All Exams >
JAMB >
Biology for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Support & Movement in Animals for JAMB Exam
Pick out the correct match.- a)Pelvis = 3 bones
- b)Sternum = 14 bones
- c)Ribs = 20 bones
- d)Face = 5 bones
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Pick out the correct match.
a)
Pelvis = 3 bones
b)
Sternum = 14 bones
c)
Ribs = 20 bones
d)
Face = 5 bones
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The pelvic girdle, as above, is made up of three fused bones: the ischium, the ilium, and the pubis. The pubis forms the anterior part of the pelvic girdle. It is a flattened, irregular-shaped bone that articulates with the pubic symphysis, a cartilaginous joint.
A sesamoid bone is- a)Palatine
- b)Patella
- c)Pterygoid
- d)Presphenoid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A sesamoid bone is
a)
Palatine
b)
Patella
c)
Pterygoid
d)
Presphenoid
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Patella is the small bone in knee joint between femur and tibia. It is a sesamoid bone developed in the tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle.
Which of the following facial bones is unpaired?- a)Nasal
- b)Vomer
- c)Palatine
- d)Lacrimal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following facial bones is unpaired?
a)
Nasal
b)
Vomer
c)
Palatine
d)
Lacrimal
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
The unpaired bones of the human skull are: frontal, occipital, ethmoid, sphenoid, mandible and vomer. The frontal bone is self explanatory in name.
Which of the following statements about the mechanism of muscle contraction are correct?A. Acetylcholine is released when the neural signal reaches the motor end plate.B. Muscle contraction is initiated by a signal sent by CNS via a sensory neuron.C. During muscle contraction, the isotropic band gets elongated.D. Repeated activation of the muscle can lead to accumulation of lactic acid.- a)B and C are correct.
- b)A and D are correct.
- c)A, Band C are correct.
- d)A and C are correct.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about the mechanism of muscle contraction are correct?
A. Acetylcholine is released when the neural signal reaches the motor end plate.
B. Muscle contraction is initiated by a signal sent by CNS via a sensory neuron.
C. During muscle contraction, the isotropic band gets elongated.
D. Repeated activation of the muscle can lead to accumulation of lactic acid.
a)
B and C are correct.
b)
A and D are correct.
c)
A, Band C are correct.
d)
A and C are correct.
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Following are the correct statements about the mechanism of muscle contraction:
(i) Acetylcholine is released when the neural signal reaches the motor end plate.
(ii) Repeated activation of the muscles can lead to lactic acid accumulation.
So, the correct answer is (B).
(i) Acetylcholine is released when the neural signal reaches the motor end plate.
(ii) Repeated activation of the muscles can lead to lactic acid accumulation.
So, the correct answer is (B).
The contractile unit of muscle is a part of myofibril between- a)A band and I band
- b)Z line and Z line
- c)Z line and A band
- d)Z line and I band
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The contractile unit of muscle is a part of myofibril between
a)
A band and I band
b)
Z line and Z line
c)
Z line and A band
d)
Z line and I band
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
The region between two Z lines is called a sarcomere; sarcomeres can be considered the primary structural and functional unit of muscle tissue. Ultrastructure of a group of myofibrils, showing the sarcoplasmic reticulum and transverse tubules, which constitute the two membrane systems within a muscle fibre.
ATPase enzyme needed for muscle contraction is located in- a)Myosin
- b)Actin
- c)Troponin
- d)Actinin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
ATPase enzyme needed for muscle contraction is located in
a)
Myosin
b)
Actin
c)
Troponin
d)
Actinin
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
During muscle contraction, hydrolysis of ATP into ADP and inorganic phosphate occurs. The energy released during the process raises the meromyosin head to a high-energy state. The enzyme myosin ATPase catalyses the reaction in the presence of Ca2+ and Mg2+.


Which one of the following is anatomically correct for the human body?- a)Cranial nerves: 10 pairs
- b)Floating ribs: 2 pairs
- c)Collar bones: 3 pairs
- d)Salivary glands: 1 pair
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is anatomically correct for the human body?
a)
Cranial nerves: 10 pairs
b)
Floating ribs: 2 pairs
c)
Collar bones: 3 pairs
d)
Salivary glands: 1 pair

|
Smrity answered |
Ya correct option is B in the rib cage of human body the floating ribs only 2 pairs .
Read the statements carefully and comment on them.
A. A bands of muscle fibre are dark and contain myosin.
B. I bands of muscle fibre are light and contain actin.
C. During muscle contraction, the A bands contract.
D. The part between two Z lines is called sarcomere.
E. The central part of the thin filament not overlapped by the thick filament is the H zone.
- a)A, C and E are correct, while B and D are incorrect.
- b)A, B and D are correct, while C and E are incorrect.
- c)A, B and C are correct, while D and E are incorrect.
- d)A and B are correct, while C, D and E are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the statements carefully and comment on them.
A. A bands of muscle fibre are dark and contain myosin.
B. I bands of muscle fibre are light and contain actin.
C. During muscle contraction, the A bands contract.
D. The part between two Z lines is called sarcomere.
E. The central part of the thin filament not overlapped by the thick filament is the H zone.
a)
A, C and E are correct, while B and D are incorrect.
b)
A, B and D are correct, while C and E are incorrect.
c)
A, B and C are correct, while D and E are incorrect.
d)
A and B are correct, while C, D and E are incorrect.

|
Arohi Shinde answered |
Statement E is correct
Which of the following is/are not correctly matched pairs?
(i) Ball and socket joint — Between humerus and pectoral girdle
(ii) Pivot joint — Between carpal and metacarpal
(iii) Saddle joint — Between atlas and axis
(iv) Gliding joint — Between the carpals
(v) Fibrous joint — In flat skull bones
- a)(ii) and (iii)
- b)(i) and (iv)
- c)(v) only
- d)(ii) only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are not correctly matched pairs?
(i) Ball and socket joint — Between humerus and pectoral girdle
(ii) Pivot joint — Between carpal and metacarpal
(iii) Saddle joint — Between atlas and axis
(iv) Gliding joint — Between the carpals
(v) Fibrous joint — In flat skull bones
(i) Ball and socket joint — Between humerus and pectoral girdle
(ii) Pivot joint — Between carpal and metacarpal
(iii) Saddle joint — Between atlas and axis
(iv) Gliding joint — Between the carpals
(v) Fibrous joint — In flat skull bones
a)
(ii) and (iii)
b)
(i) and (iv)
c)
(v) only
d)
(ii) only
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Pivot joint — between atlas and axis.
Saddle joint — between carpal and metacarpal.
Saddle joint — between carpal and metacarpal.
Which one of the following membranes secretes a watery fluid that lubricates and cushions the joint?- a)Tendons
- b)Synovial membrane
- c)Ligaments
- d)Cartilage
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following membranes secretes a watery fluid that lubricates and cushions the joint?
a)
Tendons
b)
Synovial membrane
c)
Ligaments
d)
Cartilage
|
|
DSP answered |
Synovial membrane present in synovial joints secrere synovial fluid
The joints between the carpal bones are- a)gliding joints
- b)hinge joints
- c)saddle joints
- d)pivot joints
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The joints between the carpal bones are
a)
gliding joints
b)
hinge joints
c)
saddle joints
d)
pivot joints
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Joints between carpal bones are gliding joints. A gliding joint is a type of synovial joint whose articular surface is usually flat, permitting only back-and-forth and side-to-side movements.
The pectoral girdle is constituted by- a)Ilium and ischium
- b)Radius and ulna
- c)Maxilla and mandible
- d)Scapula and clavicle
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The pectoral girdle is constituted by
a)
Ilium and ischium
b)
Radius and ulna
c)
Maxilla and mandible
d)
Scapula and clavicle
|
|
Prerna Basu answered |
The correct answer is option 'D': Scapula and clavicle.
The pectoral girdle, also known as the shoulder girdle, is the skeletal framework that connects the upper limbs (arms) to the axial skeleton. It consists of two main bones: the scapula (shoulder blade) and the clavicle (collarbone). Let's discuss these bones in more detail:
Scapula:
The scapula is a large, flat triangular bone located on the back of the shoulder. It is commonly referred to as the shoulder blade. The scapula has several important features, including:
1. Spine: The spine of the scapula is a prominent ridge that runs diagonally across the posterior surface of the bone. It serves as an attachment site for muscles and ligaments.
2. Acromion process: The acromion process is a bony projection that extends from the top of the scapula. It forms the outer edge of the shoulder and articulates with the clavicle.
3. Glenoid cavity: The glenoid cavity is a shallow, socket-like structure on the lateral aspect of the scapula. It is the point of articulation with the head of the humerus, forming the shoulder joint.
Clavicle:
The clavicle is a long, S-shaped bone that connects the sternum (breastbone) to the scapula. It is positioned horizontally above the first rib and acts as a strut between the arm and the axial skeleton. The clavicle has several important landmarks, including:
1. Sternal end: The sternal end of the clavicle is the medial (closer to the midline of the body) portion that articulates with the sternum.
2. Acromial end: The acromial end of the clavicle is the lateral (further from the midline of the body) portion that articulates with the acromion process of the scapula.
Functions of the Pectoral Girdle:
The pectoral girdle serves several important functions, including:
1. Support: It provides support and stability to the upper limbs, allowing for the wide range of motion of the arms.
2. Muscle attachment: The pectoral girdle serves as an attachment site for various muscles that move the arms and shoulders.
3. Protection: It helps protect vital structures, such as the brachial plexus (nerves) and blood vessels that pass through the shoulder region.
In conclusion, the pectoral girdle is constituted by the scapula and clavicle. These bones provide support, stability, and mobility to the upper limbs, allowing for various arm and shoulder movements.
The pectoral girdle, also known as the shoulder girdle, is the skeletal framework that connects the upper limbs (arms) to the axial skeleton. It consists of two main bones: the scapula (shoulder blade) and the clavicle (collarbone). Let's discuss these bones in more detail:
Scapula:
The scapula is a large, flat triangular bone located on the back of the shoulder. It is commonly referred to as the shoulder blade. The scapula has several important features, including:
1. Spine: The spine of the scapula is a prominent ridge that runs diagonally across the posterior surface of the bone. It serves as an attachment site for muscles and ligaments.
2. Acromion process: The acromion process is a bony projection that extends from the top of the scapula. It forms the outer edge of the shoulder and articulates with the clavicle.
3. Glenoid cavity: The glenoid cavity is a shallow, socket-like structure on the lateral aspect of the scapula. It is the point of articulation with the head of the humerus, forming the shoulder joint.
Clavicle:
The clavicle is a long, S-shaped bone that connects the sternum (breastbone) to the scapula. It is positioned horizontally above the first rib and acts as a strut between the arm and the axial skeleton. The clavicle has several important landmarks, including:
1. Sternal end: The sternal end of the clavicle is the medial (closer to the midline of the body) portion that articulates with the sternum.
2. Acromial end: The acromial end of the clavicle is the lateral (further from the midline of the body) portion that articulates with the acromion process of the scapula.
Functions of the Pectoral Girdle:
The pectoral girdle serves several important functions, including:
1. Support: It provides support and stability to the upper limbs, allowing for the wide range of motion of the arms.
2. Muscle attachment: The pectoral girdle serves as an attachment site for various muscles that move the arms and shoulders.
3. Protection: It helps protect vital structures, such as the brachial plexus (nerves) and blood vessels that pass through the shoulder region.
In conclusion, the pectoral girdle is constituted by the scapula and clavicle. These bones provide support, stability, and mobility to the upper limbs, allowing for various arm and shoulder movements.
The joint in which one of the two bones is fixed in its place and bears a peg like process over which the other bone rotates is called- a)hinge joint
- b)saddle joint
- c)pivot joint
- d)angular joint
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The joint in which one of the two bones is fixed in its place and bears a peg like process over which the other bone rotates is called
a)
hinge joint
b)
saddle joint
c)
pivot joint
d)
angular joint
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Pivot joint allows only a rotatory movement of one bone on the other, which remains stationary. A rounded end of one bone fits into a shallow pit of another bone. E.g., joint between atlas and axis vertebrae which enables the head to turn from side to side.
What is the name of joint between ribs and sternum?- a)Cartilaginous joint
- b)Angular joint
- c)Gliding joint
- d)Fibrous joints
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the name of joint between ribs and sternum?
a)
Cartilaginous joint
b)
Angular joint
c)
Gliding joint
d)
Fibrous joints
|
|
Dishani Khanna answered |
The name of the joint between ribs and sternum is a cartilaginous joint.
Which one of the following pairs of structures is correctly matched with their description?- a)Tibia and fibula — Both form parts of knee joint
- b)Joint between atlas and axis — Pivot joint
- c)Shoulder joint and elbow joint — Ball and socket type of joint
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs of structures is correctly matched with their description?
a)
Tibia and fibula — Both form parts of knee joint
b)
Joint between atlas and axis — Pivot joint
c)
Shoulder joint and elbow joint — Ball and socket type of joint
d)
None of these
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Only tibia connects to the femur to form the knee joint with the patella. Shoulder joint is of ball-and-socket type and elbow joint is a hinge joint.
Which one of the following is the correct description of a certain part of a normal human skeleton?- a)Parietal bone and the temporal bone of the skull are joined fibrous joint
- b)First vertebra is axis which articulates with the occipital condyles
- c)The 9th and 10th pairs of ribs are called the floating ribs
- d)Glenoid cavity is a depression to which the thigh bone articulates
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the correct description of a certain part of a normal human skeleton?
a)
Parietal bone and the temporal bone of the skull are joined fibrous joint
b)
First vertebra is axis which articulates with the occipital condyles
c)
The 9th and 10th pairs of ribs are called the floating ribs
d)
Glenoid cavity is a depression to which the thigh bone articulates
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Parietal bone and temporal bone of the skull are joined by fibrous joint (immovable joint). First cervical vertebra is atlas. The last two pairs (11th and 12th) of ribs are called flothing ribs. Glenoid cavity is a depression to which humaerus articulates.
The joint of radio-ulna with the upper arm is- a)hinge joint
- b)pivot joint
- c)socket joint
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The joint of radio-ulna with the upper arm is
a)
hinge joint
b)
pivot joint
c)
socket joint
d)
none of these
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The joint of radio-ulna with the upper arm is a hinge joint. This joint allows the movement only in a single plane.
Which of the following pairs is correctly matched?- a)Hinge joint - Between vertebrae
- b)Gliding joint - Between zygapo- physes of the successive vertebrae
- c)Cartilaginous joint - Skull bones
- d)Fibrous joint - Between phalanges.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pairs is correctly matched?
a)
Hinge joint - Between vertebrae
b)
Gliding joint - Between zygapo- physes of the successive vertebrae
c)
Cartilaginous joint - Skull bones
d)
Fibrous joint - Between phalanges.
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The gliding joint allows sliding movements of two bones over each other. The joint between zygapophyses of successive vertebrae is of this type.
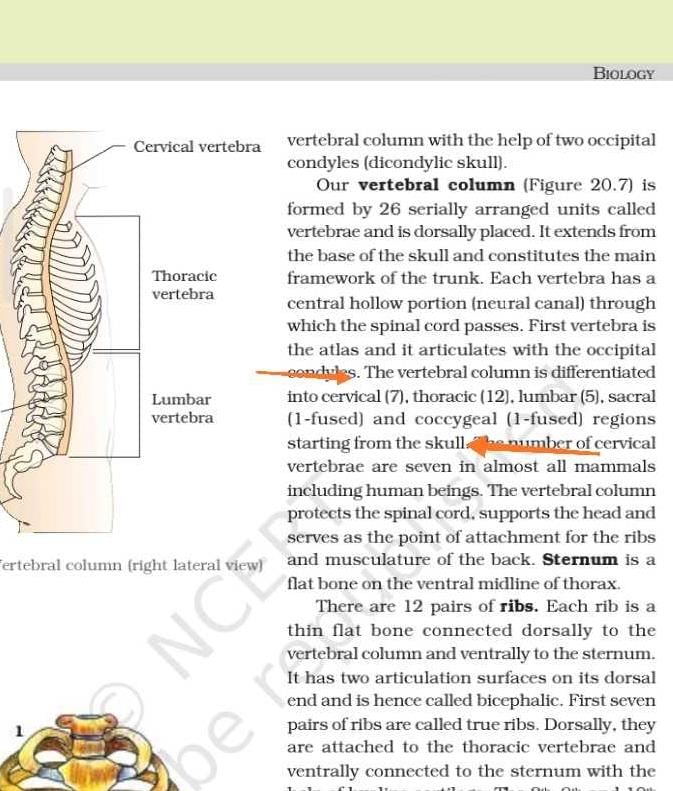
In the pelvic girdle of man, A B, C, D and E, respectively, represent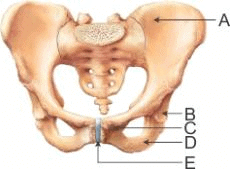
- a)A – Ischium, B – Acetabulum, C – Pubis, D – Ilium, E – Pubic symphysis
- b)A – Ilium, B – Pubis, C – Acetabulum, D – Pubic symphysis, E – Ischium
- c)A – Pubis, B – Acetabulum, C – Ilium, D – Ischium, E – Pubic symphysis
- d)A – Ilium, B – Acetabulum, C – Pubis, D – Ischium, E – Pubic symphysis
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the pelvic girdle of man, A B, C, D and E, respectively, represent
a)
A – Ischium, B – Acetabulum, C – Pubis, D – Ilium, E – Pubic symphysis
b)
A – Ilium, B – Pubis, C – Acetabulum, D – Pubic symphysis, E – Ischium
c)
A – Pubis, B – Acetabulum, C – Ilium, D – Ischium, E – Pubic symphysis
d)
A – Ilium, B – Acetabulum, C – Pubis, D – Ischium, E – Pubic symphysis

|
Aniket Chawla answered |
The pelvic girdle is made up of three fused bones that are ischium, ilium, and pubis. The pubis forms the anterior part of the pelvic girdle. It is a flattened, irregular- shaped bone that articulates with the pubic symphysis, a cartilaginous joint.
The acetabulum is a concave surface of the pelvis, the head of the femur meets the pelvis at the acetabulum to form the hip joint.Choose the pair of characteristics and example of a synovial joint in humans.
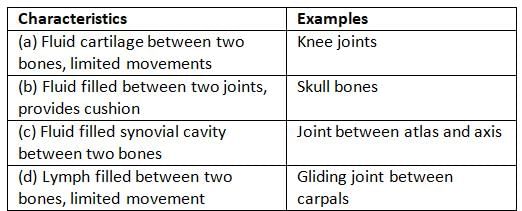
- a)(a)
- b)(b)
- c)(c)
- d)(d)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the pair of characteristics and example of a synovial joint in humans.


a)
(a)
b)
(b)
c)
(c)
d)
(d)

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Synovial joints are characterised by the presence of a fluid filled synovial cavity between the articulating surfaces of the two bones. These joints help in locomotion and many other movements. Ball and socket joint (between humerus and pectoral girdle), hinge joint (knee joint), pivot joint (between atlas and axis), gliding joint (between the carpals) and saddle joint (between carpal and metacarpal of thumb) are some examples.
What is a defining characteristic of synovial joints?- a) Connection via ligaments
- b) Presence of a fluid-filled synovial cavity
- c) Presence of cartilage
- d) Lack of movement
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is a defining characteristic of synovial joints?
a)
Connection via ligaments
b)
Presence of a fluid-filled synovial cavity
c)
Presence of cartilage
d)
Lack of movement

|
Bs Academy answered |
Synovial joints are characterized by the presence of a synovial cavity filled with synovial fluid, which allows for a greater range of motion.
Topic in NCERT: Joints
Line in NCERT: "synovial joints are characterised by the presence of a fluid filled synovial cavity between the articulating surfaces of the two bones."
Chapter doubts & questions for Support & Movement in Animals - Biology for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Support & Movement in Animals - Biology for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for JAMB
221 videos|172 docs|126 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup