All Exams >
BPSC (Bihar) >
Environment & Additional Topics for State PSC Exams >
All Questions
All questions of Marine Organisms for BPSC (Bihar) Exam
What are the examples of Lotic Water?- a)Streams, River and Spring
- b)River, lake and Pond
- c)Swamps and Lakes
- d)Lakes and Ponds
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the examples of Lotic Water?
a)
Streams, River and Spring
b)
River, lake and Pond
c)
Swamps and Lakes
d)
Lakes and Ponds
|
|
Rahul Mehta answered |
The correct answer is Streams, River and Spring.
- The pond is not an example of a Lotic ecosystem.
Key Points
- The lotic water is a classification of the freshwater bodies on the basis of the flow of the water.
- The lotic water is composed of flowing water bodies.
- The water of these types of water bodies does not stay in one place but rather moves or flows from one place to another.
- In the first option, we are given streams, rivers, and springs.
- Streams, rivers, and springs are all flowing bodies of water.
- Hence, these are all examples of lotic water.
- A river is a flowing body of water.
- Lakes and ponds are still bodies of water.
- Hence, the river is an example of lotic water and the lake and ponds are examples of lentic water.
- Swamps and lakes are both still bodies of water.
- Hence, these are both examples of lentic water.
- Lakes and ponds are both still bodies of water.
- Hence, these are both examples of lentic water.
- From the above information, we can conclude that the streams, rivers, and springs are examples of lotic water.
Consider the following statements regarding biodiversity hotspots:1. A biodiversity hotspot is a biogeographic region that is both a significant reservoir of biodiversity and is threatened with destruction.
2. Globally, the total number of biodiversity hotspots has witnessed a decline over the years.
3. The Himalayas and the Western Ghats are the only two biodiversity hotspots in India.Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?- a)1 and 3 only
- b)2 and 3 only
- c)3 only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements regarding biodiversity hotspots:
1. A biodiversity hotspot is a biogeographic region that is both a significant reservoir of biodiversity and is threatened with destruction.
2. Globally, the total number of biodiversity hotspots has witnessed a decline over the years.
3. The Himalayas and the Western Ghats are the only two biodiversity hotspots in India.
2. Globally, the total number of biodiversity hotspots has witnessed a decline over the years.
3. The Himalayas and the Western Ghats are the only two biodiversity hotspots in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
a)
1 and 3 only
b)
2 and 3 only
c)
3 only
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Rahul Mehta answered |
A biodiversity hotspot
- It is a biogeographic region that is both a significant reservoir of biodiversity and is threatened with destruction. Hence, Statement 1 is correct.
- These regions have a very high level of species richness (not species evenness) and a high degree of endemism (that is, species confined to that region and not found anywhere else). These hotspots are also regions of accelerated habitat loss.
- Initially, 25 biodiversity hotspots were identified but subsequently, nine more have been added to the list, bringing the total number of biodiversity hotspots in the world to 34. As of today, their number is 35. Hence statement 2 is not correct.
- The biodiversity hotspots hold especially high numbers of endemic species, yet their combined area of remaining habitat covers only 2.3% of the Earth's land surface.
- Each hotspot faces extreme threats and has already lost at least 70% of its original natural vegetation. Over 50% of the world‘s plant species and 42% of all terrestrial vertebrate species are endemic in nature.
- Biodiversity Hotspots in India
- Himalaya
- Includes the entire Indian Himalayan region (and that falling in Pakistan, Tibet, Nepal, Bhutan, China and Myanmar)
- Indo-Burma
- Includes entire North-eastern India, except Assam and Andaman group of Islands (and Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia and southern China)
- Sundalands
- Includes Nicobar group of Islands (and Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Brunei, Philippines)
- The Western Ghats and Sri Lanka
- Includes entire Western Ghats (and Sri Lanka)
- Hence statement 3 is not correct.
- Himalaya
Which of the following describes a lentic ecosystem?- a)ponds, rivers and marshes
- b)springs, lakes and swamps
- c)rivers, stream and spring
- d)lakes, ponds and pools
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following describes a lentic ecosystem?
a)
ponds, rivers and marshes
b)
springs, lakes and swamps
c)
rivers, stream and spring
d)
lakes, ponds and pools
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
CONCEPT:
- An ecosystem forms the basic building block of an environment.
- It consists of both biotic and abiotic components and their continuous interactions with each other.
- Ecosystems can broadly be classified into two types, namely:
- Natural ecosystem – naturally occurring
- Artificial ecosystem – man-made ecosystems
An aquatic ecosystem includes standing fresh water, running fresh water, as well as the ocean and seas around the world.
Lentic ecosystem
- Lentic ecosystems are those water bodies whose water is still.
- These ecosystems range in size from very small ponds or pools that may be temporary, to large lakes.
- Examples: ponds, marshes, pools, ditches, lakes, and swamps.
Lotic ecosystem
- Lotic ecosystems are those water bodies whose water is flowing.
- These ecosystems can vary in size dramatically from small trickling streams to mile-wide rivers that travel for thousands of miles.
- Examples: rivers, streams, canals, and springs.
Thus, lakes, ponds, and pools are examples of a lentic ecosystem.
Which of the following ecosystems has the highest net primary productivity?- a)Rainforest
- b)Extreme desert
- c)Lakes and streams
- d)Mid-latitude grassland
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following ecosystems has the highest net primary productivity?
a)
Rainforest
b)
Extreme desert
c)
Lakes and streams
d)
Mid-latitude grassland
|
|
Gitanjali Roy answered |
The rainforest ecosystem has the highest net primary productivity among the given options. Net primary productivity (NPP) refers to the rate at which energy is stored through the process of photosynthesis by plants in an ecosystem, minus the energy that is used up by the plants themselves through respiration.
Rainforest ecosystem is characterized by its dense vegetation, high species diversity, and abundant rainfall. These factors contribute to its high net primary productivity. Here's a detailed explanation of why the rainforest has the highest NPP:
1. Abundant sunlight:
- Rainforests receive high levels of sunlight due to their location near the equator where sunlight is more direct and intense.
- The availability of abundant sunlight ensures optimal conditions for photosynthesis, the process through which plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
2. High rainfall:
- Rainforests receive high amounts of rainfall throughout the year, which provides a constant supply of water for plant growth.
- Water is essential for photosynthesis as it is a key component in the process of converting carbon dioxide and light energy into glucose.
3. Dense vegetation:
- Rainforests are characterized by their dense and diverse vegetation, with a variety of plant species occupying different layers.
- The dense vegetation allows for efficient capture of sunlight and maximizes the surface area available for photosynthesis.
4. Nutrient-rich soil:
- Rainforest soils are generally nutrient-rich due to the rapid decomposition of organic matter and the constant recycling of nutrients through the dense vegetation.
- These nutrient-rich soils provide essential elements for plant growth, contributing to higher productivity.
5. High species diversity:
- Rainforests are known for their high species diversity, with a wide range of plant species coexisting in the ecosystem.
- The presence of different species occupying different niches allows for efficient utilization of available resources, leading to increased productivity.
Overall, the combination of abundant sunlight, high rainfall, dense vegetation, nutrient-rich soil, and high species diversity makes the rainforest ecosystem the most productive in terms of net primary productivity.
Rainforest ecosystem is characterized by its dense vegetation, high species diversity, and abundant rainfall. These factors contribute to its high net primary productivity. Here's a detailed explanation of why the rainforest has the highest NPP:
1. Abundant sunlight:
- Rainforests receive high levels of sunlight due to their location near the equator where sunlight is more direct and intense.
- The availability of abundant sunlight ensures optimal conditions for photosynthesis, the process through which plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
2. High rainfall:
- Rainforests receive high amounts of rainfall throughout the year, which provides a constant supply of water for plant growth.
- Water is essential for photosynthesis as it is a key component in the process of converting carbon dioxide and light energy into glucose.
3. Dense vegetation:
- Rainforests are characterized by their dense and diverse vegetation, with a variety of plant species occupying different layers.
- The dense vegetation allows for efficient capture of sunlight and maximizes the surface area available for photosynthesis.
4. Nutrient-rich soil:
- Rainforest soils are generally nutrient-rich due to the rapid decomposition of organic matter and the constant recycling of nutrients through the dense vegetation.
- These nutrient-rich soils provide essential elements for plant growth, contributing to higher productivity.
5. High species diversity:
- Rainforests are known for their high species diversity, with a wide range of plant species coexisting in the ecosystem.
- The presence of different species occupying different niches allows for efficient utilization of available resources, leading to increased productivity.
Overall, the combination of abundant sunlight, high rainfall, dense vegetation, nutrient-rich soil, and high species diversity makes the rainforest ecosystem the most productive in terms of net primary productivity.
Quinine is used for treatment of which disease ?- a)Blood Cancer
- b)Malaria
- c)Asthma
- d)Hypertension
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Quinine is used for treatment of which disease ?
a)
Blood Cancer
b)
Malaria
c)
Asthma
d)
Hypertension
|
|
Rahul Mehta answered |
Quinine is a medication used to treat parasite causing malaria disease.
- It is extracted from the bark of the cinchona tree.
- Quinine was first isolated in 1820.
- Quinine is also used for the treatment of babesiosis.
- Quinine is the ingredient in tonic water that gives it its bitter taste.
- Quinine is on the world health organization's list of essential medicines.
- Malaria is caused by plasmodium parasite.
Drugs like vincristine and vinblastine extracted from vinca rosea are used for the treatment of blood cancer.
Reserpine extracted from the plant serpentine is used for the treatment of systolic hypertension.
Select the food chain found in forest/grassland ecosystem:- a)Phytoplanktons → Water fleas → Small fish → Tuna
- b)Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk
- c)Leaf litter → Algae → Crabs → Small carnivorous fish → Large carnivorus fish
- d)Dead organic matter → Fungi → Bacteria
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the food chain found in forest/grassland ecosystem:
a)
Phytoplanktons → Water fleas → Small fish → Tuna
b)
Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk
c)
Leaf litter → Algae → Crabs → Small carnivorous fish → Large carnivorus fish
d)
Dead organic matter → Fungi → Bacteria
|
|
Rahul Mehta answered |
Concept:
Food chain: A food chain shows the feeding relationship between different organisms in a particular environment and/or habitat. A food chain shows how energy is passed from the sun to producers, from producers to consumers, and from consumers to decomposes such as fungi. They also show how animals depend on other organisms for food.
- Food chain is distributed between Autotrophs, Hetrotrops, and Decomposers i.e Producers, consumers and decomposers.
- Autotrophs produce their own food like plants, trees and some algae.
- Heterotrophs are consumers i.e. animals, man, insects etc.
- Decomposers are bacteria, fungi etc.
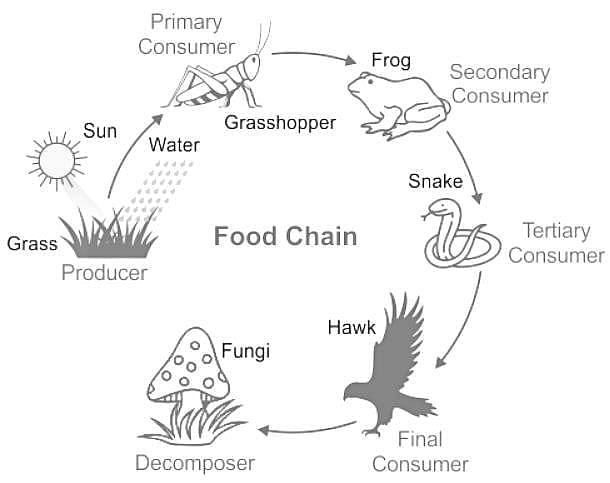
Thus, the correct sequence is Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk.
The largest ecosystem of the Earth is-- a)Biosphere
- b)Hydrosphere
- c)Lithosphere
- d)Biome
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The largest ecosystem of the Earth is-
a)
Biosphere
b)
Hydrosphere
c)
Lithosphere
d)
Biome
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
An ecosystem is an interaction of biological community organisms between each other and their physical environment.
The lithosphere is the outer part of the Earth it is made up of the crust and the top part of the upper mantle.
A biome is a large community of vegetation and wildlife which are adapted to a specific climate.
The five major types of the biome are:
The lithosphere is the outer part of the Earth it is made up of the crust and the top part of the upper mantle.
A biome is a large community of vegetation and wildlife which are adapted to a specific climate.
The five major types of the biome are:
- aquatic
- grassland
- forest
- desert
- tundra
What is the primary function of seagrass beds in coastal waters?- a)To provide shelter for marine invertebrates
- b)To filter heavy metals from the water
- c)To reduce wave and current energy
- d)To serve as a source of sediment
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
To provide shelter for marine invertebrates
b)
To filter heavy metals from the water
c)
To reduce wave and current energy
d)
To serve as a source of sediment
|
|
Muskaan Dey answered |
The primary function of seagrass beds in coastal waters is to reduce wave and current energy. Seagrass beds are underwater meadows composed of grass-like plants that grow in shallow coastal waters. They play a crucial role in the health and stability of coastal ecosystems due to their unique characteristics and functions.
Wave and Current Energy Reduction
Seagrass beds act as natural buffers against wave and current energy. The dense root systems and above-ground biomass of seagrass plants dissipate the force of waves and currents, which helps to protect the coastlines from erosion. The flexibility and resistance of seagrass blades also contribute to reducing the impact of waves and currents. As a result, seagrass beds can stabilize coastlines and provide a natural defense against coastal erosion and storm damage.
Habitat and Shelter
Seagrass beds provide essential habitat and shelter for a wide variety of marine organisms. The dense and complex structure of seagrass meadows offers refuge, breeding grounds, and nurseries for many species, including fish, crustaceans, and mollusks. Seagrass beds are particularly important for juvenile stages of various marine organisms, as they provide protection from predators and offer abundant food sources.
Carbon Sequestration
Seagrass beds are highly efficient at capturing and storing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis. The plants absorb CO2 and convert it into organic matter, which is then stored in the plant's tissues and sediments. This carbon sequestration helps mitigate climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Water Quality Improvement
Seagrass beds play a significant role in improving water quality in coastal areas. They act as natural filters by trapping and removing sediments, nutrients, and pollutants from the water column. Seagrass roots and rhizomes bind the sediment, preventing it from being washed away with currents. The plants also absorb excess nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, which can cause harmful algal blooms and degrade water quality.
Biodiversity and Food Web Support
Seagrass beds support a diverse range of species, contributing to the overall biodiversity of coastal ecosystems. The plants provide food and habitat for herbivores, which in turn attract predators and support a complex food web. The presence of seagrass beds enhances the productivity and stability of coastal ecosystems and sustains the populations of many marine organisms.
In conclusion, while seagrass beds provide habitat, filter water, and support biodiversity, their primary function in coastal waters is to reduce wave and current energy. They act as natural buffers, protecting coastlines from erosion and storm damage. Seagrass beds are essential for the health and stability of coastal ecosystems and play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of these fragile environments.
Wave and Current Energy Reduction
Seagrass beds act as natural buffers against wave and current energy. The dense root systems and above-ground biomass of seagrass plants dissipate the force of waves and currents, which helps to protect the coastlines from erosion. The flexibility and resistance of seagrass blades also contribute to reducing the impact of waves and currents. As a result, seagrass beds can stabilize coastlines and provide a natural defense against coastal erosion and storm damage.
Habitat and Shelter
Seagrass beds provide essential habitat and shelter for a wide variety of marine organisms. The dense and complex structure of seagrass meadows offers refuge, breeding grounds, and nurseries for many species, including fish, crustaceans, and mollusks. Seagrass beds are particularly important for juvenile stages of various marine organisms, as they provide protection from predators and offer abundant food sources.
Carbon Sequestration
Seagrass beds are highly efficient at capturing and storing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis. The plants absorb CO2 and convert it into organic matter, which is then stored in the plant's tissues and sediments. This carbon sequestration helps mitigate climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Water Quality Improvement
Seagrass beds play a significant role in improving water quality in coastal areas. They act as natural filters by trapping and removing sediments, nutrients, and pollutants from the water column. Seagrass roots and rhizomes bind the sediment, preventing it from being washed away with currents. The plants also absorb excess nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, which can cause harmful algal blooms and degrade water quality.
Biodiversity and Food Web Support
Seagrass beds support a diverse range of species, contributing to the overall biodiversity of coastal ecosystems. The plants provide food and habitat for herbivores, which in turn attract predators and support a complex food web. The presence of seagrass beds enhances the productivity and stability of coastal ecosystems and sustains the populations of many marine organisms.
In conclusion, while seagrass beds provide habitat, filter water, and support biodiversity, their primary function in coastal waters is to reduce wave and current energy. They act as natural buffers, protecting coastlines from erosion and storm damage. Seagrass beds are essential for the health and stability of coastal ecosystems and play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of these fragile environments.
Very minute plants floating in the water are called- a)nekton
- b)phytoplankton
- c)benthos
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Very minute plants floating in the water are called
a)
nekton
b)
phytoplankton
c)
benthos
d)
None of the above
|
|
Rahul Mehta answered |
- Some animals eat both plants as well as other animals, those who heart both are called omnivores.
- The omnivores eat plant food as well as the meat of other animals.
- Some of the examples are Man, dogs, crows, and ants.
- Man is called an omnivore because he eats both, plant food as well as the meat of animals.
- There is another type of producer and consumer who are extremely small.
- Planktons:
- They are very minute or microscopic organisms freely floating on the surface of the water in a pond, lake, river, or ocean.
- Planktons float near the surface of the water and provide food for many fish and other aquatic animals.
- There are two types of planktons:
- Phytoplanktons:
- The microscopic aquatic plants freely floating on the surface of the water in a pond, lake, river, or ocean.
- The free-floating alga is an example of phytoplanktons.
- Phytoplanktons are capable of producing food by the process of photosynthesis.
- Zooplanktons:
- The microscopic aquatic animals freely floating on water are called zooplanktons.
- The free-floating protozoa are an example of zooplanktons.
- A very, very small fish is also zooplankton.
- Phytoplanktons:
The second trophic level in a lake is?- a)Fungi
- b)Benthos
- c)Zooplankton
- d)Phytoplankton
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The second trophic level in a lake is?
a)
Fungi
b)
Benthos
c)
Zooplankton
d)
Phytoplankton
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
- A lake ecosystem is an aquatic food chain. It consists of different trophic levels.
- The first trophic level is phytoplankton.
- They produce their own food.
- Zooplankton is the primary consumer in aquatic food chains.
- They feed upon phytoplankton. They are present in the second trophic level.
- Hence, the second most important trophic level in a lake is zooplankton.
- Small fishes feed upon zooplankton.
- They are present in the third trophic level. Similarly, big fishes and other bigger aquatic animals are present in the fourth trophic level which feed upon small fishes.
- Thus, the correct answer is 'Zooplankton.
Coal, limestone, petroleum, animal shells are all related to:- a)Oxygen cycle
- b)Phosphorus cycle
- c)Nitrogen cycle
- d)Carbon cycle
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Coal, limestone, petroleum, animal shells are all related to:
a)
Oxygen cycle
b)
Phosphorus cycle
c)
Nitrogen cycle
d)
Carbon cycle
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
The carbon cycle describes the process in which carbon atoms continually travel from the atmosphere to the Earth and then back into the atmosphere.
Since our planet and its atmosphere form a closed environment, the amount of carbon in this system does not change. Where the carbon is located in the atmosphere.
On Earth, most carbon is stored in rocks and sediments, while the rest is located in the ocean, atmosphere, and in living organisms. These are the reservoirs, or sinks, through which carbon cycles.
Carbon is released back into the atmosphere when organisms die, volcanoes erupt, fires blaze, fossil fuels are burned, and through a variety of other mechanisms.
Thus, coal, limestone, petroleum, and animal shells are all result of the Carbon Cycle. Hence, Option 4 is the correct answer.
Since our planet and its atmosphere form a closed environment, the amount of carbon in this system does not change. Where the carbon is located in the atmosphere.
On Earth, most carbon is stored in rocks and sediments, while the rest is located in the ocean, atmosphere, and in living organisms. These are the reservoirs, or sinks, through which carbon cycles.
Carbon is released back into the atmosphere when organisms die, volcanoes erupt, fires blaze, fossil fuels are burned, and through a variety of other mechanisms.
Thus, coal, limestone, petroleum, and animal shells are all result of the Carbon Cycle. Hence, Option 4 is the correct answer.
Which of the following statement is/are correct?1. The non-living constituents are said to include the producers, consumers and decomposers.
2. The living organisms may include habitat, gases, solar radiation, temperature, moisture and inorganic and organic nutrients.Choose the correct option from below.- a)1 only
- b)2 only
- c)Both 1 and 2
- d)Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is/are correct?
1. The non-living constituents are said to include the producers, consumers and decomposers.
2. The living organisms may include habitat, gases, solar radiation, temperature, moisture and inorganic and organic nutrients.
2. The living organisms may include habitat, gases, solar radiation, temperature, moisture and inorganic and organic nutrients.
Choose the correct option from below.
a)
1 only
b)
2 only
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
Rahul Mehta answered |
- An ecosystem has two components the biotic components consisting of living things, and the abiotic portion, consisting of elements that are not alive.
- The nonliving constituents are said to include the following category, habitat, gases, solar radiation, temperature, moisture, and inorganic and organic nutrients.
- Hence, Statement 1 is incorrect.
- The living organisms may be sub-divided into producers, consumers, and decomposers. Abiotic Components include basic inorganic and organic components of the environment or habitat of the organism.
- Hence, Statement 2 is incorrect.
- The inorganic components of an ecosystem are carbon dioxide, water nitrogen, calcium phosphate all of which are involved in the matter cycle (biogeochemical cycles).
- The organic components of an ecosystem are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids, all of which are synthesized by the biota (flora and fauna) of an ecosystem and are reached to the ecosystem as their wastes, dead remains etc. the climate 'microclimate' temperature, light soil etc. are abiotic components of the ecosystems.
The pyramid of energy in any ecosystem is- a)Always upright
- b)May be upright and inverted
- c)Always inverted
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The pyramid of energy in any ecosystem is
a)
Always upright
b)
May be upright and inverted
c)
Always inverted
d)
None of the above
|
|
Rahul Mehta answered |
The pyramid of energy in any ecosystem is always upright. This means that the amount of energy present at each trophic level decreases as you move up the food chain. This happens because energy is lost as it is transferred from one trophic level to the next, through processes such as respiration, heat loss, and incomplete digestion. As a result, there is less energy available to organisms at higher trophic levels, which limits the number of individuals that can be supported. Therefore, the pyramid of energy is always upright, with the base representing the primary producers, and the top representing the apex predators.
Which of the following regions has maximum bio-diversity?- a)Temperate rainforest
- b)Taiga
- c)Tropical rain forest
- d)Mangroves
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following regions has maximum bio-diversity?
a)
Temperate rainforest
b)
Taiga
c)
Tropical rain forest
d)
Mangroves
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
- Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as lowland equatorial evergreen rainforest.
- A mangrove is a shrub or small tree that grows in coastal saline or brackish water.
- The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species.
- Mangroves occur worldwide in the tropics and subtropics, mainly between latitudes 25° N and 25° S.
- Tropical Rainforests has the maximum bio-diversity among the given options.
Which of the following is not an artificial ecosystem?- a)Reservoir of a dam
- b)Paddy-field
- c)Forest
- d)Garden
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an artificial ecosystem?
a)
Reservoir of a dam
b)
Paddy-field
c)
Forest
d)
Garden
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
The ecosystem is completely dependent on solar radiation.
- For eg. forests, oceans, grasslands, lakes, rivers, and deserts.
- This type of ecosystem is known as the Natural ecosystem.
- Man-made ecosystems are those ecosystems that are dependent on solar energy.
- For eg. agricultural fields and aquaculture ponds.
- Such ecosystems are also dependent on fossil fuels.
- For eg. urban and industrial ecosystems.
- An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the non-living components of their environment, interacting as a system.
- These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows.
- A forest ecosystem is a functional unit or a system that comprises soil, trees, insects, animals, birds, and man as its interacting units.
Consider the following statements:1. Estuaries, intertidal zones, rocky and sandy shores, tropical reefs and regions of the open ocean are major marine ecosystems.
2. Lentic ecosystem includes river, stream or spring.Which of the above statements is/are correct?- a)1 Only
- b)2 Only
- c)Both 1 and 2
- d)Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. Estuaries, intertidal zones, rocky and sandy shores, tropical reefs and regions of the open ocean are major marine ecosystems.
2. Lentic ecosystem includes river, stream or spring.
2. Lentic ecosystem includes river, stream or spring.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
2 Only
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
Ecosystem:
- Ecosystem is an open system with inputs, internal transfers and outputs of energy and nutrients.
- Sunlight is the initial energy source for nearly all ecosystems.
- The different types of ecosystems are-
- Natural Ecosystem:
- Terrestrial ecosystem
- Aquatic ecosystem
- Lentic - lake, pond or swamp
- Lotic - river, stream or spring. Hence, statement 2 is incorrect.
- Artificial Ecosystem:
- Dams
- Gardens
- Botanical parks
- Zoos
- Aquariums
- Natural Ecosystem:
- Aquatic ecosystem include standing fresh water (such as lakes), running fresh water (such as streams), as well as the ocean and seas around the world.
- Estuaries, intertidal zones, rocky and sandy shores, tropical reefs and regions of the open ocean are major marine ecosystems. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
Chapter doubts & questions for Marine Organisms - Environment & Additional Topics for State PSC Exams 2025 is part of BPSC (Bihar) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for BPSC (Bihar) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Marine Organisms - Environment & Additional Topics for State PSC Exams in English & Hindi are available as part of BPSC (Bihar) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for BPSC (Bihar) Exam by signing up for free.
Environment & Additional Topics for State PSC Exams
93 videos|160 docs|51 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










