All Exams >
Grade 2 >
Science for Grade 2 >
All Questions
All questions of What Plants Need for Grade 2 Exam
The part of the plant which grows above the ground.- a)Root
- b)Fruit
- c)Shoot
- d)Flower
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The part of the plant which grows above the ground.
a)
Root
b)
Fruit
c)
Shoot
d)
Flower
|
|
Shounak Khanna answered |
The part of the plant which grows above the ground is called the shoot. Let us understand this in detail:
Plant Parts:
Plants have different parts that perform specific functions. These parts include:
- Roots: The part of the plant that grows below the ground and absorbs water and nutrients from the soil.
- Stem: The part of the plant that supports the leaves, flowers, and fruits and transports water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant.
- Leaves: The part of the plant that carries out photosynthesis, a process by which plants make their food.
- Flowers: The reproductive part of the plant that produces seeds.
- Fruit: The part of the plant that contains seeds and is produced after the flower is fertilized.
Shoot:
The shoot is the part of the plant that grows above the ground. It includes the stem, leaves, flowers, and fruits. The shoot performs the following functions:
- Supports the plant: The stem of the shoot provides support to the plant and holds it upright.
- Photosynthesis: The leaves of the shoot carry out photosynthesis, a process by which plants make their food.
- Reproduction: The flowers of the shoot are the reproductive part of the plant that produces seeds.
- Seed dispersal: The fruits of the shoot contain seeds and help in their dispersal.
Therefore, the correct answer to the given question is option 'C' - Shoot.
Plant Parts:
Plants have different parts that perform specific functions. These parts include:
- Roots: The part of the plant that grows below the ground and absorbs water and nutrients from the soil.
- Stem: The part of the plant that supports the leaves, flowers, and fruits and transports water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant.
- Leaves: The part of the plant that carries out photosynthesis, a process by which plants make their food.
- Flowers: The reproductive part of the plant that produces seeds.
- Fruit: The part of the plant that contains seeds and is produced after the flower is fertilized.
Shoot:
The shoot is the part of the plant that grows above the ground. It includes the stem, leaves, flowers, and fruits. The shoot performs the following functions:
- Supports the plant: The stem of the shoot provides support to the plant and holds it upright.
- Photosynthesis: The leaves of the shoot carry out photosynthesis, a process by which plants make their food.
- Reproduction: The flowers of the shoot are the reproductive part of the plant that produces seeds.
- Seed dispersal: The fruits of the shoot contain seeds and help in their dispersal.
Therefore, the correct answer to the given question is option 'C' - Shoot.
Fibrous root is present in-- a)Bean
- b)Carrot
- c)Banana
- d)Beetroot
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Fibrous root is present in-
a)
Bean
b)
Carrot
c)
Banana
d)
Beetroot
|
|
Pankaj Gupta answered |
Explanation:
- Fibrous roots are the ones that arise from the base of the stem and spread in different directions forming a tangled mass of roots, which is why they are also called adventitious roots.
- Banana is a plant that possesses fibrous roots.
- The root system of banana is a complex network of roots that grows horizontally and superficially in the soil.
- The fibrous root system of the banana plant is shallow and wide-spreading, which helps it to absorb nutrients and water efficiently from the soil.
- Bean and Beetroot possess tap roots, whereas Carrot possesses a modified tap root called a taproot.
- The taproot system consists of a single dominant root that grows vertically into the soil, and it is found in dicotyledonous plants.
Which of the following plants will not be able to survive?
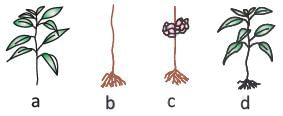
- a)(a) and (b)
- b)(b) and (c)
- c)(c) and (d)
- d)(a) and, (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following plants will not be able to survive?


a)
(a) and (b)
b)
(b) and (c)
c)
(c) and (d)
d)
(a) and, (b) and (c)

|
Learning Education answered |
Plants require stem, leaves, roots for its survival. In this,
plant (a) does not have roots in it.
Plant (b) does not have leaves
plant (c) does not have stem.
So only plant (d) can survive because it has all the parts(roots, stem and leaves) in it.
plant (a) does not have roots in it.
Plant (b) does not have leaves
plant (c) does not have stem.
So only plant (d) can survive because it has all the parts(roots, stem and leaves) in it.
Select the animal which gives birth to a young one.- a)Whale
- b)Insect
- c)Frog
- d)Snake
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the animal which gives birth to a young one.
a)
Whale
b)
Insect
c)
Frog
d)
Snake
|
|
Saikat Joshi answered |
The correct answer is option 'A', Whale.
A whale is a marine mammal that gives birth to a young one. Let's dive into more details and explore why the other options are not the correct answers.
1. Whale:
- Whales are mammals and give live birth to their young ones.
- They have internal fertilization, where the male whale transfers sperm to the female's reproductive system, resulting in pregnancy.
- The female whale carries the developing fetus inside her body until it is fully developed and ready to be born.
- Once the young whale is born, it is nourished with milk produced by the mother until it can fend for itself.
2. Insect:
- Insects, such as bees, butterflies, ants, and beetles, do not give birth to live young ones.
- Most insects undergo a process called metamorphosis, where they go through distinct stages of development, including egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
- The female insect lays eggs, which hatch into larvae or nymphs. These young ones undergo further development and transformation before becoming adults.
3. Frog:
- Frogs are amphibians and reproduce through external fertilization.
- The female frog lays eggs in water, and the male frog releases sperm to fertilize them.
- The fertilized eggs develop into tadpoles, which undergo metamorphosis before becoming adult frogs.
- The tadpoles hatch from the eggs and live in the water until they undergo metamorphosis and develop into adult frogs.
4. Snake:
- Snakes are reptiles and reproduce through internal fertilization.
- The male snake transfers sperm to the female snake's reproductive system during mating.
- The female snake then lays eggs, which are fertilized internally.
- The eggs are then laid outside the body and develop into young snakes, which are independent from birth.
In conclusion, out of the given options, the animal that gives birth to a young one is the whale. Whales are mammals and give live birth to their offspring, providing them with nourishment and care until they are ready to survive on their own.
A whale is a marine mammal that gives birth to a young one. Let's dive into more details and explore why the other options are not the correct answers.
1. Whale:
- Whales are mammals and give live birth to their young ones.
- They have internal fertilization, where the male whale transfers sperm to the female's reproductive system, resulting in pregnancy.
- The female whale carries the developing fetus inside her body until it is fully developed and ready to be born.
- Once the young whale is born, it is nourished with milk produced by the mother until it can fend for itself.
2. Insect:
- Insects, such as bees, butterflies, ants, and beetles, do not give birth to live young ones.
- Most insects undergo a process called metamorphosis, where they go through distinct stages of development, including egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
- The female insect lays eggs, which hatch into larvae or nymphs. These young ones undergo further development and transformation before becoming adults.
3. Frog:
- Frogs are amphibians and reproduce through external fertilization.
- The female frog lays eggs in water, and the male frog releases sperm to fertilize them.
- The fertilized eggs develop into tadpoles, which undergo metamorphosis before becoming adult frogs.
- The tadpoles hatch from the eggs and live in the water until they undergo metamorphosis and develop into adult frogs.
4. Snake:
- Snakes are reptiles and reproduce through internal fertilization.
- The male snake transfers sperm to the female snake's reproductive system during mating.
- The female snake then lays eggs, which are fertilized internally.
- The eggs are then laid outside the body and develop into young snakes, which are independent from birth.
In conclusion, out of the given options, the animal that gives birth to a young one is the whale. Whales are mammals and give live birth to their offspring, providing them with nourishment and care until they are ready to survive on their own.
Fruits provide protection to the __________.- a)Seed
- b)Flower
- c)Leaf
- d)Plant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Fruits provide protection to the __________.
a)
Seed
b)
Flower
c)
Leaf
d)
Plant
|
|
Jithin Iyer answered |
Introduction:
Fruits play an important role in the life cycle of plants. They are not only delicious and nutritious for humans and animals, but they also serve as a protective covering for seeds.
Explanation:
Fruits are the mature ovaries of flowering plants. After pollination and fertilization, the ovary develops into a fruit, which contains one or more seeds. The main purpose of a fruit is to protect and disperse the seeds. Let's explore how fruits provide protection to the seeds.
Protection from External Factors:
1. Physical Protection: Fruits provide a physical barrier around the seeds, shielding them from external factors such as wind, rain, and temperature fluctuations. For example, the hard shell of a coconut fruit protects the seed inside.
2. Predation Prevention: Fruits often have tough or thick skin, making it difficult for animals to access the seeds. This protects the seeds from being eaten or damaged by herbivores. For instance, the thick skin of a watermelon protects the seeds inside.
Enhancing Seed Dispersal:
1. Attracting Animals: Fruits are often brightly colored and have a sweet or fragrant smell to attract animals. When animals eat the fruit, they also consume the seeds. Later, the seeds are expelled in a different location through animal droppings. This dispersal mechanism helps seeds to spread and grow in new areas.
2. Utilizing Wind or Water: Some fruits have adaptations that aid in wind or water dispersal. For example, the wing-like structures on the seeds of a maple tree allow them to be carried by the wind to new locations. Similarly, fruits of water plants have air-filled structures that help them float and disperse via water currents.
Conclusion:
Fruits are an essential part of a plant's life cycle, providing protection to the seeds and aiding in their dispersal. They serve as a protective covering, shielding the seeds from external factors and preventing predation. Fruits also attract animals or utilize wind and water to disperse the seeds, ensuring the survival and growth of new plants in different areas.
Fruits play an important role in the life cycle of plants. They are not only delicious and nutritious for humans and animals, but they also serve as a protective covering for seeds.
Explanation:
Fruits are the mature ovaries of flowering plants. After pollination and fertilization, the ovary develops into a fruit, which contains one or more seeds. The main purpose of a fruit is to protect and disperse the seeds. Let's explore how fruits provide protection to the seeds.
Protection from External Factors:
1. Physical Protection: Fruits provide a physical barrier around the seeds, shielding them from external factors such as wind, rain, and temperature fluctuations. For example, the hard shell of a coconut fruit protects the seed inside.
2. Predation Prevention: Fruits often have tough or thick skin, making it difficult for animals to access the seeds. This protects the seeds from being eaten or damaged by herbivores. For instance, the thick skin of a watermelon protects the seeds inside.
Enhancing Seed Dispersal:
1. Attracting Animals: Fruits are often brightly colored and have a sweet or fragrant smell to attract animals. When animals eat the fruit, they also consume the seeds. Later, the seeds are expelled in a different location through animal droppings. This dispersal mechanism helps seeds to spread and grow in new areas.
2. Utilizing Wind or Water: Some fruits have adaptations that aid in wind or water dispersal. For example, the wing-like structures on the seeds of a maple tree allow them to be carried by the wind to new locations. Similarly, fruits of water plants have air-filled structures that help them float and disperse via water currents.
Conclusion:
Fruits are an essential part of a plant's life cycle, providing protection to the seeds and aiding in their dispersal. They serve as a protective covering, shielding the seeds from external factors and preventing predation. Fruits also attract animals or utilize wind and water to disperse the seeds, ensuring the survival and growth of new plants in different areas.
Trunk is the main stem of the tree. It divides into many branches higher up in the tree. The _____ of the tree protects the trunk.- a)Stem
- b)Bark
- c)Pigment
- d)Roots
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Trunk is the main stem of the tree. It divides into many branches higher up in the tree. The _____ of the tree protects the trunk.
a)
Stem
b)
Bark
c)
Pigment
d)
Roots
|
|
Naina Saha answered |
Introduction:
The trunk of a tree is the main part of the tree that extends from the ground to the upper branches. It serves as the support structure for the tree and is responsible for transporting water, nutrients, and sugars between the roots and leaves. The trunk is protected by a layer called the bark, which plays a vital role in the tree's growth, development, and protection.
Explanation:
The correct answer is option 'B' - Bark. Let's understand why the bark of the tree protects the trunk:
Bark as a Protective Layer:
1. The bark is the outermost layer of the tree trunk and serves as a protective covering. It shields the inner tissues of the trunk from external factors such as extreme temperatures, physical damage, pathogens, and insects.
2. Bark acts as a barrier against mechanical injuries like cuts, abrasions, and impacts. It helps prevent damage to the delicate living tissues beneath it.
3. The bark also acts as a defense mechanism against harmful pathogens and insects. It contains chemical compounds and secondary metabolites that deter pests and prevent the entry of disease-causing organisms.
4. In some tree species, the bark may have a rough or textured surface, which can deter climbing animals or insects from reaching the trunk and causing harm.
Bark and Growth:
1. The outermost layer of the bark is called the epidermis. It is responsible for protecting the underlying tissues and preventing water loss through evaporation.
2. Just beneath the epidermis is the phloem, a vascular tissue that transports sugars produced in the leaves to other parts of the tree. The phloem is essential for the tree's growth and development.
3. The innermost layer of the bark is the cambium, a layer of actively dividing cells. It is responsible for the growth of new bark and wood tissues.
4. As the tree grows, the bark expands and develops fissures or cracks. This allows the trunk to accommodate the increase in girth without restricting the growth of the tree.
Bark and Identification:
1. The bark of different tree species can vary in color, texture, and pattern. It can be smooth, rough, thick, thin, or even peeling.
2. These unique characteristics of the bark can help in identifying and distinguishing between different tree species.
3. Some tree barks have distinctive features such as deep furrows or corky ridges, which aid in species identification.
Conclusion:
The bark of a tree serves as a protective layer for the trunk. It defends against external factors and provides a physical barrier to prevent damage to the delicate inner tissues. Additionally, the bark plays a crucial role in the growth and development of the tree by transporting sugars, accommodating growth, and providing unique characteristics for species identification.
The trunk of a tree is the main part of the tree that extends from the ground to the upper branches. It serves as the support structure for the tree and is responsible for transporting water, nutrients, and sugars between the roots and leaves. The trunk is protected by a layer called the bark, which plays a vital role in the tree's growth, development, and protection.
Explanation:
The correct answer is option 'B' - Bark. Let's understand why the bark of the tree protects the trunk:
Bark as a Protective Layer:
1. The bark is the outermost layer of the tree trunk and serves as a protective covering. It shields the inner tissues of the trunk from external factors such as extreme temperatures, physical damage, pathogens, and insects.
2. Bark acts as a barrier against mechanical injuries like cuts, abrasions, and impacts. It helps prevent damage to the delicate living tissues beneath it.
3. The bark also acts as a defense mechanism against harmful pathogens and insects. It contains chemical compounds and secondary metabolites that deter pests and prevent the entry of disease-causing organisms.
4. In some tree species, the bark may have a rough or textured surface, which can deter climbing animals or insects from reaching the trunk and causing harm.
Bark and Growth:
1. The outermost layer of the bark is called the epidermis. It is responsible for protecting the underlying tissues and preventing water loss through evaporation.
2. Just beneath the epidermis is the phloem, a vascular tissue that transports sugars produced in the leaves to other parts of the tree. The phloem is essential for the tree's growth and development.
3. The innermost layer of the bark is the cambium, a layer of actively dividing cells. It is responsible for the growth of new bark and wood tissues.
4. As the tree grows, the bark expands and develops fissures or cracks. This allows the trunk to accommodate the increase in girth without restricting the growth of the tree.
Bark and Identification:
1. The bark of different tree species can vary in color, texture, and pattern. It can be smooth, rough, thick, thin, or even peeling.
2. These unique characteristics of the bark can help in identifying and distinguishing between different tree species.
3. Some tree barks have distinctive features such as deep furrows or corky ridges, which aid in species identification.
Conclusion:
The bark of a tree serves as a protective layer for the trunk. It defends against external factors and provides a physical barrier to prevent damage to the delicate inner tissues. Additionally, the bark plays a crucial role in the growth and development of the tree by transporting sugars, accommodating growth, and providing unique characteristics for species identification.
Study the flow chart and choose the correct statement.
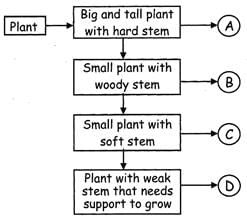
- a)A is a Rose plant
- b)B is a Hibiscus plant
- c)C is a Banyan tree
- d)D is a Shrub
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the flow chart and choose the correct statement.


