All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT Based Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Body Fluids and Circulation for NEET Exam
Carotid artery supplies- a)Oxygenated blood to lungs
- b)Oxygenated blood to intestine
- c)Oxygenated blood to brain
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Carotid artery supplies
a)
Oxygenated blood to lungs
b)
Oxygenated blood to intestine
c)
Oxygenated blood to brain
d)
None of these
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
The carotid arteries are major blood vessels in the neck that supply blood to the brain, neck, and face. There are two carotid arteries, one on the right and one on the left. In the neck, each carotid artery branches into two divisions:
(i) The internal carotid artery supplies blood to the brain.
(ii) The external carotid artery supplies blood to the face and neck.
So, the correct answer is 'Oxygenated blood to brain'
(i) The internal carotid artery supplies blood to the brain.
(ii) The external carotid artery supplies blood to the face and neck.
So, the correct answer is 'Oxygenated blood to brain'
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: The SA node acts as pacemaker.
Statement 2: The SA node is located in the wall of the right atrium near the inter-atrial septum.- a)Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
- b)Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
- c)Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
- d)Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: The SA node acts as pacemaker.
Statement 2: The SA node is located in the wall of the right atrium near the inter-atrial septum.
Statement 1: The SA node acts as pacemaker.
Statement 2: The SA node is located in the wall of the right atrium near the inter-atrial septum.
a)
Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
b)
Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
c)
Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
d)
Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The heart beat originates from the SA node which acts a pacemaker. SA node lies in the wall of the right atrium near the opening of the superior vena cava.
In ECG, P-R interval corresponds to
- a)time delay in A-V node
- b)S-A nodal conduction time
- c)increased ventricular contraction
- d)time interval between onset of ventricular contraction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In ECG, P-R interval corresponds to
a)
time delay in A-V node
b)
S-A nodal conduction time
c)
increased ventricular contraction
d)
time interval between onset of ventricular contraction
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
- Each peak in the ECG is identified with a letter from P to T that corresponds to a specific electrical activity of the heart.
- The P- wave represents the electrical excitation or depolarization of the atria.
- The QRS complex represents the depolarization of the ventricles which initiates the ventricular contraction.
- The contraction starts shortly after Q and marks the beginning of the systole.
- The T- wave represents the return of the ventricles from excited to a normal state or repolarization.
- The end of the T-wave marks the end of systole.
So, the correct option is 'Time delay in A-V node'.
The problem of electrical discontinuity caused in the normal heart by the connective tissue separating the atria from the ventricles is solved by?
- a)Having the A-V node function as a secondary pacemaker
- b)Coordinating electrical activity in the atria with electrical activity in the ventricles by connecting them via the bundle of His
- c)Having an ectopic pacemaker
- d)Coordinating electrical activity in the atria with electrical activity in the ventricles by connecting them via the vagus nerve
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The problem of electrical discontinuity caused in the normal heart by the connective tissue separating the atria from the ventricles is solved by?
a)
Having the A-V node function as a secondary pacemaker
b)
Coordinating electrical activity in the atria with electrical activity in the ventricles by connecting them via the bundle of His
c)
Having an ectopic pacemaker
d)
Coordinating electrical activity in the atria with electrical activity in the ventricles by connecting them via the vagus nerve
|
|
Sanaya Mishra answered |
Solution:
The connective tissue separating the atria from the ventricles is called the atrioventricular (AV) node. This node acts as an electrical insulator and prevents electrical signals from directly passing between the atria and ventricles. This separation is necessary for the normal functioning of the heart, as it allows the atria to contract first, pumping blood into the ventricles before they contract and pump blood out of the heart.
To overcome this electrical discontinuity, the heart has a specialized conducting system that connects the atria and ventricles and coordinates their electrical activity. This system starts with the sinoatrial (SA) node, located in the right atrium, which acts as the primary pacemaker of the heart. The electrical signals generated by the SA node spread through the atria, causing them to contract.
The electrical signals then pass through the AV node, which slows down the conduction of the signal, allowing the ventricles time to fill with blood. After a brief delay, the electrical signals pass through the bundle of His, a specialized bundle of fibers that divides into the left and right bundle branches, which then spread through the ventricles and cause them to contract.
Coordinating electrical activity in the atria with electrical activity in the ventricles by connecting them via the bundle of His:
The bundle of His is a specialized group of cells that conducts electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles. It is an essential part of the heart's electrical conduction system and helps coordinate the contraction of the atria and ventricles. The bundle of His is located in the interventricular septum and divides into the left and right bundle branches, which then spread through the ventricles and cause them to contract. By connecting the electrical activity in the atria with the electrical activity in the ventricles via the bundle of His, the electrical discontinuity caused by the connective tissue separating the atria from the ventricles is solved.
The connective tissue separating the atria from the ventricles is called the atrioventricular (AV) node. This node acts as an electrical insulator and prevents electrical signals from directly passing between the atria and ventricles. This separation is necessary for the normal functioning of the heart, as it allows the atria to contract first, pumping blood into the ventricles before they contract and pump blood out of the heart.
To overcome this electrical discontinuity, the heart has a specialized conducting system that connects the atria and ventricles and coordinates their electrical activity. This system starts with the sinoatrial (SA) node, located in the right atrium, which acts as the primary pacemaker of the heart. The electrical signals generated by the SA node spread through the atria, causing them to contract.
The electrical signals then pass through the AV node, which slows down the conduction of the signal, allowing the ventricles time to fill with blood. After a brief delay, the electrical signals pass through the bundle of His, a specialized bundle of fibers that divides into the left and right bundle branches, which then spread through the ventricles and cause them to contract.
Coordinating electrical activity in the atria with electrical activity in the ventricles by connecting them via the bundle of His:
The bundle of His is a specialized group of cells that conducts electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles. It is an essential part of the heart's electrical conduction system and helps coordinate the contraction of the atria and ventricles. The bundle of His is located in the interventricular septum and divides into the left and right bundle branches, which then spread through the ventricles and cause them to contract. By connecting the electrical activity in the atria with the electrical activity in the ventricles via the bundle of His, the electrical discontinuity caused by the connective tissue separating the atria from the ventricles is solved.
Heart pumps blood more forcefully in older persons than younger ones due to- a)Decrease in oxygen content of blood
- b)Decrease in elasticity of arteries
- c)Fall in nutrient content of blood
- d)Increase in elasticity of arteries
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Heart pumps blood more forcefully in older persons than younger ones due to
a)
Decrease in oxygen content of blood
b)
Decrease in elasticity of arteries
c)
Fall in nutrient content of blood
d)
Increase in elasticity of arteries
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
As one ages, arteries lose their elasticity. Consequently the heart has to pump the blood more forcefully in order to fulfill the need of the body cells.
Find the incorrect answer from the following?- a)Veins are typically larger in diameter than arteries
- b)Because of their small size,capillaries contain blood that is moving more quickly than in other parts of the circulatory system
- c)The walls of arteries are elastic,enabling them to stretch and shrink during changes in blood pressure
- d)Veins contain more blood than any other part of the circulatory system
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the incorrect answer from the following?
a)
Veins are typically larger in diameter than arteries
b)
Because of their small size,capillaries contain blood that is moving more quickly than in other parts of the circulatory system
c)
The walls of arteries are elastic,enabling them to stretch and shrink during changes in blood pressure
d)
Veins contain more blood than any other part of the circulatory system
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
On an average, capillaries are about 1 mm long and 8 mm in diameter. Although each capillary is very narrow, there are so many of them that the capillaries have the greatest total cross sectional area of any other type of vessel. Consequently, the blood decreases in velocity as it passes through the capillary beds, allowing more time for it to exchange materials with the surrounding extracellular fluid. Blood also loses most of its pressure in passing through the vast capillary networks and so is under very low pressure when it enters the veins.
In which of the following situations, there is a risk factorfor children acquiring erythroblastosis foetalis?- a)Mother is Rh -ve and father is Rh -ve
- b)Mother is Rh -ve and father is Rh +ve
- c)Mother is Rh +ve and father is Rh +ve
- d)Mother is Rh +ve and father is Rh -ve
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following situations, there is a risk factorfor children acquiring erythroblastosis foetalis?
a)
Mother is Rh -ve and father is Rh -ve
b)
Mother is Rh -ve and father is Rh +ve
c)
Mother is Rh +ve and father is Rh +ve
d)
Mother is Rh +ve and father is Rh -ve
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
During first pregnancy, Rh antigens of the foetus do not get exposed to the Rh -ve blood of the mother as the two bloods are well separated by placenta. However, at the time of delivery, there are chances of exposure of the maternal blood to small amounts of Rh +ve blood of the foetus. Thus mother's body starts preparing antibodies against Rh antigens in her blood. In case of subsequent pregnancies, the Rh antbodies from the mother can leak into the blood of the Rh +ve foetus and destroy the foetal RBCS This could be fatal for the foetus or could cause severe anaemia and jaundice. This condition is called erythroblastosis foetalis.
Consider the following statements (A-C) each with one or two blanks.
(A) (1) are the most abundant cells (60-65 percent) of the total WBCs and (2) are the least (0.5-1 percent) among them.
(B) Platelets are cell fragments produced from (3).
(C) During clot formation, fibrins are formed by the conversion of inactive (4) in the plasma by the enzyme (5)
Which one of the following options, gives the correct fill ups for the respective blank numbers from (1) to (5) in the statements ?- a)(1)-Neutrophils, (2)-basophils, (4)-fibrinogens, (5)-thrombin
- b)(3)-mast cells, (4)-thrombokinase, (5)-prothrombin
- c)(3)-megakaryocytes, (4)-prothrombin, (5)-thrombin
- d)(1)-Basophils, (2)-neutrophils, (3)-reticulocytes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements (A-C) each with one or two blanks.
(A) (1) are the most abundant cells (60-65 percent) of the total WBCs and (2) are the least (0.5-1 percent) among them.
(B) Platelets are cell fragments produced from (3).
(C) During clot formation, fibrins are formed by the conversion of inactive (4) in the plasma by the enzyme (5)
Which one of the following options, gives the correct fill ups for the respective blank numbers from (1) to (5) in the statements ?
(A) (1) are the most abundant cells (60-65 percent) of the total WBCs and (2) are the least (0.5-1 percent) among them.
(B) Platelets are cell fragments produced from (3).
(C) During clot formation, fibrins are formed by the conversion of inactive (4) in the plasma by the enzyme (5)
Which one of the following options, gives the correct fill ups for the respective blank numbers from (1) to (5) in the statements ?
a)
(1)-Neutrophils, (2)-basophils, (4)-fibrinogens, (5)-thrombin
b)
(3)-mast cells, (4)-thrombokinase, (5)-prothrombin
c)
(3)-megakaryocytes, (4)-prothrombin, (5)-thrombin
d)
(1)-Basophils, (2)-neutrophils, (3)-reticulocytes
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Blood platelets are cell fragments rather than true cells, they are formed from megakaryocytes (very large cells of bone marrow).
During ventricular systole:- a)Oxygenated blood is pumped into the pulmonary artery and deoxygenated blood is pumped into the artery
- b)Oxygenated blood is pumped into the aorta and deoxygenated blood is pumped into the pulmonary vein
- c)Oxygenated blood is pumped into the pulmonary vein and deoxygenated blood is pumped into the pulmonary artery
- d)Oxygenated blood is pumped into the aorta and deoxygenated blood is pumped into the pulmonary artery
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
During ventricular systole:
a)
Oxygenated blood is pumped into the pulmonary artery and deoxygenated blood is pumped into the artery
b)
Oxygenated blood is pumped into the aorta and deoxygenated blood is pumped into the pulmonary vein
c)
Oxygenated blood is pumped into the pulmonary vein and deoxygenated blood is pumped into the pulmonary artery
d)
Oxygenated blood is pumped into the aorta and deoxygenated blood is pumped into the pulmonary artery
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Due to contraction of the ventricles (ventricular systole), the pressure inside the ventricles rises, that force open the semilunar valves of aorta and pulmonary artery so that the blood enters into these vessels. Oxygenated blood is pumped into the aorta from the left ventricle while deoxygenated blood is pumped into the pulmonary artery from the right ventricle.
Which of the following statement(s) regarding the cardiac system is/are correct?
(i) Human heart is an ectodermal derivative.
(ii) Mitral valve guards the opening between the right atrium and left ventricle.
(iii) SAN is located on the left upper corner of the right atrium.
(iv) Stroke x Heart rate = Cardiac output.- a)(i) only
- b)(i) and (ii)
- c)(ii) and (iii)
- d)(iv) only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement(s) regarding the cardiac system is/are correct?
(i) Human heart is an ectodermal derivative.
(ii) Mitral valve guards the opening between the right atrium and left ventricle.
(iii) SAN is located on the left upper corner of the right atrium.
(iv) Stroke x Heart rate = Cardiac output.
(i) Human heart is an ectodermal derivative.
(ii) Mitral valve guards the opening between the right atrium and left ventricle.
(iii) SAN is located on the left upper corner of the right atrium.
(iv) Stroke x Heart rate = Cardiac output.
a)
(i) only
b)
(i) and (ii)
c)
(ii) and (iii)
d)
(iv) only
|
|
Nishtha Shah answered |
Cardiac System
The cardiac system is a complex network of structures and processes that work together to pump and circulate blood throughout the body. Understanding the different components and functions of the cardiac system is essential for understanding how the heart and circulatory system function as a whole.
(i) Human heart is an ectodermal derivative.
This statement is incorrect. The human heart is not derived from the ectoderm, but from the mesoderm. During embryonic development, the heart forms from the mesodermal layer, specifically the splanchnic mesoderm. The splanchnic mesoderm gives rise to the cardiogenic area, which eventually differentiates into the heart tube. This tube then undergoes further development to form the four chambers of the heart.
(ii) Mitral valve guards the opening between the right atrium and left ventricle.
This statement is incorrect. The mitral valve, also known as the bicuspid valve, is located between the left atrium and left ventricle. It consists of two leaflets or cusps that prevent the backflow of blood from the left ventricle to the left atrium during ventricular contraction.
(iii) SAN is located on the left upper corner of the right atrium.
This statement is incorrect. The sinoatrial node (SAN), also known as the pacemaker of the heart, is located in the upper part of the right atrium near the opening of the superior vena cava. It is responsible for initiating the electrical impulses that regulate the rhythm of the heart.
(iv) Stroke x Heart rate = Cardiac output.
This statement is correct. Cardiac output is the amount of blood pumped by the heart per minute, and it is calculated by multiplying the stroke volume (the amount of blood pumped with each heartbeat) by the heart rate (the number of heartbeats per minute). Therefore, the formula for cardiac output is stroke volume x heart rate.
In summary, the correct statement regarding the cardiac system is option (iv) only, which states that the formula for cardiac output is stroke volume x heart rate.
The cardiac system is a complex network of structures and processes that work together to pump and circulate blood throughout the body. Understanding the different components and functions of the cardiac system is essential for understanding how the heart and circulatory system function as a whole.
(i) Human heart is an ectodermal derivative.
This statement is incorrect. The human heart is not derived from the ectoderm, but from the mesoderm. During embryonic development, the heart forms from the mesodermal layer, specifically the splanchnic mesoderm. The splanchnic mesoderm gives rise to the cardiogenic area, which eventually differentiates into the heart tube. This tube then undergoes further development to form the four chambers of the heart.
(ii) Mitral valve guards the opening between the right atrium and left ventricle.
This statement is incorrect. The mitral valve, also known as the bicuspid valve, is located between the left atrium and left ventricle. It consists of two leaflets or cusps that prevent the backflow of blood from the left ventricle to the left atrium during ventricular contraction.
(iii) SAN is located on the left upper corner of the right atrium.
This statement is incorrect. The sinoatrial node (SAN), also known as the pacemaker of the heart, is located in the upper part of the right atrium near the opening of the superior vena cava. It is responsible for initiating the electrical impulses that regulate the rhythm of the heart.
(iv) Stroke x Heart rate = Cardiac output.
This statement is correct. Cardiac output is the amount of blood pumped by the heart per minute, and it is calculated by multiplying the stroke volume (the amount of blood pumped with each heartbeat) by the heart rate (the number of heartbeats per minute). Therefore, the formula for cardiac output is stroke volume x heart rate.
In summary, the correct statement regarding the cardiac system is option (iv) only, which states that the formula for cardiac output is stroke volume x heart rate.
Which of the following sequences is truly a systemic circulation pathway?- a)Right ventricle → Pulmonary aorta → Tissues → Pulmonary veins → Left auricle
- b)Right auricle → Left ventricle → Aorta → Tissues → Veins → Right auricle
- c)Left auricle → Left ventricle → Pulmonary aorta → Tissues → Right auricle
- d)Left auricle → Left ventricle → Aorta → Arteries → Tissues → Veins → Right atrium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following sequences is truly a systemic circulation pathway?
a)
Right ventricle → Pulmonary aorta → Tissues → Pulmonary veins → Left auricle
b)
Right auricle → Left ventricle → Aorta → Tissues → Veins → Right auricle
c)
Left auricle → Left ventricle → Pulmonary aorta → Tissues → Right auricle
d)
Left auricle → Left ventricle → Aorta → Arteries → Tissues → Veins → Right atrium
|
|
Poulomi Basu answered |
To left ventricle to aorta to systemic arteries to systemic capillaries to systemic veins to right atrium
b)Left atrium to left ventricle to pulmonary arteries to pulmonary capillaries to pulmonary veins to right atrium
c)Right atrium to right ventricle to pulmonary arteries to pulmonary capillaries to pulmonary veins to left atrium
d)Left atrium to left ventricle to aorta to systemic arteries to systemic capillaries to systemic veins to right atrium
The correct answer is d) Left atrium to left ventricle to aorta to systemic arteries to systemic capillaries to systemic veins to right atrium. This sequence represents the pathway of blood flow in the systemic circulation, where oxygenated blood is pumped from the left side of the heart to the rest of the body and deoxygenated blood returns to the right side of the heart.
b)Left atrium to left ventricle to pulmonary arteries to pulmonary capillaries to pulmonary veins to right atrium
c)Right atrium to right ventricle to pulmonary arteries to pulmonary capillaries to pulmonary veins to left atrium
d)Left atrium to left ventricle to aorta to systemic arteries to systemic capillaries to systemic veins to right atrium
The correct answer is d) Left atrium to left ventricle to aorta to systemic arteries to systemic capillaries to systemic veins to right atrium. This sequence represents the pathway of blood flow in the systemic circulation, where oxygenated blood is pumped from the left side of the heart to the rest of the body and deoxygenated blood returns to the right side of the heart.
Pacemaker is situated in heart- a)In the wall of right atrium
- b)On interauricular septum
- c)On interventricular septum
- d)In the wall of left atrium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Pacemaker is situated in heart
a)
In the wall of right atrium
b)
On interauricular septum
c)
On interventricular septum
d)
In the wall of left atrium
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Sino-atrial node, also called pacemaker is situated in the right upper corner of the right atrium.
Read the following statements and select the correct ones.
(i) Nodal tissue is specialised cardiac musculature in human heart which has the ability to generate action potential due to an external stimuli
(ii) Position of SAN - right corner of right atrium
(iii) Position of AVN - right corner of ventricle
(iv) AV bundle continues from AVN
(v) Purkinje fibres are modified cardiac muscle fibres that originate from the atrioventricular node and spread into the two ventricles.- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(i) and (iii)
- c)(ii), (iv) and (v)
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements and select the correct ones.
(i) Nodal tissue is specialised cardiac musculature in human heart which has the ability to generate action potential due to an external stimuli
(ii) Position of SAN - right corner of right atrium
(iii) Position of AVN - right corner of ventricle
(iv) AV bundle continues from AVN
(v) Purkinje fibres are modified cardiac muscle fibres that originate from the atrioventricular node and spread into the two ventricles.
(i) Nodal tissue is specialised cardiac musculature in human heart which has the ability to generate action potential due to an external stimuli
(ii) Position of SAN - right corner of right atrium
(iii) Position of AVN - right corner of ventricle
(iv) AV bundle continues from AVN
(v) Purkinje fibres are modified cardiac muscle fibres that originate from the atrioventricular node and spread into the two ventricles.
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(i) and (iii)
c)
(ii), (iv) and (v)
d)
all of these
|
|
Sharmila Banerjee answered |
Position of SAN and AVN in the Human Heart
Nodal tissue is specialized cardiac musculature in the human heart that plays a crucial role in generating and coordinating the electrical signals responsible for the heartbeat. Let's examine the given statements and identify the correct ones.
(i) Nodal tissue is specialized cardiac musculature in the human heart which has the ability to generate action potential due to an external stimulus.
- This statement is correct. The nodal tissue, specifically the sinoatrial node (SAN) and atrioventricular node (AVN), are responsible for generating and conducting electrical impulses throughout the heart.
(ii) Position of SAN - right corner of right atrium.
- This statement is correct. The SAN is located in the right corner of the right atrium, near the opening of the superior vena cava.
(iii) Position of AVN - right corner of ventricle.
- This statement is incorrect. The AVN is located at the base of the right atrium, near the interatrial septum, and not in the right corner of the ventricle.
(iv) AV bundle continues from AVN.
- This statement is correct. The atrioventricular bundle, also known as the bundle of His, is a continuation of the electrical pathway from the AVN. It extends through the interventricular septum and divides into the right and left bundle branches, which further distribute the electrical signals to the respective ventricles.
(v) Purkinje fibers are modified cardiac muscle fibers that originate from the atrioventricular node and spread into the two ventricles.
- This statement is correct. Purkinje fibers are specialized conducting fibers that originate from the AVN and spread throughout the walls of the ventricles. They facilitate the rapid and synchronized contraction of the ventricles.
In conclusion, the correct statements are (ii), (iv), and (v). The SAN is indeed located in the right corner of the right atrium, the AV bundle continues from the AVN, and Purkinje fibers originate from the AVN and spread into the two ventricles.
Nodal tissue is specialized cardiac musculature in the human heart that plays a crucial role in generating and coordinating the electrical signals responsible for the heartbeat. Let's examine the given statements and identify the correct ones.
(i) Nodal tissue is specialized cardiac musculature in the human heart which has the ability to generate action potential due to an external stimulus.
- This statement is correct. The nodal tissue, specifically the sinoatrial node (SAN) and atrioventricular node (AVN), are responsible for generating and conducting electrical impulses throughout the heart.
(ii) Position of SAN - right corner of right atrium.
- This statement is correct. The SAN is located in the right corner of the right atrium, near the opening of the superior vena cava.
(iii) Position of AVN - right corner of ventricle.
- This statement is incorrect. The AVN is located at the base of the right atrium, near the interatrial septum, and not in the right corner of the ventricle.
(iv) AV bundle continues from AVN.
- This statement is correct. The atrioventricular bundle, also known as the bundle of His, is a continuation of the electrical pathway from the AVN. It extends through the interventricular septum and divides into the right and left bundle branches, which further distribute the electrical signals to the respective ventricles.
(v) Purkinje fibers are modified cardiac muscle fibers that originate from the atrioventricular node and spread into the two ventricles.
- This statement is correct. Purkinje fibers are specialized conducting fibers that originate from the AVN and spread throughout the walls of the ventricles. They facilitate the rapid and synchronized contraction of the ventricles.
In conclusion, the correct statements are (ii), (iv), and (v). The SAN is indeed located in the right corner of the right atrium, the AV bundle continues from the AVN, and Purkinje fibers originate from the AVN and spread into the two ventricles.
Find the correct descending order of percentage proportion of leucocytes in human blood.- a)Neutrophils → Basophils → Lymphocytes → Acidophils (Eosinophil) → Monocytes
- b)Monocytes → Neutrophils → Lymphocytes → Acidophils → Basophils
- c)Neutrophils → Lymphocytes → Monocytes → Acidophils → Basophils
- d)Lymphocytes → Acidophils → Basophils → Neutrophils → Monocytes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the correct descending order of percentage proportion of leucocytes in human blood.
a)
Neutrophils → Basophils → Lymphocytes → Acidophils (Eosinophil) → Monocytes
b)
Monocytes → Neutrophils → Lymphocytes → Acidophils → Basophils
c)
Neutrophils → Lymphocytes → Monocytes → Acidophils → Basophils
d)
Lymphocytes → Acidophils → Basophils → Neutrophils → Monocytes
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Neutrophils (40-70%) + Lymphocytes (20-40%) → Monocytes (2-10%) → Acidophils (1-6%) → Basophils (0-1%).
Which of these cells are phagocytic?- a)Eosinophils
- b)Lymphocytes
- c)Basophils
- d)Monocytes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these cells are phagocytic?
a)
Eosinophils
b)
Lymphocytes
c)
Basophils
d)
Monocytes

|
EduRev NEET answered |
- Monocytes and neutrophils are phagocytic white blood cells or leukocytes.
- These cells engulf and destroy foreign particles and various pathogenic organisms by the process of phagocytosis.
Line in NCERT: "Neutrophils and monocytes (6-8 per cent) are phagocytic cells which destroy foreign organisms entering the body."
Which one of the following statements is correct with regardto the principle of safe blood transfusion?
- a)The donor's red blood corpuscles should not containantibodies against the recipient's serum.
- b)The recipient's serum should not contain antigens against the donor's antibodies.
- c)The recipient's serum should not contain the antibodies against the red blood corpuscles of the donor.
- d)The recipient's red blood corpuscles should not contain antibodies against the donor's antigen.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is correct with regardto the principle of safe blood transfusion?
a)
The donor's red blood corpuscles should not containantibodies against the recipient's serum.
b)
The recipient's serum should not contain antigens against the donor's antibodies.
c)
The recipient's serum should not contain the antibodies against the red blood corpuscles of the donor.
d)
The recipient's red blood corpuscles should not contain antibodies against the donor's antigen.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The correct option is C The recipient’s serum should not contain the antibodies against the RBCs of the donor
“A” and “B” are the two surface antigens that are present on the surface of the RBCs. If antigen “A” is found on the RBCs, then anti-B antibodies are developed in the plasma of that individual. If antigen “B” is found on the RBCs, then that individual tends to develop anti-A antibodies in the plasma. The blood transfusion should be done in such a way that the recipient’s serum (plasma without the clotting factors) does not contain antibodies against the antigens present on the surface of the RBCs of the donor. The blood of the donor should properly match with the blood of the recipient. Otherwise, it will result in the destruction or clumping of the red blood cells.
“A” and “B” are the two surface antigens that are present on the surface of the RBCs. If antigen “A” is found on the RBCs, then anti-B antibodies are developed in the plasma of that individual. If antigen “B” is found on the RBCs, then that individual tends to develop anti-A antibodies in the plasma. The blood transfusion should be done in such a way that the recipient’s serum (plasma without the clotting factors) does not contain antibodies against the antigens present on the surface of the RBCs of the donor. The blood of the donor should properly match with the blood of the recipient. Otherwise, it will result in the destruction or clumping of the red blood cells.
Right atrium receives blood from- a)Pulmonary aorta
- b)Pulmonary veins
- c)Inferior vena cava
- d)Superior and inferior vena cav
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Right atrium receives blood from
a)
Pulmonary aorta
b)
Pulmonary veins
c)
Inferior vena cava
d)
Superior and inferior vena cav
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Superior vena cava and inferior vena cava are the large veins. Superior vena cava brings deoxygenated blood from upper part of the body while inferior vena cava brings blood from lower part of the body into the right atrium of the heart.
A red blood cell, entering the right side of the heart passes by or through the following structures.
1. Atrioventricular valves
2. Semilunar valves
3. Right atrium
4. Right ventricle
5. SAN
Which of the following options represents the correct sequence?- a)2 → 3 → 1→ 4 → 5
- b)3 → 1 → 5 → 2 → 4
- c)3 → 5 → 1 → 2 → 4
- d)5 → 3 → 1 → 4 → 2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A red blood cell, entering the right side of the heart passes by or through the following structures.
1. Atrioventricular valves
2. Semilunar valves
3. Right atrium
4. Right ventricle
5. SAN
Which of the following options represents the correct sequence?
1. Atrioventricular valves
2. Semilunar valves
3. Right atrium
4. Right ventricle
5. SAN
Which of the following options represents the correct sequence?
a)
2 → 3 → 1→ 4 → 5
b)
3 → 1 → 5 → 2 → 4
c)
3 → 5 → 1 → 2 → 4
d)
5 → 3 → 1 → 4 → 2
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
Red blood cell (blood) will first meet SAN in the right atrium. Then from the right atrium it passes into right ventricle through atrio ventricular valve. From the right ventricle it enters into pulmonary artery through semilunar valve.
Which of the following statements about the functions and characteristics of blood cells is/are correct?i. Basophils are the most abundant type of WBCs and play a major role in phagocytosis.ii. Eosinophils help in resisting infections and constitute 2-3% of total WBCs.iii. The average lifespan of erythrocytes is about 120 days before being destroyed in the liver.iv. Neutrophils and monocytes are phagocytic cells which destroy foreign organisms entering the body.- a)ii and iv
- b)i and iii
- c)iii and iv
- d)i and ii
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about the functions and characteristics of blood cells is/are correct?
i. Basophils are the most abundant type of WBCs and play a major role in phagocytosis.
ii. Eosinophils help in resisting infections and constitute 2-3% of total WBCs.
iii. The average lifespan of erythrocytes is about 120 days before being destroyed in the liver.
iv. Neutrophils and monocytes are phagocytic cells which destroy foreign organisms entering the body.
a)
ii and iv
b)
i and iii
c)
iii and iv
d)
i and ii
|
|
Anand Chaudhary answered |
Overview of Blood Cell Functions
Understanding the functions and characteristics of blood cells is essential for grasping human physiology. Let's analyze each statement provided.
Statement Analysis
Final Conclusion
Based on the analysis, the correct statements are ii and iv. Therefore, the answer is option 'A'. Understanding these roles helps in comprehending how the immune system functions and responds to various pathogens.
Understanding the functions and characteristics of blood cells is essential for grasping human physiology. Let's analyze each statement provided.
Statement Analysis
- i. Basophils are the most abundant type of WBCs and play a major role in phagocytosis.
- Incorrect: Basophils are not the most abundant; neutrophils hold that title. Additionally, basophils primarily release histamine and are involved in allergic responses, not phagocytosis. - ii. Eosinophils help in resisting infections and constitute 2-3% of total WBCs.
- Correct: Eosinophils are indeed involved in combating parasitic infections and allergic reactions, making up about 2-3% of the white blood cell count. - iii. The average lifespan of erythrocytes is about 120 days before being destroyed in the liver.
- Incorrect: While the lifespan of erythrocytes (red blood cells) is approximately 120 days, they are typically destroyed in the spleen, not the liver. - iv. Neutrophils and monocytes are phagocytic cells which destroy foreign organisms entering the body.
- Correct: Both neutrophils and monocytes are key players in the immune system, engaging in phagocytosis to eliminate pathogens.
Final Conclusion
Based on the analysis, the correct statements are ii and iv. Therefore, the answer is option 'A'. Understanding these roles helps in comprehending how the immune system functions and responds to various pathogens.
All veins carry deoxygenated blood except- a)Pulmonary vein
- b)Hepatic vein
- c)Hepatic portal vein
- d)Renal vein
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
All veins carry deoxygenated blood except
a)
Pulmonary vein
b)
Hepatic vein
c)
Hepatic portal vein
d)
Renal vein
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
All veins carry deoxygenated blood from different parts of the body to heart, Pulmonary veins is the only vein that carries oxtgenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
The lymph serves to- a)Return the interstitial fluid to the blood
- b)Return the WBCs and RBCs to the lymph nodes
- c)Transport CO2 to the lungs
- d)Transport O2 to the brain
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The lymph serves to
a)
Return the interstitial fluid to the blood
b)
Return the WBCs and RBCs to the lymph nodes
c)
Transport CO2 to the lungs
d)
Transport O2 to the brain
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Lymph return the interstitial fluid back to the blood, This interstitial fluid, also called extracellular fluid, is filtered from og blood without its cellular component.
In which one of the following pairs, two terms represent the same thing?- a)Lymphocyte - leucocyte
- b)Plasma - serum
- c)Mitral valve - bicuspid valve
- d)Atrioventricular node - pacemaker
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which one of the following pairs, two terms represent the same thing?
a)
Lymphocyte - leucocyte
b)
Plasma - serum
c)
Mitral valve - bicuspid valve
d)
Atrioventricular node - pacemaker
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The opening between the left atrium and left ventricle is guarded by a bisuspid valve, also known as mitral valve.
Which of the following walls separate the right and left atria?- a)Thin, intra-atrial septum
- b)Thin, inter-atrial septum
- c)Thick, inter-atrial septum
- d) Thick, intra-atrial septum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following walls separate the right and left atria?
a)
Thin, intra-atrial septum
b)
Thin, inter-atrial septum
c)
Thick, inter-atrial septum
d)
Thick, intra-atrial septum

|
Top Rankers answered |
A thin, muscular wall called as the inter-atrial septum separates the right and the left atria, whereas a thick-walled, inter-ventricular septum separates the left and the right ventricles.
Compared to blood the lymph has- a)More RBCs and less WBCs
- b)No plasma
- c)Plasma without protiens
- d)More WBCs and no RBCs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Compared to blood the lymph has
a)
More RBCs and less WBCs
b)
No plasma
c)
Plasma without protiens
d)
More WBCs and no RBCs
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Lymph is a fluid connective tissue containing lymph plasma and cells. The cells in lymph are floating amoeboid cells called WBCs (white blood cells) which are monthly lymphocytes. RBCs and platelets are absent in lymph.
'X' is the rhythmic contraction and relaxation in the aorta and its main arteries. What is X?- a)Heartbeat
- b)Heart rate
- c)Pulse
- d)Cardiac output
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
'X' is the rhythmic contraction and relaxation in the aorta and its main arteries. What is X?
a)
Heartbeat
b)
Heart rate
c)
Pulse
d)
Cardiac output
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Pulse is the rhythmic contraction and relaxation in the aorta and its main aeteries. It is a regular jerk of an artery. It is same as the heart rate because an artery pulses every time the heart beats.
What happens when the pacemaker becomes nonfunctional?- a)Only auricles contract rhythmically
- b)Only ventricles contract rhythmically
- c)Cardiac muscles do not undergo co-ordinated rhythmic movements
- d)Auricles and ventricles contract rhythmically
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What happens when the pacemaker becomes nonfunctional?
a)
Only auricles contract rhythmically
b)
Only ventricles contract rhythmically
c)
Cardiac muscles do not undergo co-ordinated rhythmic movements
d)
Auricles and ventricles contract rhythmically
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
The SA node possesses a unique property of self-excitation, which enables it to act as the pacemaker of heart. It spontaneously generates a wave of contraction which spreads over both the auricles more or less simultaneously along the muscle fibres that fan out from the pacemaker. The pacemaker establishes the basic rhythm at which the heart beats. Thus, if the pacemaker becomes nonfunction, then the cardiac muscles do not undergo co-ordinated rhythmic movements.
In a standard ECG which one of the following alphabets is the correct representation of the respective activity of the human heart?- a)S - start of systole
- b)T - end of diastole
- c)P - depolarisation of the atria
- d)R - repolarisastion of ventricles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a standard ECG which one of the following alphabets is the correct representation of the respective activity of the human heart?
a)
S - start of systole
b)
T - end of diastole
c)
P - depolarisation of the atria
d)
R - repolarisastion of ventricles
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
In a standard ECG, the P wave is a small upward wave that represents depolarisation of atria which leads to contraction of both atria.
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect about lymph?
(i) Lymph is colourful as it has haemoglobin but no RBC.
(ii) It contains specialised lymphocytes which are responsible for immunity of the body.
(iii) Lymph is an important carrier for nutrients and hormones.
(iv) Fats are absorbed through lymph in the lacteals present in the intestinal villi.- a)i only
- b)iii and iv
- c)ii and iii
- d)iv only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect about lymph?
(i) Lymph is colourful as it has haemoglobin but no RBC.
(ii) It contains specialised lymphocytes which are responsible for immunity of the body.
(iii) Lymph is an important carrier for nutrients and hormones.
(iv) Fats are absorbed through lymph in the lacteals present in the intestinal villi.
(i) Lymph is colourful as it has haemoglobin but no RBC.
(ii) It contains specialised lymphocytes which are responsible for immunity of the body.
(iii) Lymph is an important carrier for nutrients and hormones.
(iv) Fats are absorbed through lymph in the lacteals present in the intestinal villi.
a)
i only
b)
iii and iv
c)
ii and iii
d)
iv only
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Lymph is a colourless fluid containing lymphocytes which are involved in immune response of the body.
Which of the following blood groups is a universal recipient in blood transfusion?- a)Group AB
- b)Group B
- c)Group A
- d)Group O
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following blood groups is a universal recipient in blood transfusion?
a)
Group AB
b)
Group B
c)
Group A
d)
Group O
|
|
Sreemoyee Pillai answered |
Universal Recipient: Group AB
Group AB blood is known as the universal recipient in blood transfusions. This means individuals with AB blood can receive blood from any other blood group without experiencing an adverse reaction. Here's why:
Blood Group Characteristics:
- Antigens and Antibodies:
- Blood groups are classified based on the presence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells.
- Group AB has both A and B antigens, while it lacks anti-A and anti-B antibodies in the plasma.
- Compatibility:
- When a person with AB blood receives blood from groups A, B, AB, or O, there are no antibodies to react against the incoming blood antigens.
- This lack of reaction allows for safe transfusions from any blood type.
Comparison with Other Blood Groups:
- Group O:
- Known as the universal donor, group O blood can be given to anyone, but individuals with group O can only receive blood from other group O donors.
- Group A and B:
- Individuals with group A can only receive A and O, while group B can only receive B and O, limiting their transfusion options.
Clinical Importance:
- Emergency Situations:
- In emergencies, knowing that AB individuals can receive blood from any type saves critical time and reduces the risk of transfusion reactions.
In conclusion, the unique composition of blood group AB allows it to accept blood from all other groups, making it the universal recipient in blood transfusion scenarios.
Group AB blood is known as the universal recipient in blood transfusions. This means individuals with AB blood can receive blood from any other blood group without experiencing an adverse reaction. Here's why:
Blood Group Characteristics:
- Antigens and Antibodies:
- Blood groups are classified based on the presence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells.
- Group AB has both A and B antigens, while it lacks anti-A and anti-B antibodies in the plasma.
- Compatibility:
- When a person with AB blood receives blood from groups A, B, AB, or O, there are no antibodies to react against the incoming blood antigens.
- This lack of reaction allows for safe transfusions from any blood type.
Comparison with Other Blood Groups:
- Group O:
- Known as the universal donor, group O blood can be given to anyone, but individuals with group O can only receive blood from other group O donors.
- Group A and B:
- Individuals with group A can only receive A and O, while group B can only receive B and O, limiting their transfusion options.
Clinical Importance:
- Emergency Situations:
- In emergencies, knowing that AB individuals can receive blood from any type saves critical time and reduces the risk of transfusion reactions.
In conclusion, the unique composition of blood group AB allows it to accept blood from all other groups, making it the universal recipient in blood transfusion scenarios.
A certain road accident patient with unknown blood group needs immediate blood transfusion. His one doctor friend at once offers his blood. What was the blood group of the doctor?- a)Blood group B
- b)Blood group AB
- c)Blood group O
- d)Blood group A
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A certain road accident patient with unknown blood group needs immediate blood transfusion. His one doctor friend at once offers his blood. What was the blood group of the doctor?
a)
Blood group B
b)
Blood group AB
c)
Blood group O
d)
Blood group A
|
|
Manoj Majumdar answered |
Explanation:
Doctor's Blood Group:
- Since the doctor can offer his blood immediately, it means he is compatible for blood transfusion with the patient.
- The universal blood donor is of blood group O, as they can donate to any blood group.
Conclusion:
- The doctor's blood group must be O.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' - Blood group O.
Doctor's Blood Group:
- Since the doctor can offer his blood immediately, it means he is compatible for blood transfusion with the patient.
- The universal blood donor is of blood group O, as they can donate to any blood group.
Conclusion:
- The doctor's blood group must be O.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' - Blood group O.
To measure ECG, usually how many electrodes are connected to a patient?- a)Three
- b)Two
- c)One
- d)Four
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
To measure ECG, usually how many electrodes are connected to a patient?
a)
Three
b)
Two
c)
One
d)
Four

|
Lead Academy answered |
To measure a standard ECG, a patient is connected to the machine with three electrical leads-one to each wrist and one to the left ankle. It continuously monitors heart activity.
What is the duration of a single cardiac cycle?- a) 0.5 seconds
- b) 0.8 seconds
- c) 1.0 seconds
- d) 1.5 seconds
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the duration of a single cardiac cycle?
a)
0.5 seconds
b)
0.8 seconds
c)
1.0 seconds
d)
1.5 seconds
|
|
Ameya Mehta answered |
Understanding Cardiac Cycle Duration
The cardiac cycle refers to the sequence of events that occur within the heart during one complete heartbeat. The duration of a single cardiac cycle varies based on factors such as heart rate, but it is typically around 0.8 seconds in a resting adult.
Key Components of the Cardiac Cycle
- Phases of the Cardiac Cycle
Each cycle consists of two main phases: diastole (relaxation) and systole (contraction).
- Diastole: The heart chambers fill with blood.
- Systole: The heart pumps blood out to the body.
- Heart Rate Influence
The duration of the cardiac cycle is inversely related to heart rate. For example:
- At a resting heart rate of about 75 beats per minute, each cardiac cycle lasts approximately 0.8 seconds (60 seconds/75 beats).
- As heart rate increases (e.g., during exercise), the duration of each cycle decreases.
Why Option B is Correct
- Typical Duration
The average duration of 0.8 seconds is based on the average resting heart rate and normal physiological conditions.
- Clinical Relevance
Understanding the duration helps in diagnosing and monitoring various cardiac conditions. A prolonged or shortened cycle might indicate underlying heart issues.
In conclusion, the duration of a single cardiac cycle is approximately 0.8 seconds in a healthy adult at rest, making option 'B' the correct answer.
The cardiac cycle refers to the sequence of events that occur within the heart during one complete heartbeat. The duration of a single cardiac cycle varies based on factors such as heart rate, but it is typically around 0.8 seconds in a resting adult.
Key Components of the Cardiac Cycle
- Phases of the Cardiac Cycle
Each cycle consists of two main phases: diastole (relaxation) and systole (contraction).
- Diastole: The heart chambers fill with blood.
- Systole: The heart pumps blood out to the body.
- Heart Rate Influence
The duration of the cardiac cycle is inversely related to heart rate. For example:
- At a resting heart rate of about 75 beats per minute, each cardiac cycle lasts approximately 0.8 seconds (60 seconds/75 beats).
- As heart rate increases (e.g., during exercise), the duration of each cycle decreases.
Why Option B is Correct
- Typical Duration
The average duration of 0.8 seconds is based on the average resting heart rate and normal physiological conditions.
- Clinical Relevance
Understanding the duration helps in diagnosing and monitoring various cardiac conditions. A prolonged or shortened cycle might indicate underlying heart issues.
In conclusion, the duration of a single cardiac cycle is approximately 0.8 seconds in a healthy adult at rest, making option 'B' the correct answer.
In veins, valves are present to check backward flow of blood flowing at: - a)Atmospheric pressure
- b)High pressure
- c)Low pressure
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In veins, valves are present to check backward flow of blood flowing at:
a)
Atmospheric pressure
b)
High pressure
c)
Low pressure
d)
All of the above
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Veins brings blood from different body parts to the heart. The flow of blood in veins is not so fast because the blood in veins is under low pressure. Veins posses valves which present backward flow of blood.
Which of the following chambers of the heart has the thickest muscular wall?- a)Left atrium
- b)Right atrium
- c)Right ventricle
- d)Left ventricle
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following chambers of the heart has the thickest muscular wall?
a)
Left atrium
b)
Right atrium
c)
Right ventricle
d)
Left ventricle
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Left ventricle has the thickest muscular wall as it has to pump the oxygenated blood with great force to all visceral organs and parts of body through aorta.
In the above diagram, which blood vessel represents vena cava?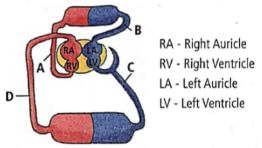
- a)C
- b)D
- c)A
- d)B
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the above diagram, which blood vessel represents vena cava?

a)
C
b)
D
c)
A
d)
B
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
In the given diagram 'D' represent the vena cava. Vena cava is either of two large veins that carry deoxygenated blood into the right atrium.
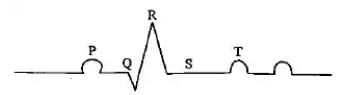
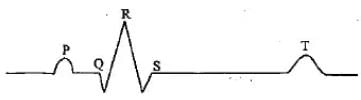
Which of the following is the diagrammatic representation of standard electrocardiogram(ECG)?- a)
- b)
- c)

- d)
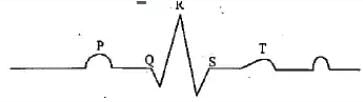
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the diagrammatic representation of standard electrocardiogram(ECG)?
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Priya Menon answered |
A normal electrogram (ECG) is composed of a ‘P’ wave, a QRS wave (complex), and a T wave. The ‘P’ wave is a small upward wave that represents electrical excitation or atrial depolarization which leads to contraction of both the atria. QRS wave (complex) begins after a fraction of a second of the P wave. It begins as a small downward deflection (Q) and continues as a larger upright (R) and triangular wave, ending as a downward wave (S) at its base. It represents ventricular depolarization. The ‘T’ wave is dome-shaped which represents ventricular repolarization. The potential generated by the recovery of the ventricle from the depolarization state is called the repolarization wave. The end of the ‘T’ wave marks the end of the systole.
What is the nature of blood passing through blood vessels A, B, C and D respectively?
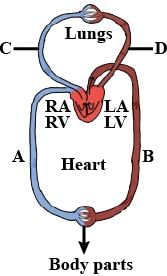
- a)A - Deoxygenated, B - Oxygenated, C - Deoxygenated, D - Oxygenated
- b)A - Deoxygenated, B - Deoxygenated, C - Oxygenated, D - Oxygenated
- c)A - Oxygenated, B - Oxygenated, C - Deoxygenated, D - Deoxygenated
- d)A - Oxygenated, B - Deoxygenated, C - Oxygenated, D - Deoxygenated
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the nature of blood passing through blood vessels A, B, C and D respectively?


a)
A - Deoxygenated, B - Oxygenated, C - Deoxygenated, D - Oxygenated
b)
A - Deoxygenated, B - Deoxygenated, C - Oxygenated, D - Oxygenated
c)
A - Oxygenated, B - Oxygenated, C - Deoxygenated, D - Deoxygenated
d)
A - Oxygenated, B - Deoxygenated, C - Oxygenated, D - Deoxygenated
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
'A' is vena cava that carries deoxygenated blood
'B' is aorta that carries oxygenated blood
'C' is pulmonary artery that carries deoxygenated blood
'D' is pulmonary vein that carries oxygenated blood.
'B' is aorta that carries oxygenated blood
'C' is pulmonary artery that carries deoxygenated blood
'D' is pulmonary vein that carries oxygenated blood.
In the given figure of the heart which of the labelled part (1,2,3,4,5) carries oxygenated blood?
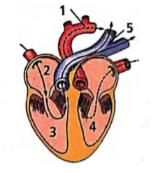
- a)1, 2, 3 and 4
- b)1 and 5
- c)1 and 4
- d)3 and 5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given figure of the heart which of the labelled part (1,2,3,4,5) carries oxygenated blood?


a)
1, 2, 3 and 4
b)
1 and 5
c)
1 and 4
d)
3 and 5
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
The labelled parts '1' and '4' are aorta and left ventricle respectively, which carry oxygenated blood. Left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from left auricle which received it from pulmonary veins and this oxygenaed blood then moves into the aorta to be supplied to the whole body.
Which of the following match is correct?

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following match is correct?


a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The structure given in option 'b' is of basophil. Basophils secrete histamine, serotonin, heparin, etc. and are involved in inflammatory reactions. The structure given in option'a is of neutrophil. Its percentage is 40-70%. The structure given in option 'cis of eosinophil. Its percentage is 1-6%. The structure given in option 'd' is of monocyte. Its percentage is 2-10% and is phagocytic in function.
Consider the following four statements and select the correct option stating which ones are true (T) and which ones are false (F)?
I. Proteins contribute 6-8% of the blood plasma
II. Plasma contains very high amount of minerals
III. Plasma without the clotting factors is called serum
IV. Glucose, amino acids, lipids, etc., are also present in the plasma as they are always in transit in the body.
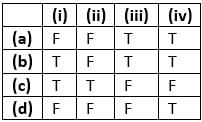
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following four statements and select the correct option stating which ones are true (T) and which ones are false (F)?
I. Proteins contribute 6-8% of the blood plasma
II. Plasma contains very high amount of minerals
III. Plasma without the clotting factors is called serum
IV. Glucose, amino acids, lipids, etc., are also present in the plasma as they are always in transit in the body.

I. Proteins contribute 6-8% of the blood plasma
II. Plasma contains very high amount of minerals
III. Plasma without the clotting factors is called serum
IV. Glucose, amino acids, lipids, etc., are also present in the plasma as they are always in transit in the body.

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Plasma contains small amounts of minerals like Na+,Mg2+, Ca2+, HCO3- Cl- etc.
In the given figure the durations of the events of the cardiac cycle are given. Identify these events and select the correct option.
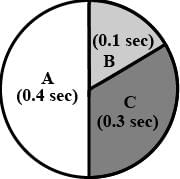
- a)A - Auricular systole
B - Joint diastole
C - Ventricular systole - b)A - Ventricular systole
B - Joint diastole
C - Auricular systole - c)A - Ventricular systole
B - Auricular systole
C - Joint diastole - d)A - Joint diastole
B - Auricular systole
C - Ventricular systole
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given figure the durations of the events of the cardiac cycle are given. Identify these events and select the correct option.


a)
A - Auricular systole
B - Joint diastole
C - Ventricular systole
B - Joint diastole
C - Ventricular systole
b)
A - Ventricular systole
B - Joint diastole
C - Auricular systole
B - Joint diastole
C - Auricular systole
c)
A - Ventricular systole
B - Auricular systole
C - Joint diastole
B - Auricular systole
C - Joint diastole
d)
A - Joint diastole
B - Auricular systole
C - Ventricular systole
B - Auricular systole
C - Ventricular systole
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Duration of joint diastole is 0.4 sec, that of auricular systole is 0.1 sec and that of ventricular systole is 0.3 sec.
Consider the following statements each with one or two blanks.
(i) Left auriculoventricular aperture is guarded by (1) valve while right auriculoventricular aperture is guarded by (2) valve.
(ii) In man left auricle receives (3) blood by (4) pulmonary veins.
(iii) (5) ions play a significant role in clotting.
Which one of the following options, gives the correct fill-ups for the respective blank numbers from (1) to (5) in the statements?- a)(3)-deoxygenated, (4)-four, (5)-magnesium
- b)(1) biscuspid valve, (2) tricuspid valve (5)-calcium
- c)(1)-tricuspid valve, (2)-bicuspid valve, (3)-oxygenated, (4)-two
- d)(1)-bicuspid valve, (2) tricuspid valve, (5)-sodium
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements each with one or two blanks.
(i) Left auriculoventricular aperture is guarded by (1) valve while right auriculoventricular aperture is guarded by (2) valve.
(ii) In man left auricle receives (3) blood by (4) pulmonary veins.
(iii) (5) ions play a significant role in clotting.
Which one of the following options, gives the correct fill-ups for the respective blank numbers from (1) to (5) in the statements?
(i) Left auriculoventricular aperture is guarded by (1) valve while right auriculoventricular aperture is guarded by (2) valve.
(ii) In man left auricle receives (3) blood by (4) pulmonary veins.
(iii) (5) ions play a significant role in clotting.
Which one of the following options, gives the correct fill-ups for the respective blank numbers from (1) to (5) in the statements?
a)
(3)-deoxygenated, (4)-four, (5)-magnesium
b)
(1) biscuspid valve, (2) tricuspid valve (5)-calcium
c)
(1)-tricuspid valve, (2)-bicuspid valve, (3)-oxygenated, (4)-two
d)
(1)-bicuspid valve, (2) tricuspid valve, (5)-sodium
|
|
Ruchi Dey answered |
Statement Analysis:
(i) Left auriculoventricular aperture is guarded by (1) valve while right auriculoventricular aperture is guarded by (2) valve.
(ii) In man left auricle receives (3) blood by (4) pulmonary veins.
(iii) (5) ions play a significant role in clotting.
Correct Fill-Ups:
(1) Biscuspid valve
(2) Tricuspid valve
(3) Oxygenated
(4) Four
(5) Calcium
Explanation:
(i) The left auriculoventricular aperture is guarded by a biscuspid valve, which is also known as the mitral valve. The right auriculoventricular aperture is guarded by a tricuspid valve.
(ii) In human beings, the left auricle receives oxygenated blood from four pulmonary veins, which is then pumped into the left ventricle and then to the rest of the body.
(iii) Calcium ions play a significant role in the process of clotting of blood. Calcium is required for the activation of several clotting factors, which leads to the formation of a clot at the site of injury.
(i) Left auriculoventricular aperture is guarded by (1) valve while right auriculoventricular aperture is guarded by (2) valve.
(ii) In man left auricle receives (3) blood by (4) pulmonary veins.
(iii) (5) ions play a significant role in clotting.
Correct Fill-Ups:
(1) Biscuspid valve
(2) Tricuspid valve
(3) Oxygenated
(4) Four
(5) Calcium
Explanation:
(i) The left auriculoventricular aperture is guarded by a biscuspid valve, which is also known as the mitral valve. The right auriculoventricular aperture is guarded by a tricuspid valve.
(ii) In human beings, the left auricle receives oxygenated blood from four pulmonary veins, which is then pumped into the left ventricle and then to the rest of the body.
(iii) Calcium ions play a significant role in the process of clotting of blood. Calcium is required for the activation of several clotting factors, which leads to the formation of a clot at the site of injury.
Rate of heart beat is determined by- a)Purkinje fibres
- b)Papillary muscles
- c)SA node
- d)AV node
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Rate of heart beat is determined by
a)
Purkinje fibres
b)
Papillary muscles
c)
SA node
d)
AV node
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The cardiac impulse originates from SA node. This impulse is of highest rhythmicity. By determining the rate of discharge of the cardiac impulse the SA node determines the rate of heart beat.
In the following table of human ABO blood groups fill-up the blanks (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) front the options}; below.
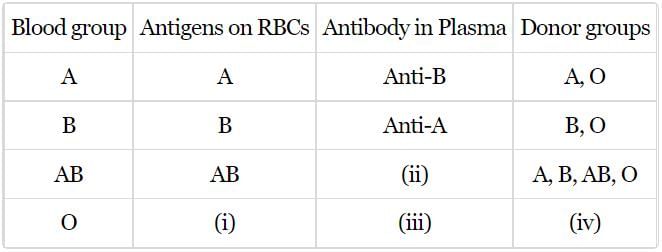
- a)i - Nil, ii - Nil, iii - Nil, iv - O
- b)i - Nil, ii - Nil, iii - Anti-A, B, iv - AB
- c)i - Nil, ii - Anti-A, B, iii - Nil, iv - O
- d)i - Nil, ii - Nil, iii - Anti-A, B, iv - O
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following table of human ABO blood groups fill-up the blanks (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) front the options}; below.


a)
i - Nil, ii - Nil, iii - Nil, iv - O
b)
i - Nil, ii - Nil, iii - Anti-A, B, iv - AB
c)
i - Nil, ii - Anti-A, B, iii - Nil, iv - O
d)
i - Nil, ii - Nil, iii - Anti-A, B, iv - O
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
(i) for O blood group the antigens are absent on the RBCs, III) the plasma therefore contains antibodies for both antigen A and antigen B,
(ii) for AB blood group the surface of RBC has both antigen A and B, therefore no antibodies in the plasma.
(iv) the donor group of O is only O group.
So, the correct answer is 'i - Nil, ii - Nil, iii - Anti-A, B, iv - O'
(ii) for AB blood group the surface of RBC has both antigen A and B, therefore no antibodies in the plasma.
(iv) the donor group of O is only O group.
So, the correct answer is 'i - Nil, ii - Nil, iii - Anti-A, B, iv - O'
A drop of each of the following is placed separately onfour slides. Which of them will not coagulate?
- a)Blood serum
- b)Blood from pulmonary artery
- c)Whole blood from pulmonary vein
- d)Blood plasma
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A drop of each of the following is placed separately onfour slides. Which of them will not coagulate?
a)
Blood serum
b)
Blood from pulmonary artery
c)
Whole blood from pulmonary vein
d)
Blood plasma
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The correct answer is blood serum.
Explanation:
-
Blood serum is the liquid part of the blood that remains after coagulation has occurred, meaning the clotting factors (like fibrinogen) have been removed. Because serum lacks these clotting factors, it does not coagulate.
-
Blood from the pulmonary artery, whole blood from the pulmonary vein, and blood plasma all contain clotting factors and can coagulate under the right conditions.
Therefore, the substance that will not coagulate is blood serum.
Final Answer: 1 (Blood serum)
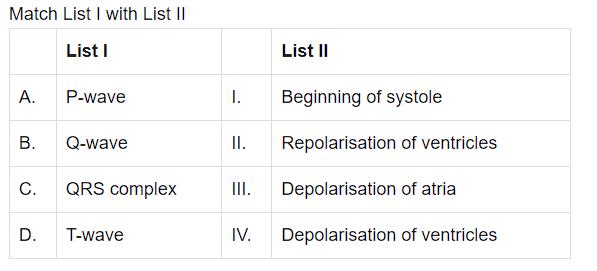
- a)1-I, 2-III, 3-IV, 4-II
- b)1- III , 2- I, 3-IV, 4- II
- c)1-III, 2-IV, 3-II, 4-I
- d)1-IV, 2 -II, 3-I, 4-II
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
1-I, 2-III, 3-IV, 4-II
b)
1- III , 2- I, 3-IV, 4- II
c)
1-III, 2-IV, 3-II, 4-I
d)
1-IV, 2 -II, 3-I, 4-II

|
Arien Instructors answered |
The P-wave represents the electrical excitation (or depolarisation) of the atria, which leads to the contraction of both the atria.
The contraction starts shortly after Q and marks the beginning of the systole.
The T-wave represents the return of the ventricles from excited to normal state (repolarisation).
The contraction starts shortly after Q and marks the beginning of the systole.
The T-wave represents the return of the ventricles from excited to normal state (repolarisation).
Choose the schematic diagram which properly respresents pulmonary circulation in humans.- a)

- b)
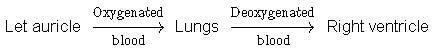
- c)
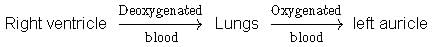
- d)
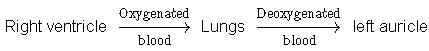
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the schematic diagram which properly respresents pulmonary circulation in humans.
a)

b)
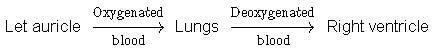
c)
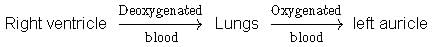
d)
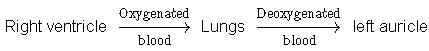
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Pulmonary circulation is the movement of blood between heart and lungs. During this pathway deoxygenated blood entering the right atrium, moves into the right ventricle From here it moves through the pulmonary arch into the lungs for oxygenation. Then from lungs oxygenated blood moves into the left atrium through pulmonary veins.
Chordae tendineae are found in- a)ventricles of heart
- b)joints of legs
- c)ventricles of brain
- d)atria of heart
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Chordae tendineae are found in
a)
ventricles of heart
b)
joints of legs
c)
ventricles of brain
d)
atria of heart
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Chordae tendineae are the special fibrous cords attached to the flaps of tricuspid valve on one end and on the other end with the special muscles of the ventricular wall, the papillary muscles.
Study the given figure and identify the cells labelled as A, B, C and D.
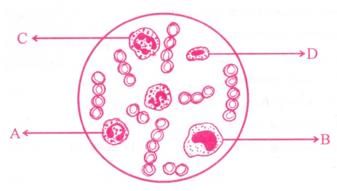
- a)A - Eosinophil, B - Erythrocyte
C - Neutrophil, D - Basophil - b)A - Eosinophil, B - Lymphocyte
C - Neutrocyte, D - Monocyte - c)A - Erythrocyte, B - Basophil,
C - Neutrophil, D - Lymphocyte - d)A - Eosinophil, B - Monocyte
C - Neutrophil, D - Lymphocyte
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the given figure and identify the cells labelled as A, B, C and D.


a)
A - Eosinophil, B - Erythrocyte
C - Neutrophil, D - Basophil
C - Neutrophil, D - Basophil
b)
A - Eosinophil, B - Lymphocyte
C - Neutrocyte, D - Monocyte
C - Neutrocyte, D - Monocyte
c)
A - Erythrocyte, B - Basophil,
C - Neutrophil, D - Lymphocyte
C - Neutrophil, D - Lymphocyte
d)
A - Eosinophil, B - Monocyte
C - Neutrophil, D - Lymphocyte
C - Neutrophil, D - Lymphocyte
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
The diagram shows the different types of blood cells.
The label A refers to eosinophils. The nucleus of these cells is bilobed. They are involved in allergic and inflammatory reactions.
The label B refers to monocytes. They have a kidney-shaped nucleus.
The label C refers to neutrophils. They have a multilobed nucleus. the monocytes and neutrophils are involved in phagocytosis.
The label D refers to lymphocytes. They have a large circular nucleus. They form the immune T cells and B cells.
The label A refers to eosinophils. The nucleus of these cells is bilobed. They are involved in allergic and inflammatory reactions.
The label B refers to monocytes. They have a kidney-shaped nucleus.
The label C refers to neutrophils. They have a multilobed nucleus. the monocytes and neutrophils are involved in phagocytosis.
The label D refers to lymphocytes. They have a large circular nucleus. They form the immune T cells and B cells.
The given figure illustrates a section through the human heart.
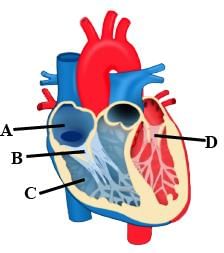
Which labelled part represents the site for the generation of action potential in human heart?- a)A
- b)B
- c)C
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The given figure illustrates a section through the human heart.

Which labelled part represents the site for the generation of action potential in human heart?

Which labelled part represents the site for the generation of action potential in human heart?
a)
A
b)
B
c)
C
d)
D
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
A' is SA node that is the site for generation of action potential in human heart.
Chapter doubts & questions for Body Fluids and Circulation - NCERT Based Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Body Fluids and Circulation - NCERT Based Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









