All Exams >
Class 8 >
Year 8 Physics (Cambridge) >
All Questions
All questions of Measuring motion for Class 8 Exam
Rahul and Ravi are playing in a ground. They start running from the same point X simultaneously in the ground and reach point Y at the same time by following paths marked 1 and 2 respectively, as shown in the figure.Q. Which of the following is correct statement for the given situation?- a)Rahul covers a longer distance with a lower speed.
- b)Rahul covers a longer distance with a higher speed.
- c)Rahul and Ravi both cover different distances with same speed.
- d)Ravi covers a shorter distance with higher speed.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rahul and Ravi are playing in a ground. They start running from the same point X simultaneously in the ground and reach point Y at the same time by following paths marked 1 and 2 respectively, as shown in the figure.
Q. Which of the following is correct statement for the given situation?
a)
Rahul covers a longer distance with a lower speed.
b)
Rahul covers a longer distance with a higher speed.
c)
Rahul and Ravi both cover different distances with same speed.
d)
Ravi covers a shorter distance with higher speed.

|
Nitin Iyer answered |
Rahul and Ravi both cover different distances XOY and XY respectively at the same time. Rahul covers more distance than Ravi in the same time. Hence Rahul covers longer distance with a higher speed.
Study the given Venn diagram, Which of the motions described by different bodies are most likely to be I, II and III?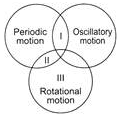
- a)

- b)

- c)
- d)

Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the given Venn diagram, Which of the motions described by different bodies are most likely to be I, II and III?

a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Option 1,2 and 3 are rotatory motion. Rotatory motion, also referred to as rotational motion or circular motion, is physical motion that happens when an object rotates or spins on an axis.
One centimeter on a scale is divided into 20 equal divisions. The least count (minimum value) of this scale is
- a)20 cm
- b)1 cm
- c)0.1 cm
- d)0.05 cm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One centimeter on a scale is divided into 20 equal divisions. The least count (minimum value) of this scale is
a)
20 cm
b)
1 cm
c)
0.1 cm
d)
0.05 cm

|
Arjun Desai answered |
As 20 divisions = 1 cm
∴ 1 division = 1/20 cm
= 0.05cm
∴ 1 division = 1/20 cm
= 0.05cm
Which of the following statements is incorrect?- a)Motion of a vehicle on a straight road is not rectilinear motion.
- b)Motion of honeybees is the example of random motion.
- c)Cubit is the length of a forearm.
- d)Centigrade is not the SI unit of temperature.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
a)
Motion of a vehicle on a straight road is not rectilinear motion.
b)
Motion of honeybees is the example of random motion.
c)
Cubit is the length of a forearm.
d)
Centigrade is not the SI unit of temperature.
|
|
Divyansh Verma answered |
Rectilinear motion is another name for straight-line motion.
While measuring the length of a wooden box, the reading at one end is 1.5 cm and the other end is 4.7 cm. What is the length of the wooden box?- a)4.7 cm
- b)1.5 cm
- c)3.2 cm
- d)6.2 cm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
While measuring the length of a wooden box, the reading at one end is 1.5 cm and the other end is 4.7 cm. What is the length of the wooden box?
a)
4.7 cm
b)
1.5 cm
c)
3.2 cm
d)
6.2 cm

|
Raj Mukherjee answered |
The length of the wooden box = Difference between the reading at both the ends = 4.7−1.5 = 3.2 cm
Write the similarities and differences between the motion of a bicycle and a ceiling fan that has been switched on.- a)Both have circular motion; a bicycle moves in a straight line, and a fan has rotating blades.
- b)Both have circular motion; a bicycle moves in a straight line, and a fan moves in a circle.
- c)Both have circular motion; a bicycle moves in a circle, and a fan moves in a circle.
- d)Both have rectilinear motion; a bicycle moves in a straight line, and a fan moves in a straight path.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Both have circular motion; a bicycle moves in a straight line, and a fan has rotating blades.
b)
Both have circular motion; a bicycle moves in a straight line, and a fan moves in a circle.
c)
Both have circular motion; a bicycle moves in a circle, and a fan moves in a circle.
d)
Both have rectilinear motion; a bicycle moves in a straight line, and a fan moves in a straight path.

|
Praveen Kumar answered |
Both a bicycle's wheels and a ceiling fan's blades exhibit circular motion. The bicycle's wheels rotate in a circle while moving forward, and the fan blades rotate in a circular path. The main difference is that the bicycle moves through space, while the fan's motion is confined to rotation around its axis.
If a distance-time graph is a straight line sloping downwards from left to right, the object is:- a)Moving towards the origin
- b)Moving away from the origin
- c)Accelerating
- d)Decelerating
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a distance-time graph is a straight line sloping downwards from left to right, the object is:
a)
Moving towards the origin
b)
Moving away from the origin
c)
Accelerating
d)
Decelerating

|
Focus Academy answered |
A straight line sloping downwards from left to right on a distance-time graph indicates that the object is moving away from the origin (assuming the origin represents the starting point). This could represent a scenario where the object is moving in the opposite direction of the origin with a constant speed (if the line is straight) or decreasing speed (if it curves downwards gradually).
A piece of thread folded 6 times is placed along a 15 cm long measuring scale as shown in the figure. The length of the thread is between

- a)0.15-0.50 m
- b)0.50m-1.0m
- c)1.0m-1.5m
- d)1.5m-2.0m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A piece of thread folded 6 times is placed along a 15 cm long measuring scale as shown in the figure. The length of the thread is between

a)
0.15-0.50 m
b)
0.50m-1.0m
c)
1.0m-1.5m
d)
1.5m-2.0m

|
Subham Verma answered |
Length of each fold of thread placed along scale = 13.5 cm
As thread is folded 6 times
∴ Length of the thread = (13.5×6) cm
= 81 cm = 0.81 m
As thread is folded 6 times
∴ Length of the thread = (13.5×6) cm
= 81 cm = 0.81 m
In circular motion, the- a)Direction of motion is fixed
- b)Direction of motion changes continuously
- c)Acceleration is zero
- d)Velocity is constant.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In circular motion, the
a)
Direction of motion is fixed
b)
Direction of motion changes continuously
c)
Acceleration is zero
d)
Velocity is constant.
|
|
Muskaan Joshi answered |
Circular motion is the movement of an object along a circular path. In this type of motion, the object continuously changes its direction while maintaining a constant speed. The correct answer to the question is option 'B' - the direction of motion changes continuously. Let's understand why this is the correct answer in detail.
Direction of Motion
In circular motion, the object moves around a center point in a circular path. As it moves, the direction of the object constantly changes. At any given point on the circular path, the object is moving tangentially to that point. This means that the object is moving perpendicular to the radius of the circle at that point. Therefore, the direction of motion is not fixed but changes continuously.
Velocity
Velocity is a vector quantity that includes both magnitude (speed) and direction. In circular motion, the object maintains a constant speed as it moves around the circle. However, the direction of motion changes continuously, which means the velocity of the object also changes. Therefore, the velocity is not constant in circular motion.
Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. In circular motion, even though the speed of the object remains constant, its direction changes continuously. This change in direction indicates a change in velocity. As a result, there is a non-zero acceleration in circular motion. The object is constantly accelerating towards the center of the circle, which is called centripetal acceleration.
Centripetal Force
The centripetal acceleration in circular motion is caused by a force called the centripetal force. This force acts towards the center of the circle, pulling the object inward. It is responsible for keeping the object in its circular path. Without this force, the object would move in a straight line tangent to the circle. The centripetal force is required to constantly change the object's direction of motion, thereby causing the continuous change in direction.
In conclusion, in circular motion, the direction of motion changes continuously, the velocity is not constant, and there is a non-zero acceleration. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B'.
Direction of Motion
In circular motion, the object moves around a center point in a circular path. As it moves, the direction of the object constantly changes. At any given point on the circular path, the object is moving tangentially to that point. This means that the object is moving perpendicular to the radius of the circle at that point. Therefore, the direction of motion is not fixed but changes continuously.
Velocity
Velocity is a vector quantity that includes both magnitude (speed) and direction. In circular motion, the object maintains a constant speed as it moves around the circle. However, the direction of motion changes continuously, which means the velocity of the object also changes. Therefore, the velocity is not constant in circular motion.
Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. In circular motion, even though the speed of the object remains constant, its direction changes continuously. This change in direction indicates a change in velocity. As a result, there is a non-zero acceleration in circular motion. The object is constantly accelerating towards the center of the circle, which is called centripetal acceleration.
Centripetal Force
The centripetal acceleration in circular motion is caused by a force called the centripetal force. This force acts towards the center of the circle, pulling the object inward. It is responsible for keeping the object in its circular path. Without this force, the object would move in a straight line tangent to the circle. The centripetal force is required to constantly change the object's direction of motion, thereby causing the continuous change in direction.
In conclusion, in circular motion, the direction of motion changes continuously, the velocity is not constant, and there is a non-zero acceleration. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B'.
Given figure shows a measuring cylinder (incm3) before and after the immersion of an irregular solid object. The volume of the object is 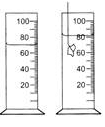
- a)82 cm3
- b)12 cm3
- c)30 cm3
- d)18 cm3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Given figure shows a measuring cylinder (incm3) before and after the immersion of an irregular solid object. The volume of the object is

a)
82 cm3
b)
12 cm3
c)
30 cm3
d)
18 cm3

|
Shounak Joshi answered |
Initial volume of water in the cylinder, (before the immersion of the object)
V1 = 70cm3
Final volume in the cylinder (after the immersion of the object)
V2 = 82cm3
Hence, volume of the object immersed in the cylinder = Final volume - Initial volume
= 82 cm3−70 cm3
= 12 cm3
V1 = 70cm3
Final volume in the cylinder (after the immersion of the object)
V2 = 82cm3
Hence, volume of the object immersed in the cylinder = Final volume - Initial volume
= 82 cm3−70 cm3
= 12 cm3
While measuring the length of a knitting needle, the reading of the scale at one end is 3.0 cm and at the other end is 33.1 cm. What is the length of the needle?- a)36.1 cm
- b)33.1 cm
- c)30.1 cm
- d)30.0 cm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
While measuring the length of a knitting needle, the reading of the scale at one end is 3.0 cm and at the other end is 33.1 cm. What is the length of the needle?
a)
36.1 cm
b)
33.1 cm
c)
30.1 cm
d)
30.0 cm

|
Get Idea answered |
The length of the needle is calculated by subtracting the initial reading from the final reading: 33.1 cm - 3.0 cm = 30.1 cm.
Why could you not use an elastic measuring tape to measure distance? What would be some of the problems you would meet in telling someone about a distance you measured with an elastic tape?- a)Elastic tapes stretch and do not provide accurate measurements.
- b)Elastic tapes are too short for measuring long distances.
- c)Elastic tapes are difficult to read accurately.
- d)Elastic tapes are not designed for outdoor use.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Elastic tapes stretch and do not provide accurate measurements.
b)
Elastic tapes are too short for measuring long distances.
c)
Elastic tapes are difficult to read accurately.
d)
Elastic tapes are not designed for outdoor use.

|
Get Idea answered |
An elastic measuring tape is not suitable for measuring distances accurately because it stretches under tension. This stretching can lead to inaccurate measurements, especially over long distances. The lack of precision makes it difficult to provide reliable measurements.
Give two examples of periodic motion.- a)A child on a swing and a car moving on a road
- b)A pendulum in a clock and the orbit of the Earth around the Sun
- c)A spinning top and a bird flying in the sky
- d)A leaf falling from a tree and a river flowing
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
A child on a swing and a car moving on a road
b)
A pendulum in a clock and the orbit of the Earth around the Sun
c)
A spinning top and a bird flying in the sky
d)
A leaf falling from a tree and a river flowing

|
Get Idea answered |
Periodic motion refers to movements that repeat at regular intervals. Examples include a pendulum in a clock, which swings back and forth in a regular pattern, and the orbit of the Earth around the Sun, which follows a consistent cycle. Both exhibit repetitive and predictable motion
Two identical metal balls A and 8 moving in opposite directions with different speeds hit each other at point X as shown in the figure. Changes will most likely appear in their 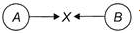 1. Shapes
1. Shapes
2. Speeds
3. Directions
4. Volumes- a)1 and 3
- b)2 and 3
- c)2 and 4
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two identical metal balls A and 8 moving in opposite directions with different speeds hit each other at point X as shown in the figure. Changes will most likely appear in their
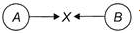
1. Shapes
2. Speeds
3. Directions
4. Volumes
2. Speeds
3. Directions
4. Volumes
a)
1 and 3
b)
2 and 3
c)
2 and 4
d)
1, 2 and 3

|
Sahil Desai answered |
In case of collision, changes are most likely to be appear in the speed and direction of both the balls.
A level teaspoon is approximately 5 ml. How many level teaspoons in 1.5 litres?- a) 20
- b) 30
- c) 300
- d) 3,000
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
20
b)
30
c)
300
d)
3,000
|
|
Subset Academy answered |
1.5l = 1,500ml so to find the answer divide 1,500 by 5
Which of the following motions is/are periodic as well as oscillatory motion?
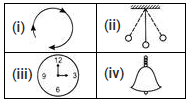
- a)(i), (ii) and (iii)
- b)(ii) only
- c)(i), (iii) and (iv)
- d)(iii) only
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following motions is/are periodic as well as oscillatory motion?

a)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
b)
(ii) only
c)
(i), (iii) and (iv)
d)
(iii) only

|
Subham Rane answered |
Only (ii) shows to and fro as well as interval. Hence, (ii) is the correct option.
What do we use to measure curved lengths?- a)Thread
- b)Wood
- c)Sand
- d)Paper
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What do we use to measure curved lengths?
a)
Thread
b)
Wood
c)
Sand
d)
Paper

|
Get Idea answered |
Measuring Curved Lengths
- Thread: Threads are commonly used to measure curved lengths. You can wrap a thread around the curve and then measure the length of the thread to determine the curved length accurately.
- Wood: While wood can be used for measuring straight lengths, it is not an ideal tool for measuring curved lengths as it cannot conform to the shape of the curve.
- Sand: Sand is not a practical tool for measuring curved lengths as it would not provide an accurate measurement and would be messy to work with.
- Paper: Paper is also not suitable for measuring curved lengths as it is a flat and rigid material that cannot adapt to the shape of the curve.
Therefore, the most appropriate tool for measuring curved lengths is a thread due to its flexibility and ability to conform to the shape of the curve.
In which year, SI system was recommended by general conference of weights and measures?- a)1950
- b)1971
- c)1960
- d)1980
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which year, SI system was recommended by general conference of weights and measures?
a)
1950
b)
1971
c)
1960
d)
1980

|
Get Idea answered |
Year of Recommendation for SI System
- General Conference of Weights and Measures: The SI system was recommended by the General Conference of Weights and Measures in 1971.
- Significance: This recommendation marked a significant milestone in the standardization of units of measurement worldwide.
- Implementation: The SI system, also known as the International System of Units, is now widely used in scientific, engineering, and everyday applications.
- Consistency: The adoption of the SI system has helped to promote consistency and accuracy in measurements across different fields and industries.
- Updates: The SI system continues to be updated and refined to ensure its relevance and effectiveness in modern measurement practices.
5 kilometres are equal to- a)5,00,000 metre
- b)50,000 metre
- c)5000 metre
- d)500 metre
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
5 kilometres are equal to
a)
5,00,000 metre
b)
50,000 metre
c)
5000 metre
d)
500 metre

|
Get Idea answered |
Conversion of Kilometres to Metres:
- 1 kilometre = 1000 metres
- 5 kilometres = 5 * 1000 = 5000 metres
Explanation:
- When converting kilometres to metres, we need to multiply the number of kilometres by 1000 because 1 kilometre is equal to 1000 metres.
- Therefore, 5 kilometres is equal to 5 * 1000 = 5000 metres.
Correct Answer:
- C: 5000 metre
Therefore, the correct answer is option C: 5000 metre.
Jake has three cups of tea every day but he never drinks an entire cup. On average he throws away 25 millilitres each cup. Approximately how much tea does he waste in a calendar month consisting of 30 days?- a) 75 ml
- b) 750 ml
- c) 1.25 litres
- d) 2.25 litres
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
75 ml
b)
750 ml
c)
1.25 litres
d)
2.25 litres
|
|
C K Academy answered |
3 (cups) x 30 (days) x 25 (ml waste) = 2,250 millilitres or 2.25 litres
A pendulum swings backwards and forwards passing through Y, middle point of the oscillation. The first time the pendulum passes through Y, a stopwatch is started. 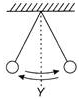 The twenty-first time the pendulum pass through Y, the stopwatch is stopped. The reading is T. What is the time period of the pendulum?
The twenty-first time the pendulum pass through Y, the stopwatch is stopped. The reading is T. What is the time period of the pendulum? - a)T/40
- b)T/21
- c)T/20
- d)T/10
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A pendulum swings backwards and forwards passing through Y, middle point of the oscillation. The first time the pendulum passes through Y, a stopwatch is started.

The twenty-first time the pendulum pass through Y, the stopwatch is stopped. The reading is T. What is the time period of the pendulum?
a)
T/40
b)
T/21
c)
T/20
d)
T/10

|
Anagha Nambiar answered |
The time taken to complete one oscillation is called the time period of a pendulum.

Here the time period is the time taken to move from Y to B then back to A and then to Y. The reading of stopwatch = T Number of oscillations = 10

Here the time period is the time taken to move from Y to B then back to A and then to Y. The reading of stopwatch = T Number of oscillations = 10
∴ Time taken
= 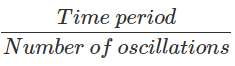 = T/10
= T/10
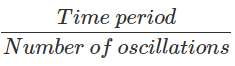 = T/10
= T/10Which unit is commonly used to measure distance?- a)Kilogram
- b)Meter
- c)Liter
- d)Second
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which unit is commonly used to measure distance?
a)
Kilogram
b)
Meter
c)
Liter
d)
Second

|
Focus Academy answered |
The meter (option B) is the SI unit for measuring distance or length. Kilogram (option A) is the SI unit for mass, liter (option C) is the SI unit for volume, and second (option D) is the SI unit for time.
Four pieces of wooden sticks P, Q, R and S are placed along the length of 15 cm long scale as shown in figure. What is the average length of these sticks? 
- a)2.0 cm
- b)2.5 cm
- c)2.6 cm
- d)2.9 cm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Four pieces of wooden sticks P, Q, R and S are placed along the length of 15 cm long scale as shown in figure. What is the average length of these sticks?

a)
2.0 cm
b)
2.5 cm
c)
2.6 cm
d)
2.9 cm

|
Pragati Das answered |
P = 2.1 cm; Q = 3.0 cm; R = 3.1 cm; S = 2.5 cm
Average length of these sticks
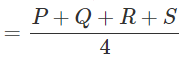
= 2.6cm
Average length of these sticks
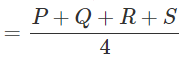
= 2.6cm
The height of a person is 1.65 m. Express it into cm and mm.- a)165 cm and 1650 mm
- b)165 cm and 165 mm
- c)160 cm and 1650 mm
- d)160 cm and 1600 mm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
165 cm and 1650 mm
b)
165 cm and 165 mm
c)
160 cm and 1650 mm
d)
160 cm and 1600 mm

|
Get Idea answered |
The height of 1.65 metres can be converted to 165 centimetres and 1650 millimetres. This is because 1 metre equals 100 centimetres and 1000 millimetres. Thus, 1.65 metres equals 165 centimetres and 1650 millimetres.
Chapter doubts & questions for Measuring motion - Year 8 Physics (Cambridge) 2025 is part of Class 8 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 8 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 8 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Measuring motion - Year 8 Physics (Cambridge) in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 8 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 8 Exam by signing up for free.
Year 8 Physics (Cambridge)
8 videos|39 docs|11 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