a)
A is a Rose plant
b)
B is a Hibiscus plant
c)
C is a Banyan tree
d)
D is a Shrub

|
Keystone Instructors answered |
- 'B' is a Hibiscus plant which is a small plant with woody stem.
In desert plants, leaves are modified into thorns. How do thorns help a plant?- a)They Catch food
- b)They store water
- c)They protect the plant from being eaten by animals
- d)They make the plant attract bees
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In desert plants, leaves are modified into thorns. How do thorns help a plant?
a)
They Catch food
b)
They store water
c)
They protect the plant from being eaten by animals
d)
They make the plant attract bees
|
|
Rajdeep Banerjee answered |
Thorns in Desert Plants: Their Role and Significance
Desert plants have evolved unique adaptations to survive in their harsh and arid environments. One such adaptation is the modification of leaves into thorns. These thorns play a crucial role in helping the plant thrive in desert conditions. One of the main functions of thorns in desert plants is water storage.
Water Storage
Thorns in desert plants act as water reservoirs, allowing the plant to store and conserve water. In arid regions where water is scarce, plants need to find ways to minimize water loss and maximize water absorption. By modifying their leaves into thorns, desert plants can reduce the surface area exposed to the dry air, thus minimizing water loss through transpiration. Additionally, thorns have a waxy, protective coating that further reduces water loss.
Moreover, the structure of thorns allows them to collect dew and moisture from the air. The sharp and pointed shape of thorns helps in condensing moisture, which then drips down to the base of the plant, where it can be absorbed by the roots. This ability to capture and retain moisture is crucial for the survival of desert plants in their arid habitats.
Protection from Herbivores
Another important role of thorns in desert plants is protection. In desert ecosystems, where food sources are limited, plants need to defend themselves against herbivores and grazing animals. Thorns act as a deterrent, making it difficult for animals to feed on the plant's leaves or branches.
The sharp and pointed structure of thorns can cause discomfort or pain to animals attempting to eat the plant. This defense mechanism reduces the likelihood of herbivory, allowing the plant to conserve its limited resources, including water and nutrients, for its own survival.
Conclusion
In conclusion, thorns in desert plants serve multiple purposes and are a crucial adaptation to thrive in arid environments. They primarily function as water storage structures, minimizing water loss and maximizing water absorption. Additionally, thorns provide protection against herbivores, ensuring the survival and growth of the plant. These modifications allow desert plants to effectively adapt to their extreme habitats and maintain their ecological niche in the desert ecosystem.
Desert plants have evolved unique adaptations to survive in their harsh and arid environments. One such adaptation is the modification of leaves into thorns. These thorns play a crucial role in helping the plant thrive in desert conditions. One of the main functions of thorns in desert plants is water storage.
Water Storage
Thorns in desert plants act as water reservoirs, allowing the plant to store and conserve water. In arid regions where water is scarce, plants need to find ways to minimize water loss and maximize water absorption. By modifying their leaves into thorns, desert plants can reduce the surface area exposed to the dry air, thus minimizing water loss through transpiration. Additionally, thorns have a waxy, protective coating that further reduces water loss.
Moreover, the structure of thorns allows them to collect dew and moisture from the air. The sharp and pointed shape of thorns helps in condensing moisture, which then drips down to the base of the plant, where it can be absorbed by the roots. This ability to capture and retain moisture is crucial for the survival of desert plants in their arid habitats.
Protection from Herbivores
Another important role of thorns in desert plants is protection. In desert ecosystems, where food sources are limited, plants need to defend themselves against herbivores and grazing animals. Thorns act as a deterrent, making it difficult for animals to feed on the plant's leaves or branches.
The sharp and pointed structure of thorns can cause discomfort or pain to animals attempting to eat the plant. This defense mechanism reduces the likelihood of herbivory, allowing the plant to conserve its limited resources, including water and nutrients, for its own survival.
Conclusion
In conclusion, thorns in desert plants serve multiple purposes and are a crucial adaptation to thrive in arid environments. They primarily function as water storage structures, minimizing water loss and maximizing water absorption. Additionally, thorns provide protection against herbivores, ensuring the survival and growth of the plant. These modifications allow desert plants to effectively adapt to their extreme habitats and maintain their ecological niche in the desert ecosystem.
Study the following chart:Grass → x → Y → SnakeIdentify x and y from the following- a)Cow, Wolf
- b)Cat, Dog
- c)Grasshopper, Frog
- d)Grasshopper, Lion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following chart:
Grass → x → Y → Snake
Identify x and y from the following
a)
Cow, Wolf
b)
Cat, Dog
c)
Grasshopper, Frog
d)
Grasshopper, Lion
|
|
Sameer Datta answered |
Unfortunately, there is no chart provided for me to study. Please provide the chart or provide more information about the topic you would like me to study.
Small openings present on leaves help in exchange for games.- a)Veins
- b)Stomata
- c)Lentis
- d)Lamina
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Small openings present on leaves help in exchange for games.
a)
Veins
b)
Stomata
c)
Lentis
d)
Lamina
|
|
Bhavana Basak answered |
Stomata: Small Openings on Leaves for Gas Exchange
Introduction:
Stomata are small openings present on the surface of leaves that play a crucial role in the exchange of gases, including oxygen and carbon dioxide, between the plant and its environment. These tiny structures are essential for the process of photosynthesis and respiration in plants. Let's explore the significance of stomata in more detail.
Structure of Stomata:
Stomata are mainly found on the lower surface of leaves, although they can also be present on stems and other plant parts. Each stoma consists of two specialized cells known as guard cells, which surround a pore. The guard cells can change shape to open or close the stomatal pore, thereby regulating the exchange of gases.
Functions of Stomata:
1. Gas Exchange: The primary function of stomata is to facilitate the exchange of gases between the plant and its surroundings. During photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide through open stomata and release oxygen as a byproduct. In contrast, during respiration, plants take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide through the same stomatal openings.
2. Water Regulation: Stomata also play a crucial role in water regulation within plants. When the stomata are open, water vapor is released through a process called transpiration. This helps in cooling the plant and maintaining the moisture balance. However, excessive transpiration can lead to water loss, causing the plant to wilt. Therefore, the ability of stomata to open and close helps in regulating water loss and preventing dehydration.
3. Photosynthesis: Stomata are vital for the process of photosynthesis, as they enable the entry of carbon dioxide, which is a key ingredient for this biochemical process. Carbon dioxide enters the leaves through open stomata and is utilized by the chloroplasts within the plant cells to produce glucose and oxygen.
4. Gas Diffusion: Apart from carbon dioxide and oxygen, stomata also allow the diffusion of other gases, such as nitrogen and ethylene. This diffusion is vital for various physiological processes in plants, including growth, development, and response to environmental stimuli.
Conclusion:
In summary, stomata are small openings present on the surface of leaves that enable the exchange of gases between plants and their surroundings. These structures play a crucial role in the processes of photosynthesis, respiration, water regulation, and gas diffusion. Understanding the functions and structure of stomata helps us appreciate the remarkable adaptation of plants to their environment.
Introduction:
Stomata are small openings present on the surface of leaves that play a crucial role in the exchange of gases, including oxygen and carbon dioxide, between the plant and its environment. These tiny structures are essential for the process of photosynthesis and respiration in plants. Let's explore the significance of stomata in more detail.
Structure of Stomata:
Stomata are mainly found on the lower surface of leaves, although they can also be present on stems and other plant parts. Each stoma consists of two specialized cells known as guard cells, which surround a pore. The guard cells can change shape to open or close the stomatal pore, thereby regulating the exchange of gases.
Functions of Stomata:
1. Gas Exchange: The primary function of stomata is to facilitate the exchange of gases between the plant and its surroundings. During photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide through open stomata and release oxygen as a byproduct. In contrast, during respiration, plants take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide through the same stomatal openings.
2. Water Regulation: Stomata also play a crucial role in water regulation within plants. When the stomata are open, water vapor is released through a process called transpiration. This helps in cooling the plant and maintaining the moisture balance. However, excessive transpiration can lead to water loss, causing the plant to wilt. Therefore, the ability of stomata to open and close helps in regulating water loss and preventing dehydration.
3. Photosynthesis: Stomata are vital for the process of photosynthesis, as they enable the entry of carbon dioxide, which is a key ingredient for this biochemical process. Carbon dioxide enters the leaves through open stomata and is utilized by the chloroplasts within the plant cells to produce glucose and oxygen.
4. Gas Diffusion: Apart from carbon dioxide and oxygen, stomata also allow the diffusion of other gases, such as nitrogen and ethylene. This diffusion is vital for various physiological processes in plants, including growth, development, and response to environmental stimuli.
Conclusion:
In summary, stomata are small openings present on the surface of leaves that enable the exchange of gases between plants and their surroundings. These structures play a crucial role in the processes of photosynthesis, respiration, water regulation, and gas diffusion. Understanding the functions and structure of stomata helps us appreciate the remarkable adaptation of plants to their environment.
Which of the following part is known as the food storehouse of the plant?- a)Stem
- b)Leaves
- c)Root
- d)Shoot
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following part is known as the food storehouse of the plant?
a)
Stem
b)
Leaves
c)
Root
d)
Shoot
|
|
Pranav Singh answered |
Stem is the food storehouse of the plant.
Among the following, who is known as a producer?- a)Insects
- b)Grass
- c)Cow
- d)Tiger
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following, who is known as a producer?
a)
Insects
b)
Grass
c)
Cow
d)
Tiger
|
|
Nikhil Singh answered |
Explanation:
Producer: A producer is an organism that can make its own food by using energy from the sun or chemicals in the environment.
Out of the given options, only grass is known as a producer because it can make its own food by using energy from the sun through the process of photosynthesis.
Let's understand the process of photosynthesis in detail:
Photosynthesis: It is a process in which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll. In this process, plants absorb light energy from the sun and convert it into chemical energy, which is stored in the form of glucose.
Chlorophyll: It is a green pigment found in the leaves of plants that helps in capturing sunlight and converting it into energy.
Process of Photosynthesis: The process of photosynthesis can be divided into two stages:
1. Light-dependent Reactions: In this stage, chlorophyll in the plant's cells absorbs light energy from the sun and converts it into chemical energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate).
2. Light-independent Reactions: In this stage, the chemical energy generated in the previous stage is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This stage occurs in the chloroplasts of the plant cells.
Thus, grass is known as a producer because it can produce its own food through the process of photosynthesis using energy from the sun.
Producer: A producer is an organism that can make its own food by using energy from the sun or chemicals in the environment.
Out of the given options, only grass is known as a producer because it can make its own food by using energy from the sun through the process of photosynthesis.
Let's understand the process of photosynthesis in detail:
Photosynthesis: It is a process in which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll. In this process, plants absorb light energy from the sun and convert it into chemical energy, which is stored in the form of glucose.
Chlorophyll: It is a green pigment found in the leaves of plants that helps in capturing sunlight and converting it into energy.
Process of Photosynthesis: The process of photosynthesis can be divided into two stages:
1. Light-dependent Reactions: In this stage, chlorophyll in the plant's cells absorbs light energy from the sun and converts it into chemical energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate).
2. Light-independent Reactions: In this stage, the chemical energy generated in the previous stage is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This stage occurs in the chloroplasts of the plant cells.
Thus, grass is known as a producer because it can produce its own food through the process of photosynthesis using energy from the sun.
The given figure shows two animals X and Y. Select the option that groups animals which show similar eating habits like that of X and Y, respectively.

- a)Python, Caribou
- b)Clouded leopard, Skunk
- c)Goldfish, Capybara
- d)Opossum, Bison
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The given figure shows two animals X and Y. Select the option that groups animals which show similar eating habits like that of X and Y, respectively.

a)
Python, Caribou
b)
Clouded leopard, Skunk
c)
Goldfish, Capybara
d)
Opossum, Bison
|
|
Anjali Gupta answered |
Goldfish and fish are Carnivores. Rat and Capybara are Gnawers.
Look the sentence below:
“ LOST ANIMAL: The animal we seek is an amphibian it feeds on insects only. You will be amazed by the number of eggs that it can lay ”
Based on given information, which of the following statements is true about the lost animal?- a)It is a carnivore
- b)It gives birth to young ones
- c)It lives only on land
- d)It lays one egg at a time.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Look the sentence below:
“ LOST ANIMAL: The animal we seek is an amphibian it feeds on insects only. You will be amazed by the number of eggs that it can lay ”
Based on given information, which of the following statements is true about the lost animal?
“ LOST ANIMAL: The animal we seek is an amphibian it feeds on insects only. You will be amazed by the number of eggs that it can lay ”
Based on given information, which of the following statements is true about the lost animal?
a)
It is a carnivore
b)
It gives birth to young ones
c)
It lives only on land
d)
It lays one egg at a time.
|
|
Neha Shah answered |
Unfortunately, you did not provide a sentence for me to analyze.
Which of the following can live both in the water and on the land?- a)Frog
- b)Fish
- c)Dog
- d)Bird
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following can live both in the water and on the land?
a)
Frog
b)
Fish
c)
Dog
d)
Bird
|
|
Aditya Shah answered |
Correct answer is A. Frog can live both in the water and on the land.
Sunlight is trapped by a substance called ________ present in the leaves.- a)Stomata
- b)Chlorophyll
- c)Veins
- d)Lamina.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Sunlight is trapped by a substance called ________ present in the leaves.
a)
Stomata
b)
Chlorophyll
c)
Veins
d)
Lamina.
|
|
Stuti Kaur answered |
Sunlight is trapped by a substance called Chlorophyll present in the leaves.
Chlorophyll is a pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant cells, particularly in the leaves. It plays a vital role in the process of photosynthesis, where plants convert sunlight into chemical energy.
Explanation:
1. Chlorophyll and its function:
- Chlorophyll is a green pigment that gives plants their characteristic color. It absorbs light energy from the sun, particularly in the red and blue regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, while reflecting green light.
- This pigment is mainly found in the chloroplasts, which are specialized organelles responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells.
- Chlorophyll molecules are arranged in clusters called photosystems within the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts. These photosystems contain chlorophyll molecules that capture sunlight.
2. Photosynthesis and the role of chlorophyll:
- Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose (a form of sugar) and release oxygen as a byproduct.
- Sunlight energy is absorbed by chlorophyll molecules in the chloroplasts. This energy excites the electrons within the chlorophyll molecules, allowing them to move to a higher energy level.
- These energized electrons are then passed through a series of electron carriers within the thylakoid membranes, creating an electron transport chain.
- The energy from this electron transport chain is used to generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate), a molecule that stores energy.
- In addition to ATP production, the energized electrons are also used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose molecules, a process known as carbon fixation.
3. Trapping sunlight:
- Chlorophyll is primarily responsible for trapping sunlight during photosynthesis. Its structure allows it to absorb light energy and transfer it to other molecules in the photosystems.
- The energy absorbed by chlorophyll is used to drive the chemical reactions involved in photosynthesis, including the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
- Without chlorophyll, plants would not be able to capture sunlight effectively, leading to a decrease in their ability to produce energy-rich molecules like glucose.
In conclusion, chlorophyll is the substance present in the leaves of plants that traps sunlight and plays a crucial role in the process of photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll is a pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant cells, particularly in the leaves. It plays a vital role in the process of photosynthesis, where plants convert sunlight into chemical energy.
Explanation:
1. Chlorophyll and its function:
- Chlorophyll is a green pigment that gives plants their characteristic color. It absorbs light energy from the sun, particularly in the red and blue regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, while reflecting green light.
- This pigment is mainly found in the chloroplasts, which are specialized organelles responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells.
- Chlorophyll molecules are arranged in clusters called photosystems within the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts. These photosystems contain chlorophyll molecules that capture sunlight.
2. Photosynthesis and the role of chlorophyll:
- Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose (a form of sugar) and release oxygen as a byproduct.
- Sunlight energy is absorbed by chlorophyll molecules in the chloroplasts. This energy excites the electrons within the chlorophyll molecules, allowing them to move to a higher energy level.
- These energized electrons are then passed through a series of electron carriers within the thylakoid membranes, creating an electron transport chain.
- The energy from this electron transport chain is used to generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate), a molecule that stores energy.
- In addition to ATP production, the energized electrons are also used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose molecules, a process known as carbon fixation.
3. Trapping sunlight:
- Chlorophyll is primarily responsible for trapping sunlight during photosynthesis. Its structure allows it to absorb light energy and transfer it to other molecules in the photosystems.
- The energy absorbed by chlorophyll is used to drive the chemical reactions involved in photosynthesis, including the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
- Without chlorophyll, plants would not be able to capture sunlight effectively, leading to a decrease in their ability to produce energy-rich molecules like glucose.
In conclusion, chlorophyll is the substance present in the leaves of plants that traps sunlight and plays a crucial role in the process of photosynthesis.
Direction: Select the odd one out- a)root
- b)shoot
- c)trees
- d)leaves
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Select the odd one out
a)
root
b)
shoot
c)
trees
d)
leaves
|
|
Pranav Singh answered |
Root, shoot and leaves are the part of plant, tree is a type of plants.
Which is these is obtained from plants?- a)Paper
- b)Animals
- c)Medicine
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is these is obtained from plants?
a)
Paper
b)
Animals
c)
Medicine
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Pranav Singh answered |
Both paper and medicines are obtained from plants.
Fruits develop from __________.- a)leaves
- b)flowers
- c)seeds
- d)stem
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Fruits develop from __________.
a)
leaves
b)
flowers
c)
seeds
d)
stem
|
|
Pranav Singh answered |
Fruits develop from flower.
To which category does this animal in the figure belong?
- a)Herbivore
- b)Carnivore
- c)Omnivore
- d)Producer
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
To which category does this animal in the figure belong?

a)
Herbivore
b)
Carnivore
c)
Omnivore
d)
Producer
|
|
Anjali Gupta answered |
Horse is a plant eater animal so, it is a herbivore.
Choose the correct option
(i) Fruit is a fleshy part of a tree
(ii) Shoot grows below the ground
(iii) Flower is the reproductive part of a plant
(iv) Roots absorb food from soil and transport it to the leaves only.
T = true
F = False
- a)TTFF
- b)FTFT
- c)TFTF
- d)FFTT
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct option
(i) Fruit is a fleshy part of a tree
(ii) Shoot grows below the ground
(iii) Flower is the reproductive part of a plant
(iv) Roots absorb food from soil and transport it to the leaves only.
(i) Fruit is a fleshy part of a tree
(ii) Shoot grows below the ground
(iii) Flower is the reproductive part of a plant
(iv) Roots absorb food from soil and transport it to the leaves only.
T = true
F = False
a)
TTFF
b)
FTFT
c)
TFTF
d)
FFTT
|
|
Ameya Singh answered |
The correct option is (c) TFTF. Let's break down each statement to understand why this is the correct answer:
(i) Fruit is a fleshy part of a tree: This statement is true. Fruits are the mature ovaries of flowering plants and are typically fleshy or juicy. They contain seeds and are formed from the ovary of a flower after fertilization. Fruits are important for seed dispersal and are often consumed by animals and humans.
(ii) Shoot grows below the ground: This statement is false. Shoots are the above-ground part of a plant that includes stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits. They are responsible for photosynthesis and reproduction. Roots, on the other hand, are the part of the plant that grows below the ground and absorbs water and nutrients from the soil.
(iii) Flower is the reproductive part of a plant: This statement is true. Flowers are the reproductive structures of flowering plants. They produce pollen and eggs, which are necessary for sexual reproduction. Flowers are often brightly colored and have attractive scents to attract pollinators like bees, butterflies, and birds.
(iv) Roots absorb food from the soil and transport it to the leaves: This statement is false. While roots do absorb water and minerals from the soil, they do not absorb food. The leaves of a plant are responsible for photosynthesis, where they use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose (food) for the plant. The transport of water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves is done through specialized tissues called xylem and phloem.
In summary, the correct answer is option (c) TFTF, as statements (i), (iii), and (iv) are true, while statement (ii) is false.
(i) Fruit is a fleshy part of a tree: This statement is true. Fruits are the mature ovaries of flowering plants and are typically fleshy or juicy. They contain seeds and are formed from the ovary of a flower after fertilization. Fruits are important for seed dispersal and are often consumed by animals and humans.
(ii) Shoot grows below the ground: This statement is false. Shoots are the above-ground part of a plant that includes stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits. They are responsible for photosynthesis and reproduction. Roots, on the other hand, are the part of the plant that grows below the ground and absorbs water and nutrients from the soil.
(iii) Flower is the reproductive part of a plant: This statement is true. Flowers are the reproductive structures of flowering plants. They produce pollen and eggs, which are necessary for sexual reproduction. Flowers are often brightly colored and have attractive scents to attract pollinators like bees, butterflies, and birds.
(iv) Roots absorb food from the soil and transport it to the leaves: This statement is false. While roots do absorb water and minerals from the soil, they do not absorb food. The leaves of a plant are responsible for photosynthesis, where they use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose (food) for the plant. The transport of water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves is done through specialized tissues called xylem and phloem.
In summary, the correct answer is option (c) TFTF, as statements (i), (iii), and (iv) are true, while statement (ii) is false.
Select the modified stem from the following.- a)Potato
- b)Carrot
- c)Radish
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the modified stem from the following.
a)
Potato
b)
Carrot
c)
Radish
d)
None of the above
|
|
Mihir Saha answered |
Modified Stem in Potato
Modified stem is a type of stem that has been modified to store food and water. In the case of potato, it is the underground stem which is the modified stem.
Potato is a type of stem vegetable that belongs to the family Solanaceae. It is a starchy, tuberous crop that is widely cultivated all over the world. The stem of the potato plant is short and thick, and it grows underground. This underground stem is called a tuber, and it is the modified stem that stores food and water.
The potato tuber has several eyes or buds on its surface, which can grow into new potato plants. These buds are also called "potato eyes". When the potato tuber is planted in soil, the eyes sprout and grow into new potato plants. The stem of the new potato plant also grows underground, and it produces new tubers which are the edible part of the potato plant.
Therefore, the modified stem in potato is the underground stem or tuber which stores food and water.
Modified stem is a type of stem that has been modified to store food and water. In the case of potato, it is the underground stem which is the modified stem.
Potato is a type of stem vegetable that belongs to the family Solanaceae. It is a starchy, tuberous crop that is widely cultivated all over the world. The stem of the potato plant is short and thick, and it grows underground. This underground stem is called a tuber, and it is the modified stem that stores food and water.
The potato tuber has several eyes or buds on its surface, which can grow into new potato plants. These buds are also called "potato eyes". When the potato tuber is planted in soil, the eyes sprout and grow into new potato plants. The stem of the new potato plant also grows underground, and it produces new tubers which are the edible part of the potato plant.
Therefore, the modified stem in potato is the underground stem or tuber which stores food and water.
Which among these animals are more closely related than the others?- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among these animals are more closely related than the others?
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Rahul Verma answered |
Leaves in desert plants get modified into thorns to avoid evaporation of water through transpiration. So it helps in storage of water.
In addition to stem, branches and leaves, the shoot of a plant bears- a)Fruits
- b)Flowers
- c)Buds
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In addition to stem, branches and leaves, the shoot of a plant bears
a)
Fruits
b)
Flowers
c)
Buds
d)
All of these
|
|
Arka Sharma answered |
Parts of a Plant Shoot
Plant shoot consists of various parts that perform different functions.
Stem, Branches, and Leaves
The stem provides support to the plant and helps in the transport of water and nutrients. Branches grow out of the stem and support the leaves. Leaves are the main site of photosynthesis in plants.
Fruits
Fruits are the mature ovaries of flowering plants. They contain seeds and develop from the ovary after fertilization. Fruits are important for the dispersal of seeds and are often consumed by animals for their sweet taste.
Flowers
Flowers are the reproductive structures of flowering plants. They contain male and female reproductive organs necessary for pollination and fertilization. Flowers produce seeds after fertilization, which develop into fruits.
Buds
Buds are undeveloped or embryonic shoots that can grow into branches, leaves, or flowers. They are important for the growth and development of the plant.
All of These
The shoot of a plant bears fruits, flowers, and buds in addition to stems, branches, and leaves. These parts work together to ensure the survival and reproduction of the plant.
Plant shoot consists of various parts that perform different functions.
Stem, Branches, and Leaves
The stem provides support to the plant and helps in the transport of water and nutrients. Branches grow out of the stem and support the leaves. Leaves are the main site of photosynthesis in plants.
Fruits
Fruits are the mature ovaries of flowering plants. They contain seeds and develop from the ovary after fertilization. Fruits are important for the dispersal of seeds and are often consumed by animals for their sweet taste.
Flowers
Flowers are the reproductive structures of flowering plants. They contain male and female reproductive organs necessary for pollination and fertilization. Flowers produce seeds after fertilization, which develop into fruits.
Buds
Buds are undeveloped or embryonic shoots that can grow into branches, leaves, or flowers. They are important for the growth and development of the plant.
All of These
The shoot of a plant bears fruits, flowers, and buds in addition to stems, branches, and leaves. These parts work together to ensure the survival and reproduction of the plant.
Which of these is an important function of the roots of a plant?- a)To absorb oxygen from the atmosphere
- b)To absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
- c)To absorb water and minerals from the soil
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these is an important function of the roots of a plant?
a)
To absorb oxygen from the atmosphere
b)
To absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
c)
To absorb water and minerals from the soil
d)
All of these
|
|
Pranav Singh answered |
- Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
Which of the following statements is correct?- a)Lamina is the outline of a leaf.
- b)Thin and Bushy roots are tap roots.
- c)Stomata are present on the stem.
- d)Stem carries water and minerals from roots to plant.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct?
a)
Lamina is the outline of a leaf.
b)
Thin and Bushy roots are tap roots.
c)
Stomata are present on the stem.
d)
Stem carries water and minerals from roots to plant.
|
|
Anjali Gupta answered |
Stem carries water and minerals from roots to the other parts of the plant.
Direction: Select the odd one out- a)cactus
- b)rose
- c)cotton
- d)hibiscus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Select the odd one out
a)
cactus
b)
rose
c)
cotton
d)
hibiscus
|
|
Pranav Singh answered |
Rose, cotton and hibiscus are shrubs, cactus is a desert plant.
The function of Long and thick Trunk of Elephant is-- a)Break branches and leaves
- b)Drinking water
- c)Suck water and blow into mouth
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The function of Long and thick Trunk of Elephant is-
a)
Break branches and leaves
b)
Drinking water
c)
Suck water and blow into mouth
d)
All of the above
|
|
Nishanth Sharma answered |
Function of Long and Thick Trunk of Elephant
The long and thick trunk of an elephant serves several important functions. It is a highly versatile and specialized organ that plays a crucial role in the daily life of an elephant. Let's explore these functions in detail:
1. Breaking branches and leaves:
The trunk of an elephant is incredibly strong and flexible, allowing it to easily break branches and pluck leaves from trees. Elephants are herbivores and require a large amount of plant matter to sustain themselves. Their trunk acts as a tool to gather food efficiently, reaching even the highest leaves and branches that are out of their reach.
2. Drinking water:
Elephants need to drink a significant amount of water each day to stay hydrated, especially in their natural habitats where water can be scarce. The trunk acts as a long hose-like appendage that enables the elephant to suck up water from various sources, such as rivers, lakes, or even small watering holes. The elephant can then release the water into its mouth for drinking.
3. Sucking water and blowing into the mouth:
In addition to using their trunks for drinking, elephants can also suck up water and store it in their trunk. This stored water can be used later for various purposes, such as bathing or spraying themselves to cool down on hot days. They can also blow the stored water into their mouths, aiding in the swallowing process.
Summary:
In summary, the long and thick trunk of an elephant is a multi-purpose organ that enables the animal to break branches and leaves for food, drink water by sucking it up and blowing it into their mouths, and carry out various other tasks. The trunk is a remarkable adaptation that allows elephants to thrive in their environments and carry out essential activities for their survival.
The long and thick trunk of an elephant serves several important functions. It is a highly versatile and specialized organ that plays a crucial role in the daily life of an elephant. Let's explore these functions in detail:
1. Breaking branches and leaves:
The trunk of an elephant is incredibly strong and flexible, allowing it to easily break branches and pluck leaves from trees. Elephants are herbivores and require a large amount of plant matter to sustain themselves. Their trunk acts as a tool to gather food efficiently, reaching even the highest leaves and branches that are out of their reach.
2. Drinking water:
Elephants need to drink a significant amount of water each day to stay hydrated, especially in their natural habitats where water can be scarce. The trunk acts as a long hose-like appendage that enables the elephant to suck up water from various sources, such as rivers, lakes, or even small watering holes. The elephant can then release the water into its mouth for drinking.
3. Sucking water and blowing into the mouth:
In addition to using their trunks for drinking, elephants can also suck up water and store it in their trunk. This stored water can be used later for various purposes, such as bathing or spraying themselves to cool down on hot days. They can also blow the stored water into their mouths, aiding in the swallowing process.
Summary:
In summary, the long and thick trunk of an elephant is a multi-purpose organ that enables the animal to break branches and leaves for food, drink water by sucking it up and blowing it into their mouths, and carry out various other tasks. The trunk is a remarkable adaptation that allows elephants to thrive in their environments and carry out essential activities for their survival.
The growth of a seed into a baby plant.- a)Photosynthesis
- b)Respiration
- c)Nutrition
- d)Germination
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The growth of a seed into a baby plant.
a)
Photosynthesis
b)
Respiration
c)
Nutrition
d)
Germination
|
|
Manoj Yadav answered |
Germination:
Germination is the process by which a seed transforms into a baby plant or seedling. It is the initial stage of growth in plants and involves the activation of the dormant embryo inside the seed.
The Process:
During germination, the seed absorbs water, which softens the seed coat and triggers the release of enzymes. These enzymes break down stored food materials, such as starch, proteins, and lipids, present in the seed. This breakdown provides the necessary nutrients for the developing plant.
Factors affecting Germination:
Several factors can influence germination, including water availability, temperature, light, and oxygen. Optimal conditions for germination vary depending on the plant species.
Water:
Water is essential for germination as it activates the enzymes responsible for breaking down stored food materials. It also helps in softening the seed coat, allowing the emerging root and shoot to penetrate the soil.
Temperature:
Different plants have different temperature requirements for germination. Some plants prefer cooler temperatures, while others require warmer conditions. Generally, moderate temperatures between 20-30°C promote successful germination.
Light:
Light requirements for germination vary among plant species. Some seeds require light for germination, while others need darkness. Light can affect the production of hormones that regulate germination.
Oxygen:
Like other living organisms, plants require oxygen for respiration, even during germination. Oxygen is necessary for the breakdown of stored food materials to release energy.
Conclusion:
Germination is the process by which a seed transforms into a baby plant. It involves the absorption of water, activation of enzymes, and breakdown of stored food materials to provide nutrition for the growing seedling. Water, temperature, light, and oxygen are essential factors that influence germination. Understanding these factors and providing the optimal conditions can promote successful germination and the growth of healthy plants.
Germination is the process by which a seed transforms into a baby plant or seedling. It is the initial stage of growth in plants and involves the activation of the dormant embryo inside the seed.
The Process:
During germination, the seed absorbs water, which softens the seed coat and triggers the release of enzymes. These enzymes break down stored food materials, such as starch, proteins, and lipids, present in the seed. This breakdown provides the necessary nutrients for the developing plant.
Factors affecting Germination:
Several factors can influence germination, including water availability, temperature, light, and oxygen. Optimal conditions for germination vary depending on the plant species.
Water:
Water is essential for germination as it activates the enzymes responsible for breaking down stored food materials. It also helps in softening the seed coat, allowing the emerging root and shoot to penetrate the soil.
Temperature:
Different plants have different temperature requirements for germination. Some plants prefer cooler temperatures, while others require warmer conditions. Generally, moderate temperatures between 20-30°C promote successful germination.
Light:
Light requirements for germination vary among plant species. Some seeds require light for germination, while others need darkness. Light can affect the production of hormones that regulate germination.
Oxygen:
Like other living organisms, plants require oxygen for respiration, even during germination. Oxygen is necessary for the breakdown of stored food materials to release energy.
Conclusion:
Germination is the process by which a seed transforms into a baby plant. It involves the absorption of water, activation of enzymes, and breakdown of stored food materials to provide nutrition for the growing seedling. Water, temperature, light, and oxygen are essential factors that influence germination. Understanding these factors and providing the optimal conditions can promote successful germination and the growth of healthy plants.
Oil is not abstained from which of the following plant?- a)Mango plant
- b)Sunflower plant
- c)Mustard plant
- d)Coconut plant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Oil is not abstained from which of the following plant?
a)
Mango plant
b)
Sunflower plant
c)
Mustard plant
d)
Coconut plant
|
|
Prateek Saini answered |
Answer:
Introduction:
In this question, we are asked to identify the plant from which oil is not abstained. We are given four options: Mango plant, Sunflower plant, Mustard plant, and Coconut plant. We need to determine which plant does not produce oil.
Explanation:
Let's analyze each option one by one:
a) Mango plant:
Mango plants do not produce oil. The fruit of the mango plant contains a single large seed, called the mango kernel or mango stone. However, this kernel does not yield oil. Mangoes are primarily consumed as a fruit and are known for their delicious taste.
b) Sunflower plant:
Sunflower plants are one of the major sources of edible oil. The seeds of the sunflower plant are highly prized for their oil content. Sunflower oil is commonly used for cooking purposes and is known for its light flavor and high smoking point.
c) Mustard plant:
Mustard plants produce oil that is commonly known as mustard oil. The seeds of the mustard plant are crushed or pressed to extract the oil. Mustard oil is widely used in cooking, particularly in Indian and Asian cuisines. It has a strong flavor and is often used for its distinctive taste and aroma.
d) Coconut plant:
Coconut plants are another significant source of oil. The coconut itself is a fruit, and the oil is extracted from the copra, which is the dried kernel of the coconut. Coconut oil is widely used for cooking, as well as for various other purposes such as skin and hair care.
Conclusion:
After analyzing all the options, we can conclude that the plant from which oil is not abstained is the Mango plant. While sunflower, mustard, and coconut plants all produce oil, the mango plant does not yield oil.
Introduction:
In this question, we are asked to identify the plant from which oil is not abstained. We are given four options: Mango plant, Sunflower plant, Mustard plant, and Coconut plant. We need to determine which plant does not produce oil.
Explanation:
Let's analyze each option one by one:
a) Mango plant:
Mango plants do not produce oil. The fruit of the mango plant contains a single large seed, called the mango kernel or mango stone. However, this kernel does not yield oil. Mangoes are primarily consumed as a fruit and are known for their delicious taste.
b) Sunflower plant:
Sunflower plants are one of the major sources of edible oil. The seeds of the sunflower plant are highly prized for their oil content. Sunflower oil is commonly used for cooking purposes and is known for its light flavor and high smoking point.
c) Mustard plant:
Mustard plants produce oil that is commonly known as mustard oil. The seeds of the mustard plant are crushed or pressed to extract the oil. Mustard oil is widely used in cooking, particularly in Indian and Asian cuisines. It has a strong flavor and is often used for its distinctive taste and aroma.
d) Coconut plant:
Coconut plants are another significant source of oil. The coconut itself is a fruit, and the oil is extracted from the copra, which is the dried kernel of the coconut. Coconut oil is widely used for cooking, as well as for various other purposes such as skin and hair care.
Conclusion:
After analyzing all the options, we can conclude that the plant from which oil is not abstained is the Mango plant. While sunflower, mustard, and coconut plants all produce oil, the mango plant does not yield oil.
What are the similarities between the plants bearing the flowers as shows?


- a)They have weak stems
- b)They have woody stem
- c)They have very big leaves
- d)They grow along the ground
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the similarities between the plants bearing the flowers as shows?




a)
They have weak stems
b)
They have woody stem
c)
They have very big leaves
d)
They grow along the ground
|
|
Pranav Singh answered |
- Rose and hibiscus plants have woody stem.
Study the given relationship between plants.Storage stem: Ginger :: Leaf : XWhich of the following can be placed at X?- a)Sugarcane
- b)Carrot
- c)Cabbage
- d)Beetroot.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the given relationship between plants.
Storage stem: Ginger :: Leaf : X
Which of the following can be placed at X?
a)
Sugarcane
b)
Carrot
c)
Cabbage
d)
Beetroot.
|
|
Bhavana Basak answered |
Storage stem: Ginger :: Leaf : Cabbage
Plant parts can be classified based on their functions and structures. In this analogy, the relationship between storage stem and ginger is similar to the relationship between leaf and cabbage. Let's break down the explanation:
Storage Stem and Ginger:
- Ginger is a plant that stores nutrients in its underground stem, known as a rhizome. The rhizome of ginger is used both for culinary and medicinal purposes.
- Therefore, the storage stem of ginger serves as a reservoir for storing nutrients and energy for the plant.
Leaf and Cabbage:
- Cabbage is a leafy vegetable that belongs to the Brassica family. The edible part of cabbage is formed by its densely packed leaves.
- Leaves are essential plant organs that perform functions such as photosynthesis, gas exchange, and transpiration. In the case of cabbage, its leaves are the main part that is consumed.
Applying the Analogy:
- Just like ginger stores nutrients in its storage stem, cabbage stores nutrients in its leaves.
- Therefore, the correct answer to the analogy "Storage stem: Ginger :: Leaf : X" is "Leaf : Cabbage."
Conclusion:
- By understanding the relationship between different plant parts and their functions, we can make connections and draw analogies between them. In this case, the analogy highlights the importance of storage stems in plants like ginger and the significance of leaves in plants like cabbage.
Plant parts can be classified based on their functions and structures. In this analogy, the relationship between storage stem and ginger is similar to the relationship between leaf and cabbage. Let's break down the explanation:
Storage Stem and Ginger:
- Ginger is a plant that stores nutrients in its underground stem, known as a rhizome. The rhizome of ginger is used both for culinary and medicinal purposes.
- Therefore, the storage stem of ginger serves as a reservoir for storing nutrients and energy for the plant.
Leaf and Cabbage:
- Cabbage is a leafy vegetable that belongs to the Brassica family. The edible part of cabbage is formed by its densely packed leaves.
- Leaves are essential plant organs that perform functions such as photosynthesis, gas exchange, and transpiration. In the case of cabbage, its leaves are the main part that is consumed.
Applying the Analogy:
- Just like ginger stores nutrients in its storage stem, cabbage stores nutrients in its leaves.
- Therefore, the correct answer to the analogy "Storage stem: Ginger :: Leaf : X" is "Leaf : Cabbage."
Conclusion:
- By understanding the relationship between different plant parts and their functions, we can make connections and draw analogies between them. In this case, the analogy highlights the importance of storage stems in plants like ginger and the significance of leaves in plants like cabbage.
Animals that eat both plants and flesh of other animals.- a)Carnivore
- b)Omnivore
- c)Herbivore
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Animals that eat both plants and flesh of other animals.
a)
Carnivore
b)
Omnivore
c)
Herbivore
d)
All of these
|
|
Mira Chauhan answered |
Carnivores:
Carnivores are animals that primarily feed on the flesh of other animals. They have specialized adaptations such as sharp teeth and claws to help them catch and kill their prey. Examples of carnivores include lions, tigers, and wolves.
Herbivores:
Herbivores are animals that eat only plants and plant-based materials. They have specialized digestive systems that allow them to break down and extract nutrients from plant matter. Examples of herbivores include cows, horses, and rabbits.
Omnivores:
Omnivores are animals that have the ability to eat both plants and the flesh of other animals. They have a more flexible diet and can adapt to a wider range of food sources. Omnivores have a combination of sharp and flat teeth to help them consume both plant and animal matter. Examples of omnivores include humans, bears, and pigs.
Explanation:
The correct answer to the question is option 'B' - Omnivore. Omnivores are the only category of animals that eat both plants and the flesh of other animals. They have a diverse diet that includes a combination of plant-based foods and animal protein. This allows them to obtain a wide range of nutrients from different sources.
Omnivores have adaptations that help them consume both plant and animal matter. For example, humans have both sharp incisor teeth for biting into fruits and vegetables, as well as flat molars for grinding and chewing plant matter. Bears have sharp teeth and claws for catching and killing prey, but they also consume a significant amount of plant material.
It is important to note that not all animals fit neatly into one category. Some animals may predominantly eat plants but also consume small amounts of animal flesh, while others may primarily consume meat but also eat some plant material. However, the term "omnivore" is used to describe animals that have a balanced diet and consume both plants and the flesh of other animals.
Carnivores are animals that primarily feed on the flesh of other animals. They have specialized adaptations such as sharp teeth and claws to help them catch and kill their prey. Examples of carnivores include lions, tigers, and wolves.
Herbivores:
Herbivores are animals that eat only plants and plant-based materials. They have specialized digestive systems that allow them to break down and extract nutrients from plant matter. Examples of herbivores include cows, horses, and rabbits.
Omnivores:
Omnivores are animals that have the ability to eat both plants and the flesh of other animals. They have a more flexible diet and can adapt to a wider range of food sources. Omnivores have a combination of sharp and flat teeth to help them consume both plant and animal matter. Examples of omnivores include humans, bears, and pigs.
Explanation:
The correct answer to the question is option 'B' - Omnivore. Omnivores are the only category of animals that eat both plants and the flesh of other animals. They have a diverse diet that includes a combination of plant-based foods and animal protein. This allows them to obtain a wide range of nutrients from different sources.
Omnivores have adaptations that help them consume both plant and animal matter. For example, humans have both sharp incisor teeth for biting into fruits and vegetables, as well as flat molars for grinding and chewing plant matter. Bears have sharp teeth and claws for catching and killing prey, but they also consume a significant amount of plant material.
It is important to note that not all animals fit neatly into one category. Some animals may predominantly eat plants but also consume small amounts of animal flesh, while others may primarily consume meat but also eat some plant material. However, the term "omnivore" is used to describe animals that have a balanced diet and consume both plants and the flesh of other animals.
Select the odd one out on the basis of feedings on flesh of dead animals.- a)
 Crow
Crow - b)
 Lion
Lion - c)
 Vulture
Vulture - d)
 Hyena
Hyena
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the odd one out on the basis of feedings on flesh of dead animals.
a)

Crow
b)

Lion
c)

Vulture
d)

Hyena
|
|
Glitz Classes answered |
The odd one out is: b) Lion
Explanation:
Lions are primarily hunters rather than scavengers, whereas the other animals—crows, vultures, and hyenas—are known to feed on dead animals as part of their diet.
Which of the following animals can change body colouring to protect themselves from their enemies?- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following animals can change body colouring to protect themselves from their enemies?
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Rahul Verma answered |
Chameleon is an animal which changes the colour of the body according to its habitat to protect from predators.
In the below diagram, the arrows represent:
- a)preparation of food by plants
- b)absorption of water and minerals
- c)release of carbon dioxide
- d)all the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the below diagram, the arrows represent:


a)
preparation of food by plants
b)
absorption of water and minerals
c)
release of carbon dioxide
d)
all the above
|
|
Glitz Classes answered |
Plants need water, minerals and carbon dioxide to prepare food. Water and minerals are absorbed from the soil through the roots.
Four of Mr. Sisodia's pupils made statements about different parts of plants.
 Q. Which of the pupils made an INCORRECT statement?
Q. Which of the pupils made an INCORRECT statement?
- a)Anant and Adya only
- b)Vihaan and Vidushi only
- c)Vihaan only
- d)Adya only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Four of Mr. Sisodia's pupils made statements about different parts of plants.

Q. Which of the pupils made an INCORRECT statement?
a)
Anant and Adya only
b)
Vihaan and Vidushi only
c)
Vihaan only
d)
Adya only
|
|
Rahul Verma answered |
Correct Option is D. As Plants like grass and wheat have fibrous roots and tap roots and Leaves of Plants like fenugreek and lettuce are not edible.
The animal lives on trees-- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The animal lives on trees-
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Anjali Gupta answered |
Monkey is an arboreal animal which has a habitat on trees.
In order to grow a new money plant, you should cut the plant at the place indicated by the line.
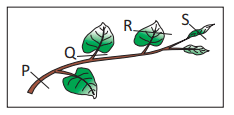
- a)Q
- b)P
- c)R
- d)S
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In order to grow a new money plant, you should cut the plant at the place indicated by the line.

a)
Q
b)
P
c)
R
d)
S
|
|
Rahul Verma answered |
New plants can reproduce by vegetative propagation.
Direction: Select the odd one out- a)money plant
- b)grapevine
- c)bean
- d)pumpkin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Select the odd one out
a)
money plant
b)
grapevine
c)
bean
d)
pumpkin

|
Kds Coaching answered |
Money plant, grapevine, and bean are all climbers—plants that need support to grow upward. Pumpkin is a creeper, which means it spreads along the ground and does not climb upward. Therefore, the odd one out is pumpkin.
Which one of the following statements is true for the given plant?- a)The plant has a strong and thick stem.
- b)The plant has tendrils to get support.
- c)The plant can line in dry conditions.
- d)The plant does not make its own food.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is true for the given plant?
a)
The plant has a strong and thick stem.
b)
The plant has tendrils to get support.
c)
The plant can line in dry conditions.
d)
The plant does not make its own food.
|
|
Anjali Gupta answered |
Weak stems have tendrils to climb on other supports.
Direction: Select the odd one out- a)table
- b)chair
- c)door
- d)medicine
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Select the odd one out
a)
table
b)
chair
c)
door
d)
medicine
|
|
Pranav Singh answered |
Table, chair and doors are obtained from wood.
The leaves of ___________ are used as food.- a)anion
- b)cabbage
- c)eggs
- d)ginger
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The leaves of ___________ are used as food.
a)
anion
b)
cabbage
c)
eggs
d)
ginger
|
|
Pranav Singh answered |

- The leaves of cabbage are used as food.
Chapter doubts & questions for What Plants Need - Science for Grade 2 2025 is part of Grade 2 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 2 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 2 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of What Plants Need - Science for Grade 2 in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 2 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 2 Exam by signing up for free.
Science for Grade 2
40 videos|133 docs|77 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup

















