All Exams >
UCAT >
Quantitative Reasoning for UCAT >
All Questions
All questions of Ratios, Proportions & Scales for UCAT Exam
The ratio of the first and second-class fares between the two stations is 6 : 4 and the number of passengers traveling by first and second-class is 1 : 30. If Rs. 2100 is collected as fare, what is the amount collected from first class passengers?- a)Rs.250
- b)Rs. 200
- c)Rs. 150
- d)Rs. 100
- e)Rs. 225
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of the first and second-class fares between the two stations is 6 : 4 and the number of passengers traveling by first and second-class is 1 : 30. If Rs. 2100 is collected as fare, what is the amount collected from first class passengers?
a)
Rs.250
b)
Rs. 200
c)
Rs. 150
d)
Rs. 100
e)
Rs. 225

|
Elite Coaching Classes answered |
Ratio of the amounts collected from 1st and 2nd class = (6 × 1): (4 × 30) = 1 : 20.
∴ Amount collected from 1st class passengers = 1/21 x 2100 = 100
∴ Amount collected from 1st class passengers = 1/21 x 2100 = 100
B's income is twice that of A, while C's income is three times that of A. If the total income of A, B, and C is Rs. 60,000, the income of B will be __ - a)Rs. 30000
- b)Rs. 25000
- c)Rs. 20000
- d)Rs. 10000
- e)Rs. 15000
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
B's income is twice that of A, while C's income is three times that of A. If the total income of A, B, and C is Rs. 60,000, the income of B will be __
a)
Rs. 30000
b)
Rs. 25000
c)
Rs. 20000
d)
Rs. 10000
e)
Rs. 15000
|
|
Swati Sharma answered |
Let's denote A's income as x.
According to the given information:
B's income = 2x
C's income = 3x
The total income of A, B, and C is Rs. 60,000:
x + 2x + 3x = 60,000
6x = 60,000
x = 10,000
Therefore,
A's income is Rs. 10,000.
∴ B 's income is 2x = 2 × 10,000 = Rs. 20,000.
Divide Rs. 390 among 3 persons A, B and C such that 3 times A’s share, 2 times B’s share and 4 times C’s share are all equal. The shares of A, B and C are respectively- a)Rs. 120, Rs. 180, Rs. 90
- b)Rs. 60, Rs. 90, Rs. 45
- c)Rs. 240, Rs. 157, Rs. 90
- d)Rs. 80, Rs. 110, Rs. 25
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Divide Rs. 390 among 3 persons A, B and C such that 3 times A’s share, 2 times B’s share and 4 times C’s share are all equal. The shares of A, B and C are respectively
a)
Rs. 120, Rs. 180, Rs. 90
b)
Rs. 60, Rs. 90, Rs. 45
c)
Rs. 240, Rs. 157, Rs. 90
d)
Rs. 80, Rs. 110, Rs. 25
e)
None of these

|
Elite Coaching Classes answered |
3A = 2B = 4C. Also A + B + C = 390.
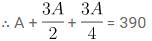
⇒ (4 + 6 + 3)A = 390 × 4
⇒ A = 120,
∴ B = 180 and C = 90
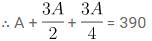
⇒ (4 + 6 + 3)A = 390 × 4
⇒ A = 120,
∴ B = 180 and C = 90
The ratio of two numbers is 9 : 5. If 9 is added to the greater number and 5 is subtracted from the smaller number, the greater number becomes thrice the smaller one. Find the numbers.- a)72, 40
- b)18, 10
- c)36, 20
- d)24, 32
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of two numbers is 9 : 5. If 9 is added to the greater number and 5 is subtracted from the smaller number, the greater number becomes thrice the smaller one. Find the numbers.
a)
72, 40
b)
18, 10
c)
36, 20
d)
24, 32
e)
None of these
|
|
Jack Taylor answered |
Given:
The ratio of two numbers is 9 : 5.
If 9 is added to the greater number and 5 is subtracted from the smaller number, the greater number becomes thrice the smaller one.
Let's assume the two numbers are 9x and 5x
Equation:
9x + 9 = 3(5x - 5)
9x + 9 = 15x - 15
24 = 6x
x = 4
Calculating the numbers:
Greater number = 9x = 9 * 4 = 36
Smaller number = 5x = 5 * 4 = 20
Therefore, the numbers are 36 and 20. Hence, the correct answer is option C.
The ratio of two numbers is 9 : 5.
If 9 is added to the greater number and 5 is subtracted from the smaller number, the greater number becomes thrice the smaller one.
Let's assume the two numbers are 9x and 5x
Equation:
9x + 9 = 3(5x - 5)
9x + 9 = 15x - 15
24 = 6x
x = 4
Calculating the numbers:
Greater number = 9x = 9 * 4 = 36
Smaller number = 5x = 5 * 4 = 20
Therefore, the numbers are 36 and 20. Hence, the correct answer is option C.
300 coins consists of 1 rupee, 50 paise and 25 paise coins, their values being in the ratio of 10 : 4 : C. Find the number of coins of each type.- a)100, 80, 120
- b)80, 90, 100
- c)100, 100, 80
- d)60, 80, 100
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
300 coins consists of 1 rupee, 50 paise and 25 paise coins, their values being in the ratio of 10 : 4 : C. Find the number of coins of each type.
a)
100, 80, 120
b)
80, 90, 100
c)
100, 100, 80
d)
60, 80, 100
e)
None of these
|
|
Swati Sharma answered |
Value of rupee coins = 10 i.e. 10 coins.
Value of 50 p coins = 4 i.e. 8 coins.
Value of 25 p coins = Rs. 3 i.e. 12 coins.
∴ Ratio of coins = 10 : 8 : 12 ⇒ 5 : 4 : 6.
∴ Number of rupee coins = 5/15 × 300 = 100.
Number of 50 P coins = 4/15 × 300
= 80 and N
Number of 25 P coins = 6/15 × 300
= 120
Value of 50 p coins = 4 i.e. 8 coins.
Value of 25 p coins = Rs. 3 i.e. 12 coins.
∴ Ratio of coins = 10 : 8 : 12 ⇒ 5 : 4 : 6.
∴ Number of rupee coins = 5/15 × 300 = 100.
Number of 50 P coins = 4/15 × 300
= 80 and N
Number of 25 P coins = 6/15 × 300
= 120
A man has 25 paise, 50 paise and 1 Rupee coins. There are 220 coins in all and the total amount is 160. If there are thrice as many 1 Rupee coins as there are 25 paise coins, then what is the number of 50 paise coins?- a)60
- b)120
- c)40
- d)80
- e)70
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A man has 25 paise, 50 paise and 1 Rupee coins. There are 220 coins in all and the total amount is 160. If there are thrice as many 1 Rupee coins as there are 25 paise coins, then what is the number of 50 paise coins?
a)
60
b)
120
c)
40
d)
80
e)
70
|
|
Swati Sharma answered |
Let the 25 paise coins be 'x'
So, one rupees coins = 3x
50 paise coins = 220 – x – (3x) = 220 – (4x)
According to the questions,
3x + [(220 – 4x)/2] + x/4 =160
⇒ (12x + 440 – 8x + x)/4 = 160
⇒ 5x + 440 = 640
⇒ 5x = 200
⇒ x = 40
So, 50 paise coins = 220 – (4x) = 220 – (4 × 40) = 60
∴ The number of 50 paise coin is 60.
A bag has ₹ 785 in the denomination of ₹ 2, ₹ 5 and ₹ 10 coins. The coins are in the ratio of 6 : 9 : 10. How many coins of ₹ 5 are in the bag?- a)60
- b)12
- c)45
- d)24
- e)40
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A bag has ₹ 785 in the denomination of ₹ 2, ₹ 5 and ₹ 10 coins. The coins are in the ratio of 6 : 9 : 10. How many coins of ₹ 5 are in the bag?
a)
60
b)
12
c)
45
d)
24
e)
40

|
Elite Coaching Classes answered |
Let the number of coins of ₹ 2, ₹ 5 and ₹ 10 be 6x, 9x, and 10x respectively
⇒ (2 × 6x) + (5 × 9x) + (10 × 10x) = 785
⇒ 157x = 785
∴ x = 5
Number of coins of ₹ 5 = 9x = 9 × 5 = 45
∴ 45 coins of ₹ 5 are in the bag
When a sum of money was equally distributed among 49 children, each child received Rs. 20. If the same amount is equally distributed among children, such that each child gets Rs. 3.5, find the number of children.- a)280
- b)246
- c)245
- d)240
- e)255
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When a sum of money was equally distributed among 49 children, each child received Rs. 20. If the same amount is equally distributed among children, such that each child gets Rs. 3.5, find the number of children.
a)
280
b)
246
c)
245
d)
240
e)
255
|
|
Swati Sharma answered |
Number of children 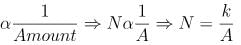
49 = k/20
K = 49 × 20
⇒ N = 49 × 20 /3.5
= 280.
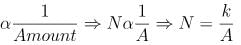
49 = k/20
K = 49 × 20
⇒ N = 49 × 20 /3.5
= 280.
The cost of a diamond varies as the square of its weight. A diamond weighing 20 decigrams costs Rs. 4,800. Find the cost of a diamond of the same kind weighing 8 decigrams.- a)Rs. 762
- b)Rs. 760
- c)Rs. 764
- d)Rs. 768
- e)Rs. 765
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The cost of a diamond varies as the square of its weight. A diamond weighing 20 decigrams costs Rs. 4,800. Find the cost of a diamond of the same kind weighing 8 decigrams.
a)
Rs. 762
b)
Rs. 760
c)
Rs. 764
d)
Rs. 768
e)
Rs. 765

|
Elite Coaching Classes answered |
C α W2
⇒ C = kW2. 4800
= k(20)2
⇒ k = 12.
Now C = 12(8)2
⇒ C =768.
⇒ C = kW2. 4800
= k(20)2
⇒ k = 12.
Now C = 12(8)2
⇒ C =768.
In one alloy there is 60% gold in its total mass, while in another alloy it is 35%. 12 kg of the first alloy was melted together with 8 kg of the second one to form a third alloy. Find the percentage of gold in the new alloy.- a)50%
- b)49%
- c)45%
- d)48%
- e)46%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In one alloy there is 60% gold in its total mass, while in another alloy it is 35%. 12 kg of the first alloy was melted together with 8 kg of the second one to form a third alloy. Find the percentage of gold in the new alloy.
a)
50%
b)
49%
c)
45%
d)
48%
e)
46%

|
Elite Coaching Classes answered |
Amount of gold in 1st alloy = 0.6 × 12 = 7.2 kg.
Amount of gold in 2nd alloy = 0.35 × 8 =2.8 kg.
∴ required % age of gold = (7.2 + 2.8) / (12 + 8) × 100
= (10 / 20) × 100
= 50 %.
Amount of gold in 2nd alloy = 0.35 × 8 =2.8 kg.
∴ required % age of gold = (7.2 + 2.8) / (12 + 8) × 100
= (10 / 20) × 100
= 50 %.
In a bag, there are coins of 5ps, 10ps, and 25ps in a ratio of 3 : 2 : 1. If there are Rs. 60 in all, how many 5ps coins are there?- a)100
- b)200
- c)300
- d)400
- e)500
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a bag, there are coins of 5ps, 10ps, and 25ps in a ratio of 3 : 2 : 1. If there are Rs. 60 in all, how many 5ps coins are there?
a)
100
b)
200
c)
300
d)
400
e)
500
|
|
Swati Sharma answered |
60 Rupees = 60 × 100 = 6000 paise
⇒ 5 × 3x + 10 × 2x + 25 × 1x = 6000
⇒ 15x + 20x + 25x = 6000
⇒ 60x = 6000
⇒ x = 100
∴ Number of 5 paise coins = 3x = 3 × 100 = 300
The ratio of A’s salary to B’s was 4 : 5. A’s salary is increased by 10% and B’s by 20%, what is the ratio of their salaries now?- a)14:11
- b)15:14
- c)11:15
- d)12:15
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of A’s salary to B’s was 4 : 5. A’s salary is increased by 10% and B’s by 20%, what is the ratio of their salaries now?
a)
14:11
b)
15:14
c)
11:15
d)
12:15
e)
None of these

|
Elite Coaching Classes answered |
Present ratio = 4 : 5.
Increase of 10% and 20%.
∴New ratio of salaries will be 4 × 1.1 :5 × 1.2
= 11 : 15.
Increase of 10% and 20%.
∴New ratio of salaries will be 4 × 1.1 :5 × 1.2
= 11 : 15.
Find the ratio of the diagonal of a square of side 30 cm, to its side.- a)√2: 3
- b)√3: 4
- c)1 : √2
- d)√2: 1
- e)√3: 1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the ratio of the diagonal of a square of side 30 cm, to its side.
a)
√2: 3
b)
√3: 4
c)
1 : √2
d)
√2: 1
e)
√3: 1

|
Elite Coaching Classes answered |
Diagonal of a square = √2 side.
Hence this is the required ratio. So the required ratio is √2: 1.
Hence this is the required ratio. So the required ratio is √2: 1.
A sum of money at simple interest amounts to Rs. 815 in 3 years and Rs. 854 in 4 years. The sum is- a)Rs. 650
- b)Rs. 690
- c)Rs. 698
- d)Rs. 700
- e)Rs. 680
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A sum of money at simple interest amounts to Rs. 815 in 3 years and Rs. 854 in 4 years. The sum is
a)
Rs. 650
b)
Rs. 690
c)
Rs. 698
d)
Rs. 700
e)
Rs. 680
|
|
Swati Sharma answered |
Simple Interest for 1 year = Rs. (854 − 815)
= Rs. 39
Simple Interest for 3 years = Rs. 39 × 3
⇒ Rs. 117
Principal = Rs. 815 − Rs. 117
⇒ Rs. 698
∴ The sum is Rs. 698.
Rs.750 are divided among A, B and C in such a manner that A : B is 5 : 2 and B : C is 7 : 13. What is A’s share?- a)Rs.140
- b)Rs. 350
- c)Rs. 250
- d)Rs. 260
- e)Rs.280
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rs.750 are divided among A, B and C in such a manner that A : B is 5 : 2 and B : C is 7 : 13. What is A’s share?
a)
Rs.140
b)
Rs. 350
c)
Rs. 250
d)
Rs. 260
e)
Rs.280
|
|
Swati Sharma answered |
A : B = 5 : 2
B : C = 7 : 13
A : B : C = 5 × 7 : 2 × 7 : 2 × 13 = 35 : 14 : 26
Total Sum = 750
⇒ 35 x + 14x + 26x = 750
⇒ x = 10
So, A's share = 35 × 10 = Rs 350
∴ The required answer is Rs 350
u : v = 4 : 7 and v : w = 9 : 7. If u = 72, then what is the value of w?- a)98
- b)77
- c)63
- d)49
- e)56
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
u : v = 4 : 7 and v : w = 9 : 7. If u = 72, then what is the value of w?
a)
98
b)
77
c)
63
d)
49
e)
56

|
Elite Coaching Classes answered |
u : v = 4 : 7 and v : w = 9 : 7
To make ratio v equal in both cases
We have to multiply the 1st ratio by 9 and 2nd ratio by 7
u : v = 9 × 4 : 9 × 7 = 36 : 63 ----(i)
v : w = 9 × 7 : 7 × 7 = 63 : 49 ----(ii)
Form (i) and (ii), we can see that the ratio v is equal in both cases
So, Equating the ratios we get,
u ∶ v ∶ w = 36 ∶ 63 ∶ 49
⇒ u ∶ w = 36 ∶ 49
When u = 72,
⇒ w = 49 × 72/36 = 98
∴ Value of w is 98
If a : b = 3 : 2, b : c = 2 : 1, c : d = 1/3 : 1/7 and d : e = 1/4 : 1/5 find a : b : c : d : e.- a)100 : 75 : 30 : 15 : 12
- b)100 : 30 : 75 : 12 : 15
- c)105 : 70 : 35 : 15 : 12
- d)105 : 35 : 70 : 15 : 12
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a : b = 3 : 2, b : c = 2 : 1, c : d = 1/3 : 1/7 and d : e = 1/4 : 1/5 find a : b : c : d : e.
a)
100 : 75 : 30 : 15 : 12
b)
100 : 30 : 75 : 12 : 15
c)
105 : 70 : 35 : 15 : 12
d)
105 : 35 : 70 : 15 : 12
e)
None of these

|
Elite Coaching Classes answered |
a : b = 3 : 2 now check which options satisfied this ratio
1) a : b = 100 : 75 = 4 : 3 not equal to 3 : 2
2) a : b = 100 : 30 = 10 : 3 not equal to 3 : 2
3) a : b = 105 : 70 = 21 : 14 = 3 : 2 which is equal to 3 : 2
4) a : b = 105 : 35 = 21 : 7 = 3 : 1 which is not equal to 3 : 2
hence option 3 is correct option
A is two years older than B and B is twice as old as C. If the total age of A, B and C is 27 yrs. The age of B is- a)8 yrs
- b)9 yrs
- c)10 yrs
- d)11 yrs
- e)7 yrs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A is two years older than B and B is twice as old as C. If the total age of A, B and C is 27 yrs. The age of B is
a)
8 yrs
b)
9 yrs
c)
10 yrs
d)
11 yrs
e)
7 yrs
|
|
Swati Sharma answered |
Let age of c be x
⇒ Age of B = 2x
⇒ Age of A = 2x + 2
⇒ x + 2x + 2x + 2 = 27
⇒ 5x = 25
⇒ x = 5
∴ The age of B is 5 × 2 = 10 years.
200 g of 25% sulphuric acid solution was added to 300 g of 40% sulphuric acid solution. Find the concentration of the acid in the mixture.- a)14%
- b)24%
- c)44%
- d)34%
- e)12%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
200 g of 25% sulphuric acid solution was added to 300 g of 40% sulphuric acid solution. Find the concentration of the acid in the mixture.
a)
14%
b)
24%
c)
44%
d)
34%
e)
12%
|
|
Swati Sharma answered |
Amount of acid in the 1st solution = 0.25 × 200 = 50 g.
Amount of acid in the 2nd solution = 0.4 × 300 = 120 g.
Total amount of acid = 50 + 120 = 170 g.
∴ Required concentration = 170 / (200 + 300) × 100 = 34%
Amount of acid in the 2nd solution = 0.4 × 300 = 120 g.
Total amount of acid = 50 + 120 = 170 g.
∴ Required concentration = 170 / (200 + 300) × 100 = 34%
The salaries of P, Q, and R are in the ratio of 5 ∶ 3 ∶ 7. If R gets Rs. 3600 more than Q, then what is the salary of P?- a)Rs. 900
- b)Rs. 6300
- c)Rs. 4500
- d)Rs. 3600
- e)Not Attempted
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The salaries of P, Q, and R are in the ratio of 5 ∶ 3 ∶ 7. If R gets Rs. 3600 more than Q, then what is the salary of P?
a)
Rs. 900
b)
Rs. 6300
c)
Rs. 4500
d)
Rs. 3600
e)
Not Attempted
|
|
Swati Sharma answered |
Let the salary of P = 5x
Q = 3x and R = 7x
According to the question,
R gets Rs. 3600 more than Q,
⇒ 7x = 3x + 3600
⇒ 4x = 3600 ⇒ x = 900
∴ The salary of P = 5 × 900 = Rs 4500
Chapter doubts & questions for Ratios, Proportions & Scales - Quantitative Reasoning for UCAT 2025 is part of UCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the UCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for UCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Ratios, Proportions & Scales - Quantitative Reasoning for UCAT in English & Hindi are available as part of UCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UCAT Exam by signing up for free.
Quantitative Reasoning for UCAT
31 videos|37 docs|23 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









