All Exams >
Grade 2 >
Geography for Grade 2 >
All Questions
All questions of Life in a Village for Grade 2 Exam
What were punch-marked coins used for?- a)Religious offerings
- b)Trade and transactions
- c)Agriculture
- d)Decoration
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What were punch-marked coins used for?
a)
Religious offerings
b)
Trade and transactions
c)
Agriculture
d)
Decoration
|
|
Preethi Dasgupta answered |
Trade and transactions
Punch-marked coins were used primarily for trade and transactions during ancient times. Here's why:
- Medium of Exchange: Punch-marked coins were one of the earliest forms of coinage used in ancient India. They were standardized pieces of metal with markings punched on them to indicate their value.
- Facilitated Trade: These coins played a crucial role in facilitating trade and commerce by providing a common medium of exchange that could be easily recognized and accepted by different communities.
- Standardized Value: The punch marks on these coins helped establish their value and authenticity, making them widely accepted across different regions for various transactions.
- Barter System: Before the introduction of coins, transactions were often carried out through the barter system. Punch-marked coins revolutionized trade by providing a more efficient and convenient means of exchange.
- Economic Development: The use of punch-marked coins contributed to the growth of economic activities, as it allowed for smoother and more organized trade between different groups and regions.
Overall, punch-marked coins served as a vital tool for conducting trade and transactions, laying the foundation for the development of a more sophisticated monetary system in ancient India.
Odd One Out - Craftspersons:
A) Blacksmith
B) Potter
C) Carpenter
D) Grihapatis- a)A, B, C
- b)B, C, D
- c)A, C, D
- d)A, B, D
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Odd One Out - Craftspersons:
A) Blacksmith
B) Potter
C) Carpenter
D) Grihapatis
A) Blacksmith
B) Potter
C) Carpenter
D) Grihapatis
a)
A, B, C
b)
B, C, D
c)
A, C, D
d)
A, B, D
|
|
Priyanka Mukherjee answered |
Understanding the Odd One Out
In this task, we need to identify which craftsperson does not belong with the others based on their specific trades or skills.
Craftspersons Explained
- Blacksmith: A blacksmith works primarily with metal, forging and shaping it into tools, weapons, and various objects.
- Potter: A potter specializes in working with clay, creating pottery items such as pots, bowls, and vases.
- Carpenter: A carpenter is skilled in woodworking, constructing buildings, furniture, and other wooden structures.
- Grihapati: This term refers to a household master or a person who is in charge of managing a home. It is not a craftsperson in the traditional sense.
Identifying the Odd One Out
In this group, the odd one out is:
- Potter (Option B): Unlike the blacksmith and carpenter who are both tradespeople engaged in crafting physical tools and structures, the potter focuses on a specific medium (clay). However, the term "Grihapati" does not refer to a craftsperson at all, making it the true outlier in terms of profession.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option 'B' as it identifies a specific craftsperson whose medium is distinct compared to the others while also not fitting the broader labor category that includes manual trades. In contrast, "Grihapati" represents a position related to household management rather than a craft.
In this task, we need to identify which craftsperson does not belong with the others based on their specific trades or skills.
Craftspersons Explained
- Blacksmith: A blacksmith works primarily with metal, forging and shaping it into tools, weapons, and various objects.
- Potter: A potter specializes in working with clay, creating pottery items such as pots, bowls, and vases.
- Carpenter: A carpenter is skilled in woodworking, constructing buildings, furniture, and other wooden structures.
- Grihapati: This term refers to a household master or a person who is in charge of managing a home. It is not a craftsperson in the traditional sense.
Identifying the Odd One Out
In this group, the odd one out is:
- Potter (Option B): Unlike the blacksmith and carpenter who are both tradespeople engaged in crafting physical tools and structures, the potter focuses on a specific medium (clay). However, the term "Grihapati" does not refer to a craftsperson at all, making it the true outlier in terms of profession.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option 'B' as it identifies a specific craftsperson whose medium is distinct compared to the others while also not fitting the broader labor category that includes manual trades. In contrast, "Grihapati" represents a position related to household management rather than a craft.
Who were the three different kinds of people living in most villages in the southern and northern parts of the subcontinent?- a)Vellalar, uzhavar, and adimai
- b)Grama bhojaka, grihapatis, and dasa karmakara
- c)Craftspersons, blacksmith, carpenter, and weaver
- d)Sangam poets, kings, and merchants
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who were the three different kinds of people living in most villages in the southern and northern parts of the subcontinent?
a)
Vellalar, uzhavar, and adimai
b)
Grama bhojaka, grihapatis, and dasa karmakara
c)
Craftspersons, blacksmith, carpenter, and weaver
d)
Sangam poets, kings, and merchants
|
|
Maitri Bajaj answered |
Types of People in Villages
In the villages of both southern and northern parts of the Indian subcontinent, three primary groups of people were commonly found:
Grama Bhojaka
- This was the village headman or chief, responsible for the administration and governance of the village.
- The Grama Bhojaka played a crucial role in maintaining law and order, resolving disputes, and overseeing agricultural activities.
Grihapatis
- Grihapatis were affluent landowners or householders who owned large tracts of land.
- They often played a significant role in the local economy by managing agricultural production and employing laborers.
- They were influential in social and political matters within the village.
Dasa Karmakaras
- These were the laborers or workers who engaged in various tasks necessary for the village's functioning.
- Dasa Karmakaras typically included agricultural workers, artisans, and other manual laborers who contributed to the agricultural and craft-based economy of the village.
- They formed the backbone of the village's labor force, facilitating trade and production.
Conclusion
These three groups—Grama Bhojaka, Grihapatis, and Dasa Karmakaras—played distinctive yet interrelated roles in the socio-economic framework of village life. Understanding their functions helps in grasping the dynamics of rural society in historical contexts.
In the villages of both southern and northern parts of the Indian subcontinent, three primary groups of people were commonly found:
Grama Bhojaka
- This was the village headman or chief, responsible for the administration and governance of the village.
- The Grama Bhojaka played a crucial role in maintaining law and order, resolving disputes, and overseeing agricultural activities.
Grihapatis
- Grihapatis were affluent landowners or householders who owned large tracts of land.
- They often played a significant role in the local economy by managing agricultural production and employing laborers.
- They were influential in social and political matters within the village.
Dasa Karmakaras
- These were the laborers or workers who engaged in various tasks necessary for the village's functioning.
- Dasa Karmakaras typically included agricultural workers, artisans, and other manual laborers who contributed to the agricultural and craft-based economy of the village.
- They formed the backbone of the village's labor force, facilitating trade and production.
Conclusion
These three groups—Grama Bhojaka, Grihapatis, and Dasa Karmakaras—played distinctive yet interrelated roles in the socio-economic framework of village life. Understanding their functions helps in grasping the dynamics of rural society in historical contexts.
Match the Location:
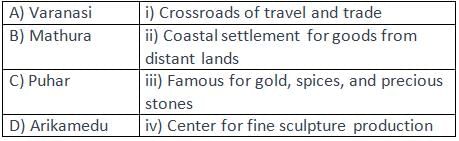
- a)A) ii, B) iii, C) i, D) iv
- b)A) iii, B) iv, C) i, D) ii
- c)A) ii, B) i, C) iii, D) iv
- d)A) iv, B) ii, C) iii, D) i
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the Location:


a)
A) ii, B) iii, C) i, D) iv
b)
A) iii, B) iv, C) i, D) ii
c)
A) ii, B) i, C) iii, D) iv
d)
A) iv, B) ii, C) iii, D) i

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
Each location corresponds to its unique characteristic mentioned in the passage.
Analogy - Kushanas:Silk Route :: Satavahanas:______- a)Northern Black Polished Ware
- b)Coastal Settlements
- c)Lords of Dakshinapatha
- d)Megalithic Burials
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Analogy - Kushanas:Silk Route :: Satavahanas:______
a)
Northern Black Polished Ware
b)
Coastal Settlements
c)
Lords of Dakshinapatha
d)
Megalithic Burials

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
The Kushanas controlled the Silk Route, and the Satavahanas were known as lords of the dakshinapatha.
The Kushanas ruled over Central Asia and North-West India around 2000 years ago, and their two major centers of power were Peshawar and _______.- a)Ujjain
- b)Taxila
- c)Mathura
- d)Varanasi
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The Kushanas ruled over Central Asia and North-West India around 2000 years ago, and their two major centers of power were Peshawar and _______.
a)
Ujjain
b)
Taxila
c)
Mathura
d)
Varanasi

|
Coachify answered |
The passage mentions Mathura as one of the major centers of power for the Kushanas.
What evidence from Arikamedu suggests contact with Rome?- a)Northern Black Polished Ware
- b)Stamped red-glazed pottery
- c)Roman lamps, glassware, and gems
- d)Dyeing vats for cloth
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What evidence from Arikamedu suggests contact with Rome?
a)
Northern Black Polished Ware
b)
Stamped red-glazed pottery
c)
Roman lamps, glassware, and gems
d)
Dyeing vats for cloth
|
|
Subset Academy answered |
The passage mentions various finds at Arikamedu, including Roman lamps, glassware, and gems, indicating contact with Rome.
What was the significance of the Silk Route for rulers like the Kushanas?- a)Cultural exchange
- b)Tax collection
- c)Agricultural development
- d)Religious pilgrimages
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What was the significance of the Silk Route for rulers like the Kushanas?
a)
Cultural exchange
b)
Tax collection
c)
Agricultural development
d)
Religious pilgrimages

|
Rohini Seth answered |
The passage states that rulers like the Kushanas controlled the Silk Route to benefit from taxes, tributes, and gifts brought by traders traveling along the route.
Which city served as a center for trade, travel, and fine sculpture around 2000 years ago?- a)Puhar
- b)Varanasi
- c)Mathura
- d)Arikamedu
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which city served as a center for trade, travel, and fine sculpture around 2000 years ago?
a)
Puhar
b)
Varanasi
c)
Mathura
d)
Arikamedu

|
Vp Classes answered |
Mathura is described in the passage as an important settlement for more than 2500 years, serving as a crossroads for travel and trade, with fortifications, shrines, and fine sculpture production.
Which of the following towns is known as a significant historical urban center in ancient India?- a) Kolkata
- b) Tamluk
- c) Mumbai
- d) Delhi
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following towns is known as a significant historical urban center in ancient India?
a)
Kolkata
b)
Tamluk
c)
Mumbai
d)
Delhi

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Tamluk, known in ancient times as Tamralipti, was a significant urban center and port city that facilitated trade and cultural exchanges, particularly with regions like Southeast Asia and beyond.
What role did urban centers play as populations grew during this historical period?- a)Urban centers served as military fortresses to protect against invasions
- b)Urban centers functioned as religious pilgrimage sites for spiritual enlightenment
- c)Urban centers developed into capitals of Janapadas and Mahajanapadas or emerged around trading hubs
- d)Urban centers were primarily agricultural settlements for food production
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Urban centers served as military fortresses to protect against invasions
b)
Urban centers functioned as religious pilgrimage sites for spiritual enlightenment
c)
Urban centers developed into capitals of Janapadas and Mahajanapadas or emerged around trading hubs
d)
Urban centers were primarily agricultural settlements for food production

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
With the increase in population, urban centers played a crucial role by developing into capitals of Janapadas and Mahajanapadas or growing around trading centers. These cities not only served as administrative and political hubs but also facilitated economic activities and cultural exchanges, shaping the socio-political landscape of the region.
How did the use of punch-marked coins contribute to the efficiency of trade during ancient times?- a)Punch-marked coins were used as amulets for protection during long journeys
- b)Punch-marked coins were standardized units of value accepted across various regions
- c)Punch-marked coins were primarily used for ornamental purposes in jewelry
- d)Punch-marked coins were exchanged based on their weight in gold or silver
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Punch-marked coins were used as amulets for protection during long journeys
b)
Punch-marked coins were standardized units of value accepted across various regions
c)
Punch-marked coins were primarily used for ornamental purposes in jewelry
d)
Punch-marked coins were exchanged based on their weight in gold or silver

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
The use of punch-marked coins in ancient times contributed to the efficiency of trade by providing standardized units of value that were widely accepted across different regions. This uniformity in currency simplified commercial transactions and facilitated smoother trade interactions, promoting economic growth and cultural exchange.
In North Indian villages, what role did the largest landowner typically play?- a)Chief Justice
- b)Village Headman
- c)Tax Collector
- d)Religious Leader
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Chief Justice
b)
Village Headman
c)
Tax Collector
d)
Religious Leader

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
The largest landowner in North Indian villages usually served as the village headman. This individual had various responsibilities such as tax collection, acting as a mediator between the king and the village, and occasionally overseeing judicial matters. This position held significant influence within the village community.
During the period between 200 BCE and 300 CE, which ancient Tamil dynasties were prominent rulers of Tamil Nadu, actively engaging in trade and commerce?- a)The Mauryas, Guptas, and Kushans
- b)The Cholas, Pandyas, and Cheras
- c)The Satavahanas, Vakatakas, and Rashtrakutas
- d)The Pallavas, Kadambas, and Gangas
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
The Mauryas, Guptas, and Kushans
b)
The Cholas, Pandyas, and Cheras
c)
The Satavahanas, Vakatakas, and Rashtrakutas
d)
The Pallavas, Kadambas, and Gangas

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
The Cholas, Pandyas, and Cheras were significant dynasties in ancient Tamil Nadu between 200 BCE and 300 CE. They not only ruled the region but also actively participated in trade, both internally and overseas. This period witnessed a flourishing trade network, as evidenced by the discovery of Roman coins in the region, indicating trade connections with the Roman Empire.
Which of the following best describes the role of a gramani in North Indian villages?- a) Tax collector for the king
- b) Religious leader
- c) Agricultural worker
- d) Military commander
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following best describes the role of a gramani in North Indian villages?
a)
Tax collector for the king
b)
Religious leader
c)
Agricultural worker
d)
Military commander

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
A gramani or grama bhojaka served as the village headman, responsible for collecting taxes from villagers on behalf of the king. This role was often hereditary and crucial for maintaining local governance.
What evidence supports the use of iron in the subcontinent around 3000 years ago?- a)Megalithic burials
- b)Sangam literature
- c)Punch-marked coins
- d)Mathura inscriptions
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What evidence supports the use of iron in the subcontinent around 3000 years ago?
a)
Megalithic burials
b)
Sangam literature
c)
Punch-marked coins
d)
Mathura inscriptions

|
Praveen Kumar answered |
The passage mentions that some of the largest collections of iron tools and weapons were found in megalithic burials.
Which of the following themes is NOT typically found in Sangam poetry?- a) Love (akam)
- b) Philosophical discourse
- c) Nature
- d) Heroism (puram)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following themes is NOT typically found in Sangam poetry?
a)
Love (akam)
b)
Philosophical discourse
c)
Nature
d)
Heroism (puram)

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Philosophical discourse is not a typical theme of Sangam poetry, which primarily focuses on love (akam) and heroism (puram). The poetry reflects the social and emotional experiences of the time rather than abstract philosophical ideas.
What type of increased agricultural technique was introduced during the second urbanization?- a) Crop transplantation
- b) Hydroponics
- c) Organic farming
- d) Crop rotation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What type of increased agricultural technique was introduced during the second urbanization?
a)
Crop transplantation
b)
Hydroponics
c)
Organic farming
d)
Crop rotation

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Crop transplantation was a new technique introduced during this period, which allowed for higher yields and better management of agricultural resources, further enhancing food security and urban growth.
Which ancient South Indian city was known to have distinct living and harbor areas, along with warehouses for storing goods during the period under discussion?- a)Arikamedu
- b)Kaveripattinam
- c)Mahabalipuram
- d)Mamallapuram
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Arikamedu
b)
Kaveripattinam
c)
Mahabalipuram
d)
Mamallapuram

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Kaveripattinam was an ancient South Indian city that had separate living and harbor areas, along with warehouses for storing goods. This segregation of living and trade spaces highlights the organized urban planning and commercial activities that were prevalent during that time.
What types of trade items were excavated at Arikamedu during the period of the Cholas, Pandyas, and Cheras?- a)Silk, spices, and precious stones
- b)Pottery, terracotta, and Roman amphorae
- c)Tea, porcelain, and jade
- d)Ivory, gold, and ebony
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Silk, spices, and precious stones
b)
Pottery, terracotta, and Roman amphorae
c)
Tea, porcelain, and jade
d)
Ivory, gold, and ebony

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Excavations at Arikamedu revealed trade items such as pottery, terracotta, and Roman amphorae. These artifacts provide valuable insights into the trading practices and cultural exchanges that took place between South India and other regions during that historical period.
What does the term "Sangam literature" refer to?- a) Poetry from the Gupta Empire
- b) Historical accounts of the Indus Valley
- c) Early Tamil writings
- d) A collection of religious texts
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What does the term "Sangam literature" refer to?
a)
Poetry from the Gupta Empire
b)
Historical accounts of the Indus Valley
c)
Early Tamil writings
d)
A collection of religious texts

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Sangam literature refers to the earliest known Tamil writings, created during literary assemblies in Madurai. This body of work is notable for its focus on secular themes, contrasting with much of early Indian literature that was religious in nature.
What role did iron tools play in agricultural development during the second urbanization?- a) They helped clear land for farming.
- b) They were used solely for crafting weapons.
- c) They were used in trade with foreign nations.
- d) They served as currency.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What role did iron tools play in agricultural development during the second urbanization?
a)
They helped clear land for farming.
b)
They were used solely for crafting weapons.
c)
They were used in trade with foreign nations.
d)
They served as currency.

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Iron tools, such as axes and ploughshares, facilitated the clearing of land for farming, significantly enhancing agricultural productivity and contributing to the surplus needed for urban growth.
Which of the following was a significant outcome of increased trade during the second urbanization?- a) Isolation from foreign cultures
- b) Decline of agricultural practices
- c) Abandonment of cities
- d) Formation of guilds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following was a significant outcome of increased trade during the second urbanization?
a)
Isolation from foreign cultures
b)
Decline of agricultural practices
c)
Abandonment of cities
d)
Formation of guilds

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
The growth of trade led to the formation of guilds, or shrenis, which supported craftsmen and traders by providing resources, training, and a framework for commercial activities. This fostered economic interdependence and community organization.
Which regions were significant trade partners with Indian kingdoms during ancient times?- a)France and Spain
- b)China and Japan
- c)Sri Lanka and Burma
- d)Russia and Ukraine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
France and Spain
b)
China and Japan
c)
Sri Lanka and Burma
d)
Russia and Ukraine

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
During ancient times, Indian kingdoms engaged in trade with various regions, including Sri Lanka and Burma. These trade partnerships facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural influences between different civilizations. The ports on the east and west coasts of India, such as Bhrigukachchii, Surparaka, and Tamralipti, played crucial roles as hubs for maritime trade with these regions.
What was the primary function of merchant and craft guilds in medieval towns?- a)Providing military training to members
- b)Distributing agricultural products
- c)Offering training, materials, and facilitating the distribution of goods
- d)Building religious institutions
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Providing military training to members
b)
Distributing agricultural products
c)
Offering training, materials, and facilitating the distribution of goods
d)
Building religious institutions

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Merchant and craft guilds in medieval towns primarily focused on providing training, materials, and facilitating the distribution of goods among their members. Craft guilds, in particular, aimed at maintaining high standards of craftsmanship and passing on skills to apprentices, ensuring the quality of goods produced. Merchant guilds, on the other hand, were more involved in regulating trade practices and protecting the interests of their members in commercial activities.
How did the use of iron tools contribute to the process of urbanisation during the Second Urbanisation in India?- a)Enabled the construction of monumental architecture
- b)Facilitated the development of written language systems
- c)Improved agricultural productivity and land clearance
- d)Enhanced maritime trade networks
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Enabled the construction of monumental architecture
b)
Facilitated the development of written language systems
c)
Improved agricultural productivity and land clearance
d)
Enhanced maritime trade networks

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
The widespread adoption of iron tools during the Second Urbanisation in India played a crucial role in enhancing agricultural productivity and land clearance. These tools enabled people to clear forests, cultivate land more efficiently, and support the growth of towns and cities. The use of iron tools significantly contributed to the expansion of agricultural practices and the development of urban centers during this period.
What role did trade networks play in the economic development of medieval towns?- a)Trade networks had no impact on the economic growth of towns
- b)Trade networks led to the decline of urban centers
- c)Trade networks promoted economic prosperity by facilitating the exchange of goods
- d)Trade networks primarily focused on religious activities
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Trade networks had no impact on the economic growth of towns
b)
Trade networks led to the decline of urban centers
c)
Trade networks promoted economic prosperity by facilitating the exchange of goods
d)
Trade networks primarily focused on religious activities

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Trade networks played a pivotal role in the economic development of medieval towns by promoting economic prosperity through the facilitation of trade and exchange of goods. These networks connected towns with distant regions, fostering commercial relationships and enabling the flow of commodities, ideas, and technologies. As a result, towns thrived as centers of commerce and cultural exchange, contributing to their growth and development.
In which regions were the Northern Black Polished Ware commonly found during this historical period?- a)Himalayan foothills and Tibetan Plateau
- b)Western Ghats and Malabar Coast
- c)Gangetic Plains, Bihar, and parts of central-eastern and southern India
- d)Deccan Plateau and Eastern Coastal Plains
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Himalayan foothills and Tibetan Plateau
b)
Western Ghats and Malabar Coast
c)
Gangetic Plains, Bihar, and parts of central-eastern and southern India
d)
Deccan Plateau and Eastern Coastal Plains

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
The Northern Black Polished Ware, a specific type of black pottery made of clay, was commonly found in regions like the Gangetic Plains, Bihar, and parts of central-eastern and southern India. This distinctive pottery style provides insights into the material culture and trade networks of the ancient civilizations that utilized them.
Choose the correct answer based on the information in the passage.
Ashoka, a unique ruler
The most famous Mauryan ruler was Ashoka. He was the first ruler who tried to take his message to the people through inscriptions. Most of Ashoka’s inscriptions were in Prakrit and were written in the Brahmi script.Q. What made Ashoka a unique ruler according to the passage?- a)His military conquests
- b)His inscriptions and message to the people
- c)His alliance with Chanakya
- d)His architectural achievements
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct answer based on the information in the passage.
Ashoka, a unique ruler
The most famous Mauryan ruler was Ashoka. He was the first ruler who tried to take his message to the people through inscriptions. Most of Ashoka’s inscriptions were in Prakrit and were written in the Brahmi script.
Ashoka, a unique ruler
The most famous Mauryan ruler was Ashoka. He was the first ruler who tried to take his message to the people through inscriptions. Most of Ashoka’s inscriptions were in Prakrit and were written in the Brahmi script.
Q. What made Ashoka a unique ruler according to the passage?
a)
His military conquests
b)
His inscriptions and message to the people
c)
His alliance with Chanakya
d)
His architectural achievements

|
Praveen Kumar answered |
The passage mentions that Ashoka was unique because he tried to take his message to the people through inscriptions.
The Silk Road, a historic network of trade routes, played a crucial role in connecting different civilizations. Traders from China to the Mediterranean exchanged goods, ideas, and cultures. The route extended overland and across seas, facilitating the flow of silk, spices, precious metals, and knowledge. This exchange not only shaped the economies of the involved regions but also contributed to a rich tapestry of cultural diversity.Q. What was the primary function of the Silk Road according to the passage?
A) Military conquests
B) Cultural exchange and trade
C) Agricultural development
D) Architectural achievements- a)A, B
- b)B, C
- c)A, D
- d)B
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The Silk Road, a historic network of trade routes, played a crucial role in connecting different civilizations. Traders from China to the Mediterranean exchanged goods, ideas, and cultures. The route extended overland and across seas, facilitating the flow of silk, spices, precious metals, and knowledge. This exchange not only shaped the economies of the involved regions but also contributed to a rich tapestry of cultural diversity.
Q. What was the primary function of the Silk Road according to the passage?
A) Military conquests
B) Cultural exchange and trade
C) Agricultural development
D) Architectural achievements
A) Military conquests
B) Cultural exchange and trade
C) Agricultural development
D) Architectural achievements
a)
A, B
b)
B, C
c)
A, D
d)
B

|
Praveen Kumar answered |
The passage highlights that the Silk Road played a crucial role in connecting civilizations through cultural exchange and trade, contributing to the economies and cultural diversity of the involved regions.
Analogy - Traders:South India :: Northern Black Polished Ware:______- a)Craftspersons
- b)Silk Route
- c)Roman Empire
- d)Sangam Literature
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Analogy - Traders:South India :: Northern Black Polished Ware:______
a)
Craftspersons
b)
Silk Route
c)
Roman Empire
d)
Sangam Literature

|
Praveen Kumar answered |
Traders carried goods like Northern Black Polished Ware along trade routes, just as they carried goods along the Silk Route.
Analogy - Punch-marked Coins:Trade :: Sangam Literature:______- a)Education
- b)Poetry Assemblies
- c)Irrigation
- d)Megalithic Burials
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Analogy - Punch-marked Coins:Trade :: Sangam Literature:______
a)
Education
b)
Poetry Assemblies
c)
Irrigation
d)
Megalithic Burials

|
Coachify answered |
Punch-marked coins are associated with trade, and Sangam literature was composed in assemblies of poets known as Sangams.
What was a significant factor leading to the emergence of urban centers during the second urbanization?- a) Decrease in population density
- b) Increased agricultural production
- c) Decline in trade
- d) Political instability
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What was a significant factor leading to the emergence of urban centers during the second urbanization?
a)
Decrease in population density
b)
Increased agricultural production
c)
Decline in trade
d)
Political instability

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Increased agricultural production was a significant factor that led to the emergence of urban centers, as it created food surpluses that supported larger populations and facilitated the growth of crafts and trade.
Which archaeological evidence is associated with the period of the second urbanization?- a) Bronze statues
- b) Terracotta figurines
- c) Stone tablets
- d) Punch-marked coins
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which archaeological evidence is associated with the period of the second urbanization?
a)
Bronze statues
b)
Terracotta figurines
c)
Stone tablets
d)
Punch-marked coins

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Punch-marked coins are significant archaeological evidence from the period of second urbanization, indicating the development of trade and economic systems. These coins illustrate the evolving monetary systems in ancient India.
What purpose were ring wells believed to serve based on the discoveries in places like Kumrahar near Patna?- a)Religious Ceremonies
- b)Water Storage or Drainage
- c)Agricultural Irrigation
- d)Defensive Structures
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Religious Ceremonies
b)
Water Storage or Drainage
c)
Agricultural Irrigation
d)
Defensive Structures

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Ring wells, discovered in locations like Kumrahar near Patna, were likely used for water storage or drainage purposes. These structures consisted of ceramic pots stacked with rings on top of each other, suggesting their potential utility in managing water resources or facilitating drainage systems within the vicinity.
In the context of South Indian villages, what term refers to wealthy landowners?- a) Krishakas
- b) Kadaisiyar
- c) Uzhavars
- d) Vellalar
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the context of South Indian villages, what term refers to wealthy landowners?
a)
Krishakas
b)
Kadaisiyar
c)
Uzhavars
d)
Vellalar

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Wealthy landowners in South Indian villages were referred to as vellalar, who played significant roles in the agricultural economy and social structure of their communities.
What type of goods were commonly exported from Arikamedu?- a) Agricultural produce
- b) Weapons
- c) Precious metals
- d) Textiles and glass-shell bangles
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What type of goods were commonly exported from Arikamedu?
a)
Agricultural produce
b)
Weapons
c)
Precious metals
d)
Textiles and glass-shell bangles

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Arikamedu was known for exporting textiles and glass-shell bangles, among other goods. Its strategic location and trade links with Rome allowed it to thrive as a center of commerce and craftsmanship.
What event marks the beginning of the second urbanization in historical contexts?- a) Increased agricultural production
- b) The rise of craft guilds
- c) The discovery of iron tools
- d) The fall of the Roman Empire
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What event marks the beginning of the second urbanization in historical contexts?
a)
Increased agricultural production
b)
The rise of craft guilds
c)
The discovery of iron tools
d)
The fall of the Roman Empire

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
The second urbanization began primarily due to increased agricultural production, which allowed for surplus food and supported the growth of urban centers. This shift from rural to urban living was a crucial development in shaping societies during this period.
Craftspersons in villages formed associations known as shrenis, which not only provided training but also served as:- a)Educational institutions
- b)Temples
- c)Banks
- d)Legal forums
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Craftspersons in villages formed associations known as shrenis, which not only provided training but also served as:
a)
Educational institutions
b)
Temples
c)
Banks
d)
Legal forums
|
|
Eduskill Classes answered |
The passage mentions that shrenis of craftspersons served as banks where money was deposited, invested, and part of the interest used to support religious institutions.
Around 2500 years ago, iron tools such as axes and ploughshares were used for:- a)Hunting
- b)Clearing forests and agriculture
- c)Building monuments
- d)Making jewelry
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Around 2500 years ago, iron tools such as axes and ploughshares were used for:
a)
Hunting
b)
Clearing forests and agriculture
c)
Building monuments
d)
Making jewelry

|
Rainbow Rise Classes answered |
The passage states that iron tools, including axes for clearing forests and iron ploughshares, were in use around 2500 years ago, contributing to increased agricultural production.
Match the Occupation:
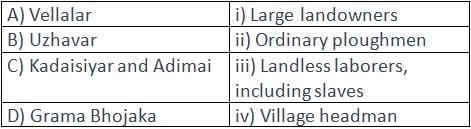
- a)A) ii, B) iii, C) i, D) iv
- b)A) i, B) ii, C) iii, D) iv
- c)A) ii, B) i, C) iii, D) iv
- d)A) iv, B) ii, C) iii, D) i
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the Occupation:


a)
A) ii, B) iii, C) i, D) iv
b)
A) i, B) ii, C) iii, D) iv
c)
A) ii, B) i, C) iii, D) iv
d)
A) iv, B) ii, C) iii, D) i

|
Indu Gupta answered |
Each category corresponds to a specific occupation mentioned in the passage.
What was a defining characteristic of the urban centers that emerged in ancient India?- a) They had no external trade connections.
- b) They were hubs for political, religious, and economic activities.
- c) They specialized in only one trade.
- d) They were primarily agrarian.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What was a defining characteristic of the urban centers that emerged in ancient India?
a)
They had no external trade connections.
b)
They were hubs for political, religious, and economic activities.
c)
They specialized in only one trade.
d)
They were primarily agrarian.

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
The emerging urban centers in ancient India became hubs for various activities, including political administration, religious practices, and economic trade. This multifaceted role contributed to their significance in regional development.
What were ring wells used for in urban centers during the second urbanization?- a) Storage of agricultural produce
- b) Water reservoirs
- c) Drains, toilets, or garbage disposal
- d) Religious ceremonies
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What were ring wells used for in urban centers during the second urbanization?
a)
Storage of agricultural produce
b)
Water reservoirs
c)
Drains, toilets, or garbage disposal
d)
Religious ceremonies

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Ring wells were likely utilized as drains, toilets, or garbage disposal systems, showcasing advancements in urban sanitation and infrastructure during the period of second urbanization.
In which region of India was the city of Arikamedu located?- a) West Bengal
- b) Tamil Nadu
- c) Near Puducherry
- d) Gujarat
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which region of India was the city of Arikamedu located?
a)
West Bengal
b)
Tamil Nadu
c)
Near Puducherry
d)
Gujarat

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Arikamedu is located near Puducherry and was an important archaeological site and trading center during the second urbanization. It played a significant role in trade with the Roman Empire, reflecting the interconnectedness of ancient economies.
What key contribution did the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea provide regarding trade?- a) Detailed accounts of trade activities at ports
- b) Religious practices in India
- c) Agricultural techniques used in ancient India
- d) Historical narratives of Indian dynasties
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What key contribution did the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea provide regarding trade?
a)
Detailed accounts of trade activities at ports
b)
Religious practices in India
c)
Agricultural techniques used in ancient India
d)
Historical narratives of Indian dynasties

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea is a Greek text that provided detailed accounts of trade activities at various ports, highlighting the extent and nature of commerce between India and other regions, notably the Roman Empire.
Which of the following was a notable feature of the urban centers developed during the second urbanization?- a) Nomadic settlements
- b) Wooden structures
- c) Improved sanitation systems
- d) Lack of infrastructure
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following was a notable feature of the urban centers developed during the second urbanization?
a)
Nomadic settlements
b)
Wooden structures
c)
Improved sanitation systems
d)
Lack of infrastructure

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Urban centers during the second urbanization featured improved sanitation systems, including advanced drainage and waste disposal methods like ring wells, reflecting a growing sophistication in urban planning and public health.
What was one significant development in the evolution of trade as societies progressed over time?- a)Invention of the wheel for transportation
- b)Transition from bartering to using coins as a medium of exchange
- c)Introduction of paper money as a form of currency
- d)Adoption of a universal trading language
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Invention of the wheel for transportation
b)
Transition from bartering to using coins as a medium of exchange
c)
Introduction of paper money as a form of currency
d)
Adoption of a universal trading language

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
As societies progressed, one significant development in trade was the shift from bartering to using coins as a medium of exchange. This transition made transactions more standardized and facilitated smoother trade interactions between individuals and communities.
What major impact did the Second Urbanisation have on the societal and economic landscape of ancient India?- a)Shift towards a barter-based economy
- b)Emergence of a centralized bureaucratic system
- c)Expansion of agricultural practices and trade networks
- d)Decline in artisanal craftsmanship
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Shift towards a barter-based economy
b)
Emergence of a centralized bureaucratic system
c)
Expansion of agricultural practices and trade networks
d)
Decline in artisanal craftsmanship

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
The Second Urbanisation in ancient India brought about a significant expansion in agricultural practices and trade networks. The adoption of iron tools allowed for more efficient land cultivation, leading to increased agricultural productivity. This, in turn, supported the growth of towns and cities, fostering economic development and facilitating trade networks across the region.
Which ports were crucial for maritime trade in ancient India?- a)Alexandria and Constantinople
- b)Venice and Genoa
- c)Bhrigukachchii, Surparaka, and Tamralipti
- d)London and Amsterdam
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Alexandria and Constantinople
b)
Venice and Genoa
c)
Bhrigukachchii, Surparaka, and Tamralipti
d)
London and Amsterdam

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Ports such as Bhrigukachchii, Surparaka, and Tamralipti played crucial roles in facilitating maritime trade in ancient India. These ports served as vital hubs for commercial activities, connecting Indian kingdoms with foreign lands and enabling the exchange of goods, cultures, and ideas across the seas. The strategic locations of these ports contributed to the flourishing trade networks and the economic prosperity of the regions they served.
Analogy - Silk Route:Trade :: Sangam Literature:______- a)Religion
- b)Poetry
- c)Warfare
- d)Agriculture
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Analogy - Silk Route:Trade :: Sangam Literature:______
a)
Religion
b)
Poetry
c)
Warfare
d)
Agriculture

|
Gunjan Lakhani answered |
The Silk Route is associated with trade, and Sangam Literature is associated with poetry.
Chapter doubts & questions for Life in a Village - Geography for Grade 2 2025 is part of Grade 2 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 2 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 2 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Life in a Village - Geography for Grade 2 in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 2 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 2 Exam by signing up for free.
Geography for Grade 2
46 docs|11 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









