All Exams >
ACT >
Science for ACT >
All Questions
All questions of Transport in Plants for ACT Exam
Root hairs absorb water from soil with the help of
a) Root pressure
b) Osmatic pressure
c) Suction pressure
d) Turger pressure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Osmotic Pressure is the right option. As because roots need water for transportation. They dont have water at first but the surrounding soil does have. So, due to hypertonic state, roots absorb water by osmosis.
The molecules which move from higher to lower regions are called as- a)Imbibition
- b)Diffusion
- c)Osmosis
- d)Guttation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The molecules which move from higher to lower regions are called as
a)
Imbibition
b)
Diffusion
c)
Osmosis
d)
Guttation
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
In diffusion, molecules move in a random fashion, the net result being substances moving from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration.
Select the correct statement:- a)The translocation in phloem is unidirectional, whereas it is bidirectional in the xylem
- b)Pinus seeds cannot germinate and establish without the presence of mycorrhizae.
- c)Absorption of water by seeds and dry wood is an example of facilitated diffusion.
- d)The apoplast is a system of interconnected protoplasts.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement:
a)
The translocation in phloem is unidirectional, whereas it is bidirectional in the xylem
b)
Pinus seeds cannot germinate and establish without the presence of mycorrhizae.
c)
Absorption of water by seeds and dry wood is an example of facilitated diffusion.
d)
The apoplast is a system of interconnected protoplasts.
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Pinus seeds cannot germinate without mycorrhizae due to lack of water as because the mycorrhizal symbiotic association
helps the plant in formation of root.
helps the plant in formation of root.
The ingredient not used for preserving food stuff is
a) Vinegar
b) Salt and sugar
c) Sugar and vinegar
d) Ethanol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Pooja Saha answered |
For preserving food stuff vinegar, salt and sugar is used. Ethanol is antiseptic in nature but not used for preserving food stuff.
Main function of lenticel is- a)Bleeding
- b)Transpiration
- c)Gaseous exchange
- d)Guttation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Main function of lenticel is
a)
Bleeding
b)
Transpiration
c)
Gaseous exchange
d)
Guttation

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
Lenticels are minute pore in stems through which exchangeof gases takes place between plant and atmosphere.
Water molecules are attracted to each other in the liquid phase more than to water in the gas phase- a)Adhesion
- b)Surface tension
- c)cohesion
- d)capillarity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Water molecules are attracted to each other in the liquid phase more than to water in the gas phase
a)
Adhesion
b)
Surface tension
c)
cohesion
d)
capillarity

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
Water molecules are attracted to each other in the liquid phase more than to water in the gas phase due to surface tension.
The movement of diffusion is- a)active
- b)Passive
- c)facilitated
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The movement of diffusion is
a)
active
b)
Passive
c)
facilitated
d)
none of the above
|
|
Aashna Khanna answered |
Passive movement of diffusion
Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. It is a passive process that does not require energy input from the cell or organism.
Explanation
Diffusion is a form of passive transport, which means it does not require any energy input from the cell or organism. This is in contrast to active transport, which requires energy input to move particles against their concentration gradient.
In diffusion, particles move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This is due to the random motion of particles, which causes them to spread out over time. The rate of diffusion is influenced by several factors, including the concentration gradient, temperature, and the size and shape of the particles.
Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport that involves the movement of particles across a membrane with the help of transport proteins. This process also does not require energy input from the cell or organism.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the movement of diffusion is a passive process that does not require energy input from the cell or organism. It involves the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, due to the random motion of particles. Facilitated diffusion is another type of passive transport that involves the movement of particles across a membrane with the help of transport proteins.
Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. It is a passive process that does not require energy input from the cell or organism.
Explanation
Diffusion is a form of passive transport, which means it does not require any energy input from the cell or organism. This is in contrast to active transport, which requires energy input to move particles against their concentration gradient.
In diffusion, particles move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This is due to the random motion of particles, which causes them to spread out over time. The rate of diffusion is influenced by several factors, including the concentration gradient, temperature, and the size and shape of the particles.
Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport that involves the movement of particles across a membrane with the help of transport proteins. This process also does not require energy input from the cell or organism.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the movement of diffusion is a passive process that does not require energy input from the cell or organism. It involves the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, due to the random motion of particles. Facilitated diffusion is another type of passive transport that involves the movement of particles across a membrane with the help of transport proteins.
Stomata close down if relative humidity of atmosphere falls below- a)50%
- b)70%
- c)80%
- d)60%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Stomata close down if relative humidity of atmosphere falls below
a)
50%
b)
70%
c)
80%
d)
60%

|
Shivani Tiwari answered |
Relative humidity of atmosphere also influencetheopening and closing of stomata. If relative humidity of atmosphere comes below 50% stomata close down.
Water in the soil available to plants is- a)Gravitational water
- b)Capillary water
- c)Hygroscopic water
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Water in the soil available to plants is
a)
Gravitational water
b)
Capillary water
c)
Hygroscopic water
d)
None of the above
|
|
Ruchi Singh answered |
Explanation:
Water in the soil available to plants is referred to as capillary water. This water is held in the soil pores by capillary forces and is accessible to plant roots for absorption.
Types of Soil Water:
There are three types of soil water, namely:
1. Gravitational Water
2. Capillary Water
3. Hygroscopic Water
Gravitational Water:
Gravitational water is the water that drains rapidly through the soil due to the force of gravity. It is not available to plants as it moves down beyond the root zone. This water is usually lost as runoff or percolates deeper into the ground.
Capillary Water:
Capillary water is the water that is held in the soil pores against the force of gravity. It is available to plants as it is held in the root zone. Capillary water is crucial for plant growth as it provides the necessary moisture and nutrients for absorption by the roots. This water moves upward through the soil by capillary action, ensuring that the root zone remains adequately moist.
Hygroscopic Water:
Hygroscopic water is the water that is tightly bound to the soil particles and is unavailable to plants. This water is held so tightly that it cannot be removed by plant roots. It is considered as soil moisture at hygroscopic equilibrium and is not accessible for plant uptake.
Conclusion:
Water in the soil available to plants is capillary water, as it is held against the force of gravity in the root zone and is accessible for absorption by plant roots. Gravitational water drains rapidly, while hygroscopic water is tightly bound to the soil particles and not available for plant uptake.
Water in the soil available to plants is referred to as capillary water. This water is held in the soil pores by capillary forces and is accessible to plant roots for absorption.
Types of Soil Water:
There are three types of soil water, namely:
1. Gravitational Water
2. Capillary Water
3. Hygroscopic Water
Gravitational Water:
Gravitational water is the water that drains rapidly through the soil due to the force of gravity. It is not available to plants as it moves down beyond the root zone. This water is usually lost as runoff or percolates deeper into the ground.
Capillary Water:
Capillary water is the water that is held in the soil pores against the force of gravity. It is available to plants as it is held in the root zone. Capillary water is crucial for plant growth as it provides the necessary moisture and nutrients for absorption by the roots. This water moves upward through the soil by capillary action, ensuring that the root zone remains adequately moist.
Hygroscopic Water:
Hygroscopic water is the water that is tightly bound to the soil particles and is unavailable to plants. This water is held so tightly that it cannot be removed by plant roots. It is considered as soil moisture at hygroscopic equilibrium and is not accessible for plant uptake.
Conclusion:
Water in the soil available to plants is capillary water, as it is held against the force of gravity in the root zone and is accessible for absorption by plant roots. Gravitational water drains rapidly, while hygroscopic water is tightly bound to the soil particles and not available for plant uptake.
Which one of the following theories for ascent of sap was proposed by the eminent Indian scientist J. C. Bose?- a)Relay pump theory
- b)Transpiration pull theory
- c)Root pressure theory
- d)Pulsation theory
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following theories for ascent of sap was proposed by the eminent Indian scientist J. C. Bose?
a)
Relay pump theory
b)
Transpiration pull theory
c)
Root pressure theory
d)
Pulsation theory
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
A common vital force theory about the ascent of sap was put forward by J.C. Bose (1923). It is called the pulsation theory. The theory believes that the innermost cortical cells of the root absorb water from the outer side and pump the same into xylem channels. So the correct option is 'Pulsation theory'.
Passive water absorption by root system is due to- a)Force created in root
- b)High respiratory activity of root
- c)Osmotic pressure in shoot
- d)Tension in sap due to transpiration
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Passive water absorption by root system is due to
a)
Force created in root
b)
High respiratory activity of root
c)
Osmotic pressure in shoot
d)
Tension in sap due to transpiration

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
Absorption of water by root system is passive due to tension in sap created by transpiration. No energy molecule is required in this process, so it is passive in nature.
Pinus seeds cannot germinate without- a)pressure
- b)mycorrhiza
- c)water
- d)soil
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Pinus seeds cannot germinate without
a)
pressure
b)
mycorrhiza
c)
water
d)
soil

|
Kajal Bose answered |
The fungus provides minerals and water to the roots, inturn the roots provide sugars and N-containing compounds to themycorrhizae. Some plants have an obligate association with themycorrhizae.
The ratio of number of stomata to the total number of epidermal cells and stomata per unit leaf area is called- a)Stomatal count
- b)Epidermal index
- c)Stomatal index
- d)Stomatal ratio
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of number of stomata to the total number of epidermal cells and stomata per unit leaf area is called
a)
Stomatal count
b)
Epidermal index
c)
Stomatal index
d)
Stomatal ratio

|
Nilanjan Chakraborty answered |
Stomatal index is the ratio of number of stomata to the total number of epidermal cells and stomata per unit area of leaf.
When separated by a semipermeable membrane, water enters the sugar solution. What would you call the sugar solution- a)Osmotic inactive
- b)Osmotically reactive
- c)Osmotically active
- d)Less osmotic
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When separated by a semipermeable membrane, water enters the sugar solution. What would you call the sugar solution
a)
Osmotic inactive
b)
Osmotically reactive
c)
Osmotically active
d)
Less osmotic

|
Subhankar Datta answered |
When two solution are separated by a semipermeable membrane, water enters the sugar solution. Themovement of water always occurs from higher concentration to lower concentration. Such solution are called osmotically active.
The concentration of minerals in the soil is usually- a)Higher than the concentration of minerals in root
- b)Diluted in than in root
- c)Lower than the concentration of minerals in root
- d)Equilibrium in both soil and root
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The concentration of minerals in the soil is usually
a)
Higher than the concentration of minerals in root
b)
Diluted in than in root
c)
Lower than the concentration of minerals in root
d)
Equilibrium in both soil and root

|
Pankaj Banerjee answered |
The concentration of minerals in the soil is usually lower than the concentration of minerals in the root.
Diffusion rate is affected by- a)Pressure and soil
- b)Water and pressure
- c)Gradient concentration and pressure
- d)Soil and water
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Diffusion rate is affected by
a)
Pressure and soil
b)
Water and pressure
c)
Gradient concentration and pressure
d)
Soil and water

|
Bhavya Yadav answered |
Diffusion rates are affected by the gradient of concentration, the permeability of the membrane separating them, temperature and pressure.
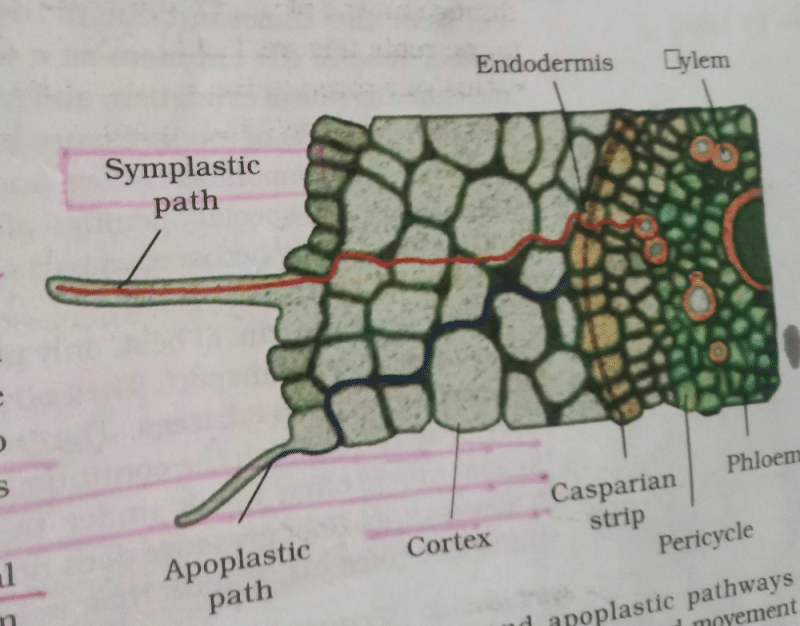
Which of the following statements are true?
(A) The apoplastic movement of water occurs exclusively through the cell wall without crossing any membranes.
(B) Solutes present in a cell (or in any solution) increase the free energy of water or water potential.
(C) The symplastic movement occurs from cell to cell through the plasmodesmata.
(D) Membrane permeability depends on membrane composition and the chemical nature of the solute.- a)A, B and D only
- b)B and D only
- c)A and B only
- d)A, C and D only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements are true?
(A) The apoplastic movement of water occurs exclusively through the cell wall without crossing any membranes.
(B) Solutes present in a cell (or in any solution) increase the free energy of water or water potential.
(C) The symplastic movement occurs from cell to cell through the plasmodesmata.
(D) Membrane permeability depends on membrane composition and the chemical nature of the solute.
(A) The apoplastic movement of water occurs exclusively through the cell wall without crossing any membranes.
(B) Solutes present in a cell (or in any solution) increase the free energy of water or water potential.
(C) The symplastic movement occurs from cell to cell through the plasmodesmata.
(D) Membrane permeability depends on membrane composition and the chemical nature of the solute.
a)
A, B and D only
b)
B and D only
c)
A and B only
d)
A, C and D only
|
|
Anwesha Pati answered |
Ya D is right because only Opt. B is wrong.As solute decreases the water potential.
In plants, capillarity is aided by the small diameter of- a)Trachery elements
- b)Cortical cells
- c)Parenchyma cells
- d)Phloem tissue
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In plants, capillarity is aided by the small diameter of
a)
Trachery elements
b)
Cortical cells
c)
Parenchyma cells
d)
Phloem tissue

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
In plants capillarity is aided by the small diameter of the tracheary elements – the tracheids and vessel elements.
Water potential of pure water and its solution are- a)0 and 0
- b)0 and less than 1
- c)0 and more than 1
- d)0 and 1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Water potential of pure water and its solution are
a)
0 and 0
b)
0 and less than 1
c)
0 and more than 1
d)
0 and 1

|
Vaibhav Basu answered |
The water potential of pure water at standard temperatures, which is not under any pressure, is taken to be zero. If some solute is dissolved in pure water, the solution has fewer freewater and the concentration of water decreases, reducing its water potential.
In wall of guard cell, cellulose microfibrils are arranged- a)Transversely
- b)Tangently
- c)Radially
- d)Obliquely
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In wall of guard cell, cellulose microfibrils are arranged
a)
Transversely
b)
Tangently
c)
Radially
d)
Obliquely

|
Jatin Chakraborty answered |
The cells surrounding the stomata pore is called guard cell. It is bean shaped in dicots and dumbbellshape in monocots. Cellulose microfibrils are arranged radially in guard cell.
The flow of water upward through the xylem in plants can achieve fairly high rates up to 15 m height- a)Transpiration
- b)guttation
- c)evaporation
- d)Transpiration pull
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The flow of water upward through the xylem in plants can achieve fairly high rates up to 15 m height
a)
Transpiration
b)
guttation
c)
evaporation
d)
Transpiration pull

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
The flow of water upward through the xylem in plants can achieve fairly high rates, up to 15 metres per hour. The water is mainly pulled through the plant and that the driving force for this process is transpiration from the leaves. This is referred to as the cohesion-tension-transpiration pull model.
The neighbouring cells are connected through cytoplasmic strands that extend through- a)Cytoplasmic streaming
- b)Apoplast
- c)Imbibition
- d)Plasmodesmata
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The neighbouring cells are connected through cytoplasmic strands that extend through
a)
Cytoplasmic streaming
b)
Apoplast
c)
Imbibition
d)
Plasmodesmata

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
Neighbouring cells are connected through cytoplasmic strands that extend through plasmodesmata. During symplastic movement, the water travels through the cells – their cytoplasm; intercellular movement is through the plasmodesmata.
Transport of water and mineral in plants take place through- a)Collenchymas tissues
- b)Phloem tissues
- c)Parenchyma
- d)Xylem tissues
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Transport of water and mineral in plants take place through
a)
Collenchymas tissues
b)
Phloem tissues
c)
Parenchyma
d)
Xylem tissues

|
Srishti Sen answered |
Transport of water and mineral in plant take place through xylem tissue present in vascular bundles. Vessels and tracheids are main water conducting elements of xylem.
ψp denotes to- a)Pressure potential
- b)Water potential
- c)Solute potential
- d)Negative potential
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
ψp denotes to
a)
Pressure potential
b)
Water potential
c)
Solute potential
d)
Negative potential

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
Pressure potential is usually positive, though in plants negative potential or tension inthe water column in the xylem plays a major role in water transport up a stem. Pressure potential is denoted as ψp.
Cohesion-tension theory is related to- a)Transpiration
- b)Respiration
- c)Ascent of sap
- d)Photosynthesis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cohesion-tension theory is related to
a)
Transpiration
b)
Respiration
c)
Ascent of sap
d)
Photosynthesis

|
Pankaj Banerjee answered |
Ans.
Cohesion Tension theory was proposed by botanist Henry Dixon in 1939. It states that water in xylem is pulled upward by air's drying power, which creates a continuous negative pressure called tension. The tension extends all the way from leaves to the roots that may be 100 feets below.Most of the water a plant takes up is lost by evaporation, typically from stomata on the plant's leaves this process is called transpiration. Transpiration's effect on water inside a plant is a bit like what happens when you suck a drink through a straw. Transpiration puts negative pressure (pulls) on continuous columns of water that fill the narrow conductive tubes of xylem. A column of water resists breaking into droplets as it moves through a narrow conduit such as xylem tube(water molecules are connected by hydrogen bond).Thus the negative pressure created by transpiration(tension) pulls on the entire column of water that fills the xylem tube.
Because of the water's cohesion the tension extends from leaves that may be 100 of feet in the air down through stems, into young roots where water is being absorbed from the soil.
Because of the water's cohesion the tension extends from leaves that may be 100 of feet in the air down through stems, into young roots where water is being absorbed from the soil.
Some carrier proteins allow diffusion by both molecules cross the membrane in the same direction is- a)Antiport
- b)Symport
- c)Uniport
- d)Aquaporins
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Some carrier proteins allow diffusion by both molecules cross the membrane in the same direction is
a)
Antiport
b)
Symport
c)
Uniport
d)
Aquaporins

|
Palak Khanna answered |
Some carrier or transport proteins allow diffusion only if two types of molecules move together. In a symport, both molecules cross the membrane in the same direction.
The excess water collected in the form of droplets around special openings of veins near tip of leaves is called as- a)Guttation
- b)Transpiration
- c)Bleeding
- d)Oozation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The excess water collected in the form of droplets around special openings of veins near tip of leaves is called as
a)
Guttation
b)
Transpiration
c)
Bleeding
d)
Oozation

|
Shounak Nair answered |
The excess water collects in the form of droplets around special openings of veins near the tip of grass blades, and leaves of many herbaceous parts. Such water loss in its liquid phaseis known as guttation.
The pathway of the movement of water through the cell wall only is called- a)Symplast pathway
- b)Vacuolar pathway
- c)Plasmodesmata pathway
- d)Apoplast pathway
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The pathway of the movement of water through the cell wall only is called
a)
Symplast pathway
b)
Vacuolar pathway
c)
Plasmodesmata pathway
d)
Apoplast pathway
|
|
Dhivya L answered |
Movement of water through plants is of 2 types
Apoplast and Symplast.
In apoplast pathway water movement is through the cell wall and intercellular spaces between the cells.
In symplast water movement occurs through the cytoplasm and plasmodesmata between the cells .
so option d is correct
Apoplast and Symplast.
In apoplast pathway water movement is through the cell wall and intercellular spaces between the cells.
In symplast water movement occurs through the cytoplasm and plasmodesmata between the cells .
so option d is correct
Munch hypothesis is based on- a)Translocation of food due to turgor pressure gradient and imbibition force
- b)Translocation of food due to turgor pressure gradient
- c)Translocation of food due to imbibition force
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Munch hypothesis is based on
a)
Translocation of food due to turgor pressure gradient and imbibition force
b)
Translocation of food due to turgor pressure gradient
c)
Translocation of food due to imbibition force
d)
None of the above

|
Suraksha Kamble answered |
Munch explained the translocation of the organic food material through the phloem tissue. This flow occurs along the gradient of the turgor pressure from a region of higher solute concentration to a region of lower solute concentration.
So option B is correct.
So option B is correct.
Special structures found on margins and tips of leaves made of parenchyma tissue and water pores through which guttation take place.- a)Nodes
- b)Stomatal pores
- c)Hydathodes
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Special structures found on margins and tips of leaves made of parenchyma tissue and water pores through which guttation take place.
a)
Nodes
b)
Stomatal pores
c)
Hydathodes
d)
All of these
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Hydathodes are special pore bearing structures present on the margins of leaves of trees like banana and strawberry. Guttation occurs through them due to high root pressure ealry in the morning.
Cohesion-tension theory is related- a)Photosynthesis
- b)Ascent of sap
- c)Respiration
- d)Transpiration
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cohesion-tension theory is related
a)
Photosynthesis
b)
Ascent of sap
c)
Respiration
d)
Transpiration

|
Moumita Khanna answered |
The process of movement of water and minerals from roots to leaves in plant through xylem tissues is called ascent of sap. The most accepted theory of ascent of sap is cohesion-tension theory
Water reaches the top of a plant due to- a)Root pressure
- b)Transpiration
- c)Diffusion
- d)Capillarity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Water reaches the top of a plant due to
a)
Root pressure
b)
Transpiration
c)
Diffusion
d)
Capillarity

|
Maya Sengupta answered |
Water moves from the xylem over the leaf to the air spaces by the apoplast and symplast and after that vanishes through the stomata (transpiration). It is the transpiration of water from leaves which is the primary main thrust for the development of water in xylem.
Various ions, and water from soil can be transported upto a small height in stems by- a)Turger pressure
- b)Suction pressure
- c)Osmotic pressure
- d)Root pressure
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Various ions, and water from soil can be transported upto a small height in stems by
a)
Turger pressure
b)
Suction pressure
c)
Osmotic pressure
d)
Root pressure

|
Dipanjan Mehta answered |
As various ions from the soil are actively transported into the vascular tissues of the roots, water follows (its potential gradient) and increases the pressure inside the xylem. This positive pressure is called rootpressure, and can be responsible for pushing up water to small heights.
Chapter doubts & questions for Transport in Plants - Science for ACT 2025 is part of ACT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Transport in Plants - Science for ACT in English & Hindi are available as part of ACT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Science for ACT
486 videos|517 docs|337 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup