All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT Based Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Cell Cycle and Cell Division for NEET Exam
Consider the given cellat metaphase-I stage undergoing normal meisois.
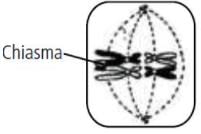 Which of the following gametes will not be formed from this cell?
Which of the following gametes will not be formed from this cell?
- a)
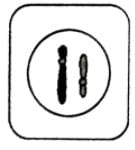
- b)
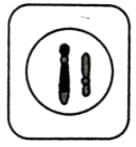
- c)
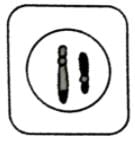
- d)
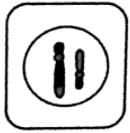
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the given cellat metaphase-I stage undergoing normal meisois.

Which of the following gametes will not be formed from this cell?
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Lead Academy answered |
The G₂ phase of the cell cycle is a period of rapid cell growth and protein synthesis, during which the cell prepares for mitotic division. This phase follows DNA replication in the S phase and precedes the M phase (mitosis), ensuring that the cell has all the necessary components for successful division.
Select the incorrect statement regarding S phase of interphase- a)It occurs between G1 and G2
- b)DNA replicates in the nucleus in this phase
- c)Centrioles duplicate in the cytoplasm
- d)As DNA is doubled, the number of chromosomes also doubles
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrect statement regarding S phase of interphase
a)
It occurs between G1 and G2
b)
DNA replicates in the nucleus in this phase
c)
Centrioles duplicate in the cytoplasm
d)
As DNA is doubled, the number of chromosomes also doubles
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
S or synthesis phase marks the period during which DNA synthesis or replication takes place. DNA synthesis or replication takes place. During this time the amount of DNA per cell doubles, however, there is no increase in the chromosome number.
Which of the following phases of the cell cycle is not a part of interphase?- a)S
- b)G1
- c)G0
- d)M
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following phases of the cell cycle is not a part of interphase?
a)
S
b)
G1
c)
G0
d)
M
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Interphase in a cell cycle has three stages —G1,S and G2.M− phase is not a part of interphase.
What is true about telophase stage of mitosis?- a)Chromosomes lose their identity as discrete elements
- b)Chromosomes cluster at opposite spindle poles
- c)Nuclear envelope, nucleolus, Golgi complex and ER reform
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is true about telophase stage of mitosis?
a)
Chromosomes lose their identity as discrete elements
b)
Chromosomes cluster at opposite spindle poles
c)
Nuclear envelope, nucleolus, Golgi complex and ER reform
d)
All of these
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
During telophase, the individual chromosomes are no longer seen and chromatin material tends to collect in a mass at the two poles. Chromosomes cluster at opposite spindle poles and their identity is lost as discrete elements. Nuclear envelope assembles around the chromosome clusters. Nucleolus, Golgi complex and ER reform.
Microtubules are absent in- a)Mitochondria
- b)Flagella
- c)Spindle fibres
- d)Centriole
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Microtubules are absent in
a)
Mitochondria
b)
Flagella
c)
Spindle fibres
d)
Centriole
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Microtubule is a microscopic tubular structure, with an external diameter of 24 nm and of variable length, found in a wide range of eukaryotic cells. Microtubules are composed of numerous subunits of the globular protein tubulin and occur singly or in pairs, triplets, or bundles. Microtubules help cells to maintain their shape. They also occur in cilia and eukaryotic flagella and the centrioles and form the spindle during nuclear division. A further role is in the intracellular transport of materials and movement of organelles.
Select the correct option:Centrioles undergo duplication during _______(i) of ________(ii), and begin to move towards opposite poles of the cell during ________(iii) stage of _________(iv).- a)(i) - S phase, (ii) - Interphase, (iii) - Prophase, (iv) - Mitosis
- b)(i) - S phase, (ii) - Interphase, (iii) - Anaphase, (iv) - Mitosis
- c)(i) - Prophase, (ii) - Mitosis, (iii) - Metaphase, (iv) - Mitosis
- d)(i) - Prophase, (ii) - Mitosis, (iii) - Anaphase, (iv) - Mitosis
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct option:Centrioles undergo duplication during _______(i) of ________(ii), and begin to move towards opposite poles of the cell during ________(iii) stage of _________(iv).
a)
(i) - S phase, (ii) - Interphase, (iii) - Prophase, (iv) - Mitosis
b)
(i) - S phase, (ii) - Interphase, (iii) - Anaphase, (iv) - Mitosis
c)
(i) - Prophase, (ii) - Mitosis, (iii) - Metaphase, (iv) - Mitosis
d)
(i) - Prophase, (ii) - Mitosis, (iii) - Anaphase, (iv) - Mitosis
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
In animal cells, during the S phase of interphase, DNA replication begins in the nucleus and the centriole duplicates in the cytoplasm. These duplicated centrioles move towards opposite poles of the cell in prophase of mitosis.
If the tissue has at a given time 1024 cells, how many cycles of mitosis had the original parental single-cell undergone?- a)512
- b)10
- c)1024
- d)256
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the tissue has at a given time 1024 cells, how many cycles of mitosis had the original parental single-cell undergone?
a)
512
b)
10
c)
1024
d)
256
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Each cycle produces 2 daughter cells. It is calculated by the formula (2number of cycles= number of daughter cells). Ten cycles are required to produce 1024 cells as follows:
210 = 1024.
While in mitosis, the daughter cells resemble each other and also the parent cell; in meiosis they differ not only from parent cell in having half the number of chromosomes, but also differ among themselves qualitatively in genetic constitution due to- a)Segregation and crossing over only
- b)Independent assortment and segregation only
- c)Independent assortment and crossing over only
- d)Crossing over, independent assortment and segregation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
While in mitosis, the daughter cells resemble each other and also the parent cell; in meiosis they differ not only from parent cell in having half the number of chromosomes, but also differ among themselves qualitatively in genetic constitution due to
a)
Segregation and crossing over only
b)
Independent assortment and segregation only
c)
Independent assortment and crossing over only
d)
Crossing over, independent assortment and segregation

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Metaphase is characterized by the alignment of chromosomes at the cell's equator, also known as the metaphase plate. This alignment ensures that each daughter cell will receive an equal and identical set of chromosomes when the chromosomes are pulled apart in the subsequent anaphase.
Lampbrush chromosomes are seen in which typical stage?- a)Mitotic anaphase
- b)Mitotic prophase
- c)Mitotic metaphase
- d)Meiotic prophase
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Lampbrush chromosomes are seen in which typical stage?
a)
Mitotic anaphase
b)
Mitotic prophase
c)
Mitotic metaphase
d)
Meiotic prophase
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The lampbrush chromosomes occuring in prophase of meiosis II are highly elongated special kind of synapsed mid-prophase or diplotene chromosome bivalents which have already undergone crossing over. Lampbrush chromosomes occur in pairs. Each chromosome of a pair has a double main axis due to presence of two elongated chromatids. Both the adjacent chromatids bear rows of large number of chromomeres. Two adjacent chromomeres are separated by interchromomeric stretches. Many of the chromomeres give out lateral projections or loops. The lateral loops provide a test tube or lampbrush-like appearance to the chromosome pair. Lateral loops take part in rapid transcription of DNA to mRNA meant for synthesis of yolk and other substances required for growth and development of Meiocyte.
Meiosis consists of - a)Two cell divisions without any DNA replication
- b)Two cell divisions in which chromosome number in reduced to half
- c)Two cell divisions with only two rounds of chromosome replication
- d)A single cell division with chromosome replication
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Meiosis consists of
a)
Two cell divisions without any DNA replication
b)
Two cell divisions in which chromosome number in reduced to half
c)
Two cell divisions with only two rounds of chromosome replication
d)
A single cell division with chromosome replication
|
|
Pooja Mukherjee answered |
Explanation:
Cell Divisions in Meiosis:
- Meiosis consists of two cell divisions, namely Meiosis I and Meiosis II.
- During Meiosis I, homologous chromosomes are separated, reducing the chromosome number to half.
- Meiosis II is similar to mitosis, where sister chromatids are separated.
Chromosome Number Reduction:
- The main purpose of Meiosis is to produce gametes with half the chromosome number of the parent cell.
- This reduction in chromosome number is essential for sexual reproduction to maintain the chromosome number across generations.
Importance of Meiosis:
- Meiosis leads to genetic diversity through processes like crossing over and independent assortment.
- It ensures the variability of offspring by shuffling genetic material during gamete formation.
Comparison with Mitosis:
- In contrast to mitosis, where a single cell division occurs, Meiosis involves two successive divisions.
- Meiosis includes stages like prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II.
Conclusion:
- In summary, Meiosis is a crucial process in sexual reproduction that involves two cell divisions, resulting in the reduction of the chromosome number to half. This ensures genetic diversity and the formation of genetically unique gametes.
Cell Divisions in Meiosis:
- Meiosis consists of two cell divisions, namely Meiosis I and Meiosis II.
- During Meiosis I, homologous chromosomes are separated, reducing the chromosome number to half.
- Meiosis II is similar to mitosis, where sister chromatids are separated.
Chromosome Number Reduction:
- The main purpose of Meiosis is to produce gametes with half the chromosome number of the parent cell.
- This reduction in chromosome number is essential for sexual reproduction to maintain the chromosome number across generations.
Importance of Meiosis:
- Meiosis leads to genetic diversity through processes like crossing over and independent assortment.
- It ensures the variability of offspring by shuffling genetic material during gamete formation.
Comparison with Mitosis:
- In contrast to mitosis, where a single cell division occurs, Meiosis involves two successive divisions.
- Meiosis includes stages like prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II.
Conclusion:
- In summary, Meiosis is a crucial process in sexual reproduction that involves two cell divisions, resulting in the reduction of the chromosome number to half. This ensures genetic diversity and the formation of genetically unique gametes.
The members of a homologous pair of chromosomes- a)Are identical in size and appearance
- b)Contain identical genetic information
- c)Separate and move to opposite poles of the cell during mitosis
- d)Are found only in haploid cells
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The members of a homologous pair of chromosomes
a)
Are identical in size and appearance
b)
Contain identical genetic information
c)
Separate and move to opposite poles of the cell during mitosis
d)
Are found only in haploid cells
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Homologous chormosomes are chormosomes having same structural features. In dipilod nuclei, pairs of homologous chromosomes can be identified at the start of meiosis. One member of each pair comes from the female parent and other from the male parent. Homologous chromosomes have the same pattern of genes along the chromosome but the nature of the genes may differ.
An anther has 1200 pollen grain. How many PMCs must have been there to produce them?- a)1200
- b)300
- c)150
- d)2400
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An anther has 1200 pollen grain. How many PMCs must have been there to produce them?
a)
1200
b)
300
c)
150
d)
2400
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Meiosis of one Pollen Mother Cell (PMC) produces 4 haploid pollen grains. Thus, for producing 1200 pollen grains 1200/4=300 PMCs are required.
Which of the following statements regarding the cell cycle is/are correct?i. DNA replication occurs continuously throughout the cell cycle.ii. The cell cycle consists of a series of stages that lead to the division of a cell into two daughter cells.iii. Cell growth in terms of cytoplasmic increase is a continuous process.iv. The distribution of replicated chromosomes to daughter nuclei is a simple and straightforward event.- a) ii and iii
- b) i and iv
- c) ii and iv
- d) i, iii, and iv
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements regarding the cell cycle is/are correct?
i. DNA replication occurs continuously throughout the cell cycle.
ii. The cell cycle consists of a series of stages that lead to the division of a cell into two daughter cells.
iii. Cell growth in terms of cytoplasmic increase is a continuous process.
iv. The distribution of replicated chromosomes to daughter nuclei is a simple and straightforward event.
a)
ii and iii
b)
i and iv
c)
ii and iv
d)
i, iii, and iv
|
|
Mansi Chakraborty answered |
Understanding the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is a series of stages that a cell goes through leading to its division. Let's analyze the statements provided:
i. DNA replication occurs continuously throughout the cell cycle.
- This statement is incorrect. DNA replication specifically occurs during the S phase (Synthesis phase) of interphase, not continuously throughout the entire cell cycle.
ii. The cell cycle consists of a series of stages that lead to the division of a cell into two daughter cells.
- This statement is correct. The cell cycle includes stages such as G1, S, G2, and M phase, which culminate in cell division (mitosis).
iii. Cell growth in terms of cytoplasmic increase is a continuous process.
- This statement is also correct. Cell growth does occur continuously as cells prepare for division, with gradual increases in cytoplasmic volume.
iv. The distribution of replicated chromosomes to daughter nuclei is a simple and straightforward event.
- This statement is misleading. The distribution of chromosomes during mitosis is a complex process involving several checkpoints and mechanisms to ensure accuracy.
Conclusion
Based on the evaluations:
- Correct Statements: ii and iii
- Incorrect Statements: i and iv
Thus, the correct answer is option a) ii and iii. The cell cycle is indeed a structured series of stages leading to division, with continuous growth occurring, while DNA replication is not continuous and chromosome distribution is complex.
The cell cycle is a series of stages that a cell goes through leading to its division. Let's analyze the statements provided:
i. DNA replication occurs continuously throughout the cell cycle.
- This statement is incorrect. DNA replication specifically occurs during the S phase (Synthesis phase) of interphase, not continuously throughout the entire cell cycle.
ii. The cell cycle consists of a series of stages that lead to the division of a cell into two daughter cells.
- This statement is correct. The cell cycle includes stages such as G1, S, G2, and M phase, which culminate in cell division (mitosis).
iii. Cell growth in terms of cytoplasmic increase is a continuous process.
- This statement is also correct. Cell growth does occur continuously as cells prepare for division, with gradual increases in cytoplasmic volume.
iv. The distribution of replicated chromosomes to daughter nuclei is a simple and straightforward event.
- This statement is misleading. The distribution of chromosomes during mitosis is a complex process involving several checkpoints and mechanisms to ensure accuracy.
Conclusion
Based on the evaluations:
- Correct Statements: ii and iii
- Incorrect Statements: i and iv
Thus, the correct answer is option a) ii and iii. The cell cycle is indeed a structured series of stages leading to division, with continuous growth occurring, while DNA replication is not continuous and chromosome distribution is complex.
Assertion (A): In animals, diploid somatic cells primarily undergo mitosis, with exceptions like haploid male honey bees.Reason (R): Plants can show mitotic divisions in both haploid and diploid cells, demonstrating greater versatility in cell division. - a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): In animals, diploid somatic cells primarily undergo mitosis, with exceptions like haploid male honey bees.
Reason (R): Plants can show mitotic divisions in both haploid and diploid cells, demonstrating greater versatility in cell division.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
- The Assertion is true; it accurately reflects that in the animal kingdom, mitotic cell division predominantly occurs in diploid somatic cells, with exceptions such as haploid male honey bees.
- The Reason is also true, as it correctly states that plants can undergo mitotic divisions in both haploid and diploid cells.
- However, the Reason does not explain the Assertion directly, as the flexibility of cell division in plants does not relate to the primary mitotic nature of animal cells.
Line in NCERT: "In animals, mitotic cell division is only seen in the diploid somatic cells. However, there are few exceptions to this where haploid cells divide by mitosis, for example, male honey bees. Against this, the plants can show mitotic divisions in both haploid and diploid cells."
During anaphasic movements of chromosomes, ______ of each chromosome is/are towards the pole and _____ of the chromosome trail(s) behind.- a)Centromere, arms
- b)Arms, centromere
- c)Chromatids, centromere
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During anaphasic movements of chromosomes, ______ of each chromosome is/are towards the pole and _____ of the chromosome trail(s) behind.
a)
Centromere, arms
b)
Arms, centromere
c)
Chromatids, centromere
d)
None of these
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
In anaphasic movement of chromosomes, the centromeres lead the path while the arms trail behind. As a result the anaphasic chromosomes appear V., L, J- and I-shaped. The shapes are formed respectively in metacentric, submetacentric, acrocentric and telocentric chromosomes.
At which stage of mitosis, the two daughter chromatids separate from each other, migrate towards the opposite poles and are now referred to as chromosomes of the future daughter nuclei?- a)Prophase
- b)Metaphase
- c)Anaphase
- d)Telophase
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
At which stage of mitosis, the two daughter chromatids separate from each other, migrate towards the opposite poles and are now referred to as chromosomes of the future daughter nuclei?
a)
Prophase
b)
Metaphase
c)
Anaphase
d)
Telophase
|
|
Simran Dey answered |
Explanation:
Anaphase:
In the anaphase stage of mitosis, the two daughter chromatids separate from each other. This separation is facilitated by the shortening of microtubules attached to the kinetochores of the sister chromatids. As the microtubules shorten, the sister chromatids are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell.
Migrate towards opposite poles:
During anaphase, the separated daughter chromatids migrate towards the opposite poles of the cell. This movement ensures that each daughter cell will receive an equal and identical set of chromosomes.
Referred to as chromosomes of the future daughter nuclei:
Once the daughter chromatids have reached the opposite poles of the cell, they are now referred to as chromosomes of the future daughter nuclei. These chromosomes will eventually be enclosed within new nuclear membranes to form the nuclei of the two daughter cells.
In conclusion, anaphase is a crucial stage of mitosis where the separation and migration of daughter chromatids occur, ensuring the equal distribution of genetic material to the daughter cells.
Anaphase:
In the anaphase stage of mitosis, the two daughter chromatids separate from each other. This separation is facilitated by the shortening of microtubules attached to the kinetochores of the sister chromatids. As the microtubules shorten, the sister chromatids are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell.
Migrate towards opposite poles:
During anaphase, the separated daughter chromatids migrate towards the opposite poles of the cell. This movement ensures that each daughter cell will receive an equal and identical set of chromosomes.
Referred to as chromosomes of the future daughter nuclei:
Once the daughter chromatids have reached the opposite poles of the cell, they are now referred to as chromosomes of the future daughter nuclei. These chromosomes will eventually be enclosed within new nuclear membranes to form the nuclei of the two daughter cells.
In conclusion, anaphase is a crucial stage of mitosis where the separation and migration of daughter chromatids occur, ensuring the equal distribution of genetic material to the daughter cells.
Mitotic spindle is mainly composed of _________ protein.- a)Tubulin
- b)Myosin
- c)Actin
- d)Actomyosin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mitotic spindle is mainly composed of _________ protein.
a)
Tubulin
b)
Myosin
c)
Actin
d)
Actomyosin
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Spindle fibres are structures formed from mictrobubules in the cytoplasm during cell division. Microtubules are made up of tubulin protein. Spindle fiberes move chromatids or chromosomes diametrically apart and gather them in two d=clusters at opposite ends (poles) of the cell.
Meiosis involves one cycle of ______- a)Separation of chromosomes
- b)Cytokinesis
- c)Karyokinesis
- d)DNA replication
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Meiosis involves one cycle of ______
a)
Separation of chromosomes
b)
Cytokinesis
c)
Karyokinesis
d)
DNA replication

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- Meiosis is divided into two stages- meiosis I and meiosis II.
- In each stage, the cell undergoes separation of chromosomes during anaphase I and anaphase II, cytokinesis and karyokinesis.
To build up food reserves in the cytoplasm, chromosomes become unfolded to start transcription of mRNA and rRNA, during which phase of meiosis I? - a)Diakinesis
- b)Zygotene
- c)Diplotene
- d)Leptotene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
To build up food reserves in the cytoplasm, chromosomes become unfolded to start transcription of mRNA and rRNA, during which phase of meiosis I?
a)
Diakinesis
b)
Zygotene
c)
Diplotene
d)
Leptotene
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
In diplotene stage of meiosis I, the chromosomes may unfold to nearly form and start transcription of mRNA and rRNA to build up food reserves in the cytoplasm. This process is most pronounced in the primary oocytes of amphibians, reptiles and birds. In some species, the chromosomes enlarge greatly, assuming lampbrush form.
Human cells in culture show a cell cycle to be completed in approximately - a)42 hours
- b)24 hours
- c)24 minutes
- d)24 seconds
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Human cells in culture show a cell cycle to be completed in approximately
a)
42 hours
b)
24 hours
c)
24 minutes
d)
24 seconds
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
(i) Cell division is the process by which a cell divides to form to nearly equal daughter cell which resembles the parent. The cell cycle is the sequence of events which occur during the cell growth and cell division. It is completed into two steps interphase and M-phase.
(ii) In the cell cycle interphase is the period between the end of one division to the beginning of next cell division. It is known as the resting phase. In the case of human beings it is around 24 hours then the M phase takes place.
(ii) In the cell cycle interphase is the period between the end of one division to the beginning of next cell division. It is known as the resting phase. In the case of human beings it is around 24 hours then the M phase takes place.
The correct sequence of phases of cell cycle is?- a)G2→M→G1→S
- b)S→G2→M→G1
- c)G1→S→G2→M
- d)M→G1→S→G2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct sequence of phases of cell cycle is?
a)
G2→M→G1→S
b)
S→G2→M→G1
c)
G1→S→G2→M
d)
M→G1→S→G2
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The cell cycle starts from interphase. Interphase is the phase in the cell cycle that prepares a cell nucleus for division. It has three stages — G1, S and G2 G1, Phase is the longest stage of interphase, also first growth phase or post-mitotic gap phase. Both and its nucleus grow in size. There is synthesis proteins, nucleotides, amino acids for histones an rich compounds. In S-Phase chromosomes along with their DNAs replicate. DNA content doubles during this phase. In G2-Phase there is increased synthesis of RNA and proteins. Cell organelles or their precursorsmultiply. Cell grows in Size.
Which phase of mitosis is essentially the reverse of prophase in terms of nuclear changes?- a)S – phase
- b)Anaphase
- c)Telophase
- d)Interphase
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which phase of mitosis is essentially the reverse of prophase in terms of nuclear changes?
a)
S – phase
b)
Anaphase
c)
Telophase
d)
Interphase
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
During telophase of mitosis viscosity of cytoplasm decreases. A new nuclear membrane is formed (either from older nuclear envelope or ER) around each set of chromosomes. Chromosomes overlap farming chromatin. The nucleolar organiser region of satellite chromosomes produce nucleolus for each daughter nucleus. Nucleoplasm surrounds in the area of chromatin. The gel state of spindle is converted into sol state and disappears. In this way two daughter nuclei are formed at the poles of spindle. Hence this phase is just reverse of prophase.
Doubling of the number of chromosomes can be achieved by disrupting mitotic cell division soon after :
- a)Metaphase
- b)Telophase
- c)Prophase
- d)Anaphase
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Doubling of the number of chromosomes can be achieved by disrupting mitotic cell division soon after :
a)
Metaphase
b)
Telophase
c)
Prophase
d)
Anaphase

|
EduRev NEET answered |
The doubling of the number of chromosomes can be achieved by disrupting mitotic cell division soon after DNA replication has occurred and before the separation of sister chromatids. This stage of mitosis is the metaphase, where chromosomes align in the center of the cell, prior to separation in anaphase.
If mitosis is disrupted after this point, sister chromatids cannot separate, leading to a doubling of the chromosome number in the resulting cells.
So, the correct answer is : option D
Amitosis usually occurs in- a)Eukaryotic cells
- b)Prokaryotic cells
- c)Meristems
- d)Spore mother cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Amitosis usually occurs in
a)
Eukaryotic cells
b)
Prokaryotic cells
c)
Meristems
d)
Spore mother cells
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Amitosis is a method of direct cell division in which the nucleus divides into two daughter nuclei without showing differentiation of chromosomes and development of spindle. It is commonly seen in prokaryotes.
Best material to study meiosis is- a)Root tip
- b)Ovary
- c)Young anther
- d)Pollen grain
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Best material to study meiosis is
a)
Root tip
b)
Ovary
c)
Young anther
d)
Pollen grain
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Meiosis takes place in reproductive organs. It results in formation of gametes with half the normal chromosome number. Young anthers are the best material to study meiosis.
Four different steps that occur during meiosis are given in the following list.
(i) Complete separation of chromatids
(ii) Pairing of homologous chromosomes
(iii) Lining up of paired chromosomes on equator
(iv) Crossing over between chromatids
Select the correct sequential arrangement of the steps.- a)(ii), (iii), (iv), (i)
- b)(iii), (ii), (iv), (i)
- c)(ii), (iv), (iii), (i)
- d)(iii), (i), (ii), (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Four different steps that occur during meiosis are given in the following list.
(i) Complete separation of chromatids
(ii) Pairing of homologous chromosomes
(iii) Lining up of paired chromosomes on equator
(iv) Crossing over between chromatids
Select the correct sequential arrangement of the steps.
(i) Complete separation of chromatids
(ii) Pairing of homologous chromosomes
(iii) Lining up of paired chromosomes on equator
(iv) Crossing over between chromatids
Select the correct sequential arrangement of the steps.
a)
(ii), (iii), (iv), (i)
b)
(iii), (ii), (iv), (i)
c)
(ii), (iv), (iii), (i)
d)
(iii), (i), (ii), (iv)
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs in zygotene and crossing over occurs in pachytene stage of prophase I of meiosis I. Paired chromosomes line up on equator in metaphase I. Then there is complete separation of chromatids in anaphase I of meiosis I.
Cell would normally proceed to mitosis without interruption- a)Once it has entered the S phase
- b)Once it has entered the G2 phase
- c)At any time during cell division activity
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cell would normally proceed to mitosis without interruption
a)
Once it has entered the S phase
b)
Once it has entered the G2 phase
c)
At any time during cell division activity
d)
None of these
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The availability of mitogen and energy rich compounds decide wheter G1 phase will be arrested (G0 phase) or undergo S-phase. This point is called check point or G1 cyclin or G1 point. Once the check point of G1-phase is crossed and cell has entered S-phase, cell cycle will go on further division till completion.
A cell's division time is 1 minute. In 20 minutes, a culture tube (culture medium) is 1/8th filled with cells. When the tube will be fully filled?- a)21 minutes
- b)23 minutes
- c)60 minutes
- d)120 minutes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A cell's division time is 1 minute. In 20 minutes, a culture tube (culture medium) is 1/8th filled with cells. When the tube will be fully filled?
a)
21 minutes
b)
23 minutes
c)
60 minutes
d)
120 minutes
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
In 20 mins. Culture tube 1/8th filled with cells. Each cell divides every minute producing two daughter cells.
Hence, 21 min = 1/8 × 2 = 1/4
In 22 min 1/4 × 2 = 1/2
In 23 min 1/2 × 2 = 1
That means, in 23 minutes the culture tube will be completely filled.
Hence, 21 min = 1/8 × 2 = 1/4
In 22 min 1/4 × 2 = 1/2
In 23 min 1/2 × 2 = 1
That means, in 23 minutes the culture tube will be completely filled.
The separation of two chromatids of each chromosome at early anaphase is initiated by- a)The interaction of centromere with the chromosomal fibres
- b)The elongation of metaphasic spindle
- c)The force of repulsion between the dividend kinetochores
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The separation of two chromatids of each chromosome at early anaphase is initiated by
a)
The interaction of centromere with the chromosomal fibres
b)
The elongation of metaphasic spindle
c)
The force of repulsion between the dividend kinetochores
d)
All of these
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Kinetochore is a plate-like structure by which microtubules of the spindle attach to the centromere of a chromosome during nuclear division. The centromere of each chromosome divides into two, so that each chormatied comes to have its own centromere. The two chromatids now start repelling each otherand separate completely to become daughter chromosmes. the daughter or new chromosmes. The daughter or new chromosomes move towards the poles of spindle along the path of their chromosome fibres.
Crossing over in diploid organism is responsible for- a)Dominance of genes
- b)Linkage between genes
- c)Segregation of alleles
- d)Recombination of linked allele
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Crossing over in diploid organism is responsible for
a)
Dominance of genes
b)
Linkage between genes
c)
Segregation of alleles
d)
Recombination of linked allele
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Crossing over is a process of exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of two homologous chromosomes and and leads to recombination of genes. It is an enzyme mediated process.
Disjunction refers to- a)The separation of homologous chromosomes at anaphase - I
- b)The type of chromosomal aberration in which there is loss of a part of a chromosome
- c)Incompatibility in fungi and other thallophytes
- d)Modification of gene action by a nonallelic gene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Disjunction refers to
a)
The separation of homologous chromosomes at anaphase - I
b)
The type of chromosomal aberration in which there is loss of a part of a chromosome
c)
Incompatibility in fungi and other thallophytes
d)
Modification of gene action by a nonallelic gene
|
|
Pranjal Shah answered |
Understanding Disjunction
Disjunction is a critical process in cell division, particularly during meiosis. It specifically refers to the separation of homologous chromosomes, which is essential for the proper distribution of genetic material to daughter cells.
What Happens During Disjunction?
- Meiosis Overview: Meiosis consists of two consecutive cell divisions, meiosis I and meiosis II. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair up and undergo recombination, leading to genetic diversity.
- Anaphase I Role: Disjunction occurs during anaphase I, where homologous chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell. This ensures that each daughter cell receives one chromosome from each homologous pair.
Importance of Disjunction
- Genetic Variation: Disjunction contributes to genetic variation in gametes, which is vital for evolution and adaptation in populations.
- Chromosomal Stability: Proper disjunction prevents aneuploidy, a condition where cells have an abnormal number of chromosomes, which can lead to developmental disorders and diseases.
Clarification of Other Options
- Option B: Refers to chromosomal aberrations, specifically deletion, which is unrelated to disjunction.
- Option C: Discusses incompatibility in fungi, not relevant to chromosome behavior.
- Option D: Involves gene action modification, distinct from the process of disjunction.
Conclusion
Disjunction is integral to meiosis, ensuring the correct separation of homologous chromosomes during anaphase I, which is crucial for maintaining genetic integrity and diversity. Understanding this concept is essential for grasping the fundamentals of genetics and cell biology, particularly for NEET aspirants.
Disjunction is a critical process in cell division, particularly during meiosis. It specifically refers to the separation of homologous chromosomes, which is essential for the proper distribution of genetic material to daughter cells.
What Happens During Disjunction?
- Meiosis Overview: Meiosis consists of two consecutive cell divisions, meiosis I and meiosis II. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair up and undergo recombination, leading to genetic diversity.
- Anaphase I Role: Disjunction occurs during anaphase I, where homologous chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell. This ensures that each daughter cell receives one chromosome from each homologous pair.
Importance of Disjunction
- Genetic Variation: Disjunction contributes to genetic variation in gametes, which is vital for evolution and adaptation in populations.
- Chromosomal Stability: Proper disjunction prevents aneuploidy, a condition where cells have an abnormal number of chromosomes, which can lead to developmental disorders and diseases.
Clarification of Other Options
- Option B: Refers to chromosomal aberrations, specifically deletion, which is unrelated to disjunction.
- Option C: Discusses incompatibility in fungi, not relevant to chromosome behavior.
- Option D: Involves gene action modification, distinct from the process of disjunction.
Conclusion
Disjunction is integral to meiosis, ensuring the correct separation of homologous chromosomes during anaphase I, which is crucial for maintaining genetic integrity and diversity. Understanding this concept is essential for grasping the fundamentals of genetics and cell biology, particularly for NEET aspirants.
Assertion (A): In adult animals, certain cells like heart cells do not undergo mitotic division and enter a quiescent stage.Reason (R): Cells in the quiescent stage (G0) remain metabolically active but do not proliferate unless necessary. - a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): In adult animals, certain cells like heart cells do not undergo mitotic division and enter a quiescent stage.
Reason (R): Cells in the quiescent stage (G0) remain metabolically active but do not proliferate unless necessary.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
- The Assertion is true because it correctly states that certain adult animal cells, such as heart cells, do not divide and enter a quiescent stage.
- The Reason is also true as it accurately describes the nature of cells in the G0 phase, indicating they are metabolically active but not proliferative.
- Furthermore, the Reason correctly explains the Assertion by providing the functional context of why these cells do not divide.
Line in NCERT: "Some cells in the adult animals do not appear to exhibit division (e.g., heart cells) and many other cells divide only occasionally, as needed to replace cells that have been lost because of injury or cell death. These cells that do not divide further exit G₁ phase to enter an inactive stage called quiescent stage (G) of the cell cycle. Cells in this stage remain metabolically active but no longer proliferate unless called on to do so depending on the requirement of the organism."
______ is the best stage to count the number and study the morphology of chromosomes.- a)Prophase
- b)Metaphase
- c)Anaphase
- d)Telophase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
______ is the best stage to count the number and study the morphology of chromosomes.
a)
Prophase
b)
Metaphase
c)
Anaphase
d)
Telophase
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
Metaphase is the best phase to count total number of chromosomes in any species and detailed study of morphology of chromosome. Idiogram (arrangement of chromosomes in a series of decreasing length) can be drawn in the stage.
The role of mitosis is not merely to divide a cell into two daughter cells but to ensure genetic continuity from one cell generation to another cell generation. The mechanism ensuring genetic continuity is - a)Formation of cells with new chromosomes
- b)Formation of two daughter cells
- c)Formation of two cells with identical DNA
- d)Halving the chromosome number between the two new cells
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The role of mitosis is not merely to divide a cell into two daughter cells but to ensure genetic continuity from one cell generation to another cell generation. The mechanism ensuring genetic continuity is
a)
Formation of cells with new chromosomes
b)
Formation of two daughter cells
c)
Formation of two cells with identical DNA
d)
Halving the chromosome number between the two new cells
|
|
Rahul Majumdar answered |
Explanation:
Mitosis is a process of cell division in which a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells, each containing the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. The role of mitosis is not merely to divide a cell into two daughter cells but to ensure genetic continuity from one cell generation to another cell generation. The mechanism ensuring genetic continuity is the formation of two cells with identical DNA.
Importance of genetic continuity:
Genetic continuity is essential for the survival of a species. Without genetic continuity, each new generation of cells would be different from the previous generation, leading to genetic diversity and the loss of important traits. Mitosis ensures genetic continuity by producing two daughter cells that are identical to the parent cell.
Role of mitosis in ensuring genetic continuity:
During mitosis, the genetic material of the parent cell is replicated and then divided equally between the two daughter cells. This ensures that each daughter cell has the same genetic information as the parent cell, ensuring genetic continuity.
The process of mitosis:
The process of mitosis can be divided into four main stages:
1. Prophase: During this stage, the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
2. Metaphase: During this stage, the chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell, and the spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes.
3. Anaphase: During this stage, the spindle fibers pull the sister chromatids apart, and the chromosomes move towards opposite poles of the cell.
4. Telophase: During this stage, the chromosomes reach the poles of the cell, and the nuclear envelope reforms around each set of chromosomes.
Cytokinesis:
After the completion of mitosis, the cell undergoes cytokinesis, in which the cytoplasm divides, and two daughter cells are formed. Each daughter cell has the same genetic information as the parent cell, ensuring genetic continuity.
Mitosis is a process of cell division in which a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells, each containing the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. The role of mitosis is not merely to divide a cell into two daughter cells but to ensure genetic continuity from one cell generation to another cell generation. The mechanism ensuring genetic continuity is the formation of two cells with identical DNA.
Importance of genetic continuity:
Genetic continuity is essential for the survival of a species. Without genetic continuity, each new generation of cells would be different from the previous generation, leading to genetic diversity and the loss of important traits. Mitosis ensures genetic continuity by producing two daughter cells that are identical to the parent cell.
Role of mitosis in ensuring genetic continuity:
During mitosis, the genetic material of the parent cell is replicated and then divided equally between the two daughter cells. This ensures that each daughter cell has the same genetic information as the parent cell, ensuring genetic continuity.
The process of mitosis:
The process of mitosis can be divided into four main stages:
1. Prophase: During this stage, the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
2. Metaphase: During this stage, the chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell, and the spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes.
3. Anaphase: During this stage, the spindle fibers pull the sister chromatids apart, and the chromosomes move towards opposite poles of the cell.
4. Telophase: During this stage, the chromosomes reach the poles of the cell, and the nuclear envelope reforms around each set of chromosomes.
Cytokinesis:
After the completion of mitosis, the cell undergoes cytokinesis, in which the cytoplasm divides, and two daughter cells are formed. Each daughter cell has the same genetic information as the parent cell, ensuring genetic continuity.
During meiosis - I in humans, one of the daughter cells receives- a)Only maternal chromosomes
- b)A mixture of maternal and paternal chromosomes
- c)Same number of chromosomes as present in parent cell
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During meiosis - I in humans, one of the daughter cells receives
a)
Only maternal chromosomes
b)
A mixture of maternal and paternal chromosomes
c)
Same number of chromosomes as present in parent cell
d)
None of the above
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
During pachytene sub-stage of meiosis I, crossing over i.e. exhcnage of genetic material takes place between homologous, which results in recombinations. The two homologous chromosomes are contributed by different parents. One of them is partnerl chromosome and the other one is maternal chormosome.
During meiosis -I, chromosome number?- a)is reduced to half
- b)doubles up
- c)remains the same
- d)either (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During meiosis -I, chromosome number?
a)
is reduced to half
b)
doubles up
c)
remains the same
d)
either (a) and (b)
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Meiosis is the type of cell division by which gamete cells (eggs and sperm) are produced. Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions and one cytoplasmic division that produce four haploid cells. The first division (meiosis 1) is the reductional division during which number of chromosomes is reduced to half. The second division (meiosis II) separates the chromatids. It is called equational division as chromosome number remains the same as produced after meiosis-l.
At what phase of meiosis there are two cells, each with separated sister chromatids that have been moved to opposite spindle poles?- a)Anaphase II
- b)Anaphase I
- c)Telophase II
- d)Telophase I
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At what phase of meiosis there are two cells, each with separated sister chromatids that have been moved to opposite spindle poles?
a)
Anaphase II
b)
Anaphase I
c)
Telophase II
d)
Telophase I
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Anaphase II, where the centromeres are cleaved, allows the kinetochores to pull the sister chromatids apart. The sister chromatids by convention are now called sister chromosomes and they are pulled towards opposte poles.
The cells that do not divide further, exit G1 phase to enter an inactive stage called_____of the cell cycle.- a)G1 stage
- b)G2 stage
- c)S stage
- d)G0 stage
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The cells that do not divide further, exit G1 phase to enter an inactive stage called_____of the cell cycle.
a)
G1 stage
b)
G2 stage
c)
S stage
d)
G0 stage
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
The phase in which cells fail to divide further (do not enter S- phase after G1 -phase) and undergo differentiation is known as G0 phase or quiescent stage. It occurs due to non availability of mitogen and energy rich compounds. The cells remain metabolically active, grow in size and differentiate for particular function after attaining a particular shape.
Read the following statements about cell division and select the correct ones.
(i) M phase represents the phase when actual cell division occurs and I phase represents the phase between two successive M phases.
(ii) In the 24 hours average duration of cell cycle of a human cell, cell division proper lasts for only about an hour.
(iii) M phase constitutes more than 95% of the duration of cell cycle.- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(i) and (iii)
- d)(i), (ii) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements about cell division and select the correct ones.
(i) M phase represents the phase when actual cell division occurs and I phase represents the phase between two successive M phases.
(ii) In the 24 hours average duration of cell cycle of a human cell, cell division proper lasts for only about an hour.
(iii) M phase constitutes more than 95% of the duration of cell cycle.
(i) M phase represents the phase when actual cell division occurs and I phase represents the phase between two successive M phases.
(ii) In the 24 hours average duration of cell cycle of a human cell, cell division proper lasts for only about an hour.
(iii) M phase constitutes more than 95% of the duration of cell cycle.
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(i) and (iii)
d)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
|
|
Nilesh Choudhury answered |
Answer:
The correct statements about cell division are:
(i) M phase represents the phase when actual cell division occurs and I phase represents the phase between two successive M phases.
(ii) In the 24 hours average duration of cell cycle of a human cell, cell division proper lasts for only about an hour.
Explanation:
Cell division is a fundamental process that allows organisms to grow, develop, and repair damaged tissues. It involves the replication and distribution of genetic material to ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. The cell cycle consists of several phases, including interphase (I phase) and mitosis (M phase).
(i) M phase represents the phase when actual cell division occurs and I phase represents the phase between two successive M phases:
- The cell cycle is divided into two main phases: interphase (I phase) and mitosis (M phase).
- Interphase is further divided into three subphases: G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase.
- During interphase, the cell undergoes growth, DNA replication, and preparation for cell division.
- M phase, or mitosis, is the phase when actual cell division occurs. It consists of several stages, including prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- After mitosis, the cell enters interphase again, completing one full cycle of cell division.
(ii) In the 24 hours average duration of cell cycle of a human cell, cell division proper lasts for only about an hour:
- The duration of the cell cycle varies among different organisms and cell types.
- In general, the average duration of the cell cycle in humans is approximately 24 hours.
- However, the actual process of cell division, which occurs during mitosis, is relatively short.
- Mitosis typically lasts for only about an hour, while interphase occupies the majority of the cell cycle duration.
Therefore, both statements (i) and (ii) are correct. M phase represents the phase when actual cell division occurs, and I phase represents the phase between two successive M phases. In the 24 hours average duration of the cell cycle of a human cell, cell division proper lasts for only about an hour.
The correct statements about cell division are:
(i) M phase represents the phase when actual cell division occurs and I phase represents the phase between two successive M phases.
(ii) In the 24 hours average duration of cell cycle of a human cell, cell division proper lasts for only about an hour.
Explanation:
Cell division is a fundamental process that allows organisms to grow, develop, and repair damaged tissues. It involves the replication and distribution of genetic material to ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. The cell cycle consists of several phases, including interphase (I phase) and mitosis (M phase).
(i) M phase represents the phase when actual cell division occurs and I phase represents the phase between two successive M phases:
- The cell cycle is divided into two main phases: interphase (I phase) and mitosis (M phase).
- Interphase is further divided into three subphases: G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase.
- During interphase, the cell undergoes growth, DNA replication, and preparation for cell division.
- M phase, or mitosis, is the phase when actual cell division occurs. It consists of several stages, including prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- After mitosis, the cell enters interphase again, completing one full cycle of cell division.
(ii) In the 24 hours average duration of cell cycle of a human cell, cell division proper lasts for only about an hour:
- The duration of the cell cycle varies among different organisms and cell types.
- In general, the average duration of the cell cycle in humans is approximately 24 hours.
- However, the actual process of cell division, which occurs during mitosis, is relatively short.
- Mitosis typically lasts for only about an hour, while interphase occupies the majority of the cell cycle duration.
Therefore, both statements (i) and (ii) are correct. M phase represents the phase when actual cell division occurs, and I phase represents the phase between two successive M phases. In the 24 hours average duration of the cell cycle of a human cell, cell division proper lasts for only about an hour.
Among eukaryotes, replication of DNA takes place in :- a)S phase
- b)G1 phase
- c)G2 phase
- d)M phase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among eukaryotes, replication of DNA takes place in :
a)
S phase
b)
G1 phase
c)
G2 phase
d)
M phase
|
|
Akshita Pillai answered |
Overview of DNA Replication in Eukaryotes
DNA replication is a crucial process that ensures genetic information is accurately copied and passed on during cell division. In eukaryotic cells, this process occurs specifically during the S phase of the cell cycle.
Phases of the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle consists of several phases:
- G1 Phase: This is the first gap phase, where the cell grows and prepares for DNA synthesis. No replication occurs during this phase.
- S Phase: This is the synthesis phase. Here, DNA replication occurs, resulting in the duplication of the genetic material. Each chromosome is replicated to form sister chromatids.
- G2 Phase: This is the second gap phase, where the cell continues to grow and produces proteins necessary for mitosis. DNA replication is already complete by this stage.
- M Phase: This is the mitotic phase, where the cell divides. The replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. No DNA replication occurs in this phase.
Importance of the S Phase
- Accuracy of Replication: The S phase is critical for ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes.
- Cell Cycle Regulation: The transition into the S phase is tightly regulated by various checkpoints to prevent errors in DNA replication that could lead to mutations or cancer.
Conclusion
In summary, DNA replication in eukaryotes exclusively takes place during the S phase of the cell cycle. This phase is essential for the proper duplication of genetic material, ensuring that each new cell has the correct information needed for functioning and growth. Thus, the correct answer to the question is option 'A'.
DNA replication is a crucial process that ensures genetic information is accurately copied and passed on during cell division. In eukaryotic cells, this process occurs specifically during the S phase of the cell cycle.
Phases of the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle consists of several phases:
- G1 Phase: This is the first gap phase, where the cell grows and prepares for DNA synthesis. No replication occurs during this phase.
- S Phase: This is the synthesis phase. Here, DNA replication occurs, resulting in the duplication of the genetic material. Each chromosome is replicated to form sister chromatids.
- G2 Phase: This is the second gap phase, where the cell continues to grow and produces proteins necessary for mitosis. DNA replication is already complete by this stage.
- M Phase: This is the mitotic phase, where the cell divides. The replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. No DNA replication occurs in this phase.
Importance of the S Phase
- Accuracy of Replication: The S phase is critical for ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes.
- Cell Cycle Regulation: The transition into the S phase is tightly regulated by various checkpoints to prevent errors in DNA replication that could lead to mutations or cancer.
Conclusion
In summary, DNA replication in eukaryotes exclusively takes place during the S phase of the cell cycle. This phase is essential for the proper duplication of genetic material, ensuring that each new cell has the correct information needed for functioning and growth. Thus, the correct answer to the question is option 'A'.
What does (i) and (ii) represent in the given flowchart?
- a)(i) = 2n
(ii) = n - b)(i) = n
(ii) = n - c)(i) = n
(ii) = 2n - d)(i) = 2n
(ii) = 2n
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What does (i) and (ii) represent in the given flowchart?

a)
(i) = 2n
(ii) = n
(ii) = n
b)
(i) = n
(ii) = n
(ii) = n
c)
(i) = n
(ii) = 2n
(ii) = 2n
d)
(i) = 2n
(ii) = 2n
(ii) = 2n
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Meiosis I consists of separation of the homologous chromosomes, each made up of two sister chormatids into two cells. Entire haploid content of chomosomes is contained in each of the resulting daughter cells. The first meiotic division therefore reduces the ploidy of the original cell by a factor of 2. Meiosis II consists of decoupling of each chormosome sister strands (chromatids) and segregating the individual chromatids into haploid daughter cells. The two cells resulting from meiosis I divide during meiosis II, creating 4 haploid daughter cells.
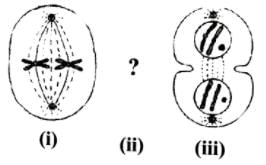 In above sequence of figures showing different stages of cell division, the missing stage (ii) is
In above sequence of figures showing different stages of cell division, the missing stage (ii) is- a)
- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

In above sequence of figures showing different stages of cell division, the missing stage (ii) is
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Figure (i) shows metaphase II and figure (iii) shows telophase II, Hence, the missing figure is that of anphase II.
The given graph shows the change in DNA content during various phases (A to D) in a typical mitotic cell cycle. Identify the phases and select the correct option.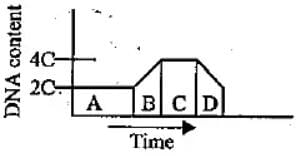
- a)A - G2, B - G1, C - S, D - M
- b)A - G, B - S, C - G2, D - M
- c)A - G1, B - S, C - G2, D - M
- d)A - M, B - G1, C - S, D - G2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The given graph shows the change in DNA content during various phases (A to D) in a typical mitotic cell cycle. Identify the phases and select the correct option.

a)
A - G2, B - G1, C - S, D - M
b)
A - G, B - S, C - G2, D - M
c)
A - G1, B - S, C - G2, D - M
d)
A - M, B - G1, C - S, D - G2
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
During G1 phase, DNA content is 2C.S phase is marked by replication of DNA and the amount of DNA per cell is doubled. During G2 phase, synthesis of RNA and proteins takes place. During mitosis, DNA content gets equally distributed among two daughter cells.
The figure given below shows a cell undergoing meiosis.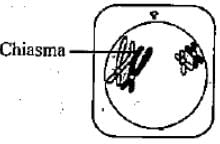
Which of the options below shows the next stage in the process?- a)
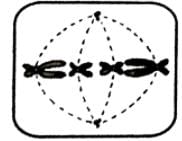
- b)
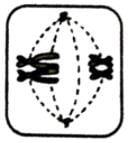
- c)

- d)
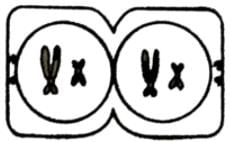
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The figure given below shows a cell undergoing meiosis.

Which of the options below shows the next stage in the process?
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The given figure is showing diplotene stage of prophase I of meiosis I. Next stage would be metaphase I.
Identify the given figures showing meiotic phases and select the correct option.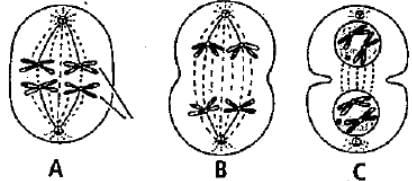
- a)A - Metaphase, B - Anaphase, C - Telophase
- b)A - Metaphase I, B - Anaphase I, C - Telophase I
- c)A - Metaphase II, B - Anaphase II, C - Telophase II
- d)A - Anaphase I, B -Metaphase I, C - Telophase I
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the given figures showing meiotic phases and select the correct option.

a)
A - Metaphase, B - Anaphase, C - Telophase
b)
A - Metaphase I, B - Anaphase I, C - Telophase I
c)
A - Metaphase II, B - Anaphase II, C - Telophase II
d)
A - Anaphase I, B -Metaphase I, C - Telophase I
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
All the stages are of the meiosis 1 because here we can see the bivalent or tetrad stages. Metaphase is the stage where chromosome comes on the equator and bivalent arrange themselves on the equatorial plate. Then anaphase 1 involves the separation of a homologous chromosome which start moving up to opposite poles and each tetrad is divided into two daughter cells. So anaphase involves the production of chromosome number and is also known as disjunction. Telophase 1 shows the formation of two daughter nuclei but the chromosome number is half then the chromosome number of mother cell and nuclear membrane reappears.
If 2n = 4, then identify the figures A, B and C, as per the following codes and select the correct option.
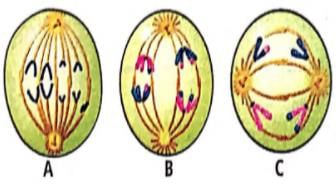
Anaphase of meiosis I = (i)
Anaphase of mitosis = (ii)
Anaphase of meiosis II = (iii)- a)A - (ii), B - (i), C - (iii)
- b)A - (iii), B - (ii), C - (i)
- c)A - (i), B - (ii), C - (iii)
- d)A - (iii), B - (i), C - (ii)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If 2n = 4, then identify the figures A, B and C, as per the following codes and select the correct option.

Anaphase of meiosis I = (i)
Anaphase of mitosis = (ii)
Anaphase of meiosis II = (iii)

Anaphase of meiosis I = (i)
Anaphase of mitosis = (ii)
Anaphase of meiosis II = (iii)
a)
A - (ii), B - (i), C - (iii)
b)
A - (iii), B - (ii), C - (i)
c)
A - (i), B - (ii), C - (iii)
d)
A - (iii), B - (i), C - (ii)
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
During anaphase of mitosis, each chromosome arranged at metaphase plate is split and two daughter chromatids are formed. Centromeres split and chromatids move to opposite poles. During anphase I of meiosis I, the homologous chormosomes separate, while sister chromatids remain associated at their centromeres. Anaphase II of meiosis II begins with simultanoeus splitting of the centromere of each chromosome allowing them to move towards oppostie poles of the cell.
During cell division, the spindle fibres get attached to condensing chromosome at a highly differentiated region. This region is called as- a)Chromosome
- b)Chromocentre
- c)Centriole
- d)Kinetochore
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
During cell division, the spindle fibres get attached to condensing chromosome at a highly differentiated region. This region is called as
a)
Chromosome
b)
Chromocentre
c)
Centriole
d)
Kinetochore
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The key feature of metaphase is the attachment of spindle fibers to kinetochores of chromosomes. Kinetochores are disc-shaped structure at the surface of the centromeres. These structures serve as the site of attachment of spindle fibres to the chromosomes that are moved toward poles.
In a somatic cell cycle, DNA synthesis takes place in which of the following phases?- a)S phase
- b)G1 phase
- c)G2 phase
- d)Prometaphase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a somatic cell cycle, DNA synthesis takes place in which of the following phases?
a)
S phase
b)
G1 phase
c)
G2 phase
d)
Prometaphase

|
Infinity Academy answered |
- The cell cycle consists of several distinct phases, including interphase and mitosis. Interphase, which is the longest phase of the cell cycle, can be further divided into three subphases: G1 (gap phase 1), S (synthesis phase), and G2 (gap phase 2).
- During the S phase, DNA synthesis occurs. This is the period when the cell replicates its DNA to ensure that each daughter cell produced during cell division receives a complete set of genetic information.
- The DNA replication process involves unwinding and separating the two strands of the DNA double helix and synthesising new complementary strands using the existing strands as templates. As a result, each chromosome is duplicated, and sister chromatids are formed, which remain attached at the centromere.
- After the S phase, the cell progresses into the G2 phase, where it prepares for cell division. The subsequent phase is mitosis, which includes prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, leading to the separation of sister chromatids and the formation of two identical daughter cells.
- Therefore, DNA synthesis occurs specifically during the S phase of the somatic cell cycle.
Chapter doubts & questions for Cell Cycle and Cell Division - NCERT Based Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Cell Cycle and Cell Division - NCERT Based Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









