All Exams >
SSS 2 >
Chemistry for SSS 2 >
All Questions
All questions of Periodic Table for SSS 2 Exam
Atomic number of the element which is surrounded by elements with atomic numbers 17, 34, 36 and 53 in the modern periodic table is- a)18
- b)35
- c)37
- d)52
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Atomic number of the element which is surrounded by elements with atomic numbers 17, 34, 36 and 53 in the modern periodic table is
a)
18
b)
35
c)
37
d)
52
|
|
Ashwin Saha answered |
The atomic number of an element represents the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element. In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. Based on the information given, we can determine the atomic number of the element surrounded by elements with atomic numbers 17, 34, 36, and 53.
Identify the elements:
- The atomic number 17 corresponds to chlorine (Cl).
- The atomic number 34 corresponds to selenium (Se).
- The atomic number 36 corresponds to krypton (Kr).
- The atomic number 53 corresponds to iodine (I).
Determine the missing element:
To find the missing element, we need to look for an element that fits between atomic numbers 34 and 36. The atomic number 35 corresponds to the element bromine (Br). Therefore, bromine is the element surrounded by elements with atomic numbers 17, 34, 36, and 53.
The correct answer is option 'B' (35).
Identify the elements:
- The atomic number 17 corresponds to chlorine (Cl).
- The atomic number 34 corresponds to selenium (Se).
- The atomic number 36 corresponds to krypton (Kr).
- The atomic number 53 corresponds to iodine (I).
Determine the missing element:
To find the missing element, we need to look for an element that fits between atomic numbers 34 and 36. The atomic number 35 corresponds to the element bromine (Br). Therefore, bromine is the element surrounded by elements with atomic numbers 17, 34, 36, and 53.
The correct answer is option 'B' (35).
What type of oxide would Eka-aluminium form?- a)EO3
- b)E2O3
- c)E3O2
- d)EO
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What type of oxide would Eka-aluminium form?
a)
EO3
b)
E2O3
c)
E3O2
d)
EO
|
|
Ashwini dubey answered |
Understanding Eka-Aluminium and Its Oxide Form
Eka-aluminium, known as Gallium (Ga), is a chemical element that belongs to the group of metals in the periodic table. It is important to understand how it reacts and what kind of oxides it forms.
Oxide Formation in Gallium
Gallium typically forms oxides in specific ratios, and the most common oxide it produces is Ga2O3.
Reason for the Answer (E2O3)
- Valency of Gallium:
- Gallium has a valency of +3, which means it can lose three electrons to form compounds.
- Combining with Oxygen:
- Oxygen typically has a valency of -2. To balance the charges, two Gallium atoms (each with a +3 charge) will combine with three oxygen atoms (each with a -2 charge).
- Chemical Formula Derivation:
- The ratio of Gallium to Oxygen in the oxide is thus 2:3, leading to the formula Ga2O3, which corresponds to option E2O3.
Other Options Explained
- EO3: This would imply a different valency not applicable to Gallium.
- E3O2: This would suggest a higher ratio of Gallium, which is not stable.
- EO: Represents a 1:1 ratio, which is also incorrect for Gallium.
Conclusion
Given the chemical properties and valency of Gallium, the oxide it forms is best represented by the formula E2O3, confirming option 'B' as the correct answer.
Eka-aluminium, known as Gallium (Ga), is a chemical element that belongs to the group of metals in the periodic table. It is important to understand how it reacts and what kind of oxides it forms.
Oxide Formation in Gallium
Gallium typically forms oxides in specific ratios, and the most common oxide it produces is Ga2O3.
Reason for the Answer (E2O3)
- Valency of Gallium:
- Gallium has a valency of +3, which means it can lose three electrons to form compounds.
- Combining with Oxygen:
- Oxygen typically has a valency of -2. To balance the charges, two Gallium atoms (each with a +3 charge) will combine with three oxygen atoms (each with a -2 charge).
- Chemical Formula Derivation:
- The ratio of Gallium to Oxygen in the oxide is thus 2:3, leading to the formula Ga2O3, which corresponds to option E2O3.
Other Options Explained
- EO3: This would imply a different valency not applicable to Gallium.
- E3O2: This would suggest a higher ratio of Gallium, which is not stable.
- EO: Represents a 1:1 ratio, which is also incorrect for Gallium.
Conclusion
Given the chemical properties and valency of Gallium, the oxide it forms is best represented by the formula E2O3, confirming option 'B' as the correct answer.
X and Y are two elements having similar properties which obey Newland’s Law of Octaves. The minimum and maximum number of elements in between X and Y, respectively are- a)6 and 13
- b)6 and 8
- c)7 and 15
- d)8 and 14
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
X and Y are two elements having similar properties which obey Newland’s Law of Octaves. The minimum and maximum number of elements in between X and Y, respectively are
a)
6 and 13
b)
6 and 8
c)
7 and 15
d)
8 and 14
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
X and Y are two elements having similar properties which obey Newlands’s Law of Octaves. The minimum and maximum number of elements in between X and Y respectively are 6 and 8.
Three elements B, Si and Ge are- a)metals
- b)non-metals
- c)metalloids
- d)metal, non-metal and metalloid, respectively
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Three elements B, Si and Ge are
a)
metals
b)
non-metals
c)
metalloids
d)
metal, non-metal and metalloid, respectively
|
|
Pranita mehta answered |
**Explanation:**
The elements B (Boron), Si (Silicon), and Ge (Germanium) are all located in Group 14 of the periodic table.
**1. Metalloids:**
Metalloids are elements that have properties of both metals and non-metals. They are located along the zigzag line on the periodic table, separating the metals from the non-metals.
**Boron (B):**
- Boron is a metalloid element.
- It is a non-metallic element that is typically brittle in its pure form.
- Boron is a poor conductor of electricity but can act as a semiconductor at high temperatures.
- It has properties of both metals and non-metals, making it a metalloid.
**Silicon (Si):**
- Silicon is a metalloid element.
- It is the second most abundant element in the Earth's crust and is widely used in the technology industry.
- Silicon has a shiny, metallic appearance but is a poor conductor of electricity at room temperature.
- It is used extensively in the production of computer chips and other electronic devices.
- Like boron, silicon has properties of both metals and non-metals, classifying it as a metalloid.
**Germanium (Ge):**
- Germanium is also a metalloid element.
- It has a similar shiny, metallic appearance to silicon.
- Germanium is a semiconductor and has useful electrical properties.
- It is used in transistors, solar cells, and other electronic applications.
- Similar to boron and silicon, germanium exhibits properties of both metals and non-metals, making it a metalloid.
Therefore, the correct answer is option **C) metalloids**, as all three elements B, Si, and Ge are metalloids.
The elements B (Boron), Si (Silicon), and Ge (Germanium) are all located in Group 14 of the periodic table.
**1. Metalloids:**
Metalloids are elements that have properties of both metals and non-metals. They are located along the zigzag line on the periodic table, separating the metals from the non-metals.
**Boron (B):**
- Boron is a metalloid element.
- It is a non-metallic element that is typically brittle in its pure form.
- Boron is a poor conductor of electricity but can act as a semiconductor at high temperatures.
- It has properties of both metals and non-metals, making it a metalloid.
**Silicon (Si):**
- Silicon is a metalloid element.
- It is the second most abundant element in the Earth's crust and is widely used in the technology industry.
- Silicon has a shiny, metallic appearance but is a poor conductor of electricity at room temperature.
- It is used extensively in the production of computer chips and other electronic devices.
- Like boron, silicon has properties of both metals and non-metals, classifying it as a metalloid.
**Germanium (Ge):**
- Germanium is also a metalloid element.
- It has a similar shiny, metallic appearance to silicon.
- Germanium is a semiconductor and has useful electrical properties.
- It is used in transistors, solar cells, and other electronic applications.
- Similar to boron and silicon, germanium exhibits properties of both metals and non-metals, making it a metalloid.
Therefore, the correct answer is option **C) metalloids**, as all three elements B, Si, and Ge are metalloids.
Which pair of atomic numbers represents elements in the same group?- a)6, 12
- b)11, 19
- c)4, 16
- d)8, 17
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which pair of atomic numbers represents elements in the same group?
a)
6, 12
b)
11, 19
c)
4, 16
d)
8, 17
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
The difference between atomic numbers is 8.
Which of the following elements will form an acidic oxide?- a)An element with atomic number 3
- b)An element with atomic number 7
- c)An element with atomic number 12
- d)A element with atomic number 19
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following elements will form an acidic oxide?
a)
An element with atomic number 3
b)
An element with atomic number 7
c)
An element with atomic number 12
d)
A element with atomic number 19
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Metallic character increases down a group and decreases along a period. Thus, metallic character increases in the order: Be, Mg, Ca.
Elements A, B and C Constitute a Dobereiner’s triad. If the atomic mass of element A is 7 and that of element C is 39, then what is the atomic mass of element B?- a)23
- b)46
- c)22
- d)32
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Elements A, B and C Constitute a Dobereiner’s triad. If the atomic mass of element A is 7 and that of element C is 39, then what is the atomic mass of element B?
a)
23
b)
46
c)
22
d)
32
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
A, B and C are the elements of a Dobereiner's triad. If the atomic masses of A and C are 7 and 39 respectively, then according to Dobereiner's triad law, the atomic mass of B is the average of the atomic masses of A and C.
So, the average of the atomic masses of A and C
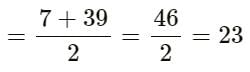
Therefore, the atomic mass of B is 23.
So, the average of the atomic masses of A and C
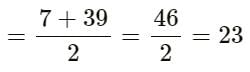
Therefore, the atomic mass of B is 23.
An element which is an essential constituent of all organic compounds belongs to- a)Group 1
- b)Group 2
- c)Group 14
- d)Group 15
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An element which is an essential constituent of all organic compounds belongs to
a)
Group 1
b)
Group 2
c)
Group 14
d)
Group 15
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
The essential constituent of all organic matter is carbon which belongs to group 17.
Where would you locate the element with electronic configuration 2, 8 in the modern period table?- a)Group 2
- b)Group 8
- c)Group 10
- d)Group 18
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Where would you locate the element with electronic configuration 2, 8 in the modern period table?
a)
Group 2
b)
Group 8
c)
Group 10
d)
Group 18
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Elements with electronic configuration (2, 8) is an inert gas i.e., neon and hence belongs to group 18.
Which of the given element A, B, C, D and E with atomic numbers 2, 3, 7, 10 and 30, respectively belong to the same period?- a)A, B, C
- b)B, C, D
- c)A, D, E
- d)B, D, E
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the given element A, B, C, D and E with atomic numbers 2, 3, 7, 10 and 30, respectively belong to the same period?
a)
A, B, C
b)
B, C, D
c)
A, D, E
d)
B, D, E
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
2nd period contains elements with atomic numbers 3 (Li), 7 (N) 10 (Ne).
Which of the following does not increase while moving down the group of the periodic table?- a)Atomic radius
- b)Valence
- c)Metallic character
- d)Number of shells in on element
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following does not increase while moving down the group of the periodic table?
a)
Atomic radius
b)
Valence
c)
Metallic character
d)
Number of shells in on element
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
In a group valency of all elements is fixed because of having the same outer shell electronic configuration while all the remaining three properties increase down the group.
Which one of the following elements exhibit maximum number of valence electrons?- a)Na
- b)P
- c)Al
- d)Si
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following elements exhibit maximum number of valence electrons?
a)
Na
b)
P
c)
Al
d)
Si
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
- Electronic configuration of Na, Al, Si and P are 2, 8 1, 2, 8, 3, 2, 8, 4, and 2, 8, 5 respectively.
- Valence electrons in Na, Al, Si and P are 1,3,4 and 5.
- Hence phosphorus has maximum number of valence electrons.
The elements A, B, C, D and E have atomic number 9, 11, 17, 12 and 13 respectively. Which pair of elements belong to the same group?- a)A and C
- b)A and D
- c)A and E
- d)B and D
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The elements A, B, C, D and E have atomic number 9, 11, 17, 12 and 13 respectively. Which pair of elements belong to the same group?
a)
A and C
b)
A and D
c)
A and E
d)
B and D
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Let us take a look at the electronic configurations of the given elements,
A: (2, 7)
B: (2, 8, 1)
C: (2, 8, 7)
D: (2, 8, 2)
E: (2, 8, 3)
We can see that elements A and C both have 7 valence electrons. Thus, both the elements belong to the same group.
So, the correct option is A.
A: (2, 7)
B: (2, 8, 1)
C: (2, 8, 7)
D: (2, 8, 2)
E: (2, 8, 3)
We can see that elements A and C both have 7 valence electrons. Thus, both the elements belong to the same group.
So, the correct option is A.
The element with atomic number 14 is hard and forms acidic oxide and a covalent halide. To which of the following categories does the element belong?- a)Metal
- b)Non-metal
- c)Metalloid
- d)Left hand side element
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The element with atomic number 14 is hard and forms acidic oxide and a covalent halide. To which of the following categories does the element belong?
a)
Metal
b)
Non-metal
c)
Metalloid
d)
Left hand side element
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Since the element with atomic number 14 i.e., Si forms an acidic oxide and a covalent halide, it must be metalloid.
Which of the following elements would lose an electron easily?- a)Na
- b)Mg
- c)Ca
- d)K
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following elements would lose an electron easily?
a)
Na
b)
Mg
c)
Ca
d)
K
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
Larger the atomic radius of an element, more easily it can lose its valence electrons. K has the largest atomic radius, therefore it can lose on electron more easily.
The correct sequences of atomic radii is- a)Na > Mg > Al > Si
- b)Si >Al > Mg > Na
- c)Al > Si > Na > Mg
- d)Si > Al > Na > Mg
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct sequences of atomic radii is
a)
Na > Mg > Al > Si
b)
Si >Al > Mg > Na
c)
Al > Si > Na > Mg
d)
Si > Al > Na > Mg
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Within a period, atomic radii decrease from left to right.
Which of the following gives the correct increasing order of the atomic radii of O, F and N?- a)F, O, N
- b)O, F, N
- c)N, F, O
- d)O, N, F
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following gives the correct increasing order of the atomic radii of O, F and N?
a)
F, O, N
b)
O, F, N
c)
N, F, O
d)
O, N, F
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
Atomic radius decreases across a period because nuclear charges increase across a period. When the charge increases, the electrons are pulled towards the nucleus with greater force decreasing the size of the atomic radius. Hence Fluorine has the least radius as its atomic number is larger than oxygen and nitrogen. The same case is with oxygen, it has more number of positive charges than nitrogen. Hence nitrogen has the largest size than oxygen and then fluorine.
The two elements for which Mendeleev left blank places in his original periodic table were- a)Al, Ga
- b)As, Sb
- c)Ga, Ge
- d)Si, Ti
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The two elements for which Mendeleev left blank places in his original periodic table were
a)
Al, Ga
b)
As, Sb
c)
Ga, Ge
d)
Si, Ti
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
- Though only 63, elements were known at the time when Mendeleev started his work, he left some places vacant for elements to be discovered later.
- While developing his Periodic Table of the elements,he named aka-Aluminum to the element just below of Aluminium.
- Mendeleev gave the name eka-Aluminium to a compound which contains aluminium, a mixture of aluminium and an unknown element.
- The unknown element he predicted would have properties similar to those of aluminium and which have rare isotope of aluminium.
- It was later discovered as Gallium with an atomic weight of 68 and atomic number of 31.
- Germanium was named as Aka-Silicon first and was later discovered.
- Germanium has atomic number 32 and an atomic weight of 72.
Hence, Mendeleev left the gaps for the elements with predicted atomic weight 68 & 72 respectively are discovered later as Gallium & Germanium.
Which of the following elements does not lose an electrons easily?- a)Na
- b)Mg
- c)Al
- d)F
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following elements does not lose an electrons easily?
a)
Na
b)
Mg
c)
Al
d)
F
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
Elements of 2nd period have smaller size than those of the corresponding elements of the 3rd period. Further is a period, halogen has the smallest size. Among Na, F, Mg and Al, F has the smallest size and hence it does not lose an electron easily.
Which among the following is the most reactive halogen?- a)F
- b)Cl
- c)Br
- d)I
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is the most reactive halogen?
a)
F
b)
Cl
c)
Br
d)
I
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
Elements which differ in atomic numbers by 8 i.e., 9 (fluorine) and 17 (chlorine).
Arrange the following elements in the order of the their increasing non-metallic character Li, O, C, Be, F- a)F < O < C < Be < Li
- b)F < C < O < Be < Li
- c)Li < Be < C < O < F
- d)F < O < Be < C < Li
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following elements in the order of the their increasing non-metallic character Li, O, C, Be, F
a)
F < O < C < Be < Li
b)
F < C < O < Be < Li
c)
Li < Be < C < O < F
d)
F < O < Be < C < Li
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Non-metallic character increases from left to right in a period i.e., Li < Be < C < O < F.
Which of the following statement(s) about the modern periodic table are incorrect
(i) The elements in the modern periodic table are arranged on the basis of their decreasing atomic number.
(ii) Isotopes are placed in adjoining group(s) in the periodic table
(iii) The elements in the modern period table are arranged on the basis of their increasing atomic masses.
(iv) The elements in the modern periodic table are arranged on the basis of their increasing atomic number.- a)(i) only
- b)(iv) only
- c)(i), (ii) and (iii)
- d)(i), (ii), and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement(s) about the modern periodic table are incorrect
(i) The elements in the modern periodic table are arranged on the basis of their decreasing atomic number.
(ii) Isotopes are placed in adjoining group(s) in the periodic table
(iii) The elements in the modern period table are arranged on the basis of their increasing atomic masses.
(iv) The elements in the modern periodic table are arranged on the basis of their increasing atomic number.
(i) The elements in the modern periodic table are arranged on the basis of their decreasing atomic number.
(ii) Isotopes are placed in adjoining group(s) in the periodic table
(iii) The elements in the modern period table are arranged on the basis of their increasing atomic masses.
(iv) The elements in the modern periodic table are arranged on the basis of their increasing atomic number.
a)
(i) only
b)
(iv) only
c)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
d)
(i), (ii), and (iv)
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
Elements in the Modern Periodic Table are arranged based on their increasing atomic number hence option (i) is wrong. In the modern periodic table atomic mass is not a criteria hence option (ii) is wrong. Isotopes are given the same position in the periodic table hence option (iii) is wrong.
Which of the following are the characteristics of isotopes of an element?
(i) Isotopes of an element have same atomic masses
(ii) Isotopes of an element have same atomic number
(iii) Isotopes of an element show same chemical properties
(iv) Isotopes of an element show same physical properties- a)(i) and (iv)
- b)(ii), (iii) and (iv)
- c)(ii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are the characteristics of isotopes of an element?
(i) Isotopes of an element have same atomic masses
(ii) Isotopes of an element have same atomic number
(iii) Isotopes of an element show same chemical properties
(iv) Isotopes of an element show same physical properties
(i) Isotopes of an element have same atomic masses
(ii) Isotopes of an element have same atomic number
(iii) Isotopes of an element show same chemical properties
(iv) Isotopes of an element show same physical properties
a)
(i) and (iv)
b)
(ii), (iii) and (iv)
c)
(ii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iii)
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
Isotopes of an element have same atomic number but different atomic masses. They show same chemical properties but different physical properties.
Chapter doubts & questions for Periodic Table - Chemistry for SSS 2 2025 is part of SSS 2 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the SSS 2 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for SSS 2 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Periodic Table - Chemistry for SSS 2 in English & Hindi are available as part of SSS 2 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSS 2 Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for SSS 2
2 videos|64 docs|19 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









