-bond
III. coordinate bond
IV. electrostatic force of attraction
V. H-bond due to dipole-dipole interaction
VI. H-bond due to ion-dipole interaction Select the correct types of bonds/interactions.- a)I, II and III
- b)I, III and IV
- c)I, III, V and VI
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Different kinds of bonds and interaction present within CuSO4 • 5H2O. They can be
I. σ-bond
II. π-bond
III. coordinate bond
IV. electrostatic force of attraction
V. H-bond due to dipole-dipole interaction
VI. H-bond due to ion-dipole interaction
II. π-bond
III. coordinate bond
IV. electrostatic force of attraction
V. H-bond due to dipole-dipole interaction
VI. H-bond due to ion-dipole interaction
Select the correct types of bonds/interactions.
a)
I, II and III
b)
I, III and IV
c)
I, III, V and VI
d)
All of these
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
IV. Electrostatic force of attraction between
V. H2O molecules joined together by dipole-dipole interaction.
VI. Outer H2O molecule joined to
Can you explain the answer of this question below:In which of the following species is the underlined carbon having sp3-hybridisation? [AIEEE-2002]- A:CH3COOH
- B:CH3CH2OH
- C: CH3COCH3
- D:CH2=CH_CH3
The answer is d.
In which of the following species is the underlined carbon having sp3-hybridisation?
[AIEEE-2002]
A:
CH3COOH
B:
CH3CH2OH
C:
CH3COCH3
D:
CH2=CH_CH3
|
|
Om Desai answered |

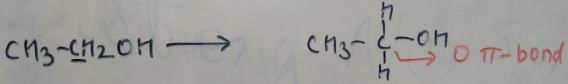
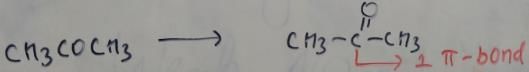
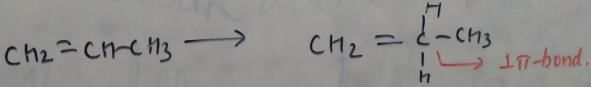
From this figure, we can clearly see that in CH3CH2OH, we have no pi bond. While other compounds have pi bond. For carbon, only sp3 hybridization has no pi bond. So CH3CH2OH has sp3 hybridized carbon atom.
In which of the following species is the underlined carbon having sp3-hybridisation? [AIEEE-2002]- a)CH3COOH
- b)CH3CH2OH
- c) CH3COCH3
- d)CH2=CH_CH3
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following species is the underlined carbon having sp3-hybridisation?
[AIEEE-2002]
a)
CH3COOH
b)
CH3CH2OH
c)
CH3COCH3
d)
CH2=CH_CH3
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |

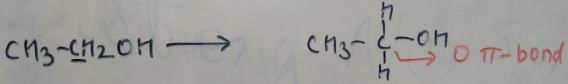
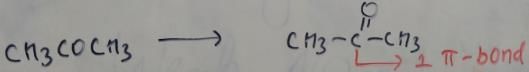
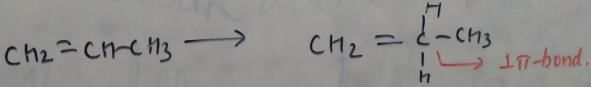
From this figure, we can clearly see that in CH3CH2OH, we have no pi bond. While other compounds have pi bond. For carbon, only sp3 hybridization has no pi bond. So CH3CH2OH has sp3 hybridized carbon atom.
A pi-bond is formed by the overlap of:- a)p-p orbitals in sidewise manner
- b)s-p orbitals
- c)s-s orbitals
- d)p-p orbitals in end to end fashion
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A pi-bond is formed by the overlap of:
a)
p-p orbitals in sidewise manner
b)
s-p orbitals
c)
s-s orbitals
d)
p-p orbitals in end to end fashion
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
pi-bond is always formed by sidewise overlapping of p – p orbitals in sidewise manner.
Bond order of 1.5 is shown by : [2012] - a)O2+
- b)O2-
- c)O22+
- d)O2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Bond order of 1.5 is shown by : [2012]
a)
O2+
b)
O2-
c)
O22+
d)
O2
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
N₂=N+N = 7e⁻+7e⁻ = 14e- which has bond order =3
O₂=8e⁻+8e⁻ = 16e⁻ which has bond order = 2
O₂⁺=8e⁻+8e⁻ - 1e⁻ = 15e⁻ which has bond order= 2.5
O₂⁻ = 8e⁻ +8e⁻ +1e⁻ =17 e⁻ which has bond order=1.5
So option B is correct .
Which of the following is nonpolar but contains polar bonds?- a)HCI
- b)CO2
- c)NH3
- d)NO2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is nonpolar but contains polar bonds?
a)
HCI
b)
CO2
c)
NH3
d)
NO2
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
This is why molecules like carbon dioxide are nonpolar despite having the polar carbon oxygen bonds. Molecules that contain non-polar bonds are not polar unless the central atom has one or more nonbonded pairs of electrons.
The correct order of increasing bond length of
I. C— H
II. C— O
III. C— C
- a)I< II< III< IV
- b)I< IV < II< III
- c)Ill < IV < II < l
- d)II < I < III < IV
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of increasing bond length of
I. C— H
II. C— O
III. C— C
I. C— H
II. C— O
III. C— C
a)
I< II< III< IV
b)
I< IV < II< III
c)
Ill < IV < II < l
d)
II < I < III < IV

|
Amrita Sen answered |
H is smallest in size thus, (C— H)bond length is least.
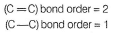
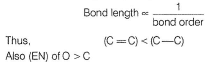
Hence, bonding pair in (C— O) is nearer to nucleus decreasing bond length as compared to (C— C).
Thus, I < IV < II < III.
Hence, bonding pair in (C— O) is nearer to nucleus decreasing bond length as compared to (C— C).
Thus, I < IV < II < III.
Which of the following compounds has a 3-centre bond?[1996]- a)Diborane
- b)Carbon dioxide
- c)Boron trifluroide
- d)Ammonia
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compounds has a 3-centre bond?[1996]
a)
Diborane
b)
Carbon dioxide
c)
Boron trifluroide
d)
Ammonia

|
Krish Saha answered |
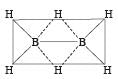
The bond represented by dots form the 3-centred electron pair bond. The idea of three centred electron pair bond B–H–B bridges is necessitated because diborane does not have sufficient electrons to form normal covalent bonds. It has only 12 electrons instead of 14 required to give simple ethane like structure for diborane.
Valence Bond Theory was developed in the year- a)1916
- b)1927
- c)1930
- d)1932
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Valence Bond Theory was developed in the year
a)
1916
b)
1927
c)
1930
d)
1932
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The valence bond (VB) theory of bonding was mainly developed by Walter Heitler and Fritz London in 1927, and later modified by Linus Pauling to take bond direction into account. The VB approach concentrates on forming bonds in localized orbitals between pairs of atoms, and hence retains the simple idea of Lewis structures and electron pairs.
Expansion of octet can not take place in- a)N
- b)S
- c)Si
- d)P
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Expansion of octet can not take place in
a)
N
b)
S
c)
Si
d)
P

|
Harshad Nair answered |
N(7) = 1s22s22p3
Nitrogen does not have (2d) orbitals. Thus, (more than 8) electrons cannot be accomodated in second orbit.
Nitrogen does not have (2d) orbitals. Thus, (more than 8) electrons cannot be accomodated in second orbit.
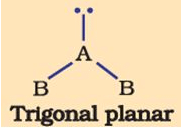
The shape of the below molecule is
- a)trigonal
- b)rigonal planar
- c)see saw
- d)bent
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The shape of the below molecule is

a)
trigonal
b)
rigonal planar
c)
see saw
d)
bent
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The order of Repulsion: lone pair-lone pair > lone pair-bond pair > bond pair-bond pair
Due to the extra lone pair electron, the shape becomes bent.
Select the correct statement about valence bond approach.- a)Each bond is formed by maximum overlap for its maximum stability
- b)It represents localised electron model of bonding
- c)Most of the electrons retain the same orbital locations as in separated atoms
- d)All of the above are correct statements
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement about valence bond approach.
a)
Each bond is formed by maximum overlap for its maximum stability
b)
It represents localised electron model of bonding
c)
Most of the electrons retain the same orbital locations as in separated atoms
d)
All of the above are correct statements
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
(a) Hs maximum overlap - correct.
(c) Based on valence bond approach,-no prediction of change of structure due to (Ip-Ip), (Ip-bp) repulsions- correct.
(c) Based on valence bond approach,-no prediction of change of structure due to (Ip-Ip), (Ip-bp) repulsions- correct.
N2 and O2 are converted into monocations, N2+ and O2+ respectively. Which of the following statements is wrong ? [1997]- a)In N2, the N—N bond weakens
- b)In O2, the O—O bond order increases
- c)In O2, paramagnetism decreases
- d)N2+ becomes diamagnetic
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
N2 and O2 are converted into monocations, N2+ and O2+ respectively. Which of the following statements is wrong ? [1997]
a)
In N2, the N—N bond weakens
b)
In O2, the O—O bond order increases
c)
In O2, paramagnetism decreases
d)
N2+ becomes diamagnetic

|
Rohan Unni answered |
We know that in O2 bond, the order is 2 and in O2– bond, the order is 1.5. Therefore the wrong statements is (b)
Which of the following angle corresponds to sp2 hybridisation?a)120∘b)180∘c)90∘d)109∘Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Samridhi Pillai answered |
sp2 hybridisation gives three sp2 hybrid orbitals which are planar triangular forming an angle of 120° with each other.
The electronic configurations of three elements A, B and C are given below.
Answer the questions from 14 to 17 on the basis of these configurations.
A ls22s22p6
B ls22s22p63s23p3
C ls22s22p63s23p
The electronic configurations of three elements A, B and C are given below.
Answer the questions from 14 to 17 on the basis of these configurations.
A ls22s22p6
B ls22s22p63s23p3
C ls22s22p63s23p
Pick out the pair of species having identical shapes for both the molecules.- a)BF3 , PCl3
- b)PF , IF5
- c)CF4,SF4
- d)XeF2 , CO2
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Pick out the pair of species having identical shapes for both the molecules.
a)
BF3 , PCl3
b)
PF , IF5
c)
CF4,SF4
d)
XeF2 , CO2
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Both XeF2 & CO2 have linear structures. Both are actually linear Tri-atomic molecules.
Which molecule has a trigonal pyramidal shape?- a)AB4E
- b)AB2E2
- c)AB3E
- d)AB2E
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which molecule has a trigonal pyramidal shape?
a)
AB4E
b)
AB2E2
c)
AB3E
d)
AB2E
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
AB3E: trigonal pyramidal (central atom + 3 outer atoms make a pyramid)
→ start with AB4 molecule (tetrahedral) and replace a B atom w/ lone pair
→ lone pair electrons push bonding electrons away
→ bond angles are now less than 109.5°
→ start with AB4 molecule (tetrahedral) and replace a B atom w/ lone pair
→ lone pair electrons push bonding electrons away
→ bond angles are now less than 109.5°
Polarity in a molecule and hence the dipole moment depends primarily on electronegativity of the constituent atoms and shape of a molecule. Which of the following has the highest dipole moment? - a)CO2
- b)HI
- c)H2O
- d)SO2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Polarity in a molecule and hence the dipole moment depends primarily on electronegativity of the constituent atoms and shape of a molecule. Which of the following has the highest dipole moment?
a)
CO2
b)
HI
c)
H2O
d)
SO2
|
|
Isha Kulkarni answered |
H2O will have highest dipole moment due to maximum difference in electronegativity of H and O atoms.
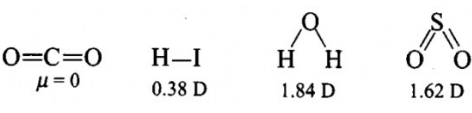
If one of the electrons (1s2) of helium is taken in excited state then bond order of He2 is- a)0 (zero)
- b)1
- c)0.5
- d)2.0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If one of the electrons (1s2) of helium is taken in excited state then bond order of He2 is
a)
0 (zero)
b)
1
c)
0.5
d)
2.0
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
Number of electrons in bonding orbital = 4 and in anti-bonding orbitai = 0
In which of the following cases, covalent bonds are cleaved?- a)Boiling of H2O
- b)Melting of KCN
- c)Boiling of CF4
- d)Melting of SiO2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following cases, covalent bonds are cleaved?
a)
Boiling of H2O
b)
Melting of KCN
c)
Boiling of CF4
d)
Melting of SiO2
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
SiO2 is a network covalent compound that has an extremely high melting and boiling point, because many silicon-oxygen bonds have to be broken in order for it to achieve the necessary freedom. To clarify, SiO2, which has a tetrahedral network lattice formation, shows that each silicon is actually bonded to 4 oxygens; each oxygen is bonded to 2 silicon. These are excess bonds aside from the ones of SiO2 which are broken.
bond lengths are lower in elements havinga)crystal structureb)double bondc)triple bondd)single bondCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Single bond has higher bond length than multiple bond.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-14) This section contains 14 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. Assuming that Hund’s rule is violated, the bond order and magnetic nature of the diatomic molecule B2 is[IIT JEE 2010]- a)1 and diamagnetic
- b)0 and diamagnetic
- c)1 and paramagnetic
- d)0 and paramagnetic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-14) This section contains 14 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Assuming that Hund’s rule is violated, the bond order and magnetic nature of the diatomic molecule B2 is
[IIT JEE 2010]
a)
1 and diamagnetic
b)
0 and diamagnetic
c)
1 and paramagnetic
d)
0 and paramagnetic
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
B2 (10 electrons)
MO electronic configuration is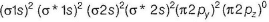
MO electronic configuration is
Bonding electrons = 6
Anti-bonding electrons = 4
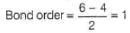
No unpaired electron-diamagnetic
Anti-bonding electrons = 4
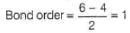
No unpaired electron-diamagnetic
In which of the following ionizion processes, the bond order has increased and the magnetic behaviour has changed [AIEEE-2007]- a)NO → NO+
- b)O2 →
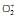
- c)N2 →
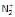
- d)C2 →
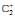
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following ionizion processes, the bond order has increased and the magnetic behaviour has changed [AIEEE-2007]
a)
NO → NO+
b)
O2 → 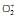
c)
N2 → 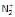
d)
C2 → 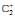
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
N2: bond order 3, paramagnetic
N2-: bond order 2.5, paramagnetic
C2: bond order 2, diamagnetic
C2+: bond order 1.5, paramagnetic
NO: bond order 2.5, paramagnetic
NO+: bond order 3, paramagnetic
O2: bond order 2, paramagnetic
O2+: bond order 2.5, paramagnetic
Therefore, option a is correct
N2-: bond order 2.5, paramagnetic
C2: bond order 2, diamagnetic
C2+: bond order 1.5, paramagnetic
NO: bond order 2.5, paramagnetic
NO+: bond order 3, paramagnetic
O2: bond order 2, paramagnetic
O2+: bond order 2.5, paramagnetic
Therefore, option a is correct
Polarity in a molecule and hence the dipole moment depends primarily on electronegativity of the constituent atoms and shape of a molecule. Which of the following has the highest dipole moment? a)CO2b)HIc)H2Od)SO2Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
H2O will have highest dipole moment due to maximum difference in electronegativity of H and O atoms.
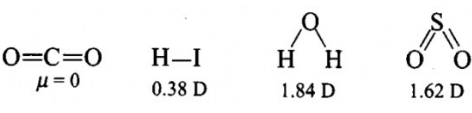
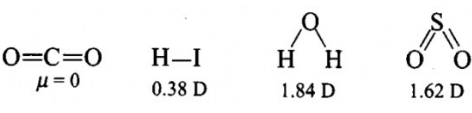
Which of the following has pπ – dπ bonding?- a)NO3–
- b)SO32– [2002]
- c)BO33–
- d)CO32–
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following has pπ – dπ bonding?
a)
NO3–
b)
SO32– [2002]
c)
BO33–
d)
CO32–

|
Smruti Sucharita answered |
Answer is b bcoz Sulphur has d orbital...
Q. Which of the following species contain at least one atom that violates the octet rule?a)O— Cl—-Ob)F— Xe— Fc)PCI5d)SF6Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
(a) Octet of Cl expanded to (9).
(b) Octet Xe expanded to (10).
(c) Octet of P expanded to (10).
(b) Octet Xe expanded to (10).
(c) Octet of P expanded to (10).
Dipole moment of 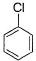 is 1.5 D. Thus, dipole moment
is 1.5 D. Thus, dipole moment 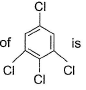
- a)0.00 D
- b)1.5 D
- c)2.0 D
- d)3.0 D
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Dipole moment of 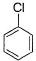 is 1.5 D. Thus, dipole moment
is 1.5 D. Thus, dipole moment 
a)
0.00 D
b)
1.5 D
c)
2.0 D
d)
3.0 D
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
If one considers following molecule, it is
Symmetrical and thus
In the given species
In which of the following molecules octet rule is not followed?- a)NH3
- b)CH4
- c)CO2
- d)NO
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following molecules octet rule is not followed?
a)
NH3
b)
CH4
c)
CO2
d)
NO
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
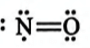
For NO, the octet rule is not followed due to the presence of odd electrons on N.
In BrF3 molecule, the lone pairs occupy equatorial positions to minimize [2004]- a)lone pair - bond pair repulsion only
- b)bond pair - bond pair repulsion only
- c)lone pair - lone pair repulsion and lone pair -bond pair repulsion
- d)lone pair - lone pair repulsion only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In BrF3 molecule, the lone pairs occupy equatorial positions to minimize [2004]
a)
lone pair - bond pair repulsion only
b)
bond pair - bond pair repulsion only
c)
lone pair - lone pair repulsion and lone pair -bond pair repulsion
d)
lone pair - lone pair repulsion only

|
Abhishek Choudhary answered |
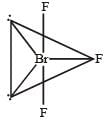
In BrF3, both bond pairs as well as lone pairs of electrons are present. Due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons (lp) in the valence shell, the bond angle is contracted and the molecule takes the T-shape. This is due to greater repulsion between two lone pairs or between a lone pair and a bond pair than between the two bond pairs.
Which of the following species is paramagnetic ?- a)NO-
- b)O22-
- c)CN-
- d)CO
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following species is paramagnetic ?
a)
NO-
b)
O22-
c)
CN-
d)
CO
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
NO has an odd number of electrons and, therefore, must be paramagnetic. e. CO is diamagnetic because all of its electrons are paired.
Which is the correct order of the bond angle?- a)NH3 < NF3
- b)H2O > Cl2O
- c)PH3 < SbH3
- d)H2Te < H2S
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the correct order of the bond angle?
a)
NH3 < NF3
b)
H2O > Cl2O
c)
PH3 < SbH3
d)
H2Te < H2S

|
Nitin Patel answered |
The high electronegativity of F pulls the bonding electrons farther away from N than in NH3. Thus, repulsion between bond pairs is iess in NF3 than in NH3. Flence, the lone pair in N causes a greater distortion than NH3.
(b) as in (a)
Going down the group in periodic table, as size of central atom increases, repulsion increases.
Select the correct statement(s) about IF7.- a)I atom is sp3d3-hybridised
- b)I atom is in highest oxidation state
- c)There are five I—F longest and two I—F shortest bonds
- d)It has pentagonal bipyramidal structure
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement(s) about IF7.
a)
I atom is sp3d3-hybridised
b)
I atom is in highest oxidation state
c)
There are five I—F longest and two I—F shortest bonds
d)
It has pentagonal bipyramidal structure
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Iodine heptafluoride, also known as iodine(VII) fluoride or iodine fluoride, is an interhalogen compound with the chemical formula IF7.[2][3] It has an unusual pentagonal bipyramidal structure, as predicted by VSEPR theory.[4] The molecule can undergo a pseudorotational rearrangement called the Bartell mechanism, which is like the Berry mechanism but for a heptacoordinated system.[5] It forms colourless crystals, which melt at 4.5 degC: the liquid range is extremely narrow, with the boiling point at 4.77 degC. The dense vapor has a mouldy, acrid odour. The molecule has D5h symmetry. In IF7 out of 7 Flourine atoms 5 of them are placed on a plane in Pentagon shape .In remaining 2 flourines one is placed above the plane and other below the plane each at 90 degrees
Which of the following is nonpolar?- a)CI3CCH3
- b)PCI5
- c)CH2CI2
- d)NH3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is nonpolar?
a)
CI3CCH3
b)
PCI5
c)
CH2CI2
d)
NH3
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
(b) PCI5 triangular bipyramidal, symmetrical, no lone pair.
Which of the following molecule doesn’t have a lone pair?- a)BeCl2
- b)XeF4
- c)NH3
- d)H2O
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following molecule doesn’t have a lone pair?
a)
BeCl2
b)
XeF4
c)
NH3
d)
H2O
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
BeCl2 has no lone pairs on the beryllium. Thus, the electrons on the chlorides willtry to stay far apart from each other, since their corresponding electrons repel each other (while experiencing no deflection from electrons on a central atom). Thus themolecule is linear in shape.
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-16) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q.
In which of the following I is more volatile than II?
- a)
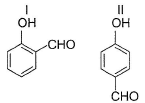
- b)
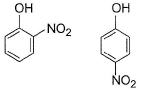
- c)

- d)
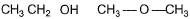
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-16) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q.
In which of the following I is more volatile than II?
In which of the following I is more volatile than II?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
I. Intermolecular H-bonding makes boiling point higher than that of I. Thus, I is more volatile
II. Ortho nitrophenol is more volatile than para nitrophenol because O-Nitrophenol has intramolecular hydrogen bonding whereas para nitrophenol has inter molecular H bonding and so boils relatively at higher temperature
(c) BP of H2O > > H2S
(d) BP of CH3CH2OH (due to H-bonding) > > CH3— O — CH3
A qualitative measure of the stability of an ionic compound is provided- a)ionization enthalpy
- b)lattice enthalpy
- c)Electron affinity
- d)electron gain enthalpy
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A qualitative measure of the stability of an ionic compound is provided
a)
ionization enthalpy
b)
lattice enthalpy
c)
Electron affinity
d)
electron gain enthalpy

|
Sounak Chaudhary answered |
stability of ionic bond is directly propotional to lattice energy.
Hydrogen bonds are formed in many compounds e.g., H2O, HF, NH3 . The boiling point of such compounds depends to a large extent on the strength of hydrogen bond and the number of hydrogen bonds. The correct decreasing order of the boiling points of above compounds is :
- a)HF > H2O > NH3
- b)H2O > HF > NH3
- c)NH3 > HF > H2O
- d)NH3 > H2O > HF
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen bonds are formed in many compounds e.g., H2O, HF, NH3 . The boiling point of such compounds depends to a large extent on the strength of hydrogen bond and the number of hydrogen bonds. The correct decreasing order of the boiling points of above compounds is :
a)
HF > H2O > NH3
b)
H2O > HF > NH3
c)
NH3 > HF > H2O
d)
NH3 > H2O > HF
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
H2O>HF>NH3
Strength of hydrogen bonding depends on the size and electronegativity of the atom.
Smaller the size of the atom, greater is the electronegativity and hence stronger is the H−bonding. Thus, the order of strength of H-bonding is H...F>H...O>H...N.
But each HF molecule is linked only to two other HF molecules while each H2O molecule is linked to four other H2O molecules through H−bonding.
Hence, the decreasing order of boiling points is H2O>HF>NH3.
The common features among the species CN–, CO ad NO+ are- a) Bond order three and isoelectronic
- b) Bond order three and weak field ligands
- c) Bond order two and acceptors
- d) Isoelectronic and weak field ligands
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The common features among the species CN–, CO ad NO+ are
a)
Bond order three and isoelectronic
b)
Bond order three and weak field ligands
c)
Bond order two and acceptors
d)
Isoelectronic and weak field ligands
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
According to M.O theory,
CN−,CO and NO+ are isoelectronic (14e−) and bond order is 3.
a is the correct answer.
Covalent nature of NaF, Na2O and Na3N in the increasing order is- a)Na3N < Na2O < NaF
- b)NaF < Na2O < Na3N
- c)Na2O < NaF < Na3N
- d)Na2O < Na3 N < NaF
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Covalent nature of NaF, Na2O and Na3N in the increasing order is
a)
Na3N < Na2O < NaF
b)
NaF < Na2O < Na3N
c)
Na2O < NaF < Na3N
d)
Na2O < Na3 N < NaF

|
Rohan Chakraborty answered |
By Fajans' rule,
Smaller the size of cation, larger the size of anion. Larger the charge on cation or anion, larger the polarising power and thus, greater the covalent nature.
NaF, Na2O, Na3N, Na+ is same.
Smaller the size of cation, larger the size of anion. Larger the charge on cation or anion, larger the polarising power and thus, greater the covalent nature.
NaF, Na2O, Na3N, Na+ is same.
Chapter doubts & questions for Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - Physical Chemistry for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - Physical Chemistry for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily


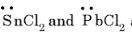 are bent shape molecule.
are bent shape molecule.
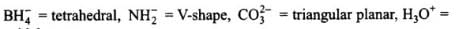 pyramidal.
pyramidal.