All Exams >
JAMB >
Biology for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Evidence of Evolution for JAMB Exam
Which of the following organs in man is vestigial : [CPMT 77]- a)Pinna
- b)Wisdom tooth
- c)Fossa ovalis
- d)Ileum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following organs in man is vestigial : [CPMT 77]
a)
Pinna
b)
Wisdom tooth
c)
Fossa ovalis
d)
Ileum

|
Surya answered |
Vestigial organs means evidence for the evolution.. so as per the given option...wisdom teeth is the vestigial organ...so the option B is correct...
Dinosaurs originated : [CPMT 86]- a)After evolution of mammals
- b)With mammals
- c)Much before mammals
- d)Before mammals and they formed them
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Dinosaurs originated : [CPMT 86]
a)
After evolution of mammals
b)
With mammals
c)
Much before mammals
d)
Before mammals and they formed them
|
|
Siddiq Zayeda answered |
Mammals appeared on the earth long before the extinction of the dinosaurs; in fact, dinosaurs and mammals originated within 10 million years of each other, in the late Triassic about 200 million years ago.........
Fossils are most commonly preserved in______.- a)Sedimentary rocks
- b)Igneous rocks
- c)Metamorphic rocks
- d)Any type of rock
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Fossils are most commonly preserved in______.
a)
Sedimentary rocks
b)
Igneous rocks
c)
Metamorphic rocks
d)
Any type of rock

|
Prerana M N answered |
Sedimentary rocks are mostly involved in forming fossils, owing to the way in which they are formed.
Homologous organs have :[MP PMT 01]- a)Similar origin and similar or dissimilar functions
- b)Dissimilar origin and structure
- c)Dissimilar origin and function
- d)Dissimilar origin and similar functions
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Homologous organs have :
[MP PMT 01]
a)
Similar origin and similar or dissimilar functions
b)
Dissimilar origin and structure
c)
Dissimilar origin and function
d)
Dissimilar origin and similar functions
|
|
Afifa Aaliya answered |
Organs such as bats of wings, wings of birds, seals of flippers, arms of humans have common underlying anatomy. That was present in last common Ancestors. forelimbs are homologous organs. homology refers to the traits inherited by two different organisms from common ancestry. so it has similar origin and different or similar functions.
So option " A " is correct answer.
So option " A " is correct answer.
There are no life in which era :[CPMT 80]- a)Messozoic era
- b)Palaeozoic era
- c)Coenozoic era
- d)Azoic era
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
There are no life in which era :
[CPMT 80]
a)
Messozoic era
b)
Palaeozoic era
c)
Coenozoic era
d)
Azoic era
|
|
Ayeshashreya Mishra answered |
During Azoic era, the earth was with out plants and animals. The rock layers which were formed soon after azoic era contains the remains of limy sea plants.The word "Azoic" is derived from the Greek, a- meaning without and zoon meaning animal (or living being), it was first used to mean without life.....
An era ''age of birds and mammals'' is : [CPMT 93]- a)Mesozoic
- b)Palaecozoic
- c)Coenozoic
- d)Cretaceous
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An era ''age of birds and mammals'' is : [CPMT 93]
a)
Mesozoic
b)
Palaecozoic
c)
Coenozoic
d)
Cretaceous
|
|
Afifa Aaliya answered |
The Cenozoic era is the most recent of the three major sub division of the animal history. The other two are the Mesozoic and Peliozoic eras. The Cenozoic era only about 65 million years. From the end of the Cretaceous period and the extension of non avian dinosaurs to the present. The Cenozoic is sometimes called as age of mammals because the largest land animals have been mammals during that time.
So option " C " is correct answer.
So option " C " is correct answer.
Mortality in babies is an example of ______- a)Stabilizing selection
- b)Directional selection
- c)Disruptive selection
- d)Abortion selection
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mortality in babies is an example of ______
a)
Stabilizing selection
b)
Directional selection
c)
Disruptive selection
d)
Abortion selection

|
EduRev NEET answered |
- Mortality in babies is an example of stabilizing selection.
- It is all depended on the baby’s birth weight.
- The optimum birth weight is 7.3 pounds which favor this selection.
- Newborn infants with less than 5.5 pounds and more than 10 pounds have the highest mortality rate.
Links between organisms that show branching pattern of evolutionary relationships are shown by- a)Phylogenetic trees
- b)Living fossils
- c)Comparative embryology
- d)Two fossil layers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Links between organisms that show branching pattern of evolutionary relationships are shown by
a)
Phylogenetic trees
b)
Living fossils
c)
Comparative embryology
d)
Two fossil layers
|
|
Krithika Kumar answered |
Phylogenetic trees are diagrams that show the evolutionary relationships between different organisms. They are used to display the branching pattern of evolutionary relationships between organisms. The diagram looks like a tree with branches that represent different groups of organisms. These branches are called clades, and they represent groups of organisms that have descended from a common ancestor.
Phylogenetic trees are constructed based on a variety of data, including:
1. Morphological characteristics: The physical features of organisms, such as their shape, size, and structure.
2. Molecular data: DNA and RNA sequences are used to compare the genetic makeup of different organisms.
3. Fossil records: The study of fossils provides evidence of the evolutionary history of organisms.
Phylogenetic trees are an important tool for understanding the relationships between organisms and how they have evolved over time. They can be used to answer questions about the origins of different species and how they are related to one another.
In conclusion, phylogenetic trees are diagrams that show the branching pattern of evolutionary relationships between organisms. They are constructed based on a variety of data, including morphological characteristics, molecular data, and fossil records. They are an important tool for understanding the evolutionary history of organisms.
Phylogenetic trees are constructed based on a variety of data, including:
1. Morphological characteristics: The physical features of organisms, such as their shape, size, and structure.
2. Molecular data: DNA and RNA sequences are used to compare the genetic makeup of different organisms.
3. Fossil records: The study of fossils provides evidence of the evolutionary history of organisms.
Phylogenetic trees are an important tool for understanding the relationships between organisms and how they have evolved over time. They can be used to answer questions about the origins of different species and how they are related to one another.
In conclusion, phylogenetic trees are diagrams that show the branching pattern of evolutionary relationships between organisms. They are constructed based on a variety of data, including morphological characteristics, molecular data, and fossil records. They are an important tool for understanding the evolutionary history of organisms.
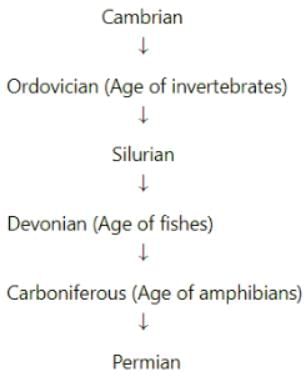
What is correct arrangement of periods of palaeozoic era in ascending order in geological time scale?- a)Cambrian → Devonian → Ordovician → Silurian → Carboniferous → Permian
- b)Cambrian → Ordovician → Silurian → Devonian → Carboniferous → Permian
- c)Cambrian → Ordovician Devonian → Silurian → Carboniferous → Permian
- d)Silurian → Devonian → Cambrian → Ordovician Permian → Carboniferous
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is correct arrangement of periods of palaeozoic era in ascending order in geological time scale?
a)
Cambrian → Devonian → Ordovician → Silurian → Carboniferous → Permian
b)
Cambrian → Ordovician → Silurian → Devonian → Carboniferous → Permian
c)
Cambrian → Ordovician Devonian → Silurian → Carboniferous → Permian
d)
Silurian → Devonian → Cambrian → Ordovician Permian → Carboniferous
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Palaezoic era is the era of ancient life and correct arrangement of periods in this era is:

Evolution of birds and mammals occurred in : [CPMT 83]- a)Eocene and oligocene periods
- b)Silurian and Devonian periods
- c)Carboniferous and Permain epochs
- d)Jurasic period
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Evolution of birds and mammals occurred in :
[CPMT 83]
a)
Eocene and oligocene periods
b)
Silurian and Devonian periods
c)
Carboniferous and Permain epochs
d)
Jurasic period
|
|
Baishali Joshi answered |
The evolution of birds and mammals occurred in Jurassic period. The earliest birds were derived from a clade of theropod dinosaurs named paraves. Mammals evolved 10 times faster in the middle of the Jurassic period.
If a starfish possess 6 arms instead of 5, it is an example of :[CPMT 84]- a)Variation
- b)Metamorphosis
- c)Biogenesis
- d)Evolution
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a starfish possess 6 arms instead of 5, it is an example of :
[CPMT 84]
a)
Variation
b)
Metamorphosis
c)
Biogenesis
d)
Evolution
|
|
Afifa Aaliya answered |
If a starfish possess 6 arms instead of 5 it's an example of variations. Because it is in difference between cells individual organisms of any species caused either genetic difference. Variations may show physical appearance, metabolism, fertility.., etc..,
So option " A " is correct answer.
So option " A " is correct answer.
The mesozoic era of earth is called the : [CPMT 84]- a)Age of amphibians
- b)Age of armoured fishes
- c)Age of primitive man
- d)Age of ruling reptiles
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The mesozoic era of earth is called the : [CPMT 84]
a)
Age of amphibians
b)
Age of armoured fishes
c)
Age of primitive man
d)
Age of ruling reptiles
|
|
Yamuna Mani answered |
Mesozoic era or middle life era is the life diversified rapidly and giant reptiles,dinosaurs and other monstrous beads roamed the earth. so it is called as age of reptiles era.
Branch of biology which deals with fossils :[CPMT 75]- a)Ethology
- b)Ecology
- c)Palaeontology
- d)Ormitholgoy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Branch of biology which deals with fossils :
[CPMT 75]
a)
Ethology
b)
Ecology
c)
Palaeontology
d)
Ormitholgoy
|
|
Debolina Chopra answered |
Palaeontology is the branch of biology that deals with fossils. Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of ancient organisms that provide valuable information about the history of life on Earth. Palaeontologists study fossils to understand the evolution, diversity, and ecological interactions of organisms that lived in the past.
1. Definition of Palaeontology:
Palaeontology is the scientific study of fossils, including their formation, identification, classification, and interpretation. It combines elements of biology, geology, and paleoecology to reconstruct the ancient history of life on Earth.
2. Importance of Fossils:
Fossils are crucial evidence for understanding the evolutionary processes that have shaped life on our planet. They provide insights into the anatomy, behavior, and ecology of extinct organisms, as well as the past environments in which they lived. Fossils also help in dating rock layers, determining ancient climate conditions, and documenting the history of biodiversity.
3. Scope of Palaeontology:
Palaeontology covers a wide range of topics, including:
- Taxonomy: Classifying and identifying fossil organisms.
- Morphology: Studying the structure and form of fossil remains.
- Phylogeny: Reconstructing the evolutionary relationships between different species.
- Paleobiology: Understanding the biology and behavior of extinct organisms.
- Paleoecology: Investigating ancient ecosystems and their interactions.
- Biostratigraphy: Using fossils to date and correlate rock layers.
- Taphonomy: Examining the processes that lead to fossilization.
4. Methods and Techniques:
Palaeontologists use various methods and techniques to study fossils, including:
- Excavation: Careful removal of fossils from their geological context.
- Preparation: Cleaning and preserving fossil specimens for further analysis.
- Comparative Anatomy: Comparing fossil remains with living organisms to infer their characteristics.
- Microscopy: Examining fossil structures at a microscopic level.
- Radiometric Dating: Using radioactive isotopes to determine the age of rocks and fossils.
- CT Scanning: Non-destructive imaging of fossils to reveal internal structures.
In conclusion, palaeontology is a branch of biology that focuses on the study of fossils. It plays a crucial role in understanding the history of life on Earth, providing insights into evolution, biodiversity, and ancient ecosystems.
1. Definition of Palaeontology:
Palaeontology is the scientific study of fossils, including their formation, identification, classification, and interpretation. It combines elements of biology, geology, and paleoecology to reconstruct the ancient history of life on Earth.
2. Importance of Fossils:
Fossils are crucial evidence for understanding the evolutionary processes that have shaped life on our planet. They provide insights into the anatomy, behavior, and ecology of extinct organisms, as well as the past environments in which they lived. Fossils also help in dating rock layers, determining ancient climate conditions, and documenting the history of biodiversity.
3. Scope of Palaeontology:
Palaeontology covers a wide range of topics, including:
- Taxonomy: Classifying and identifying fossil organisms.
- Morphology: Studying the structure and form of fossil remains.
- Phylogeny: Reconstructing the evolutionary relationships between different species.
- Paleobiology: Understanding the biology and behavior of extinct organisms.
- Paleoecology: Investigating ancient ecosystems and their interactions.
- Biostratigraphy: Using fossils to date and correlate rock layers.
- Taphonomy: Examining the processes that lead to fossilization.
4. Methods and Techniques:
Palaeontologists use various methods and techniques to study fossils, including:
- Excavation: Careful removal of fossils from their geological context.
- Preparation: Cleaning and preserving fossil specimens for further analysis.
- Comparative Anatomy: Comparing fossil remains with living organisms to infer their characteristics.
- Microscopy: Examining fossil structures at a microscopic level.
- Radiometric Dating: Using radioactive isotopes to determine the age of rocks and fossils.
- CT Scanning: Non-destructive imaging of fossils to reveal internal structures.
In conclusion, palaeontology is a branch of biology that focuses on the study of fossils. It plays a crucial role in understanding the history of life on Earth, providing insights into evolution, biodiversity, and ancient ecosystems.
Praying mantis is a good example of- a)Warning colouration
- b)Social insects
- c)Mullerianmimcry
- d)Camouflage
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Praying mantis is a good example of
a)
Warning colouration
b)
Social insects
c)
Mullerianmimcry
d)
Camouflage

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Camouflage is a method to avoid predators from praying by mixing with surroundings. Praying mantis is an example of camouflage.
Galapagos islands are connected with which scientist : [BHU 80]- a)Wallace
- b)Lamarck
- c)Malthus
- d)Darwin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Galapagos islands are connected with which scientist :
[BHU 80]
a)
Wallace
b)
Lamarck
c)
Malthus
d)
Darwin
|
|
Nayanika Patel answered |
The name of Charles Darwin and his famous book The Origin of Species will forever be linked with the Galapagos Islands. Although he was only in the Galapagos for five weeks in 1835, it was the wildlife that he saw there that inspired him to develop his Theory of Evolution.
Wings of locust, pigeon, and bat are example of :[CPMT 84]- a)Vestigial organs
- b)Analogous organs
- c)Homologous organs
- d)Evolution
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Wings of locust, pigeon, and bat are example of :
[CPMT 84]
a)
Vestigial organs
b)
Analogous organs
c)
Homologous organs
d)
Evolution
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
The organs which have different embryonic origin but perform same function are called as analogous organs, e.g., wings of bat and insects. The organs which have same embryonic origin but adapted to perform different functions are known as homologous organs, e.g., wing of bat and forelimb of humans.
Theory of evolution is mainly concerend with : [CPMT 73]- a)Spontaneous generation
- b)Theory of special creation
- c)Gradual change
- d)Conditions of environment
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Theory of evolution is mainly concerend with : [CPMT 73]
a)
Spontaneous generation
b)
Theory of special creation
c)
Gradual change
d)
Conditions of environment
|
|
Shalini Chauhan answered |
The Theory of Evolution
The theory of evolution is a fundamental concept in biology that explains the diversity of life on Earth. It describes how species change over time through gradual processes, primarily driven by natural selection and genetic variation.
Key Concepts of the Theory of Evolution:
- Gradual Change:
Evolution posits that species undergo gradual changes over long periods. These changes accumulate, leading to the emergence of new species from common ancestors.
- Natural Selection:
A mechanism proposed by Charles Darwin, natural selection suggests that individuals with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce. This process results in the adaptation of species to their environments.
- Genetic Variation:
Genetic diversity within populations provides the raw material for evolution. Mutations, gene flow, and sexual reproduction contribute to this variation, allowing populations to adapt to changing environments.
- Common Descent:
The theory also posits that all living organisms share a common ancestor. Over time, species diverge and evolve into different forms, leading to the rich diversity of life we observe today.
Conclusion:
In summary, the theory of evolution is mainly concerned with gradual change driven by natural selection, genetic variation, and common descent. Unlike spontaneous generation or the theory of special creation, which propose alternative explanations for the origin of life, the theory of evolution provides a scientific framework for understanding how life adapts and evolves over time.
The theory of evolution is a fundamental concept in biology that explains the diversity of life on Earth. It describes how species change over time through gradual processes, primarily driven by natural selection and genetic variation.
Key Concepts of the Theory of Evolution:
- Gradual Change:
Evolution posits that species undergo gradual changes over long periods. These changes accumulate, leading to the emergence of new species from common ancestors.
- Natural Selection:
A mechanism proposed by Charles Darwin, natural selection suggests that individuals with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce. This process results in the adaptation of species to their environments.
- Genetic Variation:
Genetic diversity within populations provides the raw material for evolution. Mutations, gene flow, and sexual reproduction contribute to this variation, allowing populations to adapt to changing environments.
- Common Descent:
The theory also posits that all living organisms share a common ancestor. Over time, species diverge and evolve into different forms, leading to the rich diversity of life we observe today.
Conclusion:
In summary, the theory of evolution is mainly concerned with gradual change driven by natural selection, genetic variation, and common descent. Unlike spontaneous generation or the theory of special creation, which propose alternative explanations for the origin of life, the theory of evolution provides a scientific framework for understanding how life adapts and evolves over time.
Who was the first to explain recapitulatin theory :[CPMT 78, 80]- a)Weismann
- b)Muller and Haeckel
- c)Darwin
- d)Malthus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who was the first to explain recapitulatin theory :
[CPMT 78, 80]
a)
Weismann
b)
Muller and Haeckel
c)
Darwin
d)
Malthus

|
Sandy Naaz answered |
The theory of recapitulation, also called the biogenetic law or embryological parallelism—often expressed using Ernst Haeckel's phrase "ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny"—is a historical hypothesis that the development of the embryo of an animal, from fertilization to gestation or hatching (ontogeny), goes through ...
Evolution of different species in a given area starting from a point and spreading to other geographical areas is known as- a)Migration
- b)Divergent evolution
- c)Adaptive radiation
- d)Natural selection
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Evolution of different species in a given area starting from a point and spreading to other geographical areas is known as
a)
Migration
b)
Divergent evolution
c)
Adaptive radiation
d)
Natural selection
|
|
Mansi Deshpande answered |
Adaptive Radiation:
Adaptive radiation is the evolution of different species in a given area starting from a point and spreading to other geographical areas. It is a type of divergent evolution that occurs when a single ancestral species evolves into many different species to adapt to different ecological niches. The term "adaptive radiation" was coined by the American evolutionary biologist Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1897.
Factors that contribute to adaptive radiation:
1. Ecological opportunity: When new habitats or resources become available, organisms can exploit them and evolve to fill new niches.
2. Morphological innovation: Morphological innovation can allow organisms to exploit new resources or habitats.
3. Competition: Competition for resources can drive organisms to evolve different adaptations, leading to adaptive radiation.
Examples of adaptive radiation:
1. Darwin's finches: The Galápagos Islands are home to a number of different finch species that evolved from a common ancestor. Each species has a specialized beak that allows it to feed on different types of food.
2. Hawaiian honeycreepers: The Hawaiian Islands are home to a diverse group of birds known as honeycreepers. These birds evolved from a single ancestral species and have adapted to different ecological niches on the islands.
3. Australian marsupials: Australia is home to a number of different marsupial species that evolved from a common ancestor. These marsupials have adapted to different ecological niches, such as the kangaroo, koala, and Tasmanian devil.
Conclusion:
Adaptive radiation is an important process in the evolution of new species. It allows organisms to adapt to new environments and resources and can lead to the development of new ecological niches. The study of adaptive radiation can provide insights into the mechanisms of evolution and the factors that contribute to biodiversity.
Adaptive radiation is the evolution of different species in a given area starting from a point and spreading to other geographical areas. It is a type of divergent evolution that occurs when a single ancestral species evolves into many different species to adapt to different ecological niches. The term "adaptive radiation" was coined by the American evolutionary biologist Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1897.
Factors that contribute to adaptive radiation:
1. Ecological opportunity: When new habitats or resources become available, organisms can exploit them and evolve to fill new niches.
2. Morphological innovation: Morphological innovation can allow organisms to exploit new resources or habitats.
3. Competition: Competition for resources can drive organisms to evolve different adaptations, leading to adaptive radiation.
Examples of adaptive radiation:
1. Darwin's finches: The Galápagos Islands are home to a number of different finch species that evolved from a common ancestor. Each species has a specialized beak that allows it to feed on different types of food.
2. Hawaiian honeycreepers: The Hawaiian Islands are home to a diverse group of birds known as honeycreepers. These birds evolved from a single ancestral species and have adapted to different ecological niches on the islands.
3. Australian marsupials: Australia is home to a number of different marsupial species that evolved from a common ancestor. These marsupials have adapted to different ecological niches, such as the kangaroo, koala, and Tasmanian devil.
Conclusion:
Adaptive radiation is an important process in the evolution of new species. It allows organisms to adapt to new environments and resources and can lead to the development of new ecological niches. The study of adaptive radiation can provide insights into the mechanisms of evolution and the factors that contribute to biodiversity.
In the developmental history of mammalian heart, it is observed that it passes through a two chambered fish like heart, three chambered frog like heart and finally four chambered stage
To which hypothesis can this above cited statement be approximated?- a)Lamarck's principle
- b)Mendelian principle
- c)Biogenetic law
- d)Hardy Weinberg law
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the developmental history of mammalian heart, it is observed that it passes through a two chambered fish like heart, three chambered frog like heart and finally four chambered stage
To which hypothesis can this above cited statement be approximated?
To which hypothesis can this above cited statement be approximated?
a)
Lamarck's principle
b)
Mendelian principle
c)
Biogenetic law
d)
Hardy Weinberg law
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Biogenetic law or Recapitulation theory was given by Ernst Haeckel in 1866. It states that 'ontogeny repeats phylogeny'. Ontogeny is the life history of an organism while phylogeny is the evolutionary history of the race of that organism. This means that an organism repeats its ancestral history during its development.
Which one of the following describes correctly the homologous structures?- a)Organs with anatomical similarities, but performing different functions
- b)Organs with anatomical dissimilarities, but performing same function
- c)Organs that have no function now, but had important function in ancestors
- d)Organs appearing only in embryonic stage and disappearing later in the adult
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following describes correctly the homologous structures?
a)
Organs with anatomical similarities, but performing different functions
b)
Organs with anatomical dissimilarities, but performing same function
c)
Organs that have no function now, but had important function in ancestors
d)
Organs appearing only in embryonic stage and disappearing later in the adult
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Homologous organs have a common origin and are built on the same basic pattern but perform different functions and are modified accordingly.
Jurassic period belongs to the ______ era.- a)Cenozoic
- b)Mesozoic
- c)Palaeozoic
- d)Proterozoic
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Jurassic period belongs to the ______ era.
a)
Cenozoic
b)
Mesozoic
c)
Palaeozoic
d)
Proterozoic
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
The Jurassic Period was the second section of the Mesozoic Era. It happened from 199.6 to 145.5 million years back, after the Triassic Period and going before the Cretaceous Period.
Refer the given statements and select the correct one
(i) Fossils are remains of hard parts of life forms in Rocks
(ii) A study of fossils in different sedimentary layers indicates the geological period in which they live.
(iii) Radio isotopen are often used to determine the age of the fossils
(iv) Study of fossils is called paleontology- a)(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- b)(ii) and (iv)
- c)(i), (iii) and (iv)
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Refer the given statements and select the correct one
(i) Fossils are remains of hard parts of life forms in Rocks
(ii) A study of fossils in different sedimentary layers indicates the geological period in which they live.
(iii) Radio isotopen are often used to determine the age of the fossils
(iv) Study of fossils is called paleontology
(i) Fossils are remains of hard parts of life forms in Rocks
(ii) A study of fossils in different sedimentary layers indicates the geological period in which they live.
(iii) Radio isotopen are often used to determine the age of the fossils
(iv) Study of fossils is called paleontology
a)
(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
b)
(ii) and (iv)
c)
(i), (iii) and (iv)
d)
None of these
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The fossils can be defined as remains of impressions of the hard parts of the past life-forms in the strata of the earth. Fossils provide one of the most acceptable evidences in support of evolution, because we can study the evolutionary past of individuals in the form of their fossils. The study of fossils is known as paleontology. The evidence of evolution based on the knowledge of fossils is called paleontological evidence. Living organisms living in various ages and entombed in various starta of rocks provide concrete clues to the variety of life that existed in the past.
Age of the fossils can be determined by three methods: (i) Radioactive clock method (II) Radioactive carbon method and (iii) Potassium Organ method.
Age of the fossils can be determined by three methods: (i) Radioactive clock method (II) Radioactive carbon method and (iii) Potassium Organ method.
Given below are four statements (i) - (iv) regarding geological time scale. Read them carefully.
(i) Palaeozoic era is the era of ancient life
(ii) Ordovician period is the age of vertebrates
(iii) Carboniferous period is the age of reptiles
(iv) Proterozoic era is the era of early life
Which of the above two statements are incorrect?- a)(i) and (iv)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(ii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below are four statements (i) - (iv) regarding geological time scale. Read them carefully.
(i) Palaeozoic era is the era of ancient life
(ii) Ordovician period is the age of vertebrates
(iii) Carboniferous period is the age of reptiles
(iv) Proterozoic era is the era of early life
Which of the above two statements are incorrect?
(i) Palaeozoic era is the era of ancient life
(ii) Ordovician period is the age of vertebrates
(iii) Carboniferous period is the age of reptiles
(iv) Proterozoic era is the era of early life
Which of the above two statements are incorrect?
a)
(i) and (iv)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(ii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iii)
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Ordovician period existed about 500 million years ago and is the age of invertebrates. Carboniferous period that existed 350 million years ago is the age of amphibians.
Which of the following sets do not have homologous organs : - a)Wings of mosquito and butterfly
- b)All of them
- c)Mouth parts of cockroach and butter fly
- d)Wings of butterfly and bird
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following sets do not have homologous organs :
a)
Wings of mosquito and butterfly
b)
All of them
c)
Mouth parts of cockroach and butter fly
d)
Wings of butterfly and bird

|
Gundappa Karamadi answered |
Origin is different and function same
Which ape is closely related to the man?- a)Orangutan
- b)Chimpanzee
- c)Gibbon
- d)Gorilla
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which ape is closely related to the man?
a)
Orangutan
b)
Chimpanzee
c)
Gibbon
d)
Gorilla
|
|
Gargi Yadav answered |
The ape that is closely related to man is the chimpanzee.
Chimpanzees, scientifically known as Pan troglodytes, are the closest living relatives to humans. They share a common ancestor with humans, with whom they have a high degree of genetic similarity. Here is an explanation of why chimpanzees are considered to be closely related to humans:
1. Genetic Similarity:
- Humans and chimpanzees share approximately 98.7% of their DNA.
- This high degree of genetic similarity indicates a close evolutionary relationship between the two species.
2. Common Ancestor:
- Humans and chimpanzees diverged from a common ancestor around 6 to 7 million years ago.
- Over time, this common ancestor gave rise to two distinct lineages, one leading to humans and the other to chimpanzees.
3. Physical Similarities:
- Chimpanzees and humans share several physical characteristics, such as opposable thumbs, forward-facing eyes, and complex social behaviors.
- These similarities suggest a common evolutionary history and a close relationship.
4. Behavioral Similarities:
- Chimpanzees exhibit complex behaviors, including tool use, hunting, and communication.
- These behaviors are similar to those observed in early human ancestors, providing further evidence of a shared ancestry.
5. Social Structure:
- Chimpanzees live in social groups, similar to human societies.
- They form complex social hierarchies, maintain social bonds, and engage in cooperative activities.
- These social behaviors parallel many aspects of human social organization.
In conclusion, the chimpanzee is closely related to humans due to the high degree of genetic similarity, shared ancestry, physical and behavioral similarities, and similar social structures. Studying chimpanzees helps scientists gain insights into human evolution, behavior, and biology.
Chimpanzees, scientifically known as Pan troglodytes, are the closest living relatives to humans. They share a common ancestor with humans, with whom they have a high degree of genetic similarity. Here is an explanation of why chimpanzees are considered to be closely related to humans:
1. Genetic Similarity:
- Humans and chimpanzees share approximately 98.7% of their DNA.
- This high degree of genetic similarity indicates a close evolutionary relationship between the two species.
2. Common Ancestor:
- Humans and chimpanzees diverged from a common ancestor around 6 to 7 million years ago.
- Over time, this common ancestor gave rise to two distinct lineages, one leading to humans and the other to chimpanzees.
3. Physical Similarities:
- Chimpanzees and humans share several physical characteristics, such as opposable thumbs, forward-facing eyes, and complex social behaviors.
- These similarities suggest a common evolutionary history and a close relationship.
4. Behavioral Similarities:
- Chimpanzees exhibit complex behaviors, including tool use, hunting, and communication.
- These behaviors are similar to those observed in early human ancestors, providing further evidence of a shared ancestry.
5. Social Structure:
- Chimpanzees live in social groups, similar to human societies.
- They form complex social hierarchies, maintain social bonds, and engage in cooperative activities.
- These social behaviors parallel many aspects of human social organization.
In conclusion, the chimpanzee is closely related to humans due to the high degree of genetic similarity, shared ancestry, physical and behavioral similarities, and similar social structures. Studying chimpanzees helps scientists gain insights into human evolution, behavior, and biology.
Which of the following is true?- a)Wings of birds and insects are homologous organs.
- b)Human hands and wings of birds are analogous organs.
- c)Human hands and wings of bats are analogous organs.
- d)Flipper of seal and wings of birds are homologous organs.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is true?
a)
Wings of birds and insects are homologous organs.
b)
Human hands and wings of birds are analogous organs.
c)
Human hands and wings of bats are analogous organs.
d)
Flipper of seal and wings of birds are homologous organs.
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Flipper of seal and wing of birds are modified forelimbs, thus, have same fundamental structure but have different functions. Flippers are meant for swimming and wings are meant for flying. Therefore, these organs are homologous oroans.
Industrial melanism is an example of -- a)Mutation
- b)Natural selection
- c)Neo Darwinism
- d)Neo Lamarckism
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Industrial melanism is an example of -
a)
Mutation
b)
Natural selection
c)
Neo Darwinism
d)
Neo Lamarckism

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Natural selection is the most widely accepted theory concerning the principal causal mechanism of evolutionary change profounded by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace. It results from the differential reproduction (some members of a population produce abundant offspring, some only a few and still others none), one phenotype as compared with other phenotypes in the same population. This determines the relative share of different genotypes which individuals possess and propagate in a population. Industrial melanism supports evolution by natural selection. It is an adaptation where the moths living in the industrial areas developed melanin pigments to match their bodies to the tree trunks.
Read the given statements (i) - (iv) regarding evolution and select the incorrect ones
(i) The oceanic water rich in mixture of organic compounds was termed by J.B.S. Haldane (1920) as 'hot dilute soap of organic substances'.
(ii) The term coacervate was given by Syndey Fox.
(iii) First cellular form of life appeared approximately 2000 mya on earth.
(iv) The first geological time scale was developed by Georges Cuvier.
- a)(ii) and (iv)
- b)(i) and (ii)
- c)(ii) and (iii)
- d)(iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements (i) - (iv) regarding evolution and select the incorrect ones
(i) The oceanic water rich in mixture of organic compounds was termed by J.B.S. Haldane (1920) as 'hot dilute soap of organic substances'.
(ii) The term coacervate was given by Syndey Fox.
(iii) First cellular form of life appeared approximately 2000 mya on earth.
(iv) The first geological time scale was developed by Georges Cuvier.
(i) The oceanic water rich in mixture of organic compounds was termed by J.B.S. Haldane (1920) as 'hot dilute soap of organic substances'.
(ii) The term coacervate was given by Syndey Fox.
(iii) First cellular form of life appeared approximately 2000 mya on earth.
(iv) The first geological time scale was developed by Georges Cuvier.
a)
(ii) and (iv)
b)
(i) and (ii)
c)
(ii) and (iii)
d)
(iii) and (iv)
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Correct answer is A.
Earliest fossil form in the phylogeny of horse is : [CBSE 94]- a)Mesohippus
- b)Equus
- c)Eohippus
- d)Merychippus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Earliest fossil form in the phylogeny of horse is : [CBSE 94]
a)
Mesohippus
b)
Equus
c)
Eohippus
d)
Merychippus
|
|
Tejas Chakraborty answered |
Hoofed animals like-horse orginated in Eocene epoch in North America. First horse-like animals from which the modern horse Equus evolved was Hyracotherium (old name Eohippus). The fossil record is most complete in horse.
Fossils are dated by : [CPMT 74, AFMC 80]- a)Amount of calcium residue
- b)Amount of radioactive carbon compound
- c)Association with other mammlas
- d)Structure of bones
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Fossils are dated by :
[CPMT 74, AFMC 80]
a)
Amount of calcium residue
b)
Amount of radioactive carbon compound
c)
Association with other mammlas
d)
Structure of bones
|
|
Shivani Dasgupta answered |
Fossils are dated using various methods, and one such method is the use of radioactive carbon compounds. This method, known as radiocarbon dating or carbon-14 dating, allows scientists to determine the age of organic remains by measuring the amount of radioactive carbon-14 present in the sample.
Radiocarbon dating is based on the fact that carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope of carbon that is constantly formed in the atmosphere by cosmic rays. This carbon-14 is then absorbed by living organisms, such as plants and animals, through the process of photosynthesis or consumption. When these organisms die, the carbon-14 in their bodies begins to decay at a predictable rate.
The decay of carbon-14 is measured by its half-life, which is the time it takes for half of the carbon-14 atoms to decay into nitrogen-14. The half-life of carbon-14 is approximately 5730 years. By measuring the ratio of carbon-14 to carbon-12 in a fossil, scientists can determine how long it has been since the organism died.
To determine the age of a fossil using radiocarbon dating, scientists extract a small sample of organic material, such as bone or wood, from the fossil. They then measure the amount of carbon-14 in the sample using a technique called accelerator mass spectrometry. This method allows for incredibly precise measurements of carbon-14 levels, even for samples that are thousands of years old.
By comparing the amount of carbon-14 in the sample to the known levels of carbon-14 in the atmosphere at the time the organism died, scientists can calculate the age of the fossil. This method is particularly useful for dating fossils that are less than 50,000 years old.
In conclusion, fossils are dated using radiocarbon dating, which involves measuring the amount of radioactive carbon-14 in the sample. This method allows scientists to determine the age of organic remains by comparing the carbon-14 levels to known atmospheric levels. Radiocarbon dating is a valuable tool in paleontology and archaeology, providing insights into the age and history of ancient organisms.
Radiocarbon dating is based on the fact that carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope of carbon that is constantly formed in the atmosphere by cosmic rays. This carbon-14 is then absorbed by living organisms, such as plants and animals, through the process of photosynthesis or consumption. When these organisms die, the carbon-14 in their bodies begins to decay at a predictable rate.
The decay of carbon-14 is measured by its half-life, which is the time it takes for half of the carbon-14 atoms to decay into nitrogen-14. The half-life of carbon-14 is approximately 5730 years. By measuring the ratio of carbon-14 to carbon-12 in a fossil, scientists can determine how long it has been since the organism died.
To determine the age of a fossil using radiocarbon dating, scientists extract a small sample of organic material, such as bone or wood, from the fossil. They then measure the amount of carbon-14 in the sample using a technique called accelerator mass spectrometry. This method allows for incredibly precise measurements of carbon-14 levels, even for samples that are thousands of years old.
By comparing the amount of carbon-14 in the sample to the known levels of carbon-14 in the atmosphere at the time the organism died, scientists can calculate the age of the fossil. This method is particularly useful for dating fossils that are less than 50,000 years old.
In conclusion, fossils are dated using radiocarbon dating, which involves measuring the amount of radioactive carbon-14 in the sample. This method allows scientists to determine the age of organic remains by comparing the carbon-14 levels to known atmospheric levels. Radiocarbon dating is a valuable tool in paleontology and archaeology, providing insights into the age and history of ancient organisms.
Which theory explains the origin of universe?- a)Molecular theory
- b)Darwin theory
- c)Lamarck theory
- d)Big bang theory
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which theory explains the origin of universe?
a)
Molecular theory
b)
Darwin theory
c)
Lamarck theory
d)
Big bang theory

|
Nayanika Reddy answered |
Origin of universe is explained by big bang theory. According to this theory, whole universe was concentrated into single sphere. Due to same unknown region, there was explosion in it that forms different galaxies still moving away from each other.
Chapter doubts & questions for Evidence of Evolution - Biology for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Evidence of Evolution - Biology for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for JAMB
221 videos|172 docs|126 tests
|


















