All Exams >
Commerce >
Economics Class 12 >
All Questions
All questions of CBSE Practice Questions for Commerce Exam
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Commercial banks contribute to the quantum of money supply in the economy through credit creation.Rcason(R): As they do have note-issuing authority.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Commercial banks contribute to the quantum of money supply in the economy through credit creation.
Rcason(R): As they do have note-issuing authority.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
Commercial banks contribute to quantum of money supply in the economy through credit creation.
Commercial banks do not have the note-issuing authority, but they do contribute to the money supply in the economy.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): In case of currency appreciation, less rupees are to be paid to buy one US dollar.Reason (R): Currency appreciation leads to increase in value of domestic currency in reference to foreign currency. So, less is needed to pay for the same amount.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): In case of currency appreciation, less rupees are to be paid to buy one US dollar.
Reason (R): Currency appreciation leads to increase in value of domestic currency in reference to foreign currency. So, less is needed to pay for the same amount.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Amita Das answered |
Export of goods and services from India to the US would mean inflow of foreign exchange to India.
छोटानागपुर पठार कितने राज्यों में फैला है?- a)4
- b)3
- c)6
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
छोटानागपुर पठार कितने राज्यों में फैला है?
a)
4
b)
3
c)
6
d)
5
|
|
Sanjay Rana answered |
यह 5 राज्यों में फैला है: बिहार, झारखंड, छत्तीसगढ़ पश्चिम बंगाल, ओडिशा

निम्नलिखित में से कौन सा जोड़ा सही ढंग से मेल नहीं खाता है?बांध / झील - नदी- a)गोविंद सागर - सतलज
- b)कोलेरु झील - कृष्ण
- c)उकाई जलाशय - लेकिन
- d)वुलर झील - झेलम
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
निम्नलिखित में से कौन सा जोड़ा सही ढंग से मेल नहीं खाता है?
बांध / झील - नदी
a)
गोविंद सागर - सतलज
b)
कोलेरु झील - कृष्ण
c)
उकाई जलाशय - लेकिन
d)
वुलर झील - झेलम
|
|
Kavita Mehta answered |
कोल्लेरू झील भारत की सबसे बड़ी ताजे पानी की झीलों में से एक है जो आंध्र प्रदेश राज्य में स्थित है। यह कृष्णा और गोदावरी डेल्टा के बीच स्थित है।
Read the following case study paragraph carefully and answer the question based on the same.The central bank of India i.e. Reserve Bank of India is the apex institution that controls the entire financial market. It’s one of the major functions is to maintain the reserve of foreign exchange. Also, it intervenes in the foreign exchange market to stabilize the excessive fluctuation in the foreign exchange rate.In other words, it is the central bank’s job to control a country’s economy through monetary policy; if the economy is moving slowly or going backward, there are steps that the central bank can take to boost the economy. These steps, whether they are asset purchases or printing more money, all involve injecting more cash into the economy. The simple supply and demand economic projection occurs and currency will devalue.When the opposite occurs, and the economy is growing, the central bank will use various methods to keep that growth steady and in-line with other economic factors such as wages and prices. Whatever the central bank does or doesn’t do, will affect the currency of that country. Sometimes, it is within the central bank’s interest to purposefully affect the value of a currency. For example, if the economy is heavily reliant on exports and their currency value becomes too high, importers of that country’s commodities will seek cheaper supply; hence directly affecting the economy.Q. Which of the following steps should be taken by the central bank if there is an excessive rise in the foreign exchange rate?- a)Supply foreign exchange from its stock
- b)Demand more of other foreign exchange
- c)Not intervene in the market as the exchange rate is determined by the market forces
- d)Help the central government to stabilize the foreign exchange rate.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following case study paragraph carefully and answer the question based on the same.
The central bank of India i.e. Reserve Bank of India is the apex institution that controls the entire financial market. It’s one of the major functions is to maintain the reserve of foreign exchange. Also, it intervenes in the foreign exchange market to stabilize the excessive fluctuation in the foreign exchange rate.
In other words, it is the central bank’s job to control a country’s economy through monetary policy; if the economy is moving slowly or going backward, there are steps that the central bank can take to boost the economy. These steps, whether they are asset purchases or printing more money, all involve injecting more cash into the economy. The simple supply and demand economic projection occurs and currency will devalue.
When the opposite occurs, and the economy is growing, the central bank will use various methods to keep that growth steady and in-line with other economic factors such as wages and prices. Whatever the central bank does or doesn’t do, will affect the currency of that country. Sometimes, it is within the central bank’s interest to purposefully affect the value of a currency. For example, if the economy is heavily reliant on exports and their currency value becomes too high, importers of that country’s commodities will seek cheaper supply; hence directly affecting the economy.
Q. Which of the following steps should be taken by the central bank if there is an excessive rise in the foreign exchange rate?
a)
Supply foreign exchange from its stock
b)
Demand more of other foreign exchange
c)
Not intervene in the market as the exchange rate is determined by the market forces
d)
Help the central government to stabilize the foreign exchange rate.
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
As regards control on rise in the price of the foreign exchange, Central Bank will increase the Bank role. It will attract foreign Direct Investment, that will increase the flow of foreign exchange and it will automatically control the price of foreign exchange. Simultaneously, it will increase the job potentials due to induction of MNCs and common man will be benefitted.
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:The Centre on Saturday increased the budgetary allocation for the environment ministry from last fiscal by nearly five percent for 2020-21 with no change in the amount allotted to pollution abatement and climate change action plan.Union Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, allocated ₹ 3,100 crore for the ministry out of which ₹ 460 crore were allotted to control pollution, which is the same as the money it received in the last budget.Control of pollution has been conceptualized to provide financial assistance to Pollution Control Boards/Committees and funding to National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).Similarly, budget for pollution abatement, which was cut by 50 percent last year from 2018-19, remained unchanged at ₹ 10 crore.The minister also announced that states, which are formulating and implementing plans for ensuring cleaner air in cities above one million population should be encouraged.Real GDP and Welfare are ___________ related with each other.- a)Directly
- b)Indirectly
- c)Inversely
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
The Centre on Saturday increased the budgetary allocation for the environment ministry from last fiscal by nearly five percent for 2020-21 with no change in the amount allotted to pollution abatement and climate change action plan.
Union Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, allocated ₹ 3,100 crore for the ministry out of which ₹ 460 crore were allotted to control pollution, which is the same as the money it received in the last budget.
Control of pollution has been conceptualized to provide financial assistance to Pollution Control Boards/Committees and funding to National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).
Similarly, budget for pollution abatement, which was cut by 50 percent last year from 2018-19, remained unchanged at ₹ 10 crore.
The minister also announced that states, which are formulating and implementing plans for ensuring cleaner air in cities above one million population should be encouraged.
Real GDP and Welfare are ___________ related with each other.
a)
Directly
b)
Indirectly
c)
Inversely
d)
None of the above

|
Tarun Chakraborty answered |
Understanding the Relationship Between Real GDP and Welfare
Real GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is a measure of the economic performance of a country, adjusted for inflation, representing the total value of goods and services produced over a specific time period. Welfare, on the other hand, refers to the overall well-being and quality of life of individuals within a society. The relationship between Real GDP and welfare can be understood as follows:
Direct Relationship
- Economic Growth: When Real GDP increases, it typically indicates economic growth, which can lead to higher employment rates and increased income levels for individuals. This upliftment often translates to better living standards.
- Increased Resources: A growing economy generates more resources that can be allocated towards social services, education, healthcare, and infrastructure, thereby enhancing the welfare of the population.
- Investment in Welfare Programs: Higher GDP allows governments to invest more in welfare programs aimed at poverty alleviation, education improvement, and public health, directly impacting the quality of life.
Limitations of GDP as a Welfare Metric
- Quality of Growth Matters: While there is a direct correlation, it is essential to note that not all growth leads to increased welfare. For example, growth driven by environmental degradation or inequality can harm overall well-being.
- Non-Economic Factors: Welfare also encompasses social, emotional, and environmental factors that GDP does not capture, such as happiness, community, and ecological health.
Conclusion
The relationship between Real GDP and welfare is primarily direct, as economic growth generally leads to improvements in living standards and overall quality of life. However, for sustainable welfare improvement, it is crucial to focus on the quality and distribution of that growth.
Real GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is a measure of the economic performance of a country, adjusted for inflation, representing the total value of goods and services produced over a specific time period. Welfare, on the other hand, refers to the overall well-being and quality of life of individuals within a society. The relationship between Real GDP and welfare can be understood as follows:
Direct Relationship
- Economic Growth: When Real GDP increases, it typically indicates economic growth, which can lead to higher employment rates and increased income levels for individuals. This upliftment often translates to better living standards.
- Increased Resources: A growing economy generates more resources that can be allocated towards social services, education, healthcare, and infrastructure, thereby enhancing the welfare of the population.
- Investment in Welfare Programs: Higher GDP allows governments to invest more in welfare programs aimed at poverty alleviation, education improvement, and public health, directly impacting the quality of life.
Limitations of GDP as a Welfare Metric
- Quality of Growth Matters: While there is a direct correlation, it is essential to note that not all growth leads to increased welfare. For example, growth driven by environmental degradation or inequality can harm overall well-being.
- Non-Economic Factors: Welfare also encompasses social, emotional, and environmental factors that GDP does not capture, such as happiness, community, and ecological health.
Conclusion
The relationship between Real GDP and welfare is primarily direct, as economic growth generally leads to improvements in living standards and overall quality of life. However, for sustainable welfare improvement, it is crucial to focus on the quality and distribution of that growth.
Read the news report given below and answer the question that follow:In a 40 minute long speech Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the demonetization of existing notes of ₹500 and ₹1,000 during a televised address on Tuesday evening.Modi announced that the notes of ₹500 and ₹1,000 “will not be legal tender from midnight tonight” and these will be “just worthless pieces of paper. The PM also urged people to ‘join this mahayojna against the ills of corruption.Here is a guide for you explaining everything about the move.What is demonetization of currency?Demonetization for us means that the Reserve Bank of India has withdrawn the old `500 and ₹1,000 notes as an official mode of payment. According to Investopedia, demonetization is the act of stripping a currency unit of its status as legal tender.What was the reason?The reasoning given by Modi was: (A) To tackle black money in the economy. (B) To lower the cash circulation in the country which “is directly related to corruption in our country, “ according to PM Modi. (C) To eliminate fake currency and dodgy funds which have been used by terror groups to fund terrorism in India. (D) The move is estimated to scoop out more than ₹5 lakh crore black money from the economy, according to Baba Ramdev, a staunch Modi supporter.Q. Why is demonetisation termed as the mahayojna by the Prime Minister?- a)It is to curb the ills of corruption.
- b)It is to tackle the black money.
- c)It is to digitalise the economy.
- d)All of the above.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the news report given below and answer the question that follow:
In a 40 minute long speech Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the demonetization of existing notes of ₹500 and ₹1,000 during a televised address on Tuesday evening.
Modi announced that the notes of ₹500 and ₹1,000 “will not be legal tender from midnight tonight” and these will be “just worthless pieces of paper. The PM also urged people to ‘join this mahayojna against the ills of corruption.
Here is a guide for you explaining everything about the move.
What is demonetization of currency?
Demonetization for us means that the Reserve Bank of India has withdrawn the old `500 and ₹1,000 notes as an official mode of payment. According to Investopedia, demonetization is the act of stripping a currency unit of its status as legal tender.
What was the reason?
The reasoning given by Modi was: (A) To tackle black money in the economy. (B) To lower the cash circulation in the country which “is directly related to corruption in our country, “ according to PM Modi. (C) To eliminate fake currency and dodgy funds which have been used by terror groups to fund terrorism in India. (D) The move is estimated to scoop out more than ₹5 lakh crore black money from the economy, according to Baba Ramdev, a staunch Modi supporter.
Q. Why is demonetisation termed as the mahayojna by the Prime Minister?
a)
It is to curb the ills of corruption.
b)
It is to tackle the black money.
c)
It is to digitalise the economy.
d)
All of the above.

|
Rakesh Bhatki answered |
D)
Read the below case and answer the question that follow:In a 40-minute long speech Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the demonetisation of existing notes of ₹ 500 and ₹ 1,000 during a televised address on Tuesday evening.Modi announced that the notes of ₹ 500 and ₹ 1,000 will not be legal tender from midnight tonight and these will be “just worthless pieces of paper''. The PM also urged people to ‘join this mahayojna against the ills of corruption.Q. ______________ is issued by the government of India.- a)Coins
- b)₹500 note
- c)₹1000 note
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the below case and answer the question that follow:
In a 40-minute long speech Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the demonetisation of existing notes of ₹ 500 and ₹ 1,000 during a televised address on Tuesday evening.
Modi announced that the notes of ₹ 500 and ₹ 1,000 will not be legal tender from midnight tonight and these will be “just worthless pieces of paper''. The PM also urged people to ‘join this mahayojna against the ills of corruption.
Q. ______________ is issued by the government of India.
a)
Coins
b)
₹500 note
c)
₹1000 note
d)
All of these
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
It is the sole responsibility of the Government of India to mint coins of all denominations.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Equity in agriculture called for land reforms which primarily refer to change of ownership from tillers to Zamindars.Reason (R): The Zamindari system introduced by the British Raj led to the destruction of the agricultural sector in India so the land reforms had to be introduced.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Equity in agriculture called for land reforms which primarily refer to change of ownership from tillers to Zamindars.
Reason (R): The Zamindari system introduced by the British Raj led to the destruction of the agricultural sector in India so the land reforms had to be introduced.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Om Desai answered |
In post-independent India, equity in agriculture called for land reforms which primarily refer to change in the ownership of landholdings from Zamindars to tillers.
Read the following hypothetical text and answer the question that follow:The performance of the Indian economy during the period of first seven five-year plans (1950-1990) was satisfactory if not very impressive. On the eve of independence, India was an industrially backward country, but during this period of first seven plans our industries became far more diversified, with the stress being laid on the public investments in the industrial sector. The policy of import substitution led to protection of the domestic industries against the foreign producersbut we failed to promote a strong export surplus. Although public sector expanded to a large extent but it could not bring desired level of improvement in the secondary sector. Excessive government regulations prevented the natural trajectory of growth of entrepreneurship as there was no competition, no innovation and no modernization on the front of the industrial sector. Many Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) incurred huge losses due to operational inefficiencies, red-tapism, poor technology and other similar reasons. These PSUs continued to function because it was difficult to close a government undertaking even it is a drain on country’s limited resources. On the Agricultural front, due to the measures taken under the Green Revolution, India more or less became self-sufficient in the production of food grains. So, the needs for reform of economic policy was widely felt in the context of changing global economic scenario to achieve desired growth in the country.Q. Which of the following was not a reason for the public sector to play a major role in the initial phase of Indian Economic Planning?- a)Private entrepreneurs lacked sufficient capital for investment.
- b)Government aimed at social welfare.
- c)The market was big enough to encourage private industrialists for investment.
- d)The government wanted to protect the indigenous producers from the foreign competition.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following hypothetical text and answer the question that follow:
The performance of the Indian economy during the period of first seven five-year plans (1950-1990) was satisfactory if not very impressive. On the eve of independence, India was an industrially backward country, but during this period of first seven plans our industries became far more diversified, with the stress being laid on the public investments in the industrial sector. The policy of import substitution led to protection of the domestic industries against the foreign producers
but we failed to promote a strong export surplus. Although public sector expanded to a large extent but it could not bring desired level of improvement in the secondary sector. Excessive government regulations prevented the natural trajectory of growth of entrepreneurship as there was no competition, no innovation and no modernization on the front of the industrial sector. Many Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) incurred huge losses due to operational inefficiencies, red-tapism, poor technology and other similar reasons. These PSUs continued to function because it was difficult to close a government undertaking even it is a drain on country’s limited resources. On the Agricultural front, due to the measures taken under the Green Revolution, India more or less became self-sufficient in the production of food grains. So, the needs for reform of economic policy was widely felt in the context of changing global economic scenario to achieve desired growth in the country.
Q. Which of the following was not a reason for the public sector to play a major role in the initial phase of Indian Economic Planning?
a)
Private entrepreneurs lacked sufficient capital for investment.
b)
Government aimed at social welfare.
c)
The market was big enough to encourage private industrialists for investment.
d)
The government wanted to protect the indigenous producers from the foreign competition.
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
The market was big enough to encourage private industrialists for investment.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Because of India's rapidly growing population the country's traditional agricultural practices yielded insufficient food production.Reason (R): Agricultural technological advancements offered opportunities to increase productivity.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Because of India's rapidly growing population the country's traditional agricultural practices yielded insufficient food production.
Reason (R): Agricultural technological advancements offered opportunities to increase productivity.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Priyanka Khatri answered |
In the context of India's rapidly growing population, the country's traditional agricultural practices yielded insufficient food production. By the 1960s, this low productivity led India to experience food grain shortages that were more severe than those of other developing countries. Agricultural technological advancements offered opportunities to increase productivity.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Finished goods were exported from India during the Colonial Era.Reason (R): India was a hub for raw materials for the British Industries.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Finished goods were exported from India during the Colonial Era.
Reason (R): India was a hub for raw materials for the British Industries.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Amita Das answered |
From the time of Independence, India has been one of the important trading countries, exporting primary items like cotton, raw silk, sugar, wool, jute, and indigo, etc. and importer of finished consumer goods like woollen clothes, cotton, silk, and capital goods like light machinery manufactured in Britain.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Size of multiplier is given by the inverse of LRRReason(R): There is direct relationship between LRR and value of money multiplier- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Size of multiplier is given by the inverse of LRR
Reason(R): There is direct relationship between LRR and value of money multiplier
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
The deposit multiplier is sometimes expressed as the deposit multiplier ratio, which is the inverse of the required reserve ratio. For example, if the required reserve ratio is 20%, the deposit multiplier ratio is 80%.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion: Central bank uses many tools such as Bank rate, repo rate, reverse repo rate etc. to control money supply in the economy.Reason: Commercial bank is the apex Bank of India.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Central bank uses many tools such as Bank rate, repo rate, reverse repo rate etc. to control money supply in the economy.
Reason: Commercial bank is the apex Bank of India.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Reverse Repo rate is the short term borrowing rate at which RBI borrows money from banks. The central bank uses this tool to change the money supply in the economy. An increase in the reverse repo rate means that the banks will get a higher rate of interest from RBI.
Direction: Read the report given below and answer the questions that follow:China and India are the two emerging economies of the world. As of 2019, China and India are 2nd and 5th largest country of the world, respectively in nominal basis. On PPP basis, China is at 1st and India is at 3rd place. Both countries together share 19.46% and 27.18% of total global wealth in nominal and PPP terms, respectively. Among Asian countries, China and India together contribute more than half of Asia’s GDP.In 1987, GDP (Nominal) of both countries was almost equal. But in 2019, China’s GDP is 4.78 times greater than India. On PPP basis, GDP of China is 2.38x of India. China crossed $1 trillion mark in 1998 while India crossed 9 year later in 2007 at exchange rate basis.Both countries have been neck-to-neck in GDP per capita terms. As per both methods, India was richer than China in 1990. Now in 2019, China is almost 4.61 times richer than India in nominal method and 2.30 times richer in PPP method. Per capita rank of China and India is 72th and 145th, resp, in nominal. Per capita rank of China and India is 75th and 126th, resp, in PPP.China attains maximum GDP growth rate of 19.30% in year 1970 and minimum -27.27% in 1961. India reached an all time high of 9.63% in 1988 and a record low of -5.24% in 1979. During period 1961 to 2018, China grew by more than 10% in 22 years while India never. GDP growth rate was negative in five and four years for China and India, respectively.According to CIA Factbook sector wise GDP composition of India in 2017 are as follows : Agriculture (15.4%), Industry (23%) and Services (61.5%). Sector wise GDP composition of China in 2017 are : Agriculture (8.3%), Industry (39.5%) and Services (52.2%).- Comparing China and India by Economy – The Statistic Times – 28th August, 2019China is ______________ economy.- a)Agricultural
- b)Industrial
- c)Both (A) and (B)
- d)Neither (A) nor (B)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the report given below and answer the questions that follow:
China and India are the two emerging economies of the world. As of 2019, China and India are 2nd and 5th largest country of the world, respectively in nominal basis. On PPP basis, China is at 1st and India is at 3rd place. Both countries together share 19.46% and 27.18% of total global wealth in nominal and PPP terms, respectively. Among Asian countries, China and India together contribute more than half of Asia’s GDP.
In 1987, GDP (Nominal) of both countries was almost equal. But in 2019, China’s GDP is 4.78 times greater than India. On PPP basis, GDP of China is 2.38x of India. China crossed $1 trillion mark in 1998 while India crossed 9 year later in 2007 at exchange rate basis.
Both countries have been neck-to-neck in GDP per capita terms. As per both methods, India was richer than China in 1990. Now in 2019, China is almost 4.61 times richer than India in nominal method and 2.30 times richer in PPP method. Per capita rank of China and India is 72th and 145th, resp, in nominal. Per capita rank of China and India is 75th and 126th, resp, in PPP.
China attains maximum GDP growth rate of 19.30% in year 1970 and minimum -27.27% in 1961. India reached an all time high of 9.63% in 1988 and a record low of -5.24% in 1979. During period 1961 to 2018, China grew by more than 10% in 22 years while India never. GDP growth rate was negative in five and four years for China and India, respectively.
According to CIA Factbook sector wise GDP composition of India in 2017 are as follows : Agriculture (15.4%), Industry (23%) and Services (61.5%). Sector wise GDP composition of China in 2017 are : Agriculture (8.3%), Industry (39.5%) and Services (52.2%).
- Comparing China and India by Economy – The Statistic Times – 28th August, 2019
China is ______________ economy.
a)
Agricultural
b)
Industrial
c)
Both (A) and (B)
d)
Neither (A) nor (B)
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Industry was 39.5% of China's gross domestic product (GDP).
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Supply of money is a stock variableReason (R): Supply of money is measured over a period of time, usually a fiscal year- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Supply of money is a stock variable
Reason (R): Supply of money is measured over a period of time, usually a fiscal year
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Money supply refers to the total sum of money available to the public in the economy at a point of time. Because money supply is measured at a particular point of time,it is a stock variable.
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:The country’s real gross domestic product (GDP) is likely to expand by 11 percent in the next financial year due to a faster economic recovery and on a low base, says a report. The report by domestic rating agency Brickwork Ratings said economic activities are slowly reaching Pre-COVID levels following the relaxation of the lockdown, except in sectors that remain affected by social distancing norms.“With progress in developing an effective vaccine for COVID-19 and signals of faster-than-expected recovery in the domestic economy, and also supported by a low base, we expect the real GDP to grow at 11 percent in F/Y 22, from the estimated contraction of 7 percent to 7.5 percent in F/Y 21,” the agency said.According to the first advance estimates of national income released by the National Statistical Office (NSO), the country’s GDP is estimated to contract by a record 7.7 percent during the current financial year.What will be the growth rate of GDP according to the NSO? - a)– 7.7%
- b)+7.7%
- c)+11%
- d)– 7.5%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
The country’s real gross domestic product (GDP) is likely to expand by 11 percent in the next financial year due to a faster economic recovery and on a low base, says a report. The report by domestic rating agency Brickwork Ratings said economic activities are slowly reaching Pre-COVID levels following the relaxation of the lockdown, except in sectors that remain affected by social distancing norms.
“With progress in developing an effective vaccine for COVID-19 and signals of faster-than-expected recovery in the domestic economy, and also supported by a low base, we expect the real GDP to grow at 11 percent in F/Y 22, from the estimated contraction of 7 percent to 7.5 percent in F/Y 21,” the agency said.
According to the first advance estimates of national income released by the National Statistical Office (NSO), the country’s GDP is estimated to contract by a record 7.7 percent during the current financial year.
What will be the growth rate of GDP according to the NSO?
a)
– 7.7%
b)
+7.7%
c)
+11%
d)
– 7.5%

|
Navya Sengupta answered |
Explanation:
Growth Rate of GDP According to NSO:
- The National Statistical Office (NSO) has estimated that the country's GDP will contract by a record 7.7% during the current financial year.
This indicates that the GDP is expected to shrink by 7.7% as per the first advance estimates released by the NSO. The negative growth rate suggests a contraction in the economy's overall output and performance during the specified period.
Growth Rate of GDP According to NSO:
- The National Statistical Office (NSO) has estimated that the country's GDP will contract by a record 7.7% during the current financial year.
This indicates that the GDP is expected to shrink by 7.7% as per the first advance estimates released by the NSO. The negative growth rate suggests a contraction in the economy's overall output and performance during the specified period.
Read the following hypothetical case study carefully and answer the question on the basis of the same.Since ages, farmers in India have taken recourse to debt. In the earlier times the same was from informal sources. Since independence with the efforts of the government, the formal sector has actively come into picture. Farmers borrow not only to meet their investment needs but also to satisfy their personal needs. Uncertainty of income caused by factors like crop failure caused by irregular rainfall, reduction in ground water table, locust/other pest attack, etc. These reasons push them into the clutches of the private money lenders, who charge exorbitant rates of interest which add to their miseries.Various governments in India, at different times for different reasons, introduced debt relief/waiver schemes. These schemes are used by governments as a quick means to extricate farmers from their indebtedness, helping to restore their capacity to invest and produce, in short to lessen the miseries of the farmers across India. The costs and benefits of such debt relief schemes are, however, a widely debated topic among economists. Some economists argue that such schemes are extremely beneficial to the poor and marginalised farmers while others argue that these schemes add to the fiscal burden of the government, others believe that these schemes may develop the expectation of repeated bailouts among farmers which may spoil the credit culture among farmers.Q. The rural banking structure in India consists of a set of multi-agency institutions _____________ is expected to dispense credit at cheaper rates for agricultural purposes to farmers.- a)Regional Rural Banks
- b)Small Industries Development Bank of India
- c)Both (A) and (B)
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following hypothetical case study carefully and answer the question on the basis of the same.
Since ages, farmers in India have taken recourse to debt. In the earlier times the same was from informal sources. Since independence with the efforts of the government, the formal sector has actively come into picture. Farmers borrow not only to meet their investment needs but also to satisfy their personal needs. Uncertainty of income caused by factors like crop failure caused by irregular rainfall, reduction in ground water table, locust/other pest attack, etc. These reasons push them into the clutches of the private money lenders, who charge exorbitant rates of interest which add to their miseries.
Various governments in India, at different times for different reasons, introduced debt relief/waiver schemes. These schemes are used by governments as a quick means to extricate farmers from their indebtedness, helping to restore their capacity to invest and produce, in short to lessen the miseries of the farmers across India. The costs and benefits of such debt relief schemes are, however, a widely debated topic among economists. Some economists argue that such schemes are extremely beneficial to the poor and marginalised farmers while others argue that these schemes add to the fiscal burden of the government, others believe that these schemes may develop the expectation of repeated bailouts among farmers which may spoil the credit culture among farmers.
Q. The rural banking structure in India consists of a set of multi-agency institutions _____________ is expected to dispense credit at cheaper rates for agricultural purposes to farmers.
a)
Regional Rural Banks
b)
Small Industries Development Bank of India
c)
Both (A) and (B)
d)
None of the above
|
|
Amita Das answered |
The institutional structure of rural banking today consists of a set of multi agency institutions, which are
(i) Commercial banks
(ii) Regional Rural Banks (HHBs)
(iii) C o-operatives and Land development banks
Recently, Self-Help Groups (henceforth SHGs) have also emerged.
Read the report given below and answer the question that follow:NEW DELHI: Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on Monday announced plans to sell a stake in LIC as part of her disinvestment plans for F/Y 22. In her Budget speech, the FM said her government will complete divestment of BPCL, CONCOR and SCI in F/Y 22. She said that her government will privatise two public sector banks (PSBs) and one general insurance company as well. “LIC IPO may see the light of day soon,” said Jiger Saiya, Partner and Leader - Tax & Regulatory Services at BDO India.Earlier, in an interview with ET, LIC Chairman M R Kumar had said the IPO is very much likely. “The point is that it is going to be big and we want to get the valuations right,” he had said, adding that the listing of an insurance company requires determining the embedded value of the business.LIC has started the process and would soon announce the software, which will assist it determine the right valuation. “We have floated an RFP for the actuarial firm that will undertake the exercise. This calculation will take some time. Once this process is done, we will be ready,” Kumar said on January 11.Last week, a Reuters report quoting sources suggested that the government was looking to sell 10-15 per cent in the country’s biggest insurer to improve public finances.To facilitate the sale of the LIC stake, the government will need Parliament approval to amend the LIC Act.As part of its divestment drive, four CPSEs – HAL, SAIL, Bharat Dynamics and IRCTC –have come out with offers for sale (OFSs) this financial year. They garnered ₹12,907 crore to the exchequer. In addition, IPOs of IRFC and Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders together fetched ₹1,984 crore.Also, this year, the government sold shares worth about ₹1,837 crore in private companies, in which it holds stakes through SUUTI.Four state-owned companies, NTPC, RITES, NMDC and KIOCL, completed share buybacks, adding ₹2,769 crore to the exchequer.The government is also looking to sell its entire 26.12 per cent stake in Tata Communications (TCL), erstwhile VSNL, through an OFS and strategic sale this financial year. The process of privatisation of Air India, BPCL, Pawan Hans, BEML, Shipping Corp, Neelachal Ispat Nigam Limited and Ferro Scrap Nigam Limited (FSNL) is currently underway.Q. According to Reuters, why is the government looking to sell the country's insurer?- a)To reduce revenue deficit
- b)To reduce fiscal deficit
- c)To improve public finances
- d)To get money other than taxes.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the report given below and answer the question that follow:
NEW DELHI: Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on Monday announced plans to sell a stake in LIC as part of her disinvestment plans for F/Y 22. In her Budget speech, the FM said her government will complete divestment of BPCL, CONCOR and SCI in F/Y 22. She said that her government will privatise two public sector banks (PSBs) and one general insurance company as well. “LIC IPO may see the light of day soon,” said Jiger Saiya, Partner and Leader - Tax & Regulatory Services at BDO India.
Earlier, in an interview with ET, LIC Chairman M R Kumar had said the IPO is very much likely. “The point is that it is going to be big and we want to get the valuations right,” he had said, adding that the listing of an insurance company requires determining the embedded value of the business.
LIC has started the process and would soon announce the software, which will assist it determine the right valuation. “We have floated an RFP for the actuarial firm that will undertake the exercise. This calculation will take some time. Once this process is done, we will be ready,” Kumar said on January 11.
Last week, a Reuters report quoting sources suggested that the government was looking to sell 10-15 per cent in the country’s biggest insurer to improve public finances.
To facilitate the sale of the LIC stake, the government will need Parliament approval to amend the LIC Act.
As part of its divestment drive, four CPSEs – HAL, SAIL, Bharat Dynamics and IRCTC –have come out with offers for sale (OFSs) this financial year. They garnered ₹12,907 crore to the exchequer. In addition, IPOs of IRFC and Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders together fetched ₹1,984 crore.
Also, this year, the government sold shares worth about ₹1,837 crore in private companies, in which it holds stakes through SUUTI.
Four state-owned companies, NTPC, RITES, NMDC and KIOCL, completed share buybacks, adding ₹2,769 crore to the exchequer.
The government is also looking to sell its entire 26.12 per cent stake in Tata Communications (TCL), erstwhile VSNL, through an OFS and strategic sale this financial year. The process of privatisation of Air India, BPCL, Pawan Hans, BEML, Shipping Corp, Neelachal Ispat Nigam Limited and Ferro Scrap Nigam Limited (FSNL) is currently underway.
Q. According to Reuters, why is the government looking to sell the country's insurer?
a)
To reduce revenue deficit
b)
To reduce fiscal deficit
c)
To improve public finances
d)
To get money other than taxes.
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
A Reuters report citing sources suggested the government was looking to sell 10-15 percent of the country's largest insurer to improve public finances.
निम्नलिखित में से कौन सा मार्ग मुंबई को नासिक से जोड़ता है?- a)थाल घाट
- b)पाल घाट
- c)शेंकोत्तह गैप
- d)दर्रा दर्रा
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
निम्नलिखित में से कौन सा मार्ग मुंबई को नासिक से जोड़ता है?
a)
थाल घाट
b)
पाल घाट
c)
शेंकोत्तह गैप
d)
दर्रा दर्रा
|
|
Rahul Mehta answered |
थाल घाट भी Thul घाट या कसारा घाट के रूप में बुलाया जोड़ता है नासिक से मुंबई । यह मुंबई में अग्रणी चार प्रमुख मार्गों, रेल और सड़क मार्गों में से एक है।
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Green revolution though improved the production of crops but did not increase the income of the farmers.Reason (R): The farmers sold more crops at a lesser price.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Green revolution though improved the production of crops but did not increase the income of the farmers.
Reason (R): The farmers sold more crops at a lesser price.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.

|
Gowri Chavan answered |
Explanation:
Assertion (A) is false:
The assertion that the Green Revolution did not increase the income of farmers is false. The Green Revolution, which introduced high-yielding variety seeds, modern agricultural techniques, and increased the use of fertilizers and pesticides, did lead to a significant increase in crop production. This increase in production did result in higher incomes for many farmers who were able to sell more crops.
Reason (R) is true:
The reason given for the assertion is true. Due to the increased production brought about by the Green Revolution, farmers often had to sell their crops at lower prices to compete in the market. The surplus of crops led to a decrease in prices, which affected the income of some farmers who were not able to benefit from the increased production.
Therefore, while the assertion is false because the Green Revolution did increase the income of many farmers through higher production, the reason is true as some farmers did face challenges with selling their increased crops at lower prices.
Assertion (A) is false:
The assertion that the Green Revolution did not increase the income of farmers is false. The Green Revolution, which introduced high-yielding variety seeds, modern agricultural techniques, and increased the use of fertilizers and pesticides, did lead to a significant increase in crop production. This increase in production did result in higher incomes for many farmers who were able to sell more crops.
Reason (R) is true:
The reason given for the assertion is true. Due to the increased production brought about by the Green Revolution, farmers often had to sell their crops at lower prices to compete in the market. The surplus of crops led to a decrease in prices, which affected the income of some farmers who were not able to benefit from the increased production.
Therefore, while the assertion is false because the Green Revolution did increase the income of many farmers through higher production, the reason is true as some farmers did face challenges with selling their increased crops at lower prices.
Read the following hypothetical text and answer the question that follow:The performance of the Indian economy during the period of first seven five-year plans (1950-1990) was satisfactory if not very impressive. On the eve of independence, India was an industrially backward country, but during this period of first seven plans our industries became far more diversified, with the stress being laid on the public investments in the industrial sector. The policy of import substitution led to protection of the domestic industries against the foreign producersbut we failed to promote a strong export surplus. Although public sector expanded to a large extent but it could not bring desired level of improvement in the secondary sector. Excessive government regulations prevented the natural trajectory of growth of entrepreneurship as there was no competition, no innovation and no modernization on the front of the industrial sector. Many Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) incurred huge losses due to operational inefficiencies, red-tapism, poor technology and other similar reasons. These PSUs continued to function because it was difficult to close a government undertaking even it is a drain on country’s limited resources. On the Agricultural front, due to the measures taken under the Green Revolution, India more or less became self-sufficient in the production of food grains. So, the needs for reform of economic policy was widely felt in the context of changing global economic scenario to achieve desired growth in the country.Q. Mechanization of Indian agriculture was one of the causes of ___________ in India.- a)Green Revolution
- b)White Revolution
- c)Yellow Revolution
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following hypothetical text and answer the question that follow:
The performance of the Indian economy during the period of first seven five-year plans (1950-1990) was satisfactory if not very impressive. On the eve of independence, India was an industrially backward country, but during this period of first seven plans our industries became far more diversified, with the stress being laid on the public investments in the industrial sector. The policy of import substitution led to protection of the domestic industries against the foreign producers
but we failed to promote a strong export surplus. Although public sector expanded to a large extent but it could not bring desired level of improvement in the secondary sector. Excessive government regulations prevented the natural trajectory of growth of entrepreneurship as there was no competition, no innovation and no modernization on the front of the industrial sector. Many Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) incurred huge losses due to operational inefficiencies, red-tapism, poor technology and other similar reasons. These PSUs continued to function because it was difficult to close a government undertaking even it is a drain on country’s limited resources. On the Agricultural front, due to the measures taken under the Green Revolution, India more or less became self-sufficient in the production of food grains. So, the needs for reform of economic policy was widely felt in the context of changing global economic scenario to achieve desired growth in the country.
Q. Mechanization of Indian agriculture was one of the causes of ___________ in India.
a)
Green Revolution
b)
White Revolution
c)
Yellow Revolution
d)
None of the above
|
|
Amita Das answered |
This necessitated the “Green Revolution”, which was largely due to the advent of technology, improved water supply and better agricultural practices. In addition, the increase in agricultural mechanisation and the use of crop protection systems have also contributed to the emergence of “Green Revolution” in India.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Currency held with the government and banks is not included in the Money Supply.Reason (R): Currency can be legally used to make payment of debts or other obligations.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Currency held with the government and banks is not included in the Money Supply.
Reason (R): Currency can be legally used to make payment of debts or other obligations.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Money supply includes the currency that is in circulation with the public at a particular point of time, hence it does not include the money held by government or commercial banks as it is not in circulation with the public at a given point in time.
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:The Centre on Saturday increased the budgetary allocation for the environment ministry from last fiscal by nearly five percent for 2020-21 with no change in the amount allotted to pollution abatement and climate change action plan.Union Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, allocated ₹ 3,100 crore for the ministry out of which ₹ 460 crore were allotted to control pollution, which is the same as the money it received in the last budget.Control of pollution has been conceptualized to provide financial assistance to Pollution Control Boards/Committees and funding to National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).Similarly, budget for pollution abatement, which was cut by 50 percent last year from 2018-19, remained unchanged at ₹ 10 crore.The minister also announced that states, which are formulating and implementing plans for ensuring cleaner air in cities above one million population should be encouraged.Why is the policy implemented?- a)To ensure clear air
- b)To ensure clear water
- c)To ensure clean roads
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
The Centre on Saturday increased the budgetary allocation for the environment ministry from last fiscal by nearly five percent for 2020-21 with no change in the amount allotted to pollution abatement and climate change action plan.
Union Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, allocated ₹ 3,100 crore for the ministry out of which ₹ 460 crore were allotted to control pollution, which is the same as the money it received in the last budget.
Control of pollution has been conceptualized to provide financial assistance to Pollution Control Boards/Committees and funding to National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).
Similarly, budget for pollution abatement, which was cut by 50 percent last year from 2018-19, remained unchanged at ₹ 10 crore.
The minister also announced that states, which are formulating and implementing plans for ensuring cleaner air in cities above one million population should be encouraged.
Why is the policy implemented?
a)
To ensure clear air
b)
To ensure clear water
c)
To ensure clean roads
d)
All of the above

|
Meera Rane answered |
Rationale Behind the Policy Implementation
The policy implemented by the Centre focuses primarily on ensuring cleaner air, reflecting a commitment to environmental health and public welfare.
Key Objectives of the Policy
- Air Quality Improvement: The allocation of funds specifically for pollution control indicates a targeted approach to improving air quality. With cities housing over a million inhabitants facing severe air pollution, this policy aims to tackle the issue by funding initiatives that promote cleaner air.
- Support for State Initiatives: By encouraging states to formulate and implement plans for cleaner air, the government acknowledges the importance of local action in addressing pollution. This decentralized approach empowers states to tailor solutions to their specific challenges.
- Allocation of Resources: The unchanged budget for pollution control and its clear designation for the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) highlight a sustained commitment to strategies that effectively address air pollution.
Broader Environmental Impact
While the focus is on air quality, the implications of cleaner air extend beyond just one element of the environment. Cleaner air contributes to better health outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, and overall improved quality of life for citizens.
Conclusion
In summary, the policy's primary aim is to ensure clear air, addressing a critical environmental concern that affects the health and well-being of the population. While water and road cleanliness are also important, this specific allocation and focus on air quality delineate the central objective of the implemented policy.
The policy implemented by the Centre focuses primarily on ensuring cleaner air, reflecting a commitment to environmental health and public welfare.
Key Objectives of the Policy
- Air Quality Improvement: The allocation of funds specifically for pollution control indicates a targeted approach to improving air quality. With cities housing over a million inhabitants facing severe air pollution, this policy aims to tackle the issue by funding initiatives that promote cleaner air.
- Support for State Initiatives: By encouraging states to formulate and implement plans for cleaner air, the government acknowledges the importance of local action in addressing pollution. This decentralized approach empowers states to tailor solutions to their specific challenges.
- Allocation of Resources: The unchanged budget for pollution control and its clear designation for the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) highlight a sustained commitment to strategies that effectively address air pollution.
Broader Environmental Impact
While the focus is on air quality, the implications of cleaner air extend beyond just one element of the environment. Cleaner air contributes to better health outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, and overall improved quality of life for citizens.
Conclusion
In summary, the policy's primary aim is to ensure clear air, addressing a critical environmental concern that affects the health and well-being of the population. While water and road cleanliness are also important, this specific allocation and focus on air quality delineate the central objective of the implemented policy.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Soil Erosion is the major environmental problem faced by India.Reason (R): India is an agricultural economy- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Soil Erosion is the major environmental problem faced by India.
Reason (R): India is an agricultural economy
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.

|
Isha Chopra answered |
Assertion (A): Soil Erosion is the major environmental problem faced by India.
Reason (R): India is an agricultural economy.
Explanation:
Soil erosion is indeed a major environmental problem faced by India, and this is due to various reasons. Let's analyze the given assertion and reason in detail:
Assertion (A): Soil Erosion is the major environmental problem faced by India.
Soil erosion refers to the process of the removal of topsoil by natural forces such as wind, water, and human activities. It is a significant concern for agricultural countries like India as it affects the fertility and productivity of the land, leading to reduced agricultural output and food security issues. Soil erosion can also result in the loss of vital nutrients, increased sedimentation in rivers, and degradation of water quality. Therefore, the assertion that soil erosion is a major environmental problem faced by India is true.
Reason (R): India is an agricultural economy.
India is primarily an agricultural economy, with a significant portion of its population engaged in agriculture and allied activities. The agricultural sector contributes significantly to India's GDP, employment, and food production. However, intensive agricultural practices, improper land management, deforestation, and overgrazing have led to increased soil erosion in the country. The excessive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, as well as the absence of proper soil conservation measures, further exacerbate the problem. Therefore, the reason given that India is an agricultural economy is true.
Conclusion:
Both the assertion and reason are true. However, the reason provided does not directly explain why soil erosion is a major environmental problem in India. While being an agricultural economy contributes to soil erosion, it is not the sole reason. Other factors such as improper land management, deforestation, and intensive agricultural practices also play significant roles. Hence, option 'C' is the correct answer as assertion (A) is true, but reason (R) is false.
Reason (R): India is an agricultural economy.
Explanation:
Soil erosion is indeed a major environmental problem faced by India, and this is due to various reasons. Let's analyze the given assertion and reason in detail:
Assertion (A): Soil Erosion is the major environmental problem faced by India.
Soil erosion refers to the process of the removal of topsoil by natural forces such as wind, water, and human activities. It is a significant concern for agricultural countries like India as it affects the fertility and productivity of the land, leading to reduced agricultural output and food security issues. Soil erosion can also result in the loss of vital nutrients, increased sedimentation in rivers, and degradation of water quality. Therefore, the assertion that soil erosion is a major environmental problem faced by India is true.
Reason (R): India is an agricultural economy.
India is primarily an agricultural economy, with a significant portion of its population engaged in agriculture and allied activities. The agricultural sector contributes significantly to India's GDP, employment, and food production. However, intensive agricultural practices, improper land management, deforestation, and overgrazing have led to increased soil erosion in the country. The excessive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, as well as the absence of proper soil conservation measures, further exacerbate the problem. Therefore, the reason given that India is an agricultural economy is true.
Conclusion:
Both the assertion and reason are true. However, the reason provided does not directly explain why soil erosion is a major environmental problem in India. While being an agricultural economy contributes to soil erosion, it is not the sole reason. Other factors such as improper land management, deforestation, and intensive agricultural practices also play significant roles. Hence, option 'C' is the correct answer as assertion (A) is true, but reason (R) is false.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): During colonial period, India’s export trade was export surplus.Reason (R): During the colonial period, India’s exports were more than its imports.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): During colonial period, India’s export trade was export surplus.
Reason (R): During the colonial period, India’s exports were more than its imports.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.

|
Surbhi Mishra answered |
Assertion and Reasoning in Commerce: India's Export Trade During Colonial Period
Assertion: During colonial period, India’s export trade was export surplus.
Reason: During the colonial period, India’s exports were more than its imports.
The correct choice is option B, which means that both the assertion and reasoning are true, but the reasoning is not the correct explanation of the assertion. Let's break down this question and understand why this is the correct answer.
Export Surplus:
Export surplus refers to a situation when a country's total export earnings exceed its total import expenditure. In other words, a country is exporting more goods and services than it is importing. This situation is also known as a favorable balance of trade.
Colonial Period:
The colonial period in India refers to the time when India was under British rule, from the mid-18th century to 1947. During this time, the British East India Company and later the British government controlled India's economy and trade.
India's Export Trade during Colonial Period:
During the colonial period, India's export trade was mainly based on raw materials such as cotton, jute, tea, and indigo. These raw materials were exported to Britain and other European countries, where they were processed and manufactured into finished goods. India's exports exceeded its imports during this period, which means that India had an export surplus.
Reason for India's Export Surplus:
The reason for India's export surplus during the colonial period was mainly due to the exploitative economic policies of the British government. India was forced to export its raw materials to Britain at low prices and was required to import finished goods at high prices. This resulted in an unfavorable balance of trade for India, which led to the drain of wealth from India to Britain.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, during the colonial period, India's export trade was export surplus due to the exploitative economic policies of the British government. While the assertion and reasoning in this question are both true, the reasoning is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Assertion: During colonial period, India’s export trade was export surplus.
Reason: During the colonial period, India’s exports were more than its imports.
The correct choice is option B, which means that both the assertion and reasoning are true, but the reasoning is not the correct explanation of the assertion. Let's break down this question and understand why this is the correct answer.
Export Surplus:
Export surplus refers to a situation when a country's total export earnings exceed its total import expenditure. In other words, a country is exporting more goods and services than it is importing. This situation is also known as a favorable balance of trade.
Colonial Period:
The colonial period in India refers to the time when India was under British rule, from the mid-18th century to 1947. During this time, the British East India Company and later the British government controlled India's economy and trade.
India's Export Trade during Colonial Period:
During the colonial period, India's export trade was mainly based on raw materials such as cotton, jute, tea, and indigo. These raw materials were exported to Britain and other European countries, where they were processed and manufactured into finished goods. India's exports exceeded its imports during this period, which means that India had an export surplus.
Reason for India's Export Surplus:
The reason for India's export surplus during the colonial period was mainly due to the exploitative economic policies of the British government. India was forced to export its raw materials to Britain at low prices and was required to import finished goods at high prices. This resulted in an unfavorable balance of trade for India, which led to the drain of wealth from India to Britain.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, during the colonial period, India's export trade was export surplus due to the exploitative economic policies of the British government. While the assertion and reasoning in this question are both true, the reasoning is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:Circular Income Flow in a Two Sector Economy: In the figure given we can see that upper loop shows the resources such as land, capital and entrepreneurial ability flow from households to firms in the direction shown by the arrow direction.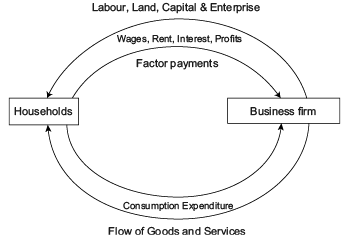 The money flows from firms to the households as factor payments in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits, shown by the arrow direction.The lower part of the figure shows the flow of money from households to firms in the form of consumption expenditure done by the households to purchase the goods and services produced by the firms, making the flow of goods and services from firms to households.Thus, we see that money flows from business firms to households as factor payments and then it flows from households to firms. Thus, there is, in fact, a circular flow of money or income. This is how the economy functions.Which of the following is not an assumption of a two sector model of Circular Flow of Income?
The money flows from firms to the households as factor payments in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits, shown by the arrow direction.The lower part of the figure shows the flow of money from households to firms in the form of consumption expenditure done by the households to purchase the goods and services produced by the firms, making the flow of goods and services from firms to households.Thus, we see that money flows from business firms to households as factor payments and then it flows from households to firms. Thus, there is, in fact, a circular flow of money or income. This is how the economy functions.Which of the following is not an assumption of a two sector model of Circular Flow of Income?- a)Domestic economy comprises only 2 sectors, the producers and the households.
- b)The households spend their entire income, so that there is no saving.
- c)Domestic economy is an open economy (no exports and imports).
- d)There is no government in the economy.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
Circular Income Flow in a Two Sector Economy: In the figure given we can see that upper loop shows the resources such as land, capital and entrepreneurial ability flow from households to firms in the direction shown by the arrow direction.

The money flows from firms to the households as factor payments in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits, shown by the arrow direction.
The lower part of the figure shows the flow of money from households to firms in the form of consumption expenditure done by the households to purchase the goods and services produced by the firms, making the flow of goods and services from firms to households.
Thus, we see that money flows from business firms to households as factor payments and then it flows from households to firms. Thus, there is, in fact, a circular flow of money or income. This is how the economy functions.
Which of the following is not an assumption of a two sector model of Circular Flow of Income?
a)
Domestic economy comprises only 2 sectors, the producers and the households.
b)
The households spend their entire income, so that there is no saving.
c)
Domestic economy is an open economy (no exports and imports).
d)
There is no government in the economy.

|
Let's Tute answered |
The two sector economy has the following assumptions:
- There are only two sectors in the economy; household sector and business sector.
- No government interventions over the economic activities.
- Business sectors do not carry out any import or export activities, creating a closed economy.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): In rural India, horticulture plays a vital role in providing food and nutrition to the rural population.Reason (R): Various horticultural activities in Indian villages have improved the economic conditions of many farmers. Such activities have become a lucrative source of livelihood for many women in rural India.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): In rural India, horticulture plays a vital role in providing food and nutrition to the rural population.
Reason (R): Various horticultural activities in Indian villages have improved the economic conditions of many farmers. Such activities have become a lucrative source of livelihood for many women in rural India.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
Blessed with a varying climate and soil conditions, India has adopted growing of diverse horticultural crops such as fruits, vegetables, tuber crops, flowers, medicinal and aromatic plants, spices and plantation crops. These crops play a vital role in providing food and nutrition, besides addressing employment concerns. The Horticulture sector contributes nearly one-third of the value of agriculture output and six per cent of Gross Domestic Product of India. India has emerged as a world leader in producing a variety of fruits like mangoes, bananas, coconuts, cashew nuts and a number of spices and is the second largest producer of fruits and vegetables. Economic condition of many farmers engaged in horticulture has improved and it has become a means of improving livelihood for many unprivileged classes.
Direction: Read the report given below and answer the questions that follow:
China and India are the two emerging economies of the world. As of 2019, China and India are 2nd and 5th largest country of the world, respectively in nominal basis. On PPP basis, China is at 1st and India is at 3rd place. Both countries together share 19.46% and 27.18% of total global wealth in nominal and PPP terms, respectively. Among Asian countries, China and India together contribute more than half of Asia’s GDP.
In 1987, GDP (Nominal) of both countries was almost equal. But in 2019, China’s GDP is 4.78 times greater than India. On PPP basis, GDP of China is 2.38x of India. China crossed $1 trillion mark in 1998 while India crossed 9 year later in 2007 at exchange rate basis.
Both countries have been neck-to-neck in GDP per capita terms. As per both methods, India was richer than China in 1990. Now in 2019, China is almost 4.61 times richer than India in nominal method and 2.30 times richer in PPP method. Per capita rank of China and India is 72th and 145th, resp, in nominal. Per capita rank of China and India is 75th and 126th, resp, in PPP.
China attains maximum GDP growth rate of 19.30% in year 1970 and minimum -27.27% in 1961. India reached an all time high of 9.63% in 1988 and a record low of -5.24% in 1979. During period 1961 to 2018, China grew by more than 10% in 22 years while India never. GDP growth rate was negative in five and four years for China and India, respectively.
According to CIA Factbook sector wise GDP composition of India in 2017 are as follows : Agriculture (15.4%), Industry (23%) and Services (61.5%). Sector wise GDP composition of China in 2017 are : Agriculture (8.3%), Industry (39.5%) and Services (52.2%).
- Comparing China and India by Economy – The Statistic Times – 28th August, 2019
India is dependent on ____________ sector for its GDP contribution.
- a)India, China
- b)India, Pakistan
- c)China, Pakistan
- d)India, Bangladesh
- e)Agriculture
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the report given below and answer the questions that follow:
China and India are the two emerging economies of the world. As of 2019, China and India are 2nd and 5th largest country of the world, respectively in nominal basis. On PPP basis, China is at 1st and India is at 3rd place. Both countries together share 19.46% and 27.18% of total global wealth in nominal and PPP terms, respectively. Among Asian countries, China and India together contribute more than half of Asia’s GDP.
In 1987, GDP (Nominal) of both countries was almost equal. But in 2019, China’s GDP is 4.78 times greater than India. On PPP basis, GDP of China is 2.38x of India. China crossed $1 trillion mark in 1998 while India crossed 9 year later in 2007 at exchange rate basis.
Both countries have been neck-to-neck in GDP per capita terms. As per both methods, India was richer than China in 1990. Now in 2019, China is almost 4.61 times richer than India in nominal method and 2.30 times richer in PPP method. Per capita rank of China and India is 72th and 145th, resp, in nominal. Per capita rank of China and India is 75th and 126th, resp, in PPP.
China attains maximum GDP growth rate of 19.30% in year 1970 and minimum -27.27% in 1961. India reached an all time high of 9.63% in 1988 and a record low of -5.24% in 1979. During period 1961 to 2018, China grew by more than 10% in 22 years while India never. GDP growth rate was negative in five and four years for China and India, respectively.
According to CIA Factbook sector wise GDP composition of India in 2017 are as follows : Agriculture (15.4%), Industry (23%) and Services (61.5%). Sector wise GDP composition of China in 2017 are : Agriculture (8.3%), Industry (39.5%) and Services (52.2%).
- Comparing China and India by Economy – The Statistic Times – 28th August, 2019
India is dependent on ____________ sector for its GDP contribution.
a)
India, China
b)
India, Pakistan
c)
China, Pakistan
d)
India, Bangladesh
e)
Agriculture
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
The services sector accounts for 53.89% of total India's GDP composition.Sector wise GDP Composition of India
- Agriculture: 15.4%
- Industry: 23%
- Services: 61.5%
Sector wise GDP Composition of China
- Agriculture: 8.3%
- Industry: 39.5%
- Services: 52.2%
India is dependent on the Agriculture sector for its GDP contribution. This can be seen from the fact that Agriculture contributes a significant portion (15.4%) to India's GDP, which is higher compared to China. The Industry and Services sectors also play important roles in India's economy, but Agriculture remains a key sector in terms of GDP contribution.
- Agriculture: 15.4%
- Industry: 23%
- Services: 61.5%
Sector wise GDP Composition of China
- Agriculture: 8.3%
- Industry: 39.5%
- Services: 52.2%
India is dependent on the Agriculture sector for its GDP contribution. This can be seen from the fact that Agriculture contributes a significant portion (15.4%) to India's GDP, which is higher compared to China. The Industry and Services sectors also play important roles in India's economy, but Agriculture remains a key sector in terms of GDP contribution.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): The small scale industries generate more employment than the large scale industries.Reason (R): Small scale industries are more 'Capital intensive industries Therefore generate more employment.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): The small scale industries generate more employment than the large scale industries.
Reason (R): Small scale industries are more 'Capital intensive industries Therefore generate more employment.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Small scale industries depended upon the business’s capital and labour. This definition is still used to demarcate between small, medium and large-scale industries.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): An increase in CRR results in decrease in the value of Multiplier.Reason (R): Banks lend money many times more than their cash reserves.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): An increase in CRR results in decrease in the value of Multiplier.
Reason (R): Banks lend money many times more than their cash reserves.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Cash Reserves Ratio (CRR) refers to the proportion of total deposits of the commercial banks which they must keep as reserves with the central bank in the form of cash. By increasing the cash reserve ratio, the commercial banks has to maintain more cash with the central bank which reduces their credit creation capacity and therefore money supply in the economy also reduces. Therefore, increase in cash reserve ratio(CRR) reduces the money supply in the economy.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion: To curb inflation , the RBI should sell the Government securities.Reason: When RBI will sell Government securities to the people and commercial banks then money will flow to RBI which reduces the lending capacity of commercial banks.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: To curb inflation , the RBI should sell the Government securities.
Reason: When RBI will sell Government securities to the people and commercial banks then money will flow to RBI which reduces the lending capacity of commercial banks.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
To control the inflationary trend, the Central Bank should sale government securities and raise the bank rate. Both of the measures given above result in reduction in the purchasing power of people.
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Investors are reluctant to invest in tidal energy projects.Reason (R): Tidal energy has high cost and low running cost. As a result, a tidal power scheme may not give returns for years.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Investors are reluctant to invest in tidal energy projects.
Reason (R): Tidal energy has high cost and low running cost. As a result, a tidal power scheme may not give returns for years.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.

|
Rohit Roy answered |
Assertion (A): Investors are reluctant to invest in tidal energy projects.
Reason (R): Tidal energy has high cost and low running cost. As a result, a tidal power scheme may not give returns for years.
Explanation:
Investing in any project requires careful consideration of its potential returns and risks. In the case of tidal energy projects, there are certain factors that make investors reluctant to invest. Let's analyze the assertion and reason given in the question.
High Cost:
- Tidal energy projects require significant upfront capital investment due to the complex infrastructure involved. Building and installing turbines, barrages, and other necessary equipment can be expensive.
- Constructing tidal power plants in coastal areas, where tidal energy is abundant, also adds to the costs as it involves dealing with harsh marine conditions.
- The high cost of tidal energy projects can deter investors who are concerned about the initial investment and the time it takes to recoup their funds.
Low Running Cost:
- While tidal energy projects have high initial costs, they have low running costs once they are operational. Unlike fossil fuel-based power plants, tidal power plants do not require ongoing fuel costs, as they rely on the natural movement of tides to generate electricity.
- This low running cost is an advantage of tidal energy projects, as it reduces the operational expenses and makes them more sustainable in the long run.
Delayed Returns:
- Tidal energy projects may take several years to start generating returns for investors. The initial construction phase, obtaining necessary permits and licenses, and conducting feasibility studies can be time-consuming processes.
- Additionally, tidal energy projects are subject to environmental considerations and may face opposition from local communities or environmentalists, leading to delays in project implementation.
- The delayed returns on investment can make investors hesitant to allocate their funds to tidal energy projects, especially when compared to other renewable energy sources that offer quicker returns.
Conclusion:
Considering the above analysis, both the assertion and reason are true. Investors are indeed reluctant to invest in tidal energy projects due to their high initial cost, low running cost, and delayed returns. The reason provided in the question correctly explains why investors may be hesitant to invest in tidal energy projects. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Reason (R): Tidal energy has high cost and low running cost. As a result, a tidal power scheme may not give returns for years.
Explanation:
Investing in any project requires careful consideration of its potential returns and risks. In the case of tidal energy projects, there are certain factors that make investors reluctant to invest. Let's analyze the assertion and reason given in the question.
High Cost:
- Tidal energy projects require significant upfront capital investment due to the complex infrastructure involved. Building and installing turbines, barrages, and other necessary equipment can be expensive.
- Constructing tidal power plants in coastal areas, where tidal energy is abundant, also adds to the costs as it involves dealing with harsh marine conditions.
- The high cost of tidal energy projects can deter investors who are concerned about the initial investment and the time it takes to recoup their funds.
Low Running Cost:
- While tidal energy projects have high initial costs, they have low running costs once they are operational. Unlike fossil fuel-based power plants, tidal power plants do not require ongoing fuel costs, as they rely on the natural movement of tides to generate electricity.
- This low running cost is an advantage of tidal energy projects, as it reduces the operational expenses and makes them more sustainable in the long run.
Delayed Returns:
- Tidal energy projects may take several years to start generating returns for investors. The initial construction phase, obtaining necessary permits and licenses, and conducting feasibility studies can be time-consuming processes.
- Additionally, tidal energy projects are subject to environmental considerations and may face opposition from local communities or environmentalists, leading to delays in project implementation.
- The delayed returns on investment can make investors hesitant to allocate their funds to tidal energy projects, especially when compared to other renewable energy sources that offer quicker returns.
Conclusion:
Considering the above analysis, both the assertion and reason are true. Investors are indeed reluctant to invest in tidal energy projects due to their high initial cost, low running cost, and delayed returns. The reason provided in the question correctly explains why investors may be hesitant to invest in tidal energy projects. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): In rural India, horticulture plays a vital role in providing food and nutrition to the rural population.Reason (R): Various horticultural activities in Indian villages have improved the economic conditions of many farmers. Such activities have become a lucrative source of livelihood for many women in the rural India.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): In rural India, horticulture plays a vital role in providing food and nutrition to the rural population.
Reason (R): Various horticultural activities in Indian villages have improved the economic conditions of many farmers. Such activities have become a lucrative source of livelihood for many women in the rural India.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
Horticulture crops perform a vital role in the Indian economy by generating employment, providing raw material to various food processing industries, and higher farm profitability due to higher production and export earnings from foreign exchange.
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): The minimum value of investment multiplier is equal to one.Reason (R): The minimum value of investment multiplier is 1, when MPC is 0 and MPC can never be negative.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): The minimum value of investment multiplier is equal to one.
Reason (R): The minimum value of investment multiplier is 1, when MPC is 0 and MPC can never be negative.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Priyanka Khatri answered |
K = 1/1 – MPC
= 1/1 – 0 = 1
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): The Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) is essential for ensuring that banks maintain a certain level of liquid assets.
Reason (R): A higher SLR allows banks to lend more money to customers, thereby increasing overall credit in the economy.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): The Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) is essential for ensuring that banks maintain a certain level of liquid assets.
Reason (R): A higher SLR allows banks to lend more money to customers, thereby increasing overall credit in the economy.
Reason (R): A higher SLR allows banks to lend more money to customers, thereby increasing overall credit in the economy.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
Learning Educators answered |
- The Assertion is correct. The SLR is indeed a requirement for banks to maintain a portion of their deposits in liquid assets to ensure stability and solvency.
- The Reason is false. A higher SLR actually restricts the amount of money banks can lend since it mandates that a larger portion of their deposits be held as liquid assets rather than being available for lending.
- Therefore, the Reason does not correctly explain the Assertion, making Option C the correct choice.
Read the report given below and answer the questions that follow:When, at a particular price level, aggregate demand for final goods equals aggregate supply of final goods, the final goods or product market reaches its equilibrium. Aggregate demand for final goods consists of ex-ante consumption, ex-ante investment, government spending, etc. The rate of increase in ex-ante consumption due to a unit increment in income is called marginal propensity to consume. For simplicity we assume a constant final goods price and constant rate of interest over short run to determine the level of aggregate demand for final goods in the economy. We also assume that the aggregate supply is perfectly elastic at this price. Under such circumstances, aggregate output is determined solely by the level of aggregate demand. This is known as effective demand principle. An increase (decrease) in autonomous spending causes aggregate output of final goods to increase (decrease) by a larger amount through the multiplier process.At the price level mentioned in the case, Aggregate Supply is ____________.- a)Perfectly Elastic
- b)Perfectly Inelastic
- c)Unitary Elastic
- d)Elastic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the report given below and answer the questions that follow:
When, at a particular price level, aggregate demand for final goods equals aggregate supply of final goods, the final goods or product market reaches its equilibrium. Aggregate demand for final goods consists of ex-ante consumption, ex-ante investment, government spending, etc. The rate of increase in ex-ante consumption due to a unit increment in income is called marginal propensity to consume. For simplicity we assume a constant final goods price and constant rate of interest over short run to determine the level of aggregate demand for final goods in the economy. We also assume that the aggregate supply is perfectly elastic at this price. Under such circumstances, aggregate output is determined solely by the level of aggregate demand. This is known as effective demand principle. An increase (decrease) in autonomous spending causes aggregate output of final goods to increase (decrease) by a larger amount through the multiplier process.
At the price level mentioned in the case, Aggregate Supply is ____________.
a)
Perfectly Elastic
b)
Perfectly Inelastic
c)
Unitary Elastic
d)
Elastic

|
Arnav Chawla answered |
Understanding Aggregate Supply
Aggregate Supply (AS) refers to the total quantity of final goods and services that producers in an economy are willing to supply at a given price level over a specific time period. In this scenario, we are dealing with a perfectly elastic aggregate supply.
Definition of Perfectly Elastic Supply
- Perfectly elastic supply means that the quantity supplied can change dramatically with even a slight change in price.
- In this case, producers are willing to supply any amount of goods at the given price level, ensuring that there is no restriction on output.
Why Aggregate Supply is Perfectly Elastic Here
- The report states that we assume a constant final goods price and a constant rate of interest over the short run.
- This stability allows producers to respond freely to changes in aggregate demand without worrying about price fluctuations.
- As a result, any increase in demand directly leads to an increase in output without affecting the price level.
Implications of a Perfectly Elastic Supply
- When aggregate demand shifts, producers can meet this demand by increasing their output without raising prices.
- This characteristic ensures that the economy can respond effectively to changes in demand, supporting the principle of effective demand.
- The multiplier effect further amplifies this response, as increases in autonomous spending lead to disproportionate increases in aggregate output.
In summary, the aggregate supply being perfectly elastic at the given price level allows for a flexible response to aggregate demand changes, reinforcing the equilibrium in the final goods market.
Aggregate Supply (AS) refers to the total quantity of final goods and services that producers in an economy are willing to supply at a given price level over a specific time period. In this scenario, we are dealing with a perfectly elastic aggregate supply.
Definition of Perfectly Elastic Supply
- Perfectly elastic supply means that the quantity supplied can change dramatically with even a slight change in price.
- In this case, producers are willing to supply any amount of goods at the given price level, ensuring that there is no restriction on output.
Why Aggregate Supply is Perfectly Elastic Here
- The report states that we assume a constant final goods price and a constant rate of interest over the short run.
- This stability allows producers to respond freely to changes in aggregate demand without worrying about price fluctuations.
- As a result, any increase in demand directly leads to an increase in output without affecting the price level.
Implications of a Perfectly Elastic Supply
- When aggregate demand shifts, producers can meet this demand by increasing their output without raising prices.
- This characteristic ensures that the economy can respond effectively to changes in demand, supporting the principle of effective demand.
- The multiplier effect further amplifies this response, as increases in autonomous spending lead to disproportionate increases in aggregate output.
In summary, the aggregate supply being perfectly elastic at the given price level allows for a flexible response to aggregate demand changes, reinforcing the equilibrium in the final goods market.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): We can still encounter a barter system in the modern economic system.Reason (R): People exchange old clothes for utensils.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): We can still encounter a barter system in the modern economic system.
Reason (R): People exchange old clothes for utensils.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.

|
Arpita Nambiar answered |
Answer:
Assertion (A): We can still encounter a barter system in the modern economic system.
Reason (R): People exchange old clothes for utensils.
The correct choice is (A) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
Explanation:
Bartering is the exchange of goods and services without the use of money. In a barter system, people exchange goods and services for other goods and services that they need. The barter system is an ancient system of trade that goes back to prehistoric times. Although the barter system has largely been replaced by the use of money, it still exists in some parts of the world.
The reason given in the statement is that people exchange old clothes for utensils. This is an example of a barter system. In a barter system, people exchange goods and services for other goods and services that they need. In this case, people exchange old clothes for utensils that they need. This is a common practice in many parts of the world, especially in rural areas.
Therefore, the assertion that we can still encounter a barter system in the modern economic system is true, and the reason given is the correct explanation of the assertion. The barter system still exists in some parts of the world, especially in rural areas where people do not have access to money or prefer to use goods and services to trade.
Assertion (A): We can still encounter a barter system in the modern economic system.
Reason (R): People exchange old clothes for utensils.
The correct choice is (A) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
Explanation:
Bartering is the exchange of goods and services without the use of money. In a barter system, people exchange goods and services for other goods and services that they need. The barter system is an ancient system of trade that goes back to prehistoric times. Although the barter system has largely been replaced by the use of money, it still exists in some parts of the world.
The reason given in the statement is that people exchange old clothes for utensils. This is an example of a barter system. In a barter system, people exchange goods and services for other goods and services that they need. In this case, people exchange old clothes for utensils that they need. This is a common practice in many parts of the world, especially in rural areas.
Therefore, the assertion that we can still encounter a barter system in the modern economic system is true, and the reason given is the correct explanation of the assertion. The barter system still exists in some parts of the world, especially in rural areas where people do not have access to money or prefer to use goods and services to trade.
Read the below case and answer the question that follow:In a 40-minute long speech Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the demonetisation of existing notes of ₹ 500 and ₹ 1,000 during a televised address on Tuesday evening.Modi announced that the notes of ₹ 500 and ₹ 1,000 will not be legal tender from midnight tonight and these will be “just worthless pieces of paper''. The PM also urged people to ‘join this mahayojna against the ills of corruption.Q. ₹1 currency note is issued by ______________.- a)Finance Ministry
- b)RBI
- c)NITI Aayog
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the below case and answer the question that follow:
In a 40-minute long speech Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the demonetisation of existing notes of ₹ 500 and ₹ 1,000 during a televised address on Tuesday evening.
Modi announced that the notes of ₹ 500 and ₹ 1,000 will not be legal tender from midnight tonight and these will be “just worthless pieces of paper''. The PM also urged people to ‘join this mahayojna against the ills of corruption.
Q. ₹1 currency note is issued by ______________.
a)
Finance Ministry
b)
RBI
c)
NITI Aayog
d)
None of the above
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
The one rupee note and coins are issued by the ministry of finance and it bears the signature of the Finance Secretary.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Export of goods and services from India to the US would mean outflow of foreign exchange from India.Reason (R): Foreign exchange in terms of receipts for exports flows from the US to India.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Export of goods and services from India to the US would mean outflow of foreign exchange from India.
Reason (R): Foreign exchange in terms of receipts for exports flows from the US to India.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.

|
Amrita Sen answered |
Understanding the Assertion and Reason
The assertion (A) states that the export of goods and services from India to the US would mean an outflow of foreign exchange from India. The reason (R) claims that foreign exchange in terms of receipts for exports flows from the US to India.
Analysis of Assertion (A)
- When India exports goods and services, it receives payment in foreign currency (typically USD when exporting to the US).
- This transaction does not lead to an outflow of foreign exchange from India; instead, it results in an inflow, as India earns foreign currency from the exports.
Analysis of Reason (R)
- The reason states that foreign exchange flows from the US to India as a result of exports. This is accurate; India receives payment in foreign exchange for its exports to the US.
- Thus, the statement in reason (R) is true, as it reflects the actual flow of currency.
Conclusion
- The assertion (A) is false because it incorrectly suggests that exports lead to a foreign exchange outflow from India.
- The reason (R) is true, as it correctly describes the inflow of foreign exchange from the US to India.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D': Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
The assertion (A) states that the export of goods and services from India to the US would mean an outflow of foreign exchange from India. The reason (R) claims that foreign exchange in terms of receipts for exports flows from the US to India.
Analysis of Assertion (A)
- When India exports goods and services, it receives payment in foreign currency (typically USD when exporting to the US).
- This transaction does not lead to an outflow of foreign exchange from India; instead, it results in an inflow, as India earns foreign currency from the exports.
Analysis of Reason (R)
- The reason states that foreign exchange flows from the US to India as a result of exports. This is accurate; India receives payment in foreign exchange for its exports to the US.
- Thus, the statement in reason (R) is true, as it reflects the actual flow of currency.
Conclusion
- The assertion (A) is false because it incorrectly suggests that exports lead to a foreign exchange outflow from India.
- The reason (R) is true, as it correctly describes the inflow of foreign exchange from the US to India.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D': Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): GDP indicates the size of an economy.Reason (R): A higher GDP indicates higher economic activity.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): GDP indicates the size of an economy.
Reason (R): A higher GDP indicates higher economic activity.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.

|
Arya Reddy answered |
Explanation:
Assertion (A) and Reason (R) Analysis:
- Assertion (A): GDP indicates the size of an economy.
- Reason (R): A higher GDP indicates higher economic activity.
Correct Explanation:
- Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true because GDP does indicate the size of an economy and a higher GDP typically reflects higher economic activity.
- However, reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A) because while a higher GDP often signifies increased economic activity, it does not directly explain why GDP represents the size of an economy. GDP is a measure of the total value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders, making it an indicator of economic performance and size rather than solely economic activity.
Therefore, the correct choice is option 'B' - Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
Assertion (A) and Reason (R) Analysis:
- Assertion (A): GDP indicates the size of an economy.
- Reason (R): A higher GDP indicates higher economic activity.
Correct Explanation:
- Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true because GDP does indicate the size of an economy and a higher GDP typically reflects higher economic activity.
- However, reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A) because while a higher GDP often signifies increased economic activity, it does not directly explain why GDP represents the size of an economy. GDP is a measure of the total value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders, making it an indicator of economic performance and size rather than solely economic activity.
Therefore, the correct choice is option 'B' - Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Only a handful of states benefited from green revolution in IndiaReason (R): Success of green revolution depends on policy implementation by state government- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Only a handful of states benefited from green revolution in India
Reason (R): Success of green revolution depends on policy implementation by state government
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.

|
Surbhi Sengupta answered |
Assertion (A): Only a handful of states benefited from green revolution in India
Reason (R): Success of green revolution depends on policy implementation by state government
The correct answer is option 'A', which means both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion. Let's analyze the assertion and reason in detail:
Explanation:
Green Revolution in India:
The Green Revolution was a period of rapid agricultural development in India during the 1960s and 1970s. It aimed to increase agricultural productivity and ensure food security for the growing population. The Green Revolution focused on the introduction of high-yielding varieties of seeds, chemical fertilizers, and irrigation facilities.
Assertion (A): Only a handful of states benefited from green revolution in India
The assertion states that only a few states in India benefitted from the Green Revolution. This statement is true as the Green Revolution was initially concentrated in a few states that had favorable conditions for its implementation. These states included Punjab, Haryana, and Western Uttar Pradesh. These regions had fertile soil, access to irrigation facilities, and supportive government policies. The implementation of the Green Revolution technologies in these states resulted in a significant increase in agricultural productivity and transformed them into granaries of the country.
Reason (R): Success of green revolution depends on policy implementation by state government
The reason states that the success of the Green Revolution depends on policy implementation by the state government. This statement is also true. The success of the Green Revolution was not solely dependent on the availability of technological inputs but also on the policies and support provided by the state governments. The state governments played a crucial role in implementing and promoting the use of high-yielding varieties of seeds, providing access to irrigation facilities, offering subsidies on fertilizers, and ensuring the availability of credit to farmers. States that effectively implemented these policies witnessed the benefits of the Green Revolution.
Conclusion:
The Green Revolution in India did indeed benefit only a handful of states initially, and this was due to the successful policy implementation by the state governments. Therefore, option 'A' is the correct answer.
Reason (R): Success of green revolution depends on policy implementation by state government
The correct answer is option 'A', which means both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion. Let's analyze the assertion and reason in detail:
Explanation:
Green Revolution in India:
The Green Revolution was a period of rapid agricultural development in India during the 1960s and 1970s. It aimed to increase agricultural productivity and ensure food security for the growing population. The Green Revolution focused on the introduction of high-yielding varieties of seeds, chemical fertilizers, and irrigation facilities.
Assertion (A): Only a handful of states benefited from green revolution in India
The assertion states that only a few states in India benefitted from the Green Revolution. This statement is true as the Green Revolution was initially concentrated in a few states that had favorable conditions for its implementation. These states included Punjab, Haryana, and Western Uttar Pradesh. These regions had fertile soil, access to irrigation facilities, and supportive government policies. The implementation of the Green Revolution technologies in these states resulted in a significant increase in agricultural productivity and transformed them into granaries of the country.
Reason (R): Success of green revolution depends on policy implementation by state government
The reason states that the success of the Green Revolution depends on policy implementation by the state government. This statement is also true. The success of the Green Revolution was not solely dependent on the availability of technological inputs but also on the policies and support provided by the state governments. The state governments played a crucial role in implementing and promoting the use of high-yielding varieties of seeds, providing access to irrigation facilities, offering subsidies on fertilizers, and ensuring the availability of credit to farmers. States that effectively implemented these policies witnessed the benefits of the Green Revolution.
Conclusion:
The Green Revolution in India did indeed benefit only a handful of states initially, and this was due to the successful policy implementation by the state governments. Therefore, option 'A' is the correct answer.
Read the report given below and answer the question that follow:NEW DELHI: Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on Monday announced plans to sell a stake in LIC as part of her disinvestment plans for F/Y 22. In her Budget speech, the FM said her government will complete divestment of BPCL, CONCOR and SCI in F/Y 22. She said that her government will privatise two public sector banks (PSBs) and one general insurance company as well. “LIC IPO may see the light of day soon,” said Jiger Saiya, Partner and Leader - Tax & Regulatory Services at BDO India.Earlier, in an interview with ET, LIC Chairman M R Kumar had said the IPO is very much likely. “The point is that it is going to be big and we want to get the valuations right,” he had said, adding that the listing of an insurance company requires determining the embedded value of the business.LIC has started the process and would soon announce the software, which will assist it determine the right valuation. “We have floated an RFP for the actuarial firm that will undertake the exercise. This calculation will take some time. Once this process is done, we will be ready,” Kumar said on January 11.Last week, a Reuters report quoting sources suggested that the government was looking to sell 10-15 per cent in the country’s biggest insurer to improve public finances.To facilitate the sale of the LIC stake, the government will need Parliament approval to amend the LIC Act.As part of its divestment drive, four CPSEs – HAL, SAIL, Bharat Dynamics and IRCTC –have come out with offers for sale (OFSs) this financial year. They garnered ₹12,907 crore to the exchequer. In addition, IPOs of IRFC and Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders together fetched ₹1,984 crore.Also, this year, the government sold shares worth about ₹1,837 crore in private companies, in which it holds stakes through SUUTI.Four state-owned companies, NTPC, RITES, NMDC and KIOCL, completed share buybacks, adding ₹2,769 crore to the exchequer.The government is also looking to sell its entire 26.12 per cent stake in Tata Communications (TCL), erstwhile VSNL, through an OFS and strategic sale this financial year. The process of privatisation of Air India, BPCL, Pawan Hans, BEML, Shipping Corp, Neelachal Ispat Nigam Limited and Ferro Scrap Nigam Limited (FSNL) is currently underway.Q. What other things can the government do to improve the deficit with respect to the current Covid situation?- a)Borrowing from public
- b)Lowering government expenditure
- c)Raising government revenue
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the report given below and answer the question that follow:
NEW DELHI: Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on Monday announced plans to sell a stake in LIC as part of her disinvestment plans for F/Y 22. In her Budget speech, the FM said her government will complete divestment of BPCL, CONCOR and SCI in F/Y 22. She said that her government will privatise two public sector banks (PSBs) and one general insurance company as well. “LIC IPO may see the light of day soon,” said Jiger Saiya, Partner and Leader - Tax & Regulatory Services at BDO India.
Earlier, in an interview with ET, LIC Chairman M R Kumar had said the IPO is very much likely. “The point is that it is going to be big and we want to get the valuations right,” he had said, adding that the listing of an insurance company requires determining the embedded value of the business.
LIC has started the process and would soon announce the software, which will assist it determine the right valuation. “We have floated an RFP for the actuarial firm that will undertake the exercise. This calculation will take some time. Once this process is done, we will be ready,” Kumar said on January 11.
Last week, a Reuters report quoting sources suggested that the government was looking to sell 10-15 per cent in the country’s biggest insurer to improve public finances.
To facilitate the sale of the LIC stake, the government will need Parliament approval to amend the LIC Act.
As part of its divestment drive, four CPSEs – HAL, SAIL, Bharat Dynamics and IRCTC –have come out with offers for sale (OFSs) this financial year. They garnered ₹12,907 crore to the exchequer. In addition, IPOs of IRFC and Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders together fetched ₹1,984 crore.
Also, this year, the government sold shares worth about ₹1,837 crore in private companies, in which it holds stakes through SUUTI.
Four state-owned companies, NTPC, RITES, NMDC and KIOCL, completed share buybacks, adding ₹2,769 crore to the exchequer.
The government is also looking to sell its entire 26.12 per cent stake in Tata Communications (TCL), erstwhile VSNL, through an OFS and strategic sale this financial year. The process of privatisation of Air India, BPCL, Pawan Hans, BEML, Shipping Corp, Neelachal Ispat Nigam Limited and Ferro Scrap Nigam Limited (FSNL) is currently underway.
Q. What other things can the government do to improve the deficit with respect to the current Covid situation?
a)
Borrowing from public
b)
Lowering government expenditure
c)
Raising government revenue
d)
None of the above
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
1. Ensure safe and fair access to vaccines across regions within countries through effective coordination mechanisms between national and subnational governments, for example by sharing dose delivery projections. This is particularly important as all levels of governments must anticipate the surge in supply and ensure that the logistics and infrastructure is ready as vaccine deliveries accelerate. Involve subnational governments in vaccination campaigns to ensure faster and better territorial coverage. Involving local actors, who are better informed about the local population and infrastructure, is essential to successfully reach people that need vaccines first (e.g. the elderly, people with pre-existing illnesses and healthcare workers) and relieving the pressure on the healthcare system.
2. Consider adopting a “place-based” or territorially sensitive approach to recovery policies. Introduce, activate or reorient existing multi-level coordination bodies in order to minimise the risk of a fragmented recovery response. Use such bodies to refine strategies, develop solutions, and agree on decisions with profound economic, social, and societal implications. Strengthen the quality of micro-level data within and between regions to improve understanding of the crisis and its impact.
3. Support cooperation across municipalities and regions to help minimise disjointed responses and competition for resources during a crisis. Facilitate inter-municipal cooperation to support recovery strategies by ensuring coherent safety/mitigation guidelines, pooling resources, and strengthening investment opportunities, for example through joint borrowing. Actively pursue and promote cross-border cooperation in order to promote a coherent recovery approach across a broad territory (e.g. border closure and reopening, containment measures, exit strategies, migrant workers).
4. Strengthen national and subnational-level support to vulnerable groups to limit further deterioration in circumstances and to strengthen inclusiveness in the recovery phase. Accomplishing this can include simplifying and facilitating access to support programmes, ensuring well-targeted services, introducing adequate and/or innovative fiscal support schemes, and identifying the needs for revising fiscal equalisation policies. Use digital opportunities (e.g. e-health, e-education) to help ensure continued service delivery, being sensitive to territorial, economic, and social disparities in access.
Read the report given below and answer the questions that follow:In an economy the Aggregate Demand is determined by consumption, Government Expenditure and Net Exports in the economy. This is affected by the Savings and Investment in the economy. The Multiplier, that is investment multiplier, which is influenced by the ratio of total consumption and total income, regulates the flow of money in the economy influencing the Aggregate Demand and Supply. Any change in any of the factors leads to a big change in the economy’s equilibrium as a whole. It is to be kept in mind that the economy needs to be in equilibrium condition. When savings is less than the investments the aggregate demand is more than the aggregate supply, and vice versa.Aggregate Demand is not determined by which of the following:- a)Consumption Expenditure
- b)Investment Expenditure
- c)Net Exports
- d)Government Policies
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the report given below and answer the questions that follow:
In an economy the Aggregate Demand is determined by consumption, Government Expenditure and Net Exports in the economy. This is affected by the Savings and Investment in the economy. The Multiplier, that is investment multiplier, which is influenced by the ratio of total consumption and total income, regulates the flow of money in the economy influencing the Aggregate Demand and Supply. Any change in any of the factors leads to a big change in the economy’s equilibrium as a whole. It is to be kept in mind that the economy needs to be in equilibrium condition. When savings is less than the investments the aggregate demand is more than the aggregate supply, and vice versa.
Aggregate Demand is not determined by which of the following:
a)
Consumption Expenditure
b)
Investment Expenditure
c)
Net Exports
d)
Government Policies
|
|
Amita Das answered |
AD=C+I+G+X-M
Where,
C=Household Consumption Expenditure
I=Private Investment Expenditure
G=Government Expenditure
X-M=Net Exports
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): The maximum value of investment multiplier is equal to infinity.Reason (R): The maximum value of investment multiplier is ∞, when MPC is 1, i.e., whole additional income is converted into additional consumption.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): The maximum value of investment multiplier is equal to infinity.
Reason (R): The maximum value of investment multiplier is ∞, when MPC is 1, i.e., whole additional income is converted into additional consumption.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
K = 1/1 – MPC
= 1/1 – 1
= 1/0 = ∞
मणिपुर राज्य को नागालैंड राज्य से अलग करने वाली पहाड़ी श्रृंखला अस के नाम से जानी जाती है- a)अराकान पहाड़ियों
- b)पटकाई पहाड़ियाँ
- c)बरेल पहाड़ियों
- d)मणिपुर की पहाड़ियाँ
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
मणिपुर राज्य को नागालैंड राज्य से अलग करने वाली पहाड़ी श्रृंखला अस के नाम से जानी जाती है
a)
अराकान पहाड़ियों
b)
पटकाई पहाड़ियाँ
c)
बरेल पहाड़ियों
d)
मणिपुर की पहाड़ियाँ
|
|
Bhaskar Kapoor answered |
The hill range separating the state of Manipur from the state of Nagaland is known as:
Geographical Location
The hill range lies in the northeastern part of India, in the region known as Northeast India. It separates the two Indian states of Manipur and Nagaland.
Name of the Hill Range
The hill range that separates Manipur from Nagaland is known as the "Japfü range." It is one of the most prominent ranges in the region and is home to the highest peak in Nagaland, Mount Japfü, which stands at an elevation of 3048 meters.
Significance of the Hill Range
The Japfü range is not only a geographical feature but also holds cultural significance for the local communities living in the region. It is home to the Angami Naga tribe, who consider the region sacred and have preserved their traditional customs and beliefs.
Tourism
The Japfü range is a popular tourist destination and attracts visitors from all over the world. The hill range is a trekker's paradise and offers breathtaking views of the surrounding landscape. It is also home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, including several endemic species.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the hill range separating Manipur from Nagaland is known as the Japfü range. It is an important geographical feature and holds cultural significance for the local communities. The range is also a popular tourist destination and attracts visitors from all over the world.
Geographical Location
The hill range lies in the northeastern part of India, in the region known as Northeast India. It separates the two Indian states of Manipur and Nagaland.
Name of the Hill Range
The hill range that separates Manipur from Nagaland is known as the "Japfü range." It is one of the most prominent ranges in the region and is home to the highest peak in Nagaland, Mount Japfü, which stands at an elevation of 3048 meters.
Significance of the Hill Range
The Japfü range is not only a geographical feature but also holds cultural significance for the local communities living in the region. It is home to the Angami Naga tribe, who consider the region sacred and have preserved their traditional customs and beliefs.
Tourism
The Japfü range is a popular tourist destination and attracts visitors from all over the world. The hill range is a trekker's paradise and offers breathtaking views of the surrounding landscape. It is also home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, including several endemic species.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the hill range separating Manipur from Nagaland is known as the Japfü range. It is an important geographical feature and holds cultural significance for the local communities. The range is also a popular tourist destination and attracts visitors from all over the world.
Read the following hypothetical text and answer question that follow:India’s Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector is poised for a mega transformation in 2020, with the launch of an Alibaba-like e-marketplace, trendy yet affordable khadi products to appeal to the masses and digital data-based credit ratings to help entrepreneurs avail loans. However, the MSME sector is often considered the bulwark of the economy as it contributes around 29% to the GDP and 48% to the Indian exports. There is an urgent need of major reforms and policy interventions towards ensuring timely availability of low-cost credit, improving ease of doing business and technological upgradation, to take on the formidable challenge of creating millions of jobs, ensure equitable distribution of national income and achieving large-scale import substitution. The World Bank has recently approved loan worth $750 million to address the immediate liquidity and credit needs of India’s MSME sector that has been severely impacted by the Covid-19 crisis. This will give a push to the Atmanirbhar Bharat vision of the government.Q. _______________ are the largest employer of the labour force in India.- a)Agricultural Sector
- b)Small Scale Industries
- c)Cottage Industries
- d)Service Sector
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following hypothetical text and answer question that follow:
India’s Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector is poised for a mega transformation in 2020, with the launch of an Alibaba-like e-marketplace, trendy yet affordable khadi products to appeal to the masses and digital data-based credit ratings to help entrepreneurs avail loans. However, the MSME sector is often considered the bulwark of the economy as it contributes around 29% to the GDP and 48% to the Indian exports. There is an urgent need of major reforms and policy interventions towards ensuring timely availability of low-cost credit, improving ease of doing business and technological upgradation, to take on the formidable challenge of creating millions of jobs, ensure equitable distribution of national income and achieving large-scale import substitution. The World Bank has recently approved loan worth $750 million to address the immediate liquidity and credit needs of India’s MSME sector that has been severely impacted by the Covid-19 crisis. This will give a push to the Atmanirbhar Bharat vision of the government.
Q. _______________ are the largest employer of the labour force in India.
a)
Agricultural Sector
b)
Small Scale Industries
c)
Cottage Industries
d)
Service Sector
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
The agricultural sector is the largest employer in the Indian economy. Nearly 51% of the population is engaged in this section in one way or the other.
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Casual labourers are most vulnerable in the society.Reason (R): Casual labourers don’t have a permanent earning facility and their earning varies a lot. They can even lose their jobs with a slight dip in the economic growth.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Casual labourers are most vulnerable in the society.
Reason (R): Casual labourers don’t have a permanent earning facility and their earning varies a lot. They can even lose their jobs with a slight dip in the economic growth.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Priyanka Khatri answered |
Casual labourers are among the most vulnerable in society as they have no job security, no assets, limited skills, sparse opportunities and no surplus to sustain them. Poverty is, therefore, also closely related to nature of employment.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion ( A ) : in order to maintain the faith of depositors in the banking system, it is sufficient for the commercial banks to keep only a small part of deposits as cash Reserves.Reason ( R ) : A change in Reserve requirement affects the power of commercial bank to create the credit.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion ( A ) : in order to maintain the faith of depositors in the banking system, it is sufficient for the commercial banks to keep only a small part of deposits as cash Reserves.
Reason ( R ) : A change in Reserve requirement affects the power of commercial bank to create the credit.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Fractional-reserve banking is the system of banking operating in almost all countries worldwide, under which banks that take deposits from the public are required to hold a proportion of their deposit liabilities in liquid assets as a reserve, and are at liberty to make loans to borrowers of the balance.Bank reserves are held as cash in the bank or as balances in the bank's account at the central bank. The country's central bank determines the minimum amount that banks must hold in liquid assets, called the "reserve requirement" or "reserve ratio". Most commercial banks hold more than this minimum amount as excess reserves.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Indian economy is marching ahead towards progress.Reason (R): The contribution of agriculture in national income is declining but the contribution of industries and service sector is increasing continuously. It is an indicator of economic development of the Indian Economy.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Indian economy is marching ahead towards progress.
Reason (R): The contribution of agriculture in national income is declining but the contribution of industries and service sector is increasing continuously. It is an indicator of economic development of the Indian Economy.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Priyanka Khatri answered |
The contribution of agriculture in national income is declining, But the contribution of industries and service sector is increasing continuously. It is an indicator of economic development of the Indian economy.
Chapter doubts & questions for CBSE Practice Questions - Economics Class 12 2025 is part of Commerce exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Commerce 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of CBSE Practice Questions - Economics Class 12 in English & Hindi are available as part of Commerce exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Commerce Exam by signing up for free.
Economics Class 12
64 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









