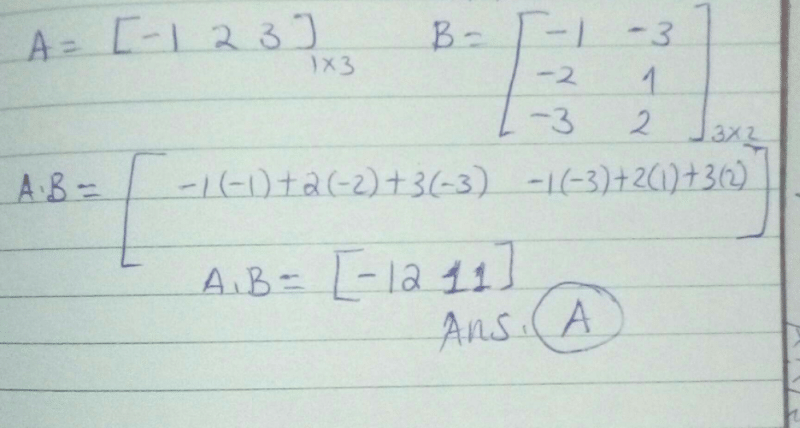All Exams >
JAMB >
Mathematics for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Matrices and Determinants for JAMB Exam
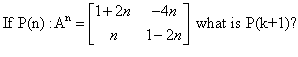
- a)
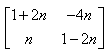
- b)
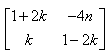
- c)
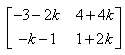
- d)
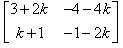
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
P(n) : An = {(1+2n, -4n), (n,(1 - 2n))}
= P(k + 1) = {(1+2(k+1), -4(k+1)), (k+1, (1 - 2(k+1)}
= {(1+2k+2, -4k-4) (k+1, 1-2k-2)}
= {(2k+3, -4k-4), (k+1, -2k-1)}
= P(k + 1) = {(1+2(k+1), -4(k+1)), (k+1, (1 - 2(k+1)}
= {(1+2k+2, -4k-4) (k+1, 1-2k-2)}
= {(2k+3, -4k-4), (k+1, -2k-1)}
If 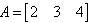 and
and 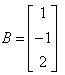 , then AB=?
, then AB=?- a)[7]
- b)[1 - 12]
- c)
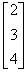
- d)[18]
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If 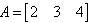 and
and 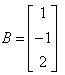 , then AB=?
, then AB=?
a)
[7]
b)
[1 - 12]
c)
d)
[18]
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
A = [2, 3, 4]
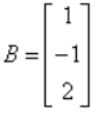 Therefore AXB = {(2*1) + (3*(-1)) + (4*2)}
Therefore AXB = {(2*1) + (3*(-1)) + (4*2)}
AXB = {2 + (-3) + 8}
AXB = 7
 Therefore AXB = {(2*1) + (3*(-1)) + (4*2)}
Therefore AXB = {(2*1) + (3*(-1)) + (4*2)}AXB = {2 + (-3) + 8}
AXB = 7
For a skew symmetric even ordered matrix A of integers, which of the following will not hold true:
- a)det(A) = 9
- b)det(A) = 81
- c)det(A) = 7
- d)det(A) = 4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For a skew symmetric even ordered matrix A of integers, which of the following will not hold true:
a)
det(A) = 9
b)
det(A) = 81
c)
det(A) = 7
d)
det(A) = 4
|
|
Aniket Dasgupta answered |
Skew Symmetric Even Ordered Matrix and Determinant
Skew Symmetric Matrix:
A skew symmetric matrix is a square matrix whose transpose is equal to its negative. In other words, if A is a skew symmetric matrix, then A^T = -A.
Example:
[0 -3 4]
[3 0 -5]
[-4 5 0]
This is a 3x3 skew symmetric matrix because A^T = -A.
Even Ordered Matrix:
An even ordered matrix is a square matrix whose order is even. In other words, if A is an even ordered matrix, then the order of A is 2n, where n is a positive integer.
Example:
[2 1 5 3]
[4 6 8 2]
[9 7 1 5]
[3 4 2 6]
This is a 4x4 even ordered matrix because the order of A is 2n=4.
Determinant of a Skew Symmetric Even Ordered Matrix:
The determinant of a skew symmetric even ordered matrix is always equal to zero. This is because the determinant of a skew symmetric matrix of odd order is always equal to zero and the determinant of any even ordered matrix can be expressed as a sum of permutations of the determinants of its n x n submatrices. Since the submatrices of a skew symmetric matrix are also skew symmetric, their determinants are equal to zero. Therefore, the determinant of a skew symmetric even ordered matrix is also equal to zero.
Solution:
a) det(A) = 9
Since the determinant of a skew symmetric even ordered matrix is always equal to zero, this statement is false. Therefore, option 'a' is not true.
b) det(A) = 81
Since the determinant of a skew symmetric even ordered matrix is always equal to zero, this statement is false. Therefore, option 'b' is not true.
c) det(A) = 7
This statement is false because the determinant of a skew symmetric even ordered matrix is always equal to zero.
d) det(A) = 4
Since the determinant of a skew symmetric even ordered matrix is always equal to zero, this statement is false. Therefore, option 'd' is not true.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'c'.
Skew Symmetric Matrix:
A skew symmetric matrix is a square matrix whose transpose is equal to its negative. In other words, if A is a skew symmetric matrix, then A^T = -A.
Example:
[0 -3 4]
[3 0 -5]
[-4 5 0]
This is a 3x3 skew symmetric matrix because A^T = -A.
Even Ordered Matrix:
An even ordered matrix is a square matrix whose order is even. In other words, if A is an even ordered matrix, then the order of A is 2n, where n is a positive integer.
Example:
[2 1 5 3]
[4 6 8 2]
[9 7 1 5]
[3 4 2 6]
This is a 4x4 even ordered matrix because the order of A is 2n=4.
Determinant of a Skew Symmetric Even Ordered Matrix:
The determinant of a skew symmetric even ordered matrix is always equal to zero. This is because the determinant of a skew symmetric matrix of odd order is always equal to zero and the determinant of any even ordered matrix can be expressed as a sum of permutations of the determinants of its n x n submatrices. Since the submatrices of a skew symmetric matrix are also skew symmetric, their determinants are equal to zero. Therefore, the determinant of a skew symmetric even ordered matrix is also equal to zero.
Solution:
a) det(A) = 9
Since the determinant of a skew symmetric even ordered matrix is always equal to zero, this statement is false. Therefore, option 'a' is not true.
b) det(A) = 81
Since the determinant of a skew symmetric even ordered matrix is always equal to zero, this statement is false. Therefore, option 'b' is not true.
c) det(A) = 7
This statement is false because the determinant of a skew symmetric even ordered matrix is always equal to zero.
d) det(A) = 4
Since the determinant of a skew symmetric even ordered matrix is always equal to zero, this statement is false. Therefore, option 'd' is not true.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'c'.
The product of two matrics 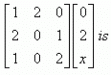
- a)
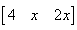
- b)
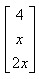
- c)
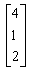
- d)
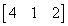
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The product of two matrics 
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
{(1*0, 2*2, 0*x) (2*0, 0*2, 1*x) (1*0, 0*2, 2*x)}
= {4, x, 2x}
= {4, x, 2x}
If A and B are two matrices conformable to multiplication such that their product AB = O(Zero matrix). Then which of the following can be true
- a)A and B are both null matrices
- b)Either of A is or B is a null matrix
- c)Either of them may be a zero matrix
- d)It is Not necessary that A = 0 or B = 0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If A and B are two matrices conformable to multiplication such that their product AB = O(Zero matrix). Then which of the following can be true
a)
A and B are both null matrices
b)
Either of A is or B is a null matrix
c)
Either of them may be a zero matrix
d)
It is Not necessary that A = 0 or B = 0
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
AB = 0 does not necessarily imply that either A or B is a null matrix
- Both matrices need not be null matrices.
- Both matrices need not be null matrices.
If A is a matrix of order 1×3 and B is a matrix of order 3×4, then order of the matrix obtained on multiplying A and B is- a)3×3
- b)4×1
- c)3×4
- d)1×4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If A is a matrix of order 1×3 and B is a matrix of order 3×4, then order of the matrix obtained on multiplying A and B is
a)
3×3
b)
4×1
c)
3×4
d)
1×4
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
In matrix 1*3 is one row and 3 columns and in 3*4 is three rows and four column hence multiplied matrix will be 1*4.
If 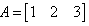 and
and 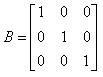 then AB = ?
then AB = ?
- a)[0]
- b)B
- c)
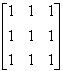
- d)A
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If 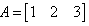 and
and 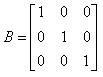 then AB = ?
then AB = ?
a)
[0]
b)
B
c)
d)
A

|
Tannya Tripathi answered |
By using multiplication of matrices, we know that no of columns of A should be equal to no of rows of B. so the order of matrix AB is1*1. here B is a identity matrix . and any matrix multiplied to identity matrix I is the matrix itself. hence AB=A.
Value of determinant is computed by adding multiples of one row to- a)another dimension
- b)another row
- c)another column
- d)another matrix
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Value of determinant is computed by adding multiples of one row to
a)
another dimension
b)
another row
c)
another column
d)
another matrix
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
Value of Determinant remains unchanged if we add equal multiples of all the elements of row (column) to corresponding elements of another row (column) If, we have a given matrix A.
If A, B are, respectively m × n, k × l matrices, then both AB and BA are defined if and only if - a)n = m , k = m
- b)m = l , n= l
- c)m = n, k = l
- d)n = k and l = m.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If A, B are, respectively m × n, k × l matrices, then both AB and BA are defined if and only if
a)
n = m , k = m
b)
m = l , n= l
c)
m = n, k = l
d)
n = k and l = m.
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
If A, B are, respectively m × n, k × l matrices, then both AB and BA are defined if and only if n = k and l = m. In particular, if both A and B are square matrices of the same order, then both AB and BA are defined.
If 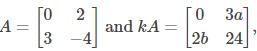 then the values of k, a and b respectively are
then the values of k, a and b respectively are- a)-6, -12, -18
- b)-6, -4, -9
- c)-6, 4, 9
- d)-6, 12, 18
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If 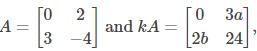 then the values of k, a and b respectively are
then the values of k, a and b respectively are
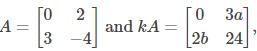 then the values of k, a and b respectively are
then the values of k, a and b respectively area)
-6, -12, -18
b)
-6, -4, -9
c)
-6, 4, 9
d)
-6, 12, 18

|
Sun Ray Institute answered |
Given,
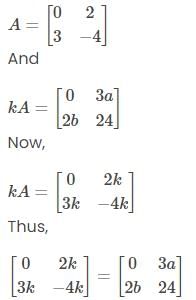
By equating the corresponding elements,
-4k = 24
k = -6
Also, 2k = 3a
2(-6) = 3a
3a = -12
a = -4
And
3k = 2b
3(-6) = 2b
2b = -18
b = -9
Therefore, k = -6, a = -4, and b = -9.
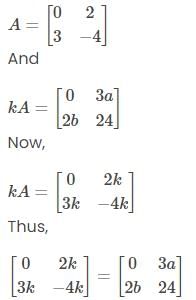
By equating the corresponding elements,
-4k = 24
k = -6
Also, 2k = 3a
2(-6) = 3a
3a = -12
a = -4
And
3k = 2b
3(-6) = 2b
2b = -18
b = -9
Therefore, k = -6, a = -4, and b = -9.
If A and B are symmetric matrices of the same order, then (AB′ –BA′) is a- a)Skew symmetric matrix
- b)Null matrix
- c)Symmetric matrix
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If A and B are symmetric matrices of the same order, then (AB′ –BA′) is a
a)
Skew symmetric matrix
b)
Null matrix
c)
Symmetric matrix
d)
None of these

|
Sun Ray Institute answered |
Given that A and B are symmetric matrices of the same order.
Let’s find the transpose of (AB′ –BA′).
(AB′ –BA′)′ = (AB′)′ – (BA′)′
= (BA′ – AB′)
= – (AB′ –BA′)
As (AB′ –BA′)′ = – (AB′ –BA′), the matrix (AB′ –BA′) is skew symmetric.
Let’s find the transpose of (AB′ –BA′).
(AB′ –BA′)′ = (AB′)′ – (BA′)′
= (BA′ – AB′)
= – (AB′ –BA′)
As (AB′ –BA′)′ = – (AB′ –BA′), the matrix (AB′ –BA′) is skew symmetric.
If A = [aij] is a square matrix of order 2 such that aij = 1, when i ≠ j and aij = 0, when i = j, then A2 is- a)
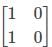
- b)
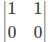
- c)
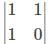
- d)
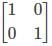
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If A = [aij] is a square matrix of order 2 such that aij = 1, when i ≠ j and aij = 0, when i = j, then A2 is
a)
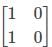
b)

c)
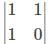
d)
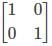

|
Sun Ray Institute answered |
Given,
A = [aij] is a square matrix of order 2 such that aij = 1, when i ≠ j and aij = 0, when i = j.
So, a11 = 0, a12 = 1, a21 = 1 and a22 = 0.
Thus,
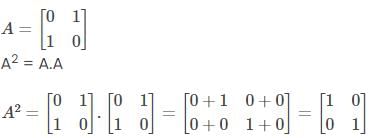
A = [aij] is a square matrix of order 2 such that aij = 1, when i ≠ j and aij = 0, when i = j.
So, a11 = 0, a12 = 1, a21 = 1 and a22 = 0.
Thus,
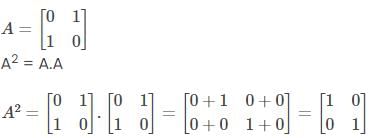
If 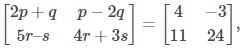 then the value of p + q - r + 2s is
then the value of p + q - r + 2s is- a)8
- b)10
- c)4
- d)-8
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If 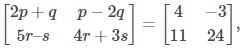 then the value of p + q - r + 2s is
then the value of p + q - r + 2s is
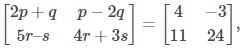 then the value of p + q - r + 2s is
then the value of p + q - r + 2s isa)
8
b)
10
c)
4
d)
-8

|
Sun Ray Institute answered |
Given,
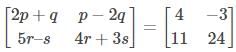
Now, by equating the corresponding elements of these two matrices, we get;
2p + q = 4….(1)
p – 2q = -3….(2)
5r – s = 11….(3)
4r + 3s = 24….(4)
By equ (1) × 2 + equ (2), we get;
4p + 2q + p – 2q = 8 – 3
5p = 5
p = 1
Substituting p = 1 in (1),
2 + q = 4
q = 4 – 2 = 2
By equ (3) × 3 + equ (4), we get;
15r – 3s + 4r + 3s = 33 + 24
19r = 57
r = 3
Substituting r = 3 in (3),
15 – s = 11
s = 15 – 11 = 4
Now,
p + q – r + 2s = 1 + 2 – 3 + 2(4) = 8
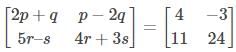
Now, by equating the corresponding elements of these two matrices, we get;
2p + q = 4….(1)
p – 2q = -3….(2)
5r – s = 11….(3)
4r + 3s = 24….(4)
By equ (1) × 2 + equ (2), we get;
4p + 2q + p – 2q = 8 – 3
5p = 5
p = 1
Substituting p = 1 in (1),
2 + q = 4
q = 4 – 2 = 2
By equ (3) × 3 + equ (4), we get;
15r – 3s + 4r + 3s = 33 + 24
19r = 57
r = 3
Substituting r = 3 in (3),
15 – s = 11
s = 15 – 11 = 4
Now,
p + q – r + 2s = 1 + 2 – 3 + 2(4) = 8
If A and B are two matrices of the order 3 × m and 3 × n, respectively, and m = n, then the order of matrix (5A – 2B) is- a)m × 3
- b)3 × 3
- c)m × n
- d)3 × n
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If A and B are two matrices of the order 3 × m and 3 × n, respectively, and m = n, then the order of matrix (5A – 2B) is
a)
m × 3
b)
3 × 3
c)
m × n
d)
3 × n

|
Sun Ray Institute answered |
Given that, the order of matrix A is 3 × m, and the order of B is 3 × n.
Also, m = n.
So, the order of matrix A and B is the same, i.e. 3 × m.
Thus, subtraction of matrices is possible and (5A – 3B) also has the same order, i.e. 3 × n.
Also, m = n.
So, the order of matrix A and B is the same, i.e. 3 × m.
Thus, subtraction of matrices is possible and (5A – 3B) also has the same order, i.e. 3 × n.
For any two matrices A and B, we have- a)AB = BA
- b)AB ≠ BA
- c)AB = O
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For any two matrices A and B, we have
a)
AB = BA
b)
AB ≠ BA
c)
AB = O
d)
None of the above

|
Sun Ray Institute answered |
For any two matrices A and B,
AB = BA and AB ≠ BA are not valid unless they follow the condition of matrix multiplication.
Also, AB = O is not true in all cases.
AB = BA and AB ≠ BA are not valid unless they follow the condition of matrix multiplication.
Also, AB = O is not true in all cases.
Total number of possible matrices of order 3 × 3 with each entry 2 or 0 is- a)9
- b)27
- c)81
- d)512
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Total number of possible matrices of order 3 × 3 with each entry 2 or 0 is
a)
9
b)
27
c)
81
d)
512

|
Sun Ray Institute answered |
We know that a matrix 3 × 3 contains 9 elements.
Given that each entry of this 3 × 3 matrix is either 0 or 2.
Thus, by simple counting principle, we can calculate the total number of possible matrices as:
Total number of possible matrices = Total number of ways in which 9 elements can take possible values
= 29
= 512
Given that each entry of this 3 × 3 matrix is either 0 or 2.
Thus, by simple counting principle, we can calculate the total number of possible matrices as:
Total number of possible matrices = Total number of ways in which 9 elements can take possible values
= 29
= 512
The Matrix  is a
is a- a)identity matrix
- b)symmetric matrix
- c)skew symmetric matrix
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The Matrix  is a
is a
 is a
is aa)
identity matrix
b)
symmetric matrix
c)
skew symmetric matrix
d)
none of these

|
Sun Ray Institute answered |
Let the given matrix be:
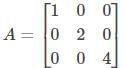
Let us find the transpose of A.
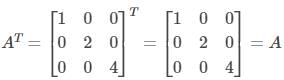
Therefore, A is a symmetric matrix.
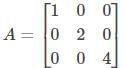
Let us find the transpose of A.
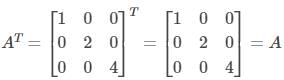
Therefore, A is a symmetric matrix.
If A is a skew-symmetric matrix, then A2 is a- a)Skew symmetric matrix
- b)Symmetric matrix
- c)Null matrix
- d)Cannot be determined
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If A is a skew-symmetric matrix, then A2 is a
a)
Skew symmetric matrix
b)
Symmetric matrix
c)
Null matrix
d)
Cannot be determined

|
Sun Ray Institute answered |
Given that A is a skew-symmetric matrix, so A′ = -A.
Consider the transpose of A2.
(A2)′ = (AA)′
= A′A′
=(-A)(-A)
= A2
⇒ (A2)′ = A2
Therefore, A2 is a symmetric matrix.
Consider the transpose of A2.
(A2)′ = (AA)′
= A′A′
=(-A)(-A)
= A2
⇒ (A2)′ = A2
Therefore, A2 is a symmetric matrix.
If A is a square matrix such that A2 = A, then (I – A)3 + A is equal to- a)I
- b)0
- c)I – A
- d)I + A
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If A is a square matrix such that A2 = A, then (I – A)3 + A is equal to
a)
I
b)
0
c)
I – A
d)
I + A

|
Sun Ray Institute answered |
Given that, A is a square matrix and A2 = A.
Consider (I + A)3, where I is the identity matrix.
Using the identity of (a + b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3ab (a + b), we get;
(I + A)3 = I3 + A3 + 3A2I + 3AI2
= I + A2(A) + 3AI + 3A
= I + A2 + 3A + 3A
= 7A + I {since it is given that A2 = A}
So, (I + A)3 = 7A + I….(1)
Now,
(I + A)3 – 7A = 7A + I – 7A [From (1)]
= I
Consider (I + A)3, where I is the identity matrix.
Using the identity of (a + b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3ab (a + b), we get;
(I + A)3 = I3 + A3 + 3A2I + 3AI2
= I + A2(A) + 3AI + 3A
= I + A2 + 3A + 3A
= 7A + I {since it is given that A2 = A}
So, (I + A)3 = 7A + I….(1)
Now,
(I + A)3 – 7A = 7A + I – 7A [From (1)]
= I
Chapter doubts & questions for Matrices and Determinants - Mathematics for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Matrices and Determinants - Mathematics for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Mathematics for JAMB
134 videos|94 docs|102 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup