All Exams >
BPSC (Bihar) >
Geography for State PSC Exams >
All Questions
All questions of Drainage Systems for BPSC (Bihar) Exam
The Amarkantak Hills is the source of which of the following rivers?
1. Narmada
2. Mahanadi
3. Tapti
4. Son
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- a)1 and 2 only
- b)2 only
- c)1, 3 and 4 only
- d)1 ,2 and 4 only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Amarkantak Hills is the source of which of the following rivers?
1. Narmada
2. Mahanadi
3. Tapti
4. Son
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
2 only
c)
1, 3 and 4 only
d)
1 ,2 and 4 only
|
|
Amrutha Kulkarni answered |
The correct answer is option D, i.e. 1 and 4 only.
Explanation:
The Amarkantak Hills, located in Madhya Pradesh, is a prominent source of two major rivers in India - the Narmada and the Son. Let's understand the origin and characteristics of both these rivers:
1. Narmada River:
- The Narmada River is one of the major rivers in India, flowing through the states of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Gujarat.
- The river originates from the Amarkantak Hills in Madhya Pradesh, at an altitude of about 1057 meters.
- It is also called the Rewa River and is considered sacred by many people.
- The river has a total length of about 1312 km, and its basin covers an area of about 98,796 square km.
- The Narmada River forms the famous Marble Rocks gorge in Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh and also creates the Dhuandhar Falls in Bhedaghat.
2. Son River:
- The Son River is a major river in northern India, flowing through the states of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, and Uttar Pradesh.
- The river originates from the Amarkantak Hills in Madhya Pradesh, at an altitude of about 775 meters.
- It is a tributary of the Ganges River and has a total length of about 784 km.
- The river is known for its scenic beauty, and also for the Sonbhadra district, which is one of the largest districts in India.
Therefore, it can be concluded that the Amarkantak Hills is the source of both the Narmada and the Son rivers, making option D the correct answer.
Explanation:
The Amarkantak Hills, located in Madhya Pradesh, is a prominent source of two major rivers in India - the Narmada and the Son. Let's understand the origin and characteristics of both these rivers:
1. Narmada River:
- The Narmada River is one of the major rivers in India, flowing through the states of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Gujarat.
- The river originates from the Amarkantak Hills in Madhya Pradesh, at an altitude of about 1057 meters.
- It is also called the Rewa River and is considered sacred by many people.
- The river has a total length of about 1312 km, and its basin covers an area of about 98,796 square km.
- The Narmada River forms the famous Marble Rocks gorge in Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh and also creates the Dhuandhar Falls in Bhedaghat.
2. Son River:
- The Son River is a major river in northern India, flowing through the states of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, and Uttar Pradesh.
- The river originates from the Amarkantak Hills in Madhya Pradesh, at an altitude of about 775 meters.
- It is a tributary of the Ganges River and has a total length of about 784 km.
- The river is known for its scenic beauty, and also for the Sonbhadra district, which is one of the largest districts in India.
Therefore, it can be concluded that the Amarkantak Hills is the source of both the Narmada and the Son rivers, making option D the correct answer.
Which one of the following does not belong to Himalayan rivers?- a)Cauvery
- b)Brahmaputra
- c)Alaknanda
- d)Gandak
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following does not belong to Himalayan rivers?
a)
Cauvery
b)
Brahmaputra
c)
Alaknanda
d)
Gandak
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Indus, Ganga, Brahmaputra, Satluj, Alaknanda, Gandak, Kosi etc are Himalayan rivers
Which of the major rivers of India does not form a delta?- a) Cauvery
- b) Godavari
- c) Krishna
- d) Narmada
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the major rivers of India does not form a delta?
a)
Cauvery
b)
Godavari
c)
Krishna
d)
Narmada
|
|
Anjali Rao answered |
Conditions for delta formation by a river:
- The river must have a gentle gradient in its lower course
- The river must carry a large amount of sediments along with it
- The coastal plains or area where the mouth of river lies should be wide
Though Narmada originates far from the Western Ghats and empties into the Arabian Sea, the river flows through a rift valley at a steep gradient which increases its speed. Also, the western coastal plains are less wider than that required for delta formation by Narmada.
Ganga is a result of the confluence of rivers –––- a) Bhagirathi and Alaknanda at DevPrayag
- b) Bhagirathi and Alaknanda at Karnaprayag
- c) Bhagirathi and Alaknanda at Gangotri
- d) Bhagirathi and Alaknanda at RudraPrayag
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ganga is a result of the confluence of rivers –––
a)
Bhagirathi and Alaknanda at DevPrayag
b)
Bhagirathi and Alaknanda at Karnaprayag
c)
Bhagirathi and Alaknanda at Gangotri
d)
Bhagirathi and Alaknanda at RudraPrayag
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Bhagirathi and Alaknanda rivers meet at DevPrayag and downstream flow as the Ganges.
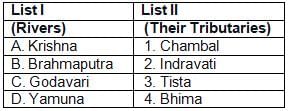
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using thecodes given below: Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?- a)1, 2 and 3
- b)1 and 3
- c)2 and 3
- d)3 only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the
codes given below:

Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
a)
1, 2 and 3
b)
1 and 3
c)
2 and 3
d)
3 only

|
Vikash Rawat answered |
Answer will be (d) 3 only coz
Chambal is yamuna tributary
sone is Ganga tributary
manas is brahamputra
Chambal is yamuna tributary
sone is Ganga tributary
manas is brahamputra
Which of the following best explain why the lower course of a river is sometimes choked with sediments?1. The valley of a river is widest in its lower course.2. The velocity of a river in its lower course is low.3. The delta sometimes develops in a river’s lower course.4. Much of the river water is drawn for irrigation in the lower course.Select the correct answer using the codes given below- a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
- b) 1, 3 and 4
- c) 1, 2 and 3
- d) 2 and 4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following best explain why the lower course of a river is sometimes choked with sediments?
1. The valley of a river is widest in its lower course.
2. The velocity of a river in its lower course is low.
3. The delta sometimes develops in a river’s lower course.
4. Much of the river water is drawn for irrigation in the lower course.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below
a)
1, 2, 3 and 4
b)
1, 3 and 4
c)
1, 2 and 3
d)
2 and 4
|
|
Kavita Mehta answered |
The river is choked because the valley of a river is widest in its lower course and the velocity of a river in its lower course is low.
Which one of the following waterfalls in India has the most height?- a)BarehiPani Falls
- b)Jog Falls
- c)Meenmutty Falls
- d)Kunchikal Falls
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following waterfalls in India has the most height?
a)
BarehiPani Falls
b)
Jog Falls
c)
Meenmutty Falls
d)
Kunchikal Falls
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
The Kunchikal falls is the highest waterfalls in India and also the second highest in Asia. The height of the waterfall is 1,493 ft is located near Agumbe in Shimoga district of Karnataka.
Which one of the following is not a tributary of river Alaknanda? - a) Bhilangana
- b) Pinder
- c) Mandakini
- d) Nandakini
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a tributary of river Alaknanda?
a)
Bhilangana
b)
Pinder
c)
Mandakini
d)
Nandakini
|
|
Akshara Mukherjee answered |
The correct answer is option 'A' (Bhilanga).
Explanation:
The Alaknanda River is a major tributary of the Ganges River and originates from the Satopanth Glacier in Uttarakhand, India. It is formed by the confluence of several tributaries, including the Bhagirathi River and the Mandakini River.
Here is the information about each of the given options and whether they are tributaries of the Alaknanda River:
a) Bhilanga: Not a tributary of the Alaknanda River.
b) Pinder: Tributary of the Alaknanda River.
c) Mandakini: Tributary of the Alaknanda River.
d) Nandakini: Tributary of the Alaknanda River.
So, the correct option is 'A' (Bhilanga) as it is not a tributary of the Alaknanda River.
Summary:
The Alaknanda River has several tributaries, including the Pinder, Mandakini, and Nandakini rivers. However, the Bhilanga River is not a tributary of the Alaknanda River.
Explanation:
The Alaknanda River is a major tributary of the Ganges River and originates from the Satopanth Glacier in Uttarakhand, India. It is formed by the confluence of several tributaries, including the Bhagirathi River and the Mandakini River.
Here is the information about each of the given options and whether they are tributaries of the Alaknanda River:
a) Bhilanga: Not a tributary of the Alaknanda River.
b) Pinder: Tributary of the Alaknanda River.
c) Mandakini: Tributary of the Alaknanda River.
d) Nandakini: Tributary of the Alaknanda River.
So, the correct option is 'A' (Bhilanga) as it is not a tributary of the Alaknanda River.
Summary:
The Alaknanda River has several tributaries, including the Pinder, Mandakini, and Nandakini rivers. However, the Bhilanga River is not a tributary of the Alaknanda River.
Which of the following pairs of waterfalls — the river is not properly matched?- a) Hundru-Swarnarekha
- b) Jonha-Rarhu
- c) Dasong-Kanchi
- d) Lodh-Barakar
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pairs of waterfalls — the river is not properly matched?
a)
Hundru-Swarnarekha
b)
Jonha-Rarhu
c)
Dasong-Kanchi
d)
Lodh-Barakar
|
|
Rahul Choudhury answered |
The Lodh Falls is a waterfall in a mid forest in Latehar district. It is located on the Burha river.
Which one of the following rivers flows into the Arabian Sea? - a) Indravati
- b) Godavari
- c) Cauvery
- d) Narmada
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following rivers flows into the Arabian Sea?
a)
Indravati
b)
Godavari
c)
Cauvery
d)
Narmada
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Narmada flows into the Gulf of Khambhat (Arabian Sea).
Which of the following rivers has the largest catchment area?- a) Narmada
- b) Mahanadi
- c) Godavari
- d) Krishna
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following rivers has the largest catchment area?
a)
Narmada
b)
Mahanadi
c)
Godavari
d)
Krishna
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
The river Godavari arises from the Nasik district of Maharashtra. It has a length of 1465 km and after it, Krishna, Mahanadi, Narmada and Kaveri are the largest rivers of peninsular India.
Arrange the following tributaries of river Indus from North to South : 1. Chenab2. Jhelum3. Ravi4. SutlejSelect the correct answer using the code given below :- a) 4-3-1-2
- b) 2-3-1-4
- c) 1-2-3-4
- d) 2-1-3-4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following tributaries of river Indus from North to South :
1. Chenab
2. Jhelum
3. Ravi
4. Sutlej
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
a)
4-3-1-2
b)
2-3-1-4
c)
1-2-3-4
d)
2-1-3-4
|
|
Arya Das answered |
The correct answer is option 'D' - 2-1-3-4. Here's the explanation:
1. Jhelum:
- The Jhelum river is the first tributary of the Indus river when moving from North to South.
- It originates from the Verinag spring in the Indian-administered union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
- It flows through the Kashmir valley and enters Pakistan.
- After traveling a distance of about 725 kilometers, it joins the Chenab river near Trimmu in Pakistan.
2. Chenab:
- The Chenab river is the second tributary of the Indus river when moving from North to South.
- It is formed by the confluence of the Chandra and Bhaga rivers in the Lahaul and Spiti district of Himachal Pradesh, India.
- It flows through the Jammu and Kashmir region before entering Pakistan.
- The Chenab river is about 960 kilometers long and is one of the major rivers of the Indus river system.
3. Ravi:
- The Ravi river is the third tributary of the Indus river when moving from North to South.
- It originates from the Bara Bhangal area in the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh.
- It flows through the states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab in India before entering Pakistan.
- The Ravi river is approximately 720 kilometers long and joins the Chenab river near Trimmu in Pakistan.
4. Sutlej:
- The Sutlej river is the fourth and final tributary of the Indus river when moving from North to South.
- It originates from the Rakshastal Lake in Tibet.
- It flows through the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab before entering Pakistan.
- The Sutlej river has a total length of about 1,550 kilometers and joins the Chenab river near Trimmu in Pakistan.
In conclusion, the correct order of the tributaries of the Indus river from North to South is Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, and Sutlej, which corresponds to option 'D' - 2-1-3-4.
1. Jhelum:
- The Jhelum river is the first tributary of the Indus river when moving from North to South.
- It originates from the Verinag spring in the Indian-administered union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
- It flows through the Kashmir valley and enters Pakistan.
- After traveling a distance of about 725 kilometers, it joins the Chenab river near Trimmu in Pakistan.
2. Chenab:
- The Chenab river is the second tributary of the Indus river when moving from North to South.
- It is formed by the confluence of the Chandra and Bhaga rivers in the Lahaul and Spiti district of Himachal Pradesh, India.
- It flows through the Jammu and Kashmir region before entering Pakistan.
- The Chenab river is about 960 kilometers long and is one of the major rivers of the Indus river system.
3. Ravi:
- The Ravi river is the third tributary of the Indus river when moving from North to South.
- It originates from the Bara Bhangal area in the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh.
- It flows through the states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab in India before entering Pakistan.
- The Ravi river is approximately 720 kilometers long and joins the Chenab river near Trimmu in Pakistan.
4. Sutlej:
- The Sutlej river is the fourth and final tributary of the Indus river when moving from North to South.
- It originates from the Rakshastal Lake in Tibet.
- It flows through the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab before entering Pakistan.
- The Sutlej river has a total length of about 1,550 kilometers and joins the Chenab river near Trimmu in Pakistan.
In conclusion, the correct order of the tributaries of the Indus river from North to South is Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, and Sutlej, which corresponds to option 'D' - 2-1-3-4.
The reservoir GB Pant Sagar is located on which river? - a) Betwa
- b) Ghaghara
- c) Kosi
- d) Rihand
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The reservoir GB Pant Sagar is located on which river?
a)
Betwa
b)
Ghaghara
c)
Kosi
d)
Rihand
|
|
Sameer Nambiar answered |
The GB Pant Sagar Reservoir
The GB Pant Sagar reservoir is a man-made lake in India that is located on the Rihand River. It is one of the largest reservoirs in India, and it is a key source of water for the surrounding regions.
The Rihand River
The Rihand River is a tributary of the Son River, which in turn is a tributary of the Ganges River. The Rihand River originates in the Kaimur Range in Uttar Pradesh and flows through Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh before joining the Son River in Bihar.
Importance of the GB Pant Sagar Reservoir
The GB Pant Sagar reservoir is an important source of water for irrigation, hydroelectric power generation, and drinking water supply. The reservoir has a storage capacity of 10.6 billion cubic meters and is used for irrigation in the surrounding areas. The Rihand hydroelectric power station, which is located at the reservoir, has a capacity of 3000 MW and is one of the largest power plants in India. The reservoir also supplies drinking water to the nearby towns and cities.
Conclusion
The GB Pant Sagar reservoir is located on the Rihand River and is an important source of water for irrigation, hydroelectric power generation, and drinking water supply. The reservoir is a key infrastructure project in India and is essential for the development of the surrounding regions.
The GB Pant Sagar reservoir is a man-made lake in India that is located on the Rihand River. It is one of the largest reservoirs in India, and it is a key source of water for the surrounding regions.
The Rihand River
The Rihand River is a tributary of the Son River, which in turn is a tributary of the Ganges River. The Rihand River originates in the Kaimur Range in Uttar Pradesh and flows through Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh before joining the Son River in Bihar.
Importance of the GB Pant Sagar Reservoir
The GB Pant Sagar reservoir is an important source of water for irrigation, hydroelectric power generation, and drinking water supply. The reservoir has a storage capacity of 10.6 billion cubic meters and is used for irrigation in the surrounding areas. The Rihand hydroelectric power station, which is located at the reservoir, has a capacity of 3000 MW and is one of the largest power plants in India. The reservoir also supplies drinking water to the nearby towns and cities.
Conclusion
The GB Pant Sagar reservoir is located on the Rihand River and is an important source of water for irrigation, hydroelectric power generation, and drinking water supply. The reservoir is a key infrastructure project in India and is essential for the development of the surrounding regions.
Which of the following rivers flows from south to north? - a) Son
- b) Krishna
- c) Mahanadi
- d) Ganga
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following rivers flows from south to north?
a)
Son
b)
Krishna
c)
Mahanadi
d)
Ganga
|
|
Kaavya Dey answered |
The correct answer is option 'A' - Son river.
Son River:
The Son river is a major river in central India, flowing from south to north. It is one of the longest rivers in India and the largest tributary of the Ganges. Here are some key points about the Son river:
- Origin: The Son river originates from the Amarkantak plateau in Madhya Pradesh. It is formed by the confluence of two rivers - the Mahanadi and the Koel.
- Flow: The Son river flows in a northerly direction through the states of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, and Bihar. It eventually joins the Ganges near Patna, the capital city of Bihar.
- Length: The Son river has a total length of about 784 kilometers. It passes through various cities and towns, including Jabalpur, Bilaspur, Ranchi, and Dehri-on-Son.
- Tributaries: The Son river has several tributaries, including the North Koel, the South Koel, the Rihand, and the Sonebari. These tributaries contribute to the overall flow of the river and its drainage basin.
- Significance: The Son river plays a vital role in the agricultural and economic activities of the regions it passes through. It provides irrigation water for farming and is also used for fishing and transportation. The river has significant hydropower potential, and several dams have been constructed along its course for generating electricity.
- Environmental concerns: Like many rivers in India, the Son river faces environmental challenges such as pollution from industrial and domestic waste. Efforts are being made to address these issues and restore the ecological health of the river.
In conclusion, the Son river is the correct answer as it flows from south to north. It is a major river in central India, originating from the Amarkantak plateau and joining the Ganges near Patna.
Son River:
The Son river is a major river in central India, flowing from south to north. It is one of the longest rivers in India and the largest tributary of the Ganges. Here are some key points about the Son river:
- Origin: The Son river originates from the Amarkantak plateau in Madhya Pradesh. It is formed by the confluence of two rivers - the Mahanadi and the Koel.
- Flow: The Son river flows in a northerly direction through the states of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, and Bihar. It eventually joins the Ganges near Patna, the capital city of Bihar.
- Length: The Son river has a total length of about 784 kilometers. It passes through various cities and towns, including Jabalpur, Bilaspur, Ranchi, and Dehri-on-Son.
- Tributaries: The Son river has several tributaries, including the North Koel, the South Koel, the Rihand, and the Sonebari. These tributaries contribute to the overall flow of the river and its drainage basin.
- Significance: The Son river plays a vital role in the agricultural and economic activities of the regions it passes through. It provides irrigation water for farming and is also used for fishing and transportation. The river has significant hydropower potential, and several dams have been constructed along its course for generating electricity.
- Environmental concerns: Like many rivers in India, the Son river faces environmental challenges such as pollution from industrial and domestic waste. Efforts are being made to address these issues and restore the ecological health of the river.
In conclusion, the Son river is the correct answer as it flows from south to north. It is a major river in central India, originating from the Amarkantak plateau and joining the Ganges near Patna.
Which river is not in existence at present? - a) Tons
- b) Saraswati
- c) Ganga
- d) Yamuna
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which river is not in existence at present?
a)
Tons
b)
Saraswati
c)
Ganga
d)
Yamuna
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
- Saraswati River refers to a river that was a distributary of the Bhagirathi and is now no more there but was active till around the 16th century AD.
- The course and condition of the Saraswati have played an important role in the development and decline of river port towns in Bengal. Initially, the major port town was Tamralipta, after its decline Saptagram rose and declined, and finally, Kolkata came up.
Rajarappa is situated on the confluence of which rivers? - a) Damodar — Behera
- b) Damodar — Sherbukhi
- c) Damodar — Barakar
- d) Damodar — Konar
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rajarappa is situated on the confluence of which rivers?
a)
Damodar — Behera
b)
Damodar — Sherbukhi
c)
Damodar — Barakar
d)
Damodar — Konar
|
|
Mayank Choudhury answered |
Location of Rajarappa
Rajarappa is a historical site located in the Ramgarh district of Jharkhand, India. It is situated on the confluence of two rivers.
Confluence of Rivers
The two rivers that meet at Rajarappa are:
- Damodar River: It is one of the most important rivers in eastern India and is also known as the "River of Sorrows" due to the devastating floods it causes in the region. It originates in the Chota Nagpur plateau and flows through Jharkhand and West Bengal before finally merging with the Hooghly River in Kolkata.
- Behera River: It is a small tributary of the Damodar River and originates in the hills of Jharkhand. It flows through the Ramgarh district and meets the Damodar River at Rajarappa.
Historical Significance
Rajarappa has a significant place in the history of Jharkhand. It was the site of a major battle between the local tribal people and the British East India Company in 1771. The tribal people, led by Raja Medini Ray, fought bravely against the British troops but were eventually defeated. The Rajarappa temple, located near the confluence of the two rivers, is also considered a sacred site by the locals and attracts a large number of devotees.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Rajarappa is located at the confluence of the Damodar and Behera rivers in the Ramgarh district of Jharkhand. The site has historical significance due to the battle fought there between the local tribal people and the British East India Company. The Rajarappa temple is also a popular pilgrimage site in the region.
Rajarappa is a historical site located in the Ramgarh district of Jharkhand, India. It is situated on the confluence of two rivers.
Confluence of Rivers
The two rivers that meet at Rajarappa are:
- Damodar River: It is one of the most important rivers in eastern India and is also known as the "River of Sorrows" due to the devastating floods it causes in the region. It originates in the Chota Nagpur plateau and flows through Jharkhand and West Bengal before finally merging with the Hooghly River in Kolkata.
- Behera River: It is a small tributary of the Damodar River and originates in the hills of Jharkhand. It flows through the Ramgarh district and meets the Damodar River at Rajarappa.
Historical Significance
Rajarappa has a significant place in the history of Jharkhand. It was the site of a major battle between the local tribal people and the British East India Company in 1771. The tribal people, led by Raja Medini Ray, fought bravely against the British troops but were eventually defeated. The Rajarappa temple, located near the confluence of the two rivers, is also considered a sacred site by the locals and attracts a large number of devotees.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Rajarappa is located at the confluence of the Damodar and Behera rivers in the Ramgarh district of Jharkhand. The site has historical significance due to the battle fought there between the local tribal people and the British East India Company. The Rajarappa temple is also a popular pilgrimage site in the region.
Which of the following three rivers of the peninsula India have the Amarkantak region as their source? - a) Narmada, Krishna Godavari
- b) Son, Mahanadi, Narmada
- c) Godavari, Krishna, Cauvery
- d) Chambal. Betwa, Luni
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following three rivers of the peninsula India have the Amarkantak region as their source?
a)
Narmada, Krishna Godavari
b)
Son, Mahanadi, Narmada
c)
Godavari, Krishna, Cauvery
d)
Chambal. Betwa, Luni
|
|
Ritika Choudhury answered |
Son, Mahanadi and Narmada rivers originate from Amarkantak region.
Which one of the following pairs of a river and its tributary is not correctly matched? - a) Godavari : Wainganga
- b) Cauvery : Bhavani
- c) Narmada : Amaravati
- d) Krishna : Bhima
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs of a river and its tributary is not correctly matched?
a)
Godavari : Wainganga
b)
Cauvery : Bhavani
c)
Narmada : Amaravati
d)
Krishna : Bhima

|
Upsc Rank Holders answered |
Amaravati River is the longest tributary of the Kaveri river.
Which of the following rivers flows through a ‘rift’ valley?- a) Ganga
- b) Brahmaputra
- c) Narmada
- d) Krishna
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following rivers flows through a ‘rift’ valley?
a)
Ganga
b)
Brahmaputra
c)
Narmada
d)
Krishna
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
Narmada River flows through a rift valley.
Which of the following rivers is not the tributary of Yamuna?
- a)Chambal
- b)Betwa
- c)Ken
- d)Gandak
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following rivers is not the tributary of Yamuna?
a)
Chambal
b)
Betwa
c)
Ken
d)
Gandak
|
|
Jaya Mehta answered |
Answer:
Explanation:
The river that is not a tributary of Yamuna is the Gandak River.
Details:
The following rivers are tributaries of Yamuna:
- Chambal River: It originates from the Vindhya Range in Madhya Pradesh and flows through Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh before joining the Yamuna River.
- Betwa River: It is a major river in central India and flows through the states of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh before merging with the Yamuna River.
- Ken River: It is a tributary of the Yamuna River and flows through the states of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
However, the Gandak River is not a tributary of the Yamuna. It is a major river in Nepal and a left-bank tributary of the Ganges in India. It is also known as the Krishna Gandaki in Nepal. The Gandak River originates in the high Himalayas and flows through Nepal and the Indian states of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Bihar before joining the Ganges River.
Explanation:
The river that is not a tributary of Yamuna is the Gandak River.
Details:
The following rivers are tributaries of Yamuna:
- Chambal River: It originates from the Vindhya Range in Madhya Pradesh and flows through Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh before joining the Yamuna River.
- Betwa River: It is a major river in central India and flows through the states of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh before merging with the Yamuna River.
- Ken River: It is a tributary of the Yamuna River and flows through the states of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
However, the Gandak River is not a tributary of the Yamuna. It is a major river in Nepal and a left-bank tributary of the Ganges in India. It is also known as the Krishna Gandaki in Nepal. The Gandak River originates in the high Himalayas and flows through Nepal and the Indian states of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Bihar before joining the Ganges River.
Which one among the following is the correct sequence of the rivers from north to south?- a) Damodar-Brahmani-Mahanadi-Tungabhadra
- b) Damodar-Mahanadi-Brahmani- Tungabhadra
- c) Brahmani-Tungabhadra-Damodar- Mahanadi
- d) Damodar-Brahmani-Tungabhadra- Mahanadi
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one among the following is the correct sequence of the rivers from north to south?
a)
Damodar-Brahmani-Mahanadi-Tungabhadra
b)
Damodar-Mahanadi-Brahmani- Tungabhadra
c)
Brahmani-Tungabhadra-Damodar- Mahanadi
d)
Damodar-Brahmani-Tungabhadra- Mahanadi
|
|
Diya Deshpande answered |
Sequence of Rivers from North to South
The correct sequence of rivers from north to south is as follows:
a) Damodar-Brahmani-Mahanadi-Tungabhadra
Explanation:
Damodar River - It originates from the Chota Nagpur plateau and flows through the states of Jharkhand and West Bengal before joining the Hugli River.
Brahmani River - It originates from the highlands of Sundargarh district of Odisha and flows through the states of Odisha and Jharkhand before joining the Bay of Bengal.
Mahanadi River - It originates from the Satpura Range in Chhattisgarh and flows through the states of Chhattisgarh and Odisha before joining the Bay of Bengal.
Tungabhadra River - It is a tributary of the Krishna River and originates from the Western Ghats in Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
Therefore, the correct sequence of rivers from north to south is Damodar-Brahmani-Mahanadi-Tungabhadra.
The correct sequence of rivers from north to south is as follows:
a) Damodar-Brahmani-Mahanadi-Tungabhadra
Explanation:
Damodar River - It originates from the Chota Nagpur plateau and flows through the states of Jharkhand and West Bengal before joining the Hugli River.
Brahmani River - It originates from the highlands of Sundargarh district of Odisha and flows through the states of Odisha and Jharkhand before joining the Bay of Bengal.
Mahanadi River - It originates from the Satpura Range in Chhattisgarh and flows through the states of Chhattisgarh and Odisha before joining the Bay of Bengal.
Tungabhadra River - It is a tributary of the Krishna River and originates from the Western Ghats in Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
Therefore, the correct sequence of rivers from north to south is Damodar-Brahmani-Mahanadi-Tungabhadra.
An important river of the Indian desert is? - a) Luni
- b) Narmada
- c) Tapi
- d) Jhelum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An important river of the Indian desert is?
a)
Luni
b)
Narmada
c)
Tapi
d)
Jhelum
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
The Luni is a river of western Rajasthan state, India. It originates in the Pushkar valley of the Aravalli Range, near Ajmer and ends in the marshy lands of Rann of Kutch in Gujarat, after travelling a distance of 495 km.
Which of the following is/are West flowing river(s) of India?1. Mahanadi2. Krishna3. Narmada4. KaverySelect the correct answer using the codes given below- a) 1, 2 and 4
- b) 2 and 3
- c) Only 3
- d) 1 and 3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are West flowing river(s) of India?
1. Mahanadi
2. Krishna
3. Narmada
4. Kavery
Select the correct answer using the codes given below
a)
1, 2 and 4
b)
2 and 3
c)
Only 3
d)
1 and 3
|
|
Garima Das answered |
West Flowing Rivers of India
The rivers in India can be broadly categorized into two types, namely, the Himalayan Rivers and the Peninsular Rivers. The Himalayan Rivers are those rivers that originate from the Himalayan mountain range, whereas the Peninsular Rivers are those rivers that originate from the Peninsular Plateau.
West Flowing Rivers of India are those rivers that flow towards the west from their origin.
The West Flowing Rivers of India are as follows:
1. Narmada River: It is one of the most significant rivers of Central India. It originates from Amarkantak in Madhya Pradesh and flows towards the west, ultimately draining into the Arabian Sea.
2. Tapti River: It is a river that originates in the Satpura Range in Madhya Pradesh and flows through Maharashtra and Gujarat before emptying into the Arabian Sea.
3. Sabarmati River: It is a river that originates in the Aravalli Range in Rajasthan and flows through Gujarat before meeting the Arabian Sea.
4. Mahi River: It is a river that originates in Madhya Pradesh and flows through Rajasthan and Gujarat before emptying into the Arabian Sea.
5. Luni River: It is a river that originates in the Pushkar valley of the Aravalli Range and flows through Rajasthan and Gujarat before disappearing into the Rann of Kutch.
Therefore, the correct answer to the given question is option (c) Only 3, which means that Narmada River is the only west flowing river of the given options.
The rivers in India can be broadly categorized into two types, namely, the Himalayan Rivers and the Peninsular Rivers. The Himalayan Rivers are those rivers that originate from the Himalayan mountain range, whereas the Peninsular Rivers are those rivers that originate from the Peninsular Plateau.
West Flowing Rivers of India are those rivers that flow towards the west from their origin.
The West Flowing Rivers of India are as follows:
1. Narmada River: It is one of the most significant rivers of Central India. It originates from Amarkantak in Madhya Pradesh and flows towards the west, ultimately draining into the Arabian Sea.
2. Tapti River: It is a river that originates in the Satpura Range in Madhya Pradesh and flows through Maharashtra and Gujarat before emptying into the Arabian Sea.
3. Sabarmati River: It is a river that originates in the Aravalli Range in Rajasthan and flows through Gujarat before meeting the Arabian Sea.
4. Mahi River: It is a river that originates in Madhya Pradesh and flows through Rajasthan and Gujarat before emptying into the Arabian Sea.
5. Luni River: It is a river that originates in the Pushkar valley of the Aravalli Range and flows through Rajasthan and Gujarat before disappearing into the Rann of Kutch.
Therefore, the correct answer to the given question is option (c) Only 3, which means that Narmada River is the only west flowing river of the given options.
Which of these west-flowing rivers flow between two mountain ranges?- a) Sharavati
- b) Narmada
- c) Mahi
- d) Sabarmati
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these west-flowing rivers flow between two mountain ranges?
a)
Sharavati
b)
Narmada
c)
Mahi
d)
Sabarmati
|
|
Arun Khatri answered |
It is one of only three major rivers in peninsular India that run from east to west (longest west flowing river), along with the Tapti River and the Mahi River. It is one of the rivers in India that flows in a rift valley, flowing west between the Satpura and Vindhya ranges.
Consider the following tributaries of river Brahmaputra :1. Lohit2. Tista3. Subansiri4. SankoshArrange the above rivers from west to east:- a)2 - 3 - 4 – 1
- b)2 - 4 - 3 – 1
- c)4 - 2 - 3 – 1
- d)3 - 1 - 2 – 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following tributaries of river Brahmaputra :
1. Lohit
2. Tista
3. Subansiri
4. Sankosh
Arrange the above rivers from west to east:
a)
2 - 3 - 4 – 1
b)
2 - 4 - 3 – 1
c)
4 - 2 - 3 – 1
d)
3 - 1 - 2 – 4

|
T.S Academy answered |
- The Brahmaputra River flows through three countries: Tibet (China), India, and Bangladesh.
- In India, the Brahmaputra flows for a length of 916 km, while its total length is 2,900 km.
- The river has numerous left and right tributaries.
- Lohit River originates in a region of Tibet.
- Teesta River rises from Tso Lhamo Lake in the North Sikkim Himalayas.
- Subansiri River originates in the Himalayas in China.
- Sankosh River originates in northern Bhutan.
Therefore,Correct Answer- Option B
Deltas are common in India for the East-flowing river systems, whereas they are nearly absent on the West coast because West-flowing rivers - a) are few
- b) have lesser water volume and carry less run-off silt
- c) originate in dry areas
- d) originate largely in the Western Ghats and have a short distance to cover to the sea
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Deltas are common in India for the East-flowing river systems, whereas they are nearly absent on the West coast because West-flowing rivers
a)
are few
b)
have lesser water volume and carry less run-off silt
c)
originate in dry areas
d)
originate largely in the Western Ghats and have a short distance to cover to the sea
|
|
Rajeev Sengupta answered |
Understanding River Deltas in India
Deltas are landforms created at river mouths where sediment is deposited as the river flows into a larger body of water, such as an ocean. The formation of deltas is influenced by various factors, especially the river's water volume and sediment load.
East-Flowing Rivers vs. West-Flowing Rivers
- Abundance of East-Flowing Rivers: India has numerous east-flowing rivers, like the Ganges and Brahmaputra, which carry large volumes of water and sediment.
- Sediment Load: These rivers originate in the Himalayas and traverse through fertile plains, picking up silt and clay, which contributes to delta formation as they slow down and deposit this material in the Bay of Bengal.
Characteristics of West-Flowing Rivers
- Fewer Rivers: The West Coast of India has fewer rivers compared to the East Coast. This limits the potential for delta formation.
- Lower Water Volume: West-flowing rivers, such as the Narmada and Tapi, typically have a lower water volume.
- Reduced Sediment Transport: Due to their shorter lengths and steeper gradients, these rivers carry less runoff and sediment to the sea.
- Origin in Dry Regions: Many of these rivers originate in the Western Ghats, which are characterized by less rainfall compared to the Himalayan region, leading to lower sediment yield.
Conclusion
In summary, the absence of significant deltas on the West Coast of India is primarily due to the lower water volume and sediment transport capacity of its rivers. This contrasts sharply with the east-flowing river systems, which are rich in sediment and capable of forming extensive deltas. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for comprehending India's diverse riverine landscapes.
Deltas are landforms created at river mouths where sediment is deposited as the river flows into a larger body of water, such as an ocean. The formation of deltas is influenced by various factors, especially the river's water volume and sediment load.
East-Flowing Rivers vs. West-Flowing Rivers
- Abundance of East-Flowing Rivers: India has numerous east-flowing rivers, like the Ganges and Brahmaputra, which carry large volumes of water and sediment.
- Sediment Load: These rivers originate in the Himalayas and traverse through fertile plains, picking up silt and clay, which contributes to delta formation as they slow down and deposit this material in the Bay of Bengal.
Characteristics of West-Flowing Rivers
- Fewer Rivers: The West Coast of India has fewer rivers compared to the East Coast. This limits the potential for delta formation.
- Lower Water Volume: West-flowing rivers, such as the Narmada and Tapi, typically have a lower water volume.
- Reduced Sediment Transport: Due to their shorter lengths and steeper gradients, these rivers carry less runoff and sediment to the sea.
- Origin in Dry Regions: Many of these rivers originate in the Western Ghats, which are characterized by less rainfall compared to the Himalayan region, leading to lower sediment yield.
Conclusion
In summary, the absence of significant deltas on the West Coast of India is primarily due to the lower water volume and sediment transport capacity of its rivers. This contrasts sharply with the east-flowing river systems, which are rich in sediment and capable of forming extensive deltas. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for comprehending India's diverse riverine landscapes.
Gandak river is associated with one of the following river systems— - a) Brahmaputra
- b) Indus
- c) Ganga
- d) None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Gandak river is associated with one of the following river systems—
a)
Brahmaputra
b)
Indus
c)
Ganga
d)
None of the above
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
The Gandak River, river in central Nepal and northern India is a left-bank tributary of the Ganges in India.
Which one of the following rivers in India has been declared as the National River? - a) Ganga
- b) Yamuna
- c) Krishna
- d) Son
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following rivers in India has been declared as the National River?
a)
Ganga
b)
Yamuna
c)
Krishna
d)
Son
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
- The Ganges is a trans-boundary river of India and Bangladesh. The 2,525 km (1,569 mi) river rises in the western Himalayas in the Indian state of Uttarakhand and flows south and east through the Gangetic Plain of North India into Bangladesh, where it empties into the Bay of Bengal. It is the third-largest river in the World by discharge.
Which one of the following rivers of India does not make a delta? Ans (b)- a) Ganga
- b) Narmada
- c) Mahanadi
- d) Kaveri
Correct answer is option ''. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following rivers of India does not make a delta?
Ans (b)
a)
Ganga
b)
Narmada
c)
Mahanadi
d)
Kaveri
|
|
Anuj Nair answered |
The Narmada, also called the Rewa, is a river in central India and the fifth-longest river in the Indian subcontinent. It is the third-longest river that flows entirely within India, after the Godavari and the Krishna.
Chapter doubts & questions for Drainage Systems - Geography for State PSC Exams 2025 is part of BPSC (Bihar) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for BPSC (Bihar) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Drainage Systems - Geography for State PSC Exams in English & Hindi are available as part of BPSC (Bihar) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for BPSC (Bihar) Exam by signing up for free.
Geography for State PSC Exams
185 videos|761 docs|272 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup