All Exams >
ACT >
Science for ACT >
All Questions
All questions of Fluid Mechanics for ACT Exam
A cylindrical vessel of 90 cm height is kept filled the brim. It has four holes 1, 2, 3, 4 which are respectively at heights of 20cm, 30 cm, 40 cm and 50 cm from the horizontal floor PQ. The water falling at the maximum horizontal distance from the vessel comes from :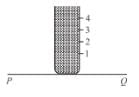
- a)hole number 4
- b)hole number 2
- c)hole number 3
- d)hole number 1
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
A cylindrical vessel of 90 cm height is kept filled the brim. It has four holes 1, 2, 3, 4 which are respectively at heights of 20cm, 30 cm, 40 cm and 50 cm from the horizontal floor PQ. The water falling at the maximum horizontal distance from the vessel comes from :

a)
hole number 4
b)
hole number 2
c)
hole number 3
d)
hole number 1
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
The maximum horizontal distance from the vessel comes from hole number 3 and 4 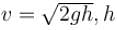 is height of hole from top.
is height of hole from top.
horizontal distance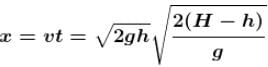
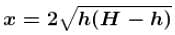
The correct answers are: hole number 4, hole number 3
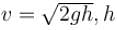 is height of hole from top.
is height of hole from top.horizontal distance
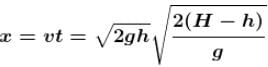
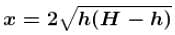
The correct answers are: hole number 4, hole number 3
A liquid of density ρ comes out with a velocity v from a horizontal tube of area of cross-section A. The reaction force exerted by the liquid on the tube is F.- a)F ∝ A
- b)F ∝ v2
- c)F ∝ v
- d)F ∝ ρ
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
A liquid of density ρ comes out with a velocity v from a horizontal tube of area of cross-section A. The reaction force exerted by the liquid on the tube is F.
a)
F ∝ A
b)
F ∝ v2
c)
F ∝ v
d)
F ∝ ρ
|
|
Fatima Siddiqui answered |
A liquid of density refers to a liquid's mass per unit volume. Density is a physical property of a substance and is typically expressed in units of grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or kilograms per liter (kg/L). It is a measure of how tightly packed the molecules are within a given volume of the liquid.
The density of a liquid can vary depending on factors such as temperature and pressure. For example, water has a density of around 1 g/cm³ at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. This means that one cubic centimeter of water has a mass of 1 gram.
The density of a liquid is an important parameter as it can affect various properties and behaviors of the substance. For instance, it can determine whether the liquid will sink or float in another liquid or solid. It can also influence the flow and viscosity of the liquid, as denser liquids tend to flow more slowly than less dense liquids.
The density of a liquid can be measured using various techniques, such as using a hydrometer or a pycnometer. These methods involve comparing the mass of a known volume of the liquid to determine its density.
Overall, the density of a liquid provides valuable information about its physical properties and behavior, making it an important parameter in scientific and industrial applications.
The density of a liquid can vary depending on factors such as temperature and pressure. For example, water has a density of around 1 g/cm³ at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. This means that one cubic centimeter of water has a mass of 1 gram.
The density of a liquid is an important parameter as it can affect various properties and behaviors of the substance. For instance, it can determine whether the liquid will sink or float in another liquid or solid. It can also influence the flow and viscosity of the liquid, as denser liquids tend to flow more slowly than less dense liquids.
The density of a liquid can be measured using various techniques, such as using a hydrometer or a pycnometer. These methods involve comparing the mass of a known volume of the liquid to determine its density.
Overall, the density of a liquid provides valuable information about its physical properties and behavior, making it an important parameter in scientific and industrial applications.
A cylindrical vessel filled with water is released... more on an inclined surface of angleθas shown in figure. The friction coefficient of surface with vessel isμ(< tanθ.)Then the constant angle made by the surface of water with the incline will be :
a)tan−1μ
b)θ + tan-1μc)cot-1μd)θ - tan-1μCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Since frictional force = pulling force
i.e. μmgcosθ = mgsinθ
tanθ = μ
θ = tan-1μ
here θ is angle made by surface of water with incline

There is a small hole near the bottom of an open tank filled with a liquid. The speed of the water ejected does not depend on :- a)acceleration due to gravity
- b)area of the hole
- c)density of the liquid
- d)height of the liquid from the hole
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
There is a small hole near the bottom of an open tank filled with a liquid. The speed of the water ejected does not depend on :
a)
acceleration due to gravity
b)
area of the hole
c)
density of the liquid
d)
height of the liquid from the hole
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
The correct answers are: area of the hole, density of the liquid
In the following figure as shown the flow of liquid through a horizontal pipe. Three tubes A, B and C are connected to the pipe. The radii of the tubes A, B and C at the junction are respectively 2 cm, 1 cm and 2 cm. It can be said that the :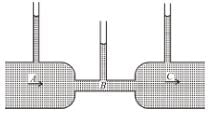
- a)Height of the liquid in the tubes A and C is the same
- b)Height of the liquid in the tubes A and B is the same
- c)Height of the liquid in all three tubes is the same
- d)Height of the liquid in the tube A is maximum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following figure as shown the flow of liquid through a horizontal pipe. Three tubes A, B and C are connected to the pipe. The radii of the tubes A, B and C at the junction are respectively 2 cm, 1 cm and 2 cm. It can be said that the :

a)
Height of the liquid in the tubes A and C is the same
b)
Height of the liquid in the tubes A and B is the same
c)
Height of the liquid in all three tubes is the same
d)
Height of the liquid in the tube A is maximum
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
As cross-section areas of both the tubes A and C are same and tube is horizontal. Hence according to equation of continuity vA = vC and therefore according to Bernoulli’s theorem PA = PC i.e. height of liquid is same in both the tube A and C.
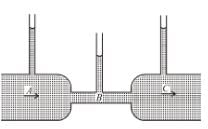
The correct answer is: Height of the liquid in the tubes A and C is the same
A closed vessel in half filled with water. There is a hole near the top of the vessel and air is pumped out from this hole.- a)The pressure at the surface of the water will decrease
- b)The force by the water on the bottom of the vessel will decrease
- c)The water level will rise up in the vessel
- d)The density of the liquid will decrease
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
A closed vessel in half filled with water. There is a hole near the top of the vessel and air is pumped out from this hole.
a)
The pressure at the surface of the water will decrease
b)
The force by the water on the bottom of the vessel will decrease
c)
The water level will rise up in the vessel
d)
The density of the liquid will decrease
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
The correct answers are: The pressure at the surface of the water will decrease, The force by the water on the bottom of the vessel will decrease
A tank, which is open at the top, contains a liquid up to a height H. A small hole is made in the side of the tank at a distance y below the liquid surface. The liquid emerging from the hole lands at a distance x from the tank.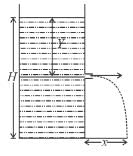
- a)The maximum value of x is H.
- b)x is maximum for y = H/2
- c)The maximum value of x will depend on the density of the liquid.
- d)If y is increased from zero to H, x will first increase and then decrease
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
A tank, which is open at the top, contains a liquid up to a height H. A small hole is made in the side of the tank at a distance y below the liquid surface. The liquid emerging from the hole lands at a distance x from the tank.

a)
The maximum value of x is H.
b)
x is maximum for y = H/2
c)
The maximum value of x will depend on the density of the liquid.
d)
If y is increased from zero to H, x will first increase and then decrease

|
Pie Academy answered |
The velocity of efflux 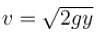
The emerging liquid moves as a projectile and reaches the ground in time t, where,
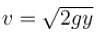
The emerging liquid moves as a projectile and reaches the ground in time t, where,
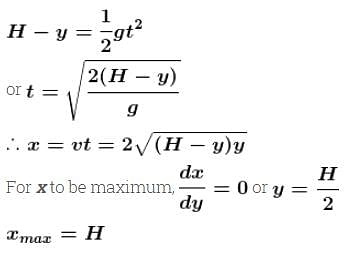
The correct answers are: If y is increased from zero to H, x will first increase and then decrease, x is maximum for y = H/2, The maximum value of x is H.
The vessel shown in the figure has two sections of areas of cross-section A1 and A2. A liquid of density  fills both the sections, up to a height h in each. Neglect atmospheric pressure. Then which of the following are correct.
fills both the sections, up to a height h in each. Neglect atmospheric pressure. Then which of the following are correct.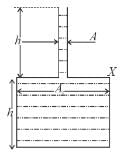
- a)The walls of the vessel at the level X exert a downward force hρg(A2 - A1) on the liquid.
- b)The force exerted by the liquid on the base of the vessel is 2hρhA2.
- c)The pressure at the base of the vessel is 2hρg.
- d)The weight of the liquid is <2hρgA2
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The vessel shown in the figure has two sections of areas of cross-section A1 and A2. A liquid of density  fills both the sections, up to a height h in each. Neglect atmospheric pressure. Then which of the following are correct.
fills both the sections, up to a height h in each. Neglect atmospheric pressure. Then which of the following are correct.
 fills both the sections, up to a height h in each. Neglect atmospheric pressure. Then which of the following are correct.
fills both the sections, up to a height h in each. Neglect atmospheric pressure. Then which of the following are correct.
a)
The walls of the vessel at the level X exert a downward force hρg(A2 - A1) on the liquid.
b)
The force exerted by the liquid on the base of the vessel is 2hρhA2.
c)
The pressure at the base of the vessel is 2hρg.
d)
The weight of the liquid is <2hρgA2
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
The correct answers are: The pressure at the base of the vessel is 2hρg. , The force exerted by the liquid on the base of the vessel is 2hρgA2. , The weight of the liquid is 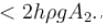 , The walls of the vessel at the level X exert a downward force
, The walls of the vessel at the level X exert a downward force 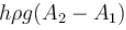 on the liquid.
on the liquid.
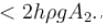 , The walls of the vessel at the level X exert a downward force
, The walls of the vessel at the level X exert a downward force 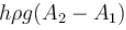 on the liquid.
on the liquid.A narrow tube completely filled with a liquids lying on a series of cylinders as shown in figure. Assuming no sliding between any surfaces, the value of acceleration of the cylinders for which liquids will not come out of the tube from anywhere is given by :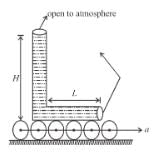
- a)2gH/L
- b)gH/2L
- c)
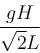
- d)gH/L
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A narrow tube completely filled with a liquids lying on a series of cylinders as shown in figure. Assuming no sliding between any surfaces, the value of acceleration of the cylinders for which liquids will not come out of the tube from anywhere is given by :

a)
2gH/L
b)
gH/2L
c)
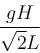
d)
gH/L

|
Pie Academy answered |
No sliding ⇒ pure rolling
Therefore, acceleration of the tube = 2a (since centre of mass of cylinders are moving at a)
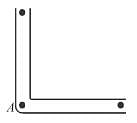
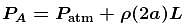 (From horizontal limb)
(From horizontal limb)Also; 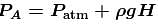
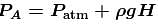
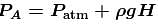
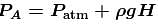
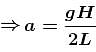
The correct answer is: 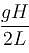
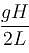
Pressure gradient in the horizontal direction in a static fluid is represented by (z-direction to vertically upwards, and x-axis is along horizontal, d is density of fluid) :- a)
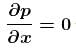
- b)
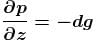
- c)
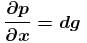
- d)
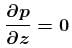
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Pressure gradient in the horizontal direction in a static fluid is represented by (z-direction to vertically upwards, and x-axis is along horizontal, d is density of fluid) :
a)
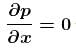
b)
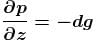
c)
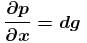
d)
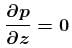

|
Pie Academy answered |
In a static fluid, pressure remains same at the same level. i.e. pressure do not vary with x-coordinate.
The correct answer is: 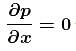
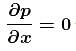
A cubical box is completely filled with mass m of a liquid and is given horizontal acceleration a as shown. Match the force due to fluid pressure on the faces of the cube with their appropriate values (assume zero pressure at minimum pressure)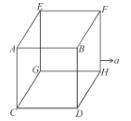
- a)force on face BFHD is mg/2
- b)force on face CGHD is
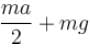
- c)force on face ABFE is ma/2
- d)force on face ACGE is ma/2
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
A cubical box is completely filled with mass m of a liquid and is given horizontal acceleration a as shown. Match the force due to fluid pressure on the faces of the cube with their appropriate values (assume zero pressure at minimum pressure)

a)
force on face BFHD is mg/2
b)
force on face CGHD is 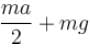
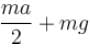
c)
force on face ABFE is ma/2
d)
force on face ACGE is ma/2

|
Pie Academy answered |
Pressure varies with height ⇒ P = ρgh
and is horizontal with acceleration ⇒ P = ρℓa
So on (A) ρgh part is zero while average of ρax is
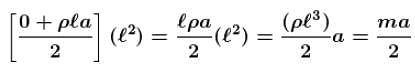
In (B) pℓa part is zero while average of pgx is
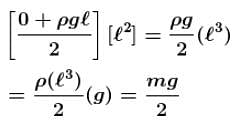
Similarly for other part.
The correct answers are: force on face ABFE is mg/2, force on face BFHD is mg/2, , force on face CGHD is 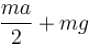
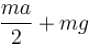
The cubical container ABCDEFGH which is completely filled with an ideal (non-viscous and incompressible) fluid, moves in a gravity free space with a acceleration of 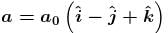 where a0 is a positive constant. Then the minimum pressure at the point will be
where a0 is a positive constant. Then the minimum pressure at the point will be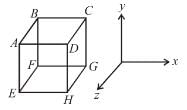
- a)B
- b)E
- c)C
- d)H
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The cubical container ABCDEFGH which is completely filled with an ideal (non-viscous and incompressible) fluid, moves in a gravity free space with a acceleration of 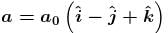 where a0 is a positive constant. Then the minimum pressure at the point will be
where a0 is a positive constant. Then the minimum pressure at the point will be
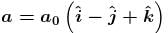 where a0 is a positive constant. Then the minimum pressure at the point will be
where a0 is a positive constant. Then the minimum pressure at the point will be
a)
B
b)
E
c)
C
d)
H

|
Pie Academy answered |

Figure shows a closed container completely filled with an ideal liquid of density ρ. In the liquid there is a spherical body of volume V and density σ attached to a string whose other end is, attached to the roof the container. The container is accelerating with an acceleration a towards right. The force exerted by the liquid on the spherical body when it is in equilibrium with respect to the liquid will be :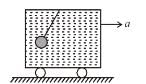
- a)
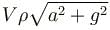
- b)
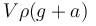
- c)
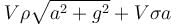
- d)
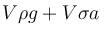
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Figure shows a closed container completely filled with an ideal liquid of density ρ. In the liquid there is a spherical body of volume V and density σ attached to a string whose other end is, attached to the roof the container. The container is accelerating with an acceleration a towards right. The force exerted by the liquid on the spherical body when it is in equilibrium with respect to the liquid will be :

a)
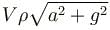
b)
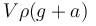
c)
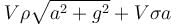
d)
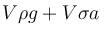

|
Pie Academy answered |
From the frame of reference of liquid, effective gravity (resultant of weight and pseudo force per unit mass  )
)
∴ Effective force due to liquid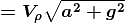
 )
)∴ Effective force due to liquid
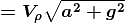
Alter :
The force exerted on spherical body by surrounding liquid is equal to sum of contact force on displaced liquid by the surrounding liquid as shown in.

Hence the force exerted in spherical body by surrounding liquid 

The correct answer is: 

A jet of water having velocity = 10 m/s and stream cross-section = 2 cm2 hits a flat plate perpendicularly, with the water splashing out parallel to plate. The plate experiences a force of :- a)20 N
- b)10 N
- c)10 N
- d)8 N
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A jet of water having velocity = 10 m/s and stream cross-section = 2 cm2 hits a flat plate perpendicularly, with the water splashing out parallel to plate. The plate experiences a force of :
a)
20 N
b)
10 N
c)
10 N
d)
8 N
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
The correct answer is: 20 N
A cylindrical container of an incompressible liquid rotates with ω as shown. The density of liquid is ρ. The liquid acquires parabolic shape. Find the height of the liquid. Radius of container is r.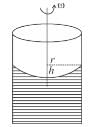
- a)
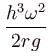
- b)
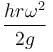
- c)
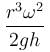
- d)
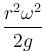
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A cylindrical container of an incompressible liquid rotates with ω as shown. The density of liquid is ρ. The liquid acquires parabolic shape. Find the height of the liquid. Radius of container is r.

a)
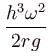
b)
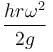
c)
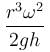
d)
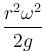

|
Pie Academy answered |
The force experienced by element dx at distance x from the centre
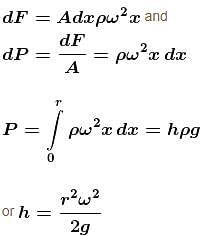
Note : This technique is employed to make parabolic telescopic mirrors.
Liquid glass is rotated and allowed to solidify while rotating.
The correct answer is: 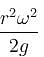
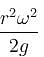
A shower head has 20 circular opening each of radius 1 mm. Shower head is connected to a pipe of radius 0.8 cm. The speed of water in the pipe is 3ms–1. Find the speed of water as it exists from the shower openings.- a)7.6 ms–1
- b)9.6 ms–1
- c)5.6 ms–1
- d)3.6 ms–1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A shower head has 20 circular opening each of radius 1 mm. Shower head is connected to a pipe of radius 0.8 cm. The speed of water in the pipe is 3ms–1. Find the speed of water as it exists from the shower openings.
a)
7.6 ms–1
b)
9.6 ms–1
c)
5.6 ms–1
d)
3.6 ms–1
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
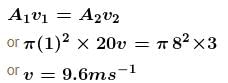
The correct answer is: 9.6 ms–1
A cylindrical container of radius R and height h is completely filled with a liquid. Two horizontal L shaped pipes of small cross-section area a are connected to the cylinder as shown in the figure. Now the two pipes are opened and fluid starts coming out of the pipes horizontally in opposite directions. Then the torque due to ejected liquid on the system is :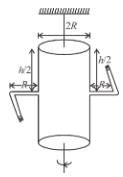
- a)4aghρg
- b)8aghρR
- c)2aghρR
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A cylindrical container of radius R and height h is completely filled with a liquid. Two horizontal L shaped pipes of small cross-section area a are connected to the cylinder as shown in the figure. Now the two pipes are opened and fluid starts coming out of the pipes horizontally in opposite directions. Then the torque due to ejected liquid on the system is :

a)
4aghρg
b)
8aghρR
c)
2aghρR
d)
None of these
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Velocity of efflux of water 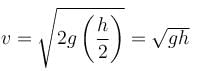
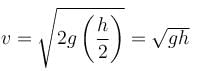
force on ejected water = Rate of change of momentum of ejected water.
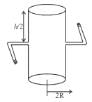
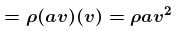
Torque of these forces about central line
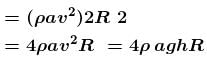
The correct answer is: 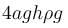
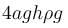
A steady stream of water falls straight down from a pipe as shown. Assume the flow is incompressible, then :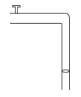
- a)pressure variation will depend upon density and exist speed of the water.
- b)the pressure in the water is lower at lower points in the stream
- c)the pressure in the water is the same at all point in the stream
- d)the pressure in the water is higher at lower points in the stream
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A steady stream of water falls straight down from a pipe as shown. Assume the flow is incompressible, then :

a)
pressure variation will depend upon density and exist speed of the water.
b)
the pressure in the water is lower at lower points in the stream
c)
the pressure in the water is the same at all point in the stream
d)
the pressure in the water is higher at lower points in the stream

|
Pie Academy answered |

The leakage begins in water tank at position P as shown in the figure. The initial gauge pressure (pressure above that of the atmosphere) at P was 5 × 105 N/m2. If the density of water is 100 kg/m2 the velocity with which water gushes out is :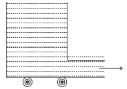
- a)3.2 ms-1
- b)2.8 ms-1
- c)32 ms-1
- d)28 ms-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The leakage begins in water tank at position P as shown in the figure. The initial gauge pressure (pressure above that of the atmosphere) at P was 5 × 105 N/m2. If the density of water is 100 kg/m2 the velocity with which water gushes out is :

a)
3.2 ms-1
b)
2.8 ms-1
c)
32 ms-1
d)
28 ms-1

|
Pie Academy answered |
The correct answer is: 32ms-1

A cuboid is filled of density ρ2 upto height and with liquid of density ρ2, also upto height h as shown. Which of the following are true :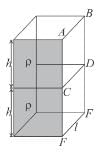
- a)Force on face ABCD due to liquid of density ρ2 is ρ1gh2ℓ
- b)Force on face ABCD due to liquid of density ρ1 is
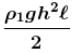
- c)Force on face CDEF due to liquid of density ρ1 is ρ1gh2ℓ
- d)Force on face CDEF due to liquid of density ρ2 is
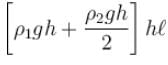
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
A cuboid is filled of density ρ2 upto height and with liquid of density ρ2, also upto height h as shown. Which of the following are true :

a)
Force on face ABCD due to liquid of density ρ2 is ρ1gh2ℓ
b)
Force on face ABCD due to liquid of density ρ1 is 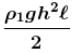
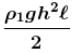
c)
Force on face CDEF due to liquid of density ρ1 is ρ1gh2ℓ
d)
Force on face CDEF due to liquid of density ρ2 is 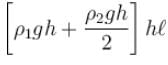
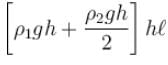
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
On ABCD avg pressure 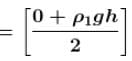
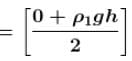
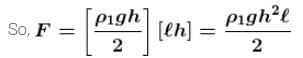
No. of contact of ρ2 and not any pressure on ABCD due to ρ2gh
On CDEF due to ρ1, at every point pressure is ρ1gh so average is also ρ1gh
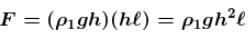 On CDEF due to ρ1 constant but ρ1 is variable so average is ρ1 will be taken.
On CDEF due to ρ1 constant but ρ1 is variable so average is ρ1 will be taken.
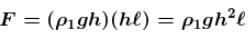 On CDEF due to ρ1 constant but ρ1 is variable so average is ρ1 will be taken.
On CDEF due to ρ1 constant but ρ1 is variable so average is ρ1 will be taken.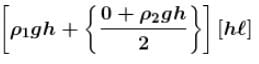
The correct answers are: Force on face ABCD due to liquid of density ρ1 is 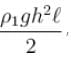
Force on face CDEF due to liquid of density ρ1 is ρ1gh2ℓ, Force on face CDEF due to liquid of density ρ2 is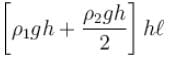
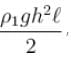
Force on face CDEF due to liquid of density ρ1 is ρ1gh2ℓ, Force on face CDEF due to liquid of density ρ2 is
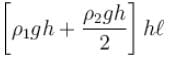
A non uniform cylinder of mass m, length l and radius r is having its centre of mass at a distance l/4 from the centre and lying on the axis of the cylinder. The cylinder is kept in a liquid of uniform density ρ. The moment of inertia of the rod about the centre of mass is I. The angular acceleration of point A relative to point B just after the rod is released from the position shown in figure is :
- a)
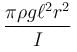
- b)
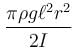
- c)
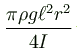
- d)
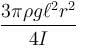
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A non uniform cylinder of mass m, length l and radius r is having its centre of mass at a distance l/4 from the centre and lying on the axis of the cylinder. The cylinder is kept in a liquid of uniform density ρ. The moment of inertia of the rod about the centre of mass is I. The angular acceleration of point A relative to point B just after the rod is released from the position shown in figure is :

a)
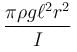
b)
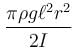
c)
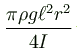
d)
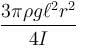
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Torque about CM :
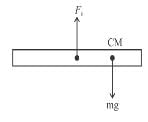
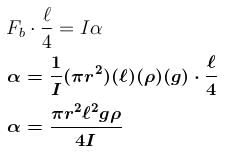
α will be same for all points.
The correct answer is: 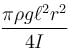
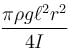
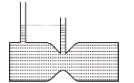
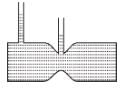
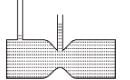
For a liquid which is following steadily, the level in the vertical tubes is best represented by :- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
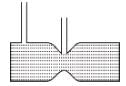
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For a liquid which is following steadily, the level in the vertical tubes is best represented by :
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
From continuity equation, velocity at cross-section (1) is more than that at cross-section (2).
Hence ; P1 < P2
The correct answer is: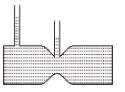
The correct answer is:

Water flows steadily from an tank as shown. Find x where the water lands. Assume area of cross-section of hole is much less than area of cross-section of tank.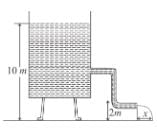
- a)8.67 m
- b)10.5 m
- c)9.38 m
- d)7.97 m
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Water flows steadily from an tank as shown. Find x where the water lands. Assume area of cross-section of hole is much less than area of cross-section of tank.

a)
8.67 m
b)
10.5 m
c)
9.38 m
d)
7.97 m
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
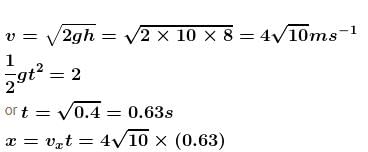
= 2.53 (3.162) = 7.97
The correct answer is: 7.97 m
The correct answer is: 7.97 m
Figure shows an ideal fluid flowing through a uniform cross-sectional tube in the vertical tube with liquid velocities vA and vB and PA and PB. Knowing that tube offers no resistance to fluid flow then which of the following is true.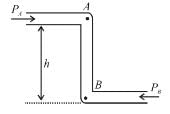
- a) PB > PA
- b)PB < PA
- c)PB = PA
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Figure shows an ideal fluid flowing through a uniform cross-sectional tube in the vertical tube with liquid velocities vA and vB and PA and PB. Knowing that tube offers no resistance to fluid flow then which of the following is true.

a)
PB > PA
b)
PB < PA
c)
PB = PA
d)
None of these
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
vA=vB
vA>vB
PA=PB
PB>PA
The volume of a liquid flowing per second out of an orifice at the bottom of a tank does not depend upon :- a)the acceleration due to gravity
- b)the density of the liquid
- c)the height of the liquid above the orifice
- d)the area of the orifice
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The volume of a liquid flowing per second out of an orifice at the bottom of a tank does not depend upon :
a)
the acceleration due to gravity
b)
the density of the liquid
c)
the height of the liquid above the orifice
d)
the area of the orifice
|
|
Xara Choudhury answered |
Explanation:
When liquid flows out of an orifice at the bottom of a tank, the volume of liquid flowing per second is determined by various factors. However, there are certain factors that do not affect the volume of liquid flowing out of the orifice. Let's analyze each option to understand why.
a) The acceleration due to gravity:
The acceleration due to gravity affects the pressure at the bottom of the tank, which in turn affects the speed at which the liquid flows out of the orifice. According to Bernoulli's principle, the pressure decreases as the speed of fluid increases. So, if the acceleration due to gravity changes, the pressure and speed of the fluid will also change, leading to a different volume of liquid flowing out per second. Therefore, option 'a' is incorrect.
b) The density of the liquid:
The density of the liquid is a measure of how tightly packed its particles are. However, it does not directly affect the volume of liquid flowing out of the orifice. The volume of liquid flowing out per second is determined by the cross-sectional area of the orifice and the speed of the fluid. The density of the liquid only affects its mass, not its volume. Therefore, the volume of liquid flowing out per second remains the same regardless of the density of the liquid. Thus, option 'b' is correct.
c) The height of the liquid above the orifice:
The height of the liquid above the orifice affects the pressure at the bottom of the tank. The greater the height, the greater the pressure and therefore, the greater the speed at which the liquid flows out of the orifice. This means that the volume of liquid flowing out per second will be larger when the height is greater. Therefore, option 'c' is incorrect.
d) The area of the orifice:
The area of the orifice directly affects the volume of liquid flowing out per second. If the orifice has a larger area, more liquid can flow through it in the same amount of time, resulting in a larger volume of liquid flowing out per second. Therefore, option 'd' is incorrect.
In conclusion, the volume of liquid flowing per second out of an orifice at the bottom of a tank does not depend upon the density of the liquid (option 'b'), as it only affects the mass of the liquid and not its volume.
When liquid flows out of an orifice at the bottom of a tank, the volume of liquid flowing per second is determined by various factors. However, there are certain factors that do not affect the volume of liquid flowing out of the orifice. Let's analyze each option to understand why.
a) The acceleration due to gravity:
The acceleration due to gravity affects the pressure at the bottom of the tank, which in turn affects the speed at which the liquid flows out of the orifice. According to Bernoulli's principle, the pressure decreases as the speed of fluid increases. So, if the acceleration due to gravity changes, the pressure and speed of the fluid will also change, leading to a different volume of liquid flowing out per second. Therefore, option 'a' is incorrect.
b) The density of the liquid:
The density of the liquid is a measure of how tightly packed its particles are. However, it does not directly affect the volume of liquid flowing out of the orifice. The volume of liquid flowing out per second is determined by the cross-sectional area of the orifice and the speed of the fluid. The density of the liquid only affects its mass, not its volume. Therefore, the volume of liquid flowing out per second remains the same regardless of the density of the liquid. Thus, option 'b' is correct.
c) The height of the liquid above the orifice:
The height of the liquid above the orifice affects the pressure at the bottom of the tank. The greater the height, the greater the pressure and therefore, the greater the speed at which the liquid flows out of the orifice. This means that the volume of liquid flowing out per second will be larger when the height is greater. Therefore, option 'c' is incorrect.
d) The area of the orifice:
The area of the orifice directly affects the volume of liquid flowing out per second. If the orifice has a larger area, more liquid can flow through it in the same amount of time, resulting in a larger volume of liquid flowing out per second. Therefore, option 'd' is incorrect.
In conclusion, the volume of liquid flowing per second out of an orifice at the bottom of a tank does not depend upon the density of the liquid (option 'b'), as it only affects the mass of the liquid and not its volume.
Which of the following is not possible?- a)
- b)

- c)
- d)
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not possible?
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Pie Academy answered |
The pressure at any point can never have different values.
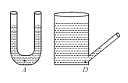
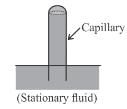
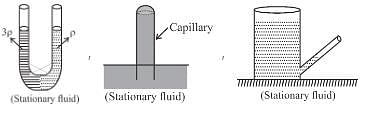
In case of insufficient length of capillary tube the shape of meniscus is as below :
The correct answers are:
A horizontal pipe carries water in the positive direction of x increase in the positive x-direction. Small identical holes are made at three different places along the pipe such that stream from them come out vertically upwards. The height upto which the water stream rise from the three holes :- a)increase in the positive x-direction
- b)decrease in the positive x-direction
- c)are the same in all
- d)are the same for the first two and less for the third hole
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A horizontal pipe carries water in the positive direction of x increase in the positive x-direction. Small identical holes are made at three different places along the pipe such that stream from them come out vertically upwards. The height upto which the water stream rise from the three holes :
a)
increase in the positive x-direction
b)
decrease in the positive x-direction
c)
are the same in all
d)
are the same for the first two and less for the third hole
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
From Bernoulli’s theorem, water coming out from all the holes has same speed. So, they will rise to the some height.
The correct answer is: are the same in all
A massless conical flask filled with a liquid is kept on a table in a vaccum. The force exerted by the liquid on the base of the flask is W1. The force exerted by the flask on the table is W2.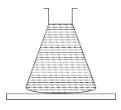
- a)The force exerted by the liquid on the walls of the flask is ((W1 – W2)
- b)W1 = W2
- c)W1 > W2
- d)W1 < W2
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
A massless conical flask filled with a liquid is kept on a table in a vaccum. The force exerted by the liquid on the base of the flask is W1. The force exerted by the flask on the table is W2.

a)
The force exerted by the liquid on the walls of the flask is ((W1 – W2)
b)
W1 = W2
c)
W1 > W2
d)
W1 < W2
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Pressure acts equally in all directions, and a liquid exerts forces on the walls of its container normal to the walls. Hence, the liquid forces on the sloping walls of the conical flask will have a net upward component.
The correct answers are: W1 > W2, The force exerted by the liquid on the walls of the flask is ((W1 – W2)
A U-tube of base length ℓ filled with same volume of two liquids of densities ρ and 2ρ is moving with an acceleration a on the horizontal plane. If the height difference between the two surfaces (open to atmosphere) becomes zero, then the height h is given by :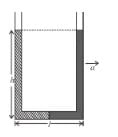
- a)
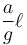
- b)
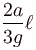
- c)
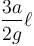
- d)
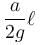
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A U-tube of base length ℓ filled with same volume of two liquids of densities ρ and 2ρ is moving with an acceleration a on the horizontal plane. If the height difference between the two surfaces (open to atmosphere) becomes zero, then the height h is given by :

a)
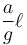
b)
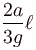
c)
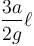
d)
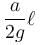
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
For the given situation, liquid of density 2ρ should be behind that of ρ.
From right limb :
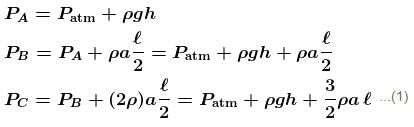
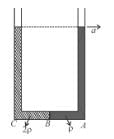
But from left limb :
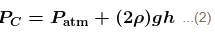
From (1) and (2) :
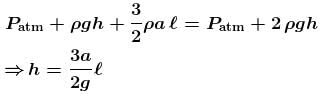
The correct answer is:
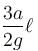
When a hole is made in the side of a container holding water, water flow out and follows a parabolic trajectory. If a hole is made in the side of the container and the container is dropped in free fall (just before the water starts coming out), the water flow (Neglect effect of the surface tension)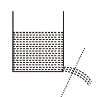
- a)diminishes
- b)curves upward
- c)goes out in a straight line
- d)stops altogether
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When a hole is made in the side of a container holding water, water flow out and follows a parabolic trajectory. If a hole is made in the side of the container and the container is dropped in free fall (just before the water starts coming out), the water flow (Neglect effect of the surface tension)

a)
diminishes
b)
curves upward
c)
goes out in a straight line
d)
stops altogether
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
When the container is at rest with respect to the Earth, there is pressure on the walls due to the weight of the water. The pressure results from the contact force between the water and the container. In free fall, both the water and the container have acceleration of g, and the contact force is zero, so removing part of a wall by making a hole produces no outward flow. (Note that some of the water is in contact with the air, which is not accelerating, so there is still atmospheric pressure on the water.)
Chapter doubts & questions for Fluid Mechanics - Science for ACT 2025 is part of ACT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Fluid Mechanics - Science for ACT in English & Hindi are available as part of ACT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Science for ACT
486 videos|517 docs|337 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup