All Exams >
Commerce >
Accountancy CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 >
All Questions
All questions of Accounting Ratios for Commerce Exam
Read the following information and answer the given questions: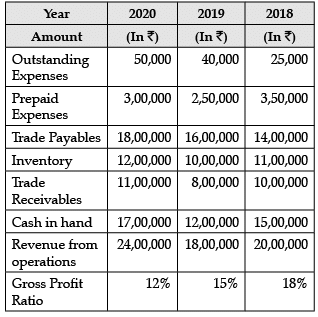 Inventory turnover ratio for the year 2020 will be______.(Choose the correct alternative)
Inventory turnover ratio for the year 2020 will be______.(Choose the correct alternative)- a)1.62 times
- b)1.82 times
- c)1.55 times
- d)1.92 times
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following information and answer the given questions:

Inventory turnover ratio for the year 2020 will be______.(Choose the correct alternative)
a)
1.62 times
b)
1.82 times
c)
1.55 times
d)
1.92 times
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of revenue from operations / Average Inventory
= ₹24,00,0000 - ₹2,88,000 / ₹11,00,000 = 1.92 times
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross Profit / Revenue from Operations
Gross Profit = 12% of ₹24,00,000 = ₹2,88,000
Read the following information and answer the given questions: Cost of Revenue from Operations for the year 2020 would be ______________.
Cost of Revenue from Operations for the year 2020 would be ______________.- a)₹21,12,000
- b)₹21,13,000
- c)₹21,15,000
- d)₹21,17,000
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following information and answer the given questions:

Cost of Revenue from Operations for the year 2020 would be ______________.
a)
₹21,12,000
b)
₹21,13,000
c)
₹21,15,000
d)
₹21,17,000
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Cost of Revenue from Operations for the year 2020 would be ₹21,12,000.
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): A high operating ratio indicates a favourable position.
Reason (R): A high operating ratio leaves a high margin to meet non-operating expenses.
- a)Both (A) and (R) are incorrect
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false .
- d)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): A high operating ratio indicates a favourable position.
Reason (R): A high operating ratio leaves a high margin to meet non-operating expenses.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are incorrect
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false .
d)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).

|
Sathish Neelambari answered |
Option (b) is the right answer as both the statements are true but the reason is no way related to the assertion of the given question
Consider the following data and answer the questions that follow: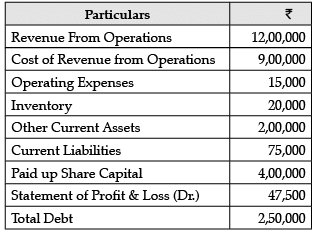 What is the Debt to Equity Ratio?
What is the Debt to Equity Ratio?- a)0.75:1
- b)1:2
- c)2:1
- d)0.63:1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following data and answer the questions that follow:

What is the Debt to Equity Ratio?
a)
0.75:1
b)
1:2
c)
2:1
d)
0.63:1
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Debt to equity Ratio = Total Debt / Shareholders' Fund
= ₹2,50,000 / ₹4,00,000 = 0.63:1
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Higher the Gross Profit ratio, good for the business, lower ratio not good for the business.Reason (R): It reflects the efficiency with which a firm produces its products. A high gross profit ratio indicates that the organization is able to produce at a relatively lower cost.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false .
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Higher the Gross Profit ratio, good for the business, lower ratio not good for the business.
Reason (R): It reflects the efficiency with which a firm produces its products. A high gross profit ratio indicates that the organization is able to produce at a relatively lower cost.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false .
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
The gross profit should be sufficient to cover all operating expenses and to build up reserves after paying all fixed interest charges and dividends.
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Liquid ratio reveals strength of liquidity of a business unit.Reason (R): Liquid ratio is the one of the various ratios used to measure the ability of a company to meet its long-term debts.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false .
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Liquid ratio reveals strength of liquidity of a business unit.
Reason (R): Liquid ratio is the one of the various ratios used to measure the ability of a company to meet its long-term debts.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false .
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Liquid ratio analyses liquid assets and liquid liabilities of a business unit in order to assess the extent of liquidity.
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Debt to Equity Ratio of 2 : 1 is considered satisfactory. Generally a Low Ratio is considered favourable.Reason (R): This ratio indicates the proportionate claims of owners and outsiders on a firm's assets. High Ratio shows claims of outsiders are greater but Low Ratio shows outsiders claims are less.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false .
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Debt to Equity Ratio of 2 : 1 is considered satisfactory. Generally a Low Ratio is considered favourable.
Reason (R): This ratio indicates the proportionate claims of owners and outsiders on a firm's assets. High Ratio shows claims of outsiders are greater but Low Ratio shows outsiders claims are less.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false .
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.

|
Manisha Patel answered |
Assertion (A): Debt to Equity Ratio of 2 : 1 is considered satisfactory. Generally a Low Ratio is considered favourable.
Reason (R): This ratio indicates the proportionate claims of owners and outsiders on a firm's assets. High Ratio shows claims of outsiders are greater but Low Ratio shows outsiders claims are less.
The given Assertion (A) states that a Debt to Equity Ratio of 2:1 is considered satisfactory, while a low ratio is considered favorable. The Reason (R) provided is that this ratio indicates the proportionate claims of owners and outsiders on a firm's assets. A high ratio shows that the claims of outsiders are greater, while a low ratio shows that the claims of outsiders are less.
Explanation:
Debt to Equity Ratio:
The debt to equity ratio is a financial ratio that compares a company's total debt to its shareholders' equity. It is a measure of the company's financial leverage and indicates the proportion of financing provided by the company's creditors (debt) compared to the financing provided by the company's owners (equity).
Interpretation of Debt to Equity Ratio:
- A Debt to Equity Ratio of 2:1 means that the company has twice as much debt as equity. This indicates that the company relies more on debt financing than on equity financing.
- A low Debt to Equity Ratio indicates that the company has a smaller proportion of debt compared to equity. This suggests that the company relies more on equity financing and has lower financial risk.
- A high Debt to Equity Ratio indicates that the company has a larger proportion of debt compared to equity. This suggests that the company relies more on debt financing and has higher financial risk.
Analysis:
The Assertion (A) states that a Debt to Equity Ratio of 2:1 is considered satisfactory. This means that the company has a balanced mix of debt and equity financing, indicating a moderate level of financial risk. A ratio lower than 2:1 would be even more favorable as it suggests a lower level of debt and lower financial risk.
The Reason (R) provided explains the significance of the Debt to Equity Ratio. It states that the ratio indicates the proportionate claims of owners and outsiders on a firm's assets. A high ratio implies that the claims of outsiders (creditors) are greater, indicating higher financial risk. On the other hand, a low ratio implies that the claims of outsiders are less, indicating lower financial risk.
Conclusion:
Both the Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and the Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). A Debt to Equity Ratio of 2:1 is considered satisfactory, and a low ratio is considered favorable as it indicates a lower level of debt and lower financial risk. The Reason (R) explains that the ratio reflects the proportionate claims of owners and outsiders on a firm's assets, with a high ratio indicating greater claims of outsiders and a low ratio indicating lesser claims of outsiders.
Reason (R): This ratio indicates the proportionate claims of owners and outsiders on a firm's assets. High Ratio shows claims of outsiders are greater but Low Ratio shows outsiders claims are less.
The given Assertion (A) states that a Debt to Equity Ratio of 2:1 is considered satisfactory, while a low ratio is considered favorable. The Reason (R) provided is that this ratio indicates the proportionate claims of owners and outsiders on a firm's assets. A high ratio shows that the claims of outsiders are greater, while a low ratio shows that the claims of outsiders are less.
Explanation:
Debt to Equity Ratio:
The debt to equity ratio is a financial ratio that compares a company's total debt to its shareholders' equity. It is a measure of the company's financial leverage and indicates the proportion of financing provided by the company's creditors (debt) compared to the financing provided by the company's owners (equity).
Interpretation of Debt to Equity Ratio:
- A Debt to Equity Ratio of 2:1 means that the company has twice as much debt as equity. This indicates that the company relies more on debt financing than on equity financing.
- A low Debt to Equity Ratio indicates that the company has a smaller proportion of debt compared to equity. This suggests that the company relies more on equity financing and has lower financial risk.
- A high Debt to Equity Ratio indicates that the company has a larger proportion of debt compared to equity. This suggests that the company relies more on debt financing and has higher financial risk.
Analysis:
The Assertion (A) states that a Debt to Equity Ratio of 2:1 is considered satisfactory. This means that the company has a balanced mix of debt and equity financing, indicating a moderate level of financial risk. A ratio lower than 2:1 would be even more favorable as it suggests a lower level of debt and lower financial risk.
The Reason (R) provided explains the significance of the Debt to Equity Ratio. It states that the ratio indicates the proportionate claims of owners and outsiders on a firm's assets. A high ratio implies that the claims of outsiders (creditors) are greater, indicating higher financial risk. On the other hand, a low ratio implies that the claims of outsiders are less, indicating lower financial risk.
Conclusion:
Both the Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and the Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). A Debt to Equity Ratio of 2:1 is considered satisfactory, and a low ratio is considered favorable as it indicates a lower level of debt and lower financial risk. The Reason (R) explains that the ratio reflects the proportionate claims of owners and outsiders on a firm's assets, with a high ratio indicating greater claims of outsiders and a low ratio indicating lesser claims of outsiders.
Read the following hypothetical extract of ABC Ltd. and answer the questions that follow: The following information are given:Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio 4 timesCurrent Liabilities ₹ 5,000Average Debtors ₹ 1,80,000Working Capital Turnover Ratio 8 timesCash Revenue from Operations 25% of Revenue from OperationsGross Profit Ratio 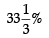 What is the Gross Profit?
What is the Gross Profit?- a)₹7,20,000
- b)₹3,20,000
- c)₹9,60,000
- d)₹1,80,000
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following hypothetical extract of ABC Ltd. and answer the questions that follow: The following information are given:
Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio 4 times
Current Liabilities ₹ 5,000
Average Debtors ₹ 1,80,000
Working Capital Turnover Ratio 8 times
Cash Revenue from Operations 25% of Revenue from Operations
Gross Profit Ratio 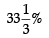
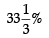
What is the Gross Profit?
a)
₹7,20,000
b)
₹3,20,000
c)
₹9,60,000
d)
₹1,80,000
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
Gross Profit = Gross Profit Ratio × Revenue from Operations
= 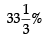 of ₹9,60,000 = ₹3,20,000
of ₹9,60,000 = ₹3,20,000
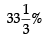 of ₹9,60,000 = ₹3,20,000
of ₹9,60,000 = ₹3,20,000 Read the following hypothetical extract of ABC Ltd. and answer the questions that follow: The following information are given:Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio 4 timesCurrent Liabilities ₹ 5,000Average Debtors ₹ 1,80,000Working Capital Turnover Ratio 8 timesCash Revenue from Operations 25% of Revenue from OperationsGross Profit Ratio 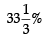 What is the working Capital?
What is the working Capital?- a)₹1,20,000
- b)₹1,80,000
- c)₹3,20,000
- d)₹2,40,000
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following hypothetical extract of ABC Ltd. and answer the questions that follow: The following information are given:
Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio 4 times
Current Liabilities ₹ 5,000
Average Debtors ₹ 1,80,000
Working Capital Turnover Ratio 8 times
Cash Revenue from Operations 25% of Revenue from Operations
Gross Profit Ratio 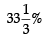
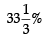
What is the working Capital?
a)
₹1,20,000
b)
₹1,80,000
c)
₹3,20,000
d)
₹2,40,000
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
Working Capital Turnover Ratio
= Revenue from Operations / Working Capital
8 = 9,60,000 /Working Capital
Working Capital = 9,60,000 / 8 = ₹ 1,20,000
Read the following information and answer the given questions: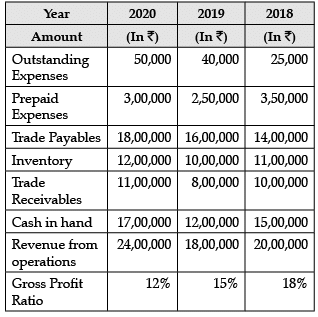 Quick Ratio for the year 2018 will be_____________. (Choose the correct alternative)
Quick Ratio for the year 2018 will be_____________. (Choose the correct alternative)- a)1.75 : 1
- b)1.8 : 1
- c)0.94 : 1
- d)1.25 : 1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following information and answer the given questions:

Quick Ratio for the year 2018 will be_____________. (Choose the correct alternative)
a)
1.75 : 1
b)
1.8 : 1
c)
0.94 : 1
d)
1.25 : 1
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Quick Assets = Trade receivables + Cash in hand
= ₹ 10,00,000 + ₹ 15,00,000
= ₹ 25,00,000
Current Liabilities = Outstanding Expenses + Trade Payables
= ₹25,000 + ₹14,00,000
= ₹ 14,25,000
Current Ratio= Current Assets / Current Liabilities
= ₹10,00,000 + ₹15,00,000 / ₹14,25,000 = 1.75 : 1
Read the following hypothetical extract of ABC Ltd. and answer the questions that follow: The following information are given:Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio 4 timesCurrent Liabilities ₹ 5,000Average Debtors ₹ 1,80,000Working Capital Turnover Ratio 8 timesCash Revenue from Operations 25% of Revenue from OperationsGross Profit Ratio 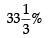 What will be the value of current assets?
What will be the value of current assets?- a)₹1,25,000
- b)₹5,000
- c)₹1,20,000
- d)₹55,000
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following hypothetical extract of ABC Ltd. and answer the questions that follow: The following information are given:
Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio 4 times
Current Liabilities ₹ 5,000
Average Debtors ₹ 1,80,000
Working Capital Turnover Ratio 8 times
Cash Revenue from Operations 25% of Revenue from Operations
Gross Profit Ratio 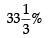
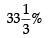
What will be the value of current assets?
a)
₹1,25,000
b)
₹5,000
c)
₹1,20,000
d)
₹55,000
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Working Capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
Current Assets = Working Capital + Current Liabilities
= ₹1,20,000 + ₹5,000
= ₹1,25,000
Consider the following data and answer the questions that follow: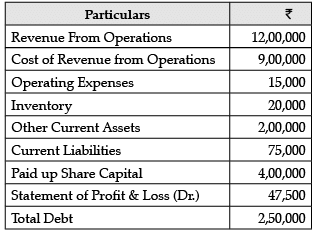 What is the quick ratio?
What is the quick ratio?- a)2.67:1
- b)2.17:1
- c)2:1
- d)3:1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following data and answer the questions that follow:

What is the quick ratio?
a)
2.67:1
b)
2.17:1
c)
2:1
d)
3:1
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Quick Ratio = Liquid Assets / Current Liabilities
= ₹2,00,000 / ₹ 75,000 = 2.67 : 1
Read the following information and answer the given questions: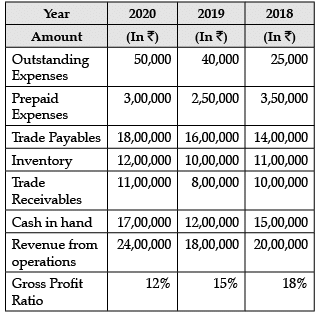 Current Ratio for the year 2020 will be_____. (Choose the correct alternative)
Current Ratio for the year 2020 will be_____. (Choose the correct alternative)- a)2 : 1
- b)1.8 : 1
- c)2.32 : 1
- d)2.4 : 1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following information and answer the given questions:

Current Ratio for the year 2020 will be_____. (Choose the correct alternative)
a)
2 : 1
b)
1.8 : 1
c)
2.32 : 1
d)
2.4 : 1
|
|
Amita Das answered |
Current Assets = Prepaid Expenses + Inventory + Trade Receivables + Cash in Hand = ₹3,00,000 + ₹12,00,000 + ₹11,00,000 +₹17,00,000
= ₹43,00,000
Current Liabilities = Outstanding Expenses + Trade Payables
= ₹50,000 + ₹18,00,000
= ₹18,50,000
Current Ratio= Current Assets / Current Liabilities
= ₹43,00,000 / ₹18,50,000 = 2.32 : 1
Consider the following data and answer the questions that follow: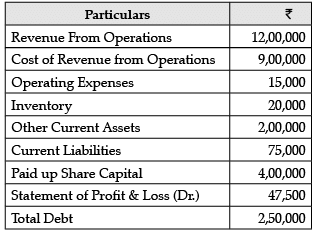 What is the working capital turnover ratio?
What is the working capital turnover ratio?- a)8 times
- b)8.28 times
- c)7.28 times
- d)8.78 times
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following data and answer the questions that follow:

What is the working capital turnover ratio?
a)
8 times
b)
8.28 times
c)
7.28 times
d)
8.78 times
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
Working Capital Turnover Ratio = Revenue from Operations / Working Capital
= ₹12,00,000 / ₹1,45,000 = 8.28 times
Read the following hypothetical extract of ABC Ltd. and answer the questions that follow: The following information are given:Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio 4 timesCurrent Liabilities ₹ 5,000Average Debtors ₹ 1,80,000Working Capital Turnover Ratio 8 timesCash Revenue from Operations 25% of Revenue from OperationsGross Profit Ratio 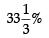 What is the revenue from operations?
What is the revenue from operations?- a)₹9,60,000
- b)₹6,40,000
- c)₹6,40,000
- d)₹7,20,000
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following hypothetical extract of ABC Ltd. and answer the questions that follow: The following information are given:
Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio 4 times
Current Liabilities ₹ 5,000
Average Debtors ₹ 1,80,000
Working Capital Turnover Ratio 8 times
Cash Revenue from Operations 25% of Revenue from Operations
Gross Profit Ratio 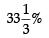
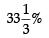
What is the revenue from operations?
a)
₹9,60,000
b)
₹6,40,000
c)
₹6,40,000
d)
₹7,20,000
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Trade Receivables Turnover ratio
= Credit Revenue from Operations / Average Trade Receivables
4 = Credit Revenue from Operations / 1,80,000
Credit Revenue from Operations = ₹1,80,000 × 4 = ₹ 7,20,000
Credit Revenue from Operations = 75% of Revenue from Operations
₹7,20,000 = 75% of Revenue from Operations Revenue from Operations = ₹9,60,000
Consider the following data and answer the questions that follow: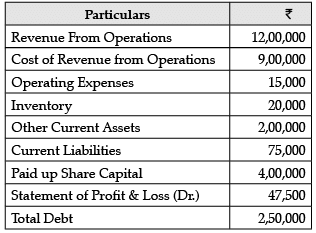 What is the Operating ratio?
What is the Operating ratio?- a)75.62%
- b)75%
- c)76.25%
- d)76%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following data and answer the questions that follow:

What is the Operating ratio?
a)
75.62%
b)
75%
c)
76.25%
d)
76%
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Operating Ratio Cost of Revenue from Operations + Operating Expenses / Revenue from Operations x 100
= ₹9,00,000+ ₹15,000 / ₹12,00,000 x 100
= 76.25%
Chapter doubts & questions for Accounting Ratios - Accountancy CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 2025 is part of Commerce exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Commerce 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Accounting Ratios - Accountancy CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 in English & Hindi are available as part of Commerce exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Commerce Exam by signing up for free.
Accountancy CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026
3 docs|77 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









